State Of Wisconsin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wisconsin () is a
 Wisconsin has been home to a wide variety of cultures over the past 14,000 years. The first people arrived around 10,000 BCE during the
Wisconsin has been home to a wide variety of cultures over the past 14,000 years. The first people arrived around 10,000 BCE during the
 The first European to visit what became Wisconsin was probably the French explorer
The first European to visit what became Wisconsin was probably the French explorer  The British gradually took over Wisconsin during the French and Indian War, taking control of Green Bay in 1761 and gaining control of all of Wisconsin in 1763. Like the French, the British were interested in little but the fur trade. One notable event in the fur trading industry in Wisconsin occurred in 1791, when two free African Americans set up a fur trading post among the Menominee at present day Marinette. The first permanent settlers, mostly French Canadians, some Anglo-
The British gradually took over Wisconsin during the French and Indian War, taking control of Green Bay in 1761 and gaining control of all of Wisconsin in 1763. Like the French, the British were interested in little but the fur trade. One notable event in the fur trading industry in Wisconsin occurred in 1791, when two free African Americans set up a fur trading post among the Menominee at present day Marinette. The first permanent settlers, mostly French Canadians, some Anglo-

 Politics in early Wisconsin were defined by the greater national debate over slavery. A free state from its foundation, Wisconsin became a center of northern abolitionism. The debate became especially intense in 1854 after
Politics in early Wisconsin were defined by the greater national debate over slavery. A free state from its foundation, Wisconsin became a center of northern abolitionism. The debate became especially intense in 1854 after
 Wisconsin's economy also diversified during the early years of statehood. While lead mining diminished, agriculture became a principal occupation in the southern half of the state. Railroads were built across the state to help transport grains to market, and industries like J.I. Case & Company in Racine were founded to build agricultural equipment. Wisconsin briefly became one of the nation's leading producers of wheat during the 1860s. Meanwhile, the lumber industry dominated in the heavily forested northern sections of Wisconsin, and sawmills sprang up in cities like
Wisconsin's economy also diversified during the early years of statehood. While lead mining diminished, agriculture became a principal occupation in the southern half of the state. Railroads were built across the state to help transport grains to market, and industries like J.I. Case & Company in Racine were founded to build agricultural equipment. Wisconsin briefly became one of the nation's leading producers of wheat during the 1860s. Meanwhile, the lumber industry dominated in the heavily forested northern sections of Wisconsin, and sawmills sprang up in cities like  Beginning in the 1890s, farmers in Wisconsin shifted from wheat to dairy production in order to make more sustainable and profitable use of their land. Many immigrants carried cheese-making traditions that, combined with the state's suitable geography and dairy research led by Stephen Babcock at the
Beginning in the 1890s, farmers in Wisconsin shifted from wheat to dairy production in order to make more sustainable and profitable use of their land. Many immigrants carried cheese-making traditions that, combined with the state's suitable geography and dairy research led by Stephen Babcock at the
 The early 20th century was also notable for the emergence of progressive politics championed by
The early 20th century was also notable for the emergence of progressive politics championed by 

 Wisconsin is bordered by the Montreal River;
Wisconsin is bordered by the Montreal River;
 Most of Wisconsin is classified as warm-summer
Most of Wisconsin is classified as warm-summer
 The
The  ''Note: Births in table add to over 100%, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of
''Note: Births in table add to over 100%, because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.''
* Since 2016, data for births of
U.S. Religious Landscape Survey
(Archived July 5, 2013), Appendix 1, p. 97. Pew Research Center, 2008. As of 2010, the Catholic Church had the highest number of adherents in Wisconsin (at 1,425,523), followed by the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America with 414,326 members, and the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod with 223,279 adherents. The
 Wisconsin's Constitution outlines the structure and function of state government, which is organized into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The
Wisconsin's Constitution outlines the structure and function of state government, which is organized into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The
 The executive branch is headed by the
The executive branch is headed by the
 Wisconsin collects personal
Wisconsin collects personal
 In 2020, Wisconsin leaned back in the Democratic party's direction as Joe Biden won the state by an even narrower margin of 0.7%. Biden's win was largely carried by Milwaukee and Dane counties with the rural areas of the state being carried by Trump.
Wisconsin has leaned Democratic in recent presidential elections, although
In 2020, Wisconsin leaned back in the Democratic party's direction as Joe Biden won the state by an even narrower margin of 0.7%. Biden's win was largely carried by Milwaukee and Dane counties with the rural areas of the state being carried by Trump.
Wisconsin has leaned Democratic in recent presidential elections, although
 At the statewide level, Wisconsin is competitive, with control regularly alternating between the two parties. In 2006, Democrats gained in a national sweep of opposition to the Bush administration, and the Iraq War. The retiring GOP 8th District Congressman, Mark Green, of Green Bay, ran against the incumbent Governor
At the statewide level, Wisconsin is competitive, with control regularly alternating between the two parties. In 2006, Democrats gained in a national sweep of opposition to the Bush administration, and the Iraq War. The retiring GOP 8th District Congressman, Mark Green, of Green Bay, ran against the incumbent Governor
 In 2019 Wisconsin's gross state product was $349.416 billion, making it 21st among U.S. states. The economy of Wisconsin is driven by
In 2019 Wisconsin's gross state product was $349.416 billion, making it 21st among U.S. states. The economy of Wisconsin is driven by
''Dairy Products''
, p. 13. It is second in milk production, after
''Wisconsin Ag News—Cranberries''
, June 27, 2017, p. 1.
2012 Census of Agriculture: United States Summary and State Data, Vol. 1
''. Washington, DC: 2014, pp. 475–476. and
 Tourism is a major industry in Wisconsin—the state's third largest, according to the Department of Tourism. Tourist destinations such as the House on the Rock near Spring Green,
Tourism is a major industry in Wisconsin—the state's third largest, according to the Department of Tourism. Tourist destinations such as the House on the Rock near Spring Green,
 Over 68% of Wisconsin residents live in urban areas, with the
Over 68% of Wisconsin residents live in urban areas, with the

 Residents of Wisconsin are referred to as Wisconsinites. The traditional prominence of references to
Residents of Wisconsin are referred to as Wisconsinites. The traditional prominence of references to
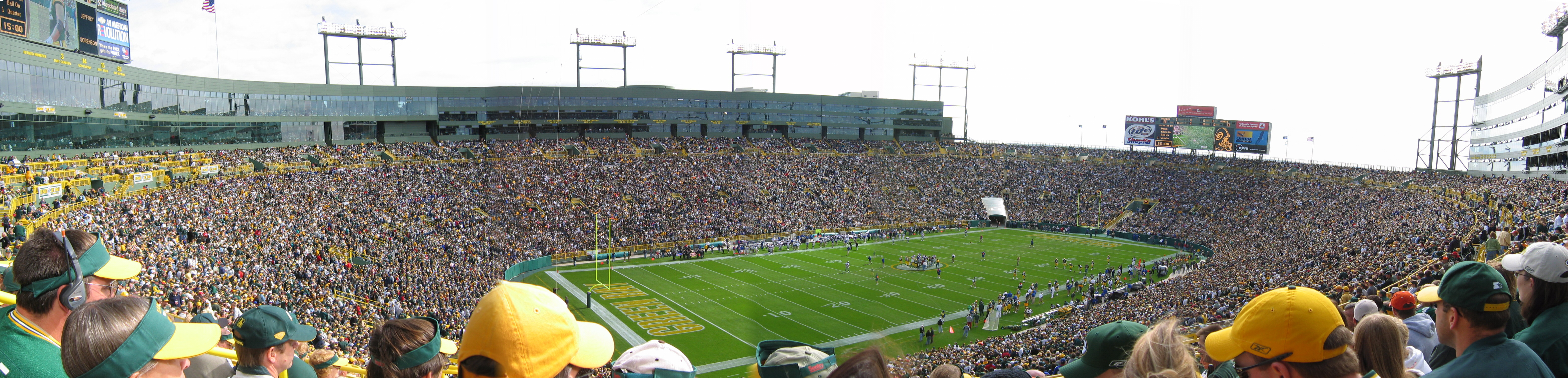 Wisconsin is represented by major league teams in three sports: football, baseball, and basketball. Lambeau Field, located in Green Bay, Wisconsin, is home to the National Football League's Green Bay Packers. The Packers have been part of the NFL since the league's second season in 1921 and hold the record for the most NFL titles, earning the city of Green Bay the nickname "Titletown USA". The Packers are the smallest city franchise in the NFL and the only one owned by shareholders statewide. The franchise was founded by "Curly" Lambeau, who played and coached for them. The Green Bay Packers are one of the most successful small-market professional sports franchises in the world and have won 13 NFL championships, including the first two AFL-NFL Championship games (Super Bowls Super Bowl I, I and Super Bowl II, II), Super Bowl XXXI and Super Bowl XLV. The state's support of the team is evidenced by the 81,000-person waiting list for season tickets to Lambeau Field.
Wisconsin is represented by major league teams in three sports: football, baseball, and basketball. Lambeau Field, located in Green Bay, Wisconsin, is home to the National Football League's Green Bay Packers. The Packers have been part of the NFL since the league's second season in 1921 and hold the record for the most NFL titles, earning the city of Green Bay the nickname "Titletown USA". The Packers are the smallest city franchise in the NFL and the only one owned by shareholders statewide. The franchise was founded by "Curly" Lambeau, who played and coached for them. The Green Bay Packers are one of the most successful small-market professional sports franchises in the world and have won 13 NFL championships, including the first two AFL-NFL Championship games (Super Bowls Super Bowl I, I and Super Bowl II, II), Super Bowl XXXI and Super Bowl XLV. The state's support of the team is evidenced by the 81,000-person waiting list for season tickets to Lambeau Field.
 The Milwaukee Brewers, the state's only major league baseball team, play in American Family Field in Milwaukee, the successor to Milwaukee County Stadium since 2001. In 1982, the Brewers won the American League Championship, marking their most successful season. The team switched from the American League to the National League starting with the 1998 season. Before the Brewers, Milwaukee had two prior Major League teams. The first team, also called the Brewers, played only one season in the newly founded American League in 1901 before moving to St. Louis and becoming the Browns, who are now the Baltimore Orioles. Milwaukee was also the home of the Atlanta Braves, Braves franchise when they moved from Boston from 1953 to 1965, winning the World Series in 1957 and the National League pennant in 1958, before they moved to Atlanta.
The Milwaukee Bucks of the National Basketball Association play home games at the Fiserv Forum. The Bucks won the NBA Championship in 1971 and 2021.
The state also has minor league teams in hockey (Milwaukee Admirals) and baseball (the Wisconsin Timber Rattlers, based in Appleton and the Beloit Sky Carp of the High-A minor leagues). In addition to these affiliated minor league teams, Wisconsin has the American Association of Professional Baseball 2020 Championship team, the Milwaukee Milkmen based in Franklin, Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, Franklin, and in 2022 the Lake Country Dockhounds will begin playing in Oconomowoc, Wisconsin, Oconomowoc. Wisconsin is also home to the Madison Mallards, the La Crosse Loggers, the Lakeshore Chinooks, the Eau Claire Express, the Fond du Lac Dock Spiders, the Green Bay Booyah, the Kenosha Kingfish, the Wisconsin Woodchucks, and the Wisconsin Rapids Rafters of the Northwoods League, a collegiate all-star summer league. In addition to the Packers, Green Bay is also the home to an indoor American football, indoor football team, the Green Bay Blizzard of the Indoor Football League, IFL. The state is home to the seven-time MISL/MASL Champion Milwaukee Wave.
Wisconsin is also home to Forward Madison FC, which is a professional soccer team that plays in the USL League One.
Wisconsin also has many college sports programs, including the Wisconsin Badgers, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the Milwaukee Panthers, Panthers of the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. The Wisconsin Badgers football former head coach Barry Alvarez led the Badgers to three Rose Bowl (game), Rose Bowl championships, including back-to-back victories in 1999 and 2000. The Badger men's basketball team won the national title in 1941 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1941 and made trips to college basketball's Final Four in 2000 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2000, 2014 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2014, and 2015 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2015. The Badgers claimed a historic dual championship in 2006 when both the NCAA Women's Ice Hockey Championship, women's and NCAA Men's Division I hockey Championship, men's hockey teams won national titles.
The Marquette Golden Eagles of the Big East Conference (1979–2013), Big East Conference, the state's other major collegiate program, is known for its Marquette Golden Eagles men's basketball, men's basketball team, which, under the direction of Al McGuire, won the NCAA National Championship in 1977 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1977. The team returned to the Final Four in 2003 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2003.
Many other schools in the University of Wisconsin system compete in the Wisconsin Intercollegiate Athletic Conference at the Division III (NCAA), Division III level. The conference is one of the most successful in the nation, claiming 107 NCAA national championships in 15 different sports as of March 30, 2015.
The Semi-Professional Northern Elite Football League consists of many teams from Wisconsin. The league is made up of former professional, collegiate, and high school players. Teams from Wisconsin include: The Green Bay Gladiators from Green Bay, The Fox Valley Force in Appleton, The Kimberly Storm in Kimberly, Wisconsin, Kimberly, The Central Wisconsin Spartans in Wausau, The Eau Claire Crush and the Chippewa Valley Predators from Eau Claire, and the Lake Superior Rage from Superior, Wisconsin, Superior. The league also has teams in Michigan and Minnesota. Teams play from May until August.
Wisconsin is home to the world's oldest operational racetrack. The Milwaukee Mile, located in Wisconsin State Fair Park in West Allis, Wisconsin, held races there that considerably predate the Indy 500.
Wisconsin is home to the nation's oldest operating velodrome in
The Milwaukee Brewers, the state's only major league baseball team, play in American Family Field in Milwaukee, the successor to Milwaukee County Stadium since 2001. In 1982, the Brewers won the American League Championship, marking their most successful season. The team switched from the American League to the National League starting with the 1998 season. Before the Brewers, Milwaukee had two prior Major League teams. The first team, also called the Brewers, played only one season in the newly founded American League in 1901 before moving to St. Louis and becoming the Browns, who are now the Baltimore Orioles. Milwaukee was also the home of the Atlanta Braves, Braves franchise when they moved from Boston from 1953 to 1965, winning the World Series in 1957 and the National League pennant in 1958, before they moved to Atlanta.
The Milwaukee Bucks of the National Basketball Association play home games at the Fiserv Forum. The Bucks won the NBA Championship in 1971 and 2021.
The state also has minor league teams in hockey (Milwaukee Admirals) and baseball (the Wisconsin Timber Rattlers, based in Appleton and the Beloit Sky Carp of the High-A minor leagues). In addition to these affiliated minor league teams, Wisconsin has the American Association of Professional Baseball 2020 Championship team, the Milwaukee Milkmen based in Franklin, Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, Franklin, and in 2022 the Lake Country Dockhounds will begin playing in Oconomowoc, Wisconsin, Oconomowoc. Wisconsin is also home to the Madison Mallards, the La Crosse Loggers, the Lakeshore Chinooks, the Eau Claire Express, the Fond du Lac Dock Spiders, the Green Bay Booyah, the Kenosha Kingfish, the Wisconsin Woodchucks, and the Wisconsin Rapids Rafters of the Northwoods League, a collegiate all-star summer league. In addition to the Packers, Green Bay is also the home to an indoor American football, indoor football team, the Green Bay Blizzard of the Indoor Football League, IFL. The state is home to the seven-time MISL/MASL Champion Milwaukee Wave.
Wisconsin is also home to Forward Madison FC, which is a professional soccer team that plays in the USL League One.
Wisconsin also has many college sports programs, including the Wisconsin Badgers, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the Milwaukee Panthers, Panthers of the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. The Wisconsin Badgers football former head coach Barry Alvarez led the Badgers to three Rose Bowl (game), Rose Bowl championships, including back-to-back victories in 1999 and 2000. The Badger men's basketball team won the national title in 1941 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1941 and made trips to college basketball's Final Four in 2000 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2000, 2014 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2014, and 2015 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2015. The Badgers claimed a historic dual championship in 2006 when both the NCAA Women's Ice Hockey Championship, women's and NCAA Men's Division I hockey Championship, men's hockey teams won national titles.
The Marquette Golden Eagles of the Big East Conference (1979–2013), Big East Conference, the state's other major collegiate program, is known for its Marquette Golden Eagles men's basketball, men's basketball team, which, under the direction of Al McGuire, won the NCAA National Championship in 1977 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1977. The team returned to the Final Four in 2003 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2003.
Many other schools in the University of Wisconsin system compete in the Wisconsin Intercollegiate Athletic Conference at the Division III (NCAA), Division III level. The conference is one of the most successful in the nation, claiming 107 NCAA national championships in 15 different sports as of March 30, 2015.
The Semi-Professional Northern Elite Football League consists of many teams from Wisconsin. The league is made up of former professional, collegiate, and high school players. Teams from Wisconsin include: The Green Bay Gladiators from Green Bay, The Fox Valley Force in Appleton, The Kimberly Storm in Kimberly, Wisconsin, Kimberly, The Central Wisconsin Spartans in Wausau, The Eau Claire Crush and the Chippewa Valley Predators from Eau Claire, and the Lake Superior Rage from Superior, Wisconsin, Superior. The league also has teams in Michigan and Minnesota. Teams play from May until August.
Wisconsin is home to the world's oldest operational racetrack. The Milwaukee Mile, located in Wisconsin State Fair Park in West Allis, Wisconsin, held races there that considerably predate the Indy 500.
Wisconsin is home to the nation's oldest operating velodrome in
Wisconsin Health and Demographic Data
La Crosse Medical Health Science Consortium
Energy Profile for Wisconsin—Economic, environmental, and energy data
Wisconsin Historical Society
The State of Wisconsin Collection
from th
UW Digital Collections Center
Wisconsin Free Speech Legacy
Wisconsin Department of Tourism
* . * * * . {{coord, 44, -90, dim:300000_region:US-WI_source:enwiki_type:adm1st, name=State of Wisconsin, display=title Wisconsin, States of the United States States and territories established in 1848 1848 establishments in the United States Midwestern United States Contiguous United States
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the upper Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
to the west, Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
to the southwest, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
to the northeast, and Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
to the north.
The bulk of Wisconsin's population live in areas situated along the shores of Lake Michigan. The largest city, Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
, anchors its largest metropolitan area, followed by Green Bay and Kenosha
Kenosha () is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the seat of Kenosha County. Per the 2020 census, the population was 99,986 which made it the fourth-largest city in Wisconsin. Situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan, Kenosh ...
, the third- and fourth-most-populated Wisconsin cities respectively. The state capital, Madison Madison may refer to:
People
* Madison (name), a given name and a surname
* James Madison (1751–1836), fourth president of the United States
Place names
* Madison, Wisconsin, the state capital of Wisconsin and the largest city known by this ...
, is currently the second-most-populated and fastest-growing city in the state. Wisconsin is divided into 72 counties and as of the 2020 census had a population of nearly 5.9 million.
Wisconsin's geography is diverse, having been greatly impacted by glaciers during the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
with the exception of the Driftless Area
The Driftless Area, a topographical and cultural region in the American Midwest, comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois.
Never covered by ice during the las ...
. The Northern Highland
The Northern Highland is a geographical region in the north central United States covering much of the northern territory of the state of Wisconsin.
The region stretches from the state border with Minnesota in the west to the Michigan border i ...
and Western Upland
The Western Upland is a geographical region covering much of the western half of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It stretches from southern Polk County, Wisconsin in the north to the state border with Illinois in the south, and from Rock County i ...
along with a part of the Central Plain occupy the western part of the state, with lowlands stretching to the shore of Lake Michigan. Wisconsin is third to Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
and Michigan in the length of its Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
coastline. The northern portion of the state is home to the Chequamegon-Nicolet National Forest.
At the time of European contact the area was inhabited by Algonquian and Siouan
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the enti ...
nations, and today is home to eleven federally recognized tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, many European settlers entered the state, most of whom emigrated from Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
. Wisconsin remains a center of German American and Scandinavian American
Nordic and Scandinavian Americans are Americans of Scandinavian and/or Nordic ancestry, including Danish Americans (estimate: 1,453,897), Faroese Americans, Finnish Americans (estimate: 653,222), Greenlandic Americans, Icelandic Americans (est ...
culture, particularly in respect to its cuisine, with foods such as bratwurst
Bratwurst () is a type of German sausage made from pork or, less commonly, beef or veal. The name is derived from the Old High German ''Brätwurst'', from ''brät-'', finely chopped meat, and ''Wurst'', sausage, although in modern German it is o ...
and kringle
Kringle (, ) is a Northern European pastry, a variety of pretzel. Pretzels were introduced by Roman Catholic monks in the 13th century in Denmark, and from there they spread throughout Scandinavia and evolved into several kinds of sweet, salty ...
. Wisconsin is home to one UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, comprising two of the most significant buildings designed by Wisconsin-born architect Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
: his studio at Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the '' Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts ...
near Spring Green and his Jacobs I House in Madison.
The state is one of the nation's leading dairy producers and is known as "America's Dairyland"; it is particularly famous for its cheese. The state is also famous for its beer, particularly and historically in Milwaukee, most notably as the headquarters of the Miller Brewing Company
The Miller Brewing Company is an American brewery and beer company in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. It was founded in 1855 by Frederick Miller. Molson Coors acquired the full global brand portfolio of Miller Brewing Company in 2016, and operates the ...
. Wisconsin has some of the most permissive alcohol laws in the country and is well known for its drinking culture
Drinking culture is the set of traditions and social behaviors that surround the consumption of alcoholic beverages as a recreational drug and social lubricant. Although alcoholic beverages and social attitudes toward drinking vary around the w ...
. Its economy is dominated by manufacturing, healthcare, information technology, and agriculture—specifically dairy, cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
and ginseng
Ginseng () is the root of plants in the genus '' Panax'', such as Korean ginseng ('' P. ginseng''), South China ginseng ('' P. notoginseng''), and American ginseng ('' P. quinquefolius''), typically characterized by the presence of ginsenosides ...
. Tourism is also a major contributor to the state's economy. The gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is oft ...
in 2020 was $348 billion.
Etymology
The word ''Wisconsin'' originates from the name given to theWisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskous ...
by one of the Algonquian-speaking Native American groups living in the region at the time of European contact. French explorer Jacques Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
was the first Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
an to reach the Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskous ...
, arriving in 1673 and calling the river ''Meskousing'' (likely ᒣᔅᑯᐤᓯᣙ ''meskowsin'') in his journal. Subsequent French writers changed the spelling from ''Meskousing'' to ''Ouisconsin'', and over time this became the name for both the Wisconsin River and the surrounding lands. English speakers anglicized
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influenc ...
the spelling from ''Ouisconsin'' to ''Wisconsin'' when they began to arrive in large numbers during the early 19th century. The legislature of Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was ...
made the current spelling official in 1845.
The Algonquian word for Wisconsin and its original meaning have both grown obscure. While interpretations vary, most implicate the river and the red sandstone that lines its banks. One leading theory holds that the name originated from the Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
word ''Meskonsing'', meaning "it lies red", a reference to the setting of the Wisconsin River as it flows through the reddish sandstone of the Wisconsin Dells. Other theories include claims that the name originated from one of a variety of Ojibwa words meaning "red stone place", "where the waters gather", or "great rock".
History
Early history
 Wisconsin has been home to a wide variety of cultures over the past 14,000 years. The first people arrived around 10,000 BCE during the
Wisconsin has been home to a wide variety of cultures over the past 14,000 years. The first people arrived around 10,000 BCE during the Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
. These early inhabitants, called Paleo-Indians, hunted now-extinct ice age animals such as the Boaz mastodon
The Boaz mastodon is the skeleton of a mastodon found near Boaz, Wisconsin, USA, in 1897. A fluted quartzite spear point found near the Boaz mastodon suggests that humans hunted mastodons in southwestern Wisconsin. It is currently on display at the ...
, a prehistoric mastodon
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of th ...
skeleton unearthed along with spear points in southwest Wisconsin. After the ice age ended around 8000 BCE, people in the subsequent Archaic period lived by hunting, fishing, and gathering food from wild plants. Agricultural societies emerged gradually over the Woodland period between 1000 BCE to 1000 CE. Toward the end of this period, Wisconsin was the heartland of the "Effigy Mound
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
culture", which built thousands of animal-shaped mounds across the landscape. Later, between 1000 and 1500 CE, the Mississippian and Oneota
Oneota is a designation archaeologists use to refer to a cultural complex that existed in the eastern plains and Great Lakes area of what is now occupied by the United States from around AD 900 to around 1650 or 1700. Based on classification de ...
cultures built substantial settlements including the fortified village at Aztalan in southeast Wisconsin. The Oneota may be the ancestors of the modern Ioway
The Iowa, also known as Ioway, and the Bah-Kho-Je or Báxoje (English: grey snow; Chiwere: Báxoje ich'é) are a Native American Siouan people. Today, they are enrolled in either of two federally recognized tribes, the Iowa Tribe of Oklahoma an ...
and Ho-Chunk nations who shared the Wisconsin region with the Menominee
The Menominee (; mez, omǣqnomenēwak meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recog ...
at the time of European contact. Other Native American groups living in Wisconsin when Europeans first settled included the Ojibwa, Sauk, Fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
, Kickapoo, and Pottawatomie
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a m ...
, who migrated to Wisconsin from the east between 1500 and 1700.
European settlements
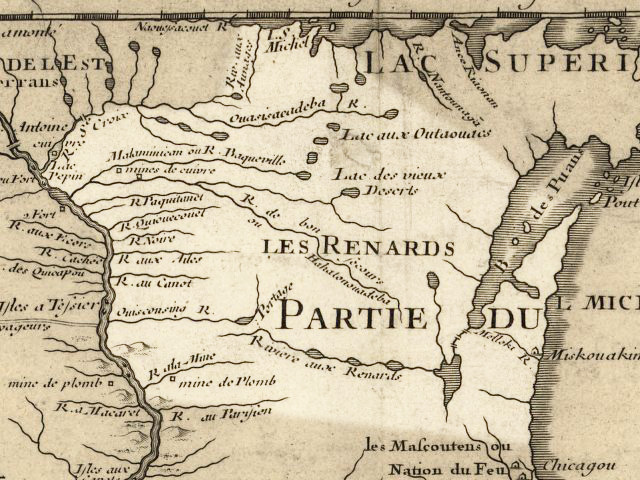
 The first European to visit what became Wisconsin was probably the French explorer
The first European to visit what became Wisconsin was probably the French explorer Jean Nicolet
Jean Nicolet (Nicollet), Sieur de Belleborne (October 1642) was a French ''coureur des bois'' noted for exploring Lake Michigan, Mackinac Island, Green Bay, and being the first European to set foot in what is now the U.S. state of Wisconsin.
Ea ...
. He canoed west from Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To ...
through the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
in 1634, and it is traditionally assumed that he came ashore near Green Bay at Red Banks. Pierre Radisson and Médard des Groseilliers
Médard Chouart des Groseilliers (1618–1696) was a French explorer and fur trader in Canada. He is often paired with his brother-in-law Pierre-Esprit Radisson, who was about 20 years younger. The pair worked together in fur trading and explor ...
visited Green Bay again in 1654–1666 and Chequamegon Bay in 1659–1660, where they traded for fur with local Native Americans. In 1673, Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and ...
became the first to record a journey on the Fox-Wisconsin Waterway all the way to the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
near Prairie du Chien
Prairie du Chien () is a city in and the county seat of Crawford County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 5,506 at the 2020 census. Its ZIP Code is 53821.
Often referred to as Wisconsin's second oldest city, Prairie du Chien was esta ...
. Frenchmen
The French people (french: Français) are an ethnic group and nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common Culture of France, French culture, History of France, history, and French language, language, identified with the cou ...
like Nicholas Perrot continued to ply the fur trade across Wisconsin through the 17th and 18th centuries, but the French made no permanent settlements in Wisconsin before Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
won control of the region following the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
in 1763. Even so, French traders continued to work in the region after the war, and some, beginning with Charles de Langlade
Charles Michel Mouet de Langlade (9 May 1729 – after 26 July 1801)''Dictionnaire Généalogique Tanguay'' was a Great Lakes fur trader and war chief who was important in protecting French territory in North America. His mother was Ottawa and hi ...
in 1764, settled in Wisconsin permanently, rather than returning to British-controlled Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.
 The British gradually took over Wisconsin during the French and Indian War, taking control of Green Bay in 1761 and gaining control of all of Wisconsin in 1763. Like the French, the British were interested in little but the fur trade. One notable event in the fur trading industry in Wisconsin occurred in 1791, when two free African Americans set up a fur trading post among the Menominee at present day Marinette. The first permanent settlers, mostly French Canadians, some Anglo-
The British gradually took over Wisconsin during the French and Indian War, taking control of Green Bay in 1761 and gaining control of all of Wisconsin in 1763. Like the French, the British were interested in little but the fur trade. One notable event in the fur trading industry in Wisconsin occurred in 1791, when two free African Americans set up a fur trading post among the Menominee at present day Marinette. The first permanent settlers, mostly French Canadians, some Anglo-New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
ers and a few African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
freedmen, arrived in Wisconsin while it was under British control. Charles de Langlade is generally recognized as the first settler, establishing a trading post at Green Bay in 1745, and moving there permanently in 1764. Settlement began at Prairie du Chien around 1781. The French residents at the trading post in what is now Green Bay, referred to the town as "La Baye". However, British fur traders referred to it as "Green Bay", because the water and the shore assumed green tints in early spring. The old French title was gradually dropped, and the British name of "Green Bay" eventually stuck. The region coming under British rule had virtually no adverse effect on the French residents as the British needed the cooperation of the French fur traders and the French fur traders needed the goodwill of the British. During the French occupation of the region licenses for fur trading had been issued scarcely and only to select groups of traders, whereas the British, in an effort to make as much money as possible from the region, issued licenses for fur trading freely, both to British and to French residents. The fur trade in what is now Wisconsin reached its height under British rule, and the first self-sustaining farms in the state were established as well. From 1763 to 1780, Green Bay was a prosperous community which produced its own foodstuff, built graceful cottages and held dances and festivities.
U.S. territory
Wisconsin became a territorial possession of the United States in 1783 after theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. In 1787, it became part of the Northwest Territory. As territorial boundaries subsequently developed, it was then part of Indiana Territory
The Indiana Territory, officially the Territory of Indiana, was created by a congressional act that President John Adams signed into law on May 7, 1800, to form an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, ...
from 1800 to 1809, Illinois Territory
The Territory of Illinois was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 1, 1809, until December 3, 1818, when the southern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Illinois. Its ...
from 1809 to 1818, and Michigan Territory from 1818 to 1836. However, the British remained in control until after the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
, the outcome of which finally established an American presence in the area. Under American control, the economy of the territory shifted from fur trading to lead mining. The prospect of easy mineral wealth drew immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
from throughout the U.S. and Europe to the lead deposits located at Mineral Point, Dodgeville, and nearby areas. Some miners found shelter in the holes they had dug, and earned the nickname "badgers", leading to Wisconsin's identity as the "Badger State". The sudden influx of white miners prompted tension with the local Native American population. The Winnebago War
The Winnebago War, also known as the Winnebago Uprising, was a brief conflict that took place in 1827 in the Upper Mississippi River region of the United States, primarily in what is now the state of Wisconsin. Not quite a war, the hostilities ...
of 1827 and the Black Hawk War
The Black Hawk War was a conflict between the United States and Native Americans led by Black Hawk, a Sauk leader. The war erupted after Black Hawk and a group of Sauks, Meskwakis (Fox), and Kickapoos, known as the " British Band", cros ...
of 1832 culminated in the forced removal of Native Americans from most parts of the state.
Following these conflicts, Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was ...
was created by an act of the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
on April 20, 1836. By fall of that year, the best prairie groves of the counties surrounding what is now Milwaukee were occupied by farmers from the New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
states.
Statehood
TheErie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
facilitated the travel of both Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United S ...
settlers and European immigrants to Wisconsin Territory. Yankees from New England and upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York State that lies north and northwest of the New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Is ...
seized a dominant position in law and politics, enacting policies that marginalized the region's earlier Native American and French-Canadian residents. Yankees also speculated in real estate, platted towns such as Racine, Beloit, Burlington, and Janesville, and established schools, civic institutions, and Congregationalist churches. At the same time, many Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, Norwegians
Norwegians ( no, nordmenn) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians are descended from the N ...
, and other immigrants also settled in towns and farms across the territory, establishing Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
institutions.
The growing population allowed Wisconsin to gain statehood on May 29, 1848, as the 30th state. Between 1840 and 1850, Wisconsin's non-Indian population had swollen from 31,000 to 305,000. More than a third of residents (110,500) were foreign born, including 38,000 Germans, 28,000 British immigrants from England, Scotland, and Wales, and 21,000 Irish. Another third (103,000) were Yankees from New England and western New York state. Only about 63,000 residents in 1850 had been born in Wisconsin.
Nelson Dewey
Nelson Webster Dewey (December 19, 1813July 21, 1889) was an American pioneer, lawyer, and politician. He was the first Governor of Wisconsin.
Early life
Dewey was born in Lebanon, Connecticut, on December 19, 1813, to Ebenezer and Lucy (né ...
, the first governor of Wisconsin, was a Democrat
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
. Dewey oversaw the transition from the territorial to the new state government. He encouraged the development of the state's infrastructure, particularly the construction of new roads, railroads, canals, and harbors, as well as the improvement of the Fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
and Wisconsin River
The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskous ...
s. During his administration, the State Board of Public Works was organized. Dewey, an abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
, was the first of many Wisconsin governors to advocate against the spread of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
into new states and territories.
Civil War

 Politics in early Wisconsin were defined by the greater national debate over slavery. A free state from its foundation, Wisconsin became a center of northern abolitionism. The debate became especially intense in 1854 after
Politics in early Wisconsin were defined by the greater national debate over slavery. A free state from its foundation, Wisconsin became a center of northern abolitionism. The debate became especially intense in 1854 after Joshua Glover __NOTOC__
Joshua Glover was a fugitive slave from St. Louis, Missouri, who sought asylum in Racine, Wisconsin, in 1852. Upon learning his whereabouts in 1854, slave owner Bennami Garland attempted to use the Fugitive Slave Act to recover him. Glo ...
, a runaway slave from Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, was captured in Racine
Jean-Baptiste Racine ( , ) (; 22 December 163921 April 1699) was a French dramatist, one of the three great playwrights of 17th-century France, along with Molière and Corneille as well as an important literary figure in the Western traditi ...
. Glover was taken into custody under the Federal Fugitive Slave Law
The fugitive slave laws were laws passed by the United States Congress in 1793 and 1850 to provide for the return of enslaved people who escaped from one state into another state or territory. The idea of the fugitive slave law was derived from ...
, but a mob of abolitionists stormed the prison where Glover was held and helped him escape to Canada. In a trial stemming from the incident, the Wisconsin Supreme Court
The Wisconsin Supreme Court is the highest appellate court in Wisconsin. The Supreme Court has jurisdiction over original actions, appeals from lower courts, and regulation or administration of the practice of law in Wisconsin.
Location
The Wi ...
ultimately declared the Fugitive Slave Law unconstitutional. The Republican Party, founded on March 20, 1854, by anti-slavery expansion activists in Ripon, Wisconsin, grew to dominate state politics in the aftermath of these events. During the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, around 91,000 troops from Wisconsin fought for the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
.
Economic progress
 Wisconsin's economy also diversified during the early years of statehood. While lead mining diminished, agriculture became a principal occupation in the southern half of the state. Railroads were built across the state to help transport grains to market, and industries like J.I. Case & Company in Racine were founded to build agricultural equipment. Wisconsin briefly became one of the nation's leading producers of wheat during the 1860s. Meanwhile, the lumber industry dominated in the heavily forested northern sections of Wisconsin, and sawmills sprang up in cities like
Wisconsin's economy also diversified during the early years of statehood. While lead mining diminished, agriculture became a principal occupation in the southern half of the state. Railroads were built across the state to help transport grains to market, and industries like J.I. Case & Company in Racine were founded to build agricultural equipment. Wisconsin briefly became one of the nation's leading producers of wheat during the 1860s. Meanwhile, the lumber industry dominated in the heavily forested northern sections of Wisconsin, and sawmills sprang up in cities like La Crosse
La Crosse is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of La Crosse County, Wisconsin, La Crosse County. Positioned alongside the Mississippi River, La Crosse is the largest city on Wisconsin's western border. La Crosse's populat ...
, Eau Claire, and Wausau. These economic activities had dire environmental consequences. By the close of the 19th century, intensive agriculture had devastated soil fertility, and lumbering had deforested most of the state. These conditions forced both wheat agriculture and the lumber industry into a precipitous decline.
 Beginning in the 1890s, farmers in Wisconsin shifted from wheat to dairy production in order to make more sustainable and profitable use of their land. Many immigrants carried cheese-making traditions that, combined with the state's suitable geography and dairy research led by Stephen Babcock at the
Beginning in the 1890s, farmers in Wisconsin shifted from wheat to dairy production in order to make more sustainable and profitable use of their land. Many immigrants carried cheese-making traditions that, combined with the state's suitable geography and dairy research led by Stephen Babcock at the University of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, ...
, helped the state build a reputation as "America's Dairyland". Meanwhile, conservationists including Aldo Leopold helped re-establish the state's forests during the early 20th century, paving the way for a more renewable lumber and paper milling industry as well as promoting recreational tourism in the northern woodlands. Manufacturing also boomed in Wisconsin during the early 20th century, driven by an immense immigrant workforce arriving from Europe. Industries in cities like Milwaukee ranged from brewing and food processing to heavy machine production and tool-making, leading Wisconsin to rank 8th among U.S. states in total product value by 1910.
20th century
 The early 20th century was also notable for the emergence of progressive politics championed by
The early 20th century was also notable for the emergence of progressive politics championed by Robert M. La Follette
Robert Marion "Fighting Bob" La Follette Sr. (June 14, 1855June 18, 1925), was an American lawyer and politician. He represented Wisconsin in both chambers of Congress and served as the 20th Governor of Wisconsin. A Republican for most of his ...
. Between 1901 and 1914, Progressive Republicans in Wisconsin created the nation's first comprehensive statewide primary election system, the first effective workplace injury compensation law, and the first state income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
, making taxation proportional to actual earnings. The progressive Wisconsin Idea
The Wisconsin Idea is a public philosophy that has influenced policy and ideals in the U.S. state of Wisconsin's education system and politics.
In education, emphasis is often placed on how the Idea articulates education's role for Wisconsin ...
also promoted the statewide expansion of the University of Wisconsin through the UW-Extension system at this time. Later, UW economics professors John R. Commons
John Rogers Commons (October 13, 1862 – May 11, 1945) was an American institutional economist, Georgist, progressive and labor historian at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Early years
John R. Commons was born in Hollansburg, Ohio on ...
and Harold Groves helped Wisconsin create the first unemployment compensation
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a comp ...
program in the United States in 1932.
In the immediate aftermath of World War II, citizens of Wisconsin were divided over issues such as creation of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, support for the European recovery, and the growth of the Soviet Union's power. However, when Europe divided into Communist and capitalist camps and the Communist revolution in China succeeded in 1949, public opinion began to move towards support for the protection of democracy and capitalism against Communist expansion.
Wisconsin took part in several political extremes in the mid to late 20th century, ranging from the anti-communist crusades of Senator Joseph McCarthy in the 1950s to the radical antiwar protests at UW-Madison that culminated in the Sterling Hall bombing in August 1970. The state undertook welfare reform under Republican Governor Tommy Thompson
Tommy George Thompson (born November 19, 1941) is an American Republican politician who most recently served as interim president of the University of Wisconsin System from 2020 to 2022. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served a ...
during the 1990s. The state's economy also underwent further transformations towards the close of the 20th century, as heavy industry and manufacturing declined in favor of a service economy
Service economy can refer to one or both of two recent economic developments:
* The increased importance of the service sector in industrialized economies. The current list of Fortune 500 companies contains more service companies and fewer manu ...
based on medicine, education, agribusiness, and tourism.
Two U.S. Navy battleships, BB-9 and BB-64, were named for the state.

21st century
In 2011, Wisconsin became the focus of some controversy when newly elected governor Scott Walker proposed, passed, and enacted the2011 Wisconsin Act 10 The 2011 Wisconsin Act 10, also known as the Wisconsin Budget Repair Bill, is legislation proposed by Republican Governor Scott Walker and passed by the Wisconsin Legislature to address a projected $3.6 billion budget deficit. The legislation prim ...
, which made large changes in the areas of collective bargaining, compensation, retirement, health insurance, and sick leave of public sector employees, among other changes. A series of major protests by union supporters took place that year in response to the changes, and Walker survived a recall election held the next year, becoming the first governor in United States history to do so. Walker enacted other bills promoting conservative governance, such as a right-to-work law
In the context of labor law in the United States, the term "right-to-work laws" refers to state laws that prohibit union security agreements between employers and labor unions which require employees who are not union members to contribute ...
, abortion restrictions, and legislation removing certain gun controls.
Geography
 Wisconsin is bordered by the Montreal River;
Wisconsin is bordered by the Montreal River; Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
and Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
to the north; by Lake Michigan to the east; by Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
to the south; and by Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
to the southwest and Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
to the northwest. A border dispute with Michigan was settled by two cases, both Wisconsin v. Michigan, in 1934 and 1935. The state's boundaries include the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
and St. Croix River in the west, and the Menominee River
The Menominee River is a river in northwestern Michigan and northeastern Wisconsin in the United States. It is approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed Dece ...
in the northeast.
With its location between the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
and the Mississippi River, Wisconsin is home to a wide variety of geographical features. The state is divided into five distinct regions. In the north, the Lake Superior Lowland
In the U.S. state of Wisconsin, the Lake Superior Lowland, also known as the Superior Coastal Plain, is a geographical region located in the far northern part of the state bordering Lake Superior. It covers about , and does not extend beyond fr ...
occupies a belt of land along Lake Superior. Just to the south, the Northern Highland
The Northern Highland is a geographical region in the north central United States covering much of the northern territory of the state of Wisconsin.
The region stretches from the state border with Minnesota in the west to the Michigan border i ...
has massive mixed hardwood and coniferous forests including the Chequamegon-Nicolet National Forest, as well as thousands of glacial lakes, and the state's highest point, Timms Hill
Timms Hill or Timm's Hill is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and is located in north-central Wisconsin in Timms Hill County Park in the Town of Hill in Price County. After being surveyed by Quentin Stevens of Ogema Tele ...
. In the middle of the state, the Central Plain has some unique sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
formations like the Dells of the Wisconsin River
The Dells of the Wisconsin River, also called the Wisconsin Dells (from Old English �dæle��, modern English “dale”), meaning “valley”, is a 5-mile (8-km) gorge on the Wisconsin River in south-central Wisconsin, USA. It is noted for it ...
in addition to rich farmland. The Eastern Ridges and Lowlands
The Eastern Ridges and Lowlands is a geographical region in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Wisconsin, between Green Bay in the north, and the border with Illinois in the south. Lake Michigan lies to the east of the region.
The Eastern R ...
region in the southeast is home to many of Wisconsin's largest cities. The ridges include the Niagara Escarpment that stretches from New York, the Black River Escarpment and the Magnesian Escarpment
The Magnesian escarpment is the most westerly of three prominent escarpments that run north-south in Wisconsin.
All three escarpments are formed by the edges of layers of sedimentary rocks. The easternmost and most prominent escarpment is the Ni ...
.
In the southwest, the Western Upland
The Western Upland is a geographical region covering much of the western half of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It stretches from southern Polk County, Wisconsin in the north to the state border with Illinois in the south, and from Rock County i ...
is a rugged landscape with a mix of forest and farmland, including many bluffs on the Mississippi River. This region is part of the Driftless Area
The Driftless Area, a topographical and cultural region in the American Midwest, comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois.
Never covered by ice during the las ...
, which also includes portions of Iowa, Illinois, and Minnesota. This area was not covered by glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s during the most recent ice age, the Wisconsin Glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
. Overall, 46% of Wisconsin's land area is covered by forest. Langlade County has a soil rarely found outside of the county called Antigo silt loam.
Wisconsin has sister-state relationships with Germany's Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Dar ...
, Japan's Chiba Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region of Honshu. Chiba Prefecture has a population of 6,278,060 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of . Chiba Prefecture borders Ibaraki Prefecture to the north, Saitama Prefecture to t ...
, Mexico's Jalisco, China's Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
, and Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
.
Climate
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Dfb''), while southern and southwestern portions are classified as hot-summer humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfa''). The highest temperature ever recorded in the state was in the Wisconsin Dells, on July 13, 1936, where it reached 114 °F (46 °C). The lowest temperature ever recorded in Wisconsin was in the village of Couderay, where it reached −55 °F (−48 °C) on both February 2 and 4, 1996. Wisconsin also receives a large amount of regular snowfall averaging around in the southern portions with up to annually in the Lake Superior snowbelt
The Snowbelt is the region near the Great Lakes in North America where heavy snowfall in the form of lake-effect snow is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off the eastern and southern shores.
Ca ...
each year.
Demographics
Population
 The
The United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of t ...
estimates that the population of Wisconsin was 5,822,434 on July 1, 2019, a 2.4% increase since the 2010 United States census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servi ...
. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 150,659 people (i.e., 614,771 births minus 464,112 deaths) and an decrease due to net migration of 12,755 people. Immigration resulted in a net increase of 59,251 people, and migration from within the U.S. resulted in a net decrease of 72,006 people.
According to the 2016 American Community Survey, 6.5% of Wisconsin's population were of Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
origin (of any race): Mexican (4.7%), Puerto Rican (0.9%), Cuban
Cuban may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean
* Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent
** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof
* Cuban citizen, a perso ...
(0.1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (0.7%). The five largest ancestry groups were: German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(40.5%), Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
(10.8%), Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
(8.8%), Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
(7.7%), and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(5.7%). German is the most common ancestry in every county in the state, except Menominee, Trempealeau, and Vernon. Wisconsin has the highest percentage of residents of Polish ancestry of any state.
Since its founding, Wisconsin has been ethnically heterogeneous. Following the period of French fur traders, the next wave of settlers were miners, many of whom were Cornish, who settled the southwestern area of the state. The next wave was dominated by "Yankees", migrants of English descent from New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
and upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York State that lies north and northwest of the New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Is ...
; in the early years of statehood, they dominated the state's heavy industry, finance, politics, and education. Between 1850 and 1900, the immigrants were mostly Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Scandinavians
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
(the largest group being Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
), Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, and Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
. In the 20th century, a number of African Americans and Mexicans settled in Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
; and after the end of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
came an influx of Hmongs.
The various ethnic groups settled in different areas of the state. Although German immigrants settled throughout the state, the largest concentration was in Milwaukee. Norwegian immigrants settled in lumbering and farming areas in the north and west. Irish, Italian, and Polish immigrants settled primarily in urban areas. Menominee County is the only county in the eastern United States with a Native American majority.
African Americans came to Milwaukee, especially from 1940 on. 86% of Wisconsin's African-American population live in four cities: Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
, Racine
Jean-Baptiste Racine ( , ) (; 22 December 163921 April 1699) was a French dramatist, one of the three great playwrights of 17th-century France, along with Molière and Corneille as well as an important literary figure in the Western traditi ...
, Beloit, Kenosha
Kenosha () is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the seat of Kenosha County. Per the 2020 census, the population was 99,986 which made it the fourth-largest city in Wisconsin. Situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan, Kenosh ...
, with Milwaukee home to nearly three-fourths of the state's black Americans. In the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
region, only Detroit and Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. ...
have a higher percentage of African-American residents.
33% of Wisconsin's Asian population is Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
, with significant communities in Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee ...
, Wausau, Green Bay, Sheboygan, Appleton, Madison Madison may refer to:
People
* Madison (name), a given name and a surname
* James Madison (1751–1836), fourth president of the United States
Place names
* Madison, Wisconsin, the state capital of Wisconsin and the largest city known by this ...
, La Crosse
La Crosse is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of La Crosse County, Wisconsin, La Crosse County. Positioned alongside the Mississippi River, La Crosse is the largest city on Wisconsin's western border. La Crosse's populat ...
, Eau Claire, Oshkosh, and Manitowoc.
Of the residents of Wisconsin, 71.7% were born in Wisconsin, 23.0% were born in a different US state, 0.7% were born in Puerto Rico, U.S. Island areas, or born abroad to American parent(s), and 4.6% were foreign born.
;Birth data
White Hispanic
White Latin Americans, or European Latin Americans, are Latin Americans who are considered white, typically due to European descent. Latin American countries have often tolerated intermarriage between different ethnic groups since the beginning ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Religion
The percentage of Wisconsin residents who belong to various affiliations as of 2014 were: Christian 81% (Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
50%, Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
29%), Mormon 0.5%, Jewish 0.5%, Muslim 0.5%, Buddhist 0.5%, Hindu 0.5%, and unaffiliated 15%.
Christianity is the predominant religion of Wisconsin. As of 2008, the three largest denominational groups in Wisconsin were Catholic, Evangelical Protestant
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being "born again", in which an individual exper ...
, and Mainline Protestant.The Pew ForumU.S. Religious Landscape Survey
(Archived July 5, 2013), Appendix 1, p. 97. Pew Research Center, 2008. As of 2010, the Catholic Church had the highest number of adherents in Wisconsin (at 1,425,523), followed by the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America with 414,326 members, and the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod with 223,279 adherents. The
Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod
The Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod (WELS), also referred to simply as the Wisconsin Synod, is an American Confessional Lutheran denomination of Christianity. Characterized as theologically conservative, it was founded in 1850 in Milwauke ...
, the synod with the fourth highest numbers of adherents in Wisconsin, has their headquarters in Waukesha, Wisconsin.
Crime
Statewide FBI Crime statistics for 2009 include 144 murders/non-negligent manslaughter; 1,108 rapes; 4,850 robberies; 8,431 aggravated assaults; and 147,486 property crimes. Wisconsin also publishes its own statistics through the Bureau of Justice Information and Analysis. The state reported 14,603 violent crimes in 2009, with a clearance rate (% solved) of 50%. The state reported 4,633 sexual assaults in 2009, with an overall clearance rate for sexual assaults of 57%.Government
 Wisconsin's Constitution outlines the structure and function of state government, which is organized into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The
Wisconsin's Constitution outlines the structure and function of state government, which is organized into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The Wisconsin Blue Book
The ''Wisconsin Blue Book'' is a biennial publication of the Wisconsin's Legislative Reference Bureau. The ''Blue Book'' is an almanac containing information on the government, economics, demographics, geography and history of the state of Wisc ...
is the primary published reference about the government and politics of the state. Re-published every two years, copies are available from state legislators.
In a 2020 study, Wisconsin was ranked as the 25th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
Executive
governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
. The current governor, Tony Evers
Anthony Steven Evers (born November 5, 1951) is an American educator and politician serving as the 46th governor of Wisconsin since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as Wisconsin's Superintendent of Public Instruction from 2009 ...
, assumed office on January 7, 2019. In addition to the governor, the executive branch includes five other elected constitutional officers: Lieutenant Governor, Secretary of State, Attorney General, Treasurer
A treasurer is the person responsible for running the treasury of an organization. The significant core functions of a corporate treasurer include cash and liquidity management, risk management, and corporate finance.
Government
The treasury ...
, and State Superintendent of Public Instruction. Four members of the Wisconsin executive branch are Democrats. The Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisconsin is a non-partisan position.
Legislative
TheWisconsin State Legislature
The Wisconsin Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The Legislature is a bicameral body composed of the upper house, Wisconsin State Senate, and the lower Wisconsin State Assembly, both of which have had Republ ...
is Wisconsin's legislative branch. The Legislature is a bicameral body consisting of the Assembly
Assembly may refer to:
Organisations and meetings
* Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions
* General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representa ...
and the Senate.
Judicial
Wisconsin's court system has four levels: municipal courts, circuit courts, the Court of Appeals, and the Supreme Court. Municipal courts typically handle cases involving local ordinance matters. The circuit courts are Wisconsin's trial courts, they haveoriginal jurisdiction
In common law legal systems original jurisdiction of a court is the power to hear a case for the first time, as opposed to appellate jurisdiction, when a higher court has the power to review a lower court's decision.
India
In India, the S ...
in all civil and criminal cases within the state. Challenges to circuit court rulings are heard by the Wisconsin Court of Appeals
The Wisconsin Court of Appeals is an intermediate appellate court that reviews contested decisions of the Wisconsin circuit courts. The Court of Appeals was created in August 1978 to alleviate the Wisconsin Supreme Court's rising number of app ...
, consisting of sixteen judges who typically sit in three-judge panels. As the state's highest appellate court, the Wisconsin Supreme Court
The Wisconsin Supreme Court is the highest appellate court in Wisconsin. The Supreme Court has jurisdiction over original actions, appeals from lower courts, and regulation or administration of the practice of law in Wisconsin.
Location
The Wi ...
may hear both appeals from lower courts and original actions. In addition to deciding cases, the Supreme Court is responsible for administering the state's court system and regulating the practice of law in Wisconsin.
Federal
In theUnited States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and pow ...
Wisconsin is represented by Ron Johnson
Ronald Harold Johnson (born April 8, 1955) is an American accountant, businessman, and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Wisconsin, a seat he has held since 2011. A Republican, Johnson was first elected to the U.S. S ...
and Tammy Baldwin
Tammy Suzanne Green Baldwin (born February 11, 1962) is an American lawyer and politician who has served as the junior United States senator from Wisconsin since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, she served three terms in the Wisconsin St ...
. Wisconsin is divided into eight congressional districts
Congressional districts, also known as electoral districts and legislative districts, electorates, or wards in other nations, are divisions of a larger administrative region that represent the population of a region in the larger congressional bod ...
.
Taxes
 Wisconsin collects personal
Wisconsin collects personal income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
es (based on five income bracket An income bracket is a category of people whose income falls within defined upper and lower levels.
In governmental planning, entire populations are divided into income brackets. These brackets are used to categorize demographic data as well as det ...
s) which range from 4% to 7.65%. The state sales
Sales are activities related to selling or the number of goods sold in a given targeted time period. The delivery of a service for a cost is also considered a sale.
The seller, or the provider of the goods or services, completes a sale in ...
and use tax
A use tax is a type of tax levied in the United States by numerous state governments. It is essentially the same as a sales tax but is applied not where a product or service was sold but where a merchant bought a product or service and then conv ...
rate is 5.0%. Fifty-nine counties have an additional sales/use tax of 0.5%. Milwaukee County and four surrounding counties have an additional temporary 0.1% tax that helps fund the Miller Park
American Family Field is a retractable roof stadium used primarily for baseball. It is located in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, just southwest of the intersection of Interstate 94 and Brewers Boulevard. It is the home of Major League Baseball's Milwauk ...
baseball stadium, which was completed in 2001.
The most common property tax assessed on Wisconsin residents is the real property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inhe ...
, or their residential property tax. Wisconsin does not impose a property tax on vehicles, but does levy an annual registration fee. Property taxes are the most important tax revenue source for Wisconsin's local governments, as well as major methods of funding school districts, vocational technical colleges, special purpose districts and tax incremental finance districts. Equalized values are based on the full market value of all taxable property in the state, except for agricultural land. In order to provide property tax relief for farmers, the value of agricultural land is determined by its value for agricultural uses, rather than for its possible development value. Equalized values are used to distribute state aid payments to counties, municipalities, and technical colleges. Assessments prepared by local assessors are used to distribute the property tax burden within individual municipalities.
Wisconsin does not assess a tax on intangible property
Intangible property, also known as incorporeal property, is something that a person or corporation can have ownership of and can transfer ownership to another person or corporation, but has no physical substance, for example brand identity or ...
. Wisconsin does not collect inheritance taxes. Until January 1, 2008, Wisconsin's estate tax
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an es ...
was decoupled from the federal estate tax laws; therefore the state imposed its own estate tax on certain large estates.
There are no toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically ...
s in Wisconsin; highway construction and maintenance are funded in part by motor fuel tax revenues, and the remaining balance is drawn from the State General Fund. Non-highway road construction and maintenance are funded by local governments (municipalities or counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
).
International relations
A Mexican consulate opened in Milwaukee on July 1, 2016. Wisconsin has had a diplomatic relationship with the Japanese prefecture of Chiba since 1990.Politics
During theCivil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, Wisconsin was a Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
state; in fact, it is the state that gave birth to the Republican Party, although ethno-religious issues in the late 19th century caused a brief split in the coalition. The Bennett Law campaign of 1890 dealt with foreign language teaching in schools. Many Germans switched to the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
because of the Republican Party's support of the law.
Wisconsin's political history encompasses, on the one hand, "Fighting Bob" La Follette and the Progressive movement
Progressivism holds that it is possible to improve human societies through political action. As a political movement, progressivism seeks to advance the human condition through social reform based on purported advancements in science, techn ...
, and on the other, the Republican and anti-Communist Joe McCarthy
Joseph Raymond McCarthy (November 14, 1908 – May 2, 1957) was an American politician who served as a Republican U.S. Senator from the state of Wisconsin from 1947 until his death in 1957. Beginning in 1950, McCarthy became the most vis ...
. From the early 20th century, the Socialist Party of America had a base in Milwaukee. The phenomenon was referred to as " sewer socialism" because the elected officials were more concerned with public works and reform than with revolution (although revolutionary socialism existed in the city as well). Its influence faded in the late 1950s largely because of the red scare and racial tensions. The first Socialist mayor of a large city in the United States was Emil Seidel
Emil Seidel (December 13, 1864 – June 24, 1947) was a prominent German-American politician. Seidel was the mayor of Milwaukee from 1910 to 1912. The first Socialist mayor of a major city in the United States, Seidel became the Vice Presidential ...
, elected mayor of Milwaukee in 1910; another Socialist, Daniel Hoan
Daniel Webster Hoan (March 12, 1881 – June 11, 1961) was an American politician who served as the 32nd Mayor of Milwaukee, Wisconsin from 1916 to 1940. A lawyer who had served as Milwaukee City Attorney from 1910 to 1916, Hoan was a promin ...
, was mayor of Milwaukee from 1916 to 1940; and a third, Frank P. Zeidler, from 1948 to 1960. Succeeding Frank Zeidler, the last of Milwaukee's Socialist mayors, Henry Maier
Henry Walter Maier (February 7, 1918 – July 17, 1994) was an American politician and the longest-serving mayor of Milwaukee, Wisconsin, holding office from 1960 to 1988. A Democrat, Maier was a powerful and controversial figure, presiding over ...
, a former Wisconsin State Senator and member of the Democratic Party was elected mayor of Milwaukee in 1960. Maier remained in office for 28 years, the longest-serving mayor in Milwaukee history. Socialist newspaper editor
An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies.
The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ...
Victor Berger was repeatedly elected as a U.S. Representative, although he was prevented from serving for some time because of his opposition to the First World War.
Through the first half of the 20th century, Wisconsin's politics were dominated by Robert La Follette
Robert Marion "Fighting Bob" La Follette Sr. (June 14, 1855June 18, 1925), was an American lawyer and politician. He represented Wisconsin in both chambers of Congress and served as the 20th Governor of Wisconsin. A Republican for most of his ...
and his sons, originally of the Republican Party, but later of the revived Progressive Party Progressive Party may refer to:
Active parties
* Progressive Party, Brazil
* Progressive Party (Chile)
* Progressive Party of Working People, Cyprus
* Dominica Progressive Party
* Progressive Party (Iceland)
* Progressive Party (Sardinia), Ita ...
. Since 1945, the state has maintained a close balance between Republicans and Democrats. Recent leading Republicans include former Governor Tommy Thompson
Tommy George Thompson (born November 19, 1941) is an American Republican politician who most recently served as interim president of the University of Wisconsin System from 2020 to 2022. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served a ...
and Congressman Jim Sensenbrenner; prominent Democrats include Senators Herb Kohl
Herbert H. Kohl (born February 7, 1935) is an American businessman and politician. Alongside his brother and father, the Kohl family created the Kohl's department stores chain, of which Kohl went on to be president and CEO. Kohl also served as a ...
and Russ Feingold
Russell Dana Feingold ( ; born March 2, 1953) is an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senator from Wisconsin from 1993 to 2011. A member of the Democratic Party, he was its nominee in the 2016 election for the same U ...
, the only Senator to vote against the Patriot Act
The USA PATRIOT Act (commonly known as the Patriot Act) was a landmark Act of the United States Congress, signed into law by President George W. Bush. The formal name of the statute is the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appro ...
in 2001, and Congressman David Obey
David Ross Obey ( ; born October 3, 1938) is an American lobbyist and former politician who served as a member of the United States House of Representatives for from 1969 to 2011. The district includes much of the northwestern portion of the st ...
.
Federal elections
 In 2020, Wisconsin leaned back in the Democratic party's direction as Joe Biden won the state by an even narrower margin of 0.7%. Biden's win was largely carried by Milwaukee and Dane counties with the rural areas of the state being carried by Trump.
Wisconsin has leaned Democratic in recent presidential elections, although
In 2020, Wisconsin leaned back in the Democratic party's direction as Joe Biden won the state by an even narrower margin of 0.7%. Biden's win was largely carried by Milwaukee and Dane counties with the rural areas of the state being carried by Trump.
Wisconsin has leaned Democratic in recent presidential elections, although Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
managed to win the state in 2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the Impeachment of Dilma Rousseff, impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses duri ...
by a narrow margin of 0.8%. This marked the first time Wisconsin voted for a Republican presidential candidate since 1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeas ...
, when every state except Minnesota and Washington D.C. went Republican. In 2012
File:2012 Events Collage V3.png, From left, clockwise: The passenger cruise ship Costa Concordia lies capsized after the Costa Concordia disaster; Damage to Casino Pier in Seaside Heights, New Jersey as a result of Hurricane Sandy; People gat ...
, Republican presidential candidate Mitt Romney chose Wisconsin Congressman Paul Ryan, a native of Janesville, as his running mate against incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and Vice President Joe Biden. Obama nevertheless carried Wisconsin by a margin of 53% to 46%. Both the 2000 and 2004 presidential elections were quite close, with Wisconsin receiving heavy doses of national advertising, in accord with its status as a "swing", or pivot, state. Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic no ...
carried the presidential vote in 2000 by 5,700 votes, and John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party, he ...
won Wisconsin in 2004 by 11,000 votes. Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
carried the state in 2008 by 381,000 votes (56%).
Republicans had a stronghold in the Fox Valley, but elected a Democrat, Steve Kagen, of Appleton, for the 8th Congressional District in 2006. However, Kagen survived only two terms and was replaced by Republican Reid Ribble in the Republican Party's sweep of Wisconsin in November 2010, the first time the Republican Party had taken back both chambers of the state legislature and the governorship in the same election. The City of Milwaukee heads the list of Wisconsin's Democratic strongholds, which also includes Madison and the state's Native American reservations. Wisconsin's largest Congressional district, the 7th, had voted Democratic since 1969. Its representative, David Obey, chaired the powerful House Appropriations Committee. However, Obey retired and the once-Democratic seat was taken by Republican Sean Duffy
Sean Patrick Duffy (born October 3, 1971) is an American politician, prosecutor, former sports commentator and reality television personality who is currently a co-host of ''The Bottom Line'' on Fox Business, as well as a contributor on Fox News. ...
in November 2010. The 2010 elections saw a huge Republican resurgence in Wisconsin. Republicans took control of the governor's office and both houses of the state legislature. Republican Ron Johnson
Ronald Harold Johnson (born April 8, 1955) is an American accountant, businessman, and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Wisconsin, a seat he has held since 2011. A Republican, Johnson was first elected to the U.S. S ...
defeated Democratic incumbent U.S. Senator Russ Feingold
Russell Dana Feingold ( ; born March 2, 1953) is an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senator from Wisconsin from 1993 to 2011. A member of the Democratic Party, he was its nominee in the 2016 election for the same U ...
and Republicans took two previously Democratic-held House seats, creating a 5–3 Republican majority House delegation.
State elections
 At the statewide level, Wisconsin is competitive, with control regularly alternating between the two parties. In 2006, Democrats gained in a national sweep of opposition to the Bush administration, and the Iraq War. The retiring GOP 8th District Congressman, Mark Green, of Green Bay, ran against the incumbent Governor
At the statewide level, Wisconsin is competitive, with control regularly alternating between the two parties. In 2006, Democrats gained in a national sweep of opposition to the Bush administration, and the Iraq War. The retiring GOP 8th District Congressman, Mark Green, of Green Bay, ran against the incumbent Governor Jim Doyle
James Edward Doyle, Jr., (born November 23, 1945) is an American attorney and politician who served as the 44th governor of Wisconsin, serving from January 6, 2003 to January 3, 2011. In his first election to the governorship, he defeated incum ...
. Green lost by 8% statewide, making Doyle the first Democratic governor to be re-elected in 32 years. The Republicans lost control of the state Senate. Although Democrats gained eight seats in the state Assembly, Republicans retained a five-vote majority. In 2008, Democrats regained control of the State Assembly by a 52–46 margin, marking the first time since 1986 that the governor and state legislature were both Democratic.
With the election of Scott Walker in 2010, Republicans won both chambers of the legislature and the governorship, the first time all three changed partisan control in the same election. His first year in office saw the introduction of the 2011 Wisconsin Act 10 The 2011 Wisconsin Act 10, also known as the Wisconsin Budget Repair Bill, is legislation proposed by Republican Governor Scott Walker and passed by the Wisconsin Legislature to address a projected $3.6 billion budget deficit. The legislation prim ...
, which removed collective bargaining rights for state employees. On February 14, 2011, the Wisconsin State Capitol
The Wisconsin State Capitol, located in Madison, Wisconsin, houses both chambers of the Wisconsin legislature along with the Wisconsin Supreme Court and the Office of the Governor. Completed in 1917, the building is the fifth to serve as the Wi ...
erupted with protests when the Legislature took up a bill that would end most collective bargaining rights for state employees, except for wages, to address the $3.6 billion deficit. The protests attracted tens of thousands of people each day, and garnered international attention. The Assembly passed the bill 53–42 on March 10 after the State Senate passed it the night before, and sent it to the Governor for his signature. In response to the bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Plac ...
, enough signatures were gathered to force a recall election
A recall election (also called a recall referendum, recall petition or representative recall) is a procedure by which, in certain polities, voters can remove an elected official from office through a referendum before that official's term of of ...
against Governor Walker. Tom Barrett, the mayor of Milwaukee and Walker's 2010 opponent, won the Democratic primary and faced Walker again. Walker won the election by 53% to 46% and became the first governor in United States history to retain his seat after a recall election.
Following the 2014 general election on November 4, 2014, the Governor, Lieutenant Governor, State Attorney General and State Treasurer were all Republicans, while the Secretary of State was a Democrat. However, Walker was defeated for a third term in 2018
File:2018 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2018 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in PyeongChang, South Korea; Protests erupt following the Assassination of Jamal Khashoggi; March for Our Lives protests take place across the Unit ...
by Democrat Tony Evers
Anthony Steven Evers (born November 5, 1951) is an American educator and politician serving as the 46th governor of Wisconsin since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as Wisconsin's Superintendent of Public Instruction from 2009 ...
. Democratic U.S. Senator Tammy Baldwin
Tammy Suzanne Green Baldwin (born February 11, 1962) is an American lawyer and politician who has served as the junior United States senator from Wisconsin since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, she served three terms in the Wisconsin St ...
was also elected to a second term and Democrats won all constitutional statewide offices on the ballot including Lieutenant Governor, Attorney General, Secretary of State, and State Treasurer, the first time this happened in Wisconsin since 1982. Later however, in April 2019, conservative judge Brian Hagedorn defeated his liberal opponent Lisa Neubauer by 6,100 votes.
Economy
 In 2019 Wisconsin's gross state product was $349.416 billion, making it 21st among U.S. states. The economy of Wisconsin is driven by
In 2019 Wisconsin's gross state product was $349.416 billion, making it 21st among U.S. states. The economy of Wisconsin is driven by manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
, agriculture, and health care. The state's economic output from manufacturing was $48.9 billion in 2008, making it the tenth largest among states in manufacturing gross domestic product. Manufacturing accounts for about 20% of the state's gross domestic product, a proportion that is third among all states. The per capita personal income was $35,239 in 2008. In March 2017, the state's unemployment rate was 3.4% (seasonally adjusted).
In quarter four of 2011, the largest employers in Wisconsin were:
# Wal-Mart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores from the United States, headquarter ...
# University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
# Milwaukee Public Schools
Milwaukee Public Schools (MPS) is the largest school district in Wisconsin. As of the 2015–16 school year, MPS served 75,568 students in 154 schools and had 9,636 full-time equivalent (FTE) staff positions. The Milwaukee Public Schools system i ...
# U.S. Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U. ...
# Wisconsin Department of Corrections
The Wisconsin Department of Corrections (WIDOC) is an administrative department in the executive branch of the state of Wisconsin responsible for corrections in Wisconsin, including state prisons and community supervision. The secretary is a cab ...
# Menards
Menards is an American home improvement retail company headquartered in Eau Claire, Wisconsin. Menards is owned by founder John Menard Jr. through his privately held company, Menard, Inc. It has 335 stores in 15 states: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, ...
# Marshfield Clinic
Marshfield Clinic Health System is an integrated health system serving Wisconsin founded in 1916. The system contains several hospitals and many clinics throughout Wisconsin, as well as a medical research institute and an education division, an ...
# Wisconsin Department of Veterans Affairs
# Target Corporation
Target Corporation ( doing business as Target and stylized in all lowercase since 2018) is an American big box department store chain headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota. It is the seventh largest retailer in the United States, and a com ...
, and
# City of Milwaukee.
Agriculture
Wisconsin produces about a quarter of America's cheese, leading the nation in cheese production."Total Cheese Production Excluding Cottage Cheese—States and United States: February 2010 and 2011" in United States Department of Agriculture''Dairy Products''
, p. 13. It is second in milk production, after
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, and third in per-capita milk production, behind California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
and Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
. Wisconsin is second in butter production, producing about one-quarter of the nation's butter. The state ranks first nationally in the production of corn for silage
Silage () is a type of fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation to the point of acidification. It can be fed to cattle, sheep and other such ruminants (cud-chewing animals). The fermentation and storage ...
, cranberries
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
U.S. Department of Agriculture''Wisconsin Ag News—Cranberries''
, June 27, 2017, p. 1.
ginseng
Ginseng () is the root of plants in the genus '' Panax'', such as Korean ginseng ('' P. ginseng''), South China ginseng ('' P. notoginseng''), and American ginseng ('' P. quinquefolius''), typically characterized by the presence of ginsenosides ...
,United States Department of Agriculture. 2012 Census of Agriculture: United States Summary and State Data, Vol. 1
''. Washington, DC: 2014, pp. 475–476. and
snap beans
Green beans are young, unripe fruits of various cultivars of the common bean (''Phaseolus vulgaris''), although immature or young pods of the runner bean (''Phaseolus coccineus''), yardlong bean ( ''Vigna unguiculata'' subsp. ''sesquipedalis' ...
for processing. It grows more than half the national crop of cranberries. and 97% of the nation's ginseng. Wisconsin is also a leading producer of oat
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
s, potatoes, carrots, tart cherries, maple syrup, and sweet corn for processing. The significance of the state's agricultural production is exemplified by the depiction of a Holstein cow, an ear of corn, and a wheel of cheese on Wisconsin's state quarter design. The state annually selects an "Alice in Dairyland
Alice in Dairyland is a program that is meant to promote Wisconsin's diverse agriculture industry. A young woman is selected every year to be Wisconsin's Agriculture Ambassador. As a contracted public relations specialist, she works with the medi ...
" to promote the state's agricultural products around the world.
A large part of the state's manufacturing sector includes commercial food processing, including well-known brands such as Oscar Mayer
Oscar Mayer is an American meat and cold cut producer known for its hot dogs, bologna, bacon, ham, and Lunchables products. The company is a subsidiary of the Kraft Heinz Company and based in Chicago, Illinois.
History Early years
German im ...
, Tombstone frozen pizza, Johnsonville brats, and Usinger's sausage. Kraft Foods
The second incarnation of Kraft Foods is an American food manufacturing and processing conglomerate, split from Kraft Foods Inc. in 2012 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It became part of Kraft Heinz in 2015.
A merger with Heinz, arran ...
alone employs more than 5,000 people in the state. Milwaukee is a major producer of beer and was formerly headquarters for Miller Brewing Company
The Miller Brewing Company is an American brewery and beer company in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. It was founded in 1855 by Frederick Miller. Molson Coors acquired the full global brand portfolio of Miller Brewing Company in 2016, and operates the ...
—the nation's second-largest brewer—until it merged with Coors. Formerly, Schlitz, Blatz, and Pabst were cornerstone breweries in Milwaukee.
Manufacturing
Wisconsin is home to a very large and diversified manufacturing economy, with special focus on transportation and capital equipment. Major Wisconsin companies in these categories include theKohler Company
Kohler Co., founded in 1873 by John Michael Kohler, is an American manufacturing company based in Kohler, Wisconsin. Kohler is best known for its plumbing products, but the company also manufactures furniture, cabinetry, tile, engines, and ...
; Mercury Marine
Mercury Marine is a marine engine division of Brunswick Corporation headquartered in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin. The main product line is outboard motors. It also produces the MerCruiser line of sterndrives and inboard motors. Some manufacturi ...
; Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation, Inc. is an American provider of industrial automation whose brands include Allen-Bradley, FactoryTalk software and LifecycleIQ Services.
Headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, Rockwell Automation employs approximately 26,000 ...
; Johnson Controls
Johnson Controls International is an American
Irish-domiciled multinational conglomerate headquartered in Cork, Ireland, that produces fire, HVAC, and security equipment for buildings. As of mid-2019, it employed 105,000 people in around 2,00 ...
; John Deere; Briggs & Stratton
Briggs & Stratton Corporation is an American manufacturer of gasoline engines with headquarters in Wauwatosa, Wisconsin.
Engine production averages 10 million units per year as of April 2015. The company reports that it has 13 large facili ...
; Milwaukee Electric Tool Company
The Milwaukee Electric Tool Corporation is an American company that develops, manufactures, and markets power tools. It is a brand and subsidiary of Techtronic Industries. Since 2016 it has been the largest supplier by volume of cordless power ...
; Miller Electric; Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar Inc. (stock symbol CAT) is an American ''Fortune'' 500 corporation and the world's largest construction-equipment manufacturer.
In 2018, Caterpillar was ranked number 65 on the ''Fortune'' 500 list and number 238 on the Global ''Fo ...
; Joy Global
Joy Global Inc. was a company that manufactured and serviced heavy equipment used in the extraction and haulage of coal and minerals in both underground and surface mining. The company had manufacturing facilities in Alabama, Pennsylvania, Te ...
; Oshkosh Corporation
Oshkosh Corporation, formerly Oshkosh Truck, is an American industrial company that designs and builds specialty trucks, military vehicles, truck bodies, airport fire apparatus, and access equipment. The corporation also owns Pierce Manufac ...
; Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depressi ...
; Case IH
Case IH is an American agricultural machinery manufacturer. It was created in 1985 when Tenneco bought selected assets of the agricultural division from International Harvester and merged it into its J.I. Case Company (IH then became Navistar).T ...
; S. C. Johnson & Son; Ashley Furniture; Ariens; and Evinrude Outboard Motors
Evinrude Outboard Motors was a North American company that built a major brand of two-stroke outboard motors for boats. Founded by Ole Evinrude in Milwaukee, Wisconsin in 1907, it was formerly owned by the publicly traded Outboard Marine Corpo ...
.
Consumer goods
Wisconsin is a major producer of paper, packaging, and other consumer goods. Major consumer products companies based in the state include SC Johnson & Co., and Diversey, Inc. Wisconsin also ranks first nationwide in the production of paper products; the lower Fox River fromLake Winnebago
Lake Winnebago ( mez, Wenepekōw Nepēhsæh, oj, Wiinibiigoo-zaaga'igan, one, kanyataláheleˀ) is a shallow freshwater lake in the north central United States, located in east central Wisconsin. At 137,700 acres it is the largest lake entire ...
to Green Bay has 24 paper mills along its stretch.
The development and manufacture of health care devices and software is a growing sector of the state's economy, with key players such as GE Healthcare
GE HealthCare is a subsidiary of American multinational conglomerate General Electric incorporated in New York and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. As of 2017, it is a manufacturer and distributor of diagnostic imaging agents and radiopharma ...
, Epic Systems
Epic Systems Corporation, or Epic, is an American privately held healthcare software company. According to the company, hospitals that use its software held medical records of 78% of patients in the United States and over 3% of patients worldwi ...
, and TomoTherapy
Tomotherapy is a radiation therapy modality, in which the patient is scanned across a modulated strip-beam, so that only one “slice” (Greek prefix “tomo-”) of the target is exposed at any one time by the linear accelerator (linac) beam. ...
.
Tourism
Circus World Museum
The Circus World Museum is a museum complex in Baraboo, Wisconsin, devoted to circus-related history. The museum features circus artifacts and exhibits and hosts daily live circus performances throughout the summer. It is owned by the Wisconsin Hi ...
in Baraboo
Baraboo is a city in the Midwest and the county seat of Sauk County, Wisconsin, United States. The largest city in the county, Baraboo is the principal city of the Baraboo Micropolitan Statistical Area. Its 2020 population was 12,556. It is situ ...
, and The Dells of the Wisconsin River
The Dells of the Wisconsin River, also called the Wisconsin Dells (from Old English �dæle��, modern English “dale”), meaning “valley”, is a 5-mile (8-km) gorge on the Wisconsin River in south-central Wisconsin, USA. It is noted for it ...
draw thousands of visitors annually, and festivals such as Summerfest
Summerfest is an annual music festival held in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. First held in 1968, Summerfest is located at Henry Maier Festival Park, adjacent to Lake Michigan and Milwaukee's central business district. Summerfest attracts app ...
and the EAA Oshkosh Airshow draw international attention, along with hundreds of thousands of visitors.
Given the large number of lakes and rivers in the state, water recreation is very popular. In the North Country, what had been an industrial area focused on timber has largely been transformed into a vacation destination. Popular interest in the environment and environmentalism, added to traditional interests in hunting and fishing, has attracted a large urban audience within driving range.
The distinctive Door Peninsula
The Door Peninsula is a peninsula in eastern Wisconsin, separating the southern part of the Green Bay from Lake Michigan. The peninsula includes northern Kewaunee County, northeastern Brown County, and the mainland portion of Door Co ...
, which extends off the eastern coast of the state, contains one of the state's tourist destinations, Door County. Door County is a popular destination for boaters because of the large number of natural harbors, bays, and boat launches on both the Green Bay and Lake Michigan sides of the peninsula that forms the county. The area draws more than two million visitors yearly to its quaint villages, seasonal cherry picking, and fish boils.
Film industry
On January 1, 2008, a newtax incentive
A tax incentive is an aspect of a government's taxation policy designed to incentivize or encourage a particular economic activity by reducing tax payments.
Tax incentives can have both positive and negative impacts on an economy. Among the posi ...
for the film industry came into effect. The first major production to take advantage was Michael Mann
Michael Kenneth Mann (born February 5, 1943) is an American director, screenwriter, and producer of film and television who is best known for his distinctive style of crime drama. His most acclaimed works include the films ''Thief'' (1981), ...
's ''Public Enemies''. While the producers spent $18 million on the film, it was reported that most of it went to out-of-state workers and for out-of-state services; Wisconsin taxpayers had provided $4.6 million in subsidies, and derived only $5 million in revenues from the film's making. This incentive was eliminated in 2013.
Energy
Wisconsin has no production of oil, gas, or coal. Its in-state electrical generation is mostly from coal. Other important electricity sources are natural gas and nuclear. The state has a mandate that ten percent of its electrical energy come from renewable sources by the end of 2015. This goal has been met, but not with in-state sources. , a third of that ten percent comes from out of state sources, mostly wind generated electricity from Minnesota and Iowa. The state has agnostic policies for developing wind power in state.Transportation
Airports
Wisconsin is served by eight commercial service airports, in addition to a number ofgeneral aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
airports. Milwaukee Mitchell International Airport
Milwaukee Mitchell International Airport is a civil–military airport south of downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States., effective May 21, 2020. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Ai ...
is the largest international commercial airport located in Wisconsin.
Intercity bus service
Wisconsin is served by multiple intercity bus operators, which provide service to 71 stops and 53 cities.Major highways
TheWisconsin Department of Transportation
The Wisconsin Department of Transportation (WisDOT) is a governmental agency of the U.S. state of Wisconsin responsible for planning, building and maintaining the state's highways. It is also responsible for planning transportation in the state ...
is responsible for planning, building and maintaining the state's highways. Eight Interstate Highways are located in the state.
Rail service
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
provides daily passenger rail service between Chicago and Milwaukee through the ''Hiawatha Service
The ''Hiawatha Service'', or simply ''Hiawatha'', is an 86-mile (138 km) train route operated by Amtrak on the western shore of Lake Michigan between Chicago, Illinois and Milwaukee, Wisconsin. However, the name was historically applied to ...
''. Also provided is cross-country service via the ''Empire Builder
The ''Empire Builder'' is an Amtrak long-distance passenger train that operates daily between Chicago and either Seattle or Portland via two sections west of Spokane. Introduced in 1929, it was the flagship passenger train of the Great Northe ...
'' with stops in several cities across Wisconsin. Commuter rail provider Metra
Metra is the commuter rail system in the Chicago metropolitan area serving the city of Chicago and its surrounding suburbs via the Union Pacific Railroad, BNSF Railway, and other railroads. The system operates 242 stations on 11 rail lines. ...
's Union Pacific North (UP-N) line has its northern terminus in Kenosha
Kenosha () is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the seat of Kenosha County. Per the 2020 census, the population was 99,986 which made it the fourth-largest city in Wisconsin. Situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan, Kenosh ...
, the only Metra line and station in the state of Wisconsin. The Hop, a modern streetcar system in Milwaukee, began service in 2018. The 2.1 mile (3.4 km) initial line runs from Milwaukee Intermodal Station
Milwaukee Intermodal Station is the main intercity bus and train station in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, located downtown. The station is served by Amtrak's ''Empire Builder'' and ''Hiawatha Service'' as well as bus companies Coach USA - Wisconsin Coac ...
to Burns Commons. The system is expected to be expanded in the future.
Important municipalities
 Over 68% of Wisconsin residents live in urban areas, with the
Over 68% of Wisconsin residents live in urban areas, with the Greater Milwaukee
The Milwaukee metropolitan area (also known as Metro Milwaukee or Greater Milwaukee) is a major metropolitan area located in Southeastern Wisconsin, consisting of the city of Milwaukee and the surrounding area. There are several definitions of the ...
area home to roughly one-third of the state's population. With more than 590,000 residents, Milwaukee is the 30th-largest city in the country. The string of cities along the western edge of Lake Michigan is generally considered to be an example of a megalopolis
A megalopolis () or a supercity, also called a megaregion, is a group of metropolitan areas which are perceived as a continuous urban area through common systems of transport, economy, resources, ecology, and so on. They are integrated enoug ...
.
With a population of nearly 260,000, Madison is consistently ranked as one of the most livable cities in both the state and country and is the fastest-growing city in Wisconsin.
Medium-size cities dot the state and anchor a network of working farms surrounding them. As of 2011, there were 12 cities in Wisconsin with a population of 50,000 or more, accounting for 73% of the state's employment.
Wisconsin has three types of municipality: cities, villages, and towns. Cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and villages
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to ...
are incorporated urban areas. Towns
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
are unincorporated minor civil divisions of counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
with limited self-government.
Education
Wisconsin, along with Minnesota and Michigan, was among theMidwestern
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
leaders in the emergent American state university movement following the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
in the United States. By the start of the 20th century, education in the state advocated the "Wisconsin Idea
The Wisconsin Idea is a public philosophy that has influenced policy and ideals in the U.S. state of Wisconsin's education system and politics.
In education, emphasis is often placed on how the Idea articulates education's role for Wisconsin ...
", which emphasized service to the people of the state. The "Wisconsin Idea" exemplified the Progressive movement within colleges and universities at the time.
Today, public post-secondary education in Wisconsin includes both the 26-campus University of Wisconsin System, with the flagship university University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
, and the 16-campus Wisconsin Technical College System
Wisconsin Technical College System (WTCS) is a system of 16 public technical colleges administered by the state of Wisconsin. The system offers more than 500 programs, awarding two-year associate degrees, one- and two-year technical diplomas, and ...
. Private colleges and universities include Alverno College, Beloit College
Beloit College is a private liberal arts college in Beloit, Wisconsin. Founded in 1846, when Wisconsin was still a territory, it is the state's oldest continuously operated college. It is a member of the Associated Colleges of the Midwest and h ...
, Cardinal Stritch University
, mottoeng = To value the better things
, established = 1937 ( years ago)
, type = Private university
, religious_affiliation = Sisters of St. Francis of Assisi (Roman Catholic)
, endowment ...
, Carroll University
Carroll University is a private university affiliated with the Presbyterian Church (USA) and located in Waukesha, Wisconsin. Established in 1846, Carroll was Wisconsin's first four-year institution of higher learning.
History
Prior to its estab ...
, Carthage College, Concordia University Wisconsin
Concordia University Wisconsin (CUW) is a private Lutheran university in Mequon, Wisconsin. It is part of the eight-member Concordia University System operated by the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod (LCMS).
The university is a coeducational in ...
, Edgewood College
Edgewood College is a private Dominican college in Madison, Wisconsin. The college occupies a campus overlooking the shores of Lake Wingra.
History
The Edgewood College property was bought in 1855 by Mr. Ashmead from Governor Leonard J. Farwe ...
, Lakeland College, Lawrence University
Lawrence University is a private liberal arts college and conservatory of music in Appleton, Wisconsin. Founded in 1847, its first classes were held on November 12, 1849. Lawrence was the second college in the U.S. to be founded as a coeducati ...
, Marquette University
Marquette University () is a private Jesuit research university in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Established by the Society of Jesus as Marquette College on August 28, 1881, it was founded by John Martin Henni, the first Bishop of the diocese of M ...
, Medical College of Wisconsin
The Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) is a private medical school, pharmacy school, and graduate school of sciences headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The school was established in 1893 and is the largest research center in eastern Wisconsin ...
, Milwaukee School of Engineering
The Milwaukee School of Engineering (MSOE) is a private university in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The campus is in the List of neighborhoods of Milwaukee, East Town neighborhood of downtown Milwaukee. The school's enrollment of 2,820 includes 224 g ...
, Ripon College, St. Norbert College
St. Norbert College (SNC) is a private Norbertine liberal arts college in De Pere, Wisconsin. Founded in October 1898 by Abbot Bernard Pennings, a Norbertine priest and educator, the school was named after Saint Norbert of Xanten. In 1952, the c ...
, Wisconsin Lutheran College
Wisconsin Lutheran College (WLC) is a private liberal arts college affiliated with the Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod and located on the border of Milwaukee and Wauwatosa, Wisconsin. It has an enrollment of about 1,200 students and is accre ...
, Viterbo University
Viterbo University is a private Catholic university in La Crosse, Wisconsin. Founded in 1890 by the Franciscan Sisters of Perpetual Adoration, Viterbo is home to three colleges with nine schools offering 48 academic programs at the associate, bac ...
, and others.
Culture


 Residents of Wisconsin are referred to as Wisconsinites. The traditional prominence of references to
Residents of Wisconsin are referred to as Wisconsinites. The traditional prominence of references to dairy farming
Dairy farming is a class of agriculture for long-term production of milk, which is processed (either on the farm or at a dairy plant, either of which may be called a dairy) for eventual sale of a dairy product. Dairy farming has a history th ...
and cheesemaking
Cheesemaking (or caseiculture) is the craft of making cheese. The production of cheese, like many other food preservation processes, allows the nutritional and economic value of a food material, in this case milk, to be preserved in concentr ...
in Wisconsin's rural economy (the state's license plates have read "America's Dairyland" since 1940) have led to the nickname (sometimes used pejoratively among non-residents) of "cheeseheads", and to the creation of "cheesehead hats" made of yellow foam in the shape of a wedge of cheese.
Numerous ethnic festivals are held throughout Wisconsin to celebrate the heritage of its citizens. Such festivals include Summerfest
Summerfest is an annual music festival held in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. First held in 1968, Summerfest is located at Henry Maier Festival Park, adjacent to Lake Michigan and Milwaukee's central business district. Summerfest attracts app ...
, Oktoberfest celebrations, Oktoberfest, Polish Fest, Festa Italiana, Irish Fest, Bastille Days, Syttende Mai (Norwegian Constitution Day), Brat(wurst) Days in Sheboygan, Pulaski, Wisconsin#Pulaski Polka Days, Polka Days, Cheese Days in Monroe, Wisconsin, Monroe and Mequon, Wisconsin, Mequon, African World Festival, Indian Summer, Arab Fest, Wisconsin Highland Games, and many others.
Art
Music
Wisconsin's music festivals include Eaux Claires, Country Fest, Country Jam USA, the Hodag Country Festival, Porterfield Country Music Festival, Country Thunder USA in Twin Lakes, and Country USA. Milwaukee hostsSummerfest
Summerfest is an annual music festival held in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. First held in 1968, Summerfest is located at Henry Maier Festival Park, adjacent to Lake Michigan and Milwaukee's central business district. Summerfest attracts app ...
, dubbed "The World's Largest Music Festival", every year. This festival is held at the lakefront Henry Maier Festival Park just south of downtown, as are a summer-long array of ethnic group, ethnic musical festivals. The Wisconsin Area Music Industry provides an annual WAMI event where it presents an awards show for top Wisconsin artists.
Architecture
The Milwaukee Art Museum, with its ''brise soleil'' designed by Santiago Calatrava, is known for its interesting architecture. Monona Terrace in Madison, a convention center designed by Taliesin architect Anthony Puttnam, is based on a 1930s design by Wisconsin nativeFrank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
. Wright's home and studio in the 20th century was at Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the '' Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts ...
, south of Spring Green. Decades after Wright's death, Taliesin remains an architectural office and school for his followers.
With the immigration of Nordic and Scandinavian Americans, northern Europeans into Wisconsin and the upper Midwest, they brought the techniques of building Log house, Log homes with them.
Alcohol culture
Drinking has long been considered a significant part of Wisconsin culture, and the state ranks at or near the top of national measures of per-capita alcohol consumption, consumption of alcohol per state, and proportion of drinkers. Consumption per-capita per-event, however, ranks low among the nation; number of events (number of times alcohol is involved) is significantly higher or highest, but consumption at each event smaller, marking Wisconsin's consumption as frequent and moderate. Factors such as cultural identification with the state's heritage of German immigration, the long-standing presence of major breweries in Milwaukee, and a cold climate are often associated with the prevalence of drinking in Wisconsin. In Wisconsin, the legal drinking age is 21, except when accompanied by a parent, guardian, or spouse who is at least 21 years old. Age requirements are waived for possessing alcohol when employed by a brewer, brewpub, beer and/or liquor wholesaler, or producer of alcohol fuel. The minimum legal age to purchase alcohol is 21, with no exceptions. The Absolute Sobriety law states that any person not of legal drinking age (currently 21) may not drive after consuming alcohol. On September 30, 2003, the Wisconsin State Legislature, state legislature, reluctant to lower a DUI offense from BAC 0.10 to 0.08, did so only as a result of federal government pressure. The Tavern League of Wisconsin, Wisconsin Tavern League opposes raising the alcoholic beverage tax. The ''Milwaukee Journal Sentinel'' series "Wasted in Wisconsin" examined this situation.Recreation
The varied landscape of Wisconsin makes the state a popular vacation destination for outdoor recreation. Winter events include skiing, ice fishing and World Championship Snowmobile Derby, snowmobile derbies. Wisconsin is situated on two Great Lakes and has many inland lakes of varied size; the state contains of water, more than all but three other states—Alaska, Michigan, and Florida. Outdoor activities are popular in Wisconsin, especially hunting and fishing. One of the most prevalent game animals is the whitetail deer. Each year in Wisconsin, well over 600,000 deer-hunting licenses are sold. In 2008, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources projected the pre-hunt deer population to be between 1.5 and 1.7 million.Sports
 Wisconsin is represented by major league teams in three sports: football, baseball, and basketball. Lambeau Field, located in Green Bay, Wisconsin, is home to the National Football League's Green Bay Packers. The Packers have been part of the NFL since the league's second season in 1921 and hold the record for the most NFL titles, earning the city of Green Bay the nickname "Titletown USA". The Packers are the smallest city franchise in the NFL and the only one owned by shareholders statewide. The franchise was founded by "Curly" Lambeau, who played and coached for them. The Green Bay Packers are one of the most successful small-market professional sports franchises in the world and have won 13 NFL championships, including the first two AFL-NFL Championship games (Super Bowls Super Bowl I, I and Super Bowl II, II), Super Bowl XXXI and Super Bowl XLV. The state's support of the team is evidenced by the 81,000-person waiting list for season tickets to Lambeau Field.
Wisconsin is represented by major league teams in three sports: football, baseball, and basketball. Lambeau Field, located in Green Bay, Wisconsin, is home to the National Football League's Green Bay Packers. The Packers have been part of the NFL since the league's second season in 1921 and hold the record for the most NFL titles, earning the city of Green Bay the nickname "Titletown USA". The Packers are the smallest city franchise in the NFL and the only one owned by shareholders statewide. The franchise was founded by "Curly" Lambeau, who played and coached for them. The Green Bay Packers are one of the most successful small-market professional sports franchises in the world and have won 13 NFL championships, including the first two AFL-NFL Championship games (Super Bowls Super Bowl I, I and Super Bowl II, II), Super Bowl XXXI and Super Bowl XLV. The state's support of the team is evidenced by the 81,000-person waiting list for season tickets to Lambeau Field.
 The Milwaukee Brewers, the state's only major league baseball team, play in American Family Field in Milwaukee, the successor to Milwaukee County Stadium since 2001. In 1982, the Brewers won the American League Championship, marking their most successful season. The team switched from the American League to the National League starting with the 1998 season. Before the Brewers, Milwaukee had two prior Major League teams. The first team, also called the Brewers, played only one season in the newly founded American League in 1901 before moving to St. Louis and becoming the Browns, who are now the Baltimore Orioles. Milwaukee was also the home of the Atlanta Braves, Braves franchise when they moved from Boston from 1953 to 1965, winning the World Series in 1957 and the National League pennant in 1958, before they moved to Atlanta.
The Milwaukee Bucks of the National Basketball Association play home games at the Fiserv Forum. The Bucks won the NBA Championship in 1971 and 2021.
The state also has minor league teams in hockey (Milwaukee Admirals) and baseball (the Wisconsin Timber Rattlers, based in Appleton and the Beloit Sky Carp of the High-A minor leagues). In addition to these affiliated minor league teams, Wisconsin has the American Association of Professional Baseball 2020 Championship team, the Milwaukee Milkmen based in Franklin, Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, Franklin, and in 2022 the Lake Country Dockhounds will begin playing in Oconomowoc, Wisconsin, Oconomowoc. Wisconsin is also home to the Madison Mallards, the La Crosse Loggers, the Lakeshore Chinooks, the Eau Claire Express, the Fond du Lac Dock Spiders, the Green Bay Booyah, the Kenosha Kingfish, the Wisconsin Woodchucks, and the Wisconsin Rapids Rafters of the Northwoods League, a collegiate all-star summer league. In addition to the Packers, Green Bay is also the home to an indoor American football, indoor football team, the Green Bay Blizzard of the Indoor Football League, IFL. The state is home to the seven-time MISL/MASL Champion Milwaukee Wave.
Wisconsin is also home to Forward Madison FC, which is a professional soccer team that plays in the USL League One.
Wisconsin also has many college sports programs, including the Wisconsin Badgers, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the Milwaukee Panthers, Panthers of the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. The Wisconsin Badgers football former head coach Barry Alvarez led the Badgers to three Rose Bowl (game), Rose Bowl championships, including back-to-back victories in 1999 and 2000. The Badger men's basketball team won the national title in 1941 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1941 and made trips to college basketball's Final Four in 2000 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2000, 2014 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2014, and 2015 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2015. The Badgers claimed a historic dual championship in 2006 when both the NCAA Women's Ice Hockey Championship, women's and NCAA Men's Division I hockey Championship, men's hockey teams won national titles.
The Marquette Golden Eagles of the Big East Conference (1979–2013), Big East Conference, the state's other major collegiate program, is known for its Marquette Golden Eagles men's basketball, men's basketball team, which, under the direction of Al McGuire, won the NCAA National Championship in 1977 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1977. The team returned to the Final Four in 2003 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2003.
Many other schools in the University of Wisconsin system compete in the Wisconsin Intercollegiate Athletic Conference at the Division III (NCAA), Division III level. The conference is one of the most successful in the nation, claiming 107 NCAA national championships in 15 different sports as of March 30, 2015.
The Semi-Professional Northern Elite Football League consists of many teams from Wisconsin. The league is made up of former professional, collegiate, and high school players. Teams from Wisconsin include: The Green Bay Gladiators from Green Bay, The Fox Valley Force in Appleton, The Kimberly Storm in Kimberly, Wisconsin, Kimberly, The Central Wisconsin Spartans in Wausau, The Eau Claire Crush and the Chippewa Valley Predators from Eau Claire, and the Lake Superior Rage from Superior, Wisconsin, Superior. The league also has teams in Michigan and Minnesota. Teams play from May until August.
Wisconsin is home to the world's oldest operational racetrack. The Milwaukee Mile, located in Wisconsin State Fair Park in West Allis, Wisconsin, held races there that considerably predate the Indy 500.
Wisconsin is home to the nation's oldest operating velodrome in
The Milwaukee Brewers, the state's only major league baseball team, play in American Family Field in Milwaukee, the successor to Milwaukee County Stadium since 2001. In 1982, the Brewers won the American League Championship, marking their most successful season. The team switched from the American League to the National League starting with the 1998 season. Before the Brewers, Milwaukee had two prior Major League teams. The first team, also called the Brewers, played only one season in the newly founded American League in 1901 before moving to St. Louis and becoming the Browns, who are now the Baltimore Orioles. Milwaukee was also the home of the Atlanta Braves, Braves franchise when they moved from Boston from 1953 to 1965, winning the World Series in 1957 and the National League pennant in 1958, before they moved to Atlanta.
The Milwaukee Bucks of the National Basketball Association play home games at the Fiserv Forum. The Bucks won the NBA Championship in 1971 and 2021.
The state also has minor league teams in hockey (Milwaukee Admirals) and baseball (the Wisconsin Timber Rattlers, based in Appleton and the Beloit Sky Carp of the High-A minor leagues). In addition to these affiliated minor league teams, Wisconsin has the American Association of Professional Baseball 2020 Championship team, the Milwaukee Milkmen based in Franklin, Milwaukee County, Wisconsin, Franklin, and in 2022 the Lake Country Dockhounds will begin playing in Oconomowoc, Wisconsin, Oconomowoc. Wisconsin is also home to the Madison Mallards, the La Crosse Loggers, the Lakeshore Chinooks, the Eau Claire Express, the Fond du Lac Dock Spiders, the Green Bay Booyah, the Kenosha Kingfish, the Wisconsin Woodchucks, and the Wisconsin Rapids Rafters of the Northwoods League, a collegiate all-star summer league. In addition to the Packers, Green Bay is also the home to an indoor American football, indoor football team, the Green Bay Blizzard of the Indoor Football League, IFL. The state is home to the seven-time MISL/MASL Champion Milwaukee Wave.
Wisconsin is also home to Forward Madison FC, which is a professional soccer team that plays in the USL League One.
Wisconsin also has many college sports programs, including the Wisconsin Badgers, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison and the Milwaukee Panthers, Panthers of the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. The Wisconsin Badgers football former head coach Barry Alvarez led the Badgers to three Rose Bowl (game), Rose Bowl championships, including back-to-back victories in 1999 and 2000. The Badger men's basketball team won the national title in 1941 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1941 and made trips to college basketball's Final Four in 2000 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2000, 2014 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2014, and 2015 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2015. The Badgers claimed a historic dual championship in 2006 when both the NCAA Women's Ice Hockey Championship, women's and NCAA Men's Division I hockey Championship, men's hockey teams won national titles.
The Marquette Golden Eagles of the Big East Conference (1979–2013), Big East Conference, the state's other major collegiate program, is known for its Marquette Golden Eagles men's basketball, men's basketball team, which, under the direction of Al McGuire, won the NCAA National Championship in 1977 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 1977. The team returned to the Final Four in 2003 NCAA Men's Division I Basketball Tournament, 2003.
Many other schools in the University of Wisconsin system compete in the Wisconsin Intercollegiate Athletic Conference at the Division III (NCAA), Division III level. The conference is one of the most successful in the nation, claiming 107 NCAA national championships in 15 different sports as of March 30, 2015.
The Semi-Professional Northern Elite Football League consists of many teams from Wisconsin. The league is made up of former professional, collegiate, and high school players. Teams from Wisconsin include: The Green Bay Gladiators from Green Bay, The Fox Valley Force in Appleton, The Kimberly Storm in Kimberly, Wisconsin, Kimberly, The Central Wisconsin Spartans in Wausau, The Eau Claire Crush and the Chippewa Valley Predators from Eau Claire, and the Lake Superior Rage from Superior, Wisconsin, Superior. The league also has teams in Michigan and Minnesota. Teams play from May until August.
Wisconsin is home to the world's oldest operational racetrack. The Milwaukee Mile, located in Wisconsin State Fair Park in West Allis, Wisconsin, held races there that considerably predate the Indy 500.
Wisconsin is home to the nation's oldest operating velodrome in Kenosha
Kenosha () is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the seat of Kenosha County. Per the 2020 census, the population was 99,986 which made it the fourth-largest city in Wisconsin. Situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan, Kenosh ...
where races have been held every year since 1927.
Sheboygan is home to Whistling Straits golf club which has hosted PGA Championships in 2004, 2010 and 2015 and the Ryder Cup golf competition between USA and Europe in 2020. The Greater Milwaukee Open, later named the U.S. Bank Championship in Milwaukee, was a PGA Tour tournament from 1968 to 2009 held annually in Brown Deer, Wisconsin, Brown Deer. In 2017, Erin Hills, a golf course in Erin, Wisconsin, approximately 30 miles northwest of Milwaukee, hosted the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open.
See also
* Index of Wisconsin-related articles * List of people from Wisconsin * Outline of Wisconsin * '''' * ''''Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * Detailed popular history and many biographies. * * * Detailed popular history & biographies. * * * * . * * * * Detailed guide to every town and city, and cultural history. :''See additional books at History of Wisconsin''External links
* * (Archived December 12, 2019) * * * *Wisconsin Health and Demographic Data
La Crosse Medical Health Science Consortium
Energy Profile for Wisconsin—Economic, environmental, and energy data
Wisconsin Historical Society
The State of Wisconsin Collection
from th
UW Digital Collections Center
Wisconsin Free Speech Legacy
Wisconsin Department of Tourism
* . * * * . {{coord, 44, -90, dim:300000_region:US-WI_source:enwiki_type:adm1st, name=State of Wisconsin, display=title Wisconsin, States of the United States States and territories established in 1848 1848 establishments in the United States Midwestern United States Contiguous United States