start-ups on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an
Why startups fail, according to their founders
Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017
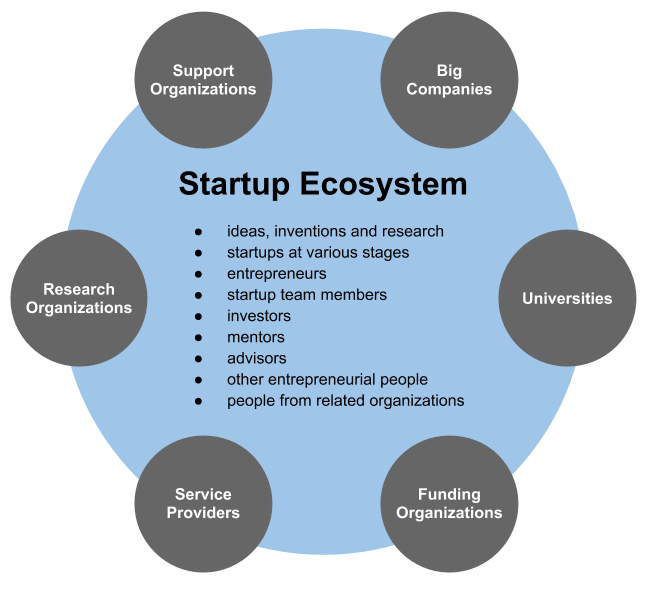 The size and maturity of the
The size and maturity of the
 Startup investing is the action of making an investment in an early-stage company. Beyond founders' own contributions, some startups raise additional investment at some or several stages of their growth. Not all startups trying to raise investments are successful in their fundraising.
In the United States, the solicitation of funds became easier for startups as result of the
Startup investing is the action of making an investment in an early-stage company. Beyond founders' own contributions, some startups raise additional investment at some or several stages of their growth. Not all startups trying to raise investments are successful in their fundraising.
In the United States, the solicitation of funds became easier for startups as result of the
entrepreneur
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values th ...
to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model
A business model describes how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-published, 2010 in economic, social, ...
. While entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values th ...
refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses that never intend to become registered, startups refer to new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo founder. At the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to be successful and influential.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders
Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017
Actions
Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will begin market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building aminimum viable product
A minimum viable product (MVP) is a version of a product with just enough features to be usable by early customers who can then provide feedback for future product development.
A focus on releasing an MVP means that developers potentially avoid ...
(MVP), i.e. a prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
, to develop and validate their business models. The startup process can take a long period of time (by some estimates, three years or longer), and hence sustaining effort is required. Over the long term, sustaining effort is especially challenging because of the high failure rates and uncertain outcomes. Having a business plan in place outlines what to do and how to plan and achieve an idea in the future. Typically, these plans outline the first 3 to 5 years of your business strategy.
Design principles
Models behind startups presenting as ventures are usually associated withdesign science A concept of design science was introduced in 1957 by R. Buckminster Fuller who defined it as a systematic form of designing. He expanded on this concept in his ''World Design Science Decade'' proposal to the International Union of Architects in 196 ...
. Design science uses design principles considered to be a coherent set of normative ideas and propositions to design and construct the company's backbone. For example, one of the initial design principles is "affordable loss".
Heuristics and biases in startup actions
Because of the lack of information, high uncertainty, the need to make decisions quickly, founders of startups use manyheuristic
A heuristic (; ), or heuristic technique, is any approach to problem solving or self-discovery that employs a practical method that is not guaranteed to be optimal, perfect, or rational, but is nevertheless sufficient for reaching an immediate, ...
s and exhibit biases
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individual, a group, ...
in their startup actions. Biases and heuristics are parts of our cognitive toolboxes in the decision-making process. They help us decide quickly as possible under uncertainty but sometimes become erroneous and fallacious.
Entrepreneurs often become overconfident about their startups and their influence on an outcome (case of ''the illusion of control''). Entrepreneurs tend to believe they have more degree of control over events, discounting the role of luck. Below are some of the most critical decision biases of entrepreneurs to start up a new business.
# Overconfidence
Confidence is a state of being clear-headed either that a hypothesis or prediction is correct or that a chosen course of action is the best or most effective. Confidence comes from a Latin word 'fidere' which means "to trust"; therefore, having ...
: Perceive a subjective certainty higher than the objective accuracy.
# Illusion of control
The illusion of control is the tendency for people to overestimate their ability to control events. It was named by U.S. psychologist Ellen Langer and is thought to influence gambling behavior and belief in the paranormal. Along with illusory supe ...
: Overemphasize how much skills, instead of chance, improve performance.
# The law of small numbers: Reach conclusions about a larger population using a limited sample.
# Availability bias
The availability heuristic, also known as availability bias, is a mental shortcut that relies on immediate examples that come to a given person's mind when evaluating a specific topic, concept, method, or decision. This heuristic, operating on the ...
: Make judgments about the probability of events based on how easy it is to think of examples.
# Escalation of commitment
Escalation of commitment is a human behavior pattern in which an individual or group facing increasingly negative outcomes from a decision, action, or investment nevertheless continue the behavior instead of altering course. The actor maintains ...
: Persist unduly with unsuccessful initiatives or courses of action.
Startups use several action principles to generate evidence as quickly as possible to reduce the downside effect of decision biases such as an escalation of commitment, overconfidence, and the illusion of control.
Mentoring
Many entrepreneurs seek feedback frommentors
Mentorship is the influence, guidance, or direction given by a mentor. A mentor is someone who teaches or gives help and advice to a less experienced and often younger person. In an organizational setting, a mentor influences the personal and p ...
in creating their startups. Mentors guide founders and impart entrepreneurial skills and may increase the self-efficacy
In psychology, self-efficacy is an individual's belief in their capacity to act in the ways necessary to reach specific goals. The concept was originally proposed by the psychologist Albert Bandura.
Self-efficacy affects every area of human endea ...
of nascent entrepreneurs. Mentoring offers direction for entrepreneurs to enhance their knowledge of how to sustain their assets relating to their status and identity and strengthen their real-time skills.
Principles
There are many principles in creating a startup. Some of the principles are listed below.Lean startup
Lean startup is a clear set of principles to create and design startups under limited resources and tremendous uncertainty to build their ventures more flexibly and at a lower cost. It is based on the idea that entrepreneurs can make their implicit assumptions about how their venture works explicit and empirically testing it. The empirical test is to de/validate these assumptions and to get an engaged understanding of the business model of the new ventures, and in doing so, the new ventures are created iteratively in a build–measure–learn loop. Hence, lean startup is a set of principles for entrepreneurial learning and business model design. More precisely, it is a set of design principles aimed for iteratively experiential learning under uncertainty in an engaged empirical manner. Typically, lean startup focuses on a few lean principles: * find a problem worth solving, then define a solution * engage early adopters for market validation * continually test with smaller, faster iterations * build a function, measure customer response, and verify/refute the idea * evidence-based decisions on when to "pivot" by changing your plan's course * maximize the efforts for speed, learning, and focusMarket validation
A key principle of startup is to validate the market need before providing a customer-centric product or service to avoid business ideas with weak demand. Market validation can be done in a number of ways, including surveys, cold calling, email responses, word of mouth or through sample research.Design thinking
Design thinking is used to understand the customers' need in an engaged manner. Design thinking and customer development can be biased because they do not remove the risk of bias because the same biases will manifest themselves in the sources of information, the type of information sought, and the interpretation of that information. Encouraging people to “consider the opposite” of whatever decision they are about to make tends to reduce biases such as overconfidence, thehindsight bias
Hindsight bias, also known as the knew-it-all-along phenomenon or creeping determinism, is the common tendency for people to perceive past events as having been more predictable than they actually were. People often believe that after an event ha ...
, and anchoring (Larrick, 2004; Mussweiler, Strack, & Pfeiffer, 2000).
Decision-making under uncertainty
In startups, many decisions are made under uncertainty, and hence a key principle for startups is to be agile and flexible. Founders can embed options to design startups in flexible manners, so that the startups can change easily in future. Uncertainty can vary within-person (I feel more uncertain this year than last year) and between-person (he feels more uncertain than she does). A study found that when entrepreneurs feel more uncertain, they identify more opportunities (within-person difference), but entrepreneurs who perceive more uncertainties than others do not identify more opportunities than others do (no between-person difference).Partnering
Startups may form partnerships with other firms to enable their business model to operate. To become attractive to other businesses, startups need to align their internal features, such as management style and products with the market situation. In their 2013 study, Kask and Linton develop two ideal profiles, or also known as configurations or archetypes, for startups that are commercializing inventions. The ''inheritor'' profile calls for a management style that is not too entrepreneurial (more conservative) and the startup should have an incremental invention (building on a previous standard). This profile is set out to be more successful (in finding a business partner) in a market that has a dominant design (a clear standard is applied in this market). In contrast to this profile is the ''originator'' which has a management style that is highly entrepreneurial and in which a radical invention or adisruptive innovation
In business theory, disruptive innovation is innovation that creates a new market and value network or enters at the bottom of an existing market and eventually displaces established market-leading firms, products, and alliances. The concept was ...
(totally new standard) is being developed. This profile is set out to be more successful (in finding a business partner) in a market that does not have a dominant design (established standard). New startups should align themselves to one of the profiles when commercializing an invention to be able to find and be attractive to a business partner. By finding a business partner, a startup has greater chances of becoming successful.
Startups usually need many different partners to realize their business idea. The commercialization process is often a bumpy road with iterations and new insights during the process. Hasche and Linton (2018) argue that startups can learn from their relationships with other firms, and even if the relationship ends, the startup will have gained valuable knowledge about how it should move on going forward. When a relationship is failing for a startup it needs to make changes. Three types of changes can be identified according to Hasche and Linton (2018):
* Change of business concept for the start up
* Change of collaboration constellation (change several relationships)
* Change of characteristic of business relationship (with the partner, e.g. from a transactional relationship to more of a collaborative type of relationship)
Entrepreneurial learning
Startups need to learn at a huge speed before running out of resources. Proactive actions (experimentation, searching, etc.) enhance a founder's learning to start a company. To learn effectively, founders often formulatefalsifiable
Falsifiability is a standard of evaluation of scientific theories and hypotheses that was introduced by the philosopher of science Karl Popper in his book ''The Logic of Scientific Discovery'' (1934). He proposed it as the cornerstone of a so ...
hypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obser ...
, build a minimum viable product (MVP), and conduct A/B testing
A/B testing (also known as bucket testing, split-run testing, or split testing) is a user experience research methodology. A/B tests consist of a randomized experiment that usually involves two variants (A and B), although the concept can be al ...
.
Business Model Design
With the key learnings from market validation, design thinking, and lean startup, founders can design a business model. However it's important not to dive into business models too early before there is sufficient learning on market validation. Paul Graham said "What I tell founders is not to sweat the business model too much at first. The most important task at first is to build something people want. If you don’t do that, it won’t matter how clever your business model is."Founders/entrepreneurs
Founders or co-founders are people involved in the initial launch of startup companies. Anyone can be a co-founder, and an existing company can also be a co-founder, but the most common co-founders are founder-CEOs,engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the l ...
s, hacker
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who uses their technical knowledge to achieve a goal or overcome an obstacle, within a computerized system by non-standard means. Though the term ''hacker'' has become associated in popu ...
s, web developer
A web developer is a programmer who develops World Wide Web applications using a client–server model. The applications typically use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript in the client, and any general-purpose programming language in the server. is used f ...
s, web designer
Web design encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance of websites. The different areas of web design include web graphic design; user interface design (UI design); authoring, including standardised code an ...
s and others involved in the ground level of a new, often venture
Venture may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
*The Ventures, an American instrumental rock band formed in 1958
*"A Venture", 1971 song by the band Yes
*''Venture'', a 2010 EP by AJR
Games
* ''Venture'' (video game), a 1981 arcade gam ...
. The founder that is responsible for the overall strategy of the startup plays the role of founder-CEOs, much like CEOs in established firms. Startup studios provide an opportunity for founders and team members to grow along with the business they help to build. In order to create forward momentum, founders must ensure that they provide opportunities for their team members to grow and evolve within the company.
The language of securities regulation in the United States
Securities regulation in the United States is the field of U.S. law that covers transactions and other dealings with securities. The term is usually understood to include both federal and state-level regulation by governmental regulatory agencies, ...
considers co-founders to be "promoters" under Regulation D. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government, created in the aftermath of the Wall Street Crash of 1929. The primary purpose of the SEC is to enforce the law against market ...
definition of "Promoter" includes: (i) Any person who, acting alone or in conjunction with one or more other persons, directly or indirectly takes initiative in founding and organizing the business or enterprise of an issuer; However, not every promoter is a co-founder. In fact, there is no formal, legal definition of what makes somebody a co-founder. The right to call oneself a co-founder can be established through an agreement with one's fellow co-founders or with permission of the board of directors, investors, or shareholders of a startup company. When there is no definitive agreement (like shareholders' agreement
A shareholders' agreement (sometimes referred to in the U.S. as a stockholders' agreement) (SHA) is an agreement amongst the shareholders or members of a company. In practical effect, it is analogous to a partnership agreement. It can be said that ...
), disputes about who the co-founders are, can arise.
Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy refers to the confidence an individual has to create a new business or startup. It has a strong relation with startup actions. Entrepreneurs' sense of self-efficacy can play a major role in how they approach goals, tasks, and challenges. Entrepreneurs with high self-efficacy—that is, those who believe they can perform well—are more likely to view difficult tasks as something to be mastered rather than something to be avoided.Stress
Entrepreneurs often feel stressed. They have internal and external pressures. Internally, they need to meet deadlines to develop the prototypes and get the product or service ready for market. Externally they are expected to meet milestones of investors and other stakeholders to ensure continued resources from them on the startups. Coping with stress is critical to entrepreneurs because of the stressful nature of start up a new firm under uncertainty. Coping with stress unsuccessfully could lead to emotional exhaustion, and the founders may close or exit the startups.Emotional exhaustion
Sustaining effort is required as the startup process can take a long period of time, by one estimate, three years or longer (Carter et al., 1996; Reynolds & Miller, 1992). Sustaining effort over the long term is especially challenging because of the high failure rates and uncertain outcomes.Founder identity and culture
Some startup founders have a more casual or offbeat attitude in their dress, office space andmarketing
Marketing is the process of exploring, creating, and delivering value to meet the needs of a target market in terms of goods and services; potentially including selection of a target audience; selection of certain attributes or themes to emph ...
, as compared to executives in established corporations. For example, startup founders in the 2010s wore hoodie
A hoodie (in some cases spelled hoody and alternatively known as a hooded sweatshirt) is a sweatshirt with a hood. Hoodies with zippers usually include two pockets on the lower front, one on either side of the zipper, while "pullover" hoodies ...
s, sneakers
Sneakers (also called trainers, athletic shoes, tennis shoes, gym shoes, kicks, sport shoes, flats, running shoes, or runners) are shoes primarily designed for sports or other forms of physical exercise, but which are now also widely used fo ...
and other casual clothes to business meetings. Their offices may have recreational facilities in them, such as pool tables, ping pong tables, football tables and pinball machine
Pinball games are a family of games in which a ball is propelled into a specially designed table where it bounces off various obstacles, scoring points either en route or when it comes to rest. Historically the board was studded with nails call ...
s, which are used to create a fun work environment, stimulate team development and team spirit, and encourage creativity. Some of the casual approaches, such as the use of "flat" organizational structures, in which regular employees can talk with the founders and chief executive officers informally, are done to promote efficiency in the workplace, which is needed to get their business off the ground.
In a 1960 study, Douglas McGregor
Douglas Murray McGregor (September 6, 1906 – October 1, 1964) was an American management professor at the MIT Sloan School of Management and president of Antioch College from 1948 to 1954. He also taught at the Indian Institute of Management Ca ...
stressed that punishments and rewards for uniformity in the workplace are not necessary because some people are born with the motivation to work without incentives. Some startups do not use a strict command and control hierarchical structure, with executives, managers, supervisors and employees. Some startups offer employees incentives such as stock option
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified dat ...
s, to increase their "buy in" from the start up (as these employees stand to gain if the company does well). This removal of stressors allows the workers and researchers in the startup to focus less on the work environment around them, and more on achieving the task at hand, giving them the potential to achieve something great for both themselves and their company.
Failure
The failure rate of startup companies is very high. A 2014 article in ''Fortune
Fortune may refer to:
General
* Fortuna or Fortune, the Roman goddess of luck
* Luck
* Wealth
* Fortune, a prediction made in fortune-telling
* Fortune, in a fortune cookie
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''The Fortune'' (1931 film) ...
'' estimated that 90% of startups ultimately fail. In a sample of 101 unsuccessful startups, companies reported that experiencing one or more of five common factors were the reason for failure; lack of consumer interest in the product or service (42% of failures), funding or cash problems (29%), personnel or staffing problems (23%), competition from rival companies (19%) and problems with pricing of the product or service (18%). In cases of funding problems it can leave employees without paychecks. Sometimes these companies are purchased by other companies if they are deemed to be viable, but oftentimes they leave employees with very little recourse to recoup lost income for worked time. More than one-third of founders believe that running out of money led to failure. Second to that, founders attribute their failure to a lack of financing or investor interest. These common mistakes and missteps that happen early in the startup journey can result in failure, but there are precautions entrepreneurs can take to help mitigate risk. For example, startup studios offer a buffer against many of the obstacles that solo entrepreneurs face, such as funding and insufficient team structure, making them a good resource for startups in their earliest phases.
Re-starters
Failed entrepreneurs, or restarters, who after some time restart in the same sector with more or less the same activities, have an increased chance of becoming a better entrepreneur. However, some studies indicate that restarters are more heavily discouraged in Europe than in the US.Training
Many institutions and universities provide training on startups. In the context of universities, some of the courses are entrepreneurship courses that also deal with the topic of startups, while other courses are specifically dedicated to startups. Startup courses are found both in traditional economic or business disciplines as well as the side of information technology disciplines. As startups are often focused on software, they are also occasionally taught while focusing on software development alongside the business aspects of a startup.Chanin, R., Sales, A., Pompermaier, L., and Prikladnicki, R. (2018). Startup software development education: a systematic mapping study. In proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE ’18), pp. 143-144. ''“The best way of learning about anything is by doing.” – Richard Branson'' Founders go through a lot to set up a startup. A startup requires patience and resilience, and training programs need to have both the business components and the psychological components. Entrepreneurship education is effective in increasing the entrepreneurial attitudes and perceived behavioral control, helping people and their businesses grow. Most of startup training falls into the mode of experiential learning (Cooper et al., 2004; Pittaway and Cope, 2007), in which students are exposed to a large extent to a real-life entrepreneurship context as new venture teams (Wu et al., 2009). An example of group-based experiential startup training is the Lean LaunchPad initiative that applies the principles of customer development (Blank and Dorf, 2012) and Lean Startup (Ries, 2011) to technology-based startup projects. As startups are typically thought to operate under a notable lack of resources, have little or no operating history, and to consist of individuals with little practical experience, it is possible to simulate startups in a classroom setting with reasonable accuracy. In fact, it is not uncommon for students to actually participate in real startups during and after their studies. Similarly, university courses teaching software startup themes often have students found mock-up startups during the courses and encourage them to make them into real startups should they wish to do so. Such mock-up startups, however, may not be enough to accurately simulate real-world startup practice if the challenges typically faced by startups (e.g. lack of funding to keep operating) are not present in the course setting. To date, much of the entrepreneurship training is yet personalized to match the participants and the training.Ecosystem
 The size and maturity of the
The size and maturity of the startup ecosystem
A startup ecosystem is formed by people, startups in their various stages and various types of organizations in a location (physical or virtual), interacting as a system to create and scale new startup companies. These organizations can be furthe ...
is where a startup is launched and where it grows to have an effect on the volume and success of the startups. The startup ecosystem consists of the individuals (entrepreneurs, venture capitalists, angel investors
An angel investor (also known as a business angel, informal investor, angel funder, private investor, or seed investor) is an individual who provides capital for a business or businesses start-up, usually in exchange for convertible debt or owners ...
, mentors, advisors); institutions and organizations (top research universities and institutes, business schools and entrepreneurship programs and centres operated by universities and colleges, non-profit entrepreneurship support organizations, government entrepreneurship programs and services, Chambers of commerce
A chamber of commerce, or board of trade, is a form of business network. For example, a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to a ...
) business incubator
Business incubator is an organization that helps startup companies and individual entrepreneurs to develop their businesses by providing a fullscale range of services starting with management training and office space and ending with venture ca ...
s and business accelerator
Startup accelerators, also known as seed accelerators, are fixed-term, Cohort (educational group), cohort-based programs, that include mentorship and educational components and culminate in a public sales pitch, pitch event or demo day. While tradi ...
s and top-performing entrepreneurial firms and startups. A region with all of these elements is considered to be a "strong" startup ecosystem.
One of the most famous startup ecosystems is Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo County ...
in California, where major computer and internet firms and top universities such as Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
create a stimulating startup environment. Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
(where Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
is located) and Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
, home of WISTA (a top research area), also have numerous creative industries, leading entrepreneurs and startup firms. Basically, attempts are being made worldwide, for example in Israel with its Silicon Wadi
Silicon Wadi ( he, סִילִיקוֹן וְאֵדֵי, ) is a region in Israel that serves as one of the global centres for advanced technology. It spans the Israeli coastal plain, and is cited as among the reasons why the country has ...
, in France with the Inovallée
Inovallée (contraction in French for the words innovation and valley) is a science park located at Meylan and Montbonnot-Saint-Martin near Grenoble in France.
Created in 1972 with the acronym ZIRST, it becomes Inovallée in 2005 and houses prima ...
or in Italy in Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into provi ...
with the AREA Science Park The Trieste AREA Science Park is composed of two neighbouring campus developments located near the exit from the motorway linking Trieste to Austria and Slovenia. It covers 50 hectares, extendable to 150, in the magnificent natural setting of the Ka ...
, to network basic research, universities and technology parks in order to create a startup-friendly ecosystem.
Although there are startups created in all types of businesses, and all over the world, some locations and business sectors are particularly associated with startup companies. The internet bubble
The dot-com bubble (dot-com boom, tech bubble, or the Internet bubble) was a stock market bubble in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet.
Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Compos ...
of the late 1990s was associated with huge numbers of internet startup companies, some selling the technology to provide internet access, others using the internet to provide services. Most of this startup activity was located in the most well-known startup ecosystem - Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo County ...
, an area of northern California renowned for the high level of startup company activity:
Startup advocates are also trying to build a community of tech startups in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
with organizations like NY Tech Meet Up and Built in NYC. In the early 2000s, the patent assets of failed startup companies were being purchased by people known as patent troll
In international law and business, patent trolling or patent hoarding is a categorical or pejorative term applied to a person or company that attempts to enforce patent rights against accused infringers far beyond the patent's actual value or ...
s, who assert those patents against companies that might be infringing the technology covered by the patents.
Investing
 Startup investing is the action of making an investment in an early-stage company. Beyond founders' own contributions, some startups raise additional investment at some or several stages of their growth. Not all startups trying to raise investments are successful in their fundraising.
In the United States, the solicitation of funds became easier for startups as result of the
Startup investing is the action of making an investment in an early-stage company. Beyond founders' own contributions, some startups raise additional investment at some or several stages of their growth. Not all startups trying to raise investments are successful in their fundraising.
In the United States, the solicitation of funds became easier for startups as result of the JOBS Act
The Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act, or JOBS Act, is a law intended to encourage funding of small businesses in the United States by easing many of the country's securities regulations. It passed with bipartisan support, and was signed into ...
. Prior to the advent of equity crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding is the online offering of private company securities to a group of people for investment and therefore it is a part of the capital markets. Because equity crowdfunding involves investment into a commercial enterprise, it ...
, a form of online investing that has been legalized in several nations, startups did not advertise themselves to the general public as investment opportunities until and unless they first obtained approval from regulators for an initial public offering
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investment ...
(IPO) that typically involved a listing of the startup's securities on a stock exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for th ...
. Today, there are many alternative forms of IPO commonly employed by startups and startup promoters that do not include an exchange listing, so they may avoid certain regulatory compliance obligations, including mandatory periodic disclosures of financial information and factual discussion of business conditions by management that investors and potential investors routinely receive from registered public companies.
Investors are generally most attracted to those new companies distinguished by their strong co-founding team, a balanced "risk/reward" profile (in which high risk due to the untested, disruptive innovations is balanced out by high potential returns) and "scalability" (the likelihood that a startup can expand its operations by serving more markets or more customers). Attractive startups generally have lower "bootstrapping
In general, bootstrapping usually refers to a self-starting process that is supposed to continue or grow without external input.
Etymology
Tall boots may have a tab, loop or handle at the top known as a bootstrap, allowing one to use fingers ...
" (self-funding of startups by the founders) costs, higher risk, and higher potential return on investment
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is a ratio between net income (over a period) and investment (costs resulting from an investment of some resources at a point in time). A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably ...
. Successful startups are typically more scalable than an established business, in the sense that the startup has the potential to grow rapidly with a limited investment of capital, labor or land. Timing has often been the single most important factor for biggest startup successes, while at the same time it's identified to be one of the hardest things to master by many serial entrepreneurs and investors.
Startups have several options for funding. Revenue-based financing Revenue-based financing or royalty-based financing (RBF) is a type of financial capital provided to small or growing businesses in which investors inject capital into a business in return for a fixed percentage of ongoing gross revenues, with paymen ...
lenders can help startup companies by providing non-dilutive growth capital
Growth capital (also called expansion capital and growth equity) is a type of private equity investment, usually a minority investment, in relatively mature companies that are looking for capital to expand or restructure operations, enter new mark ...
in exchange for a percentage of monthly revenue. Venture capital firms and angel investors may help startup companies begin operations, exchanging seed money
Seed money, sometimes known as seed funding or seed capital, is a form of securities offering in which an investor invests capital in a startup company in exchange for an equity stake or convertible note stake in the company. The term ''seed'' ...
for an equity
Equity may refer to:
Finance, accounting and ownership
* Equity (finance), ownership of assets that have liabilities attached to them
** Stock, equity based on original contributions of cash or other value to a business
** Home equity, the dif ...
stake in the firm. Venture capitalists and angel investors provide financing to a range of startups (a portfolio), with the expectation that a very small number of the startups will become viable and make money. In practice though, many startups are initially funded by the founders themselves using "bootstrapping", in which loans or monetary gifts from friends and family are combined with savings and credit card debt to finance the venture. Factoring is another option, though it is not unique to startups. Other funding opportunities include various forms of crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project or venture by raising money from a large number of people, typically via the internet. Crowdfunding is a form of crowdsourcing and alternative finance. In 2015, over was raised worldwide by crow ...
, for example equity crowdfunding, in which the startup seeks funding from a large number of individuals, typically by pitching their idea on the Internet.
Startups can receive funding via more involved stakeholders, such as startup studios. Startup studios provide funding to support the business through a successful launch, but they also provide extensive operational support, such as HR, finance and accounting, marketing, and product development, to increase the probability of success and propel growth.
Necessity of funding
While some (would-be) entrepreneurs believe that they can't start a company without funding from VC, Angel, etc. that is not the case. In fact, many entrepreneurs have founded successful businesses for almost no capital, including the founders ofMailChimp
Mailchimp is a marketing automation platform and email marketing service. "Mailchimp" is the trade name of its operator, Rocket Science Group, an American company founded in 2001 by Ben Chestnut and Mark Armstrong, with Dan Kurzius joining at a ...
, Shopify
Shopify Inc. is a Canadian multinational e-commerce company headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario. Shopify is the name of its proprietary e-commerce platform for online stores and retail point-of-sale systems. The Shopify platform offers online ret ...
, and ShutterStock
Shutterstock is an American provider of stock photography, stock footage, stock music, and editing tools; it is headquartered in New York. Founded in 2003 by programmer and photographer Jon Oringer, Shutterstock maintains a library of around ...
.
Valuations
If a company's value is based on its technology, it is often equally important for the business owners to obtainintellectual property protection
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
for their idea. The newsmagazine ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Econo ...
'' estimated that up to 75% of the value of US public companies is now based on their intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, cop ...
(up from 40% in 1980). Often, 100% of a small startup company's value is based on its intellectual property. As such, it is important for technology-oriented startup companies to develop a sound strategy for protecting their intellectual capital Intellectual capital is the result of mental processes that form a set of intangible objects that can be used in economic activity and bring income to its owner (organization), covering the competencies of its people ( human capital), the value rela ...
as early as possible. Startup companies, particularly those associated with new technology, sometimes produce huge returns to their creators and investors—a recent example of such is Google, whose creators became billionaires through their stock ownership and options.
Investing rounds
When investing in a startup, there are different types of stages in which the investor can participate. The first round is calledseed round
Seed money, sometimes known as seed funding or seed capital, is a form of securities offering in which an investor invests capital in a startup company in exchange for an equity stake or convertible note stake in the company. The term ''seed'' su ...
. The seed round generally is when the startup is still in the very early phase of execution when their product is still in the prototype phase. There is likely no performance data or positive financials as of yet. Therefore, investors rely on strength of the idea and the team in place. At this level, family friends and angel investors
An angel investor (also known as a business angel, informal investor, angel funder, private investor, or seed investor) is an individual who provides capital for a business or businesses start-up, usually in exchange for convertible debt or owners ...
will be the ones participating. At this stage the level of risk and payoff are at their greatest. The next round is called Series A
A series A round (also known as series A financing or series A investment) is the name typically given to a company's first significant round of venture capital financing. The name refers to the class of preferred stock sold to investors in exchan ...
. At this point the company already has traction and may be making revenue. In Series A rounds venture capital firms will be participating alongside angels or super angel Super angel (or "super-angel") was a term used in the early 2010s to describe venture capital investors who had once been angel investors and subsequently raised small venture capital funds.
Super angels share some characteristics of both angel inv ...
investors. The next rounds are Series B
A venture round is a type of funding round used for venture capital financing, by which startup companies obtain investment, generally from venture capitalists and other institutional investors. The availability of venture funding is among the ...
, C, and D. These three rounds are the ones leading towards the Initial Public Offering (IPO
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investment ...
). Venture capital firms and private equity
In the field of finance, the term private equity (PE) refers to investment funds, usually limited partnerships (LP), which buy and restructure financially weak companies that produce goods and provide services. A private-equity fund is both a ty ...
firms will be participating. Series B: Companies are generating consistent revenue but must scale to meet growing demand. Series C & D: Companies with strong financial performance looking to expand to new markets, develop new products, make an acquisition, and/or preparing for IPO.
History of startup investing
After theGreat Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, which was blamed in part on a rise in speculative investments in unregulated small companies, startup investing was primarily a word of mouth activity reserved for the friends and family of a startup's co-founders, business angels, and Venture Capital funds. In the United States, this has been the case ever since the implementation of the Securities Act of 1933
The Securities Act of 1933, also known as the 1933 Act, the Securities Act, the Truth in Securities Act, the Federal Securities Act, and the '33 Act, was enacted by the United States Congress on May 27, 1933, during the Great Depression and after ...
. Many nations implemented similar legislation to prohibit general solicitation and general advertising of unregistered securities, including shares offered by startup companies. In 2005, a new Accelerator investment model was introduced by Y Combinator
Y Combinator (YC) is an American technology startup accelerator launched in March 2005. It has been used to launch more than 3,000 companies, including Airbnb, Coinbase, Cruise, DoorDash, Dropbox, Instacart, Quora, PagerDuty, Reddit, Str ...
that combined fixed terms investment model with fixed period intense bootcamp style training program, to streamline the seed/early-stage investment process with training to be more systematic.
Following Y Combinator, many accelerators with similar models have emerged around the world. The accelerator model has since become very common and widely spread and they are key organizations of any Startup ecosystem
A startup ecosystem is formed by people, startups in their various stages and various types of organizations in a location (physical or virtual), interacting as a system to create and scale new startup companies. These organizations can be furthe ...
. Title II of the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act
The Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act, or JOBS Act, is a law intended to encourage funding of small businesses in the United States by easing many of the country's securities regulations. It passed with bipartisan support, and was signed int ...
(JOBS Act), first implemented on 23 September 2013, granted startups in and startup co-founders or promoters in US. the right to generally solicit and advertise publicly using any method of communication on the condition that only accredited investors are allowed to purchase the securities. However the regulations affecting equity crowdfunding in different countries vary a lot with different levels and models of freedom and restrictions. In many countries there are no limitations restricting general public from investing to startups, while there can still be other types of restrictions in place, like limiting the amount that companies can seek from investors. Due to positive development and growth of crowdfunding, many countries are actively updating their regulation in regards to crowdfunding.
Investing online
The first known investment-based crowdfunding platform for startups was launched in Feb. 2010 by Grow VC, followed by the first US. based company ProFounder launching model for startups to raise investments directly on the site, but ProFounder later decided to shut down its business due regulatory reasons preventing them from continuing, having launched their model for US. markets prior to JOBS Act. With the positive progress of the JOBS Act for crowd investing in US., equity crowdfunding platforms likeSeedInvest
SeedInvest is an equity crowdfunding platform that connects startups with investors online. The company was founded in 2012 and launched in 2013. SeedInvest has focused on building liquidity in the platform by attracting high-net-worth individ ...
and CircleUp started to emerge in 2011 and platforms such as investiere, Companisto
Companisto is an international equity-based crowdfunding website. It was founded by the lawyers David Rhotert and Tamo Zwinge in June 2012, in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of G ...
and Seedrs
Seedrs is an online equity crowdfunding company, headquartered in East London's Tech City, founded in 2009 and launched by Jeff Lynn and Carlos Silva in 2012. Since 2022 it has been a subsidiary of American crowdfunding company Republic.
In 2 ...
in Europe and OurCrowd
OurCrowd is an online global venture investing platform that empowers institutions and individual accredited investors to invest and engage in emerging technology companies at an early stage while still privately held. Based in Jerusalem, the co ...
in Israel. The idea of these platforms is to streamline the process and resolve the two main points that were taking place in the market. The first problem was for startups to be able to access capital and to decrease the amount of time that it takes to close a round of financing. The second problem was intended to increase the amount of deal flow for the investor and to also centralize the process.
Internal startups
Internal startups are a form of corporate entrepreneurship. Large or well-established companies often try to promote innovation by setting up "internal startups", new business divisions that operate atarm's length
The arm's length principle (ALP) is the condition or the fact that the parties of a transaction are independent and on an equal footing. Such a transaction is known as an "arm's-length transaction".
It is used specifically in contract law to ar ...
from the rest of the company. Examples include Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
, a research unit within the Bell System
The Bell System was a system of telecommunication companies, led by the Bell Telephone Company and later by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), that dominated the telephone services industry in North America for over one hundr ...
and Target Corporation
Target Corporation (doing business as Target and stylized in all lowercase since 2018) is an American big box department store chain headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota. It is the seventh largest retailer in the United States, and a compon ...
(which began as an internal startup of the Dayton's
Dayton's was an American department store chain founded in Minneapolis, Minnesota, in 1902 by George Draper Dayton. It operated several local high end department stores throughout Minnesota and the Upper Midwest for almost 100 years. Although it ...
department store chain) and threedegrees, a product developed by an internal startup of Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
. To accommodate startups internally, companies, such as Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
has made strides to make purchased startups and their workers feel at home in their offices, even letting them bring their dogs to work.
Unicorns
Some startups become big and they become unicorns, i.e. privately held startup companies valued at over US$1 billion. The term was coined in 2013 by venture capitalist Aileen Lee, choosing the mythical animal to represent the statistical rarity of such successful ventures. According to ''TechCrunch
TechCrunch is an American online newspaper focusing on high tech and startup companies. It was founded in June 2005 by Archimedes Ventures, led by partners Michael Arrington and Keith Teare.
In 2010, AOL acquired the company for approximately ...
'', there were 452 unicorns as of May 2019, and most of the unicorns are in the USA, followed by China. The unicorns are concentrated in a few countries. The unicorn leaders are the U.S. with 196 companies, China with 165, India with 107 and the U.K. with 16. The largest unicorns included Ant Financial
Ant Group ()'','' formerly known as Ant Financial, is an affiliate company of the Chinese conglomerate Alibaba Group. The group owns the world's largest mobile (digital) payment platform Alipay, which serves over 1.3 billion users and 80 million ...
, ByteDance
ByteDance Ltd. () is a Chinese internet technology company headquartered in Beijing and incorporated in the Cayman Islands.
Founded by Zhang Yiming, Liang Rubo and a team of others in 2012, ByteDance developed the video-sharing social network ...
, DiDi
Didi may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* "Didi" (song), a song by Khaled
* Didi, the principal character in ''Didi's Comedy Show'', a German comedy television show
* Didi Pickles, mother of Tommy and Dil in the cartoons ''Rugrats'' and ''All ...
, Uber
Uber Technologies, Inc. (Uber), based in San Francisco, provides mobility as a service, ride-hailing (allowing users to book a car and driver to transport them in a way similar to a taxi), food delivery (Uber Eats and Postmates), package ...
, Xiaomi
Corporation (; ), commonly known as Xiaomi and registered as Xiaomi Inc., is a Chinese designer and manufacturer of consumer electronics and related software, home appliances, and household items. Behind Samsung, it is the second largest ma ...
, and Airbnb
Airbnb, Inc. ( ), based in San Francisco, California, operates an online marketplace focused on short-term homestays and experiences. The company acts as a broker and charges a commission from each booking. The company was founded in 2008 b ...
. When the value of a company is over US$10 billion, the company will be called as a Decacorn. When the company is valued over US$100 billion, Hectocorn will be used.
See also
*Brand management
In marketing, brand management begins with an analysis on how a brand is currently perceived in the market, proceeds to planning how the brand should be perceived if it is to achieve its objectives and continues with ensuring that the brand is per ...
* Business incubator
Business incubator is an organization that helps startup companies and individual entrepreneurs to develop their businesses by providing a fullscale range of services starting with management training and office space and ending with venture ca ...
* Business plan
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on t ...
* Deep tech
Deep technology (deep tech) or hard tech is a classification of organization, or more typically startup company, with the expressed objective of providing technology solutions based on substantial scientific or engineering challenges. They present ...
* Innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity ...
* Liquidity event In corporate finance, a liquidity event is a transaction that enables the owners of a company to realize the value of their investment, such as a merger, acquisition or initial public offering. A liquidity event is a typical exit strategy for privat ...
* Platform cooperative
* Small business
Small businesses are types of corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships which have fewer employees and/or less annual revenue than a regular-sized business or corporation. Businesses are defined as "small" in terms of being able to ap ...
*
* Unicorn bubble
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Startup Company Entrepreneurship Private equity Types of business entity Business incubators