Square Root Of 6 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The square root of 6 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the natural number 6. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 6, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. This number appears in numerous geometric and number-theoretic contexts. It can be denoted in surd form as:
:
and in exponent form as:
:
It is an irrational
The square root of 6 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the natural number 6. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 6, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. This number appears in numerous geometric and number-theoretic contexts. It can be denoted in surd form as:
:
and in exponent form as:
:
It is an irrational
 The Babylonian method is equivalent to
The Babylonian method is equivalent to

 In plane geometry, the square root of 6 can be constructed via a sequence of
In plane geometry, the square root of 6 can be constructed via a sequence of
 Villard de Honnecourt's 13th century construction of a Gothic "fifth-point arch" with circular arcs of radius 5 has a height of twice the square root of 6, as illustrated here.
Villard de Honnecourt's 13th century construction of a Gothic "fifth-point arch" with circular arcs of radius 5 has a height of twice the square root of 6, as illustrated here.
 The square root of 6 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the natural number 6. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 6, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. This number appears in numerous geometric and number-theoretic contexts. It can be denoted in surd form as:
:
and in exponent form as:
:
It is an irrational
The square root of 6 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the natural number 6. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 6, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. This number appears in numerous geometric and number-theoretic contexts. It can be denoted in surd form as:
:
and in exponent form as:
:
It is an irrational algebraic number
An algebraic number is a number that is a root of a non-zero polynomial in one variable with integer (or, equivalently, rational) coefficients. For example, the golden ratio, (1 + \sqrt)/2, is an algebraic number, because it is a root of the po ...
. The first sixty significant digits of its decimal expansion are:
:.
which can be rounded up to 2.45 to within about 99.98% accuracy (about 1 part in 4800); that is, it differs from the correct value by about . It takes two more digits (2.4495) to reduce the error by about half. The approximation (≈ 2.449438...) is nearly ten times better: despite having a denominator of only 89, it differs from the correct value by less than , or less than one part in 47,000.
Since 6 is the product of 2 and 3, the square root of 6 is the geometric mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the ...
of 2 and 3, and is the product of the square root of 2
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as \sqrt or 2^, and is an algebraic number. Technically, it should be called the princip ...
and the square root of 3, both of which are irrational algebraic numbers.
NASA has published more than a million decimal digits of the square root of six.
Rational approximations
The square root of 6 can be expressed as the continued fraction : The successive partial evaluations of the continued fraction, which are called its ''convergents'', approach : : Their numerators are 2, 5, 22, 49, 218, 485, 2158, 4801, 21362, 47525, 211462, …, and their denominators are 1, 2, 9, 20, 89, 198, 881, 1960, 8721, 19402, 86329, …. Each convergent is a best rational approximation of ; in other words, it is closer to than any rational with a smaller denominator. Decimal equivalents improve linearly, at a rate of nearly one digit per convergent: : The convergents, expressed as , satisfy alternately the Pell's equations : When is approximated with theBabylonian method
Methods of computing square roots are numerical analysis algorithms for approximating the principal, or non-negative, square root (usually denoted \sqrt, \sqrt /math>, or S^) of a real number. Arithmetically, it means given S, a procedure for fin ...
, starting with and using , the th approximant is equal to the th convergent of the continued fraction:
:
 The Babylonian method is equivalent to
The Babylonian method is equivalent to Newton's method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method, named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valu ...
for root finding applied to the polynomial . The Newton's method update, is equal to when . The method therefore converges quadratically.
Geometry


 In plane geometry, the square root of 6 can be constructed via a sequence of
In plane geometry, the square root of 6 can be constructed via a sequence of dynamic rectangle A dynamic rectangle is a right-angled, four-sided figure (a rectangle) with dynamic symmetry which, in this case, means that aspect ratio (width divided by height) is a distinguished value in dynamic symmetry, a proportioning system and natural des ...
s, as illustrated here.
In solid geometry, the square root of 6 appears as the longest distances between corners ( vertices) of the double cube, as illustrated above. The square roots of all lower natural numbers appear as the distances between other vertex pairs in the double cube (including the vertices of the included two cubes).
The edge length of a cube with total surface area of 1 is or the reciprocal square root of 6. The edge lengths of a regular tetrahedron (), a regular octahedron (), and a cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the only r ...
() of equal total surface areas satisfy .
The edge length of a regular octahedron is the square root of 6 times the radius of an inscribed sphere (that is, the distance from the center of the solid to the center of each face).
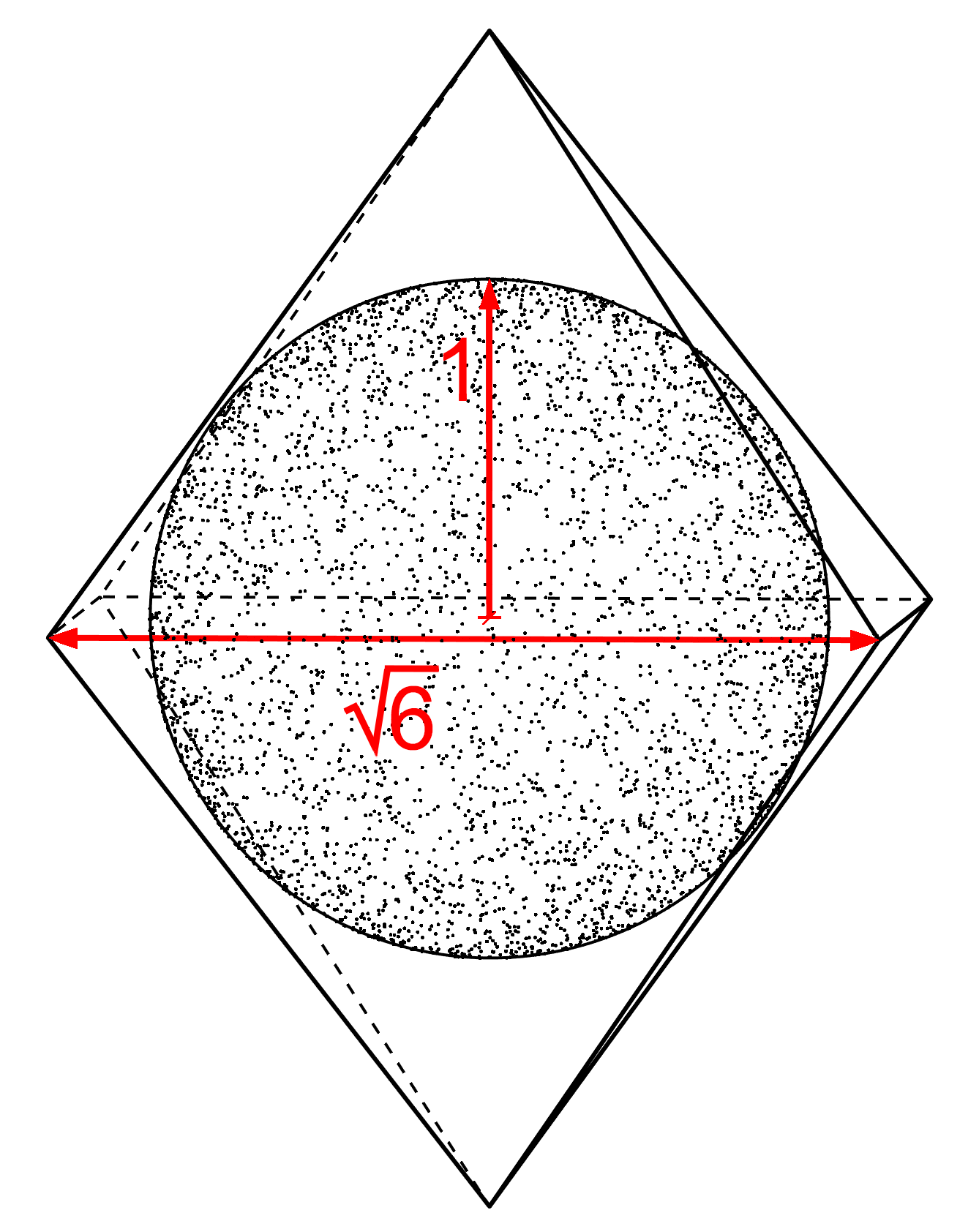
The square root of 6 appears in various other geometry contexts, such as the side length for the square enclosing an equilateral triangle of side 2 (see figure).
Trigonometry
The square root of 6, with thesquare root of 2
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as \sqrt or 2^, and is an algebraic number. Technically, it should be called the princip ...
added or subtracted, appears in several exact trigonometric values for angles at multiples of 15 degrees ( radians).
:
In culture
 Villard de Honnecourt's 13th century construction of a Gothic "fifth-point arch" with circular arcs of radius 5 has a height of twice the square root of 6, as illustrated here.
Villard de Honnecourt's 13th century construction of a Gothic "fifth-point arch" with circular arcs of radius 5 has a height of twice the square root of 6, as illustrated here.
See also
* Square root *Square root of 2
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is a positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as \sqrt or 2^, and is an algebraic number. Technically, it should be called the princip ...
* Square root of 3
* Square root of 5
* Square root of 7
The square root of 7 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the prime number 7 (number), 7. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 7, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same proper ...
References
{{Irrational number Mathematical constants Quadratic irrational numbers