Spring Triangle (Stellarium) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Spring Triangle is an astronomical asterism involving an imaginary triangle drawn upon the
The Spring Triangle is an astronomical asterism involving an imaginary triangle drawn upon the
 Spica is made up of two individual stars, Spica A and Spica B, with radii of 7.40 and 3.64 times the Sun's, respectively. Their sizes contribute greatly to the brightness of the stars. Spica A's luminosity is 12,100 times that of the Sun, while Spica B has a luminosity of 1,500. Their sizes lead to respective surface temperatures of 22,400 K and 18,500 K, much higher than the Sun. They are separated by a distance of only 0.12 AU with an orbital period of only four days. This proximity gravitationally distorts each star into an egg shape, with the pointed ends facing each other.
Spica is made up of two individual stars, Spica A and Spica B, with radii of 7.40 and 3.64 times the Sun's, respectively. Their sizes contribute greatly to the brightness of the stars. Spica A's luminosity is 12,100 times that of the Sun, while Spica B has a luminosity of 1,500. Their sizes lead to respective surface temperatures of 22,400 K and 18,500 K, much higher than the Sun. They are separated by a distance of only 0.12 AU with an orbital period of only four days. This proximity gravitationally distorts each star into an egg shape, with the pointed ends facing each other.
 Regulus, the brightest object in the constellation
Regulus, the brightest object in the constellation
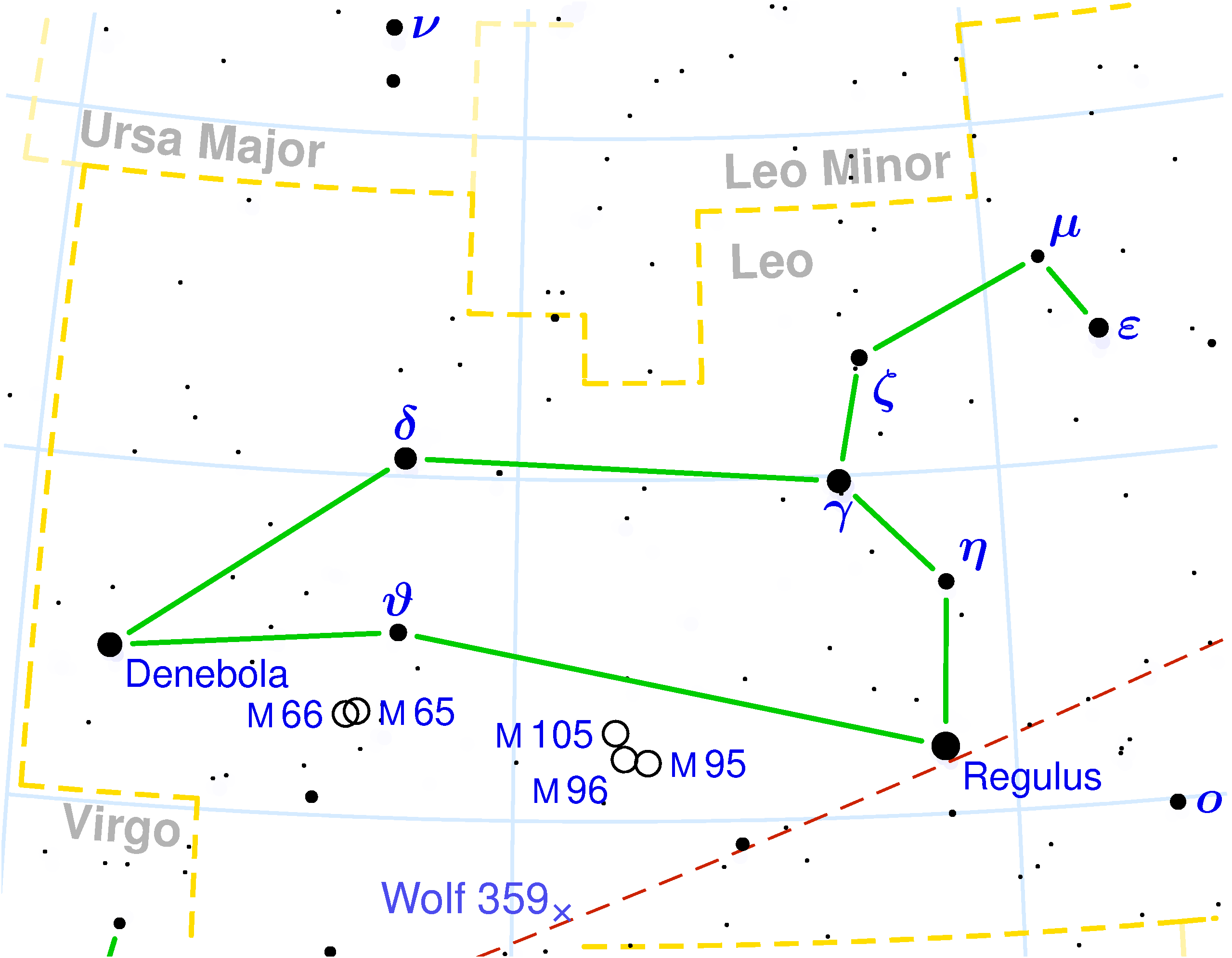 Denebola is a white main sequence star in the constellation Leo. With a distance of 36 light years from Earth, and an apparent magnitude of 2.14, it is the third brightest star in the constellation and the 62nd in the night sky. This star has often taken the place of Regulus in the Spring Triangle. While Regulus has a higher magnitude, Denebola makes the triangle more equilateral in appearance.
The star's name comes from the Arabic phrase Deneb Elased, or ðanab al-asad, meaning "the tail of the lion." This refers to the star's position in the constellation at the lion's tail end. Denebola has a mass of 1.78 solar masses and a radius of 1.728 solar radii, making it almost twice the size of our sun. It may be a Delta Scuti type variable star due to its variations in brightness; about 10 times a day the star's brightness fluctuates in magnitudes around 0.025.
Denebola is a white main sequence star in the constellation Leo. With a distance of 36 light years from Earth, and an apparent magnitude of 2.14, it is the third brightest star in the constellation and the 62nd in the night sky. This star has often taken the place of Regulus in the Spring Triangle. While Regulus has a higher magnitude, Denebola makes the triangle more equilateral in appearance.
The star's name comes from the Arabic phrase Deneb Elased, or ðanab al-asad, meaning "the tail of the lion." This refers to the star's position in the constellation at the lion's tail end. Denebola has a mass of 1.78 solar masses and a radius of 1.728 solar radii, making it almost twice the size of our sun. It may be a Delta Scuti type variable star due to its variations in brightness; about 10 times a day the star's brightness fluctuates in magnitudes around 0.025.
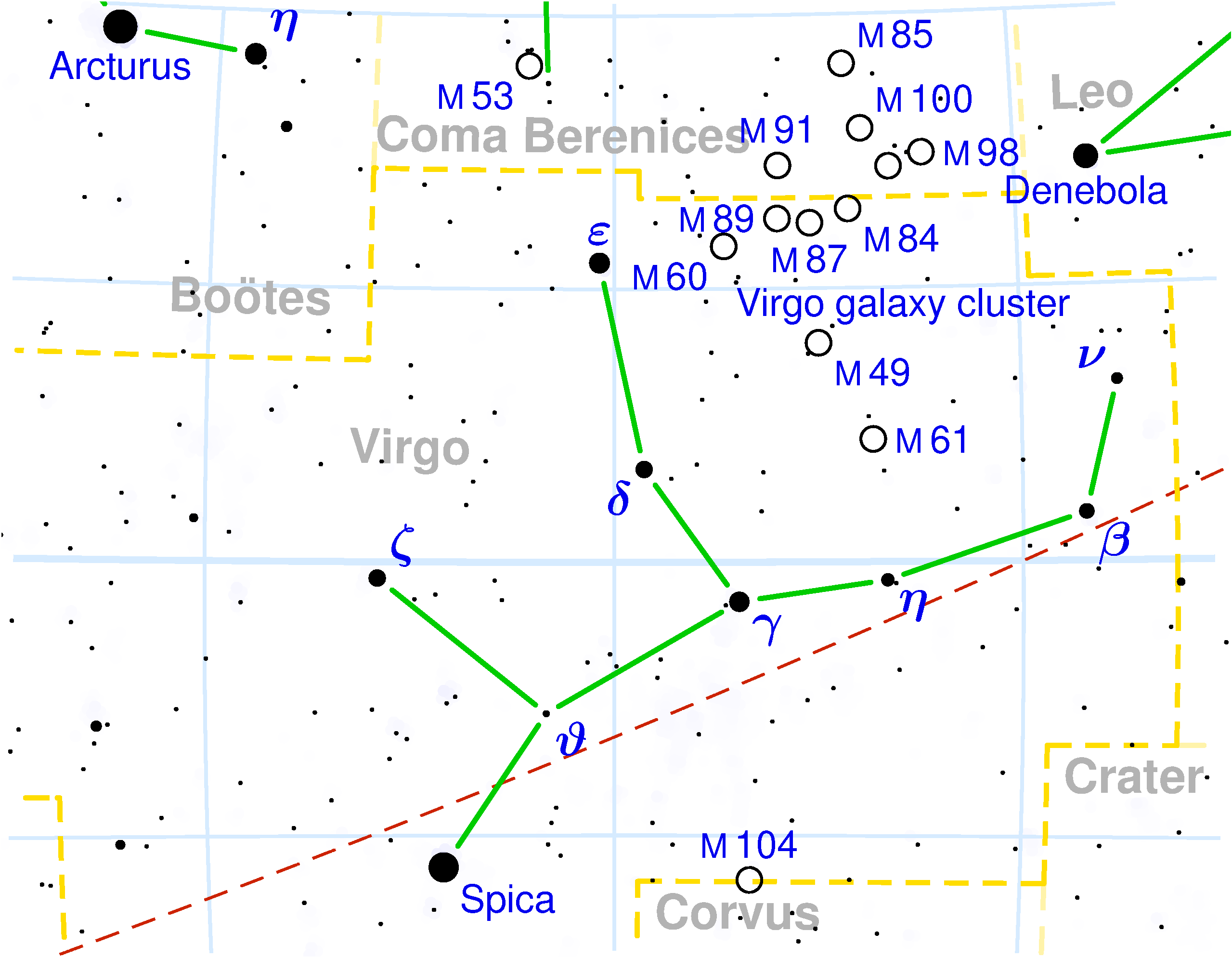
 The Spring Triangle contains multiple objects of note, with a large amount of them belonging to the Virgo Cluster. This cluster contains around 1,500 galaxies and can be seen between the stars Denebola and Vindemiatrix, with many being notable Messier objects.
The Spring Triangle contains multiple objects of note, with a large amount of them belonging to the Virgo Cluster. This cluster contains around 1,500 galaxies and can be seen between the stars Denebola and Vindemiatrix, with many being notable Messier objects.
 The brightest galaxy seen in the cluster is the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87. With an apparent magnitude of 9.6, the galaxy can be seen using a telescope, as it was first seen by Charles Messier in 1781. Located 54 million light years away and at 130,000 light years across, M87 houses several trillions of stars and around 15,000
The brightest galaxy seen in the cluster is the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87. With an apparent magnitude of 9.6, the galaxy can be seen using a telescope, as it was first seen by Charles Messier in 1781. Located 54 million light years away and at 130,000 light years across, M87 houses several trillions of stars and around 15,000
 Also known as the Butterfly Galaxies, NGC 4567 and 4586 are two unbarred spiral galaxies that are colliding. The pair were first discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1784, but did not earn their name until observer Ralph Copeland called them the Siamese Twins in the late 1800s due to their almost identical shape and structure. The galaxies are located around 52 million light years away, with a separation between the cores of around 20,000 light years. The more distant galaxy, NGC 4567, has an apparent magnitude of 11.5 and is oriented almost completely face-on with our galaxy. The closer galaxy, NGC 4568, has an apparent magnitude of 11.2 and is oriented at a diagonal. It was originally believed that the two were simply passing directly behind each other in the same line of sight, but further observations and studies have observed a high rate of star formation where the galaxies overlap, confirming that they are undergoing the early phases of collision and merging.
Also known as the Butterfly Galaxies, NGC 4567 and 4586 are two unbarred spiral galaxies that are colliding. The pair were first discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1784, but did not earn their name until observer Ralph Copeland called them the Siamese Twins in the late 1800s due to their almost identical shape and structure. The galaxies are located around 52 million light years away, with a separation between the cores of around 20,000 light years. The more distant galaxy, NGC 4567, has an apparent magnitude of 11.5 and is oriented almost completely face-on with our galaxy. The closer galaxy, NGC 4568, has an apparent magnitude of 11.2 and is oriented at a diagonal. It was originally believed that the two were simply passing directly behind each other in the same line of sight, but further observations and studies have observed a high rate of star formation where the galaxies overlap, confirming that they are undergoing the early phases of collision and merging.
Lions in the Sky and other Spring Treasures
Shows Denebola instead of
 The Spring Triangle is an astronomical asterism involving an imaginary triangle drawn upon the
The Spring Triangle is an astronomical asterism involving an imaginary triangle drawn upon the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
, with its defining vertices at Arcturus, Spica, and Regulus
Regulus is the brightest object in the constellation Leo and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation designated α Leonis, which is Latinized to Alpha Leonis, and abbreviated Alpha Leo or α Leo. Re ...
. This triangle connects the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
s of Boötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from la, Boōtēs, which comes from grc-gre, Βοώτης, Boṓtēs ...
, Virgo, and Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
. It is visible in the evening rising in the southeastern sky of the N orthern Hemisphere between March and May and setting until August, while at morning rising and setting from November to the end of February.
George Lovi of Sky & Telescope magazine had a slightly different Spring Triangle, including the tail of Leo, with Denebola replacing Regulus
Regulus is the brightest object in the constellation Leo and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation designated α Leonis, which is Latinized to Alpha Leonis, and abbreviated Alpha Leo or α Leo. Re ...
. Although Denebola is dimmer, this triangle is more nearly equilateral.
These stars, together with Cor Caroli, form parts of a larger spring asterism called the Great Diamond
The Great Diamond is an asterism. Astronomy popularizer Hans A. Rey called it the Virgin's Diamond. (In fact, long before mentioned in R. Hinckley-Allen's "Star-Names and Their Meanings", 1899, p.259, as "the celebrated Diamond of Virgo"; see ...
.
The stars of the Spring Triangle
Arcturus (α Boötes)
Arcturus is a giant orange star in the constellationBoötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from la, Boōtēs, which comes from grc-gre, Βοώτης, Boṓtēs ...
. Located only 37 light years away, it has an apparent magnitude of -0.04. It is the brightest star in the Northern Hemisphere and fourth brightest in the night sky.
Because it is spotted easily, Arcturus was identified by ancient humans and tied to mythological ideals. The star was given its name from the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
Ἀρκτοῦρος (''Arktouros''), which translates to "Guardian of the Bear." This name was selected because of the star's proximity to Ursa Major
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa ...
and Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor (Latin: 'Lesser Bear', contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, h ...
, surmising the two bear constellations were guarded by Arcturus.
Arcturus is thought to be around 6 to 8.5 billion years old, and has traveled up the red-giant branch of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as it has expanded in size. The star has a diameter of around 36 million km, making it about 26 times larger than the Sun. Despite this size difference, the mass of Arcturus is only 1.1 times that of the Sun.
With its high speed of 122 km/s (270,000 mph) and a path which crosses the galactic plane rather than residing within it, Arcturus may have formed outside of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
. The star is the namesake of a group of 52 other stars named the Arcturus moving group In astronomy, the Arcturus moving group or Arcturus stream is a moving group or stellar stream, discovered by Olin J. Eggen (1971), comprising 53 stars moving at 275,000 miles per hour, which includes the nearby bright star Arcturus. It comprises m ...
or Arcturus stream, all of which share a similar proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
. It has been proposed that these stars are remnants of an ancient dwarf satellite galaxy
A satellite galaxy is a smaller companion galaxy that travels on bound orbits within the gravitational potential of a more massive and luminous host galaxy (also known as the primary galaxy). Satellite galaxies and their constituents are bound ...
that was assimilated into the Milky Way long ago.
Spica (α Virginis)
Spica is abinary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that t ...
blue-white star pair that appears as a single point of light from Earth, and is commonly if incorrectly referred to as a single star. The star system is 250 light years away and has an apparent magnitude of 1.04. It is the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, and is the 15th brightest star in the night sky. The name Spica is derived from a Latin phrase that describes the zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. ...
sign Virgo as holding an ear of grain, ''spīca virginis.'' Virgo the Maiden is often represented as a young woman holding this stalk of grain.
The best times of the year to view this star are during early spring to late summer in the Northern Hemisphere. To find this star easily, locate the Big Dipper and follow the curve of its handle. This curve will first lead to Arcturus. Finally, "drive a spike" directly to Spica. Spica is made up of two individual stars, Spica A and Spica B, with radii of 7.40 and 3.64 times the Sun's, respectively. Their sizes contribute greatly to the brightness of the stars. Spica A's luminosity is 12,100 times that of the Sun, while Spica B has a luminosity of 1,500. Their sizes lead to respective surface temperatures of 22,400 K and 18,500 K, much higher than the Sun. They are separated by a distance of only 0.12 AU with an orbital period of only four days. This proximity gravitationally distorts each star into an egg shape, with the pointed ends facing each other.
Spica is made up of two individual stars, Spica A and Spica B, with radii of 7.40 and 3.64 times the Sun's, respectively. Their sizes contribute greatly to the brightness of the stars. Spica A's luminosity is 12,100 times that of the Sun, while Spica B has a luminosity of 1,500. Their sizes lead to respective surface temperatures of 22,400 K and 18,500 K, much higher than the Sun. They are separated by a distance of only 0.12 AU with an orbital period of only four days. This proximity gravitationally distorts each star into an egg shape, with the pointed ends facing each other.
Regulus (α Leonis)
 Regulus, the brightest object in the constellation
Regulus, the brightest object in the constellation Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
, is a quadruple star system made up of two separate pairs of stars. At 79 light years away and an apparent magnitude of 1.35, Regulus is the 21st brightest star in the sky. The name Regulus, which translates to "little king" in Latin, was given to the system by Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic Church, Catholic cano ...
in the 16th century. The star can be seen at the base of the head of Leo that looks like a backwards question mark, which is also referred to as the Sickle
Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac, between Cancer the crab to the west and Virgo the maiden to the east. It is located in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its name is Latin for lion, and to the ancient Greeks represented the Neme ...
.
The brighter pair of stars is called Regulus A, which is made up of a large visible bright blue star and its companion, Regulus D, which is possibly a white dwarf, though this is unconfirmed. This smaller companion has a mass of only 0.3 solar masses, while the mass of the larger is 3.8 solar masses. The pair are close at 0.35 AU apart, with a short orbital period of 40.11 days around a center mass. The other two stars are the main sequence orange dwarf Regulus B and its red dwarf companion Regulus C. With apparent magnitudes of 8.13 and 13.50, they can't be seen with naked eye. This means the entire system is named after its brightest star.
Regulus A appears egg-shaped due to an extreme rotational speed. While the Sun rotates on its axis once every 27 days at a speed of 7,242 kph (4,500 mph), Regulus rotates every 16 hours at 1.1 million kph (700,000 mph). Astronomers have determined that if the star rotated 10% faster it would rip itself apart.
Denebola (β Leonis)
 Denebola is a white main sequence star in the constellation Leo. With a distance of 36 light years from Earth, and an apparent magnitude of 2.14, it is the third brightest star in the constellation and the 62nd in the night sky. This star has often taken the place of Regulus in the Spring Triangle. While Regulus has a higher magnitude, Denebola makes the triangle more equilateral in appearance.
The star's name comes from the Arabic phrase Deneb Elased, or ðanab al-asad, meaning "the tail of the lion." This refers to the star's position in the constellation at the lion's tail end. Denebola has a mass of 1.78 solar masses and a radius of 1.728 solar radii, making it almost twice the size of our sun. It may be a Delta Scuti type variable star due to its variations in brightness; about 10 times a day the star's brightness fluctuates in magnitudes around 0.025.
Denebola is a white main sequence star in the constellation Leo. With a distance of 36 light years from Earth, and an apparent magnitude of 2.14, it is the third brightest star in the constellation and the 62nd in the night sky. This star has often taken the place of Regulus in the Spring Triangle. While Regulus has a higher magnitude, Denebola makes the triangle more equilateral in appearance.
The star's name comes from the Arabic phrase Deneb Elased, or ðanab al-asad, meaning "the tail of the lion." This refers to the star's position in the constellation at the lion's tail end. Denebola has a mass of 1.78 solar masses and a radius of 1.728 solar radii, making it almost twice the size of our sun. It may be a Delta Scuti type variable star due to its variations in brightness; about 10 times a day the star's brightness fluctuates in magnitudes around 0.025.
Deep Sky Objects
 The Spring Triangle contains multiple objects of note, with a large amount of them belonging to the Virgo Cluster. This cluster contains around 1,500 galaxies and can be seen between the stars Denebola and Vindemiatrix, with many being notable Messier objects.
The Spring Triangle contains multiple objects of note, with a large amount of them belonging to the Virgo Cluster. This cluster contains around 1,500 galaxies and can be seen between the stars Denebola and Vindemiatrix, with many being notable Messier objects.
Messier 87
 The brightest galaxy seen in the cluster is the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87. With an apparent magnitude of 9.6, the galaxy can be seen using a telescope, as it was first seen by Charles Messier in 1781. Located 54 million light years away and at 130,000 light years across, M87 houses several trillions of stars and around 15,000
The brightest galaxy seen in the cluster is the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87. With an apparent magnitude of 9.6, the galaxy can be seen using a telescope, as it was first seen by Charles Messier in 1781. Located 54 million light years away and at 130,000 light years across, M87 houses several trillions of stars and around 15,000 globular star clusters
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member ...
. For comparison, the Milky Way is 105,700 light years across and contains around 200 billion stars.
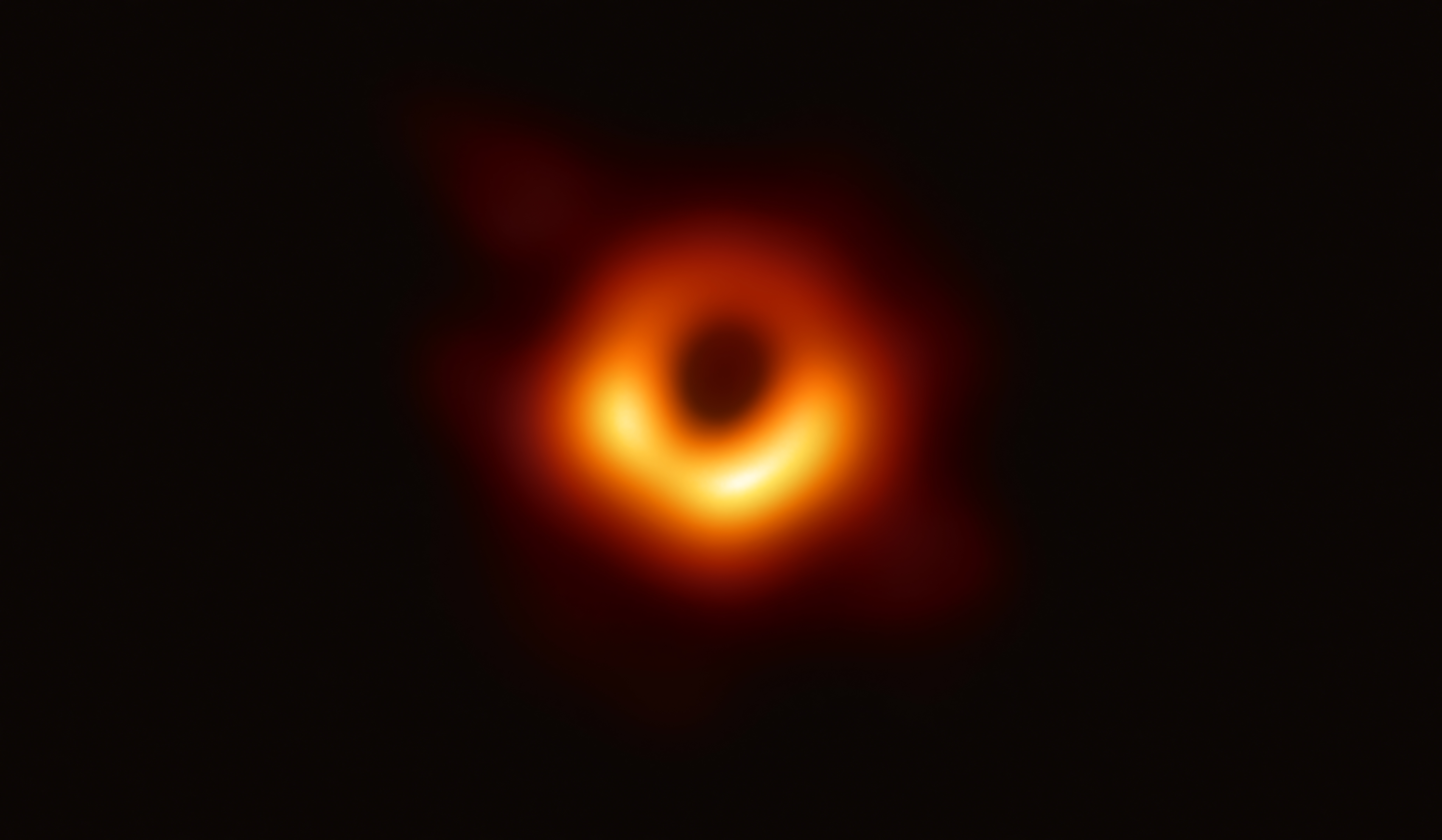
At the center of this galaxy there is a supermassive black hole (of 6.5 billion solar masses) bearing a large blue jet
Jet, Jets, or The Jet(s) may refer to:
Aerospace
* Jet aircraft, an aircraft propelled by jet engines
** Jet airliner
** Jet engine
** Jet fuel
* Jet Airways, an Indian airline
* Wind Jet (ICAO: JET), an Italian airline
* Journey to Enceladus a ...
of subatomic particles accelerated to speeds close to the speed of light. In 2019, an image of this black hole, designated M87*, was published by the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration -- the first picture of a black hole ever released.
Messier 49
Messier 49 is the brightest galaxy in the Virgo group with an apparent magnitude of 9.4. This brightness allowed M49 to be the first observed in the group, byNicolas Louis de Lacaille
Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille (; 15 March 171321 March 1762), formerly sometimes spelled de la Caille, was a French astronomer and geodesist who named 14 out of the 88 constellations. From 1750 to 1754, he studied the sky at the Cape of Good ...
in 1752. The giant elliptical galaxy is located 56 million light years from Earth, and is around 157,000 light years across, with more than 200 billion stars.
Siamese Twins Galaxies (NGC 4567 and NGC 4568)
 Also known as the Butterfly Galaxies, NGC 4567 and 4586 are two unbarred spiral galaxies that are colliding. The pair were first discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1784, but did not earn their name until observer Ralph Copeland called them the Siamese Twins in the late 1800s due to their almost identical shape and structure. The galaxies are located around 52 million light years away, with a separation between the cores of around 20,000 light years. The more distant galaxy, NGC 4567, has an apparent magnitude of 11.5 and is oriented almost completely face-on with our galaxy. The closer galaxy, NGC 4568, has an apparent magnitude of 11.2 and is oriented at a diagonal. It was originally believed that the two were simply passing directly behind each other in the same line of sight, but further observations and studies have observed a high rate of star formation where the galaxies overlap, confirming that they are undergoing the early phases of collision and merging.
Also known as the Butterfly Galaxies, NGC 4567 and 4586 are two unbarred spiral galaxies that are colliding. The pair were first discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1784, but did not earn their name until observer Ralph Copeland called them the Siamese Twins in the late 1800s due to their almost identical shape and structure. The galaxies are located around 52 million light years away, with a separation between the cores of around 20,000 light years. The more distant galaxy, NGC 4567, has an apparent magnitude of 11.5 and is oriented almost completely face-on with our galaxy. The closer galaxy, NGC 4568, has an apparent magnitude of 11.2 and is oriented at a diagonal. It was originally believed that the two were simply passing directly behind each other in the same line of sight, but further observations and studies have observed a high rate of star formation where the galaxies overlap, confirming that they are undergoing the early phases of collision and merging.
Other Objects
There are many other notable members in the triangle, including Messier 60,Messier 84
Messier 84 or M84, also known as NGC 4374, is a giant elliptical or lenticular galaxy in the constellation Virgo. Charles Messier discovered the object in 1781 in a systematic search for "nebulous objects" in the night sky. It is the 84th object ...
, and Messier 86
Messier 86 (also known as M86 or NGC 4406) is an elliptical or lenticular galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781. M86 lies in the heart of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies and forms a most conspicuous group ...
. Two named groups of galaxies are the Eyes Galaxies
The Eyes Galaxies (NGC 4435-NGC 4438, also known as Arp 120) are a pair of galaxies about 52 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. The pair are members of the string of galaxies known as Markarian's Chain.
NGC 4435
NGC 4435 is ...
(NGC 4435 and NGC 4438) and the Leo Triplet
The Leo Triplet (also known as the M66 Group) is a small group of galaxies about 35 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. This galaxy group consists of the spiral galaxies M65, M66, and NGC 3628.
Members
The table below lists ...
( NGC 3628, Messier 65
Messier 65 (also known as NGC 3623) is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 35 million light-years away in the constellation Leo, within its highly equatorial southern half. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780. With M66 and NGC 3628, ...
, Messier 66
Messier 66 or M66, also known as NGC 3627, is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the southern, equatorial half of Leo. It was discovered by French astronomer Charles Messier on 1 March 1780, who described it as "very long and very faint". This ga ...
).
See also
*Summer Triangle
The Summer Triangle is an astronomical asterism in the northern celestial hemisphere. The defining vertices of this imaginary triangle are at Altair, Deneb, and Vega, each of which is the brightest star of its constellation ( Aquila, Cygnus, ...
* Winter Triangle
* Northern Cross
References
{{reflistExternal links
Lions in the Sky and other Spring Treasures
Shows Denebola instead of
Regulus
Regulus is the brightest object in the constellation Leo and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation designated α Leonis, which is Latinized to Alpha Leonis, and abbreviated Alpha Leo or α Leo. Re ...
in the spring triangle
Asterisms (astronomy)
Leo (constellation)
Virgo (constellation)
Boötes