|
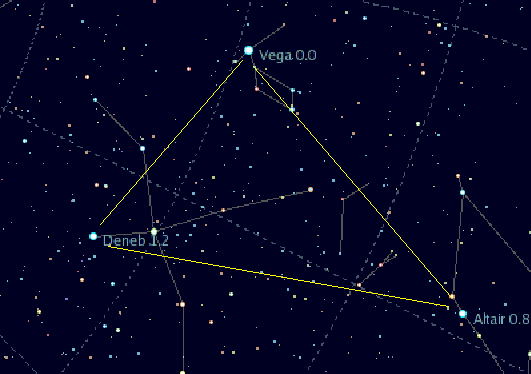
Northern Cross (asterism)
The Northern Cross is an astronomical asterism in the northern hemisphere of the celestial sphere, corresponding closely with the constellation Cygnus the swan. It is much larger than the Southern Cross and consists of the brightest stars in Cygnus: Deneb, Sadr, Gienah, Delta Cygni and Albireo. The 'head' of the cross, Deneb, is also part of the Summer Triangle asterism. Like the Summer Triangle, the Northern Cross is an indicator of the seasons. Near midnight, the Cross lies virtually overhead at mid-northern latitudes during the summer months; it can also be seen during spring in the early morning to the East. In the autumn the cross is visible in the evening to the West until November. It never dips below the horizon at or above 45° north latitude, just grazing the northern horizon at its lowest point at such locations as Minneapolis, Montréal and Turin. From the southern hemisphere it appears upside down and low in the sky during the winter months. In Johann Bayer's 17th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnus IAU
Cygnus is the Latin word for swan and may refer to: Astronomy * Cygnus (constellation), a northern constellation ** Cygnus A, a radio galaxy within the constellation ** Cygnus X (star complex), a star complex within the constellation ** Cygnus X-1, a binary system within the constellation ** Cygnus X-3, a binary system within the constellation Business & industry * Cygnus 20, a Canadian sailboat design * ''Cygnus'' (spacecraft), a space vehicle developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation and Thales Alenia Space * Cygnus Air or Gestair Cargo, a Spanish cargo airline * Cygnus Business Media, a U.S.-based business-to-business publishing company * Cygnus Solutions, a company that provided commercial support for free software and the original developer of Cygwin Other uses * ''Cygnus'' (genus), the genus of most swans * Cygnus (mythology) or Cycnus, a number of characters in Greek mythology * Cygnus X-1 (song series), a 1977–1978 two-part song series by Rush * Cygnus X (music gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β Cygni
Albireo is a double star designated Beta Cygni (β Cygni, abbreviated Beta Cyg, β Cyg). The International Astronomical Union uses the name "Albireo" specifically for the brightest star in the system. Although designated 'beta', it is fainter than Gamma Cygni, Delta Cygni, and Epsilon Cygni and is the fifth-brightest point of light in the constellation of Cygnus. Appearing to the naked eye to be a single star of magnitude 3, viewing through even a low-magnification telescope resolves it into its two components. The brighter yellow star, itself a very close binary system, makes a striking colour contrast with its fainter blue companion. Nomenclature ''β Cygni'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Cygni'') is the system's Bayer designation. The brighter of the two components is designated ''β¹ Cygni'' or ''Beta Cygni A'' and the fainter ''β² Cygni'' or ''Beta Cygni B''. The system's traditional name ''Albireo'' is a result of misunderstanding and mistranslation. It is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
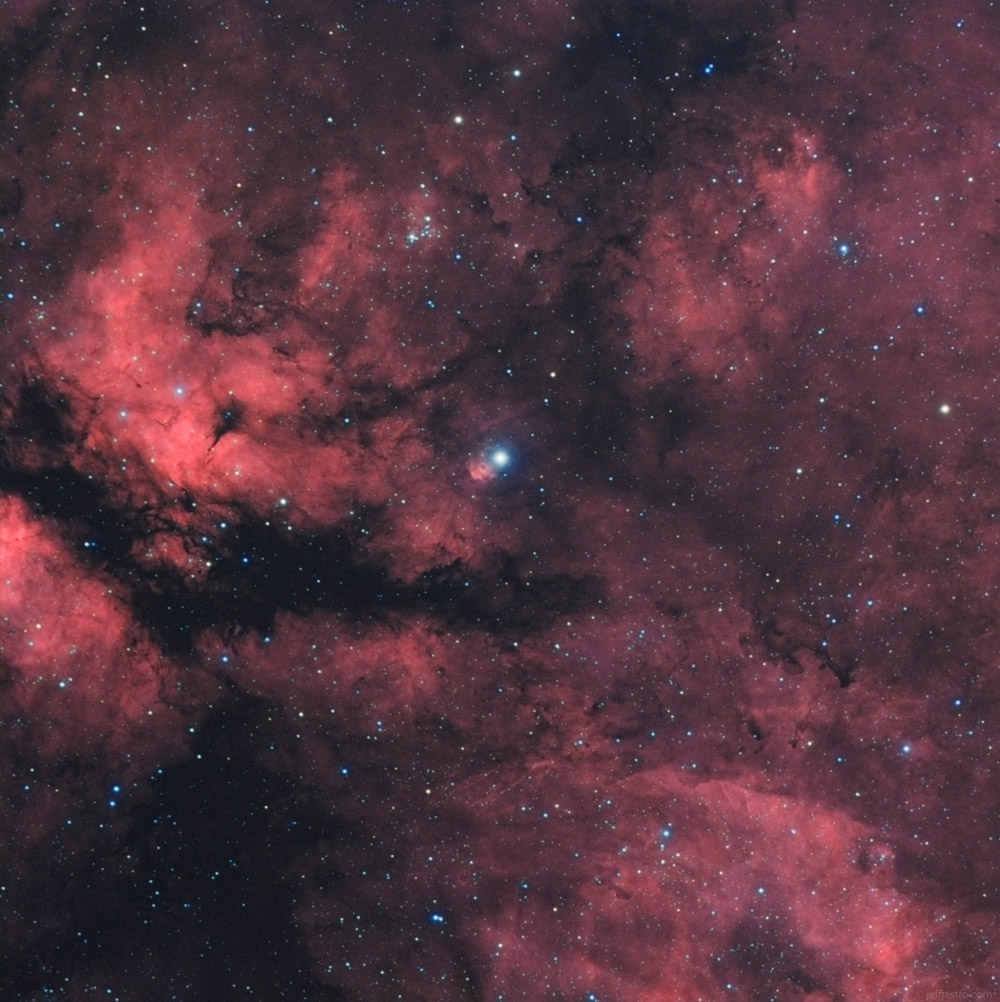
γ Cygni
Gamma Cygni (γ Cygni, abbreviated Gamma Cyg, γ Cyg), officially named Sadr , is a star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, forming the intersection of an asterism of five stars called the Northern Cross. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 1,800 light-years (560 parsecs) from the Sun. It forms the primary or 'A' component of a multiple star system designated WDS J20222+4015 (the secondary or 'BC' component is CCDM J20222+4015BC, a close pair of stars 40" away from γ Cygni). Nomenclature ''γ Cygni'' ( Latinised to ''Gamma Cygni'') is the star's Bayer designation. WDS J20222+4015A is its designation in the Washington Double Star Catalog. It bore the traditional name ''Sadr'' (also rendered ''Sadir'' or ''Sador''), derived from the Arabic صدر ''ṣadr'' "chest", the same word which gave rise to the star Schedar ( Alpha Cassiopeiae). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
δ Cygni
Delta Cygni (δ Cygni, abbreviated Delta Cyg, δ Cyg) is a binary star of a combined third-magnitude in the constellation of Cygnus. It is also part of the Northern Cross asterism whose brightest star is Deneb. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, Delta Cygni is located roughly distant from the Sun. Delta Cygni's two components are designated Delta Cygni A (officially named Fawaris ) and B. More widely separated is a faint third component, a 12th magnitude star that is moving along with the others. Together they form a triple star system. Nomenclature ''δ Cygni'' ( Latinised to ''Delta Cygni'') is the binary's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Delta Cygni A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Traditionally, Delta Cygni had no proper name. It belonged to the Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ε Cygni
Epsilon Cygni (ε Cygni, abbreviated Epsilon Cyg, ε Cyg) is multiple star system in the constellation of Cygnus. With an apparent visual magnitude of 2.48, it is readily visible to the naked eye at night as one of the brighter members of Cygnus. Based upon parallax measurement, Epsilon Cygni is about 73 light-years from the Sun. The system has three constituents: a spectroscopic binary (designated Epsilon Cygni A); an optical companion (B) and a single star (C). A's two components are themselves designated Epsilon Cygni Aa (officially named Aljanah ) and Ab. Nomenclature ''ε Cygni'' ( Latinised to ''Epsilon Cygni'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the three constituents as ''Epsilon Cygni A'', ''B'' and ''C'', and those of ''A's'' components - ''Epsilon Cygni Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Eps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α Cygni
Deneb () is a first-magnitude star in the constellation of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and the 19th brightest star in the night sky, with an average apparent magnitude of +1.25. A blue-white supergiant, Deneb rivals Rigel as the most luminous first-magnitude star. However, its distance, and hence luminosity, is poorly known; its luminosity is somewhere between 55,000 and 196,000 times that of the Sun. Its Bayer designation is α Cygni, which is Latinised to Alpha Cygni, abbreviated to Alpha Cyg or α Cyg. Nomenclature ''α Cygni'' (Latinised to ''Alpha Cygni'') is the star's designation given by Johann Bayer in 1603. The traditional name ''Deneb'' is derived from the Arabic word for "tail", from the phrase ذنب الدجاجة ''Dhanab al-Dajājah'', or "tail of the hen". The IAU Working Group on Star Names has recognised the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. The word ''magnitude'' in astronomy, unless stated otherwise, usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale dates back to the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog listed stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined in a way to closely match this historical system. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to a brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a star of magnitude 2.0 is 2.512 times as bright as a star of magnitude 3.0, 6. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Cygni
P Cygni (34 Cygni) is a variable star in the constellation Cygnus. The designation "P" was originally assigned by Johann Bayer in ''Uranometria'' as a nova. Located about 5,300 light-years (1,560 parsecs) from Earth, it is a hypergiant luminous blue variable (LBV) star of spectral type B1-2 Ia-0ep that is one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. Visibility The star is located about 5,000 to 6,000 light-years (1,500–1,800 parsecs) from Earth. Despite this vast distance, it is visible to the naked eye in suitable dark sky locations. It was unknown until the end of the 16th century, when it suddenly brightened to 3rd magnitude. It was first observed on 18 August (Gregorian) 1600 by Willem Janszoon Blaeu, a Dutch astronomer, mathematician and globe-maker. Bayer's atlas of 1603 assigned it the miscellaneous label P and the name has stuck ever since. After six years the star faded slowly, dropping below naked-eye visibility in 1626. It brightened again in 1655, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |