Spartacus Reds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Spartacus ( el, Σπάρτακος '; la, Spartacus; c. 103–71 BC) was a Thracian
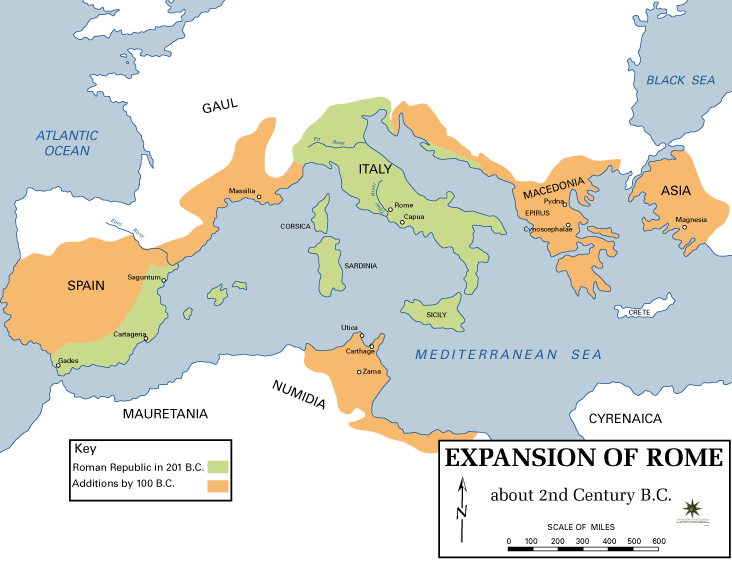 According to the differing sources and their interpretation, Spartacus was a captive taken by the legions. Spartacus was trained at the gladiatorial school (''ludus'') near Capua belonging to Lentulus Batiatus. He was a heavyweight gladiator called a murmillo. These fighters carried a large oblong shield (
According to the differing sources and their interpretation, Spartacus was a captive taken by the legions. Spartacus was trained at the gladiatorial school (''ludus'') near Capua belonging to Lentulus Batiatus. He was a heavyweight gladiator called a murmillo. These fighters carried a large oblong shield (
8:1–2
; Appian, ''Civil Wars''
; Livy, ''Periochae''
; Florus, ''Epitome'', 2.8. Plutarch claims 78 escaped, Livy claims 74, Appian "about seventy", and Florus says "thirty or rather more men". "Choppers and spits" is from ''Life of Crassus''. About 70 slaves were part of the plot. Though few in number, they seized kitchen utensils, fought their way free from the school, and seized several wagons of gladiatorial weapons and armour. The escaped slaves defeated soldiers sent after them, plundered the region surrounding Capua, recruited many other slaves into their ranks, and eventually retired to a more defensible position on Mount Vesuvius. Once free, the escaped gladiators chose Spartacus and two Gallic slaves—
9:1–3
; Frontinus, ''Stratagems''
Appian, ''Civil Wars''
; Broughton, ''Magistrates of the Roman Republic'', p. 109. The rebels also defeated a second expedition against them, nearly capturing the praetor commander, killing his lieutenants, and seizing the military equipment. Due to these successes, more and more slaves flocked to the Spartacan forces, as did many of the herdsmen and
1:117
.Plutarch, ''Crassus''
. Alarmed at the continued threat posed by the slaves, the Senate charged
1:118
. with ending the rebellion. Crassus was put in charge of eight legions, numbering upwards of 40,000 trained Roman soldiers; he treated these with harsh discipline, reviving the punishment of "
10:1–3
. After this, Crassus's legions were victorious in several engagements, forcing Spartacus farther south through Lucania as Crassus gained the upper hand. By the end of 71 BC, Spartacus was encamped in Rhegium ( According to Plutarch, Spartacus made a bargain with
According to Plutarch, Spartacus made a bargain with
9:5–6
.
 In modern times, Spartacus became an icon for communists and socialists. Karl Marx listed Spartacus as one of his heroes and described him as "the most splendid fellow in the whole of ancient history" and a "great general, noble character, real representative of the ancient
In modern times, Spartacus became an icon for communists and socialists. Karl Marx listed Spartacus as one of his heroes and described him as "the most splendid fellow in the whole of ancient history" and a "great general, noble character, real representative of the ancient

Spartacus' Uprising and Soviet Historical Writing
'. Oxford: Oxbow Books, 1987 (paperback, ). * ''Spartacus: Film and History'', edited by Martin M. Winkler. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 2007 (hardcover, ; paperback, ). * Trow, M.J. ''Spartacus: The Myth and the Man''. Stroud, United Kingdom: Sutton Publishing, 2006 (hardcover, ). * Genner, Michael. "Spartakus. Eine Gegengeschichte des Altertums nach den Legenden der Zigeuner". Two volumes. Paperback.
BBC Radio 4 – ''In Our Time'' – Spartacus
Article and full text of the Roman and Greek sources.
''Spartacus'', movie starring Kirk Douglas and Sir Peter Ustinov
''Spartacus'', television mini-series starring Goran Višnjić and Alan Bates
Starz Mini-Series airing in 2010
{{DEFAULTSORT:Spartacus 100s BC births 71 BC deaths Year of birth uncertain 1st-century BC Romans Ancient Thracians killed in battle Deaths by blade weapons Rebel slaves in ancient Rome Roman-era Thracians Roman gladiators Third Servile War Thracian people Republican era slaves and freedmen
gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
who, along with Crixus
Crixus was a Gallic gladiator and military leader in the Third Servile War between the Roman Republic and rebel slaves. Born in Gaul, he was enslaved by the Romans under unknown circumstances and trained as a gladiator in Capua. His name means " ...
, Gannicus
Gannicus was a Celtic slave, who together with the Thracian Spartacus, Crixus, Castus and Oenomaus, became one of the leaders of rebel slaves during the Third Servile War (73–71 BC). In the winter of 71 BC, Gannicus, along with Castus, broke o ...
, Castus
Castus is a Latin word meaning clean and pure.
*Lucius Artorius Castus, Roman general
*Castus and Emilius, Roman martyrs and saints
*Castus (rebel)
Castus was an enslaved Gallic man who, together with the Thracian Spartacus, the fellow Gaul Crix ...
, and Oenomaus
In Greek mythology, King Oenomaus (also Oenamaus; grc-gre, Οἰνόμαος, ''Oἱnómaos'') of Pisa, was the father of Hippodamia and the son of Ares. His name ''Oinomaos'' denotes a wine man.
Family
Oenomaeus' mother was either naiad Har ...
, was one of the escaped slave
In the United States, fugitive slaves or runaway slaves were terms used in the 18th and 19th century to describe people who fled slavery. The term also refers to the federal Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Such people are also called freed ...
leaders in the Third Servile War, a major slave uprising
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedo ...
against the Roman Republic. Little is known about him beyond the events of the war, and surviving historical accounts are sometimes contradictory. All sources agree that he was a former gladiator and an accomplished military leader.
This rebellion, interpreted by some as an example of oppressed people fighting for their freedom against a slave-owning oligarchy, has provided inspiration for many political thinkers, and has been featured in literature, television, and film. The philosopher Voltaire described the Third Servile War as "the only just war in history". Although this interpretation is not specifically contradicted by classical historians, no historical account mentions that the goal was to end slavery in the Republic.
Early life
The Greek essayist Plutarch describes Spartacus as "a Thracian of Nomadic stock", in a possible reference to the Maedi tribe. Appian says he was "a Thracian by birth, who had once served as a soldier with the Romans, but had since been a prisoner and sold for a gladiator". Florus described him as one "who, from a Thracian mercenary, had become a Roman soldier, that had deserted and became enslaved, and afterward, from consideration of his strength, a gladiator". The authors refer to theThracian tribe
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
of the Maedi, which occupied the area on the southwestern fringes of Thrace, along its border with the Roman province of Macedonia – present day south-western Bulgaria. Plutarch also writes that Spartacus's wife, a prophetess of the Maedi tribe, was enslaved with him.
The name Spartacus is otherwise manifested in the Black Sea region. Five out of twenty Kings of the Thracian Spartocid dynasty
The Spartocids () or Spartocidae was the name of a Hellenized Thracian dynasty that ruled the Hellenistic Kingdom of Bosporus between the years 438–108 BC. They had usurped the former dynasty, the Archaeanactids, a Greek dynasty of the Bospor ...
of the Cimmerian Bosporus and Pontus are known to have borne it, and a Thracian "Sparta" "Spardacus" or "Sparadokos", father of Seuthes I of the Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
, is also known.
Spartacus was around 30 years old at the time he started his revolt, which would put his birth year around 103 BC.
Enslavement and escape
 According to the differing sources and their interpretation, Spartacus was a captive taken by the legions. Spartacus was trained at the gladiatorial school (''ludus'') near Capua belonging to Lentulus Batiatus. He was a heavyweight gladiator called a murmillo. These fighters carried a large oblong shield (
According to the differing sources and their interpretation, Spartacus was a captive taken by the legions. Spartacus was trained at the gladiatorial school (''ludus'') near Capua belonging to Lentulus Batiatus. He was a heavyweight gladiator called a murmillo. These fighters carried a large oblong shield (scutum
The ''scutum'' (; plural ''scuta'') was a type of shield used among Italic peoples in antiquity, most notably by the army of ancient Rome starting about the fourth century BC.
The Romans adopted it when they switched from the military formati ...
), and used a sword with a broad, straight blade ( gladius), about 18 inches long. In 73 BC, Spartacus was among a group of gladiators plotting an escape.Plutarch, ''Crassus''8:1–2
; Appian, ''Civil Wars''
; Livy, ''Periochae''
; Florus, ''Epitome'', 2.8. Plutarch claims 78 escaped, Livy claims 74, Appian "about seventy", and Florus says "thirty or rather more men". "Choppers and spits" is from ''Life of Crassus''. About 70 slaves were part of the plot. Though few in number, they seized kitchen utensils, fought their way free from the school, and seized several wagons of gladiatorial weapons and armour. The escaped slaves defeated soldiers sent after them, plundered the region surrounding Capua, recruited many other slaves into their ranks, and eventually retired to a more defensible position on Mount Vesuvius. Once free, the escaped gladiators chose Spartacus and two Gallic slaves—
Crixus
Crixus was a Gallic gladiator and military leader in the Third Servile War between the Roman Republic and rebel slaves. Born in Gaul, he was enslaved by the Romans under unknown circumstances and trained as a gladiator in Capua. His name means " ...
and Oenomaus
In Greek mythology, King Oenomaus (also Oenamaus; grc-gre, Οἰνόμαος, ''Oἱnómaos'') of Pisa, was the father of Hippodamia and the son of Ares. His name ''Oinomaos'' denotes a wine man.
Family
Oenomaeus' mother was either naiad Har ...
—as their leaders. Although Roman authors assumed that the escaped slaves were a homogeneous group with Spartacus as their leader, they may have projected their own hierarchical view of military leadership onto the spontaneous organization, reducing other slave leaders to subordinate positions in their accounts.
Third Servile War
The response of the Romans was hampered by the absence of the Roman legions, which were engaged in fighting a revolt in Hispania and the Third Mithridatic War. Furthermore, the Romans considered the rebellion more of a policing matter than a war. Rome dispatched militia under the command of the praetorGaius Claudius Glaber
Gaius Claudius Glaber was a military commander of the late Roman Republic, holding the offices of legate and military praetor in 73 BC.
He was defeated in the Battle of Mount Vesuvius against the forces of Spartacus during the Third Servile War.
...
, who besieged Spartacus and his camp on Mount Vesuvius, hoping that starvation would force Spartacus to surrender. They were taken by surprise when Spartacus used ropes made from vines to climb down the steep side of the volcano with his men and attacked the unfortified Roman camp in the rear, killing most of the militia.Plutarch, ''Crassus''9:1–3
; Frontinus, ''Stratagems''
Appian, ''Civil Wars''
; Broughton, ''Magistrates of the Roman Republic'', p. 109. The rebels also defeated a second expedition against them, nearly capturing the praetor commander, killing his lieutenants, and seizing the military equipment. Due to these successes, more and more slaves flocked to the Spartacan forces, as did many of the herdsmen and
shepherd
A shepherd or sheepherder is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. ''Shepherd'' derives from Old English ''sceaphierde (''sceap'' 'sheep' + ''hierde'' 'herder'). ''Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations, i ...
s of the region, swelling their ranks to some 70,000. At its height, Spartacus's army included many different peoples, including Celts, Gauls, and others. Due to the previous Social War (91–87 BC), some of Spartacus's ranks were legion veterans. Of the slaves that joined Spartacus ranks, many were from the countryside. Rural slaves lived a life that better prepared them to fight in Spartacus's army. In contrast, urban slaves were more used to city life and were considered "privileged" and "lazy."
In these altercations, Spartacus proved to be an excellent tactician
A tactic is a conceptual action or short series of actions with the aim of achieving a short-term goal. This action can be implemented as one or more specific tasks. The term is commonly used in business, protest and military contexts, as well a ...
, suggesting that he may have had previous military experience. Though the rebels lacked military training
Military education and training is a process which intends to establish and improve the capabilities of military personnel in their respective roles. Military training may be voluntary or compulsory duty. It begins with recruit training, proceed ...
, they displayed skilful use of available local materials and unusual tactics against the disciplined Roman armies. They spent the winter of 73–72 BC training, arming and equipping their new recruits, and expanding their raiding territory to include the towns of Nola, Nuceria
Nocera Inferiore ( nap, Nucèrä Inferiórë or simply , , locally ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Salerno, in Campania in southern Italy. It lies west of Nocera Superiore, at the foot of Monte Albino, some 20 km east-so ...
, Thurii and Metapontum
Metapontum or Metapontium ( grc, Μεταπόντιον, Metapontion) was an important city of Magna Graecia, situated on the gulf of Tarentum, between the river Bradanus and the Casuentus (modern Basento). It was distant about 20 km from ...
.Florus, ''Epitome'', 2.8. The distance between these locations and the subsequent events indicate that the slaves operated in two groups commanded by the remaining leaders Spartacus and Crixus.
In the spring of 72 BC, the rebels left their winter encampments and began to move northward. At the same time, the Roman Senate, alarmed by the defeat of the praetorian forces, dispatched a pair of consular legions under the command of Lucius Gellius
Lucius Gellius (c. 136 BC''Oxford Classical Dictionary'',Gellius, Lucius – c. 54 BC) was a Roman politician and general who was one of two Roman Consul, Consuls of the Roman Republic, Republic in 72 BC along with Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Clodi ...
and Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Clodianus. The two legions were initially successful—defeating a group of 30,000 rebels commanded by Crixus
Crixus was a Gallic gladiator and military leader in the Third Servile War between the Roman Republic and rebel slaves. Born in Gaul, he was enslaved by the Romans under unknown circumstances and trained as a gladiator in Capua. His name means " ...
near Mount Garganus—but then were defeated by Spartacus. These defeats are depicted in divergent ways by the two most comprehensive (extant) histories of the war by Appian and Plutarch.Appian, ''Civil Wars''1:117
.Plutarch, ''Crassus''
. Alarmed at the continued threat posed by the slaves, the Senate charged
Marcus Licinius Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome." Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, I ...
, the wealthiest man in Rome and the only volunteer for the position,Appian, ''Civil Wars''1:118
. with ending the rebellion. Crassus was put in charge of eight legions, numbering upwards of 40,000 trained Roman soldiers; he treated these with harsh discipline, reviving the punishment of "
decimation
Decimation, Decimate, or variants may refer to:
* Decimation (punishment), punitive discipline
* Decimation (signal processing), reduction of digital signal's sampling rate
* Decimation (comics), 2006 Marvel crossover spinoff ''House of M''
* ''D ...
", in which one-tenth of his men were slain to make them more afraid of him than their enemy. When Spartacus and his followers, who for unclear reasons had retreated to the south of Italy, moved northward again in early 71 BC, Crassus deployed six of his legions on the borders of the region and detached his legate
Legate may refer to:
*Legatus, a higher ranking general officer of the Roman army drawn from among the senatorial class
:*Legatus Augusti pro praetore, a provincial governor in the Roman Imperial period
*A member of a legation
*A representative, ...
Mummius with two legions to maneuver behind Spartacus. Though ordered not to engage the rebels, Mummius attacked at a seemingly opportune moment but was routed.Plutarch, ''Crassus''10:1–3
. After this, Crassus's legions were victorious in several engagements, forcing Spartacus farther south through Lucania as Crassus gained the upper hand. By the end of 71 BC, Spartacus was encamped in Rhegium (
Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label= Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated popul ...
), near the Strait of Messina.
 According to Plutarch, Spartacus made a bargain with
According to Plutarch, Spartacus made a bargain with Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coas ...
n pirates to transport him and some 2,000 of his men to Sicily, where he intended to incite a slave revolt and gather reinforcements. However, he was betrayed by the pirates, who took payment and then abandoned the rebels. Minor sources mention that there were some attempts at raft and shipbuilding by the rebels as a means to escape, but that Crassus took unspecified measures to ensure the rebels could not cross to Sicily, and their efforts were abandoned. Spartacus's forces then retreated toward Rhegium. Crassus's legions followed and upon arrival built fortifications across the isthmus at Rhegium, despite harassing raids from the rebels. The rebels were now under siege and cut off from their supplies.
At this time, the legions of Pompey returned from Hispania and were ordered by the Senate to head south to aid Crassus. Crassus feared that Pompey's involvement would deprive him of credit for defeating Spartacus himself. Hearing of Pompey's involvement, Spartacus tried to make a truce with Crassus. When Crassus refused, Spartacus and his army broke through the Roman fortifications and headed to Brundusium
Brindisi ( , ) ; la, Brundisium; grc, Βρεντέσιον, translit=Brentésion; cms, Brunda), group=pron is a city in the region of Apulia in southern Italy, the capital of the province of Brindisi, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea.
Histor ...
with Crassus's legions in pursuit.
When the legions managed to catch a portion of the rebels separated from the main army, discipline among Spartacus's forces broke down as small groups independently attacked the oncoming legions. Spartacus now turned his forces around and brought his entire strength to bear on the legions in a last stand, in which the rebels were routed completely, with the vast majority of them being killed on the battlefield.
The final battle that saw the assumed defeat of Spartacus in 71 BC took place on the present territory of Senerchia
Senerchia (Sinerchia in the local dialect) is an Italian municipality with 1370 registered voters, but only 1036 inhabitants, in the Province of Avellino, located in the upper valley of the Sele River in Campania. It was the site of the defeat o ...
on the right bank of the river Sele
Sele may refer to:
Places Africa
* Sele, Burkina Faso, a village in the Ouéleni Department of Burkina Fase.
* Sele, Ethiopia, a town in Agbe municipality
Asia
* Sele, Turkey, a Turkish village in Kailar in Ottoman times
*Şələ, Azerbaijan
*Se ...
in the area that includes the border with Oliveto Citra up to those of Calabritto, near the village of Quaglietta, in the High Sele Valley, which at that time was part of Lucania. In this area, since 1899, there have been finds of armour and swords of the Roman era.
Plutarch, Appian and Florus all claim that Spartacus died during the battle, but Appian also reports that his body was never found. Six thousand survivors of the revolt captured by the legions of Crassus were crucified, lining the Appian Way from Rome to Capua.
Objectives
Classical historians were divided as to the motives of Spartacus. None of Spartacus's actions overtly suggest that he aimed at reforming Roman society or abolishing slavery. Plutarch writes that Spartacus wished to escape north intoCisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul ( la, Gallia Cisalpina, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts (Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC.
After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 200s BC it was con ...
and disperse his men back to their homes. If escaping the Italian peninsula was indeed his goal, it is not clear why Spartacus turned south after defeating the legions commanded by the consuls Lucius Publicola and Gnaeus Clodianus, which left his force a clear passage over the Alps.
Appian and Florus write that he intended to march on Rome itself. Appian also states that he later abandoned that goal, which might have been no more than a reflection of Roman fears.
Based on the events in late 73 BC and early 72 BC, which suggest independently operating groups of escaped slaves and a statement by Plutarch, it appears that some of the escaped slaves preferred to plunder Italy, rather than escape over the Alps.Plutarch ''Crassus''9:5–6
.
Legacy and recognition
Toussaint Louverture, a leader of the slave revolt that led to the independence ofHaiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, has been called the "Black Spartacus".
Adam Weishaupt, founder of the Bavarian Illuminati, often referred to himself as Spartacus within written correspondences.
In communism
 In modern times, Spartacus became an icon for communists and socialists. Karl Marx listed Spartacus as one of his heroes and described him as "the most splendid fellow in the whole of ancient history" and a "great general, noble character, real representative of the ancient
In modern times, Spartacus became an icon for communists and socialists. Karl Marx listed Spartacus as one of his heroes and described him as "the most splendid fellow in the whole of ancient history" and a "great general, noble character, real representative of the ancient proletariat
The proletariat (; ) is the social class of wage-earners, those members of a society whose only possession of significant economic value is their labour power (their capacity to work). A member of such a class is a proletarian. Marxist philo ...
". Spartacus has been a great inspiration to left-wing revolutionaries, most notably the German Spartacus League
The Spartacus League (German: ''Spartakusbund'') was a Marxism, Marxist revolutionary movement organized in Germany during World War I. It was founded in August 1914 as the "International Group" by Rosa Luxemburg, Karl Liebknecht, Clara Zetkin, ...
(1915–18), a forerunner of the Communist Party of Germany
The Communist Party of Germany (german: Kommunistische Partei Deutschlands, , KPD ) was a major political party in the Weimar Republic between 1918 and 1933, an underground resistance movement in Nazi Germany, and a minor party in West German ...
. A January 1919 uprising by communists in Germany was called the Spartacist uprising. Spartacus Books, one of the longest running collectively-run leftist book stores in North America, is also named in his honour. The village of Spartak Spartak may refer to:
In sports
*Spartak (sports society), an international fitness and sports society that unites some countries of the former Soviet Union
In Russia
*FC Spartak Moscow, a football club
*FC Spartak Kostroma, a football club
*PFC ...
, in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine, is also named after Spartacus.
In sports
Several sports clubs around the world, in particular the former Soviet and the Communist bloc, were named after the Roman gladiator.In Russia
* FC Spartak Moscow, a football club * FC Spartak Kostroma, a football club * PFC Spartak Nalchik, a football club * FC Spartak Vladikavkaz, a football club * HC Spartak Moscow, an ice hockey team * Spartak Saint Petersburg, a basketball team * Spartak Tennis Club, a tennis training facility *WBC Spartak Moscow
WBC Spartak Noginsk is a Russian women's basketball club from Noginsk, Moscow Oblast founded in 1949. During the Soviet era it was the women's basketball section of Spartak Moscow. The team enjoyed its golden era between 1977 and 1982, winning t ...
, a women's basketball team
In Ukraine
*FC Spartak Sumy
FC Spartak Sumy was a Ukrainian football club based in Sumy.
History
Yavir was established on January 12, 1982 at the village forestry Krasnopillya. In Ukrainian Yavir ( uk, Явір) means Sycamore ('' Acer pseudoplatanus''). The team started ...
, a football club
* Spartak Ivano-Frankivsk, a football team
* Zakarpattia Uzhhorod
Football Club Hoverla Uzhhorod ( ) was a Ukrainian professional football club based in Uzhhorod. Following the end of the 2015–16 season it was expelled from the Ukrainian Premier League because of debts to (current and former) players.
, a football club, formerly known as Spartak Uzhhorod
* Spartak Lviv
* Spartak Kyiv
* Spartak Odesa, a football team competed in the 1941
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January–August – 10,072 men, women and children with mental and physical disabilities are asphyxiated with carbon monoxide in a gas chamber, at Hadamar Eu ...
Soviet war league
* Spartak Kharkiv, a football team competed in the 1941
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January–August – 10,072 men, women and children with mental and physical disabilities are asphyxiated with carbon monoxide in a gas chamber, at Hadamar Eu ...
Soviet war league
In Bulgaria
* FC Spartak Varna, a football team *OFC Spartak Pleven
OFK Spartak ( bg, ОФК Спартак) is a Bulgarian municipal association football club from the city of Pleven founded on 10 September 1919. It currently competes in the Second League, the second tier of Bulgarian football. The team's great ...
, a football team
* PFC Spartak Plovdiv
PFC Spartak Plovdiv ( bg, ПФК Спартак Пловдив) is a Bulgarian football club based in Plovdiv, which currently plays in the third tier of Bulgarian football, the Third League. The club was established in 1947 and folded its seni ...
, a football team
* Spartak Sofia
FC Spartak Sofia ( bg, ФК Спартак София) was a Bulgarian football club based in Sofia, Bulgaria. The club was officially founded in 1947. The team plays in the Bulgarian Regional Division. The club's home colours are blue and white ...
, a defunct football team
In Serbia
*FK Spartak Subotica
Fudbalski klub Spartak Ždrepčeva Krv () is a professional football club from Subotica, Serbia, that plays in the Serbian SuperLiga.
The club was founded in 1945 and was named after Jovan Mikić Spartak, the leader of the Partisans in Subotic ...
, a football team
* FK Radnički, several teams
In Slovakia
*FC Spartak Trnava
FC Spartak Trnava () is a Slovak professional Association football, football club based in Trnava. Historically, it is one of the most successful clubs in the country, having won the Czechoslovak First League five times and the Czechoslovak Cup ...
, a football team
* TJ Spartak Myjava
Spartak Myjava () is a Slovak football team, based in the town of Myjava. The club was founded in 1920.
History
Spartak Myjava was founded on 8 August 1920 as Športový klub Myjava (ŠK Myjava). ŠK Myjava founder and first president of the l ...
, a football team
* FK Spartak Vráble FK or fk may refer to:
In arts and entertainment:
* Flyer Killer, fictional automated robots in the ''Terminator'' film franchise.
* Fox Kids, a former American children's television programming block.
* Funky Kong, a video game character.
Place: ...
, a football team
* FK Spartak Bánovce nad Bebravou
FK Spartak Bánovce nad Bebravou is a Slovak football team, based in the town of Bánovce nad Bebravou. The club was founded in 1931.
References
External links Official website Spartak Stadium (disambiguation) Spartak Stadium may refer to the following stadia:
* In Belarus:
**Spartak Stadium (Babruysk)
** Spartak Stadium (Mahilyow)
* In Bulgaria:
** Spartak Stadium (Varna)
* In Kazakhstan:
** Spartak Stadium (Taldykorgan)
* In Kyrgyzstan:
** Spartak Sta ...
* Barnt Green Spartak F.C.
Birmingham United Football Club is a football club originally representing the village of Barnt Green, near Bromsgrove, in Worcestershire, England. Members of the , the club are currently based in nearby Redditch and play at the Valley Stadium.
...
, an English football team
* Spartak (Cape Verde)
Associação Spartak D'Aguadinha is a sports club whose football team had played in the Premier division and plays in the Fogo Island League in Cape Verde. It is based in São Filipe's subdivision of Aguadinha located next to Bila Baxo (the ci ...
, a Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
an football team
* FC Spartak Semey
FC Spartak Semey ( kk, Spartak Fýtbol Klýby) is a Kazakh football club based in Semey. A leading club in the early years of the Kazakhstan Premier League, and under the name ''Yelimay Semipalatinsk'' (or simply "Yelimay") they were three-time ...
, a Kazakh football team
Spartacus's name was also used in athletics in the Soviet Union and communist states of Central and Eastern Europe. The Spartakiad was a Soviet bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
version of the Olympic games. Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd edition, volume 24 (part 1), p. 286, Moscow, Sovetskaya Entsiklopediya publisher, 1976. This name was also used for the mass gymnastics exhibition held every five years in Czechoslovakia. The mascot for the Ottawa Senators, Spartacat
This is a list of current and former National Hockey League (NHL) mascots, sorted alphabetically. The New York Rangers are the only team to have never had a mascot.
Current mascots Al the Octopus
Al the Octopus is the octopus mascot of the Detro ...
, is also named after him.
In popular culture

Film
* The film '' Spartacus'' (1960), which was executive-produced by and starredKirk Douglas
Kirk Douglas (born Issur Danielovitch; December 9, 1916 – February 5, 2020) was an American actor and filmmaker. After an impoverished childhood, he made his film debut in ''The Strange Love of Martha Ivers'' (1946) with Barbara Stanwyck. Do ...
, was based on Howard Fast's novel '' Spartacus'' and directed by Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick (; July 26, 1928 – March 7, 1999) was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and photographer. Widely considered one of the greatest filmmakers of all time, his films, almost all of which are adaptations of nove ...
. The phrase "I'm Spartacus!" from this film has been referenced in a number of other films, television programs, and commercials.
Television
* Fast's novel was adapted as a 2004 miniseries by the USA Network, with Goran Višnjić in the main role. * One episode of 2007–2008 BBC's docudrama '' Heroes and Villains'' features Spartacus. * The television series '' Spartacus'', starringAndy Whitfield
Andrew Whitfield (17 October 1971 – 11 September 2011) was a Welsh actor. He was best known for his leading role in the Starz television series '' Spartacus: Blood and Sand''.
Early life and career
Whitfield and his family came to live in B ...
and later Liam McIntyre in the title role, aired on the Starz
Starz (stylized as STARZ since 2016; pronounced "stars") is an American premium cable and satellite television network owned by Lions Gate Entertainment, and is the flagship property of parent subsidiary Starz Inc. Programming on Starz consist ...
premium cable network from January 2010 to April 2013.
* The History Channel's ''Barbarians Rising
''Barbarians Rising'' is an American docudrama television series executive produced by Adam Bullmore and produced by Chloe Leland and Michael Waterhouse that airs on History Channel. It premiered on June 6, 2016.
Synopsis
The series is told fro ...
'' (2016) features the story of Spartacus in its second episode entitled "Rebellion".
* The fifth series of sitcom '' Outnumbered'' had Ben Brockmans (Daniel Roche
Daniel Peter Roche ( ; born 14 October 1999) is an English actor, known for playing Ben Brockman in the BBC One sitcom '' Outnumbered''.
Life
Roche was born on 14 October 1999 to an English mother and an Irish father. He grew up in north London ...
) play Spartacus in a musical called ''Spartacus''.
* Spartacus appears in the season 6
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and po ...
premiere of ''DC's Legends of Tomorrow
''DC's Legends of Tomorrow'', or simply ''Legends of Tomorrow'', is an American time travel superhero television series developed by Greg Berlanti, Marc Guggenheim, Andrew Kreisberg, and Phil Klemmer, who are also executive producers alon ...
'', portrayed by Shawn Roberts. He is abducted and eaten by an alien.
Literature
* Howard Fast wrote the historical novel '' Spartacus'', the basis of the 1960 film of the same name. * Arthur Koestler wrote a novel about Spartacus called '' The Gladiators''. * The Scottish writerLewis Grassic Gibbon
Lewis Grassic Gibbon was the pseudonym of James Leslie Mitchell (13 February 1901 – 7 February 1935), a Scottish writer. He was best known for ''A Scots Quair'', a trilogy set in the north-east of Scotland in the early 20th century, of which ...
wrote a novel '' Spartacus''.
* The Italian writer Raffaello Giovagnoli
Raffaello Giovagnoli (Rome, 13 May 1838 – Rome, 15 July 1915) was an Italian writer, patriot and politician.
Biography Early life and career
Raffaello's mother, Clotilde Staderini, died from childbirth when Raffaello was only eleven. Becaus ...
wrote his historical novel, ''Spartacus'', in 1874. His novel has been subsequently translated and published in many European countries.
* The German writer Bertolt Brecht
Eugen Berthold Friedrich Brecht (10 February 1898 – 14 August 1956), known professionally as Bertolt Brecht, was a German theatre practitioner, playwright, and poet. Coming of age during the Weimar Republic, he had his first successes as a pl ...
wrote ''Spartacus'', his second play, before 1920. It was later renamed ''Drums in the Night
''Drums in the Night'' (''Trommeln in der Nacht'') is a play by the German playwright Bertolt Brecht. Brecht wrote it between 1919 and 1920, and it received its first theatrical production in 1922. It is in the Expressionist style of Ernst Toll ...
''.
* The Latvian writer Andrejs Upīts in 1943 wrote the play ''Spartacus''.
* The Polish writer in 1951 wrote a novel ''Uczniowie Spartakusa'' (''Spartacus's disciples'').
* The Reverend Elijah Kellogg
Elijah Kellogg, Jr. (May 20, 1813 – March 17, 1901) was an American Congregationalist minister, lecturer and author of popular boy's adventure books.
Professional life
Born in Portland, Maine, Kellogg was the son of a minister and mi ...
's ''Spartacus to the Gladiators at Capua "Spartacus to the Gladiators at Capua" is a rhetorical monologue written by Elijah Kellogg for a student competition at Bowdoin College in 1842, and later published by Epes Sargent, one of the judges, in his 1846 ''School Reader''. The piece, writt ...
'' has been used effectively by school pupils to practice their oratory skills for ages.
* Amal Donkol
Amal Abul-Qassem Donqol ( arz, أمل ابو القاسم دنقل, ; 1940 – 21 May 1983) was an Egyptian poet whose poems were influenced by Greek mythology, then pre-Islamic and Islamic imagery to modernize Arabic poetry. He was born in Al Qal ...
, the Egyptian modern poet wrote "The Last Words of Spartacus".
* Max Gallo wrote the novel ''Les Romains.Spartacus. La Revolte des Esclaves'', Librairie Artheme Fayard, 2006.
* In the '' Fate/Apocrypha'' light novel series by Yūichirō Higashide, Spartacus appears as a Berserker-class Servant summoned by the Red faction. In the anime adaptation of the novels, Spartacus is voiced by Satoshi Tsuruoka in Japanese and Josh Tomar in English. This version of Spartacus would also appear in the mobile RPG Fate/Grand Order.
*Ben Kane
Ben Kane (born 6 March 1970) is a novelist, specialising in historical fiction. He is best known for The Forgotten Legion, Spartacus and Hannibal book series. Six of his eight novels have been Sunday Times bestsellers, and his books have been ...
wrote the novels ''Spartacus: The Gladiator'' and ''Spartacus: Rebellion'', in 2012.
Music
* The "Spartacus Overture" was written by composerCamille Saint-Saëns
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (; 9 October 183516 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic music, Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Piano C ...
in 1863.
* "Love Theme From '' Spartacus''" was a hit for composer Alex North and has become a jazz standard
Jazz standards are musical compositions that are an important part of the musical repertoire of jazz musicians, in that they are widely known, performed, and recorded by jazz musicians, and widely known by listeners. There is no definitive lis ...
.
* '' Spartacus'' (1954, first staged in 1956) is a ballet, with a score by Soviet Armenian composer Aram Khachaturian.
* In 1975, Triumvirat reached the apex of their commercial success with the release of '' Spartacus'', a classic "prog rock" album.
* Australian composer Carl Vine wrote a short piano piece entitled "Spartacus", from ''Red Blues''.
* Phantom Regiment's show, "Spartacus", was the championship show of the 2008 Drum Corps International
Drum Corps International (DCI) is a governing body for junior drum and bugle corps responsible for developing and enforcing rules of competition, and for providing standardized adjudication at sanctioned drum and bugle corps competitions througho ...
season.
* Jeff Wayne
Jeffry Wayne (born 1 July 1943) is an American-British composer, musician and lyricist. In 1978, he released ''Jeff Wayne's Musical Version of The War of the Worlds'', his musical adaptation of H. G. Wells' science-fiction novel ''The War of ...
released his musical retelling, ''Jeff Wayne's Musical Version of Spartacus
''Jeff Wayne's Musical Version of Spartacus'' is a 1992 concept album produced and composed by Jeff Wayne with Lyrics by Gary Osborne, telling the story of Roman gladiator, Spartacus.
It starred Anthony Hopkins, Catherine Zeta-Jones (in her first ...
,'' in 1992.
Video games
* In '' Age of Empires: The Rise of Rome'' Expansion IV Enemies of Rome, 3: Spartacus the campaign has the player fighting against Spartacus's army. * In '' Spartacus Legends'', Spartacus appears as an endgame boss.Board games
* In the expandable miniature wargaming systemHeroscape
''Heroscape'' (stylized as "heroScape" or "HeroScape") is an expandable turn-based miniature wargaming system originally manufactured by Hasbro subsidiaries from 2004 until its discontinuation in November 2010. Geared towards younger players, th ...
, Spartacus appears as a unique gladiator hero, having been rescued by the Archkyrie Einar before his death.
Places
* Spartacus Peak on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands.See also
*Alaric I
Alaric I (; got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; c. 370 – 410 AD) was the first king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades ...
* Ambiorix
* Ardaric
* Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of ge ...
* Autaritus
Autaritus (died 238 BCE) was a leader of Gallic mercenaries in the Carthaginian army during the First Punic War.
With his men Autaritus fought in 262 BCE at the Battle of Agrigentum and remained loyal to Carthage when his countrymen defected ''en ...
* Bato
* Battle of Baduhenna Wood
The Battle of Baduhenna Wood was a battle, possibly fought (but not proven) near Heiloo, Netherlands, in 28 AD between the Frisii and a Roman army led by the Roman general Lucius Apronius.
The earliest mention of the Frisii tells of Drusus' 12 B ...
* Boudica
Boudica or Boudicca (, known in Latin chronicles as Boadicea or Boudicea, and in Welsh as ()), was a queen of the ancient British Iceni tribe, who led a failed uprising against the conquering forces of the Roman Empire in AD 60 or 61. She ...
* Fritigern
* Gaius Julius Civilis
* John of Gothia
* List of people who disappeared
Lists of people who disappeared include those whose current whereabouts are unknown, or whose deaths are unsubstantiated. Many people who disappear are eventually declared dead ''in absentia''. Some of these people were possibly subjected to enfo ...
* Totila
* Vercingetorix
* Viriathus
References
Bibliography
Classical authors
* Appian. ''Civil Wars''. Translated by J. Carter. (Harmondsworth: Penguin Books, 1996) * Florus. ''Epitome of Roman History''. (London: W. Heinemann, 1947) *Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), t ...
. ''The Seven Books of History Against the Pagans''. Translated by Roy J. Deferrari. (Washington, DC: Catholic University of America Press, 1964).
* Plutarch. ''Fall of the Roman Republic''. Translated by R. Warner. (London: Penguin Books, 1972), with special emphasis placed on "The Life of Crassus" and "The Life of Pompey".
* Sallust. ''Conspiracy of Catiline and the War of Jugurtha''. (London: Constable, 1924)
Modern historiography
* Bradley, Keith R. ''Slavery and Rebellion in the Roman World, 140 B.C.–70 B.C.'' Bloomington; Indianapolis: Indiana University Press, 1989 (hardcover, ); 1998 (paperback, ). hapter VThe Slave War of Spartacus, pp. 83–101. * Rubinsohn, Wolfgang Zeev.Spartacus' Uprising and Soviet Historical Writing
'. Oxford: Oxbow Books, 1987 (paperback, ). * ''Spartacus: Film and History'', edited by Martin M. Winkler. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 2007 (hardcover, ; paperback, ). * Trow, M.J. ''Spartacus: The Myth and the Man''. Stroud, United Kingdom: Sutton Publishing, 2006 (hardcover, ). * Genner, Michael. "Spartakus. Eine Gegengeschichte des Altertums nach den Legenden der Zigeuner". Two volumes. Paperback.
Trikont Verlag
The leftist publishing house Trikont was founded in 1967 in Munich by Gisela Erler and others. The record label has its origins in the protest and alternative movements of the 1970s and derived its name from geographical concept 'Trikont', which re ...
, München 1979/1980. Vol 1 Vol 2
* Plamen Pavlov, Stanimir Dimitrov,''Spartak – sinyt na drenva Trakija''/''Spartacus – the Son of ancient Thrace''. Sofia, 2009,
*
*Beard, Mary. ''SPQR A History of Ancient Rome.'' New York: Liveright Publishing Corporation, 2015,
External links
BBC Radio 4 – ''In Our Time'' – Spartacus
Article and full text of the Roman and Greek sources.
''Spartacus'', movie starring Kirk Douglas and Sir Peter Ustinov
''Spartacus'', television mini-series starring Goran Višnjić and Alan Bates
Starz Mini-Series airing in 2010
{{DEFAULTSORT:Spartacus 100s BC births 71 BC deaths Year of birth uncertain 1st-century BC Romans Ancient Thracians killed in battle Deaths by blade weapons Rebel slaves in ancient Rome Roman-era Thracians Roman gladiators Third Servile War Thracian people Republican era slaves and freedmen