Spacecraft which reentered in 1989 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of
 A German
A German
"Shooting the duck"
''
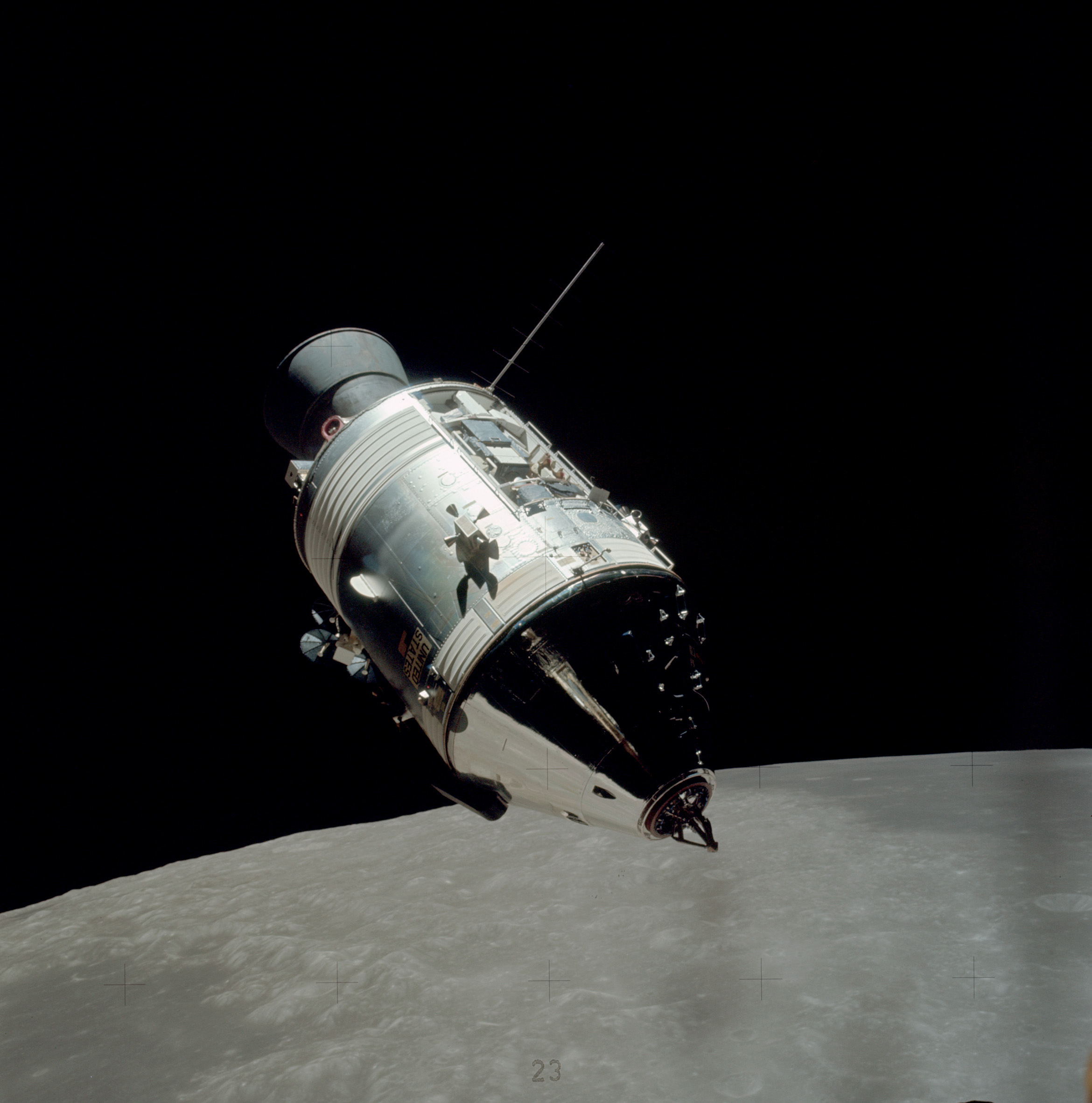 As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was Vostok 1, which carried Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961, and completed a full Earth orbit. There were five other crewed missions which used a Vostok spacecraft. The second crewed spacecraft was named ''Freedom 7'', and it performed a sub-orbital spaceflight in 1961 carrying American astronaut Alan Shepard to an altitude of just over . There were five other crewed missions using
As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was Vostok 1, which carried Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961, and completed a full Earth orbit. There were five other crewed missions which used a Vostok spacecraft. The second crewed spacecraft was named ''Freedom 7'', and it performed a sub-orbital spaceflight in 1961 carrying American astronaut Alan Shepard to an altitude of just over . There were five other crewed missions using
 A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
, Earth observation, meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not ...
, navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
, space colonization
Space colonization (also called space settlement or extraterrestrial colonization) is the use of outer space or celestial bodies other than Earth for permanent habitation or as extraterrestrial territory.
The inhabitation and territori ...
, planetary exploration
This is a timeline of Solar System exploration ordered by date of spacecraft launch. It includes:
*All spacecraft that have left Earth orbit for the purposes of Solar System exploration (or were launched with that intention but failed), includi ...
, and transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
of humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
and cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit
A single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) vehicle reaches orbit from the surface of a body using only propellants and fluids and without expending tanks, engines, or other major hardware. The term usually, but not exclusively, refers to reusable vehicles ...
vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch contro ...
(carrier rocket).
On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth ...
. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
or around other celestial bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station i ...
s) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft
A robotic spacecraft is an uncrewed spacecraft, usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather t ...
used to support scientific research are space probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or ent ...
s. Robotic spacecraft that remain in orbit around a planetary body are artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope ...
s. To date, only a handful of interstellar probes, such as ''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' and '' 11'', ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' and '' 2'', and ''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'', are on trajectories that leave the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
.
Orbital spacecraft may be recoverable or not. Most are not. Recoverable spacecraft may be subdivided by a method of reentry to Earth into non-winged space capsule
A space capsule is an often-crewed spacecraft that uses a blunt-body reentry capsule to reenter the Earth's atmosphere without wings. Capsules are distinguished from other satellites primarily by the ability to survive reentry and return a payl ...
s and winged spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes ten ...
s. Recoverable spacecraft may be reusable (can be launched again or several times, like the SpaceX Dragon and the Space Shuttle orbiters) or expendable (like the Soyuz). In recent years, more space agencies are tending towards reusable spacecraft.
Humanity has achieved space flight, but only a few nations have the technology for orbital launches: Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
( RSA or "Roscosmos"), the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
(NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
), the member states of the European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA), Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
(JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orb ...
), China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
( CNSA), India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
(ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman ...
), Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
National Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology, Taiwan National Space Organization (NSPO), Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
(ISA
Isa or ISA may refer to:
Places
* Isa, Amur Oblast, Russia
* Isa, Kagoshima, Japan
* Isa, Nigeria
* Isa District, Kagoshima, former district in Japan
* Isa Town, middle class town located in Bahrain
* Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia
* Mount Is ...
), Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(ISA
Isa or ISA may refer to:
Places
* Isa, Amur Oblast, Russia
* Isa, Kagoshima, Japan
* Isa, Nigeria
* Isa District, Kagoshima, former district in Japan
* Isa Town, middle class town located in Bahrain
* Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia
* Mount Is ...
), and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
(NADA
Nada may refer to:
Culture
* Nāda, a concept in ancient Indian metaphysics
Places
*Nada, Hainan, China
*Nada, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in the United States
*Nada, Nepal, village in Achham District, Seti Zone
* Nada, Texas, United S ...
). In addition, several private companies have developed or are developing the technology for orbital launches independently from government agencies. The most prominent examples of such companies are SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
and Blue Origin
Blue Origin, LLC is an American private spaceflight, privately funded aerospace manufacturer and sub-orbital spaceflight services company headquartered in Kent, Washington. Founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, the founder and executive chairman of Am ...
.
History
 A German
A German V-2
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed ...
became the first spacecraft when it reached an altitude of 189 km in June 1944 in Peenemünde, Germany. Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for t ...
was the first artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
(LEO) by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
on 4 October 1957. The launch ushered in new political, military, technological, and scientific developments; while the Sputnik launch was a single event, it marked the start of the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the Sputnik_1#Launch_and_mission, launch of Sputnik 1 ...
.Dougall, Walter A. (Winter 2010"Shooting the duck"
''
American Heritage American Heritage may refer to:
* ''American Heritage'' (magazine)
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language''
* American Heritage Rivers
* American Heritage School (disambiguation)
See also
*National Register of Historic Place ...
'' Apart from its value as a technological first, Sputnik 1 also helped to identify the upper atmospheric layer
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for ...
's density, through measuring the satellite's orbital changes. It also provided data on radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
-signal distribution in the ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an ...
. Pressurized nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
in the satellite's false body provided the first opportunity for meteoroid detection. Sputnik 1 was launched during the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific ...
from Site No.1/5, at the 5th Tyuratam range, in Kazakh SSR (now at the Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome ( kk, Байқоңыр ғарыш айлағы, translit=Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy, ; russian: Космодром Байконур, translit=Kosmodrom Baykonur, ) is a spaceport in an area of southern Kazakhstan leased to R ...
). The satellite traveled at , taking 96.2 minutes to complete an orbit, and emitted radio signals at 20.005 and 40.002 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one he ...
While Sputnik 1 was the first spacecraft to orbit the Earth, other man-made objects had previously reached an altitude of 100 km, which is the height required by the international organization Fédération Aéronautique Internationale
The (; FAI; en, World Air Sports Federation) is the world governing body for air sports, and also stewards definitions regarding human spaceflight. It was founded on 14 October 1905, and is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland. It maintai ...
to count as a spaceflight. This altitude is called the Kármán line
The Kármán line (or von Kármán line ) is an attempt to define a boundary between Earth's atmosphere and outer space, and offers a specific definition set by the Fédération aéronautique internationale (FAI), an international record-keeping ...
. In particular, in the 1940s there were several test launches of the V-2 rocket
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed ...
, some of which reached altitudes well over 100 km.
Spacecraft types
Crewed spacecraft
 As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was Vostok 1, which carried Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961, and completed a full Earth orbit. There were five other crewed missions which used a Vostok spacecraft. The second crewed spacecraft was named ''Freedom 7'', and it performed a sub-orbital spaceflight in 1961 carrying American astronaut Alan Shepard to an altitude of just over . There were five other crewed missions using
As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was Vostok 1, which carried Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin into space in 1961, and completed a full Earth orbit. There were five other crewed missions which used a Vostok spacecraft. The second crewed spacecraft was named ''Freedom 7'', and it performed a sub-orbital spaceflight in 1961 carrying American astronaut Alan Shepard to an altitude of just over . There were five other crewed missions using Mercury spacecraft
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbital spaceflight, orbit and return him safely, ideally ...
.
Other Soviet crewed spacecraft include the Voskhod, Soyuz, flown uncrewed as Zond/L1, L3, TKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the British C ...
, and the Salyut and '' Mir'' crewed space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station i ...
s. Other American crewed spacecraft include the Gemini spacecraft
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual ...
, the Apollo spacecraft including the Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
, the Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations in ...
space station, the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
with undetached European Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, ...
and private US Spacehab space stations-modules, and the SpaceX Crew Dragon configuration of their Dragon 2. US company Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
also developed and flown a spacecraft of their own, the CST-100
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner
is a class of two partially , commonly referred to as Starliner, but a crewed flight is yet to occur. China developed, but did not fly Shuguang, and is currently using Shenzhou (its first crewed mission was in 2003). Except for the Space Shuttle, all of the recoverable crewed orbital spacecraft were
File:NASA spacecraft comparison.jpg, alt=Drawings of Mercury, Gemini capsules and Apollo spacecraft, with their launch vehicles, American Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft
File:Vostok Spacecraft Diagram.svg, Soviet Vostok capsule
File:Voskhod 1 and 2.svg, alt=Line drawing of Voskhod capsules, Soviet Voskhod (variant of Vostok)
File:Soyuz 7K-OK(A) drawing.svg, alt=Soyuz 7K-OK(A) drawing, 1967 Soviet/Russian Soyuz spacecraft
File:Post S-7 Shenzhou spacecraft.png, alt=Drawing of Shenzhou spacecraft, Chinese Shenzhou spacecraft
The
 Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as,
Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as,



 *''
*''
is a class of two partially , commonly referred to as Starliner, but a crewed flight is yet to occur. China developed, but did not fly Shuguang, and is currently using Shenzhou (its first crewed mission was in 2003). Except for the Space Shuttle, all of the recoverable crewed orbital spacecraft were
space capsule
A space capsule is an often-crewed spacecraft that uses a blunt-body reentry capsule to reenter the Earth's atmosphere without wings. Capsules are distinguished from other satellites primarily by the ability to survive reentry and return a payl ...
s.
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ...
, crewed since November 2000, is a joint venture between Russia, the United States, Canada and several other countries.
Spaceplanes
 Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as,
Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as, airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spe ...
s. The first example of such was the North American X-15
The North American X-15 is a hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft. It was operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as part of the X-plane series of experimental aircraft. The X-15 set speed an ...
spaceplane, which conducted two crewed flights which reached an altitude of over 100 km in the 1960s. This first reusable spacecraft was air-launched on a suborbital trajectory on July 19, 1963.
The first partially reusable orbital spacecraft, a winged non-capsule, the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
, was launched by the USA on the 20th anniversary of Yuri Gagarin's flight, on April 12, 1981. During the Shuttle era, six orbiters were built, all of which have flown in the atmosphere and five of which have flown in space. ''Enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterprise ...
'' was used only for approach and landing tests, launching from the back of a Boeing 747 SCA and gliding to deadstick landings at Edwards AFB, California
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is Edw ...
. The first Space Shuttle to fly into space was '' Columbia'', followed by ''Challenger
Challenger, Challengers, or The Challengers may refer to:
Entertainment
Comics and manga
* Challenger (character), comic book character
* ''Challengers'' (manga), manga by Hinako Takanaga
Film and TV
* ''The Challengers'' (TV series), a 1979 ...
'', ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discovery ...
'', '' Atlantis'', and ''Endeavour
Endeavour or endeavor may refer to:
People
Fictional characters
* Endeavour Morse, central character of the ''Inspector Morse'' novels by Colin Dexter
* Endeavor, the hero name for the character Enji Todoroki from the anime series ''My Hero A ...
''. ''Endeavour'' was built to replace ''Challenger'' when it was lost
Lost may refer to getting lost, or to:
Geography
*Lost, Aberdeenshire, a hamlet in Scotland
* Lake Okeechobee Scenic Trail, or LOST, a hiking and cycling trail in Florida, US
History
*Abbreviation of lost work, any work which is known to have bee ...
in January 1986. ''Columbia'' broke up
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the termination of a relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping omeone in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a married couple, where a bre ...
during reentry in February 2003.
The first automatic partially reusable spacecraft was the ''Buran''-class shuttle, launched by the USSR on November 15, 1988, although it made only one flight and this was uncrewed. This spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes ten ...
was designed for a crew and strongly resembled the U.S. Space Shuttle, although its drop-off boosters used liquid propellants and its main engines were located at the base of what would be the external tank in the American Shuttle. Lack of funding, complicated by the dissolution of the USSR, prevented any further flights of Buran. The Space Shuttle was subsequently modified to allow for autonomous re-entry in case of necessity.
Per the Vision for Space Exploration, the Space Shuttle was retired in 2011 mainly due to its old age and high cost of program reaching over a billion dollars per flight. The Shuttle's human transport role is to be replaced by SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
's SpaceX Dragon 2 and Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
's CST-100 Starliner. Dragon 2's first crewed flight occurred on May 30, 2020. The Shuttle's heavy cargo transport role is to be replaced by expendable rockets such as the Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle developed by NASA. As of 2022, SLS has the highest payload capacity of any rocket in operational service, as well as the greatest liftoff thrust of any r ...
and ULA's Vulcan
Vulcan may refer to:
Mythology
* Vulcan (mythology), the god of fire, volcanoes, metalworking, and the forge in Roman mythology
Arts, entertainment and media Film and television
* Vulcan (''Star Trek''), name of a fictional race and their home p ...
rocket, as well as the commercial launch vehicles.
Scaled Composites' SpaceShipOne
SpaceShipOne is an experimental air-launched rocket-powered aircraft with sub-orbital spaceflight capability at speeds of up to 3,000 ft/s (900 m/s, 3240 km/h), using a hybrid rocket motor. The design features a unique "feathering" a ...
was a reusable suborbital spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes ten ...
that carried pilots Mike Melvill and Brian Binnie on consecutive flights in 2004 to win the Ansari X Prize. The Spaceship Company
The Spaceship Company (TSC) is a British/American spacecraft manufacturing company that was founded by Burt Rutan and Richard Branson in mid-2005 and was jointly owned by Virgin Group (70%) and Scaled Composites (30%) until 2012 when Virgin Gal ...
will build its successor SpaceShipTwo
The Scaled Composites Model 339 SpaceShipTwo (SS2) is an air-launched suborbital spaceplane type designed for space tourism. It is manufactured by The Spaceship Company, a California-based company owned by Virgin Galactic.
SpaceShipTwo is car ...
. A fleet of SpaceShipTwos operated by Virgin Galactic
Virgin Galactic is an American spaceflight company founded by Richard Branson and his British Virgin Group retains an 11.9% stake through Virgin Investments Limited. It is headquartered in California, and operates from New Mexico. The company i ...
was planned to begin reusable private spaceflight carrying paying passengers in 2014, but was delayed after the crash of VSS ''Enterprise''.
Uncrewed spacecraft


Semi-crewed – crewed as space stations or part of space stations
* Progress – uncrewed USSR/Russia cargo spacecraft *TKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the British C ...
– uncrewed USSR/Russia cargo spacecraft and space station module
* Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) – uncrewed European cargo spacecraft
* H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV) – uncrewed Japanese cargo spacecraft
* SpaceX Dragon – uncrewed private spacecraft
* '' Tianzhou'' – China's uncrewed cargo spacecraft
* Northrop Grumman Cygnus – uncrewed commercial spacecraft
Earth-orbit satellites
*Explorer 1
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites the previous year; the Soviet Union's ...
– first US satellite
* Project SCORE – first communications satellite
* Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) - orbits the Sun near L1
* Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for t ...
– world's first artificial satellite
* Sputnik 2 – first animal in orbit ( Laika)
* Korabl-Sputnik 2 – first capsule recovered from orbit (Vostok Vostok refers to east in Russian but may also refer to:
Spaceflight
* Vostok programme, Soviet human spaceflight project
* Vostok (spacecraft), a type of spacecraft built by the Soviet Union
* Vostok (rocket family), family of rockets derived from ...
precursor) – animals survived
* Syncom
Syncom (for "synchronous communication satellite") started as a 1961 NASA program for active geosynchronous communication satellites, all of which were developed and manufactured by the Space and Communications division of Hughes Aircraft Comp ...
– first geosynchronous communications satellite
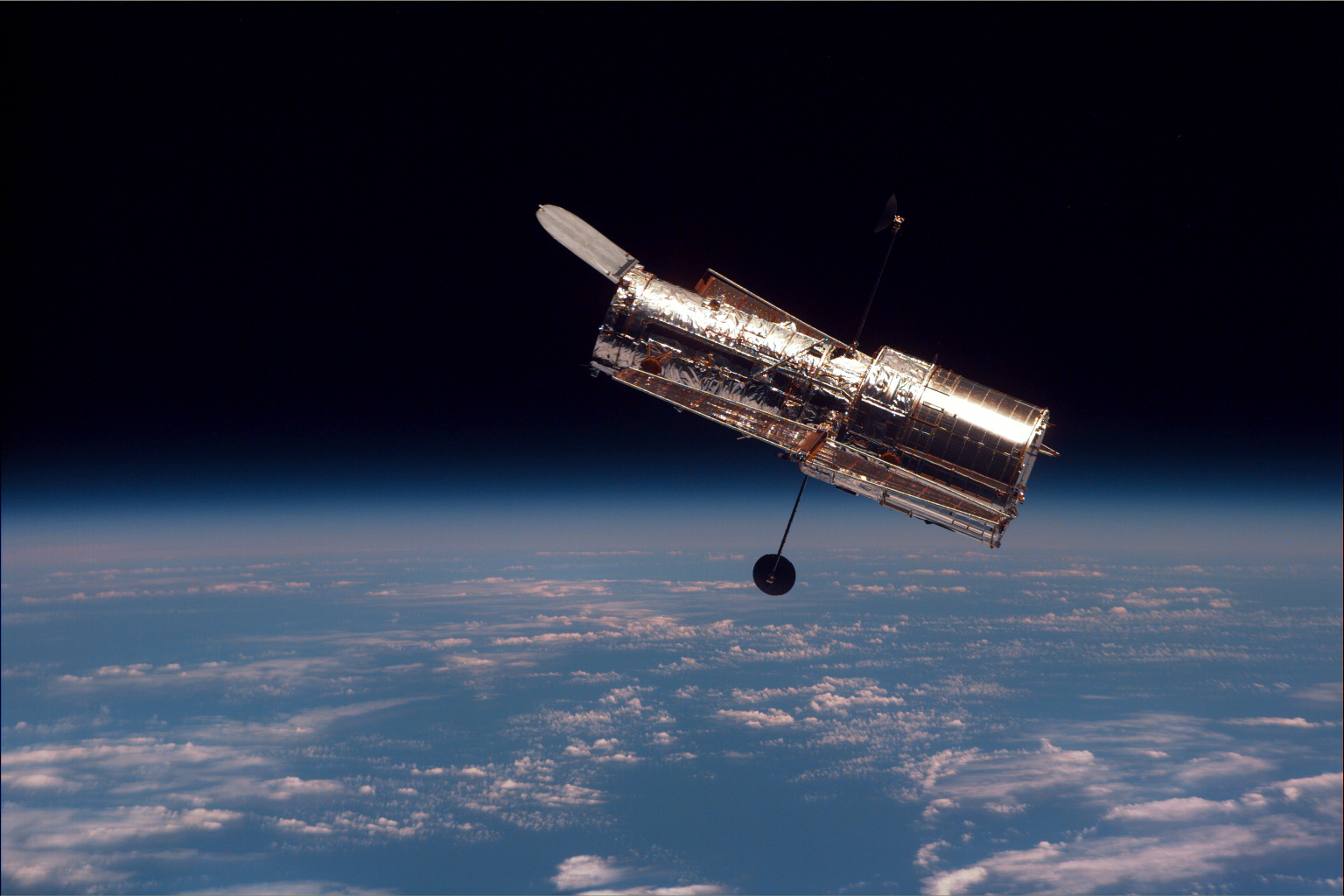
* Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
– largest orbital observatory
* X-37
The Boeing X-37, also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV), is a reusable robotic spacecraft. It is boosted into space by a launch vehicle, then re-enters Earth's atmosphere and lands as a spaceplane. The X-37 is operated by the United State ...
– spaceplane
Lunar probes
* Clementine – US Navy mission, orbited Moon, detected hydrogen at the poles * Kaguya JPN – lunar orbiter * Luna 1 – first lunar flyby *Luna 2
''Luna 2'' ( rus, Луна 2}), originally named the Second Soviet Cosmic Rocket and nicknamed Lunik 2 in contemporaneous media, was the sixth of the Soviet Union's Luna programme spacecraft launched to the Moon, E-1 No.7. It was the first spac ...
– first lunar impact
* Luna 3 – first images of lunar far side
* Luna 9 – first soft landing on the Moon
* Luna 10 – first lunar orbiter
* Luna 16 – first uncrewed lunar sample retrieval
* Lunar Orbiter
The Lunar Orbiter program was a series of five uncrewed lunar orbiter missions launched by the United States from 1966 through 1967. Intended to help select Apollo landing sites by mapping the Moon's surface, they provided the first photographs ...
– very successful series of lunar mapping spacecraft
* Lunar Prospector
''Lunar Prospector'' was the third mission selected by NASA for full development and construction as part of the Discovery Program. At a cost of $62.8 million, the 19-month mission was designed for a low polar orbit investigation of the Moon, ...
– confirmed detection of hydrogen at the lunar poles
* Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions t ...
– Identifies safe landing sites and locates Moon resources
* Lunokhod
Lunokhod ( rus, Луноход, p=lʊnɐˈxot, "Moonwalker") was a series of Soviet robotic lunar rovers designed to land on the Moon between 1969 and 1977. Lunokhod 1 was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on an extraterrestrial ...
- Soviet lunar rovers
* SMART-1 ESA – Lunar Impact
* Surveyor
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ca ...
– USA's first soft lander
* Chang'e 1 – China's first lunar mission
* Chang'e 2 – China's second lunar mission
* Chang'e 3 – China's first soft landing on the Moon
* Chang'e 4 – first soft landing on far side of the Moon
* Chang'e 5 – China's first lunar probe which completed a sample-return mission
* Chandrayaan 1
Chandrayaan-1 (, ) was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program. It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008, and operated until August 2009. The mission included a lunar orbiter and an impacto ...
– first Indian Lunar mission
* Chandrayaan 2
Chandrayaan-2 (, ; ) is the second Exploration of the Moon, lunar exploration mission developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), after Chandrayaan-1. It consists of a lunar orbiter, and also included the ''Vikram'' Lander (spa ...
– second Indian Lunar mission
Planetary probes

 *''
*''Akatsuki
may refer to:
* Akatsuki (spacecraft), an uncrewed Venus orbiter
* , any of three classes of destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy
* , any of three destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy
* ''Akatsuki'' (train), operated between Kyoto and Na ...
'' JPN – a Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
orbiter
*''Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
'' – first Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
orbiter and Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
lander
* ''Curiosity'' – Rover sent to Mars by NASA in 2012
* ''Galileo'' – first Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
orbiter and descent probe
*IKAROS
IKAROS (Interplanetary Kite-craft Accelerated by Radiation Of the Sun) is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) experimental spacecraft. The spacecraft was launched on 20 May 2010, aboard an H-IIA rocket, together with the ''Akatsuki'' (V ...
JPN – first solar-sail
Solar sails (also known as light sails and photon sails) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by sunlight on large mirrors. A number of spaceflight missions to test solar propulsion and navigation have been ...
spacecraft
* Mariner 4 – first Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
flyby, first close and high resolution images of Mars
*Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971 from LC-36B at Cape Canaveral Air ...
– first Mars orbiter
*Mariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets.
''Ma ...
– first Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
flyby, first close up images
* Mars Exploration Rovers (''Spirit
Spirit or spirits may refer to:
Liquor and other volatile liquids
* Spirits, a.k.a. liquor, distilled alcoholic drinks
* Spirit or tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol
* Volatile (especially flammable) liquids, ...
'' and '' Opportunity'')– Mars rovers
*'' Mars Express'' – Mars orbiter
*'' Mars Global Surveyor'' – Mars orbiter
*Mars Orbiter Mission
The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called ''Mangalyaan'', was a space probe orbiting Mars since 24 September 2014. It was launched on 5 November 2013 by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was India's first interplanetary missio ...
(''Mangalyaan'') - India's first Interplanetary probe
*'' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' – an advanced climate, imaging, sub-surface radar, and telecommunications Mars orbiter
*''MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoche ...
'' – first Mercury orbiter (arrival 2011)
*''Mars Pathfinder
''Mars Pathfinder'' (''MESUR Pathfinder'') is an American robotic spacecraft that landed a base station with a roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight, wheeled robot ...
'' – Mars lander, carrying the ''Sojourner
A sojourner is a person who resides temporarily in a place.
Sojourner may also refer to:
*Sojourner Truth (1797–1883), abolitionist and women's rights activist
*Albert Sojourner (1872–1951), member of the Mississippi House of Representatives
...
'' rover
*''New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' – first Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
flyby (arrival 2015)
*''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' – first Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
flyby, first close up images
*''Pioneer 11
''Pioneer 11'' (also known as ''Pioneer G'') is a robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 5, 1973, to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar winds, and cosmic rays. It was the first probe to encounter ...
'' – second Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
flyby and first Saturn flyby (first close up images of Saturn)
*Pioneer Venus
The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center.
The Pione ...
– first Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
orbiter and landers
* Vega 1 – Balloon release into Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
atmosphere and lander, mothership continued on to fly by Halley's Comet. Joint mission with Vega 2
Vega 2 (along with Vega 1) was a Soviet space probe part of the Vega program to explore Halley's comet and Venus. The spacecraft was a development of the earlier ''Venera'' craft. The name VeGa (ВеГа) combines the first two letters Russian wo ...
.
* Venera 4 – first soft landing on another planet (Venus)
*''Viking 1
''Viking 1'' was the first of two spacecraft, along with ''Viking 2'', each consisting of an orbiter and a lander, sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. The lander touched down on Mars on July 20, 1976, the first successful Mars land ...
'' – first soft landing on Mars
*''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' - flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
*''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a ...
'' – Jupiter flyby, Saturn flyby, and first flybys/images of Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
and Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather ...
* ''Hope
Hope is an optimistic state of mind that is based on an expectation of positive outcomes with respect to events and circumstances in one's life or the world at large.
As a verb, its definitions include: "expect with confidence" and "to cherish ...
'' - Mars orbiter of the United Arab Emirates in 2020
* '' Tianwen-1 '' - China's orbiter, lander and rover mission to Mars in 2020
* Perseverance - Rover sent to Mars in 2020
* Ingenuity - experimental rotorcraft sent to Mars in 2020
Other – deep space
*Cluster
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Asteroid cluster, a small asteroid family
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study t ...
* Deep Space 1
* '' Deep Impact''
* ''Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
''
* '' Hayabusa''
* Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous
''Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous – Shoemaker'' (''NEAR Shoemaker''), renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laborator ...
* Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Ro ...
* '' Stardust''
* STEREO
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration ...
– Heliospheric and solar sensing; first images of the entire Sun
* WMAP
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic mic ...
Fastest spacecraft
* Parker ''Solar Probe'' (estimated at first sun close pass, will reach at final perihelion) *Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyper ...
I and II ''Solar Probes'' ()
Furthest spacecraft from the Sun
* ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' at 156.13 AU as of April 2022, traveling outward at about
* ''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' at 122.48 AU as of December 2018, traveling outward at about
*''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a ...
'' at 122.82 AU as of January 2020, traveling outward at about
*''Pioneer 11
''Pioneer 11'' (also known as ''Pioneer G'') is a robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 5, 1973, to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar winds, and cosmic rays. It was the first probe to encounter ...
'' at 101.17 AU as of December 2018, traveling outward at about
Unfunded and canceled programs

Crewed spacecraft
* Chinese Shuguang capsule * Soviet Zond/L1 – lunar flyby capsule * Soviet L3 – capsule and lunar lander * Soviet LK – lunar lander * SovietTKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the British C ...
– space station resupply capsule
* Soviet ''Buran''-class shuttle – spaceplane
* Soviet Soyuz Kontakt
Soyuz Kontakt ''(Soyuz Contact)'' was the docking hardware of the Soviet crewed spacecraft program. The Soviet lunar human program was canceled in 1974 after many failures. Four failures of the N-1 Rocket super heavy-lift launch vehicle and th ...
capsule
* Soviet Almaz
The Almaz (russian: Алмаз, lit=Diamond) program was a highly secret Soviet military space station program, begun in the early 1960s.
Three crewed military reconnaissance stations were launched between 1973 and 1976: Salyut 2, Salyut 3 an ...
space station
* US Manned Orbiting Laboratory
The Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) was part of the United States Air Force (USAF) human spaceflight program in the 1960s. The project was developed from early USAF concepts of crewed space stations as reconnaissance satellites, and was a s ...
space station
* US Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila and the twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinised from α Aquilae and abbreviated Alpha Aql or ...
lunar lander
Multi-stage spaceplanes
* USX-20
The Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar ("Dynamic Soarer") was a United States Air Force (USAF) program to develop a spaceplane that could be used for a variety of military missions, including aerial reconnaissance, bombing, space rescue, satellite maintena ...
spaceplane
* Soviet Spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:''Buran''-class shuttle
* ESA

Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orato ...
shuttle
* Kliper
Kliper (Клипер, English: Clipper) was an early-2000s proposed partially- reusable crewed spacecraft concept by RSC Energia. Due to lack of funding from the ESA and RSA, the project was indefinitely postponed by 2006.
Designed primarily to ...
Russian semi-shuttle/semi-capsule
* Japanese HOPE-X shuttle
* Chinese Shuguang Project 921-3
Project 921-3 is a crewed spacecraft sub-system of Project 921. The term 921-3 is often used for the Chinese spaceplane program.
History
The Chinese National Manned Space Program was given the designation of Project 921 in 1992. This broad ...
shuttle
SSTO spacecraft
* RR/British Aerospace
British Aerospace plc (BAe) was a British aircraft, munitions and defence-systems manufacturer. Its head office was at Warwick House in the Farnborough Aerospace Centre in Farnborough, Hampshire. Formed in 1977, in 1999 it purchased Marconi ...
HOTOL
HOTOL, for Horizontal Take-Off and Landing, was a 1980s British design for a single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) spaceplane that was to be powered by an airbreathing jet engine. Development was being conducted by a consortium led by Rolls-Royce and B ...
* ESA Hopper
Hopper or hoppers may refer to:
Places
*Hopper, Illinois
* Hopper, West Virginia
* Hopper, a mountain and valley in the Hunza–Nagar District of Pakistan
* Hopper (crater), a crater on Mercury
People with the name
* Hopper (surname)
* Grace H ...
Orbiter
* US DC-X
The DC-X, short for Delta Clipper or Delta Clipper Experimental, was an uncrewed prototype of a reusable single-stage-to-orbit launch vehicle built by McDonnell Douglas in conjunction with the United States Department of Defense's Strategic De ...
(Delta Clipper)
* US Roton
In theoretical physics, a roton is an elementary excitation, or quasiparticle, seen in superfluid helium-4 and Bose–Einstein condensates with long-range Dipole, dipolar interactions or Spin–orbit interaction, spin-orbit coupling. The dispersi ...
Rotored-Hybrid
* US VentureStar
Spacecraft under development

Crewed
* (US-NASA; Europe-ESA) Orion – capsule * (US-SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
) Starship
A starship, starcraft, or interstellar spacecraft is a theoretical spacecraft designed for interstellar travel, traveling between planetary systems.
The term is mostly found in science fiction. Reference to a "star-ship" appears as early as 188 ...
– VTVL spacecraft
* (US-Boeing) CST-100
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner
is a class of two partially – capsule * (US-
 ; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external
; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external
NASA: Space Science Spacecraft Missions
NSSDC Master Catalog Spacecraft Query FormBasics of Spaceflight tutorial from JPL/CaltechInternational Spaceflight Museum
{{Authority control Spacecraft, Astronautics Pressure vessels
is a class of two partially – capsule * (US-
Sierra Nevada Corporation
Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) is an American, privately held aerospace and national security contractor specializing in aircraft modification and integration, space components and systems, and related technology products for cybersecurity and ...
) Dream Chaser
Dream Chaser is an American reusable lifting-body spaceplane being developed by Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) Space Systems. Originally intended as a crewed vehicle, the Dream Chaser Space System is set to be produced after the cargo varian ...
– orbital spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes ten ...
* (US-The SpaceShip company) SpaceShipTwo
The Scaled Composites Model 339 SpaceShipTwo (SS2) is an air-launched suborbital spaceplane type designed for space tourism. It is manufactured by The Spaceship Company, a California-based company owned by Virgin Galactic.
SpaceShipTwo is car ...
suborbital spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes ten ...
* (US-Blue Origin
Blue Origin, LLC is an American private spaceflight, privately funded aerospace manufacturer and sub-orbital spaceflight services company headquartered in Kent, Washington. Founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, the founder and executive chairman of Am ...
) New Shepard – VTVL capsule
* (US-XCOR) Lynx rocketplane
The XCOR Lynx was a proposed suborbital horizontal-takeoff, horizontal-landing (HTHL),
rocket-powered spaceplane that was under development by the California-based company XCOR Aerospace to compete in the emerging suborbital spaceflight marke ...
– suborbital spaceplane
* (India-DRDO) Avatar RLV -Under development, First demonstration flight in 2015.
* (India-ISRO) Gaganyaan
Gaganyaan (Sanskrit IAST: ''gagan-yāna'', ) is an Indian crewed orbital spacecraft intended to be the formative spacecraft of the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme. The spacecraft is being designed to carry three people, and a planned upgrad ...
– capsule
* (India-ISRO) RLV Technology Demonstration Programme
Reusable Launch Vehicle–Technology Demonstration Programme is a series of technology demonstration missions that has been conceived by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) as a first step towards realising a Two Stage To Orbit (TSTO) ...
– spacecraft
* (Russia-RKA) Orel – capsule
* (Europe-ESA) Smart Upper Stage for Innovative Exploration – capsule
* (Iranian Space Agency) Iranian crewed spacecraft The Iranian crewed spacecraft is a proposal by the Iranian Space Agency and Iranian Aerospace Research Institute of the Iranian Space Research Center (ISRC) to put an astronaut into space.
Iran expressed for the first time its intention to send a ...
– capsule
Uncrewed
* CNES Mars Netlander * '' Darwin14'' ESA probe * Sierra Nevada Corporation Dream Chaser – orbital cargo spaceplane *Skylon Skylon may refer to:
* Skylon (Festival of Britain), a landmark structure of the 1951 Festival of Britain
* Skylon (spacecraft), a proposed orbital spaceplane
* Skylon Tower, an observation tower in Niagara Falls, Ontario
* ''Skylon'' (album), a 20 ...
spaceplane
* ''StarChip
Breakthrough Starshot is a research and engineering project by the Breakthrough Initiatives to develop a Proof of concept, proof-of-concept fleet of light sail interstellar probes named ''Starchip'', to be capable of making the journey to the A ...
'' and '' Sprites'' - miniaturized interstellar spacecraft
* System F6—a DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Originally known as the Adv ...
Fractionated Spacecraft demonstrator
Subsystems
A spacecraft astrionics system comprises different subsystems, depending on the mission profile. Spacecraft subsystems comprise the spacecraft's bus and may include attitude determination and control (variously called ADAC, ADC, or ACS), guidance, navigation and control (GNC or GN&C), communications (comms), command and data handling (CDH or C&DH), power (EPS),thermal control
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
(TCS), propulsion, and structures. Attached to the bus are typically payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of ...
s.
; Life support
: Spacecraft intended for human spaceflight must also include a life support system
A life-support system is the combination of equipment that allows survival in an environment or situation that would not support that life in its absence. It is generally applied to systems supporting human life in situations where the outsid ...
for the crew.
 ; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external
; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
s and forces properly. The attitude control subsystem consists of sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
s and actuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) a ...
s, together with controlling algorithms. The attitude-control subsystem permits proper pointing for the science objective, sun pointing for power to the solar arrays and earth pointing for communications.
; GNC
: Guidance refers to the calculation of the commands (usually done by the CDH subsystem) needed to steer the spacecraft where it is desired to be. Navigation means determining a spacecraft's orbital elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same ...
or position. Control means adjusting the path of the spacecraft to meet mission requirements.
; Command and data handling
: The C&DH subsystem receives commands from the communications subsystem, performs validation and decoding of the commands, and distributes the commands to the appropriate spacecraft subsystems and components. The CDH also receives housekeeping data and science data from the other spacecraft subsystems and components, and packages the data for storage on a data recorder or transmission to the ground via the communications subsystem. Other functions of the CDH include maintaining the spacecraft clock and state-of-health monitoring.
; Communications
: Spacecraft, both Robotic spacecraft, robotic and Human spaceflight, crewed, utilize various communications systems for communication with terrestrial stations as well as for communication between spacecraft in space. Technologies utilized include Radio-frequency communication, RF and Free-space optical communication, optical communication. In addition, some spacecraft payloads are explicitly for the purpose of ground–ground Commsat, communication using Bent pipe, receiver/retransmitter electronic technologies.
; Power
: Spacecraft need an electrical power generation and distribution subsystem for powering the various spacecraft subsystems. For spacecraft near the Sun, Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels are frequently used to generate electrical power. Spacecraft designed to operate in more distant locations, for example Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
, might employ a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to generate electrical power. Electrical power is sent through power conditioning equipment before it passes through a power distribution unit over an electrical bus to other spacecraft components. Batteries are typically connected to the bus via a battery charge regulator, and the batteries are used to provide electrical power during periods when primary power is not available, for example when a low Earth orbit spacecraft is eclipsed by Earth.
; Thermal control
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand transit through Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and the space environment. They must operate in a vacuum with temperatures potentially ranging across hundreds of degrees Celsius as well as (if subject to reentry) in the presence of plasmas. Material requirements are such that either high melting temperature, low density materials such as beryllium and reinforced carbon–carbon or (possibly due to the lower thickness requirements despite its high density) tungsten or Ablation, ablative carbon–carbon composites are used. Depending on mission profile, spacecraft may also need to operate on the surface of another planetary body. The thermal control subsystem can be passive, dependent on the selection of materials with specific radiative properties. Active thermal control makes use of electrical heaters and certain actuators such as louvers to control temperature ranges of equipments within specific ranges.
; Spacecraft propulsion
: Spacecraft may or may not have a Spacecraft propulsion, propulsion subsystem, depending on whether or not the mission profile calls for propulsion. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, ''Swift'' spacecraft is an example of a spacecraft that does not have a propulsion subsystem. Typically though, LEO spacecraft include a propulsion subsystem for altitude adjustments (drag make-up maneuvers) and inclination adjustment maneuvers. A propulsion system is also needed for spacecraft that perform momentum management maneuvers. Components of a conventional propulsion subsystem include fuel, tankage, valves, pipes, and Rocket engine, thrusters. The thermal control system interfaces with the propulsion subsystem by monitoring the temperature of those components, and by preheating tanks and thrusters in preparation for a spacecraft maneuver.
; Structures
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand launch loads imparted by the launch vehicle, and must have a point of attachment for all the other subsystems. Depending on mission profile, the structural subsystem might need to withstand loads imparted by entry into the Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere of another planetary body, and landing on the surface of another planetary body.
; Payload
: The payload depends on the mission of the spacecraft, and is typically regarded as the part of the spacecraft "that pays the bills". Typical payloads could include scientific instruments (cameras, telescopes, or particle detectors, for example), cargo, or a Human spaceflight, human crew.
; Ground segment
: The ground segment, though not technically part of the spacecraft, is vital to the operation of the spacecraft. Typical components of a ground segment in use during normal operations include a mission operations facility where the flight operations team conducts the operations of the spacecraft, a data processing and storage facility, Earth station, ground stations to radiate signals to and receive signals from the spacecraft, and a voice and data communications network to connect all mission elements.
; Launch vehicle
: The launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch contro ...
propels the spacecraft from Earth's surface, through the atmosphere, and into an orbit, the exact orbit being dependent on the mission configuration. The launch vehicle may be Expendable launch system, expendable or Reusable launch system, reusable.
See also
*Astrionics *Commercial astronaut *Flying saucer *List of crewed spacecraft *List of fictional spacecraft *NewSpace *Spacecraft design *Space exploration *Space launch *Spaceships in science fiction *Space suit *List of spaceflight records, Spaceflight records *Starship *Timeline of Solar System exploration *U.S. Space Exploration History on U.S. StampsNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* *External links
NASA: Space Science Spacecraft Missions
NSSDC Master Catalog Spacecraft Query Form
{{Authority control Spacecraft, Astronautics Pressure vessels