|
Voskhod Spacecraft
The Voskhod (, ''"Sunrise"'') was a spacecraft built by the Soviet Union's space program for human spaceflight as part of the Voskhod programme. It was a development of and a follow-on to the Vostok spacecraft. Voskhod 1 was used for a three-man flight whereas Voskhod 2 had a crew of two. They consisted of a spherical descent module (diameter ), which housed the cosmonauts, and instruments, and a conical equipment module (mass , long, wide), which contained propellant and the engine system. Voskhod was superseded by the Soyuz spacecraft in 1967. Design The Voskhod spacecraft was, essentially, a Vostok spacecraft that had a backup solid fuel retrorocket added to the top of the descent module. The ejection seat was removed for more space and two or three crew couches were added to the interior at a 90° angle to that of the Vostok crew position. There was no provision for crew escape in the event of a launch or landing emergency. Lack of space meant that the three crew mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (russian: Сергей Павлович Королёв, Sergey Pavlovich Korolyov, sʲɪrˈɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪtɕ kərɐˈlʲɵf, Ru-Sergei Pavlovich Korolev.ogg; ukr, Сергій Павлович Корольов, Serhiy Pavlovych Korol'ov, sɛrˈɦij ˈpavlovɪtʃ koroˈlʲou̯) 14 January 1966) was a lead Soviet Aerospace engineering, rocket engineer and spacecraft designer during the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1950s and 1960s. He is regarded by many as the father of practical astronautics. He was involved in the development of the R-7 Semyorka, R-7 Rocket, Sputnik 1, launching Laika, Sputnik 3, the first luna 2, human-made object to make contact with another celestial body, Soviet space dogs#Belka and Strelka, Belka and Strelka, the first human being, Yuri Gagarin, into space, Voskhod 1, and the first person, Alexei Leonov, to conduct a Voskhod 2, spacewalk. Although Korolev trained as an aircraft designer, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmonaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod Rocket
The Voskhod rocket (russian: Восход, ''"ascent"'', ''"dawn"'') was a derivative of the Soviet R-7 ICBM designed for the human spaceflight programme but later used for launching Zenit reconnaissance satellites. It consisted of the Molniya 8K78M third stage minus the Blok L. In 1966, all R-7 variants were equipped with the uprated core stage and strap-ons of the Soyuz 11A511. The Blok I stage in the Voskhod booster used the RD-0107 engine rather than the crew rated and more powerful RD-0110 used on the Soyuz. The sole exception to this were the two manned Voskhod launches, which had RD-0108 engines, a crew-rated RD-0107 but with the same performance. All 11A57s launched after 1965 were functionally a 11A511 without the Soyuz's payload shroud and launch escape system (with the exception of the second stage propulsion system as noted above). Around 300 were flown from Baikonur and Plesetsk through 1976 (various payloads, but Zenith IMINT satellites were the most common). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharik (other)
Sharik (Russian: Шарик) means ''small ball'' in Russian. It is a common dog name in countries of the former Soviet Union and may refer to: *Sharik, a fictional dog in Bulgakov's novel ''Heart of a Dog'' *Sharik, a fictional dog in Dostoevsky's ''The House of the Dead'' *Sharik (Szarik in Polish spelling), a fictional dog in Janusz Przymanowski's '' Four Tank-Men and a Dog'' *Sharik, a fictional dog in ''Three from Prostokvashino'' *Sharik, the unofficial designation of the landing unit of Vostok Vostok refers to east in Russian but may also refer to: Spaceflight * Vostok programme, Soviet human spaceflight project * Vostok (spacecraft), a type of spacecraft built by the Soviet Union * Vostok (rocket family), family of rockets derived from ... and Voskhod spacecraft See also * Sharīk Peninsula * Ba Sharik, a village in Iran * Shariq (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 57
Kosmos 57 (russian: Космос 57 meaning ''Cosmos 57'') was an unmanned Soviet spacecraft launched on 22 February 1965. The craft was essentially an unmanned version of Voskhod 2. Its primary mission was to test the Volga airlock. The test was successful, but the craft was lost shortly after. The spaceflight is designated under the Kosmos system, placing it with many other Soviet scientific and military satellites. Mission The unmanned craft was launched three weeks before Voskhod 2. The primary objective of Voskhod 2 was to conduct a spacewalk, which relied on the inflatable Volga airlock. Kosmos 57 was to test the performance of the airlock. The airlock opened and closed successfully and the craft was re-pressurized without flaw. Destruction The unmanned spacecraft was destroyed on its third orbit around Earth. Two ground stations, one in Klyuchi and the other in Yelizovo, sent simultaneous commands, instead of sequentially as planned, instructing the craft to depres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod Spacecraft "Globus" IMP Navigation Instrument
Globus IMP instruments were spacecraft navigation instruments used in Soviet and Russian crewed spacecraft. The IMP acronym stems from the Russian expression ''Indicator of position in flight'', but the instrument is informally referred to as the ''Globus''. It displays the nadir of the spacecraft on a rotating terrestrial globe. It functions as an onboard, autonomous indicator of the spacecraft's location relative to Earth coordinates. An electro-mechanical device in the tradition of complex post-World War II clocks such as master clocks, the ''Globus'' IMP instrument incorporates hundreds of mechanical components common to horology. This instrument is a mechanical computer for navigation akin to the Norden bombsight. It mechanically computes complex functions and displays its output through mechanical displacements of the globe and other indicator components. It also modulates electric signals from other instruments. The IMP, in successively developing versions, has been used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 47
Kosmos 47 (russian: Космос 47 meaning ''Cosmos 47'') is the designation of an uncrewed test flight of a prototype Soviet Voskhod spacecraft, the first multiple-occupant spacecraft. Launched on 6 October 1964, the successful flight paved the way for the first crewed mission, Voskhod 1, which occurred just 6 days later on 12 October 1964. The spacecraft was one of many designated under the Kosmos system, which is applied to a wide variety of spacecraft of different designs and functions including test flights of crewed vehicles. Launch The launch took place on 6 October at 07:12 GMT from Gagarin's Start, Site 1/5 at Baikonur Cosmodrome onboard a Voskhod rocket s/n R15000-02. Kosmos 47 was operated in a low Earth orbit, it had a perigee of , an apogee of , an inclination of 64.8° and an orbital period The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexei Leonov
Alexei Arkhipovich Leonov. (30 May 1934 – 11 October 2019) was a Soviet and Russian cosmonaut, Air Force major general, writer, and artist. On 18 March 1965, he became the first person to conduct a spacewalk, exiting the capsule during the Voskhod 2 mission for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. He was also selected to be the first Soviet person to land on the Moon although the project was cancelled. In July 1975, Leonov commanded the Soyuz capsule in the Apollo-Soyuz mission, which docked in space for two days with an American Apollo capsule. Early life and military service Leonov was born on 30 May 1934 in Listvyanka, West Siberian Krai, Russian SFSR. His grandfather had been forced to relocate to Siberia for his role in the 1905 Russian Revolution. Alexei was the eighth of nine surviving children born to Yevdokia and Arkhip. His father was an electrician and miner. In 1936, his father was arrested and declared an "enemy of the people". Leonov wrote in his autobiography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Suit
A space suit or spacesuit is a garment worn to keep a human alive in the harsh environment of outer space, vacuum and temperature extremes. Space suits are often worn inside spacecraft as a safety precaution in case of loss of cabin pressure, and are necessary for extravehicular activity (EVA), work done outside spacecraft. Space suits have been worn for such work in Earth orbit, on the surface of the Moon, and en route back to Earth from the Moon. Modern space suits augment the basic pressure garment with a complex system of equipment and environmental systems designed to keep the wearer comfortable, and to minimize the effort required to bend the limbs, resisting a soft pressure garment's natural tendency to stiffen against the vacuum. A self-contained oxygen supply and environmental control system is frequently employed to allow complete freedom of movement, independent of the spacecraft. Three types of space suits exist for different purposes: IVA (intravehicular activity) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
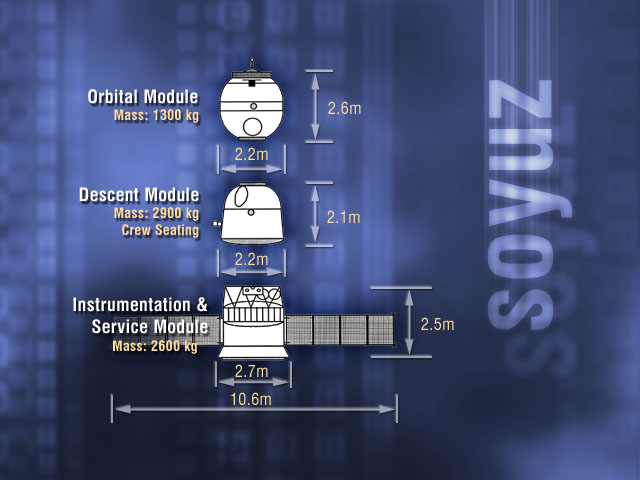
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod 2
Voskhod 2 (russian: Восход-2, , ''Sunrise-2'') was a Soviet crewed space mission in March 1965. The Vostok-based Voskhod 3KD spacecraft with two crew members on board, Pavel Belyayev and Alexei Leonov, was equipped with an inflatable airlock. It established another milestone in space exploration when Alexei Leonov became the first person to leave the spacecraft in a specialized spacesuit to conduct a 12-minute spacewalk. Crew Backup crew Reserve crew Mission parameters * Mass: * Apogee: * Perigee: * Inclination: 64.8° * Period: 90.9 min Space walk * Leonov – EVA – 18 March 1965 ** 08:28:13 GMT: The Voskhod 2 airlock is depressurized by Leonov. ** 08:32:54 GMT: Leonov opens the Voskhod 2 airlock hatch. ** 08:34:51 GMT: EVA start – Leonov leaves airlock. ** 08:47:00 GMT: EVA end – Leonov reenters airlock. ** 08:48:40 GMT: Hatch on the airlock is closed and secured by Leonov. ** 08:51:54 GMT: Leonov begins to repressurize the airlock. ** Duration: 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)