SpaceX Dragon 1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dragon, also known as Dragon 1 or Cargo Dragon, was a class of fourteen partially reusable cargo spacecraft developed by

 In 2005, NASA solicited proposals for a commercial ISS resupply cargo vehicle to replace the then-soon-to-be-retired Space Shuttle, through its Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) development program. The Dragon space capsule was a part of SpaceX's proposal, submitted to NASA in March 2006. SpaceX's COTS proposal was issued as part of a team, which also included
In 2005, NASA solicited proposals for a commercial ISS resupply cargo vehicle to replace the then-soon-to-be-retired Space Shuttle, through its Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) development program. The Dragon space capsule was a part of SpaceX's proposal, submitted to NASA in March 2006. SpaceX's COTS proposal was issued as part of a team, which also included
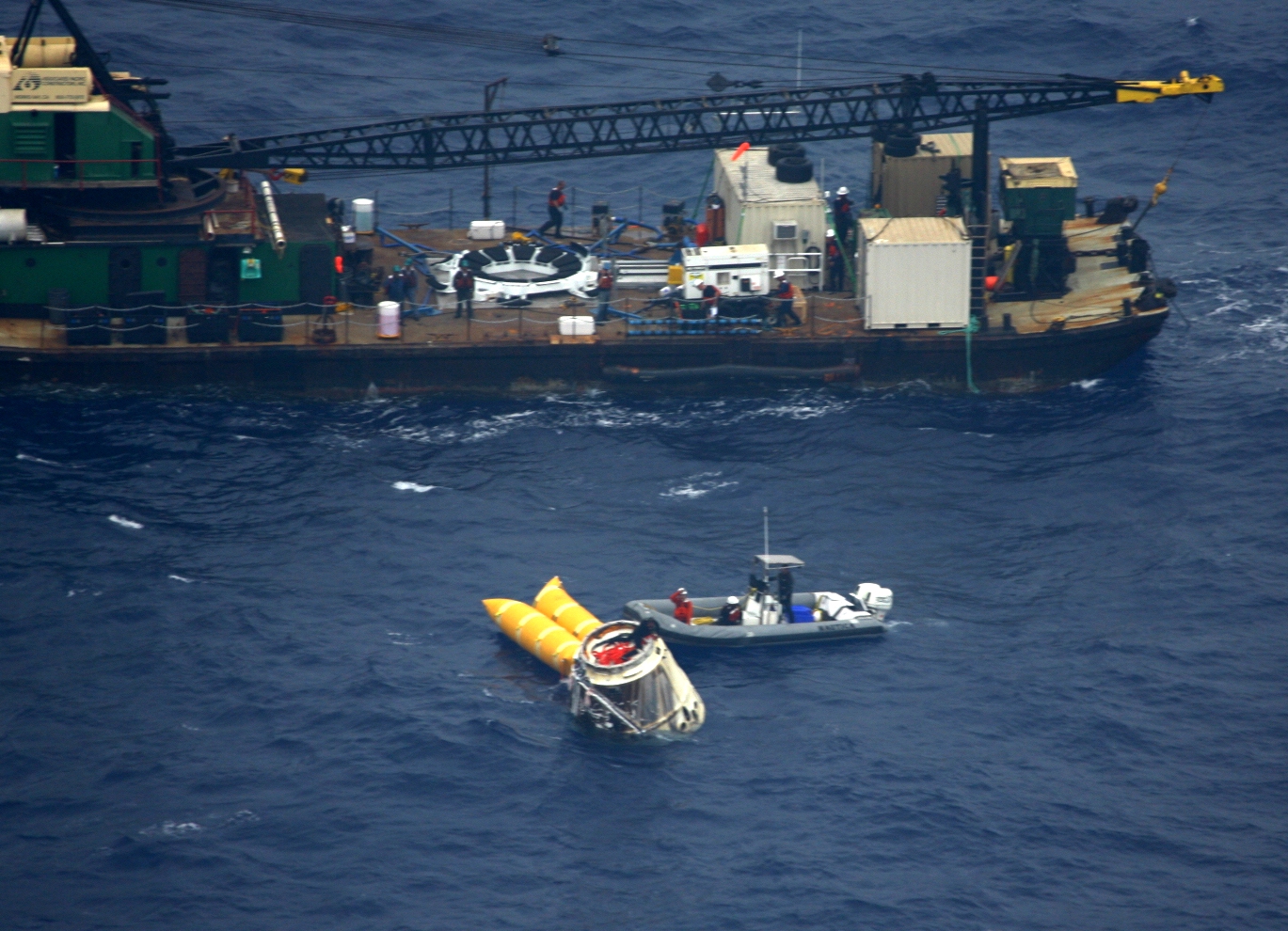

 The first flight of the Falcon 9, a private flight, occurred in June 2010 and launched a stripped-down version of the Dragon capsule. This Dragon Spacecraft Qualification Unit had initially been used as a ground test bed to validate several of the capsule's systems. During the flight, the unit's primary mission was to relay aerodynamic data captured during the ascent. It was not designed to survive re-entry, and did not.
NASA contracted for three test flights from SpaceX, but later reduced that number to two. The first Dragon spacecraft launched on its first mission – contracted to NASA as COTS Demo Flight 1 – on 8 December 2010, and was successfully recovered following re-entry to Earth's atmosphere. The mission also marked the second flight of the Falcon 9 launch vehicle. The DragonEye sensor flew again on STS-133 in February 2011 for further on-orbit testing. In November 2010, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) had issued a re-entry license for the Dragon capsule, the first such license ever awarded to a commercial vehicle.
The second Dragon flight, also contracted to NASA as a demonstration mission, launched successfully on 22 May 2012, after NASA had approved SpaceX's proposal to combine the COTS 2 and 3 mission objectives into a single Falcon 9/Dragon flight, renamed COTS 2+. Dragon conducted orbital tests of its navigation systems and abort procedures, before being grappled by the ISS'
The first flight of the Falcon 9, a private flight, occurred in June 2010 and launched a stripped-down version of the Dragon capsule. This Dragon Spacecraft Qualification Unit had initially been used as a ground test bed to validate several of the capsule's systems. During the flight, the unit's primary mission was to relay aerodynamic data captured during the ascent. It was not designed to survive re-entry, and did not.
NASA contracted for three test flights from SpaceX, but later reduced that number to two. The first Dragon spacecraft launched on its first mission – contracted to NASA as COTS Demo Flight 1 – on 8 December 2010, and was successfully recovered following re-entry to Earth's atmosphere. The mission also marked the second flight of the Falcon 9 launch vehicle. The DragonEye sensor flew again on STS-133 in February 2011 for further on-orbit testing. In November 2010, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) had issued a re-entry license for the Dragon capsule, the first such license ever awarded to a commercial vehicle.
The second Dragon flight, also contracted to NASA as a demonstration mission, launched successfully on 22 May 2012, after NASA had approved SpaceX's proposal to combine the COTS 2 and 3 mission objectives into a single Falcon 9/Dragon flight, renamed COTS 2+. Dragon conducted orbital tests of its navigation systems and abort procedures, before being grappled by the ISS'
'' Wired'' 25 May 2012 Retrieved 13 September 2012 Dragon returned to Earth on 31 May 2012, landing as scheduled in the Pacific Ocean, and was again successfully recovered. On 23 August 2012, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden announced that SpaceX had completed all required milestones under the COTS contract, and was cleared to begin operational resupply missions to the ISS.

 In 2006, Elon Musk stated that SpaceX had built "a prototype flight crew capsule, including a thoroughly tested 30-man-day life-support system". A video simulation of the launch escape system's operation was released in January 2011. Musk stated in 2010 that the developmental cost of a crewed Dragon and Falcon 9 would be between US$800 million and US$1 billion. In 2009 and 2010, Musk suggested on several occasions that plans for a crewed variant of the Dragon were proceeding and had a two-to-three-year timeline to completion. SpaceX submitted a bid for the third phase of CCDev, CCiCap.
In 2006, Elon Musk stated that SpaceX had built "a prototype flight crew capsule, including a thoroughly tested 30-man-day life-support system". A video simulation of the launch escape system's operation was released in January 2011. Musk stated in 2010 that the developmental cost of a crewed Dragon and Falcon 9 would be between US$800 million and US$1 billion. In 2009 and 2010, Musk suggested on several occasions that plans for a crewed variant of the Dragon were proceeding and had a two-to-three-year timeline to completion. SpaceX submitted a bid for the third phase of CCDev, CCiCap.
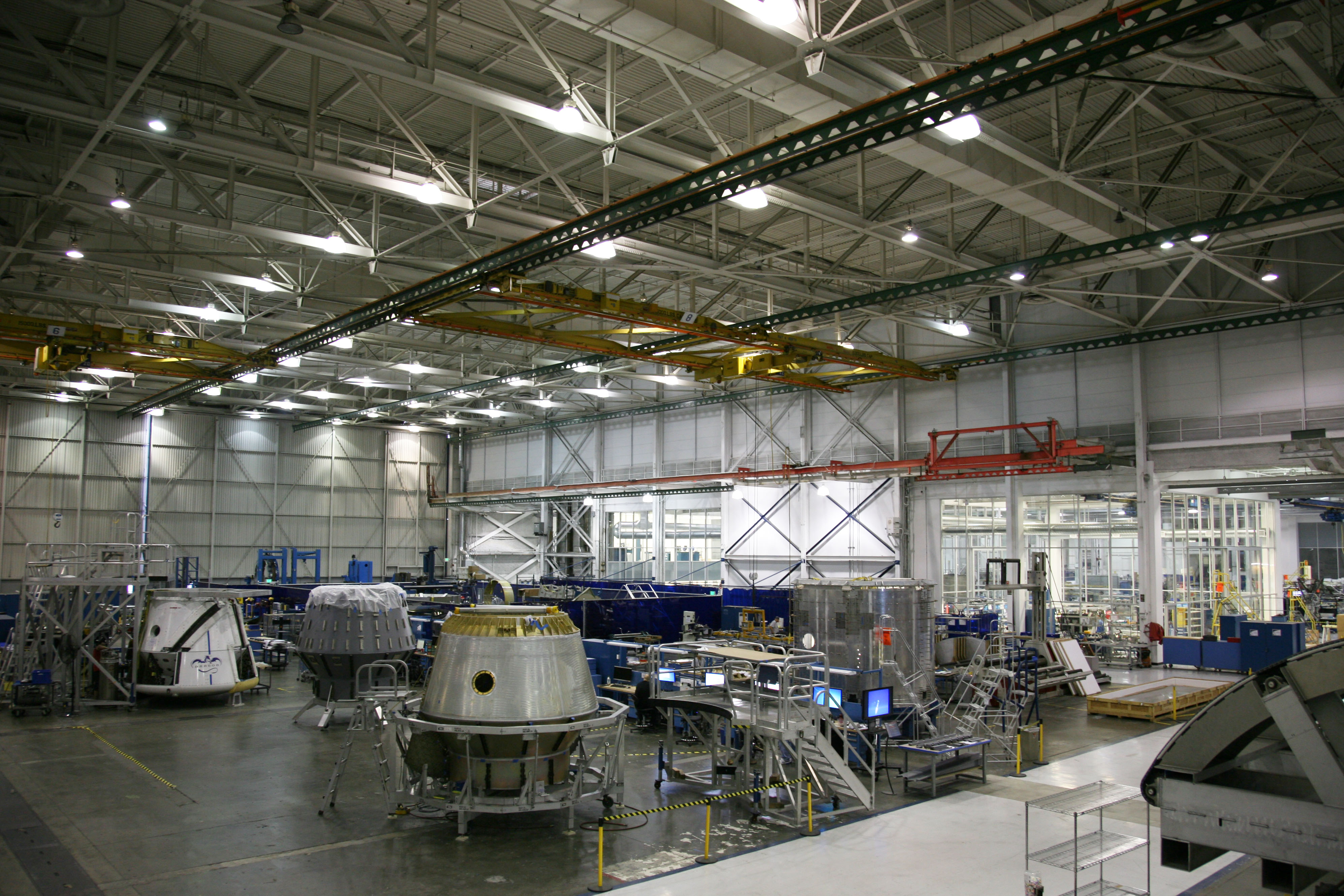 In December 2010, the SpaceX production line was reported to be manufacturing one new Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket every three months. Elon Musk stated in a 2010 interview that he planned to increase production turnover to one Dragon every six weeks by 2012. Composite materials are extensively used in the spacecraft's manufacture to reduce weight and improve structural strength.
By September 2013, SpaceX total manufacturing space had increased to nearly and the factory had six Dragons in various stages of production. SpaceX published a photograph showing the six, including the next four NASA Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) mission Dragons ( CRS-3, CRS-4,
In December 2010, the SpaceX production line was reported to be manufacturing one new Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket every three months. Elon Musk stated in a 2010 interview that he planned to increase production turnover to one Dragon every six weeks by 2012. Composite materials are extensively used in the spacecraft's manufacture to reduce weight and improve structural strength.
By September 2013, SpaceX total manufacturing space had increased to nearly and the factory had six Dragons in various stages of production. SpaceX published a photograph showing the six, including the next four NASA Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) mission Dragons ( CRS-3, CRS-4,

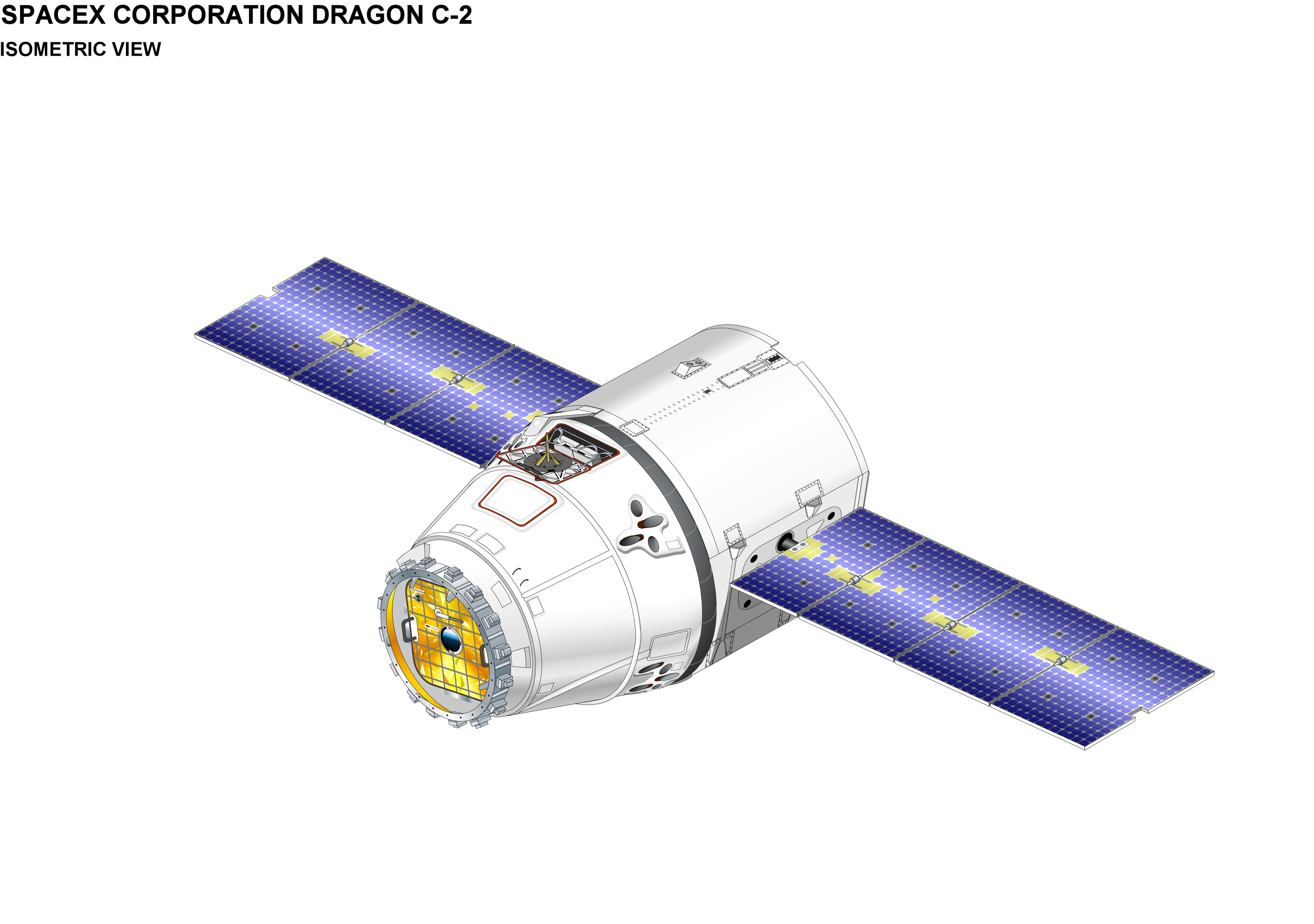 The Dragon spacecraft consists of a nose-cone cap, a conventional blunt-cone ballistic capsule, and an unpressurized cargo-carrier trunk equipped with two
The Dragon spacecraft consists of a nose-cone cap, a conventional blunt-cone ballistic capsule, and an unpressurized cargo-carrier trunk equipped with two
The trunk was first used operationally on the Dragon's CRS-2 mission in March 2013. Its solar arrays produce a peak power of 4 kW. The design was modified beginning with the fifth Dragon flight on the SpaceX CRS-3 mission to the ISS in March 2014. While the

SpaceX CCDev2 Agreement with NASA
Dragon cargo delivery to ISS (COTS 2 highlight reel)
Dragon crew transport to ISS (CG rendering)
''
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
, an American private space transportation company. The spacecraft flew 23 missions between 2010 and 2020. Dragon was launched into orbit by the company's Falcon 9 launch vehicle to resupply the International Space Station (ISS).
During its maiden flight in December 2010, Dragon became the first commercially built and operated spacecraft to be recovered successfully from orbit. On 25 May 2012, a cargo variant of Dragon became the first commercial spacecraft to successfully rendezvous with and attach to the ISS. SpaceX contracted to deliver cargo to the ISS under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services program, and Dragon began regular cargo flights in October 2012. With the Dragon spacecraft and the Orbital ATK Cygnus, NASA sought to increase its partnerships with domestic commercial aviation and aeronautics industry.
On 3 June 2017, the C106 capsule, largely assembled from previously flown components from the CRS-4 mission in September 2014, was launched again for the first time on CRS-11
SpaceX CRS-11, also known as SpX-11, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station, launched successfully on 3 June 2017. The mission was contracted by NASA and was flown by SpaceX. The mission utilized a Falcon 9 ...
, after being refurbished.
The last flight of the first version of the Dragon spacecraft (Dragon 1) launched 7 March 2020 (UTC) on cargo resupply mission ( CRS-20) to International Space Station (ISS). This mission was the last mission of SpaceX of the first Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) program, and marked the retirement of the Dragon 1 fleet. Further SpaceX commercial resupply flights to ISS under the second Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-2) program use the cargo-carrying variant of the SpaceX Dragon 2 spacecraft.
History
SpaceX begandeveloping
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
the Dragon space capsule in late 2004, making a public announcement in 2006 with a plan of entering service in 2009. Also in 2006, SpaceX won a contract to use the Dragon space capsule for commercial resupply services to the International Space Station for the American federal space agency, NASA.
NASA ISS resupply contract
Commercial Orbital Transportation Services

 In 2005, NASA solicited proposals for a commercial ISS resupply cargo vehicle to replace the then-soon-to-be-retired Space Shuttle, through its Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) development program. The Dragon space capsule was a part of SpaceX's proposal, submitted to NASA in March 2006. SpaceX's COTS proposal was issued as part of a team, which also included
In 2005, NASA solicited proposals for a commercial ISS resupply cargo vehicle to replace the then-soon-to-be-retired Space Shuttle, through its Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) development program. The Dragon space capsule was a part of SpaceX's proposal, submitted to NASA in March 2006. SpaceX's COTS proposal was issued as part of a team, which also included MD Robotics
MDA Ltd. is a Canadian space technology company headquartered in Brampton, Ontario, Canada, that provides geointelligence, robotics & space operations, and satellite systems.
History
MDA (formerly MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates) was founde ...
, the Canadian company that had built the ISS's Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supp ...
.
On 18 August 2006, NASA announced that SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
had been chosen, along with Kistler Aerospace
Rocketplane Kistler (RpK) was a reusable launch system firm originally based in Oklahoma. It was formed in 2006 after Rocketplane Limited, Inc. acquired Kistler Aerospace. NASA announced that Rocketplane Kistler had been chosen to develop crew and ...
, to develop cargo launch services for the ISS. The initial plan called for three demonstration flights of SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft to be conducted between 2008 and 2010. SpaceX and Kistler were to receive up to US$278 million and US$207 million respectively, if they met all NASA milestones, but Kistler failed to meet its obligations, and its contract was terminated in 2007. NASA later re-awarded Kistler's contract to Orbital Sciences Corporation.
Commercial Resupply Services Phase 1
On 23 December 2008, NASA awarded a US$1.6 billion Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) contract to SpaceX, with contract options that could potentially increase the maximum contract value to US$3.1 billion. The contract called for 12 flights, with an overall minimum of of cargo to be carried to the ISS. On 23 February 2009, SpaceX announced that its chosenphenolic-impregnated carbon ablator
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...
heat shield material, PICA-X, had passed heat stress tests in preparation for Dragon's maiden launch. The primary proximity-operations sensor for the Dragon spacecraft, the DragonEye, was tested in early 2009 during the STS-127
STS-127 ( ISS assembly flight 2J/A) was a NASA Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was the twenty-third flight of . The primary purpose of the STS-127 mission was to deliver and install the final two components of t ...
mission, when it was mounted near the docking port of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' and used while the Shuttle approached the International Space Station. The DragonEye's lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, or LiDAR; sometimes LADAR) is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. It can also be ...
and thermography (thermal imaging) abilities were both tested successfully. The COTS UHF Communication Unit (CUCU) and Crew Command Panel (CCP) were delivered to the ISS during the late 2009 STS-129 mission. The CUCU allows the ISS to communicate with Dragon and the CCP allows ISS crew members to issue basic commands to Dragon. In summer 2009, SpaceX hired former NASA astronaut Ken Bowersox as vice president of their new Astronaut Safety and Mission Assurance Department, in preparation for crews using the spacecraft.
As a condition of the NASA CRS contract, SpaceX analyzed the orbital radiation environment on all Dragon systems, and how the spacecraft would respond to spurious radiation events. That analysis and the Dragon design – which uses an overall Fault tolerance triple redundant computer architecture, rather than individual radiation hardening of each computer processor – was reviewed by independent experts before being approved by NASA for the cargo flights.
During March 2015, it was announced that SpaceX had been awarded an additional three missions under Commercial Resupply Services Phase 1. These additional missions are SpaceX CRS-13, SpaceX CRS-14 and SpaceX CRS-15 and would cover the cargo needs of 2017. On 24 February 2016, SpaceNews disclosed that SpaceX had been awarded a further five missions under Commercial Resupply Services Phase 1. This additional tranche of missions had SpaceX CRS-16 and SpaceX CRS-17
SpaceX CRS-17, also known as SpX-17, was a Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS) to the International Space Station that was launched aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on 4 May 2019. The mission was contracted by NASA and was flown by SpaceX.
Laun ...
manifested for FY2017 while SpaceX CRS-18, SpaceX CRS-19 and SpaceX CRS-20 and were notionally manifested for FY2018.
Commercial Resupply Services Phase 2
The ''Commercial Resupply Services-2'' (CRS-2) contract definition and solicitation period commenced in 2014. In January 2016, NASA awarded contracts toSpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
, Orbital ATK, and Sierra Nevada Corporation for a minimum of six launches each, with missions planned until at least 2024. The maximum potential value of all the contracts was announced as US$14 billion, but the minimum requirements would be considerably less. No further financial information was disclosed.
CRS-2 launches began in late 2019.
Demonstration flights


Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supp ...
and successfully berthing with the station on 25 May 2012 to offload its cargo."ISS welcomes SpaceX Dragon"'' Wired'' 25 May 2012 Retrieved 13 September 2012 Dragon returned to Earth on 31 May 2012, landing as scheduled in the Pacific Ocean, and was again successfully recovered. On 23 August 2012, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden announced that SpaceX had completed all required milestones under the COTS contract, and was cleared to begin operational resupply missions to the ISS.
Returning research materials from orbit
Dragon spacecraft can return of cargo to Earth, which can be all unpressurized disposal mass, or up to of pressurized cargo, from the ISS, and is the only current spacecraft capable of returning to Earth with a significant amount of cargo. Other than the Russian Soyuz crew capsule, Dragon is the only currently operating spacecraft designed to survive re-entry. Because Dragon allows for the return of critical materials to researchers in as little as 48 hours from splashdown, it opens the possibility of new experiments on ISS that can produce materials for later analysis on ground using more sophisticated instrumentation. For example, CRS-12 returnedmice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
that have spent time in orbit which will help give insight into how microgravity
The term micro-g environment (also μg, often referred to by the term microgravity) is more or less synonymous with the terms ''weightlessness'' and ''zero-g'', but emphasising that g-forces are never exactly zero—just very small (on the I ...
impacts blood vessels in both the brain and eyes, and in determining how arthritis develops.
Operational flights
Dragon was launched on its first operational CRS flight on 8 October 2012, and completed the mission successfully on 28 October 2012. NASA initially contractedSpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
for 12 operational missions, and later extended the CRS contract with 8 more flights, bringing the total to 20 launches until 2019. In 2016, a new batch of 6 missions under the CRS-2 contract was assigned to SpaceX; those missions are scheduled to be launched between 2020 and 2024.
Reuse of previously-flown capsules
CRS-11
SpaceX CRS-11, also known as SpX-11, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station, launched successfully on 3 June 2017. The mission was contracted by NASA and was flown by SpaceX. The mission utilized a Falcon 9 ...
, SpaceX's eleventh CRS mission, was successfully launched on 3 June 2017 from Kennedy Space Center LC-39A, being the 100th mission to be launched from that pad. This mission was the first to re-fly a previously flown Dragon capsule. This mission delivered 2,708 kilograms of cargo to the International Space Station, including Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER). The first stage of the Falcon 9 launch vehicle landed successfully at Landing Zone 1. This mission launched for the first time a refurbished Dragon capsule, serial number C106, which had flown in September 2014 on the CRS-4 mission, and was the first time since 2011 a reused spacecraft arrived at the ISS. Gemini SC-2
Gemini SC-2 (Spacecraft No. 2) was the second NASA Project Gemini full-up reentry capsule built. This McDonnell Gemini capsule was the first space capsule to be reused, flying twice in suborbital flights. SC-2 flew on Gemini 2 and OPS 0855 flights ...
capsule is the only other reused capsule, but it was only reflown suborbitally in 1966.
CRS-12, SpaceX's twelfth CRS mission, was successfully launched on the first "Block 4" version of the Falcon 9 on 14 August 2017 from Kennedy Space Center LC-39A at the first attempt. This mission delivered of pressurized mass and unpressurized. The external payload manifested for this flight was the CREAM cosmic-ray detector. Last flight of a newly built Dragon capsule; further missions will use refurbished spacecraft.
CRS-13, SpaceX's thirteenth CRS mission, was the second use of a previously flown Dragon capsule, but the first time in concordance with a reused first-stage booster. It was successfully launched on 15 December 2017 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 40
Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40), previously Launch Complex 40 (LC-40) is a launch pad for rockets located at the north end of Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida.
The launch pad was used by the United States Air Force for 55 Titan III a ...
at the first attempt. This was the first launch from SLC-40 since the AMOS-6 pad anomaly. The booster was the previously flown core from the CRS-11
SpaceX CRS-11, also known as SpX-11, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station, launched successfully on 3 June 2017. The mission was contracted by NASA and was flown by SpaceX. The mission utilized a Falcon 9 ...
mission. This mission delivered of pressurized mass and unpressurized. It returned from orbit and splashdown on 13 January 2018, making it the first space capsule to be reflown to orbit more than once.
CRS-14, SpaceX's fourteenth CRS mission, was the third reuse of a previously flown Dragon capsule. It was successfully launched on 2 April 2018 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station SLC-40. It was successfully berthed to the ISS on 4 April 2018 and remained berthed for a month before returning cargo and science experiments back to Earth.
CRS-15, CRS-16, CRS-17, CRS-18, CRS-19, and CRS-20 were all flown with previously flown capsules.
Crewed development program

 In 2006, Elon Musk stated that SpaceX had built "a prototype flight crew capsule, including a thoroughly tested 30-man-day life-support system". A video simulation of the launch escape system's operation was released in January 2011. Musk stated in 2010 that the developmental cost of a crewed Dragon and Falcon 9 would be between US$800 million and US$1 billion. In 2009 and 2010, Musk suggested on several occasions that plans for a crewed variant of the Dragon were proceeding and had a two-to-three-year timeline to completion. SpaceX submitted a bid for the third phase of CCDev, CCiCap.
In 2006, Elon Musk stated that SpaceX had built "a prototype flight crew capsule, including a thoroughly tested 30-man-day life-support system". A video simulation of the launch escape system's operation was released in January 2011. Musk stated in 2010 that the developmental cost of a crewed Dragon and Falcon 9 would be between US$800 million and US$1 billion. In 2009 and 2010, Musk suggested on several occasions that plans for a crewed variant of the Dragon were proceeding and had a two-to-three-year timeline to completion. SpaceX submitted a bid for the third phase of CCDev, CCiCap.
Development funding
In 2014, SpaceX released the total combined development costs for both the Falcon 9 launch vehicle and the Dragon capsule. NASA provided US$396 million while SpaceX provided over US$450 million to fund both development efforts.Production
 In December 2010, the SpaceX production line was reported to be manufacturing one new Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket every three months. Elon Musk stated in a 2010 interview that he planned to increase production turnover to one Dragon every six weeks by 2012. Composite materials are extensively used in the spacecraft's manufacture to reduce weight and improve structural strength.
By September 2013, SpaceX total manufacturing space had increased to nearly and the factory had six Dragons in various stages of production. SpaceX published a photograph showing the six, including the next four NASA Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) mission Dragons ( CRS-3, CRS-4,
In December 2010, the SpaceX production line was reported to be manufacturing one new Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket every three months. Elon Musk stated in a 2010 interview that he planned to increase production turnover to one Dragon every six weeks by 2012. Composite materials are extensively used in the spacecraft's manufacture to reduce weight and improve structural strength.
By September 2013, SpaceX total manufacturing space had increased to nearly and the factory had six Dragons in various stages of production. SpaceX published a photograph showing the six, including the next four NASA Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) mission Dragons ( CRS-3, CRS-4, CRS-5
SpaceX CRS-5, also known as SpX-5, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS), conducted by SpaceX for NASA, and was launched on 10 January 2015 and ended on 11 February 2015. It was the seventh flight ...
, CRS-6
SpaceX CRS-6, also known as SpX-6, was a Commercial Resupply Services, Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station, contracted to NASA. It was the eighth flight for SpaceX's uncrewed SpaceX Dragon, Dragon Comparison ...
) plus the drop-test Dragon, and the pad-abort Dragon weldment for commercial crew program.
Design

 The Dragon spacecraft consists of a nose-cone cap, a conventional blunt-cone ballistic capsule, and an unpressurized cargo-carrier trunk equipped with two
The Dragon spacecraft consists of a nose-cone cap, a conventional blunt-cone ballistic capsule, and an unpressurized cargo-carrier trunk equipped with two solar arrays
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and ...
. The capsule uses a PICA-X heat shield, based on a proprietary variant of NASA's Phenolic impregnated carbon ablator
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...
(PICA) material, designed to protect the capsule during Earth atmospheric entry, even at high return velocities from Lunar and Martian missions. The Dragon capsule is re-usable, and can fly multiple missions. The trunk is not recoverable; it separates from the capsule before re-entry and burns up in Earth's atmosphere. The trunk section, which carries the spacecraft's solar panels and allows the transport of unpressurized cargo to the ISS, was first used for cargo on the SpaceX CRS-2 mission.
The spacecraft is launched atop a Falcon 9 booster. The Dragon capsule is equipped with 16 Draco thrusters. During its initial cargo and crew flights, the Dragon capsule will land in the Pacific Ocean and be returned to the shore by ship.
For the ISS Dragon cargo flights, the ISS's Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supp ...
grapples its Flight-Releasable Grapple Fixture and berths Dragon to the station's US Orbital Segment using a Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM). The CRS Dragon does not have an independent means of maintaining a breathable atmosphere for astronauts and instead circulates in fresh air from the ISS. For typical missions, Dragon is planned to remain berthed to the ISS for about 30 days.
The Dragon capsule can transport of cargo, which can be all pressurized, all unpressurized, or a combination thereof. It can return to Earth , which can be all unpressurized disposal mass, or up to of return pressurized cargo, driven by parachute limitations. There is a volume constraint of trunk unpressurized cargo and of pressurized cargo (up or down)."The ISS CRS contract (signed 23 December 2008)"The trunk was first used operationally on the Dragon's CRS-2 mission in March 2013. Its solar arrays produce a peak power of 4 kW. The design was modified beginning with the fifth Dragon flight on the SpaceX CRS-3 mission to the ISS in March 2014. While the
outer mold line
A boilerplate spacecraft, also known as a mass simulator, is a nonfunctional craft or payload that is used to test various configurations and basic size, load, and handling characteristics of rocket launch vehicles. It is far less expensive t ...
of the Dragon was unchanged, the avionics and cargo racks were redesigned to supply substantially more electrical power to powered cargo devices, including the GLACIER freezer module and MERLIN freezer module freezer modules for transporting
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and ...
critical science payloads.
Variants and derivatives
DragonLab
SpaceX planned to fly the Dragon spacecraft in a free-flying configuration, known as DragonLab. Its subsystems include propulsion, power, thermal and environmental control (ECLSS), avionics, communications,thermal protection
A thermal cutoff is an electrical safety device (either a thermal fuse or thermal switch) that interrupts electric current when heated to a specific temperature. These devices may be for one-time use (a thermal fuse), or may be reset manually or ...
, flight software, guidance and navigation systems, and entry, descent, landing, and recovery gear. It has a total combined upmass of upon launch, and a maximum downmass of when returning to Earth. In November 2014, there were two DragonLab missions listed on the SpaceX launch manifest: one in 2016 and another in 2018. However, these missions were removed from the manifest in early 2017, with no official SpaceX statement. The American Biosatellites
A bio satellite is an artificial satellite designed to carry plants or animals in outer space. They are used to research the effects of space (cosmic radiation, weightlessness, etc.) on biological matter while in orbit around a celestial body. ...
once performed similar uncrewed payload-delivery functions, and the Russian Bion satellites still continue to do so.
List of vehicles
List of missions
''Launch dates are listed in UTC.''Specifications
DragonLab
The following specifications are published by SpaceX for the non-NASA, non-ISS commercial flights of the refurbished Dragon capsules, listed as "DragonLab" flights on the SpaceX manifest. The specifications for the NASA-contracted Dragon Cargo were not included in the 2009 DragonLab datasheet.Pressure vessel
* interior pressurized, environmentally controlled, payload volume. * Onboard environment: ; relative humidity 25~75%; 13.9~14.9 psia air pressure (958.4~1027 hPa).Unpressurized sensor bay (recoverable payload)
* unpressurized payload volume. * Sensor bay hatch opens after orbit insertion to allow full sensor access to the outer space environment, and closes before Earth atmosphere re-entry.Unpressurized trunk (non-recoverable)
* payload volume in the trunk, aft of the pressure vessel heat shield, with optional trunk extension to total length, payload volume increases to . * Supports sensors and space apertures up to in diameter.Power, communication and command systems
* Power: twinsolar panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
s providing 1500 watts average, 4000 watts peak, at 28 and 120 VDC.
* Spacecraft communication: commercial standard RS-422 and military standard 1553 serial I/O, plus Ethernet communications for IP-addressable standard payload service.
* Command uplink: 300 kbit/s.
* Telemetry/data downlink: 300 Mbit/s standard, fault-tolerant S-band
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it crosses the conventional ...
telemetry and video transmitters.
Radiation tolerance
Dragon uses a "radiation-tolerant" design in the electronic hardware and software that make up its flight computers. The system uses three pairs of computers, each constantly checking on the others, to instantiate a fault-tolerant design. In the event of a radiation upset or soft error, one of the computer pairs will perform a soft reboot. Including the flight computers, Dragon employs 18 triply-redundant processing units, for a total of 54 processors.See also
* Comparison of space station cargo vehicles * List of human spaceflight programs * Space Shuttle successors * Cargo Dragon C208 and C209Comparable vehicles
Cargo
* * * * * * *Crew
* * *References
External links
* at SpaceXSpaceX CCDev2 Agreement with NASA
Dragon cargo delivery to ISS (COTS 2 highlight reel)
Dragon crew transport to ISS (CG rendering)
''
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. It is the finest grained foliated metamorphic rock. ...
''. 30 May 2014.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dragon (spacecraft)
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
Cargo spacecraft
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
Vehicles introduced in 2010
Commercial spaceflight
Reusable spacecraft
SpaceX related lists