Southwest Pacific Force on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
South West Pacific Area (SWPA) was the name given to the Allied supreme military command in the
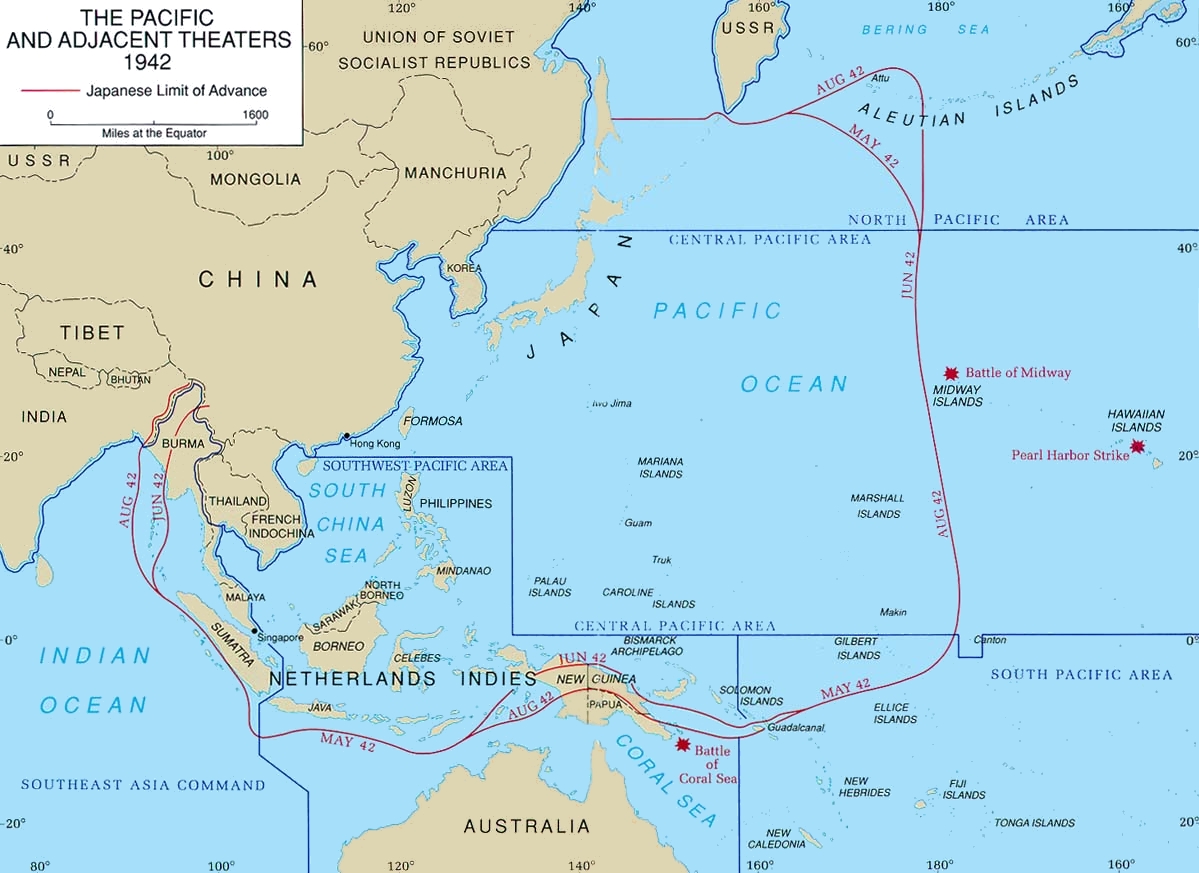 The forerunner of the South West Pacific Area was the short-lived
The forerunner of the South West Pacific Area was the short-lived
 MacArthur announced the composition of his staff, known as General Headquarters (GHQ) on 19 April. Major General Richard K. Sutherland became Chief of Staff; Brigadier General Richard J. Marshall, Deputy Chief of Staff; Colonel Charles P. Stivers, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-1; Colonel Charles A. Willoughby, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-2; Brigadier General
MacArthur announced the composition of his staff, known as General Headquarters (GHQ) on 19 April. Major General Richard K. Sutherland became Chief of Staff; Brigadier General Richard J. Marshall, Deputy Chief of Staff; Colonel Charles P. Stivers, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-1; Colonel Charles A. Willoughby, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-2; Brigadier General 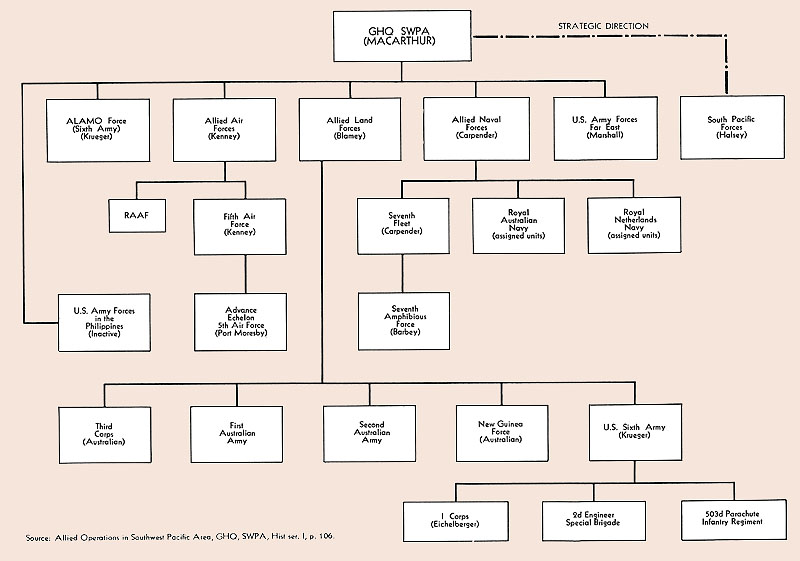 There was a major reorganisation in April 1945 for the planned invasion of Japan. All Army forces in the Pacific were placed under MacArthur's command, including those in Nimitz's Pacific Ocean Areas. A new command was formed, Army Forces Pacific (AFPAC), with GHQ operating as the headquarters of both AFPAC and SWPA. Units in POA remained under Nimitz's operational control, and the first major formation, the
There was a major reorganisation in April 1945 for the planned invasion of Japan. All Army forces in the Pacific were placed under MacArthur's command, including those in Nimitz's Pacific Ocean Areas. A new command was formed, Army Forces Pacific (AFPAC), with GHQ operating as the headquarters of both AFPAC and SWPA. Units in POA remained under Nimitz's operational control, and the first major formation, the
 In May 1942, the Australian government appointed Air Vice Marshal
In May 1942, the Australian government appointed Air Vice Marshal
 When Lieutenant General Krueger's
When Lieutenant General Krueger's
South West Pacific Theatre of World War II
The South West Pacific theatre, during World War II, was a major theatre of the war between the Allies and the Axis. It included the Philippines, the Dutch East Indies (except for Sumatra), Borneo, Australia and its mandate Territory of ...
. It was one of four major Allied commands in the Pacific War. SWPA included the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and ea ...
, the Dutch East Indies (excluding Sumatra), East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
, Australia, the Territories of Papua and New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
, and the western part of the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
. It primarily consisted of United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and Australian forces, although Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, Filipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and other Allied forces also served in the SWPA.
General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
Douglas MacArthur was appointed as the Supreme Commander, Southwest Pacific Area, on its creation on 18 April 1942. He created five subordinate commands: Allied Land Forces, Allied Air Forces, Allied Naval Forces, United States Army Forces in Australia (USAFIA), and the United States Army Forces in the Philippines. The last command disappeared when Corregidor surrendered on 6 May 1942, while USAFIA became the United States Army Services of Supply
The Services of Supply or "SOS" branch of the Army of the USA was created on 28 February 1942 by Executive Order Number 9082 "Reorganizing the Army and the War Department" and War Department Circular No. 59, dated 2 March 1942. Services of Supp ...
, Southwest Pacific Area (USASOS SWPA). In 1943 United States Army Forces in the Far East
United States Army Forces in the Far East (USAFFE) ( Filipino: ''Hukbong Katihan ng Estados Unidos sa Malayong Silangan/HKEUMS''; Spanish: ''Fuerzas del Ejército de los Estados Unidos en el Lejano Oriente'') was a military formation of the Unit ...
was reformed and assumed responsibility for administration, leaving USASOS as a purely logistical agency. Both were swept away in a reorganisation in 1945. The other three commands, Allied Land Forces, Allied Air Forces and Allied Naval Forces, remained until SWPA was abolished on 2 September 1945.
Origins
American-British-Dutch-Australian Command
The American-British-Dutch-Australian (ABDA) Command, or ABDACOM, was a short-lived, supreme command for all Allies of World War II, Allied forces in South East Asia in early 1942, during the Pacific War in World War II. The command consists of ...
(ABDA). In December 1941 and January 1942 ABDA was referred to as the South West Pacific Area. The rapid Japanese advance through the Dutch East Indies effectively divided the ABDA area in two and, in late February 1942, ABDA was dissolved at the recommendation of its commander, General Sir Archibald Wavell, who—as Commander-in-Chief in India
During the period of the Company rule in India and the British Raj, the Commander-in-Chief, India (often "Commander-in-Chief ''in'' or ''of'' India") was the supreme commander of the British Indian Army. The Commander-in-Chief and most of his ...
—retained responsibility for Allied operations in Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
and Sumatra.
Another command, established under emergency conditions when a convoy intended for supply of the Philippines, known as the Pensacola Convoy, was rerouted to Brisbane due to the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
. Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
Julian F. Barnes was ordered to assume command of all troops in the convoy on 12 December 1941 concurrent with their designation as Task Force—South Pacific, and place himself under the command of MacArthur. The next day, by radiogram, the Chief of Staff of the United States Army
The chief of staff of the Army (CSA) is a statutory position in the United States Army held by a general officer. As the highest-ranking officer assigned to serve in the Department of the Army, the chief is the principal military advisor and ...
, General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
George C. Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (December 31, 1880 – October 16, 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the US Army under Presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry ...
, ordered Barnes to assume command as Commander, US Troops in Australia and take charge of all troops and supplies. On 22 December 1941, with the convoy's arrival in Brisbane, the command was designated as United States Forces in Australia (USFIA). It was renamed U.S. Army Forces in Australia (USAFIA) on 5 January 1942. Its mission was to create a base in Australia for the support of the forces still in the Philippines.
The staff, known as the "Remember Pearl Harbor" (RPH) group, selected by the War Department War Department may refer to:
* War Department (United Kingdom)
* United States Department of War (1789–1947)
See also
* War Office, a former department of the British Government
* Ministry of defence
* Ministry of War
* Ministry of Defence
* D ...
for USAFIA arrived Melbourne 1 February 1942 aboard and in the first large convoy bearing personnel, supplies and munitions intended for transhipment to Java and Philippines as well as Australia. For a brief time, due to the increased isolation of the Philippines and before the fall of Java, USAFIA was withdrawn from MacArthur's command and placed under the ABDA with continued direction to support both Java and the Philippines.
What would replace ADBA was the subject of discussions between the Australian and New Zealand chiefs of staff that were held in Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
between 26 February and 1 March 1942. They proposed creating a new theatre of war encompassing Australia and New Zealand, under the command of Wavell's former deputy, Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
George Brett
George Howard Brett (born May 15, 1953) is an American former professional baseball player who played all of his 21 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a third baseman for the Kansas City Royals.
Brett's 3,154 career hits are second-mo ...
, who had assumed command of the US Army Forces in Australia (USAFIA) on 25 February.
The President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
, Franklin Roosevelt, and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As modern ...
, Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
, discussed the matter of command arrangements in the Pacific in Washington, D.C., on 9 March. Roosevelt proposed that the world would be divided into British and American areas of responsibility, with the United States having responsibility for the Pacific, where there would be an American supreme commander responsible to the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, that advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and the ...
. Churchill responded favourably to the proposal, and the governments of Australia and New Zealand were then consulted. They endorsed the idea of an American supreme commander, but wanted to have some input into matters of strategy.
This resulted in the creation of the Pacific War Council, which met for the first time in London on 10 February 1942. Churchill, Clement Attlee (Deputy Prime Minister) and Anthony Eden (Foreign Secretary) represented the United Kingdom, and Earle Page
Sir Earle Christmas Grafton Page (8 August 188020 December 1961) was an Australian surgeon and politician who served as the 11th Prime Minister of Australia, holding office for 19 days after the death of Joseph Lyons in 1939. He was the leade ...
represented Australia, along with representatives from the Netherlands, New Zealand, India and China. Page was replaced as the Australian representative by Stanley Bruce
Stanley Melbourne Bruce, 1st Viscount Bruce of Melbourne, (15 April 1883 – 25 August 1967) was an Australian politician who served as the eighth prime minister of Australia from 1923 to 1929, as leader of the Nationalist Party.
Born ...
in June 1942. A parallel Pacific War Council was created in Washington, D.C., that first met on 1 April 1942. It was chaired by Roosevelt, with Richard Casey and later Owen Dixon representing Australia, and Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
Mackenzie King representing Canada. The Pacific War Council never became an effective body, and had no influence on strategy, but did allow the Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 192 ...
s to put their concerns before the President.
Formation
The obvious choice for a supreme commander in the Pacific was General Douglas MacArthur. He had been ordered to leave the Philippines for Australia to take command of a reconstituted ABDA area on 22 February 1942, and had therefore been promised the command even before there were discussions on what it should be. MacArthur had solid support from the President, the Army and the American people, but not the Navy. The Commander in Chief,United States Fleet
The United States Fleet was an organization in the United States Navy from 1922 until after World War II. The acronym CINCUS, pronounced "sink us", was used for Commander in Chief, United States Fleet. This was replaced by COMINCH in December 1941 ...
, Admiral Ernest King
Ernest Joseph King (23 November 1878 – 25 June 1956) was an American naval officer who served as Commander in Chief, United States Fleet (COMINCH) and Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) during World War II. As COMINCH-CNO, he directed the U ...
, saw the Pacific lines of communication primarily as a naval responsibility and would not yield command to an Army officer and proposed a division placing all of the Solomons within the Australian area, but excluding the New Hebrides, New Caledonia, and New Zealand. While the Army planners, led by Brigadier General Dwight Eisenhower, were willing to compromise on a divided command, they objected to placing Australia and New Zealand in separate theatres. The Joint Chiefs of Staff discussed the matter between 9 and 16 March, the result of which was a decision to adopt the Navy's plan, with only minor amendments.
While this was still going on General Marshall, had contacted Brett and asked him to get the Australian government to nominate MacArthur, whose arrival in Australia was now imminent, as its choice for supreme commander. This was done on 17 March when MacArthur arrived at Batchelor, Northern Territory
Batchelor is a town in the Northern Territory of Australia. The town is the current seat and largest town of the Coomalie Shire local government area. It is located south of the territory capital, Darwin. A number of residents commute to Dar ...
. On 24 March 1942, the Combined Chiefs of Staff issued a directive formally designating the Pacific theatre an area of American strategic responsibility. On 30 March, the Joint Chiefs of Staff divided the Pacific theatre into three areas: the Pacific Ocean Areas
Pacific Ocean Areas was a major Allied military command in the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands during the Pacific War, and one of three United States commands in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater. Admir ...
(POA), under Admiral Chester Nimitz
Chester William Nimitz (; February 24, 1885 – February 20, 1966) was a fleet admiral in the United States Navy. He played a major role in the naval history of World War II as Commander in Chief, US Pacific Fleet, and Commander in C ...
; the Southwest Pacific Area (SWPA), under MacArthur; and the Southeast Pacific Area
The Southeast Pacific Area was one of the designated area commands created by the Combined Chiefs of Staff in the Pacific region during World War II. It was responsible to the Joint Chiefs of Staff via the Commander-in-Chief of the United States ...
, which never became an active theatre. The former Anzac Area
The ANZAC Area, also called the ANZAC Command, was a short-lived (29 January – 18 April 1942) naval military command for Allied forces defending the northeast approaches to Australia including the Fiji Islands, New Hebrides, and New Caledonia d ...
was divided between SWPA and the POA.
An annex defined SWPA's boundaries:
On 17 April 1942 the Prime Minister of Australia, John Curtin
John Curtin (8 January 1885 – 5 July 1945) was an Australian politician who served as the 14th prime minister of Australia from 1941 until his death in 1945. He led the country for the majority of World War II, including all but the last few ...
, directed all Australian defence forces personnel to treat orders from MacArthur "as emanating from the Commonwealth Government". The Army's workshops and fixed fortifications, and the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(RAAF)'s logistical and training infrastructure, were not placed under SWPA. Having placed its troops at MacArthur's disposal, the Australian government was adamant that it should be consulted on any alteration to the boundaries or command arrangements in SWPA. The government was particularly concerned that the Supreme Commander should not move troops outside Australia or Australian territory without its consent, as there were legal restrictions on where the Australian Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
could serve. The matter of changes in command first came up when Brett was replaced as Commander of Allied Air Forces by the Joint Chiefs of Staff. MacArthur and Curtin agreed that there would be no change to General Sir Thomas Blamey
Field marshal (Australia), Field Marshal Sir Thomas Albert Blamey, (24 January 1884 – 27 May 1951) was an Australian general of the First World War, First and Second World Wars, and the only Australian to attain the rank of field marshal.
Bl ...
's status (as Australian Army Commander-in-Chief), and that the government would be consulted about any other proposed changes. When Vice Admiral Herbert F. Leary
Herbert Fairfax Leary (May 31, 1885 – December 3, 1957) was a highly decorated officer in the United States Navy with the rank of vice admiral. A son of Rear Admiral Richard P. Leary, he distinguished himself during World War I while on the st ...
was replaced a few months later, Curtin was consulted, and concurred with the change.
General Headquarters
MacArthur became the Supreme Commander Southwest Pacific Area (SWPA) on 18 April 1942, although he preferred to use the more conventional title of Commander in Chief. MacArthur's first General Order created five subordinate commands: Allied Land Forces, Allied Air Forces, Allied Naval Forces, United States Army Forces in Australia (USAFIA), and the United States Army Forces in the Philippines. The last command had a short life. Lieutenant General Jonathan Wainwright's United States Army Forces in the Philippines disintegrated over the following three weeks, and disappeared entirely when Wainwright surrendered on Corregidor on 6 May. MacArthur announced the composition of his staff, known as General Headquarters (GHQ) on 19 April. Major General Richard K. Sutherland became Chief of Staff; Brigadier General Richard J. Marshall, Deputy Chief of Staff; Colonel Charles P. Stivers, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-1; Colonel Charles A. Willoughby, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-2; Brigadier General
MacArthur announced the composition of his staff, known as General Headquarters (GHQ) on 19 April. Major General Richard K. Sutherland became Chief of Staff; Brigadier General Richard J. Marshall, Deputy Chief of Staff; Colonel Charles P. Stivers, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-1; Colonel Charles A. Willoughby, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-2; Brigadier General Stephen J. Chamberlin
Stephen Jones Chamberlin (23 December 1889 – 23 October 1971) was a lieutenant general in the United States Army who served during World War II as General of the Army Douglas MacArthur's Assistant Chief of Staff, G-3, the staff officer in cha ...
, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-3; Colonel Lester J. Whitlock, Assistant Chief of Staff, G-4; Brigadier General Spencer B. Akin, Signal Officer; Brigadier General Hugh J. Casey, Engineer Officer; Brigadier General William F. Marquat, Antiaircraft Officer; Colonel Burdette M. Fitch, Adjutant General; and Colonel LeGrande A. Diller, Public Relations Officer.
Although Marshall had recommended that MacArthur appoint as many Australian and Dutch officers to senior positions as possible, most of his staff was made up of US Army officers who had served under him in the Philippines. The rest, including Whitlock, Fitch and Chamberlain, had been on the staff of USAFIA. MacArthur reported to Marshall that there were no qualified Dutch officers in Australia, and that the Australian Army had a critical shortage of staff officers, which he did not wish to exacerbate. Nevertheless, several Dutch and Australian army officers, as well as some American naval officers, served in junior positions on the staff.
In July, MacArthur moved his GHQ north, from Melbourne to Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Queensland, and the third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of approximately 2.6 million. Brisbane lies at the centre of the South ...
, where it was located in the AMP Building. The original intention had been to move to Townsville
Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 180,820 as of June 2018, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland; it is unofficially considered its capital. Estimated resident population, 3 ...
, but this was found to be impractical, as Townsville lacked the communications facilities that GHQ required. The Allied Air Forces and Allied Naval Forces headquarters were co-located with GHQ in the AMP building. The Advanced Headquarters of Allied Land Forces opened at St Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindi ...
, about away. The Advanced GHQ subsequently moved to Hollandia in September 1944, Leyte
Leyte ( ) is an island in the Visayas group of islands in the Philippines. It is eighth-largest and sixth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 2,626,970 as of 2020 census.
Since the accessibility of land has be ...
in October 1944, and Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
in May 1945.
 There was a major reorganisation in April 1945 for the planned invasion of Japan. All Army forces in the Pacific were placed under MacArthur's command, including those in Nimitz's Pacific Ocean Areas. A new command was formed, Army Forces Pacific (AFPAC), with GHQ operating as the headquarters of both AFPAC and SWPA. Units in POA remained under Nimitz's operational control, and the first major formation, the
There was a major reorganisation in April 1945 for the planned invasion of Japan. All Army forces in the Pacific were placed under MacArthur's command, including those in Nimitz's Pacific Ocean Areas. A new command was formed, Army Forces Pacific (AFPAC), with GHQ operating as the headquarters of both AFPAC and SWPA. Units in POA remained under Nimitz's operational control, and the first major formation, the Tenth United States Army
The Tenth United States Army was the last army level command established during the Pacific War during World War II, and included divisions from both the U.S. Army and the U.S. Marine Corps.
History
The headquarters of the Tenth Army was formed ...
, did not pass to AFPAC control until 31 July 1945. SWPA, together with the Allied Air Forces, Allied Naval Forces and Allied Land Forces, was abolished on 2 September 1945, but GHQ remained as GHQ AFPAC.
Allied Land Forces
TheAustralian Army
The Australian Army is the principal land warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Australian Air Force. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Army (CA), wh ...
's Commander in Chief, General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
Sir Thomas Blamey
Field marshal (Australia), Field Marshal Sir Thomas Albert Blamey, (24 January 1884 – 27 May 1951) was an Australian general of the First World War, First and Second World Wars, and the only Australian to attain the rank of field marshal.
Bl ...
, was appointed Commander, Allied Land Forces, SWPA. His headquarters was the existing General Headquarters (Australia), and became known as LHQ. An Australian commander was chosen as most of the land forces were Australian. In April 1942, there were 38,000 American ground troops in SWPA and 369,000 Australian. LHQ controlled five major commands: Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Sir John Lavarack
Lieutenant General Sir John Dudley Lavarack, (19 December 1885 – 4 December 1957) was an Australian Army officer who was Governor of Queensland from 1 October 1946 to 4 December 1957, the first Australian-born governor of that state.
Early l ...
's First Army, based in Queensland; Lieutenant General Sir Iven Mackay
Lieutenant General Sir Iven Giffard Mackay, (7 April 1882 – 30 September 1966) was a senior Australian Army officer who served in both world wars.
Mackay graduated from the University of Sydney in 1904 and taught physics there fr ...
's Second Army in Victoria; Lieutenant General Gordon Bennett's III Corps in Western Australia; the Northern Territory Force under Major General Edmund Herring
Lieutenant general (Australia), Lieutenant General Sir Edmund Francis Herring, (2 September 1892 – 5 January 1982) was a senior Australian Army officer during the Second World War, Lieutenant Governor of Victoria (Australi ...
; and New Guinea Force
New Guinea Force was a military command unit for Australian, United States and native troops from the Territories of Papua and New Guinea serving in the New Guinea campaign during World War II. Formed in April 1942, when the Australian First Arm ...
under Major General Basil Morris. Between them they controlled ten Australian and two American divisions. In August 1944, the Australian Army had a strength of 463,000 men and women, and there were 173,000 US Army ground personnel in SWPA. By late 1944, there were eighteen American divisions in SWPA, while the Australian Army had just seven.
When GHQ moved up to Brisbane, LHQ remained behind in Melbourne, but Blamey formed an Advanced LHQ under his Deputy Chief of the General Staff (DCGS), Major General George Alan Vasey
Major General George Alan Vasey, (29 March 1895 – 5 March 1945) was an Australian Army officer. He rose to the rank of major general during the Second World War, before being killed in a plane crash near Cairns in 1945.
A professional soldie ...
, which moved to nearby St Lucia. Major General Frank Berryman replaced Vasey as DCGS in September 1942, and remained in the post until January 1944. He resumed the post in July 1944 and remained until December 1945. When the main body of GHQ moved to Hollandia, Advanced LHQ followed, opening there on 15 December, but when the main GHQ moved to Leyte in February 1945, Advanced LHQ remained behind. A Forward Echelon LHQ was formed under Berryman that remained co-located with the main body of GHQ, while the main body of LHQ remained at Hollandia until it moved to Morotai for the operations in Borneo in April 1945.
In practice, MacArthur controlled land operations through "task forces". These reported directly to GHQ, and their commanders could control all Allied land, air, naval and service forces in their area if a Japanese land attack was imminent. The most important of these was New Guinea Force, which was formed in 1942 and was commanded personally by Blamey in September 1942, and again in September 1943. In February 1943, Lieutenant General Walter Krueger
Walter Krueger (26 January 1881 – 20 August 1967) was an American soldier and general officer in the first half of the 20th century. He commanded the Sixth United States Army in the South West Pacific Area during World War II. He rose fr ...
's Sixth Army arrived in SWPA, and its headquarters became that of Alamo Force. Alamo Force reported directly to MacArthur, and as a result Blamey did not command of the majority of American land forces in the theatre after that time, although his post was not abolished.
In March 1944, MacArthur met with Curtin and detailed his plans for the Western New Guinea campaign
The Western New Guinea campaign was a series of actions in the New Guinea campaign of World War II. Dutch East Indies KNIL, United States and Australian forces assaulted Japanese bases and positions in the northwest coastal areas of Netherl ...
, explaining that he would assume direct command of land forces when he reached the Philippines, and suggesting that Blamey could either go with him as an army commander, or remain in Australia as Commander in Chief. The new organisation went into effect in September 1944, with Lieutenant General Walter Krueger's Sixth US Army, Lieutenant General Robert Eichelberger
Robert Lawrence Eichelberger (9 March 1886 – 26 September 1961) was a general officer in the United States Army who commanded the Eighth United States Army in the Southwest Pacific Area during World War II.
A 1909 graduate of the United ...
's Eighth United States Army
The Eighth Army is a U.S. field army which is the commanding formation of all United States Army forces in South Korea. It commands U.S. and South Korean units and is headquartered at the Camp Humphreys,Vernon Sturdee
Lieutenant General Sir Vernon Ashton Hobart Sturdee, (16 April 1890 – 25 May 1966) was an Australian Army commander who served two terms as Chief of the General Staff. A regular officer of the Royal Australian Engineers who joined the M ...
's First Australian Army, Lieutenant General Leslie Morshead
Lieutenant General Sir Leslie James Morshead, (18 September 1889 – 26 September 1959) was an Australian soldier, teacher, businessman, and farmer, whose military career spanned both world wars. During the Second World War, he led the Aust ...
's I Australian Corps and Major General Oscar Griswold
Oscar Woolverton Griswold (22 October 1886 – 28 September 1959) was a United States Army lieutenant general in the first half of the 20th century. He is best known for his command of the XIV Corps in the South Pacific Area and South West Pacifi ...
's XIV Corps 14 Corps, 14th Corps, Fourteenth Corps, or XIV Corps may refer to:
* XIV Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XIV Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army prior to and during World ...
reporting directly to GHQ.''GHQ Operations Instructions'' No. 67, 9 September 1944, Australian War Memorial: Blamey Papers, 3DRL 6643 3/102 Allied Land Forces remained as an important administrative and logistical command, until it was abolished, along with SWPA, on 2 September 1945.
Allied Air Forces
The April 1942 reorganisation that created the Allied Land Forces and Allied Naval Forces also created the Allied Air Forces under Brett. Unlike MacArthur, Brett created a completely integrated headquarters, with a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) officer, Air Vice MarshalWilliam Bostock
Air Vice Marshal William Dowling Bostock, (5 February 1892 – 28 April 1968) was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). During World War II he led RAAF Command, the Air Force's main operational formation, with resp ...
, as his chief of staff. Each United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
(USAAF) staff officer was paired with a RAAF officer, with the senior staff posts divided evenly between them. A majority of command positions were held by Australians. To make up shortages of USAAF aircrew, RAAF aircrew were assigned to USAAF air groups, serving in every role except aircraft commander.
 In May 1942, the Australian government appointed Air Vice Marshal
In May 1942, the Australian government appointed Air Vice Marshal George Jones
George Glenn Jones (September 12, 1931 – April 26, 2013) was an American country musician, singer, and songwriter. He achieved international fame for his long list of hit records, including his best-known song " He Stopped Loving Her Today", ...
as Chief of the Air Staff. He became responsible for matters other than operations, such as administration and training. It soon became clear that Jones and Bostock could not get along together, but Kenney preferred to have Bostock in operational command, and although he regarded the antipathy between Jones and Bostock as a nuisance, was happy to leave arrangements the way they were.
One of MacArthur's first orders to Brett was for a bombing mission to the Philippines, an order delivered personally by Sutherland. When Brett protested, Sutherland informed him that MacArthur wanted the mission carried out. The mission was flown by Brigadier General Ralph Royce, but MacArthur personally wrote a reprimand
A reprimand is a severe, formal or official reproof. Reprimanding takes in different forms in different legal systems. A reprimand in custody may be a formal legal action issued by a government agency or professional governing board (e.g. medical ...
to Brett. Henceforth, communications with Sutherland were handled by Bostock. Further disagreements between MacArthur and Brett followed. Meanwhile, in Washington, General George Marshall and the Chief of Army Air Forces, Lieutenant General Henry Arnold, had become alarmed at Brett's integration of the USAAF and RAAF, and disturbed by his inability to work with MacArthur. On 6 July 1942 Marshall radioed MacArthur to offer him Major General George Kenney
George Churchill Kenney (August 6, 1889 – August 9, 1977) was a United States Army general during World War II. He is best known as the commander of the Allied Air Forces in the Southwest Pacific Area (SWPA), a position he held between Augu ...
or Brigadier General Jimmy Doolittle
James Harold Doolittle (December 14, 1896 – September 27, 1993) was an American military general and aviation pioneer who received the Medal of Honor for his daring raid on Japan during World War II. He also made early coast-to-coast flights ...
as a replacement for Brett; MacArthur selected Kenney.
Kenney sent home Major General Royce, Brigadier Generals Edwin S. Perrin, Albert Sneed and Martin Scanlon, and about forty colonels. In Australia he found two talented, recently arrived brigadier generals, Ennis Whitehead
Ennis Clement Whitehead (September 3, 1895 – October 12, 1964) was an early United States Army aviator and a United States Army Air Forces general during World War II. Whitehead joined the U. S. Army after the United States entered World War I ...
and Kenneth Walker. Kenney reorganised his command in August, appointing Whitehead as commander of the V Fighter Command
The V Fighter Command is a disbanded United States Air Force headquarters. It was established as the 2nd Interceptor Command in June 1941, with responsibility for air defense of the northwest United States and training fighter units in its are ...
and Walker as commander of the V Bomber Command
The V Bomber Command is an inactive United States Army Air Forces unit. It was last assigned to Fifth Air Force, based at Irumagawa AB, Japan. It was inactivated on 31 May 1946.
During World War II the unit initially controlled Fifth Air Forc ...
. Allied Air Forces was composed of both USAAF and RAAF personnel, and Kenney moved to separate them. Brigadier General Donald Wilson arrived in September and replaced Air Vice Marshal Bostock as Kenney's chief of staff, while Bostock took over the newly created RAAF Command. Walker was shot down over Rabaul in January 1943. His successor, Brigadier General Howard Ramey, disappeared in March 1943.
Kenney deviated from the normal structure of an air force by creating the Advanced Echelon (ADVON) under Whitehead. The new headquarters had the authority to alter the assignments of aircraft in the forward area, where fast-changing weather and enemy action could invalidate orders drawn up in Australia. He created the 1st, 2nd and 3rd Air Task Forces to control air operations in a forward area for a specific mission, another departure from doctrine. While Kenney was enthusiastic about this innovation, Washington did not like it and, over Kenney's objections, converted the three air task forces into the 308th, 309th and 310th Bombardment Wing
31 may refer to:
* 31 (number)
Years
* 31 BC
* AD 31
* 1931 CE ('31)
* 2031 CE ('31)
Music
* ''Thirty One'' (Jana Kramer album), 2015
* ''Thirty One'' (Jarryd James album), 2015
* "Thirty One", a song by Karma to Burn from the album '' ...
s. In June 1944, Major General St. Clair Streett's Thirteenth Air Force
The Thirteenth Air Force (Air Forces Pacific) (13 AF) was a numbered air force of the United States Air Force Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It was last headquartered at Hickam Air Force Base on the island of Oahu, Hawaii. 13 AF has never been sta ...
was added to the Allied Air Forces. Kenney created the Far East Air Forces (FEAF) from his Fifth Air Force headquarters, while ADVON became the Fifth Air Force under Whitehead. The RAAF formed the Australian First Tactical Air Force
The Australian First Tactical Air Force (No. 1 TAF) was formed on 25 October 1944 by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Its purpose was to provide a mobile force of fighter and ground attack aircraft that could support Allied army and n ...
under Air Commodore Harry Cobby
Air Commodore Arthur Henry Cobby, (26 August 1894 – 11 November 1955) was an Australian military aviator. He was the leading fighter ace of the Australian Flying Corps during World War I, with 29 victories, despite seeing active servic ...
in October 1944, and when MacArthur became commander of all Army forces in the Pacific, the Seventh Air Force
The Seventh Air Force (Air Forces Korea) (7 AF) is a Numbered Air Force of the United States Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It is headquartered at Osan Air Base, South Korea.
The command's mission is to plan and direct air component operations in ...
was added as well. Major General Paul Wurtsmith
Paul Bernard Wurtsmith (9 August 1906 – 13 September 1946) was a United States Army Air Forces general during World War II.
Enlisting in the United States Army Air Corps as a flying cadet in 1927, Wurtsmith was commissioned in 1928. Over the n ...
replaced Streett in March 1945, and Air Commodore Frederick Scherger
Air Chief Marshal (Australia), Air Chief Marshal Sir Frederick Rudolph William Scherger, (18 May 190416 January 1984) was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). He served as Chief of Air Force (Australia), Chief ...
replaced Cobby in May. Allied Air Forces was abolished on 2 September 1945.
Allied Naval Forces
Vice Admiral Leary was appointed Commander, Allied Naval Forces, in April 1942. On 7 February 1942, he had become commander of the Anzac Area to the east of Australia extending to include Fiji with headquarters in Melbourne. That command included a naval element, some air forces but without responsibility for land defense. He was answerable directly to Admiral King. The most important force under his command was Rear AdmiralJohn Gregory Crace
Vice Admiral Sir John Gregory Crace (6 February 1887 – 11 May 1968) was an Australian who came to prominence as an officer of the Royal Navy (RN). He commanded the Australian-United States Support Force, Task Force 44, at the Battle of the C ...
's Anzac Squadron
The ANZAC Squadron, also called the ''Allied Naval Squadron'', was an Allied naval warship task force which was tasked with defending northeast Australia and surrounding area in early 1942 during the Pacific Campaign of World War II. The squadr ...
. When SWPA and the Allied Naval Forces were formed in April 1942, Leary also became Commander, Southwest Pacific Force (COMSOUWESPAC), while Crace's Anzac Squadron became Task Force 44
Task Force 44 was an Allied naval task force during the Pacific Campaign of World War II. The task force consisted of warships from the United States Navy and the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). It was generally assigned as a striking force to ...
. In June, Crace was succeeded by another Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
officer, Rear Admiral Victor Crutchley
Admiral Sir Victor Alexander Charles Crutchley (2 November 1893 – 24 January 1986) was a British naval officer.
He was a First World War recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be ...
. The former Anzac Area was divided so that the Australian coastal waters were with SWPA and the sea and air lines of communication from Hawaii and North America fell in the Pacific Ocean Areas (POA) with a special provision for the South Pacific Area
The South Pacific Area (SOPAC) was a multinational U.S.-led military command active during World War II. It was a part of the U.S. Pacific Ocean Areas under Admiral Chester Nimitz.
The delineation and establishment of the Pacific Ocean Areas was ...
having a designated sub commander under Admiral Chester Nimitz
Chester William Nimitz (; February 24, 1885 – February 20, 1966) was a fleet admiral in the United States Navy. He played a major role in the naval history of World War II as Commander in Chief, US Pacific Fleet, and Commander in C ...
.
With the agreement of the Australian government, Leary was succeeded as Commander, Southwest Pacific Force, and Commander, Allied Naval Forces, by Vice Admiral Arthur S. Carpender
Arthur Schuyler Carpender (24 October 1884 – 10 January 1960) was an American admiral who commanded the Allied Naval Forces in the Southwest Pacific Area during World War II.
A 1908 graduate of the United States Naval Academy, Carpender sa ...
on 11 September 1942. Like his predecessor, he reported to King in the former role, and MacArthur in the latter. Also like Leary, Carpender was not the most senior naval officer in the theatre, as the Royal Australian Navy
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the principal naval force of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (CN) Vice Admiral Mark Hammond AM, RAN. CN is also jointly responsible to the Minister of ...
Chief of the Naval Staff (CNS), Admiral Sir Guy Royle
Guy or GUY may refer to:
Personal names
* Guy (given name)
* Guy (surname)
* That Guy (...), the New Zealand street performer Leigh Hart
Places
* Guy, Alberta, a Canadian hamlet
* Guy, Arkansas, US, a city
* Guy, Indiana, US, an unin ...
, and the Royal Netherlands Navy′s Vice Admiral Conrad Helfrich were both senior to him. However, Royle agreed to serve under Carpenter as Commander, South West Pacific Sea Frontier, which was formed on 16 March 1943.
The Southwest Pacific Force was renamed the Seventh Fleet
The Seventh Fleet is a numbered fleet of the United States Navy. It is headquartered at U.S. Fleet Activities Yokosuka, in Yokosuka, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is part of the United States Pacific Fleet. At present, it is the largest of ...
on 15 March 1943, and its task forces were renumbered to match, so Task Force 44 became Task Force 74
Task Force 74 was a naval task force that has existed twice. The first Task Force 74 was a mixed Allied force of Royal Navy, Royal Australian Navy, and United States Navy ships which operated against Japanese forces from 1943 to 1945 during th ...
. Another important component was Task Force 76
Expeditionary Strike Group SEVEN/Task Force 76 (Amphibious Force U.S. SEVENTH Fleet) is a United States Navy task force. It is part of the United States Seventh Fleet and the USN's only permanently forward-deployed expeditionary strike group ...
, the Amphibious Force, Southwest Pacific, which had been formed under Rear Admiral Daniel Barbey
Vice Admiral Daniel Edward Barbey (23 December 1889 – 11 March 1969) was an officer in the United States Navy who served in World War I and World War II. A graduate of the Naval Academy, he participated in the 1912 United States occupation of ...
on 8 January 1943. It became the VII Amphibious Force later in the year. A training centre, was established at Port Stephens, New South Wales, and another at Toorbul Point, Queensland. The VII Amphibious Forces initially consisted of the Australian Landing Ships, Infantry , and and the American attack transport
Attack transport is a United States Navy ship classification for a variant of ocean-going troopship adapted to transporting invasion forces ashore. Unlike standard troopships – often drafted from the merchant fleet – that rely on ...
, but gradually grew in size as more landing craft and landing ships arrived.
MacArthur was annoyed at the way that Royle, a Royal Navy officer, communicated directly with the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
; he was also aware that Royle had been critical of SWPA's command arrangements, and of some of his decisions. MacArthur proposed that an Australian officer, Captain John Collins, replace Royle as CNS, an appointment that Carpender also supported. Over the Admiralty's objections, Curtin appointed Collins to replace Crutchley as Commander, Task Force 44, in June 1944, at the rank of commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ''Kommodore''
* Air commodore ...
, with the intention that Collins would replace Royle when his term expired. This did not occur, because Collins was seriously wounded in Leyte Gulf
Leyte Gulf is a gulf in the Eastern Visayan region in the Philippines. The bay is part of the Philippine Sea of the Pacific Ocean, and is bounded by two islands; Samar in the north and Leyte in the west. On the south of the bay is Mindanao ...
on 21 October 1944.
MacArthur did not get along with Carpender, and twice asked for him to be replaced, only to be embarrassed in November 1943 when King replaced Carpender with Vice Admiral Thomas C. Kinkaid without informing MacArthur or seeking the approval of the Australian government. However, a face-saving formula was agreed upon. For the invasion of Leyte
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
, the Seventh Fleet was massively reinforced by ships from the Pacific Fleet. Cover was provided by Admiral William F. Halsey's Third Fleet
The United States Third Fleet is one of the numbered fleets in the United States Navy. Third Fleet's area of responsibility includes approximately fifty million square miles of the eastern and northern Pacific Ocean areas including the Bering ...
, which remained under Nimitz. At the Battle of Leyte Gulf, the divided command brought the Allies to the brink of disaster when misunderstandings arose between Kinkaid and Halsey. Allied Naval Forces was abolished, along with SWPA, on 2 September 1945.
U.S. Army Services of Supply
Under U.S. Army Forces in Australia (USAFIA) a series of bases had gradually been built in Australia, initially to support the US forces in the Philippines. Seven base sections were established in Australia to operate under USAFIA: Base Section 1 atBirdum, Northern Territory
Birdum is a locality in the Northern Territory of Australia located about south of the territory capital of Darwin.
History Railway
Birdum was the terminus of the North Australia Railway from 1929 until the outbreak of World War II.
While ...
; Base Section 2 in Townsville; Base Section 3 in Brisbane; Base Section 4 in Melbourne; Base Section 5 in Adelaide; Base Section 6 in Perth; and Base Section 7 in Sydney. On 20 July USAFIA became the United States Army Services of Supply
The Services of Supply or "SOS" branch of the Army of the USA was created on 28 February 1942 by Executive Order Number 9082 "Reorganizing the Army and the War Department" and War Department Circular No. 59, dated 2 March 1942. Services of Supp ...
, Southwest Pacific Area (USASOS SWPA), under the command of Brigadier General Richard J. Marshall, and Barnes returned to the United States.
 When Lieutenant General Krueger's
When Lieutenant General Krueger's Sixth United States Army
Sixth Army is a theater army of the United States Army. The Army service component command of United States Southern Command, its area of responsibility includes 31 countries and 15 areas of special sovereignty in Central and South America and ...
headquarters arrived in Australia in February 1943, the administrative functions were taken from USASOS and given to a new headquarters, United States Army Forces in the Far East
United States Army Forces in the Far East (USAFFE) ( Filipino: ''Hukbong Katihan ng Estados Unidos sa Malayong Silangan/HKEUMS''; Spanish: ''Fuerzas del Ejército de los Estados Unidos en el Lejano Oriente'') was a military formation of the Unit ...
(USAFFE), under MacArthur's command. This had the same name as MacArthur's old headquarters in the Philippines, but its function was different. This left USASOS with logistical responsibilities only. The new arrangement was awkward, and required considerable adjustment before it functioned properly. In September 1943, Marshall was replaced by Brigadier General James L. Frink.
The New Guinea Advanced Base was formed in Port Moresby
(; Tok Pisin: ''Pot Mosbi''), also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the largest cities in the southwestern Pacific (along with Jayapura) outside of Australia and New ...
in August 1942, and sub bases were created at Milne Bay and Oro Bay. These became Advanced Sub Base A and Advanced Sub Base B respectively in April 1943. Advanced Sub Base C was created on Goodenough Island
Goodenough Island in the Solomon Sea, also known as Nidula Island, is the westernmost of the three large islands of the D'Entrecasteaux Islands in Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. It lies to the east of mainland New Guinea and southwest ...
in April 1943, but was discontinued when the island was handed over to Sixth Army control in July. Meanwhile, Advanced Sub Base D was formed at Port Moresby in May. The sub bases became bases in August 1943. Advanced Base E was formed at Lae and Advanced Base F at Finschhafen
Finschhafen is a town east of Lae on the Huon Peninsula in Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea. The town is commonly misspelt as Finschafen or Finschaven. During World War II, the town was also referred to as Fitch Haven in the logs of some U.S ...
in November 1943, followed by Bases G and H at Hollandia and Biak
Biak is an island located in Cenderawasih Bay near the northern coast of Papua, an Indonesian province, and is just northwest of New Guinea. Biak is the largest island in its small archipelago, and has many atolls, reefs, and corals.
The large ...
respectively.
With a worldwide shipping crisis and SWPA being at the end of a very long supply line, as well as being a region without well developed transportation nets, regional logistics were almost entirely dependent on water transport. No one fleet composed the assets available to the Commander in Chief, SWPA as the U. S. Navy, Royal Navy, Royal Australian Navy, Australian Army, Netherlands East Indies Navy were under his operational command while being maintained under their respective organizations. Those assets were inadequate resulting in the creation of a large Army fleet unique to SWPA, the Permanent Local Fleet, under first USFIA, later USASOS and finally Army Forces, Western Pacific (AFWESPAC), starting with the retention of the , and from the convoy diverted to Brisbane in December 1941.
That core was augmented by vessels fleeing the Japanese advance, particularly twenty-one Dutch vessels later known as the "KPM vessels" after the Dutch shipping line's name, Koninklijke Paketvaart-Maatschappij
Koninklijke Paketvaart-Maatschappij (Dutch for Royal Packet Navigation Company), better known as KPM, was a Dutch shipping company (1888–1966) in the Netherlands East Indies, now Indonesia. It was the dominant inter-island shipping line in Indo ...
. As of 28 April 1942 the Army fleet had grown to twenty-eight ships and by 24 January 1945 that fleet of large ships exceeded ninety with a peak of ninety-eight by 1 August 1945. That number did not count a much larger fleet of small vessels, ranging from landing craft, barges and other floating equipment to seagoing vessels under 1,000 tons, including the Small Ships Section of requisitioned and locally constructed (2,712 craft) vessels manned largely by Australian civilian employees, 1,719 as of June 1945, of the U.S. Army, and many such vessels and floating equipment delivered from the United States. The permanent fleet of SWPA almost had as many vessels as the Army’s general fleet during some periods, though those vessels were often small, obsolete, in poor condition and under unorthodox management in comparison.
As the Allied forces advanced, new bases were formed, and the old ones in Australia were closed. Base Sections 5 and 6 were closed in January 1943, and Base Section 4 in June 1944. The remaining four became bases, and a Base Section was formed in Brisbane to control them. Bases 1 and 3 were closed in December 1944, leaving only Bases 2 and 7. These were deactivated in June 1945 and their functions absorbed by the Australia Base Section, as the Base Section had been renamed in February 1945. In New Guinea, Base D was closed in July 1945, and Bases A, B and E in September, leaving Bases F, G and H. Meanwhile, a series of bases were opened in the Philippines: Base K on Leyte, Base M on Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
, Base R at Batangas
Batangas, officially the Province of Batangas ( tl, Lalawigan ng Batangas ), is a province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region on Luzon. Its capital is the city of Batangas, and is bordered by the provinces of Cavite and La ...
, Base S on Cebu
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 16 ...
and base X at Manila. These came under the Luzon Base Section, which was redesignated the Philippine on 1 April 1945. On 7 June 1945, USASOS became AFWESPAC, under the command of Lieutenant General Wilhelm D. Styer, and it absorbed USAFFE.
Intelligence
In April 1942, Brigadier General Spencer Akin and his Australian counterpart at LHQ, Major General Colin Simpson, agreed to pool their resources and establish a combined intelligence organisation, known as theCentral Bureau The Central Bureau was one of two Allied signals intelligence (SIGINT) organisations in the South West Pacific area (SWPA) during World War II. Central Bureau was attached to the headquarters of the Allied Commander of the South West Pacific area ...
. The Australian, British, and US Armies, as well as the RAAF and the RAN all supplied personnel for this formation, which worked on codebreaking
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic sec ...
and decrypting Japanese message traffic. This Magic
Magic or Magick most commonly refers to:
* Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces
* Ceremonial magic, encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic
* Magical thinking, the belief that unrela ...
and Ultra
adopted by British military intelligence in June 1941 for wartime signals intelligence obtained by breaking high-level encrypted enemy radio and teleprinter communications at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park. ' ...
intelligence was vitally important to operations in SWPA.
To handle other forms of intelligence, Blamey and MacArthur created the Allied Intelligence Bureau
The Allied Intelligence Bureau (AIB) was a joint United States, Australian, Dutch and British intelligence and special operations agency during World War II. It was responsible for operating parties of spies and commandos behind Japanese lines ...
(AIB). This included the Services Reconnaissance Department
Services Reconnaissance Department (SRD), also known as Special Operations Australia (SOA) and previously known as Inter-Allied Services Department (ISD), was an Australian military intelligence and special reconnaissance unit, during World War II. ...
with its Z Special Unit
Z Special Unit () was a joint Allied special forces unit formed during the Second World War to operate behind Japanese lines in South East Asia. Predominantly Australian, Z Special Unit was a specialist reconnaissance and sabotage unit that i ...
that carried out special operations like Operation Jaywick
Operation Jaywick was a special operation undertaken in World War II. In September 1943, 14 commandos and sailors from the Allied Z Special Unit raided Japanese shipping in Singapore Harbour, sinking six ships.
Background
Special Operations ...
; Secret Intelligence Australia
{{Use British English, date=December 2014
Secret Intelligence Australia (SIA) was a British World War II intelligence unit commanded by Captain Roy Kendall who reported directly to MI6 in London. SIA was known as Section B of the Allied Intellige ...
; the Coastwatchers
The Coastwatchers, also known as the Coast Watch Organisation, Combined Field Intelligence Service or Section C, Allied Intelligence Bureau, were Allied military intelligence operatives stationed on remote Pacific islands during World War II ...
, who watched for Japanese aircraft and ships from observation posts behind Japanese lines; and the propaganda specialists of the Far Eastern Liaison Office The Far Eastern Liaison Office (FELO) was a Second World War Propaganda and Field Intelligence unit set up under the orders of the Allied Land Commander, General Sir Thomas Blamey, on 19 June 1942. FELO became one of four sections of the Allied Inte ...
(FELO). Two other important combined organisations, not part of AIB, were the Allied Translator and Interpreter Section (ATIS), which translated Japanese documents, and the Allied Geographical Section
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or sovereign state, states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alli ...
, which prepared maps and charts, and drafted appreciations of the terrain.
Since quality tended to be more important than quantity in intelligence, this proved to be a fruitful field in which the minor Allies, Australia and the Netherlands, could play a key part. Good intelligence enabled the Allied forces to minimise the risk of failures and maximise the chances of success. Moreover, the organisation built up in Australia proved to be useful after the war as well. David Horner later wrote that "it may prove that present day intelligence cooperation has proved to be the most lasting and important legacy of Australia's experience of coalition warfare in the Second World War."
Legacy
The Allied command structure in the South West Pacific Area faced the challenges of coalition warfare in several ways, with varying degrees of success. The benefits of the wartime alliances proved to be substantial, but required constant effort to maintain. For Australia and New Zealand, coalition warfare became the norm, and the experience in SWPA proved to be a formative and informative one, with many political and military lessons. Over the following decades, Australian, New Zealand and American forces would fight together again, in theKorean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
, Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
and the War on Terror
The war on terror, officially the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT), is an ongoing international counterterrorism military campaign initiated by the United States following the September 11 attacks. The main targets of the campaign are militant ...
.
Footnotes
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* {{Cite book , last=Dean , first=Peter , title=MacArthur's Coalition: US and Australian Operations in the Southwest Pacific Area, 1942-1945 , date=2018 , location= Lawrence, Kansas , publisher=University Press of Kansas , isbn=978-0-7006-2605-2 , oclc = 1012716132 Allied commands of World War II South West Pacific theatre of World War II Queensland in World War II