|
Western New Guinea Campaign
The Western New Guinea campaign was a series of actions in the New Guinea campaign of World War II. Dutch East Indies KNIL, United States and Australian forces assaulted Japanese bases and positions in the northwest coastal areas of Netherlands New Guinea and adjoining parts of the Australian Territory of New Guinea. The campaign began with Operations Reckless and Persecution, which were amphibious landings by the U.S. I Corps at Hollandia and Aitape on 22 April 1944. Fighting in western New Guinea continued until the end of the war. Major battles and sub-campaigns *Landing at Aitape * Battle of Hollandia * Battle of Wakde * Battle of Lone Tree Hill * Battle of Morotai * Battle of Biak * Battle of Noemfoor * Battle of Driniumor River * Battle of Sansapor * Aitape-Wewak campaign See also * Operation Semut * Operation Agas * Naval Base Borneo * US Naval Advance Bases *List of Royal Australian Navy bases The following is a list of current and former commissioned base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jayapura
Jayapura (formerly Dutch: ''Hollandia'') is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of . The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso Bay to the north, the sovereign state of Papua New Guinea to the east, Keerom Regency to the south, and Jayapura Regency to the west. With a population of 398,478 according to the 2020 census, Jayapura is the most populous city in the entire island of New Guinea, surpassing Port Moresby, the national capital of Papua New Guinea. It is also the fastest-growing city in Indonesia, with the population increasing by 55.23% since the previous census in 2010. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 404,004. Jayapura is the fourth largest city by economy in Eastern Indonesia—after Makassar, Denpasar, and Manado—with an estimated 2016 GDP at Rp19.48 trillion. As of 2017, it is also the second-most expensive Indonesian city to liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Semut
Operation Semut was a series of reconnaissance operations carried out by Australia's Z Special Unit in 1945, during the final stages of World War II. This operation was the part of the Borneo Campaign, and was undertaken in Sarawak, northwestern Borneo, in support of Allied operations to secure North Borneo. Another closely related operation codenamed Agas was carried out concurrently in North Borneo (present day Sabah). Both operations combined and relayed their intelligence through the Stallion Project to Australian forces and carried out guerrilla warfare against the Japanese in the region with the full support of the local population. A total of four operations were undertaken under the auspices of Operation Semut, concluding in September and October 1945. Background Early in the Pacific War, the Japanese had landed in north-west Borneo and had quickly captured the area's vital oilfields, which had begun contributing to their war effort by 1943. Allied efforts to interdict t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
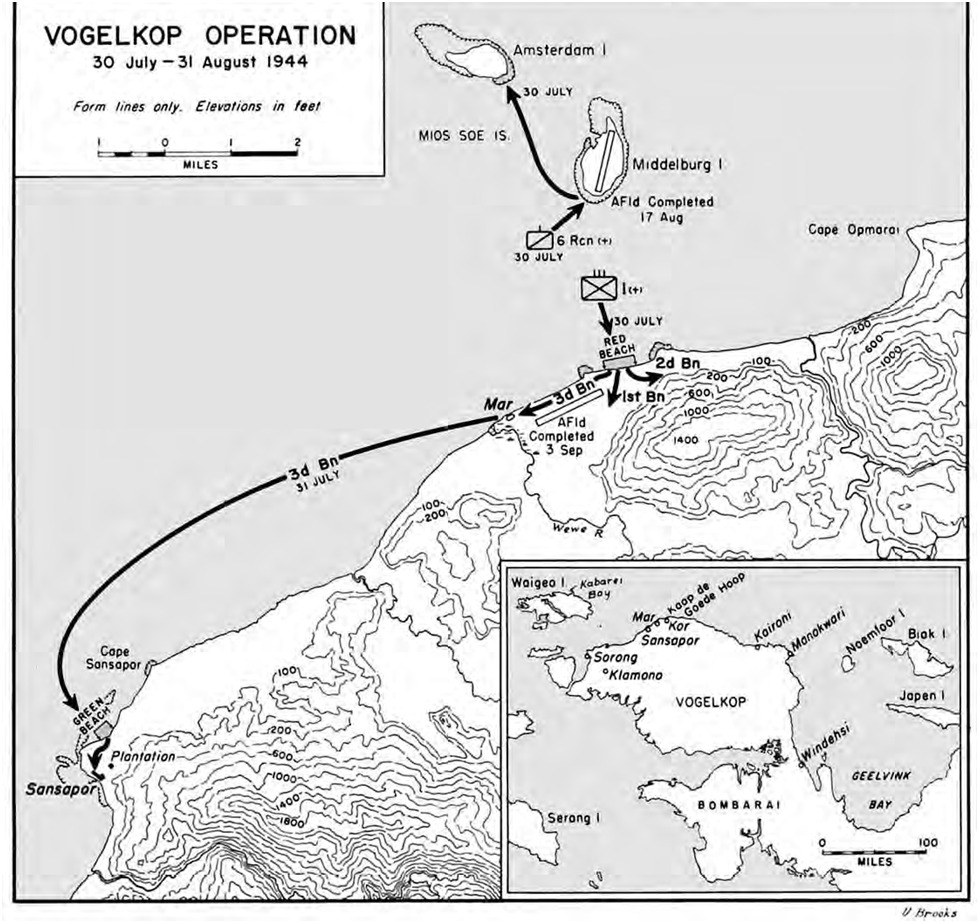
Battle Of Sansapor
The Battle of Sansapor (Operation Globetrotter) was an amphibious landing and subsequent operations around Sansapor, Dutch New Guinea on the Vogelkop Peninsula during World War II. Naval force Admiral William Fechteler's Attack Force (Task Force 77) was to have a D-Day groupment comprising 11 destroyers, 5 APDs, 16 LCIs, 3 rocket LCIs, 8 LSTs, 4 PCs, and 1 ATF. A Covering Force (Task Force 78), consisting of 1 heavy cruiser, 2 light cruisers, and 9 destroyers under the command of Admiral Russell Berkey, was to be available for support fire if needed. In preparation for Operation Typhoon (code name for the US Army landings on the Vogelkop Peninsula), on 17 June 1944, S-47, under Lieutenant Lloyd V. Young, sailed from the Admiralty Islands for Waigeo, with the mission to insert elements of the Alamo Scouts, Allied Intelligence Bureau agents, terrain experts of the Fifth Air Force, and hydrographic survey men of the VII Amphibious Force. The reconnaissance force landed near S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Driniumor River
The Battle of Driniumor River, also known as the Battle of Aitape, 10 July – 25 August 1944, was part of the Western New Guinea campaign of World War II. During the fighting, Japanese forces launched several attacks on United States forces on the Driniumor River, near Aitape in New Guinea, over the course of several weeks with the intention of retaking Aitape. After making some initial gains, the Japanese attack was contained and eventually turned back having suffered heavy casualties. The battle should not be confused with Operation Persecution, which included amphibious landings near Aitape in April 1944, or the Aitape–Wewak campaign, which began in November that year. Background The Driniumor River lies approximately east of Aitape on the north coast of what was part of the Territory of New Guinea at the time of the battle. During 1942 the Japanese had occupied much of New Guinea, but throughout 1943 the Allies had slowly gained the ascendency. By early 1944, the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Noemfoor
The Battle of Noemfoor was part of the New Guinea campaign of World War II. It took place on the island of Noemfoor, in Dutch New Guinea (now Papua, in Indonesia), between 2 July and 31 August 1944. During the battle, Allied forces landed on the island to capture Japanese bases as part of their advance through the Pacific towards the Philippines. The initial landing was largely unopposed and the Japanese defenders withdrew inland as the US troops came ashore. Sporadic fighting took place over the course of two months as the Allies secured the three airfields on the island and pushed the surviving Japanese troops to the southeastern coast. The island was later used by the Allies to support operations around Sansapor and on Morotai. Background Geography and strategic situation Noemfoor is an elliptical, almost circular shape. It is approximately in diameter and encircled by coral reefs. The landscape is dominated by limestone and coral terraces, topped by a tall hill, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Biak
The Battle of Biak was part of the Western New Guinea campaign of World War II, fought between the United States Army and the Imperial Japanese Army, Japanese Army from 27 May to 17 August 1944. Taking place on the island of Biak, in Geelvink Bay, in present-day Indonesia, it was part of General Douglas MacArthur's South West Pacific Area (command), South West Pacific Area's offensive drive to clear New Guinea in preparation for an invasion of the Philippines. It was the first major effort by the Japanese to allow uncontested landings for the purpose of creating a kill zone inland. The main Allied objective was to capture the island so that they could construct airfields there. The battle resulted in the capture of the island by Allied forces, which were then used to support operations elsewhere in the Pacific. Background The island of Biak forms part of the Schouten Islands, and dominates the entrance to Geelvink Bay, near the western end of New Guinea; its terrain and location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Morotai
The Battle of Morotai, part of the Pacific War, began on 15 September 1944, and continued until the end of the war in August 1945. The fighting started when United States and Australian forces landed on the southwest corner of Morotai, a small island in the Netherlands East Indies (NEI), which the Allies needed as a base to support the liberation of the Philippines later that year. The invading forces greatly outnumbered the island's Japanese defenders and secured their objectives in two weeks. Japanese reinforcements landed on the island between September and November, but lacked the supplies needed to effectively attack the Allied defensive perimeter. Intermittent fighting continued until the end of the war, with the Japanese troops suffering heavy loss of life from disease and starvation. Morotai's development into an Allied base began shortly after the landing, and two major airfields were ready for use in October. These and other base facilities played an important role in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lone Tree Hill
The Battle of Lone Tree Hill, is the name given to a major battle in 1944 in Dutch New Guinea, between United States and Japanese forces. Fought over the period 17 May – 2 September 1944, the battle formed part of the Western New Guinea campaign. The battle, with the associated attacks on Sawar Airfield to the north and Wakde, an island just off shore of Toem to the south, took place after the opening phase of the campaign, which saw landings at Hollandia and the Aitape in late April. Following the loss of Hollandia, to the east, in April 1944, the of coastline and surrounding area of Toem-Wakde- Sarmi was an isolated coastal salient for the Japanese. Nevertheless, elements of the Japanese 223rd and 224th Infantry Regiments, commanded by Lieutenant General Hachiro Tagami, were concentrated at Lone Tree Hill, overlooking Maffin Bay, and were blocking any further advance toward Sarmi, by the 158th Regimental Combat Team of the U.S. Army. The Japanese were in well-prepared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wakde
The Battle of Wakde ''(Operation Straight Line)'' was part of the New Guinea campaign of World War II. It was fought between the United States and Japan from 17 May 1944 to 21 May 1944 in Dutch New Guinea (now Papua, in Indonesia). The operation involved an assault on the Japanese-held Wakde island group by a reinforced US infantry battalion, which was transported from a beachhead the Allied troops had established around Arara, on the mainland, the previous day. Following the capture of the island, fighting on the mainland continued until September as Allied troops advanced west towards Sarmi. In the aftermath, the island's airbase was expanded and used to support operations around Biak and in the Marianas. Background Wakde is an island group, which lies two miles off the northeastern coast of Western New Guinea. It consists of two islands: Insoemoar and Insoemanai. Of these, Insoemoar is the largest, although it is only long, and lies on the outer side of the smaller island, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hollandia
The Battle of Hollandia (code-named Operation Reckless) was an engagement between Allies of World War II and Japanese forces during World War II. The majority of the Allied force was provided by the United States, with the bulk of two United States Army infantry divisions being committed on the ground. Air and naval support consisted largely of U.S. assets, although Australia also provided air support during preliminary operations and a naval bombardment force. The battle took place between 22 April and 6 June 1944 and formed part of the New Guinea campaign. The operation consisted of two landings, one at Tanahmerah Bay and the other at Humboldt Bay, near Hollandia. The landings were undertaken simultaneously with the amphibious invasion of Aitape ("Operation Persecution") to the east. The battle was an unqualified success for the Allied forces, resulting in a withdrawal by the Japanese to a new strategic defense line in the west of New Guinea and the abandonment of all pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Topography.png)


