south Yemen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
South Yemen ( ar, اليمن الجنوبي, al-Yaman al-Janubiyy), officially the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (, ), also referred to as Democratic Yemen (, ) or Yemen (Aden) (, ), was a
 Unlike the early decades of
Unlike the early decades of
 Since 2007, some Southerners have been actively protesting for independence, in a movement known as 'Al Hirak' or the Southern Movement. During the Yemen Civil War 2015, in response to incursions by the Houthis and military forces loyal to deposed Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, members of the Southern Movement formed 'Popular Resistance' militias. Since the Battle of Aden, these armed groups have sought to defend the South against Houthi/Saleh attempts to take over the country and have taken the current state of civil war as an opportunity to further their struggle for independence.
In late January 2018, separatists loyal to the Southern Transitional Council successfully seized control of the Saudi-backed Yemeni government headquarters in Aden in an apparent
Since 2007, some Southerners have been actively protesting for independence, in a movement known as 'Al Hirak' or the Southern Movement. During the Yemen Civil War 2015, in response to incursions by the Houthis and military forces loyal to deposed Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, members of the Southern Movement formed 'Popular Resistance' militias. Since the Battle of Aden, these armed groups have sought to defend the South against Houthi/Saleh attempts to take over the country and have taken the current state of civil war as an opportunity to further their struggle for independence.
In late January 2018, separatists loyal to the Southern Transitional Council successfully seized control of the Saudi-backed Yemeni government headquarters in Aden in an apparent
South Yemen Anthem (1969–1979)
communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the Ideology of the Communist Party of the Soviet U ...
that existed from 1967 to 1990 as a state in the Middle East in the southern and eastern provinces of the present-day Republic of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and sh ...
, including the island of Socotra
Socotra or Soqotra (; ar, سُقُطْرَىٰ ; so, Suqadara) is an island of the Republic of Yemen in the Indian Ocean, under the ''de facto'' control of the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council, a secessionist participant in Yemen� ...
.
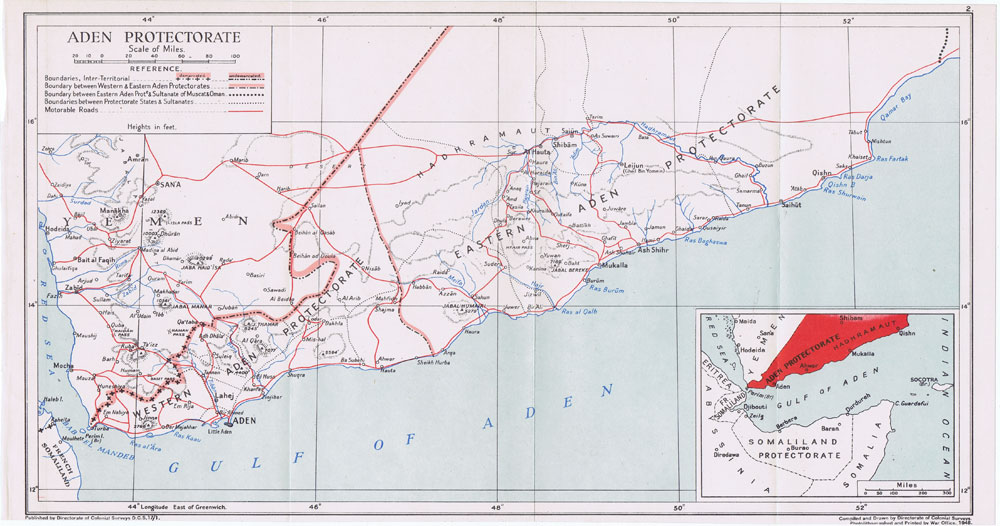
South Yemen's origins can be traced to 1874 with the creation of the British Colony of Aden and the Aden Protectorate, which consisted of two-thirds of the present-day Yemen. Prior to 1937 what was to become the Colony of Aden had been governed as a part of British India, originally as the Aden Settlement subordinate to the Bombay Presidency and then as a Chief Commissioner's province. After the collapse of Aden Protectorate, a state of emergency was declared in 1963, when the National Liberation Front (NLF) and the Front for the Liberation of Occupied South Yemen
The Front for the Liberation of Occupied South Yemen (FLOSY; ) was an Arab nationalist military organization operating in the Federation of South Arabia (a British protectorate; now Southern Yemen) in the 1960s. As the British tried to exit, ...
(FLOSY) rebelled against the British rule.
The Federation of South Arabia and the Protectorate of South Arabia merged to become the People's Republic of Yemen on 30 November 1967, which later changed its name to the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen. It became a Marxist–Leninist one-party state
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system, or single-party system is a type of sovereign state in which only one political party has the right to form the government, usually based on the existing constitution. All other parties ...
in 1969 and was supported by Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. It was the only communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the Ideology of the Communist Party of the Soviet U ...
to be established in the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
. Despite its efforts to bring stability into the region, it was involved in a brief civil war in 1986. Following the collapse of the USSR, South Yemen was unified with the Yemen Arab Republic, commonly known as "North Yemen", on 22 May 1990 to form the present-day Republic of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and sh ...
. After three years, however, a political crisis arose between the South's YSP and the North's GPC and Islah
Islah or Al-Islah (الإصلاح ,إصلاح, ') is an Arabic word, usually translated as "reform", in the sense of "to improve, to better, to put something into a better position, fundamentalism, correction, correcting something and removing v ...
parties after the parliamentary elections in 1993. South Yemen declared its secession from the North Yemen in 1994 as the Democratic Republic of Yemen
The Democratic Republic of Yemen ( '), colloquially known as South Yemen, was a breakaway state that fought against Yemen Arab Republic in the 1994 Yemeni Civil War. It was declared in May 1994 and covered all of the former South Yemen.
Th ...
. This effort ended after North Yemen occupied the area as a result of the 1994 civil war. Another attempt to restore South Yemen as a nation, with the Southern Transitional Council as its new government, began in 2017 as part of the 2014 Yemeni Civil War.
History
British rule
In 1838, Sultan Muhsin Bin Fadl of the state of Lahej ceded including Aden to the British. On 19 January 1839, the British East India Company landedRoyal Marines
The Corps of Royal Marines (RM), also known as the Royal Marines Commandos, are the UK's special operations capable commando force, amphibious light infantry and also one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy. The Corps of Royal Marine ...
at Aden to occupy the territory and stop attacks by pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
s against British shipping to India. It then became an important trading hub between British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
, and following the opening of the Suez canal in 1869, it became a coaling station for ships en route to India. Aden was ruled as part of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
until 1937, when the city of Aden became the Colony of Aden. The Aden hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated ...
and Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut ( ar, حَضْرَمَوْتُ \ حَضْرَمُوتُ, Ḥaḍramawt / Ḥaḍramūt; Hadramautic: 𐩢𐩳𐩧𐩣𐩩, ''Ḥḍrmt'') is a region in South Arabia, comprising eastern Yemen, parts of western Oman and southern S ...
to the east formed the remainder of what would become South Yemen and was not administered directly by Aden but were tied to Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
by treaties of protection with local rulers of traditional polities that, together, became known as the Aden Protectorate. Economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals a ...
was largely centered in Aden, and while the city flourished, the states of the Aden Protectorate stagnated.
Decolonization
In 1963, Aden and much of theProtectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inte ...
were joined to form the Federation of South Arabia with the remaining states that declined to join, mainly in Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut ( ar, حَضْرَمَوْتُ \ حَضْرَمُوتُ, Ḥaḍramawt / Ḥaḍramūt; Hadramautic: 𐩢𐩳𐩧𐩣𐩩, ''Ḥḍrmt'') is a region in South Arabia, comprising eastern Yemen, parts of western Oman and southern S ...
, forming the separate Protectorate of South Arabia. Both of these polities were still tied to Britain with promises of total independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the s ...
in 1968.
Two nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
groups, the Front for the Liberation of Occupied South Yemen
The Front for the Liberation of Occupied South Yemen (FLOSY; ) was an Arab nationalist military organization operating in the Federation of South Arabia (a British protectorate; now Southern Yemen) in the 1960s. As the British tried to exit, ...
( FLOSY) and the National Liberation Front (NLF), began an armed struggle known as the Aden Emergency on 14 October 1963 against British control and, with the temporary closure of the Suez Canal in 1967, the British began to withdraw. One faction, NLF, was invited to the Geneva Talks to sign the independence agreement with the British. During its occupation of Aden, the British had signed several treaties of protection with the local sheikhdoms and emirates of the Federation of South Arabia; however, these parties were excluded from the talks, and thus the agreement stated "...the handover of the territory of South Arabia to the (Yemeni) NLF...". Southern Yemen became independent as the People's Republic of Yemen on 30 November 1967, and the National Liberation Front consolidated its control in the country. On 14 December 1967, the PDRY was admitted into the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
as a member state.
1969 establishment of a Marxist-Leninist state
In June 1969 a radical Marxist wing of the NLF gained power in an event known as the Corrective Move. This radical wing reorganised the country into the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (PDRY) on 30 November 1970. Subsequently, all political parties were amalgamated into the National Liberation Front, renamed the Yemeni Socialist Party, which became the only legal party. The People's Democratic Republic of Yemen established close ties with theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, the People's Republic of China, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, and the Palestinian Liberation Organization. East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
's constitution of 1968 even served as a kind of blueprint for the PDRY's first constitution.
The new government embarked on a programme of nationalisation, introduced central planning, put limits on housing ownership and rent, and implemented land reforms. By 1973, the GDP of South Yemen increased by 25 per cent. And despite the conservative environment and resistance, women became legally equal to men, polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is marri ...
, child marriage
Child marriage is a marriage or similar union, formal or informal, between a child under a certain age – typically 18 years – and an adult or another child.
*
*
*
* The vast majority of child marriages are between a female child and a ma ...
and arranged marriage were all banned by law. Equal rights in divorce were also sanctioned. The Republic also secularised education and sharia law
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
was replaced by a state legal code.
The major communist powers assisted in the building of the PDRY's armed forces. Strong support from Moscow resulted in Soviet naval forces gaining access to naval facilities in South Yemen.
Disputes with North Yemen
 Unlike the early decades of
Unlike the early decades of East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
and West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, or North Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; vi, Việt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa), was a socialist state supported by the Soviet Union (USSR) and the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Southeast Asia that existed f ...
and South Vietnam, or China and Taiwan, the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen) and South Yemen (PDRY) remained relatively friendly, though relations were often strained. Fighting broke out in 1972, and the short-lived conflict was resolved with negotiations, where it was declared unification would eventually occur.
However, these plans were put on hold in 1979, as the PDRY funded Red rebels in the YAR, and war was only prevented by an Arab League intervention. The goal of unity was reaffirmed by the northern and southern heads of state during a summit meeting in Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the no ...
in March 1979.
In 1980, PDRY president Abdul Fattah Ismail resigned and went into exile in Moscow, having lost the confidence of his sponsors in the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
. His successor, Ali Nasir Muhammad, took a less interventionist stance toward both North Yemen and neighbouring Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
.
1986 Civil War
On 13 January 1986, a violent struggle began in Aden between Ali Nasir's supporters and supporters of the returned Ismail, who wanted power back. Fighting, known as theSouth Yemen Civil War
The South Yemen Civil War, colloquially referred to as The Events of '86 or The Events of January 13, or more simply as The Events, was a failed coup d'etat and armed conflict which took place on January 13, 1986 in South Yemen. The civil war ...
, lasted for more than a month and resulted in thousands of casualties, Ali Nasir's ouster, and Ismail's death. Some 60,000 people, including the deposed Ali Nasir, fled to the YAR. Ali Salim al-Beidh, an ally of Ismail who had succeeded in escaping the attack on pro-Ismail members of the Politburo
A politburo () or political bureau is the executive committee for communist parties. It is present in most former and existing communist states.
Names
The term "politburo" in English comes from the Russian ''Politbyuro'' (), itself a contractio ...
, then became General Secretary of the Yemeni Socialist Party.
Reforms and attempts for unification
Against the background of the perestroika in theUSSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
, the main backer of the PDRY, political reforms were started in the late 1980s. Political prisoners were released, political parties were formed and the system of justice was reckoned to be more equitable than in the North. In May 1988, the YAR and PDRY governments came to an understanding that considerably reduced tensions including agreement to renew discussions concerning unification, to establish a joint oil exploration area along their undefined border, to demilitarise the border, and to allow Yemenis unrestricted border passage on the basis of only a national identification card. In November 1989, after returning from the Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Soviet ...
, Osama bin Laden offered to send the newly formed al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
to overthrow the South Yemeni government on behalf of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
, but Prince Turki bin Faisal found the plan reckless and declined. In 1990, the parties reached a full agreement on joint governing of Yemen, and the countries were effectively merged as Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
.
Demographics
South Yemen's ethnic groups were, as of 2000, ethnic YemeniArab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
s (92.8%), Somali
Somali may refer to:
Horn of Africa
* Somalis, an inhabitant or ethnicity associated with Greater Somali Region
** Proto-Somali, the ancestors of modern Somalis
** Somali culture
** Somali cuisine
** Somali language, a Cushitic language
** Soma ...
s (3.7%), Afro-Arab (1.1%), Indians and Pakistanis (1%), and other (1.4%).
Politics and social life
South Yemen developed as a Marxist-Leninist, mostly secular society ruled first by the National Liberation Front, which later morphed into the ruling Yemeni Socialist Party.Foreign relations
The only avowedly Marxist-Leninist nation in the Middle East, South Yemen received significantforeign aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another.
...
and other assistance from the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
and East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, which stationed several hundred officers of the Stasi in the country to train the nation's secret police and establish another arms trafficking
Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organizations. The illegal trade of small ...
route to Palestine. The East Germans did not leave until 1990, when the Yemeni government declined to pay their salaries which had been terminated with the dissolution of the Stasi during German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
.
Relations between South Yemen and several of nearby states were poor. Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
only established diplomatic relations in 1976, initially hosting pro-British exiles and supporting armed clashes in the border regions of South Yemen. Relations with Oman declined through the 1970s as the South Yemen government supported the insurgent Marxist Popular Front for the Liberation of Oman. Relations with Ba'athist Iraq were also low, as South Yemen offered asylum to a number of Iraqi communists
Iraqi or Iraqis (in plural) means from Iraq, a country in the Middle East, and may refer to:
* Iraqi people or Iraqis, people from Iraq or of Iraqi descent
* A citizen of Iraq, see demographics of Iraq
* Iraqi or Araghi ( fa, عراقی), someone o ...
.
Legislature and judiciary
The Supreme People's Council was appointed by the General Command of the National Liberation Front in 1971. In Aden, there was a structured judicial system with aSupreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
.
Living standards
Despite a poor economy, the government ensured a basic level of living standards for all citizens and established awelfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equitab ...
. Income equality improved, corruption was reduced, and health and educational services expanded.
Education was paid for through general taxation.
There was no housing crisis in South Yemen. Surplus housing built by the British meant that there were few homeless people in Aden, and people built their own houses out of adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for '' mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of ...
and mud in the rural areas.
Sports
In 1976, the South Yemen national football team participated in theAsian Cup
The AFC Asian Cup is the primary association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the Asian Football Confederation (AFC), determining the continental champion of Asia. It is the second oldest cont ...
, where the team lost to Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
1-0 and to Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
8–0. They entered their only World Cup qualification campaign in 1986 and were knocked out in the first round by Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
. On 2 September 1965, South Yemen played their first international match against the United Arab Republic, to whom they lost 14–0. On 5 November 1989, South Yemen played its last international match against Guinea, to whom they lost 1–0. The team stopped playing when the North and South united in 1990 to form the modern state of Yemen.
In 1988, the South Yemen Olympic team made its debut in the Summer Olympics
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The ina ...
in Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
. Sending only eight athletes, the country won no medals. This was the only time the country went to the Olympics until unification in 1990.
Women's rights
Women's rights under the socialist government were considered the best in the region. Women became legally equal to men and were encouraged to work in public; polygamy, child marriage, and arranged marriage were all banned; and equal rights in divorce received legal sanction.Governorates
Following independence, South Yemen was divided into sixgovernorate
A governorate is an administrative division of a state. It is headed by a governor. As English-speaking nations tend to call regions administered by governors either states or provinces, the term ''governorate'' is often used in translation from ...
s (Arabic sg. ''muhafazah''), with roughly natural boundaries, each given a name by numeral. From 1967 to 1978, they were named officially by numerals only; from 1979 to 1990, they were given new official names. The islands: Kamaran (until 1972, when it was seized by North Yemen), Perim (Meyun), Socotra
Socotra or Soqotra (; ar, سُقُطْرَىٰ ; so, Suqadara) is an island of the Republic of Yemen in the Indian Ocean, under the ''de facto'' control of the UAE-backed Southern Transitional Council, a secessionist participant in Yemen� ...
, Abd-el-Kuri, Samha (inhabited), Darsah and others uninhabited from the Socotra archipelago were districts (''mudiriyah'') of the First/Aden Governorate being under Prime-Minister of the state supervision.
Economy
During British rule, economic development in South Yemen was restricted to the city of Aden, focused mainly on the port and on the British military bases. As a result, following the British withdrawal, there here was little to no industrial output or mineral wealth exploitation in the country until the mid-1980s, when significant petroleum reserves in the central regions near Shibam and Mukalla were discovered. Foreign aid was minimal, as the British government did not fulfill promises of aid and the Soviet Union offered only US$152 million from 1969 to 1980. The main sources of income were agriculture, mostly fruit, cereal crops, cattle and sheep, and fishing. The government guaranteed full employment in agriculture for rural citizens, and established a number of collective farms, however, those set up following theSoviet model
Soviet-type economic planning (STP) is the specific model of centralized planning employed by Marxist–Leninist socialist states modeled on the economy of the Soviet Union (USSR).
The post-''perestroika'' analysis of the system of the Soviet e ...
produced poorer results than cooperative-run farms.
The national budget
A budget is a calculation play, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environme ...
was 13.43 million dinars in 1976, and the gross national product was US$150 million. The total national debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The d ...
was $52.4 million.
Airlines
The following airlines had operated from the PDRY: * Aden Airways (1949–1967). Ceased operations on 30 June 1967 at the time of British withdrawal from theFederation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
and the Protectorate of South Arabia.
* Alyemda – Democratic Yemen Airlines (1961–1996). Joined Yemenia, the airline of the former YAR
*Yemen Airways (1989–1990)
Movements to revive South Yemen
 Since 2007, some Southerners have been actively protesting for independence, in a movement known as 'Al Hirak' or the Southern Movement. During the Yemen Civil War 2015, in response to incursions by the Houthis and military forces loyal to deposed Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, members of the Southern Movement formed 'Popular Resistance' militias. Since the Battle of Aden, these armed groups have sought to defend the South against Houthi/Saleh attempts to take over the country and have taken the current state of civil war as an opportunity to further their struggle for independence.
In late January 2018, separatists loyal to the Southern Transitional Council successfully seized control of the Saudi-backed Yemeni government headquarters in Aden in an apparent
Since 2007, some Southerners have been actively protesting for independence, in a movement known as 'Al Hirak' or the Southern Movement. During the Yemen Civil War 2015, in response to incursions by the Houthis and military forces loyal to deposed Yemeni president Ali Abdullah Saleh, members of the Southern Movement formed 'Popular Resistance' militias. Since the Battle of Aden, these armed groups have sought to defend the South against Houthi/Saleh attempts to take over the country and have taken the current state of civil war as an opportunity to further their struggle for independence.
In late January 2018, separatists loyal to the Southern Transitional Council successfully seized control of the Saudi-backed Yemeni government headquarters in Aden in an apparent coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, ...
against the Hadi government.
See also
*List of leaders of South Yemen
The People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (commonly referred to as South Yemen) became independent as the People's Republic of South Yemen in November 1967, after the British withdrawal from the Federation of South Arabia and the Protectorat ...
* History of Yemen
*Democratic Republic of Yemen
The Democratic Republic of Yemen ( '), colloquially known as South Yemen, was a breakaway state that fought against Yemen Arab Republic in the 1994 Yemeni Civil War. It was declared in May 1994 and covered all of the former South Yemen.
Th ...
* South Yemen Movement
* South Yemen insurgency
* Dhofar Rebellion
*Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
References
External links
South Yemen Anthem (1969–1979)
National anthem of Yemen
"United Republic" ( ar, الجمهورية المتحدة, al-Jomhuriyah al-Mottaḥedah) is the national anthem of Yemen. It was written by Abdollah Abdolwahâb Noʿmân and composed by ʾAyub Ṭâreš. The music was formerly used as the nation ...
(second and last anthem of South Yemen)
{{Authority control
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Communism in Yemen
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Atheist states
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...