Sound Vision Tour on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted as sound can travel through all forms of matter: gases, liquids, solids, and plasmas. The matter that supports the sound is called the medium. Sound cannot travel through a
The mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted as sound can travel through all forms of matter: gases, liquids, solids, and plasmas. The matter that supports the sound is called the medium. Sound cannot travel through a

 Although there are many complexities relating to the transmission of sounds, at the point of reception (i.e. the ears), sound is readily dividable into two simple elements: pressure and time. These fundamental elements form the basis of all sound waves. They can be used to describe, in absolute terms, every sound we hear.
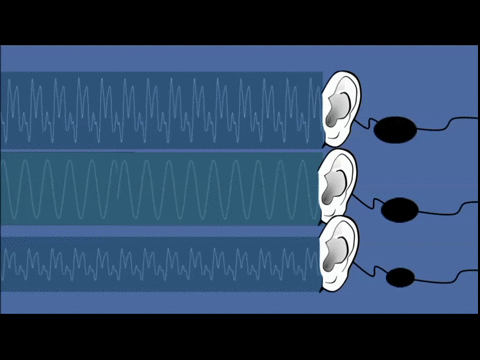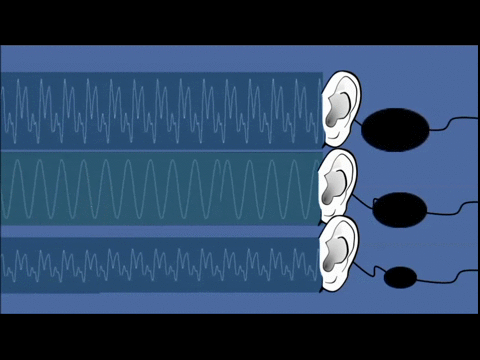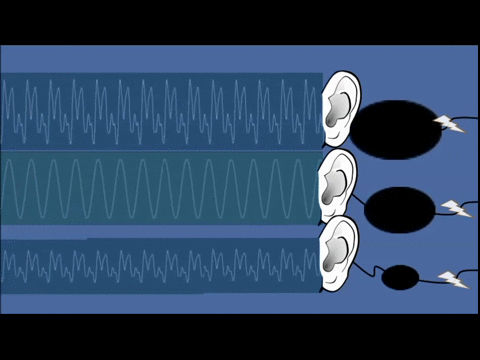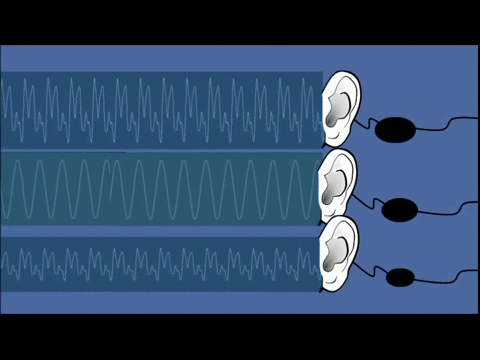
In order to understand the sound more fully, a complex wave such as the one shown in a blue background on the right of this text, is usually separated into its component parts, which are a combination of various sound wave frequencies (and noise).Handel, S. (1995)
Although there are many complexities relating to the transmission of sounds, at the point of reception (i.e. the ears), sound is readily dividable into two simple elements: pressure and time. These fundamental elements form the basis of all sound waves. They can be used to describe, in absolute terms, every sound we hear.
In order to understand the sound more fully, a complex wave such as the one shown in a blue background on the right of this text, is usually separated into its component parts, which are a combination of various sound wave frequencies (and noise).Handel, S. (1995)
Timbre perception and auditory object identification
. Hearing, 425–461.Kendall, R.A. (1986). The role of acoustic signal partitions in listener categorization of musical phrases. Music Perception, 185–213.Matthews, M. (1999). Introduction to timbre. In P.R. Cook (Ed.), Music, cognition, and computerized sound: An introduction to psychoacoustic (pp. 79–88). Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT press. Sound
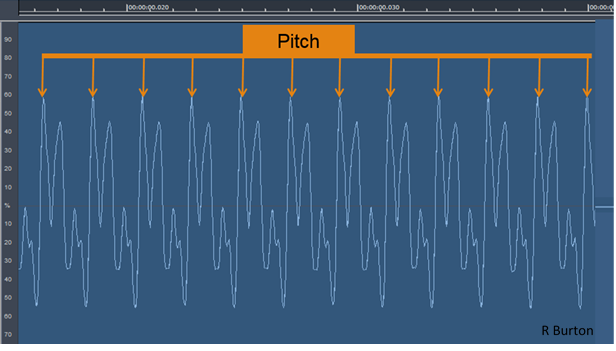 Pitch is perceived as how "low" or "high" a sound is and represents the cyclic, repetitive nature of the vibrations that make up sound. For simple sounds, pitch relates to the frequency of the slowest vibration in the sound (called the fundamental harmonic). In the case of complex sounds, pitch perception can vary. Sometimes individuals identify different pitches for the same sound, based on their personal experience of particular sound patterns. Selection of a particular pitch is determined by pre-conscious examination of vibrations, including their frequencies and the balance between them. Specific attention is given to recognising potential harmonics. Every sound is placed on a pitch continuum from low to high.
For example:
Pitch is perceived as how "low" or "high" a sound is and represents the cyclic, repetitive nature of the vibrations that make up sound. For simple sounds, pitch relates to the frequency of the slowest vibration in the sound (called the fundamental harmonic). In the case of complex sounds, pitch perception can vary. Sometimes individuals identify different pitches for the same sound, based on their personal experience of particular sound patterns. Selection of a particular pitch is determined by pre-conscious examination of vibrations, including their frequencies and the balance between them. Specific attention is given to recognising potential harmonics. Every sound is placed on a pitch continuum from low to high.
For example:
 Duration is perceived as how "long" or "short" a sound is and relates to onset and offset signals created by nerve responses to sounds. The duration of a sound usually lasts from the time the sound is first noticed until the sound is identified as having changed or ceased. Sometimes this is not directly related to the physical duration of a sound. For example; in a noisy environment, gapped sounds (sounds that stop and start) can sound as if they are continuous because the offset messages are missed owing to disruptions from noises in the same general bandwidth. This can be of great benefit in understanding distorted messages such as radio signals that suffer from interference, as (owing to this effect) the message is heard as if it was continuous.
Duration is perceived as how "long" or "short" a sound is and relates to onset and offset signals created by nerve responses to sounds. The duration of a sound usually lasts from the time the sound is first noticed until the sound is identified as having changed or ceased. Sometimes this is not directly related to the physical duration of a sound. For example; in a noisy environment, gapped sounds (sounds that stop and start) can sound as if they are continuous because the offset messages are missed owing to disruptions from noises in the same general bandwidth. This can be of great benefit in understanding distorted messages such as radio signals that suffer from interference, as (owing to this effect) the message is heard as if it was continuous.

Sounds Amazing; a KS3/4 learning resource for sound and waves (uses Flash)
Audio for the 21st Century
Audio Check: a free collection of audio tests and test tones playable on-line
More Sounds Amazing; a sixth-form learning resource about sound waves
{{Authority control Hearing Waves Acoustics Articles containing video clips
 In
In physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, sound is a vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the os ...
that propagates as an acoustic wave
Acoustic waves are types of waves that propagate through matter—such as gas, liquid, and/or solids—by causing the particles of the medium to compress and expand. These waves carry energy and are characterized by properties like acoustic pres ...
through a transmission medium
A transmission medium is a system or substance that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication. Signals are typically imposed on a wave of some kind suitable for the chosen medium. For example, data can modula ...
such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
and psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency (AF) is a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human. The SI unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz). It is the property of sound that most determines pitch.
The generally accepted ...
range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
s of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
. Different animal species have varying hearing range
Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variation bet ...
s, allowing some to even hear ultrasounds.
Definition
Sound is defined as "(a)Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
in pressure, stress, particle displacement, particle velocity, etc., propagated in a medium with internal forces (e.g., elastic or viscous), or the superposition of such propagated oscillation. (b) Auditory sensation evoked by the oscillation described in (a)." Sound can be viewed as a wave motion in air or other elastic media. In this case, sound is a stimulus. Sound can also be viewed as an excitation of the hearing mechanism that results in the perception of sound. In this case, sound is a sensation.
Acoustics
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study ofmechanical wave
In physics, a mechanical wave is a wave that is an oscillation of matter, and therefore transfers energy through a material medium.Giancoli, D. C. (2009) Physics for scientists & engineers with modern physics (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J. ...
s in gasses, liquids, and solids including vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the os ...
, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
is an ''acoustician'', while someone working in the field of acoustical engineering
Acoustical engineering (also known as acoustic engineering) is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It includes the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typical ...
may be called an ''acoustical engineer''. An audio engineer
An audio engineer (also known as a sound engineer or recording engineer) helps to produce a recording or a live performance, balancing and adjusting sound sources using equalization, dynamics processing and audio effects, mixing, reproduc ...
, on the other hand, is concerned with the recording, manipulation, mixing, and reproduction of sound.
Applications of acoustics are found in almost all aspects of modern society, subdisciplines include aeroacoustics Aeroacoustics is a branch of acoustics that studies noise generation via either turbulent fluid motion or aerodynamic forces interacting with surfaces. Noise generation can also be associated with periodically varying flows. A notable example of t ...
, audio signal processing
Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. Audio signals are electronic representations of sound waves—longitudinal waves which travel through air, consisting ...
, architectural acoustics
Architectural acoustics (also known as building acoustics) is the science and engineering of achieving a good sound within a building and is a branch of acoustical engineering. The first application of modern scientific methods to architectur ...
, bioacoustics
Bioacoustics is a cross-disciplinary science that combines biology and acoustics. Usually it refers to the investigation of sound production, dispersion and reception in animals (including humans). This involves neurophysiology, neurophysiological ...
, electro-acoustics, environmental noise
Environmental noise is an accumulation of noise pollution that occurs outside. This noise can be caused by transport, industrial, and Sport, recreational activities.
Noise is frequently described as 'unwanted sound'. Within this context, envir ...
, musical acoustics
Musical acoustics or music acoustics is a multidisciplinary field that combines knowledge from physics, psychophysics, organology (classification of the instruments), physiology, music theory, ethnomusicology, signal processing and instrument buil ...
, noise control
Noise control or noise mitigation is a set of strategies to reduce noise pollution or to reduce the impact of that noise, whether outdoors or indoors.
Overview
The main areas of noise mitigation or abatement are: transportation noise control, a ...
, psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, ...
, speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
, ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
, underwater acoustics
Underwater acoustics (also known as hydroacoustics) is the study of the propagation of sound in water and the interaction of the mechanical waves that constitute sound with the water, its contents and its boundaries. The water may be in the oce ...
, and vibration
Vibration () is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. Vibration may be deterministic if the oscillations can be characterised precisely (e.g. the periodic motion of a pendulum), or random if the os ...
.
Physics
Sound can propagate through a medium such as air, water and solids aslongitudinal wave
Longitudinal waves are waves which oscillate in the direction which is parallel to the direction in which the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal ...
s and also as a transverse wave in solids. The sound waves are generated by a sound source, such as the vibrating diaphragm of a stereo speaker. The sound source creates vibrations in the surrounding medium. As the source continues to vibrate the medium, the vibrations propagate away from the source at the speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elasticity (solid mechanics), elastic medium. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. At , the speed of sound in a ...
, thus forming the sound wave. At a fixed distance from the source, the pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
, velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
, and displacement of the medium vary in time. At an instant in time, the pressure, velocity, and displacement vary in space. The particles of the medium do not travel with the sound wave. This is intuitively obvious for a solid, and the same is true for liquids and gases (that is, the vibrations of particles in the gas or liquid transport the vibrations, while the ''average'' position of the particles over time does not change). During propagation, waves can be reflected, refracted, or attenuated by the medium.
The behavior of sound propagation is generally affected by three things:
* A complex relationship between the density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
and pressure of the medium. This relationship, affected by temperature, determines the speed of sound within the medium.
* Motion of the medium itself. If the medium is moving, this movement may increase or decrease the absolute speed of the sound wave depending on the direction of the movement. For example, sound moving through wind will have its speed of propagation increased by the speed of the wind if the sound and wind are moving in the same direction. If the sound and wind are moving in opposite directions, the speed of the sound wave will be decreased by the speed of the wind.
* The viscosity of the medium. Medium viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
determines the rate at which sound is attenuated. For many media, such as air or water, attenuation due to viscosity is negligible.
When sound is moving through a medium that does not have constant physical properties, it may be refracted (either dispersed or focused).
 The mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted as sound can travel through all forms of matter: gases, liquids, solids, and plasmas. The matter that supports the sound is called the medium. Sound cannot travel through a
The mechanical vibrations that can be interpreted as sound can travel through all forms of matter: gases, liquids, solids, and plasmas. The matter that supports the sound is called the medium. Sound cannot travel through a vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressur ...
.
Studies has shown that sound waves are able to carry a tiny amount of mass and is surrounded by a weak gravitational field.
Waves
Sound is transmitted through gases, plasma, and liquids aslongitudinal wave
Longitudinal waves are waves which oscillate in the direction which is parallel to the direction in which the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal ...
s, also called compression waves. It requires a medium to propagate. Through solids, however, it can be transmitted as both longitudinal waves and transverse waves. Longitudinal sound waves are waves of alternating pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
deviations from the equilibrium pressure, causing local regions of compression and rarefaction, while transverse waves (in solids) are waves of alternating shear stress
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross secti ...
at right angle to the direction of propagation.
Sound waves may be viewed using parabolic mirrors and objects that produce sound.
The energy carried by an oscillating sound wave converts back and forth between the potential energy of the extra compression (in case of longitudinal waves) or lateral displacement strain (in case of transverse waves) of the matter, and the kinetic energy of the displacement velocity of particles of the medium.

Timbre perception and auditory object identification
. Hearing, 425–461.Kendall, R.A. (1986). The role of acoustic signal partitions in listener categorization of musical phrases. Music Perception, 185–213.Matthews, M. (1999). Introduction to timbre. In P.R. Cook (Ed.), Music, cognition, and computerized sound: An introduction to psychoacoustic (pp. 79–88). Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT press. Sound
wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
s are often simplified to a description in terms of sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it correspond ...
plane wave
In physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of ...
s, which are characterized by these generic properties:
* Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
, or its inverse, wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
* Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
, sound pressure
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophon ...
or Intensity
* Speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elasticity (solid mechanics), elastic medium. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. At , the speed of sound in a ...
* Direction
Sound that is perceptible by humans has frequencies from about 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. In air at standard temperature and pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used ...
, the corresponding wavelengths of sound waves range from to . Sometimes speed and direction are combined as a velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
vector
Vector most often refers to:
* Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
* Disease vector, an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematics a ...
; wave number and direction are combined as a wave vector
In physics, a wave vector (or wavevector) is a vector used in describing a wave, with a typical unit being cycle per metre. It has a magnitude and direction. Its magnitude is the wavenumber of the wave (inversely proportional to the wavelength) ...
.
Transverse waves, also known as shear waves, have the additional property, '' polarization'', which is not a characteristic of longitudinal sound waves.
Speed
The speed of sound depends on the medium the waves pass through, and is a fundamental property of the material. The first significant effort towards measurement of the speed of sound was made byIsaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
. He believed the speed of sound in a particular substance was equal to the square root of the pressure acting on it divided by its density:
:
This was later proven wrong and the French mathematician Laplace
Pierre-Simon, Marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French polymath, a scholar whose work has been instrumental in the fields of physics, astronomy, mathematics, engineering, statistics, and philosophy. He summariz ...
corrected the formula by deducing that the phenomenon of sound travelling is not isothermal, as believed by Newton, but adiabatic. He added another factor to the equation— ''gamma''—and multiplied
by
,
thus coming up with the equation
.
Since
,
the final equation came up to be
,
which is also known as the Newton–Laplace equation. In this equation, ''K'' is the elastic bulk modulus, ''c'' is the velocity of sound, and is the density. Thus, the speed of sound is proportional to the square root
In mathematics, a square root of a number is a number such that y^2 = x; in other words, a number whose ''square'' (the result of multiplying the number by itself, or y \cdot y) is . For example, 4 and −4 are square roots of 16 because 4 ...
of the ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of the bulk modulus
The bulk modulus (K or B or k) of a substance is a measure of the resistance of a substance to bulk compression. It is defined as the ratio of the infinitesimal pressure increase to the resulting ''relative'' decrease of the volume.
Other mo ...
of the medium to its density.
Those physical properties and the speed of sound change with ambient conditions. For example, the speed of sound in gases depends on temperature. In air at sea level, the speed of sound is approximately using the formula . The speed of sound is also slightly sensitive, being subject to a second-order anharmonic effect, to the sound amplitude, which means there are non-linear propagation effects, such as the production of harmonics and mixed tones not present in the original sound (see parametric array A parametric array, in the field of acoustics, is a nonlinear transducer, transduction mechanism that generates narrow, nearly side lobe-free beams of low frequency sound, through the mixing and interaction of high frequency sound waves, effectively ...
). If relativistic effects are important, the speed of sound is calculated from the relativistic Euler equations.
In fresh water the speed of sound is approximately . In steel, the speed of sound is about . Sound moves the fastest in solid atomic hydrogen at about .
Sound pressure level
''Sound pressure
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophon ...
'' is the difference, in a given medium, between average local pressure and the pressure in the sound wave. A square of this difference (i.e., a square of the deviation from the equilibrium pressure) is usually averaged over time and/or space, and a square root of this average provides a root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square (abbrev. RMS, or rms) of a set of values is the square root of the set's mean square.
Given a set x_i, its RMS is denoted as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x. The RMS is also known as the quadratic mean (denote ...
(RMS) value. For example, 1 Pa RMS sound pressure (94 dBSPL) in atmospheric air implies that the actual pressure in the sound wave oscillates between (1 atm Pa) and (1 atm Pa), that is between 101323.6 and 101326.4 Pa.
As the human ear can detect sounds with a wide range of amplitudes, sound pressure is often measured as a level on a logarithmic decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a Power, root-power, and field quantities, power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whos ...
scale. The ''sound pressure level'' (SPL) or ''L''p is defined as
:
:where ''p'' is the root-mean-square sound pressure and is a '' reference sound pressure''. Commonly used reference sound pressures, defined in the standard ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
S1.1-1994, are 20 μPa in air and 1 μPa in water. Without a specified reference sound pressure, a value expressed in decibels cannot represent a sound pressure level.
Since the human ear does not have a flat spectral response, sound pressures are often frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
weighted so that the measured level matches perceived levels more closely. The International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
(IEC) has defined several weighting schemes. A-weighting attempts to match the response of the human ear to noise and A-weighted sound pressure levels are labeled dBA. C-weighting is used to measure peak levels.
Perception
A distinct use of the term ''sound'' from its use in physics is that in physiology and psychology, where the term refers to the subject of ''perception'' by the brain. The field ofpsychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, ...
is dedicated to such studies. Webster's dictionary defined sound as: "1. The sensation of hearing, that which is heard; specif.: a. Psychophysics. Sensation due to stimulation of the auditory nerves and auditory centers of the brain, usually by vibrations transmitted in a material medium, commonly air, affecting the organ of hearing. b. Physics. Vibrational energy which occasions such a sensation. Sound is propagated by progressive longitudinal vibratory disturbances (sound waves)." This means that the correct response to the question: " if a tree falls in a forest and no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound?" is "yes", and "no", dependent on whether being answered using the physical, or the psychophysical definition, respectively.
The physical reception of sound in any hearing organism is limited to a range of frequencies. Humans normally hear sound frequencies between approximately 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz), The upper limit decreases with age. Sometimes ''sound'' refers to only those vibrations with frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
that are within the hearing range
Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variation bet ...
for humans or sometimes it relates to a particular animal. Other species have different ranges of hearing. For example, dogs can perceive vibrations higher than 20 kHz.
As a signal perceived by one of the major sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditio ...
s, sound is used by many species for detecting danger, navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navig ...
, predation
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
, and communication. Earth's atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, and virtually any physical phenomenon, such as fire, rain, wind, surf, or earthquake, produces (and is characterized by) its unique sounds. Many species, such as frogs, birds, marine and terrestrial mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, have also developed special organs to produce sound. In some species, these produce song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
and speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
. Furthermore, humans have developed culture and technology (such as music, telephone and radio) that allows them to generate, record, transmit, and broadcast sound.
Noise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
is a term often used to refer to an unwanted sound. In science and engineering, noise is an undesirable component that obscures a wanted signal. However, in sound perception it can often be used to identify the source of a sound and is an important component of timbre perception (see below).
Soundscape
A soundscape is the acoustic environment as perceived by humans, in context. The term, originally coined by Michael Southworth, was popularized by R. Murray Schafer. There is a varied history of the use of soundscape depending on discipline, ...
is the component of the acoustic environment that can be perceived by humans. The acoustic environment is the combination of all sounds (whether audible to humans or not) within a given area as modified by the environment and understood by people, in context of the surrounding environment.
There are, historically, six experimentally separable ways in which sound waves are analysed. They are: pitch, duration, loudness
In acoustics, loudness is the subjectivity, subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relat ...
, timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
, sonic texture and spatial location. Some of these terms have a standardised definition (for instance in the ANSI Acoustical Terminology ANSI/ASA S1.1-2013). More recent approaches have also considered temporal envelope and temporal fine structure as perceptually relevant analyses.
Pitch
 Pitch is perceived as how "low" or "high" a sound is and represents the cyclic, repetitive nature of the vibrations that make up sound. For simple sounds, pitch relates to the frequency of the slowest vibration in the sound (called the fundamental harmonic). In the case of complex sounds, pitch perception can vary. Sometimes individuals identify different pitches for the same sound, based on their personal experience of particular sound patterns. Selection of a particular pitch is determined by pre-conscious examination of vibrations, including their frequencies and the balance between them. Specific attention is given to recognising potential harmonics. Every sound is placed on a pitch continuum from low to high.
For example:
Pitch is perceived as how "low" or "high" a sound is and represents the cyclic, repetitive nature of the vibrations that make up sound. For simple sounds, pitch relates to the frequency of the slowest vibration in the sound (called the fundamental harmonic). In the case of complex sounds, pitch perception can vary. Sometimes individuals identify different pitches for the same sound, based on their personal experience of particular sound patterns. Selection of a particular pitch is determined by pre-conscious examination of vibrations, including their frequencies and the balance between them. Specific attention is given to recognising potential harmonics. Every sound is placed on a pitch continuum from low to high.
For example: white noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, i ...
(random noise spread evenly across all frequencies) sounds higher in pitch than pink noise
Pink noise, noise, fractional noise or fractal noise is a signal (information theory), signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density (power per frequency interval) is inversely proportional to the frequenc ...
(random noise spread evenly across octaves) as white noise has more high frequency content.
Duration
 Duration is perceived as how "long" or "short" a sound is and relates to onset and offset signals created by nerve responses to sounds. The duration of a sound usually lasts from the time the sound is first noticed until the sound is identified as having changed or ceased. Sometimes this is not directly related to the physical duration of a sound. For example; in a noisy environment, gapped sounds (sounds that stop and start) can sound as if they are continuous because the offset messages are missed owing to disruptions from noises in the same general bandwidth. This can be of great benefit in understanding distorted messages such as radio signals that suffer from interference, as (owing to this effect) the message is heard as if it was continuous.
Duration is perceived as how "long" or "short" a sound is and relates to onset and offset signals created by nerve responses to sounds. The duration of a sound usually lasts from the time the sound is first noticed until the sound is identified as having changed or ceased. Sometimes this is not directly related to the physical duration of a sound. For example; in a noisy environment, gapped sounds (sounds that stop and start) can sound as if they are continuous because the offset messages are missed owing to disruptions from noises in the same general bandwidth. This can be of great benefit in understanding distorted messages such as radio signals that suffer from interference, as (owing to this effect) the message is heard as if it was continuous.
Loudness

Loudness
In acoustics, loudness is the subjectivity, subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relat ...
is perceived as how "loud" or "soft" a sound is and relates to the totalled number of auditory nerve stimulations over short cyclic time periods, most likely over the duration of theta wave cycles. This means that at short durations, a very short sound can sound softer than a longer sound even though they are presented at the same intensity level. Past around 200 ms this is no longer the case and the duration of the sound no longer affects the apparent loudness of the sound.
Timbre

Timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
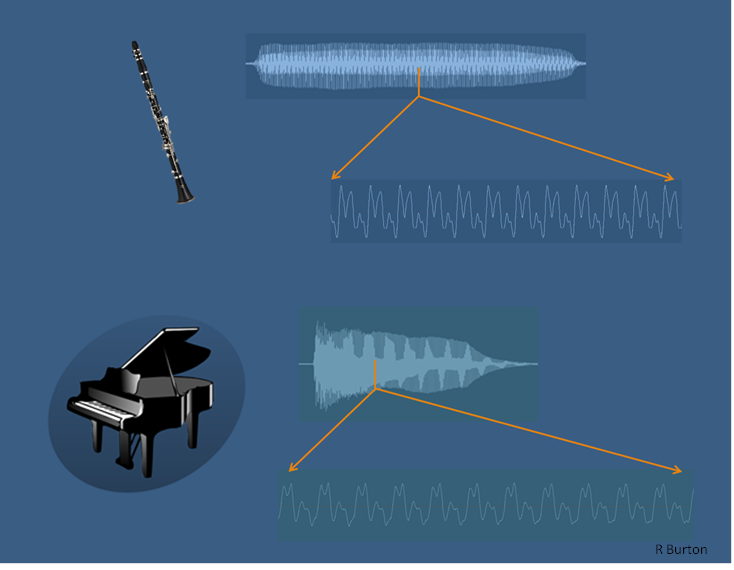
is perceived as the quality of different sounds (e.g. the thud of a fallen rock, the whir of a drill, the tone of a musical instrument or the quality of a voice) and represents the pre-conscious allocation of a sonic identity to a sound (e.g. "it's an oboe!"). This identity is based on information gained from frequency transients, noisiness, unsteadiness, perceived pitch and the spread and intensity of overtones in the sound over an extended time frame. The way a sound changes over time provides most of the information for timbre identification. Even though a small section of the wave form from each instrument looks very similar, differences in changes over time between the clarinet and the piano are evident in both loudness and harmonic content. Less noticeable are the different noises heard, such as air hisses for the clarinet and hammer strikes for the piano.
Texture
Sonic texture relates to the number of sound sources and the interaction between them. The word ''texture'', in this context, relates to the cognitive separation of auditory objects. In music, texture is often referred to as the difference betweenunison
Unison (stylised as UNISON) is a Great Britain, British trade union. Along with Unite the Union, Unite, Unison is one of the two largest trade unions in the United Kingdom, with over 1.2 million members who work predominantly in public servic ...
, polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice ( monophony) or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chord ...
and homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that provide ...
, but it can also relate (for example) to a busy cafe; a sound which might be referred to as ''cacophony
Phonaesthetics (also spelled phonesthetics in North America) is the study of the beauty and pleasantness associated with the sounds of certain words or parts of words. The term was first used in this sense, perhaps by during the mid-20th century ...
''.
Spatial location
Spatial location represents the cognitive placement of a sound in an environmental context; including the placement of a sound on both the horizontal and vertical plane, the distance from the sound source and the characteristics of the sonic environment. In a thick texture, it is possible to identify multiple sound sources using a combination of spatial location and timbre identification.Frequency
Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
is sound waves with frequencies higher than 20,000 Hz. Ultrasound is not different from audible sound in its physical properties, but cannot be heard by humans. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz.
Medical ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes Medical diagnosis, diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of ...
is commonly used for diagnostics and treatment.
Infrasound
Infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
is sound waves with frequencies lower than 20 Hz. Although sounds of such low frequency are too low for humans to hear as a pitch, these sound are heard as discrete pulses (like the 'popping' sound of an idling motorcycle). Whales, elephants and other animals can detect infrasound and use it to communicate. It can be used to detect volcanic eruptions and is used in some types of music.
See also
;Sound sources *Earphones
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an ...
* Musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
* Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects o ...
* Sound box
* Sound reproduction
;Sound measurement
* Acoustic impedance
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The International System of Units, SI unit of acoustic impeda ...
* Acoustic velocity
* Characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance (usually written Z0) of a uniform transmission line is the ratio of the amplitudes of voltage and current of a wave travelling in one direction along the line in the absence of reflections in th ...
* Mel scale
The mel scale (after the word ''melody'')
is a perceptual scale of pitches judged by listeners to be equal in distance from one another. The reference point between this scale and normal frequency measurement is defined by assigning a percept ...
* Particle acceleration
* Particle amplitude
* Particle displacement
Particle displacement or displacement amplitude is a measurement of distance of the movement of a sound particle from its equilibrium position in a medium as it transmits a sound wave.
The SI unit of particle displacement is the metre (m). In m ...
* Particle velocity
Particle velocity (denoted or ) is the velocity of a particle (real or imagined) in a medium as it transmits a wave. The SI unit of particle velocity is the metre per second (m/s). In many cases this is a longitudinal wave of pressure as with ...
* Sound energy flux
* Sound impedance
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The SI unit of acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per c ...
* Sound intensity level
* Sound power
Sound power or acoustic power is the rate at which sound energy is emitted, reflected, Acoustic transmission, transmitted or received, per unit time. It is defined as "through a surface, the product of the sound pressure, and the component of the ...
* Sound power level
;Units:
* dB, decibel
* sone - perceived loudness
In acoustics, loudness is the subjectivity, subjective perception of sound pressure. More formally, it is defined as the "attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud". The relat ...
* phon - subjective loudness
* Hz - unit of frequency
;General:
* Acoustic theory
* Beat
* Doppler effect
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described ...
* Echo
* Infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
— sound at extremely low frequencies
* List of unexplained sounds
* Musical tone
* Resonance
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximu ...
* Reverberation
In acoustics, reverberation (commonly shortened to reverb) is a persistence of sound after it is produced. It is often created when a sound is reflection (physics), reflected on surfaces, causing multiple reflections that build up and then de ...
* Sonic weaponry
* Sound synthesis
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis an ...
* Soundproofing
* Structural acoustics Structural acoustics is the study of the mechanical waves in structures and how they interact with and radiate into adjacent media. The field of structural acoustics is often referred to as vibroacoustics in Europe and Asia. People that work in t ...
References
External links
*Sounds Amazing; a KS3/4 learning resource for sound and waves (uses Flash)
Audio for the 21st Century
Audio Check: a free collection of audio tests and test tones playable on-line
More Sounds Amazing; a sixth-form learning resource about sound waves
{{Authority control Hearing Waves Acoustics Articles containing video clips