Solenopsin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Solenopsin is a
lipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipop ...
alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
with the molecular formula C17H35N found in the venom of fire ant
Fire ants are several species of ants in the genus ''Solenopsis'', which includes over 200 species. ''Solenopsis'' are stinging ants, and most of their common names reflect this, for example, ginger ants and tropical fire ants. Many of the nam ...
s (''Solenopsis''). It is considered the primary toxin in the venom and may be the component responsible for the cardiorespiratory failure
Respiratory arrest is a sickness caused by apnea (cessation of breathing) or respiratory dysfunction severe enough it will not sustain the body (such as agonal breathing). Prolonged apnea refers to a patient who has stopped breathing for a long per ...
in people who experience excessive fire ant stings.
Structurally solenopsins are a piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless ...
ring with a methyl group
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many ...
substitution at position 2 and a long hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, th ...
chain at position 6. They are typically oily at room temperature, water-insoluble, and present an absorbance peak at 232 nanometers. Fire ant venom contains other chemically related piperidines which make purification of solenopsin from ants difficult. Therefore, solenopsin and related compounds have been the target of organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
from which pure compounds can be produced for individual study. Originally synthesized in 1993, several groups have designed novel and creative methods of synthesizing enantiopure
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical anti ...
solenopsin and other alkaloidal components of ant venom
Ant venom is any of, or a mixture of, irritants and toxins inflicted by ants. Most ants spray or inject a venom, the main constituent of which is formic acid only in the case of subfamily Formicinae.
Ant stings
Of all extant ant species, about 7 ...
.
Total synthesis
Thetotal synthesis
Total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of a complex molecule, often a natural product, from simple, commercially-available precursors. It usually refers to a process not involving the aid of biological processes, which distinguishes ...
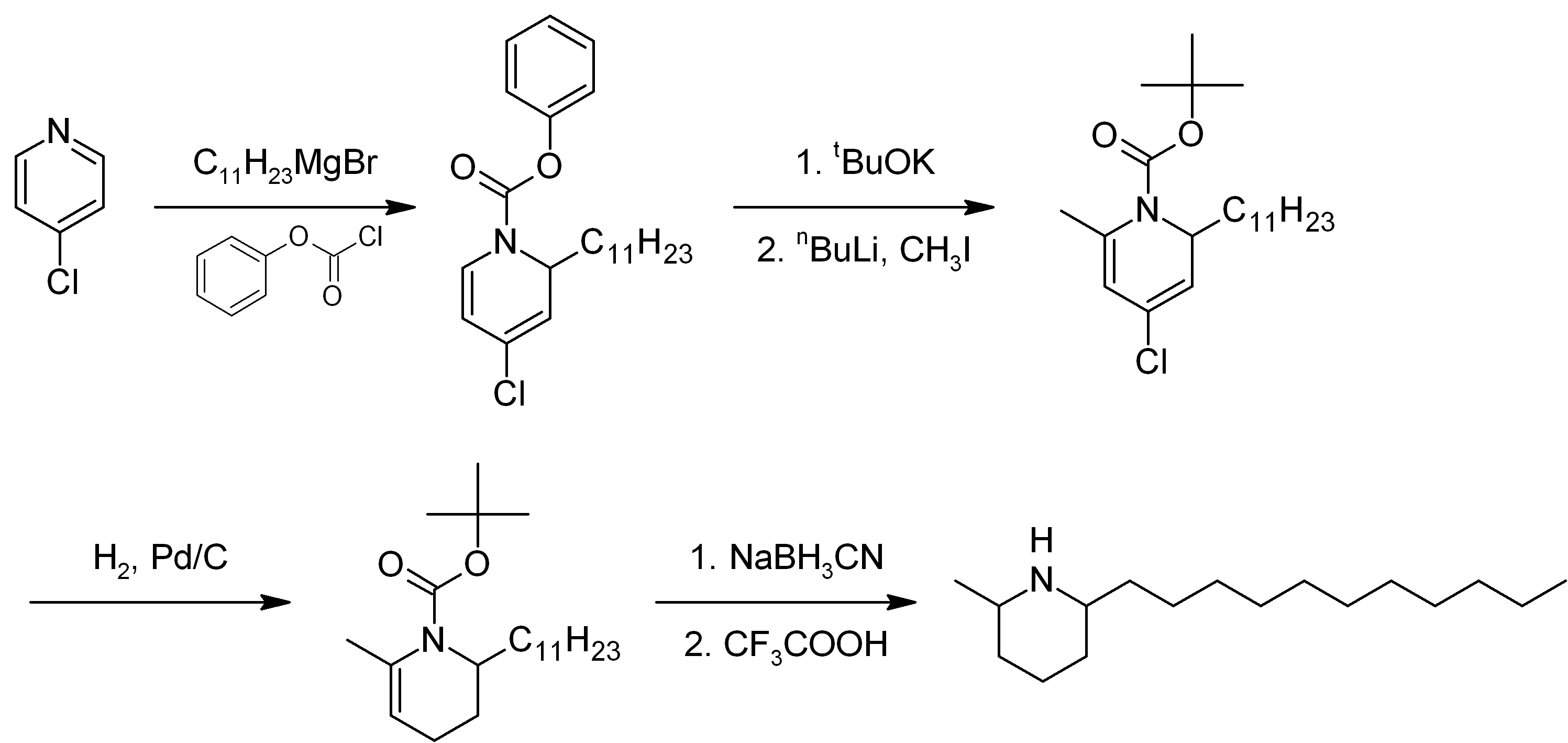
of solenopsin has been described by several methods. A proposed method of synthesis(Figure 1) starts with alkylation of 4-chloropyridine with a Grignard reagent
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide ...
derived from 1-bromoundecane, followed by reaction with phenyl chloroformate to form 4-chloro-1-(phenoxycarbonyl)-2-''n''-undecyl-1,2-dihydropyridine. The phenylcarbamate is converted to the BOC protecting group, and then pyridine is methylated at the 6 position. The pyridine ring is then reduced to a tetrahydropyridine via catalytic hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a Catalysis, catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or S ...
with Pd/C and then further reduced with sodium cyanoborohydride
Sodium cyanoborohydride is the chemical compound with the formula Na B H3 CN. It is a colourless salt, but commercial samples can appear tan. It is widely used in organic synthesis for the reduction of imines. The salt tolerates aqueous conditions ...
to a piperidine ring. The BOC group is finally removed to yield solenopsin. A number of analogs have been synthesized using modifications of this procedure.
A shorter method of synthesis stemming from commercially-available lutidine Lutidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are dimethyl derivatives of pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one met ...
has been more recently proposed.
:
Biological activities
Solenopsins are described as toxic against vertebrates and invertebrates. For example, the compound known as isosolenopsin A has been demonstrated to have stronginsecticidal
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
effects which may play a central role in the biology of fire ant
Fire ants are several species of ants in the genus ''Solenopsis'', which includes over 200 species. ''Solenopsis'' are stinging ants, and most of their common names reflect this, for example, ginger ants and tropical fire ants. Many of the nam ...
s.
In addition to its toxicity, solenopsis has a number of other biological activities. It inhibits angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting ...
''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
'' via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which i ...
(PI3K) signaling pathway, inhibits neuronal nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthases () (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and p ...
(nNOS) in a manner that appears to be non-competitive with L-arginine, and inhibits quorum-sensing
In biology, quorum sensing or quorum signalling (QS) is the ability to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation. As one example, QS enables bacteria to restrict the expression of specific genes to the high cell densities at ...
signaling in some bacteria. The biological activities of solenopsins have led researchers to propose a number of biotechnological and biomedical applications for these compounds. For instance, mentioned anti-bacterial and interference in quorum-sensing signalling apparently provide solenopsins with considerable anti-biofilm activity, which suggests the potential of analogs as new disinfectants and surface-conditioning agents. Also, solenopsins have been demonstrated to inhibit cell division and viability of Trypanosoma cruzi
''Trypanosoma cruzi'' is a species of parasitic euglenoids. Among the protozoa, the trypanosomes characteristically bore tissue in another organism and feed on blood (primarily) and also lymph. This behaviour causes disease or the likelihood of ...
, the cause of Chagas disease
Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi''. It is spread mostly by insects in the subfamily ''Triatominae'', known as "kissing bugs". The symptoms change over the cou ...
, which suggests these alkaloids as potential chemotherapeutic drugs.
Solenopsin and analogs share structural and biological properties with the sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because ...
ceramide
Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of N-acetylsphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up ...
, a major endogenous regulator of cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
, inducing mitophagy Mitophagy is the selective degradation of mitochondria by autophagy. It often occurs to defective mitochondria following damage or stress. The process of mitophagy was first described over a hundred years ago by Margaret Reed Lewis and Warren Harmo ...
and anti-proliferative effects in different tumor cell lines.
Synthetic analogs of solenopsin are being studied for the potential treatment of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
.
References
Further reading
* {{cite journal , doi = 10.1039/NP9971400637 , title = Pyrrole, pyrrolidine pyridine, piperidine, azepine and tropane alkaloids , year = 1997 , author = O'Hagan, David , journal =Natural Product Reports
''Natural Product Reports'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It publishes reviews commissioned by the editorial board on all areas of natural products research. The Executive Editor is Richa ...
, type = Review , volume = 14 , pages = 637 , issue = 6
Piperidine alkaloids
Total synthesis
Toxins