|
Mitophagy
Mitophagy is the selective degradation of mitochondria by autophagy. It often occurs to defective mitochondria following damage or stress. The process of mitophagy was first described over a hundred years ago by Margaret Reed Lewis and Warren Harmon Lewis. Ashford and Porter used electron microscopy to observe mitochondrial fragments in liver lysosomes by 1962, and a 1977 report suggested that "mitochondria develop functional alterations which would activate autophagy." The term "mitophagy" was in use by 1998. Mitophagy is key in keeping the cell healthy. It promotes turnover of mitochondria and prevents accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria which can lead to cellular degeneration. It is mediated by Atg32 (in yeast) and NIX and its regulator BNIP3 in mammals. Mitophagy is regulated by PINK1 and parkin proteins. In addition to the selective removal of damaged mitochondria, mitophagy is also required to adjust mitochondrial numbers to changing cellular metabolic needs, for stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
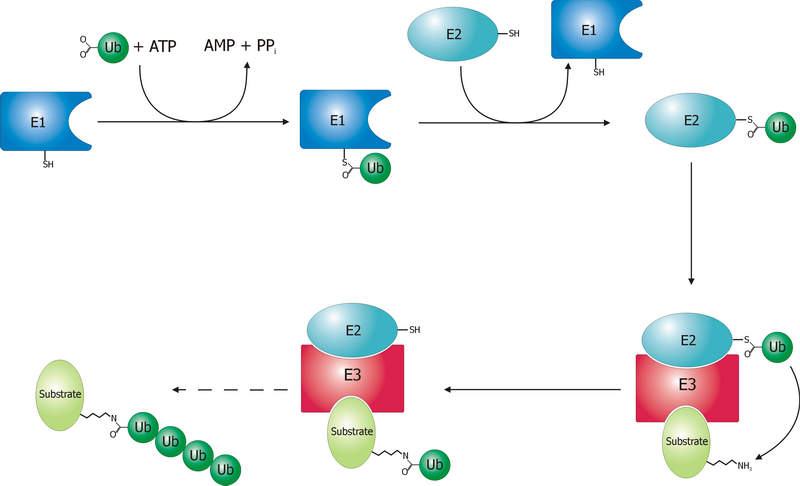
Parkin (ligase)
Parkin is a 465-amino acid residue E3 ubiquitin ligase, a protein that in humans and mice is encoded by the ''PARK2'' gene. Parkin plays a critical role in ubiquitination – the process whereby molecules are covalently labelled with ubiquitin (Ub) and directed towards degradation in proteasomes or lysosomes. Ubiquitination involves the sequential action of three enzymes. First, an E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme binds to inactive Ub in eukaryotic cells via a thioester bond and mobilises it in an ATP-dependent process. Ub is then transferred to an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme before being conjugated to the target protein via an E3 ubiquitin ligase. There exists a multitude of E3 ligases, which differ in structure and substrate specificity to allow selective targeting of proteins to intracellular degradation. In particular, parkin recognises proteins on the outer membrane of mitochondria upon cellular insult and mediates the clearance of damaged mitochondria via autophagy and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
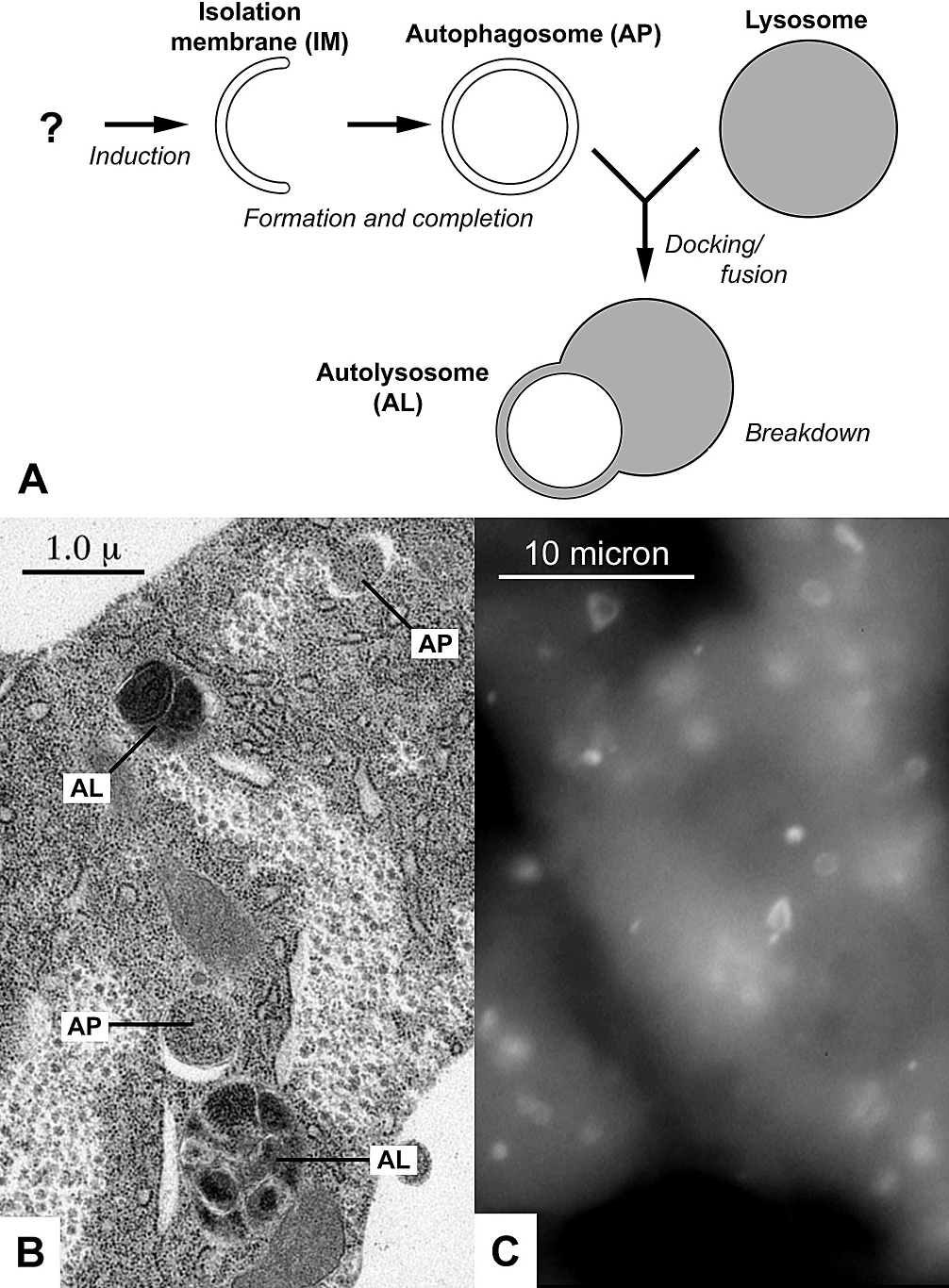
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nix (gene)
Nix is a pro-apoptotic gene that is regulated by Histotoxic hypoxia. It expresses a signaling protein related to the BH3-only family. This protein induces autophagy, an intracellular function by which cytoplasmic components are delivered to the lysosome to be broken down and used elsewhere or excreted from the cell. This protein is important in development because it allows cells to have a consistent store of cellular components. It also holds an important role in the differentiation and maturation of erythrocytes and lymphocytes by the process of mitophagy with the help of its regulator BNIP3. Using a gene knockout technique in mice, scientists have been able to attribute this pruning of mitochondria and induction of cellular necrosis to the expression of the Nix gene. The Nix protein may be associated with certain kinds of cancer formation. In mouse models, loss of Nix resulted in a delayed onset of tumors for pancreatic cancer, and was additionally associated with reduced mito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PINK1
PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) is a mitochondrial serine/threonine-protein kinase encoded by the ''PINK1'' gene. It is thought to protect cells from stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. PINK1 activity causes the parkin protein to bind to depolarized mitochondria to induce autophagy of those mitochondria. PINK1 is processed by healthy mitochondria and released to trigger neuron differentiation. Mutations in this gene cause one form of autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinson's disease. Structure PINK1 is synthesized as a 63000 Da protein which is often cleaved by PARL, between the 103-Alanine and the 104-Phenylalanine residues, into a 53000 Da fragment. PINK1 contains an N-terminal mitochondrial localization sequence, a putative transmembrane sequence, a Ser/Thr kinase domain, and a C-terminal regulatory sequence. The protein has been found to localize to the outer membrane of mitochondria, but can also be found throughout the cytosol. Experiments suggest the Ser/Thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MFN2
Mitofusin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MFN2'' gene. Mitofusins are GTPases embedded in the outer membrane of the mitochondria. In mammals MFN1 and MFN2 are essential for mitochondrial fusion. In addition to the mitofusins, OPA1 regulates inner mitochondrial membrane fusion, and DRP1 is responsible for mitochondrial fission. Mitofusin-2 (MFN2) is a mitochondrial membrane protein that plays a central role in regulating mitochondrial fusion and cell metabolism. More specifically, MFN2 is a dynamin-like GTPase embedded in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) which in turn affects mitochondrial dynamics, distribution, quality control, and function. In addition to the MFN2, OPA1 regulates inner mitochondrial membrane fusion, MFN1 is a mediator of mitochondrial fusion and DRP1 is responsible for mitochondrial fission. Structure The human mitofusin-2 protein contains 757 amino acid residues. The MFN2 comprises a large cytosolic GTPase domain at the N-te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Reed Lewis
Margaret Adaline Reed Lewis (1881–1970) was an American cell biologist and embryologist who made contributions to cancer research and cell culture techniques, and was likely the first person to successfully grow mammalian tissue ''in vitro''. She authored around 150 papers, many co-authored with her husband Warren Harmon Lewis. The Lewises developed a growth medium called the Locke-Lewis solution and jointly received the Gerhard Gold Medal from the Pathological Society of Philadelphia. Early life and education Margaret Adaline Reed was born in Kittanning, Pennsylvania, on November 9, 1881, to parents Joseph C. and Martha A. (Walker) Reed. From 1897 to 1901 she attended Goucher College (then known as Woman's College of Baltimore), where she earned an A.B. After graduation she studied at Bryn Mawr College, Columbia University, and the Universities of Zurich, Paris, and Berlin, but never earned a graduate degree. At Bryn Mawr and Columbia she researched regeneration in amphibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BNIP3
BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BNIP3'' gene. BNIP3 is a member of the apoptotic Bcl-2 protein family. It can induce cell death while also assisting with cell survival. Like many of the Bcl-2 family proteins, BNIP3 modulates the permeability state of the outer mitochondrial membrane by forming homo- and hetero-oligomers inside the membrane. Upregulation results in a decrease in mitochondrial potential, an increase in reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial swelling and fission, and an increase in mitochondrial turnover via autophagy. Sequence similarity with Bcl-2 family members was not detected. Humans and other animals (''Drosophila, Caenorhabditis''), as well as lower eukaryotes (''Dictyostelium, Trypanosoma, Cryptosporidium, Paramecium'') encode several BNIP3 paralogues including the human NIP3L, which induces apoptosis by interacting with viral and cellular anti-apoptosis proteins. Structure The righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MFN1
Mitofusin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MFN1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a mediator of mitochondrial fusion. This protein and mitofusin 2 are homologs of the ''Drosophila ''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...'' protein fuzzy onion (Fzo). They are mitochondrial membrane proteins that interact with each other to facilitate mitochondrial targeting. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into mitosome, other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitocho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MitoNEET
The CDGSH iron sulfur domain are a group of iron-sulfur (2Fe-2S) clusters and a unique 39 amino acid CDGSH domain ''C-X-C-X2-(S/T)-X3-P-X-C-D-G-(S/A/T)-H The CDGSH iron sulfur domain 1 protein (also referred to as mitoNEET) is an integral membrane protein located in the outer mitochondrial membrane and whose function may be to transport iron into the mitochondria. Iron in turn is essential for the function of several mitochondrial enzymes. The antidiabetic drug pioglitazone, in addition to binding to the nuclear receptor PPAR In the field of molecular biology, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes. PPARs play essential roles in the reg ..., also has been shown to bind mitoNEET with approximately equal affinity. References External links * {{MeshName, ZCD1+protein,+human Protein domains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |