A photovoltaic system, also called a PV system or solar power system, is an
electric power system
An electric power system is a network of electrical components deployed to supply, transfer, and use electric power. An example of a power system is the electrical grid that provides power to homes and industries within an extended area. The e ...
designed to supply usable
solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
by means of
photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including
solar panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct ...
s to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a
solar inverter to convert the output from
direct
Direct may refer to:
Mathematics
* Directed set, in order theory
* Direct limit of (pre), sheaves
* Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces
Computing
* Direct access (disambiguation), ...
to
alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
, as well as
mounting,
cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. Many utility-scale PV systems use
tracking systems that follow the sun's daily path across the sky to generate more electricity than fixed-mounted systems.
Photovoltaic systems convert light directly into electricity and are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as
concentrated solar power or
solar thermal, used for heating and cooling. A solar array only encompasses the solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as the
balance of system (BOS). PV systems range from small,
rooftop-mounted or
building-integrated systems with capacities ranging from a few to several tens of kilowatts to large,
utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, off-grid or
stand-alone systems account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or
air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
, PV systems have evolved from niche market applications into a mature technology used for mainstream electricity generation. Due to the
growth of photovoltaics, prices for PV systems have rapidly declined since their introduction; however, they vary by market and the size of the system. Nowadays, solar PV modules account for less than half of the system's overall cost, leaving the rest to the remaining BOS components and to soft costs, which include customer acquisition, permitting, inspection and interconnection, installation labor, and financing costs.
Modern system
Overview

A
photovoltaic system converts the Sun's
radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, in the form of light, into usable
electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
. It comprises the solar array and the balance of system components. PV systems can be categorized by various aspects, such as,
grid-connected vs.
stand alone systems, building-integrated vs. rack-mounted systems, residential vs. utility systems,
distributed vs. centralized systems, rooftop vs. ground-mounted systems, tracking vs. fixed-tilt systems, and new constructed vs.
retrofitted systems. Other distinctions may include, systems with microinverters vs. central inverter, systems using
crystalline silicon vs.
thin-film technology, and systems with modules.
About 99 percent of all European and 90 percent of all U.S. solar power systems are connected to the
electrical grid, while off-grid systems are somewhat more common in Australia and South Korea.
PV systems rarely use battery storage. This may change, as government incentives for distributed energy storage are implemented and investments in storage solutions gradually become economically viable for small systems.
[
] In the UK, the number of commercial systems using battery storage is gradually increasing as a result of grid constraints preventing feedback of unused electricity into the grid as well as increased electricity costs resulting in improved economics. A typical residential solar array is rack-mounted on the roof, rather than integrated into the roof or facade of the building, which is significantly more expensive. Utility-scale
solar power stations are ground-mounted, with fixed tilted solar panels rather than using expensive tracking devices. Crystalline silicon is the predominant material used in 90 percent of worldwide produced solar modules, while its rival thin-film has lost market-share.
[
] About 70 percent of all solar cells and modules are produced in China and Taiwan, only 5 percent by European and US-
manufacturers.
The installed capacity for both small rooftop systems and large solar power stations is growing rapidly and in equal parts, although there is a notable trend towards utility-scale systems, as the focus on new installations is shifting away from Europe to sunnier regions, such as the
Sunbelt in the U.S., which are less opposed to ground-mounted solar farms and cost-effectiveness is more emphasized by investors.
Driven by advances in technology and increases in manufacturing scale and sophistication, the cost of photovoltaics is declining continuously.
There are several million PV systems distributed all over the world, mostly in Europe, with 1.4 million systems in Germany alone
– as well as North America with 440,000 systems in the United States. The energy
conversion efficiency of a conventional solar module increased from 15 to 20 percent since 2004
and a PV system recoups the energy needed for its manufacture in about 2 years. In exceptionally irradiated locations, or when thin-film technology is used, the so-called
energy payback time decreases to one year or less.
and financial incentives, such as preferential
feed-in tariffs for solar-generated electricity, have also greatly supported installations of PV systems in many countries. The
levelised cost of electricity from large-scale PV systems has become competitive with conventional electricity sources in an expanding list of geographic regions, and
grid parity has been achieved in about 30 countries.
As of 2015, the
fast-growing global PV market is rapidly approaching the 200 GW mark – about 40 times the installed capacity in 2006. These systems currently contribute about 1 percent to worldwide electricity generation.
Top installers of PV systems in terms of capacity are currently China, Japan and the United States, while half of the world's capacity is installed in Europe, with Germany and Italy supplying 7% to 8% of their respective domestic electricity consumption with solar PV.
The International Energy Agency expects
solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
to become the world's largest source of electricity by 2050, with solar photovoltaics and
concentrated solar thermal contributing 16% and 11% to the global demand, respectively.
Solar grid-connection

A grid connected system is connected to a larger independent grid (typically the public electricity grid) and feeds energy directly into the grid. This energy may be shared by a residential or commercial building before or after the revenue measurement point, depending on whether the credited energy production is calculated independently of the customer's energy consumption (
feed-in tariff) or only on the difference of energy (
net metering). These systems vary in size from residential (2–10 kW
p) to solar power stations (up to tens of MW
p). This is a form of
decentralized electricity generation. Feeding electricity into the grid requires the transformation of DC into AC by a special, synchronizing
grid-tie inverter. In kilowatt-sized installations the DC side system voltage is as high as permitted (typically 1000 V except US residential 600 V) to limit ohmic losses. Most modules (60 or 72 crystalline silicon cells) generate 160 W to 300 W at 36 volts. It is sometimes necessary or desirable to connect the modules partially in parallel rather than all in series. An individual set of modules connected in series is known as a 'string'. A set of series-connected "strings" is known as an "array."
Scale of system
Photovoltaic systems are generally categorized into three distinct market segments: residential rooftop, commercial rooftop, and ground-mount utility-scale systems. Their capacities range from a few kilowatts to hundreds of megawatts. A typical residential system is around 10 kilowatts and mounted on a sloped roof, while commercial systems may reach a megawatt-scale and are generally installed on low-slope or even flat roofs. Although rooftop mounted systems are small and have a higher
cost per watt than large utility-scale installations, they account for the largest share in the market. There is, however, a growing trend towards bigger utility-scale power plants, especially in the "sunbelt" region of the planet.
Utility-scale

Large utility-scale
solar parks or farms are
power station
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ...
s and capable of providing an energy supply to large numbers of consumers.
Generated electricity is fed into the transmission grid powered by central generation plants (grid-connected or grid-tied plant), or combined with one, or many, domestic electricity generators to feed into a small
electrical grid (hybrid plant). In rare cases generated electricity is stored or used directly by island/standalone plant. PV systems are generally designed in order to ensure the highest energy yield for a given investment. Some large photovoltaic power stations such as
Solar Star,
Waldpolenz Solar Park and
Topaz Solar Farm cover tens or hundreds of hectares and have power outputs up to hundreds of
megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s.
Rooftop, mobile, and portable
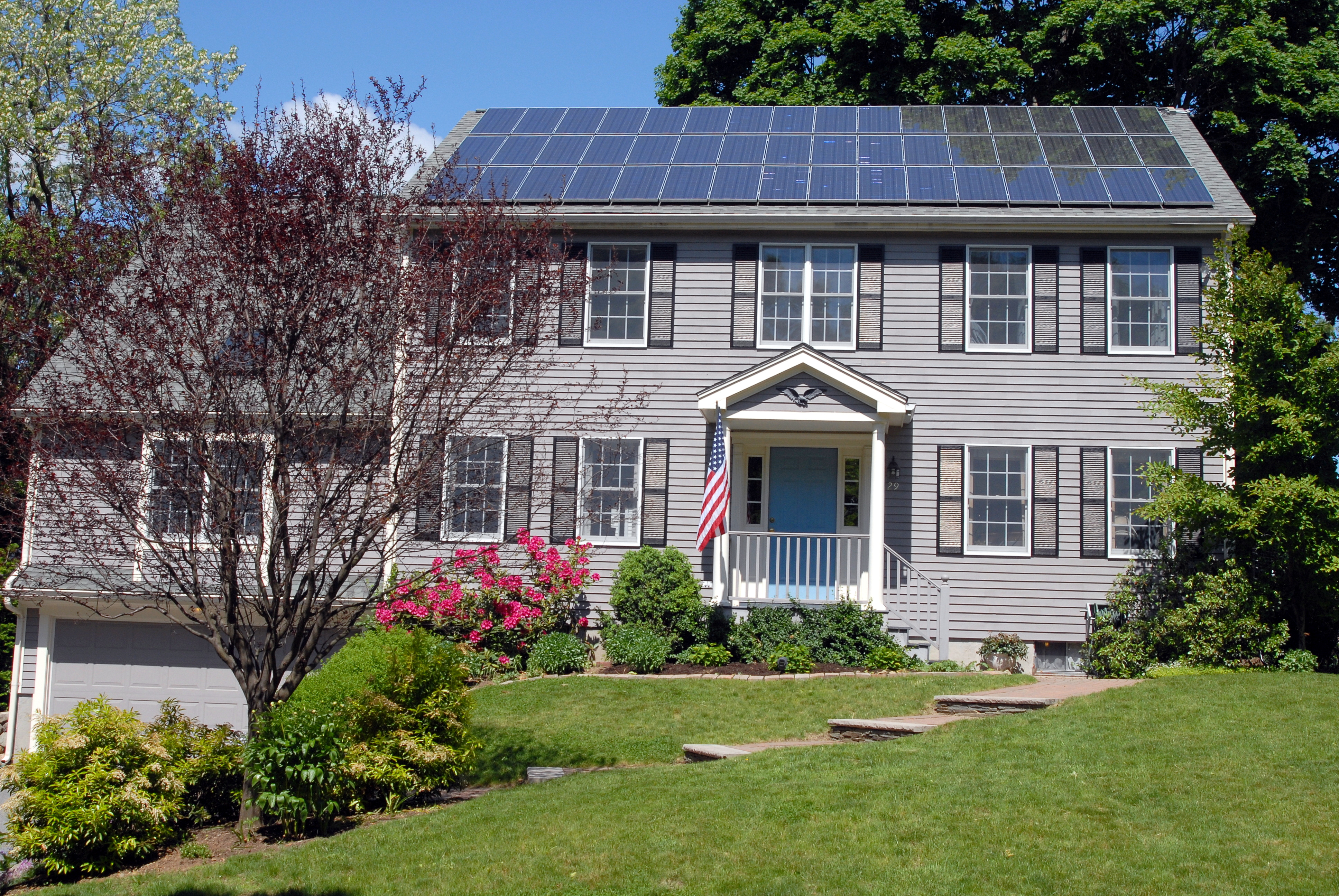

A small PV system is capable of providing enough AC electricity to power a single home, or an isolated device in the form of AC or DC electric. Military and civilian Earth observation
satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s,
street lights, construction and traffic signs,
electric car
An electric car or electric vehicle (EV) is a passenger car, passenger automobile that is propelled by an electric motor, electric traction motor, using electrical energy as the primary source of propulsion. The term normally refers to a p ...
s, solar-powered tents, and
electric aircraft
An electric aircraft is an aircraft powered by electricity.
Electric aircraft are seen as a way to reduce the environmental effects of aviation, providing zero emissions and quieter flights.
Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods, ...
may contain integrated photovoltaic systems to provide a primary or
auxiliary power source in the form of AC or DC power, depending on the design and power demands. In 2013, rooftop systems accounted for 60 percent of worldwide installations. However, there is a trend away from rooftop and towards utility-scale PV systems, as the focus of new PV installations is also shifting from Europe to countries in the sunbelt region of the planet where opposition to ground-mounted solar farms is less accentuated.
Portable and mobile PV systems provide electrical power independent of utility connections, for "off the grid" operation. Such systems are so commonly used on
recreational vehicles and boats that there are retailers specializing in these applications and products specifically targeted to them. Since recreational vehicles (RV) normally carry batteries and operate lighting and other systems on nominally 12-volt DC power, RV systems normally operate in a voltage range that can charge 12-volt batteries directly, so addition of a PV system requires only panels, a charge controller, and wiring. Solar systems on recreation vehicles are usually constrained in wattage by the physical size of the RV's roof space.
Building-integrated
In urban and suburban areas, photovoltaic arrays are often used on rooftops to supplement power use; often the building will have a connection to the
power grid, in which case the energy produced by the PV array can be sold back to the
utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings.
* In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish ...
in some sort of
net metering agreement. Some utilities use the rooftops of commercial customers and telephone poles to support their use of PV panels. Solar trees are arrays that, as the name implies, mimic the look of trees, provide shade, and at night can function as
street lights.
Performance
Uncertainties in revenue over time relate mostly to the evaluation of the solar resource and to the performance of the system itself. In the best of cases, uncertainties are typically 4% for year-to-year climate variability, 5% for solar resource estimation (in a horizontal plane), 3% for estimation of irradiation in the plane of the array, 3% for power rating of modules, 2% for losses due to dirt and
soiling, 1.5% for losses due to snow, and 5% for other sources of error. Identifying and reacting to manageable losses is critical for revenue and O&M efficiency. Monitoring of array performance may be part of contractual agreements between the array owner, the builder, and the utility purchasing the energy produced. A method to create "synthetic days" using readily available weather data and verification using the
Open Solar Outdoors Test Field make it possible to predict photovoltaic systems performance with high degrees of accuracy. This method can be used to then determine loss mechanisms on a local scale - such as those from snow
or the effects of surface coatings (e.g.
hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
or
hydrophilic) on soiling or snow losses. (Although in heavy snow environments with severe ground interference can result in annual losses from snow of 30%.)
Access to the Internet has allowed a further improvement in energy monitoring and communication. Dedicated systems are available from a number of vendors. For solar PV systems that use
microinverters (panel-level DC to AC conversion), module power data is automatically provided. Some systems allow setting performance alerts that trigger phone/email/text warnings when limits are reached. These solutions provide data for the system owner and the installer. Installers are able to remotely monitor multiple installations, and see at-a-glance the status of their entire installed base.
Components

A photovoltaic system for residential, commercial, or industrial energy supply consists of the solar array and a number of components often summarized as the
balance of system (BOS). This term is synonymous with "
Balance of plant" q.v. BOS-components include power-conditioning equipment and structures for mounting, typically one or more DC to
AC power converters, also known as
inverters, an energy storage device, a racking system that supports the solar array, electrical wiring and interconnections, and mounting for other components.
Optionally, a balance of system may include any or all of the following:
renewable energy credit revenue-grade meter,
maximum power point tracker (MPPT),
battery system and
charger,
GNSS solar tracker,
energy management software,
solar irradiance sensors,
anemometer, or task-specific accessories designed to meet specialized requirements for a system owner. In addition, a
CPV system requires
optical lenses or mirrors and sometimes a cooling system.
The terms "solar array" and "PV system" are often incorrectly used interchangeably, despite the fact that the solar array does not encompass the entire system. Moreover, "solar panel" is often used as a synonym for "solar module", although a panel consists of a string of several modules. The term "solar system" is also an often used
misnomer
A misnomer is a name that is incorrectly or unsuitably applied. Misnomers often arise because something was named long before its correct nature was known, or because an earlier form of something has been replaced by a later form to which the nam ...
for a PV system.
Solar array
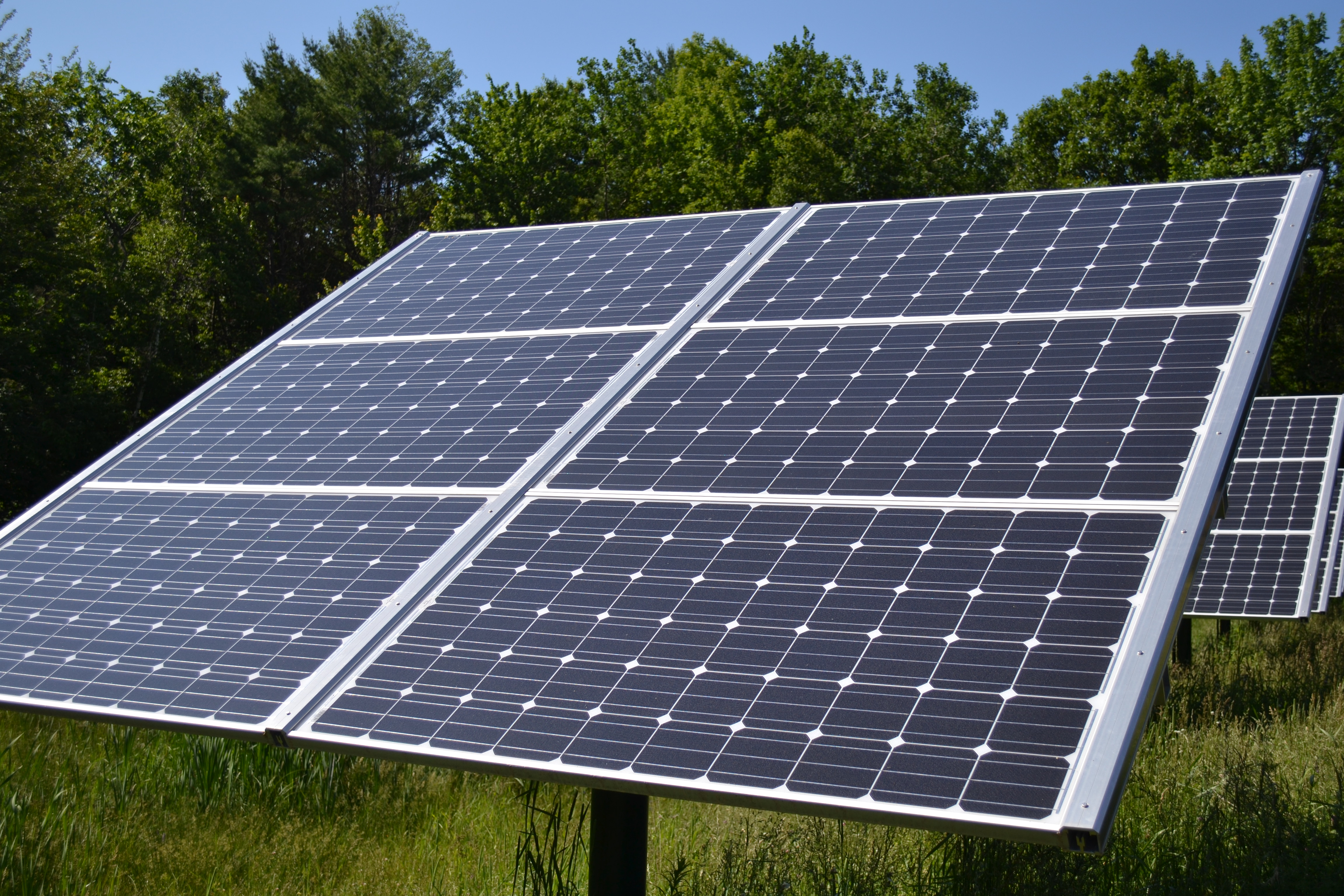


The building blocks of a photovoltaic system are solar cells. A solar cell is the electrical device that can directly convert photons energy into electricity. There are three technological generations of solar cells: the first generation (1G) of
crystalline silicon cells (c-Si), the second generation (2G) of
thin-film cells (such as
CdTe,
CIGS,
Amorphous Silicon, and
GaAs), and the third generation (3G) of
organic,
dye-sensitized,
Perovskite and
multijunction cells.
Conventional
c-Si solar cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect. s, normally wired in series, are encapsulated in a solar module to protect them from the weather. The module consists of a
tempered glass as cover, a soft and flexible
encapsulant, a rear backsheet made of a weathering and fire-resistant
material
A material is a matter, substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an Physical object, object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical property, physical ...
and an aluminium frame around the outer edge. Electrically connected and mounted on a supporting structure, solar modules build a string of modules, often called solar panel. A solar array consists of one or many such panels. A photovoltaic array, or solar array, is a linked collection of solar modules. The power that one module can produce is seldom enough to meet requirements of a home or a business, so the modules are linked together to form an array. Most PV arrays use an
inverter to convert the DC power produced by the modules into
alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
that can power
light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
s, motors, and other loads. The modules in a PV array are usually first connected in
series to obtain the desired
voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
; the individual strings are then connected in
parallel to allow the system to produce more
current. Solar panels are typically measured under STC (standard test conditions) or PTC (PVUSA test conditions), in
watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s. Typical panel ratings range from less than 100 watts to over 400 watts. The array rating consists of a summation of the panel ratings, in watts, kilowatts, or megawatts.
Modules and efficiency
A typical 150 watt
PV module is about a square meter in size. Such a module may be expected to produce 0.75
kilowatt-hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a non-SI unit of energy equal to 3.6 megajoules (MJ) in SI units, which is the energy delivered by one kilowatt of power for one hour. Kilowatt-hours are a comm ...
(kWh) every day, on average, after taking into account the weather and the latitude, for an insolation of 5 sun hours/day. Module output degrades faster at increased temperature. Allowing ambient air to flow over, and if possible behind, PV modules reduces this problem, as the airflow tend to reduce the operating temperature and, as consequence, increase the module efficiency. However, it was recently demonstrated that, in the real-world operation, considering a larger scale photovoltaic generator, increase in wind speed can increase the energy losses, following the fluid mechanics theory, as the wind interaction with the PV generator induces air flux variations that modify the heat transfer from the modules to the air.
Effective module lives are typically 25 years or more. The payback period for an investment in a PV solar installation varies greatly and is typically less useful than a calculation of
return on investment
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is the ratio between net income (over a period) and investment (costs resulting from an investment of some resources at a point in time). A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favorab ...
. While it is typically calculated to be between 10 and 20 years, the financial payback period can be far shorter with
incentives.
The temperature effect on photovoltaic modules is usually quantified by means of some coefficients relating the variations of the open‐circuit voltage, of the short‐circuit current, and of the maximum power to temperature changes. In this paper, comprehensive experimental guidelines to estimate the temperature coefficients.
Due to the low voltage of an individual
solar cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect. (typically ca. 0.5V), several cells are wired ''(see
Copper in renewable energy#Solar photovoltaic power generation)'' in series in the manufacture of a "laminate". The laminate is assembled into a protective weatherproof enclosure, thus making a photovoltaic module or
solar panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct ...
. Modules may then be strung together into a photovoltaic array. In 2012, solar panels available for consumers had an efficiency of up to about 17%, while commercially available panels can go as far as 27%. By concentrating the sunlight it is possible to achieve higher efficiencies. A group from The
Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems has created a cell that can reach 44.7% efficiency using the equivalent of "297 suns".
Shading and dirt
Photovoltaic cell electrical output is extremely sensitive to shading (the so-called "Christmas light effect"). When even a small portion of a cell or of a module or array of cells in parallel is shaded, with the remainder in sunlight, the output falls dramatically due to internal 'short-circuiting' (the electrons reversing course through the shaded portion). When connected in series, the current drawn from a string of cells is no greater than the normally small current that can flow through the shaded cell, so the current (and therefore power) developed by the string is limited. If the external load is of low enough impedance, there may be enough voltage available from the other cells in a string to force more current through the shaded cell by breaking down the junction. This breakdown voltage in common cells is between 10 and 30 volts. Instead of adding to the power produced by the panel, the shaded cell absorbs power, turning it into heat. Since the reverse voltage of a shaded cell is much greater than the forward voltage of an illuminated cell, one shaded cell can absorb the power of many other cells in the string, disproportionately affecting panel output. For example, a shaded cell may drop 8 volts, instead of adding 0.5 volts, at a high current level, thereby absorbing the power produced by 16 other cells.
[Ursula Eicker, ''Solar Technologies for Buildings'', Wiley 2003, , page 226] It is thus important that a PV installation not be shaded by trees or other obstructions. There are techniques to mitigate the losses with diodes, but these techniques also entail losses.
Several methods have been developed to determine shading losses from trees to PV systems over both large regions using
LiDAR
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
, but also at an individual system level using
3D modeling software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
.
Most modules have bypass diodes between each cell or string of cells that minimize the effects of shading and only lose the power that the shaded portion of the array would have supplied, as well as the power dissipated in the diodes. The main job of the bypass diode is to eliminate hot spots that form on cells that can cause further damage to the array, and cause fires.

Sunlight can be absorbed by dust, snow, or other impurities at the surface of the module (collectively referred to as
soiling). Soiling reduces the light that strikes the cells, which in turn reduces the power output of the PV system. Soiling losses aggregate over time, and can become large without adequate cleaning. In 2018, the global annual energy loss due to soiling was estimated to at least 3–4%.
However, soiling losses vary significantly from region to region, and within regions.
Maintaining a clean module surface will increase output performance over the life of the PV system. In one study performed in a snow-rich area (
Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
), cleaning flat mounted solar panels after 15 months increased their output by almost 100%. However, 5° tilted arrays were adequately cleaned by rainwater.
In many cases, especially in
arid regions, or in locations in close proximity to deserts, roads, industry, or agriculture, regular cleaning of the solar panels is
cost-effective
Cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) is a form of economic analysis that compares the relative costs and outcomes (effects) of different courses of action. Cost-effectiveness analysis is distinct from cost–benefit analysis, which assigns a monetar ...
. In 2018, the estimated soiling-induced revenue loss was estimated to between 5 and 7 billion euros.
The long‐term reliability of photovoltaic modules is crucial to ensure the technical and economic viability of PV as a successful energy source. The analysis of degradation mechanisms of PV modules is key to ensure current lifetimes exceeding 25 years.
Insolation and energy
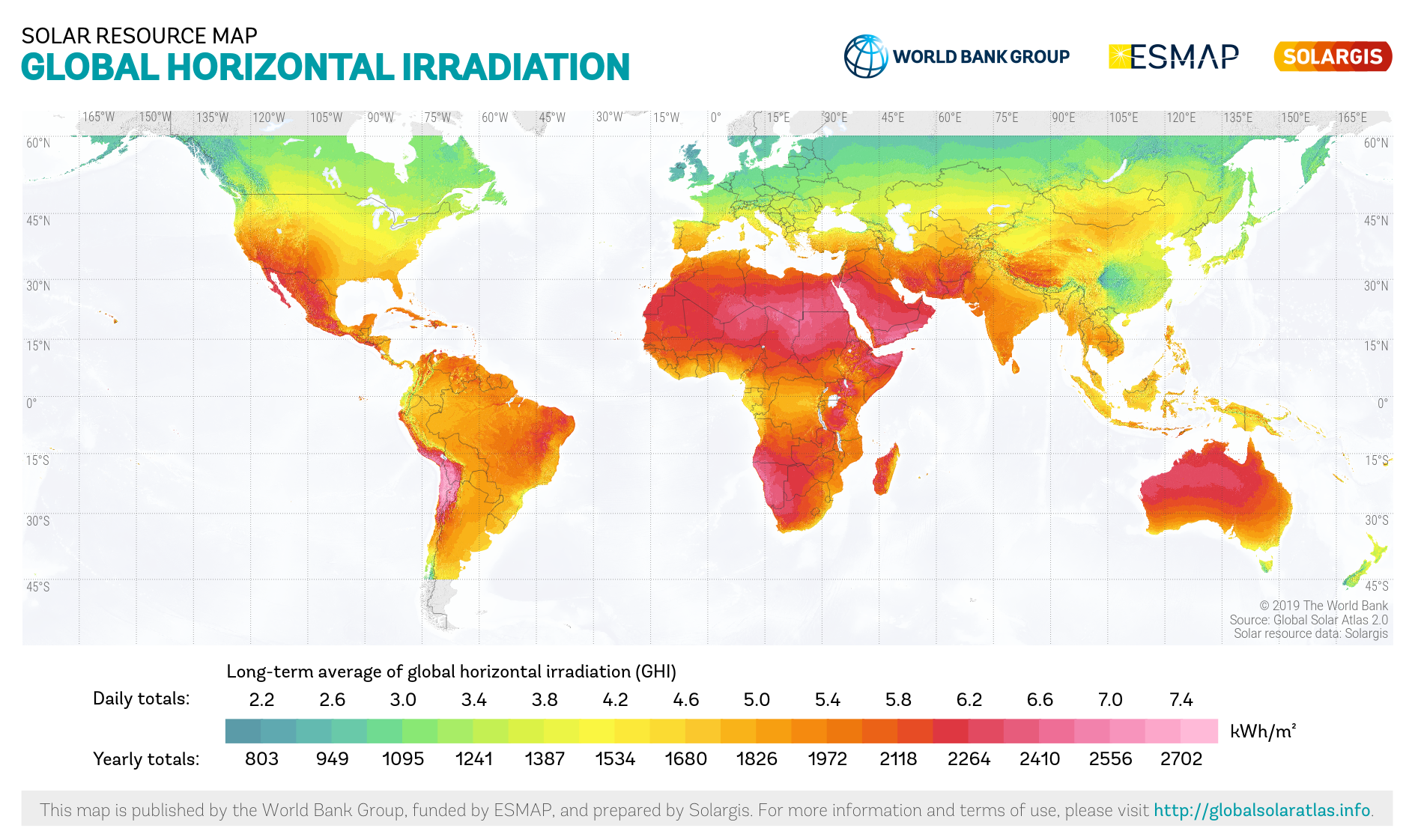 Solar insolation
Solar insolation is made up of direct, diffuse, and reflected
radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
. The absorption factor of a PV cell is defined as the fraction of incident solar irradiance that is absorbed by the cell. When the sun is at the zenith on a cloudless day, the power of the sun is about 1
kW/m
2, on the Earth's surface, to a plane that is perpendicular to the sun's rays. As such, PV arrays can
track the sun through each day to greatly enhance energy collection. However, tracking devices add cost, and require maintenance, so it is more common for PV arrays to have fixed mounts that tilt the array and face due south in the northern hemisphere or due north in the southern hemisphere. The tilt angle from horizontal can be varied for season, but if fixed, should be set to give optimal array output during the peak electrical demand portion of a typical year for a stand-alone system. This optimal module tilt angle is not necessarily identical to the tilt angle for maximum annual array energy output. The optimization of the photovoltaic system for a specific environment can be complicated as issues of solar flux, soiling, and snow losses should be taken into effect. In addition, later work has shown that spectral effects can play a role in optimal photovoltaic material selection. For example, the spectrum of the
albedo of the surroundings can play a significant role in output depending on the surface around the photovoltaic system and the type of solar cell material. A photovoltaic installation in the northern latitudes of Europe or the United States may expect to produce 1 kWh/m
2/day. A typical 1 kW photovoltaic installation in Australia or the southern latitudes of Europe or United States, may produce 3.5–5 kWh per day, dependent on location, orientation, tilt, insolation and other factors. In the
Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
desert, with less cloud cover and a better solar angle, one could ideally obtain closer to 8.3 kWh/m
2/day provided the nearly ever present wind would not blow sand onto the units. The area of the Sahara desert is over 9 million km
2. 90,600 km
2, or about 1%, could generate as much electricity as all of the world's power plants combined.
Mounting

Modules are assembled into arrays on some kind of mounting system, which may be classified as ground mount, roof mount or pole mount. For
solar parks a large rack is mounted on the ground, and the modules mounted on the rack.
For buildings, many different racks have been devised for pitched roofs. For flat roofs, racks, bins and building integrated solutions are used. Solar panel racks mounted on top of poles can be stationary or moving, see Trackers below. Side-of-pole mounts are suitable for situations where a pole has something else mounted at its top, such as a light fixture or an antenna. Pole mounting raises what would otherwise be a ground mounted array above weed shadows and livestock, and may satisfy electrical code requirements regarding inaccessibility of exposed wiring. Pole mounted panels are open to more cooling air on their underside, which increases performance. A multiplicity of pole top racks can be formed into a parking carport or other shade structure. A rack which does not follow the sun from left to right may allow seasonal adjustment up or down.
Cabling
Due to their outdoor usage, solar cables are designed to be resistant against
UV radiation and extremely high temperature fluctuations and are generally unaffected by the weather. Standards specifying the usage of
electrical wiring
Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of Electrical cable, cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.
Wiring is subject to safety standards for design and in ...
in PV systems include the
IEC 60364 by the
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
, in section 712 "Solar photovoltaic (PV) power supply systems", the British Standard
BS 7671, incorporating regulations relating to
microgeneration and photovoltaic systems, and the US UL4703 standard, in subject 4703 "Photovoltaic Wire".

A solar cable is the interconnection
cable
Cable may refer to:
Mechanical
* Nautical cable, an assembly of three or more ropes woven against the weave of the ropes, rendering it virtually waterproof
* Wire rope, a type of rope that consists of several strands of metal wire laid into a hel ...
used in
photovoltaic power generation. Solar cables interconnect
solar panels and other electrical components of a photovoltaic system. Solar cables are designed to be
UV resistant and
weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
resistant. They can be used within a large temperature range.
Specific performance requirements for material used for wiring a solar panel installation are given in national and local
electrical codes which regulate electrical installations in an area. General features required for solar cables are resistance to ultraviolet light, weather, temperature extremes of the area and insulation suitable for the voltage class of the equipment. Different jurisdictions will have specific rules regarding grounding (earthing) of solar power installations for electric shock protection and lightning protection.
Tracker

A
solar tracking system tilts a solar panel throughout the day. Depending on the type of tracking system, the panel is either aimed directly at the Sun or the brightest area of a partly clouded sky. Trackers greatly enhance early morning and late afternoon performance, increasing the total amount of power produced by a system by about 20–25% for a single axis tracker and about 30% or more for a dual axis tracker, depending on latitude.
Trackers are effective in regions that receive a large portion of sunlight directly. In diffuse light (i.e. under cloud or fog), tracking has little or no value. Because most
concentrated photovoltaics systems are very sensitive to the sunlight's angle, tracking systems allow them to produce useful power for more than a brief period each day. Tracking systems improve performance for two main reasons. First, when a solar panel is perpendicular to the sunlight, it receives more light on its surface than if it were angled. Second, direct light is used more efficiently than angled light. Special
anti-reflective coatings can improve solar panel efficiency for direct and angled light, somewhat reducing the benefit of tracking.
Trackers and sensors to optimise the performance are often seen as optional, but they can increase viable output by up to 45%. Arrays that approach or exceed one megawatt often use solar trackers. Considering clouds, and the fact that most of the world is not on the equator, and that the sun sets in the evening, the correct measure of solar power is
insolation – the average number of kilowatt-hours per square meter per day. For the weather and latitudes of the United States and Europe, typical insolation ranges from 2.26 kWh/m
2/day in northern climes to 5.61 kWh/m
2/day in the sunniest regions.
For large systems, the energy gained by using tracking systems can outweigh the added complexity. For
very large systems, the added maintenance of tracking is a substantial detriment. Tracking is not required for flat panel and low-concentration
photovoltaic systems. For high-concentration photovoltaic systems, dual axis tracking is a necessity. Pricing trends affect the balance between adding more stationary solar panels versus having fewer panels that track.
As pricing, reliability and performance of single-axis trackers have improved, the systems have been installed in an increasing percentage of utility-scale projects. According to data from WoodMackenzie/GTM Research, global solar tracker shipments hit a record 14.5 gigawatts in 2017. This represents growth of 32 percent year-over-year, with similar or greater growth projected as large-scale solar deployment accelerates.
Inverter
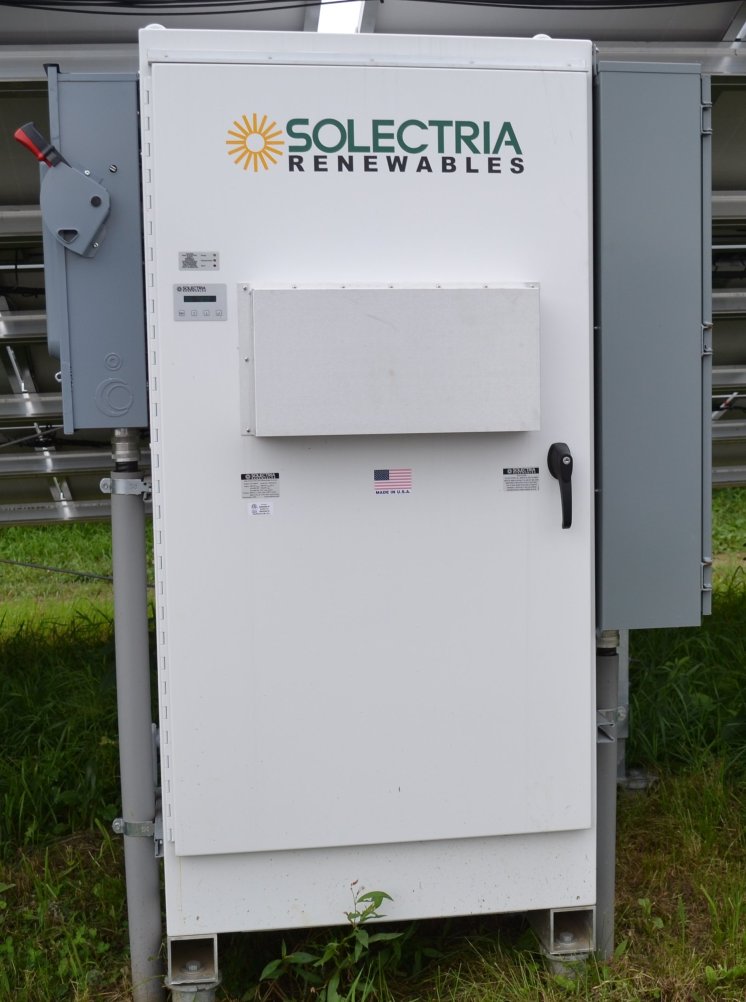


Systems designed to deliver
alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
(AC), such as grid-connected applications need an inverter to convert the
direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC) from the solar modules to AC. Grid connected inverters must supply AC electricity in sinusoidal form, synchronized to the grid frequency, limit feed in voltage to no higher than the grid voltage and disconnect from the grid if the grid voltage is turned off. Islanding inverters need only produce regulated voltages and frequencies in a sinusoidal waveshape as no synchronisation or co-ordination with grid supplies is required.
A
solar inverter may connect to a string of solar panels. In some installations a
solar micro-inverter is connected at each solar panel. For safety reasons a circuit breaker is provided both on the AC and DC side to enable maintenance. AC output may be connected through an
electricity meter
file:Hydro quebec meter.JPG, North American domestic analog signal, analog (Galileo Ferraris, Ferraris disk) electricity meter.
file:Transparent Electricity Meter found in Israel.JPG, Electricity meter with transparent plastic case (Israel)
fil ...
into the public grid. The number of
modules in the system determines the total DC watts capable of being generated by the solar array; however, the inverter ultimately governs the amount of AC watts that can be distributed for consumption. For example, a PV system comprising 11
kilowatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
s DC (kW
DC) worth of PV modules, paired with one 10-kilowatt AC (kW
AC) inverter, will be limited to the inverter's output of 10 kW. As of 2019, conversion efficiency for state-of-the-art converters reached more than 98 percent. While string inverters are used in residential to medium-sized commercial PV systems, central inverters cover the large commercial and utility-scale market. Market-share for central and string inverters are about 44 percent and 52 percent, respectively, with less than 1 percent for micro-inverters.
(MPPT) is a technique that grid connected inverters use to get the maximum possible power from the photovoltaic array. In order to do so, the inverter's MPPT system digitally samples the solar array's ever changing power output and applies the proper impedance to find the optimal ''maximum power point''.
Anti-islanding is a protection mechanism to immediately shut down the inverter, preventing it from generating AC power when the connection to the load no longer exists. This happens, for example, in the case of a blackout. Without this protection, the supply line would become an "island" with power surrounded by a "sea" of unpowered lines, as the solar array continues to deliver DC power during the power outage. Islanding is a hazard to utility workers, who may not realize that an AC circuit is still powered, and it may prevent automatic re-connection of devices. Anti-Islanding feature is not required for complete Off-Grid Systems.
Battery
Although still expensive, PV systems increasingly use rechargeable batteries to store a surplus to be later used at night.
Batteries used for grid-storage also stabilize the
electrical grid by
leveling out peak loads, and play an important role in a
smart grid
The smart grid is an enhancement of the 20th century electrical grid, using two-way communications and distributed so-called intelligent devices. Two-way flows of electricity and information could improve the delivery network. Research is main ...
, as they can charge during periods of low demand and feed their stored energy into the grid when demand is high.
Common battery technologies used in today's PV systems include the
valve regulated lead-acid battery – a modified version of the conventional
lead–acid battery
The lead–acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery first invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. It was the first type of rechargeable battery to be invented. Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead–acid batteries ha ...
–
nickel–cadmium and
lithium-ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible Intercalation (chemistry), intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically Electrical conductor, conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are c ...
batteries. Compared to the other types, lead-acid batteries have a shorter lifetime and lower energy density. However, due to their high reliability, low self discharge as well as low investment and maintenance costs, they are currently (as of 2014) the predominant technology used in small-scale, residential PV systems, as lithium-ion batteries are still being developed and about 3.5 times as expensive as lead-acid batteries. Furthermore, as storage devices for PV systems are stationary, the lower energy and power density and therefore higher weight of lead-acid batteries are not as critical as, for example, in
electric transportation Other rechargeable batteries considered for distributed PV systems include
sodium–sulfur and
vanadium redox batteries, two prominent types of a
molten salt and a
flow battery, respectively.
In 2015, Tesla Motors launched the
Powerwall, a rechargeable lithium-ion battery with the aim to revolutionize energy consumption.
PV systems with an integrated battery solution also need a
charge controller, as the varying voltage and current from the solar array requires constant adjustment to prevent damage from overcharging. Basic charge controllers may simply turn the PV panels on and off, or may meter out pulses of energy as needed, a strategy called PWM or
pulse-width modulation. More advanced charge controllers will incorporate
MPPT logic into their battery charging algorithms. Charge controllers may also divert energy to some purpose other than battery charging. Rather than simply shut off the free PV energy when not needed, a user may choose to heat air or water once the battery is full.
Monitoring and metering
The metering must be able to accumulate energy units in both directions, or two meters must be used. Many meters accumulate bidirectionally, some systems use two meters, but a unidirectional meter (with detent) will not accumulate energy from any resultant feed into the grid. In some countries, for installations over 30
kWp a frequency and a voltage monitor with disconnection of all phases is required. This is done where more solar power is being generated than can be accommodated by the utility, and the excess can not either be exported or
stored. Grid operators historically have needed to provide transmission lines and generation capacity. Now they need to also provide storage. This is normally hydro-storage, but other means of storage are used. Initially storage was used so that baseload generators could operate at full output. With
variable renewable energy, storage is needed to allow power generation whenever it is available, and consumption whenever needed.
The two variables a grid operator has are storing electricity for ''when'' it is needed, or transmitting it to ''where'' it is needed. If both of those fail, installations over 30kWp can automatically shut down, although in practice all inverters maintain voltage regulation and stop supplying power if the load is inadequate. Grid operators have the option of curtailing excess generation from large systems, although this is more commonly done with wind power than solar power, and results in a substantial loss of revenue. Three-phase inverters have the unique option of supplying reactive power which can be advantageous in matching load requirements.
Photovoltaic systems need to be monitored to detect breakdown and optimize operation. There are several
photovoltaic monitoring strategies depending on the output of the installation and its nature. Monitoring can be performed on site or remotely. It can measure production only, retrieve all the data from the inverter or retrieve all of the data from the communicating equipment (probes, meters, etc.). Monitoring tools can be dedicated to supervision only or offer additional functions. Individual inverters and battery charge controllers may include monitoring using manufacturer specific protocols and software. Energy metering of an inverter may be of limited accuracy and not suitable for revenue metering purposes. A third-party data acquisition system can monitor multiple inverters, using the inverter manufacturer's protocols, and also acquire weather-related information. Independent
smart meters may measure the total energy production of a PV array system. Separate measures such as satellite image analysis or a solar radiation meter (a
pyranometer
A pyranometer () is a type of actinometer used for measuring solar irradiance on a planar surface and it is designed to measure the solar radiation flux density (W/m2) from the hemisphere above within a wavelength range 0.3 μm to 3 μm.
A typ ...
) can be used to estimate total insolation for comparison.
Data collected from a monitoring system can be displayed remotely over the World Wide Web, such as
OSOTF.
Sizing of the photovoltaic system
Knowing the annual energy consumption in Kwh
of an institution or a family, for example of 2300Kwh, legible in its electricity bill, it is possible to calculate the number of photovoltaic panels necessary to satisfy its energy needs. By connecting to the site https://re.jrc.ec.europa.eu/pvg_tools/en/ , after selecting the location in which to install the panels or clicking on the map or typing the name of the location, you must select "Grid connected" and "Visualize results" obtaining the following table for example relating to the city of Palermo:
Provided inputs:;
Location
at/Lon;38.111,13.352
Horizon:;Calculated
Database used:;PVGIS-SARAH2
PV technology:;Crystalline silicon
PV installed
Wp;1
System loss
;14
Simulation outputs:;
Slope angle
�;35
Azimuth angle
�;0
Yearly PV energy production
Wh;1519.1
Yearly in-plane irradiation
Wh/m2;1944.62
Year-to-year variability
Wh;47.61
Changes in output due to:;
Angle of incidence
;-2.68
Spectral effects
;0.88
Temperature and low irradiance
;-7.48
Total loss
;-21.88
PV electricity cost
er kWh;
Using the
wxMaxima program, the number of panels required for an annual consumption of 2300 kWh and for a crystalline silicon technology with a slope angle of 35°, an azimut angle of 0° and total losses equal to 21.88% is 6 rounded up:
E_d : 2300 ;
E_s : 1519.1 ;
P : 300 ;
Number_panels : 1000 * E_d / ( P * E_s ) ;
5.046847914335243
On average, each family manages to consume 30% of energy directly from the photovoltaic. The storage system can bring its self-consumption to a maximum of 70%, therefore the battery storage capacity that should be in the specific case is: 4.41 Kwh which rounded up is 4.8 Kwh
Battery_capacity : 0.70 * E_d/365 ;
4.410958904109589
If the price of energy is 0.5 €/Kwh then the cost of energy excluding taxes will be 1150€ per year:
Energy_cost : E_d * 0.5;
1150.0
So if a 300W panel costs €200, the 4.8Kwh battery costs €3000, the inverter to convert the direct current into alternating current €1000, the charge regulator €100, the installation costs €1000 the total cost will be €6,300 :
Total_cost : 200*6 + 3000 + 1000 + 100 + 1000 ;
3150
which are amortized over 5.46 years:
Years : Total_cost / Energy_cost ;
5.46...
having the battery a life of 10 years and the panels 25–30 years
Other systems
This section includes systems that are either highly specialized and uncommon or still an emerging new technology with limited significance. However,
standalone or off-grid systems take a special place. They were the most common type of systems during the 1980s and 1990s, when PV technology was still very expensive and a pure niche market of small scale applications. Only in places where no electrical grid was available, they were economically viable. Although new stand-alone systems are still being deployed all around the world, their contribution to the overall installed photovoltaic capacity is decreasing. In Europe, off-grid systems account for 1 percent of installed capacity. In the United States, they account for about 10 percent. Off-grid systems are still common in Australia and South Korea, and in many developing countries.
CPV
Concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) and ''high concentrator photovoltaic'' (HCPV) systems use
optical lenses or curved mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto small but highly efficient solar cells. Besides concentrating optics, CPV systems sometime use solar trackers and cooling systems and are more expensive.
Especially HCPV systems are best suited in location with high solar irradiance, concentrating sunlight up to 400 times or more, with efficiencies of 24–28 percent, exceeding those of regular systems. Various designs of systems are commercially available but not very common. However, ongoing research and development is taking place.
CPV is often confused with CSP (
concentrated solar power) that does not use photovoltaics. Both technologies favor locations that receive much sunlight and directly compete with each other.
Hybrid

A hybrid system combines PV with other forms of generation, usually a diesel generator. Biogas is also used. The other form of generation may be a type able to modulate power output as a function of demand. However more than one renewable form of energy may be used e.g. wind. The photovoltaic power generation serves to reduce the consumption of non renewable fuel. Hybrid systems are most often found on islands.
Pellworm island in Germany and
Kythnos island in Greece are notable examples (both are combined with wind). The Kythnos plant has reduced diesel consumption by 11.2%.
In 2015, a case-study conducted in seven countries concluded that in all cases generating costs can be reduced by hybridising mini-grids and isolated grids. However, financing costs for such hybrids are crucial and largely depend on the ownership structure of the power plant. While cost reductions for state-owned utilities can be significant, the study also identified economic benefits to be insignificant or even negative for non-public utilities, such as
independent power producers.
There has also been work showing that the PV penetration limit can be increased by deploying a distributed network of PV+CHP hybrid systems in the U.S. The temporal distribution of solar flux, electrical and heating requirements for representative U.S. single family residences were analyzed and the results clearly show that hybridizing CHP with PV can enable additional PV deployment above what is possible with a conventional centralized electric generation system. This theory was reconfirmed with numerical simulations using per second solar flux data to determine that the necessary battery backup to provide for such a hybrid system is possible with relatively small and inexpensive battery systems. In addition, large PV+CHP systems are possible for institutional buildings, which again provide back up for intermittent PV and reduce CHP runtime.
*
PVT system (hybrid PV/T), also known as photovoltaic thermal hybrid solar collectors, convert solar radiation into thermal and electrical energy. Such a system combines a solar (PV) module with a
solar thermal collector in a complementary way.
*
CPVT system. A ''concentrated photovoltaic thermal hybrid'' (CPVT) system is similar to a PVT system. It uses
concentrated photovoltaics (CPV) instead of conventional PV technology, and combines it with a solar thermal collector.
* CPV/CSP system is a proposed novel solar hybrid system, combining concentrator photovoltaics with the non-PV technology of
concentrated solar power (CSP), or also known as concentrated solar thermal.
*
PV diesel system combines a photovoltaic system with a
diesel generator. Combinations with
other renewables are possible and include
wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that wind power, converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. , hundreds of thousands of list of most powerful wind turbines, large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, were generating over ...
s.
Floating solar arrays
Direct current grid
DC grids are found in electric powered transport: railways trams and trolleybuses. A few pilot plants for such applications have been built, such as the tram depots in Hannover Leinhausen, using photovoltaic contributors and Geneva (Bachet de Pesay). The 150 kW
p Geneva site feeds 600 V DC directly into the tram/trolleybus electricity network whereas before it provided about 15% of the electricity at its opening in 1999.
Standalone
A
stand-alone or off-grid system is not connected to the
electrical grid. Standalone systems vary widely in size and application from
wristwatches or
calculators to remote buildings or
spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
. If the load is to be supplied independently of solar
insolation, the generated power is stored and buffered with a battery. In non-portable applications where weight is not an issue, such as in buildings,
lead acid batteries are most commonly used for their low cost and tolerance for abuse.
A charge controller may be incorporated in the system to avoid battery damage by excessive charging or discharging. It may also help to optimize production from the solar array using a maximum power point tracking technique (
MPPT). However, in simple PV systems where the PV module voltage is matched to the battery voltage, the use of MPPT electronics is generally considered unnecessary, since the battery voltage is stable enough to provide near-maximum power collection from the PV module.
In small devices (e.g. calculators, parking meters) only
direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC) is consumed. In larger systems (e.g. buildings, remote water pumps) AC is usually required. To convert the DC from the modules or batteries into AC, an
inverter is used.
In
agricultural
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created f ...
settings, the array may be used to directly power DC
pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
s, without the need for an
inverter. In remote settings such as mountainous areas, islands, or other places where a power grid is unavailable, solar arrays can be used as the sole source of electricity, usually by charging a
storage battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prim ...
. Stand-alone systems closely relate to
microgeneration and
distributed generation.
Costs and economy
The cost of producing photovoltaic cells has dropped because of
economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
in production and technological advances in manufacturing. For large-scale installations, prices below $1.00 per watt were common by 2012. A price decrease of 50% had been achieved in Europe from 2006 to 2011, and there was a potential to lower the generation cost by 50% by 2020. Crystal silicon
solar cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect. s have largely been replaced by less expensive multicrystalline silicon solar cells, and thin film silicon solar cells have also been developed at lower costs of production. Although they are reduced in energy conversion efficiency from single crystalline "siwafers", they are also much easier to produce at comparably lower costs.
The table below shows the total (average) cost in US cents per kWh of electricity generated by a photovoltaic system. The row headings on the left show the total cost, per peak kilowatt (kW
p), of a photovoltaic installation. Photovoltaic system costs have been declining and in Germany, for example, were reported to have fallen to USD 1389/kW
p by the end of 2014.
The column headings across the top refer to the annual energy output in kWh expected from each installed kW
p. This varies by geographic region because the average
insolation depends on the average cloudiness and the thickness of atmosphere traversed by the sunlight. It also depends on the path of the sun relative to the panel and the horizon.
Panels are usually mounted at an angle based on latitude, and often they are adjusted seasonally to meet the changing solar
declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
.
Solar tracking can also be utilized to access even more perpendicular sunlight, thereby raising the total energy output.
The calculated values in the table reflect the total (average) cost in cents per kWh produced. They assume a 10% total capital cost (for instance 4%
interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
, 1% operating and maintenance cost, and
depreciation
In accountancy, depreciation refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, an actual reduction in the fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wears, and second, the allocation i ...
of the capital outlay over 20 years). Normally, photovoltaic modules have a 25-year warranty.
Learning curve
Photovoltaic systems demonstrate a learning curve in terms of
levelized cost of electricity (LCOE), reducing its cost per kWh by 32.6% for every doubling of capacity.
From the data of LCOE and cumulative installed capacity from
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) from 2010 to 2017,
the learning curve equation for photovoltaic systems is given as
* LCOE : levelized cost of electricity (in USD/kWh)
* Capacity : cumulative installed capacity of photovoltaic systems (in MW)
Regulation
Standardization
Increasing use of photovoltaic systems and integration of photovoltaic power into existing structures and techniques of supply and distribution increases the need for general standards and definitions for photovoltaic components and systems. The standards are compiled at the
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
(IEC) and apply to efficiency, durability and safety of cells, modules, simulation programs, plug connectors and cables, mounting systems, overall efficiency of inverters etc.
National regulations
United Kingdom
In the UK, PV installations are generally considered permitted development and do not require planning permission. If the property is listed or in a designated area (National Park, Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, Site of Special Scientific Interest or Norfolk Broads) then planning permission is required.
UK Solar PV installations are also subject to control under the Building Regulations 2010. Buildings regulation approval is therefore necessary for both domestic and commercial solar PV rootop installations to ensure that they meet the required safety standards. This includes ensuring that the roof can support the weight of the solar panels, that the electrical connections are safe, and that there are no fire risks.
United States
In the United States, article 690 of the National Electric Code provides general guidelines for the installation of photovoltaic systems; these may be superseded by local laws and regulations. Often a permit is required necessitating plan submissions and structural calculations before work may begin. Additionally, many locales require the work to be performed under the guidance of a licensed electrician.
The
Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) will review designs and issue permits, before construction can lawfully begin. Electrical installation practices must comply with standards set forth within the
National Electrical Code (NEC) and be inspected by the AHJ to ensure compliance with
building code,
electrical code, and
fire safety code. Jurisdictions may require that equipment has been tested, certified, listed, and labeled by at least one of the
Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories (NRTL).
[Solar Power World](_blank)
/ref> Many localities require a permit to install a photovoltaic system. A grid-tied system normally requires a licensed electrician to connect between the system and the grid-connected wiring of the building. Installers who meet these qualifications are located in almost every state.
Spain
Although Spain generates around 40% of its electricity via photovoltaic and other renewable energy sources, and cities such as Huelva and Seville boast nearly 3,000 hours of sunshine per year, in 2013 Spain issued a solar tax to account for the debt created by the investment done by the Spanish government. Those who do not connect to the grid can face up to a fine of 30 million euros (US$40 million). Such measures were finally withdrawn by 2018, when new legislation was introduced banning any taxes on renewable energy self-consumption.
Limitations
Impact on electricity network
With the increasing levels of rooftop photovoltaic systems, the energy flow becomes two-way. When there is more local generation than consumption, electricity is exported to the grid. However, electricity network traditionally is not designed to deal with the two-way energy transfer. Therefore, some technical issues may occur. For example, in Queensland, Australia, there have been more than 30% of households with rooftop PV by the end of 2017. The famous Californian 2020 duck curve appears very often for a lot of communities from 2015 onwards. An over-voltage issue may come out as the electricity flows back to the network. There are solutions to manage the over voltage issue, such as regulating PV inverter power factor, new voltage and energy control equipment at electricity distributor level, re-conductor the electricity wires, demand side management, etc. There are often limitations and costs related to these solutions. A way to calculate these costs and benefits is to use the concept of ' value of solar' (VOS), which includes the avoided costs/losses including: plant operations ans maintenance (fixed and variable); fuel; generation capacity, reserve capacity, transmission capacity, distribution capacity, and environmental and health liability. Popular Mechanics reports that VOS results show that grid-tied utility customers are being grossly under-compensated in most of the U.S. as the value of solar eclipses the net metering rate as well as two-tiered rates, which means "your neighbor's solar panels are secretly saving you money".
Implications for electricity bill management and energy investment
Customers have different specific situations, e.g. different comfort/convenience needs, different electricity tariffs, or different usage patterns. An electricity tariff may have a few elements, such as daily access and metering charge, energy charge (based on kWh, MWh) or peak demand charge (e.g. a price for the highest 30min energy consumption in a month). PV is a promising option for reducing energy charge when electricity price is reasonably high and continuously increasing, such as in Australia and Germany. However, for sites with peak demand charge in place, PV may be less attractive if peak demands mostly occur in the late afternoon to early evening, for example residential communities. Overall, energy investment is largely an economic decision and investment decisions are based on systematical evaluation of options in operational improvement, energy efficiency, onsite generation and energy storage.
Grid-connected photovoltaic system
 A grid-connected photovoltaic system, or grid-connected PV system is an
A grid-connected photovoltaic system, or grid-connected PV system is an electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
generating solar PV power system that is connected to the utility grid. A grid-connected PV system consists of solar panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct ...
s, one or several inverters, a power conditioning unit and grid connection equipment. They range from small residential and commercial rooftop systems to large utility-scale solar power stations. When conditions are right, the grid-connected PV system supplies the excess power, beyond consumption by the connected load, to the utility grid.
/ref>
Operation
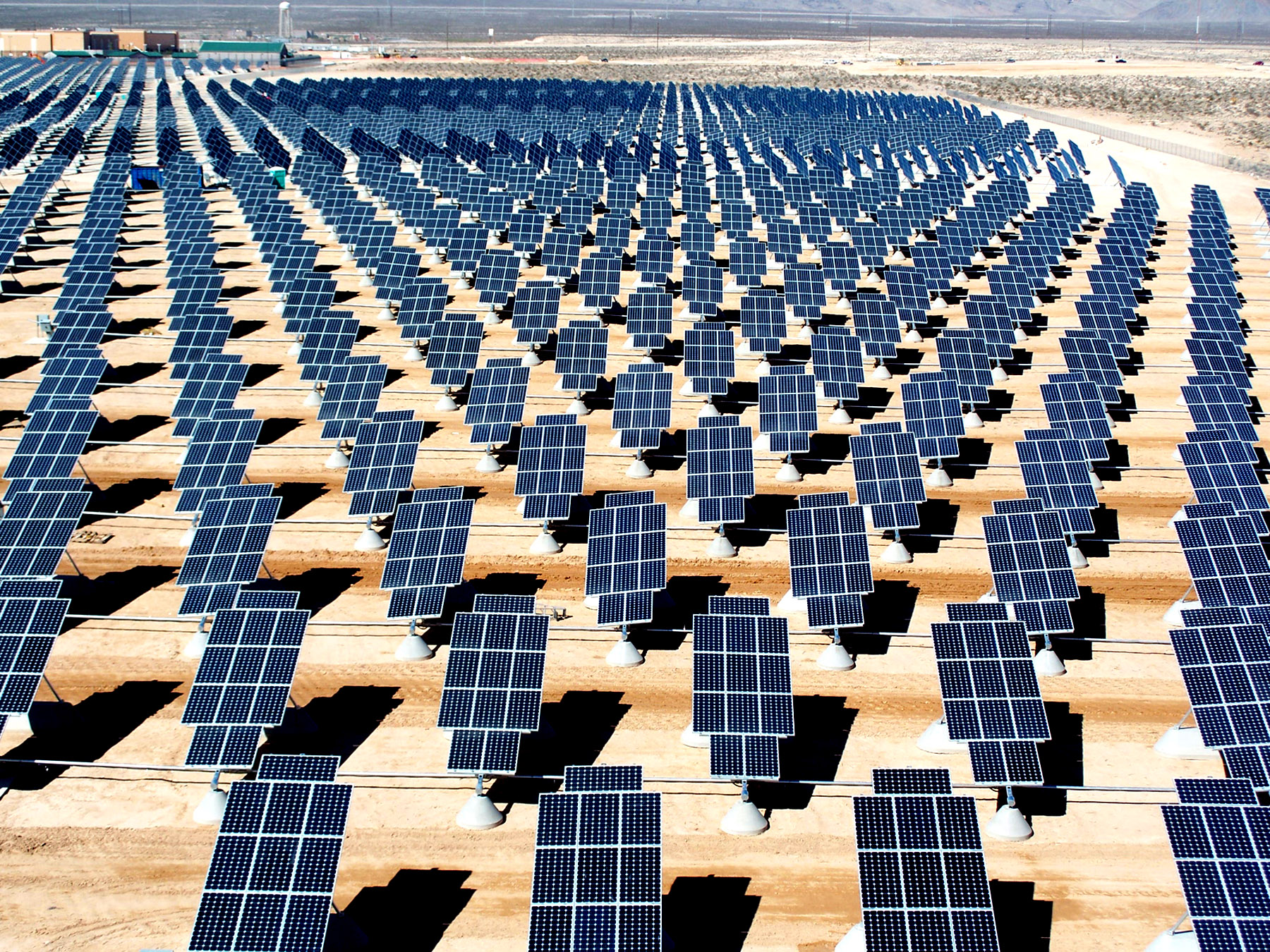 Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers. They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed. Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers. They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed. Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.
Features
Electric power from photovoltaic panels must be converted to alternating current by a special power inverter if it is intended for delivery to a power grid. The inverter sits between the solar array and the grid, and may be a large stand-alone unit or may be a collection of small inverters attached to individual solar panels as an AC module. The inverter must monitor grid voltage, waveform, and frequency. The inverter must detect failure of the grid supply, and then, must not supply power to the grid. An inverter connected to a malfunctioning power line will automatically disconnect in accordance with safety rules, which vary by jurisdiction. The location of the fault current plays a crucial part in deciding whether the protection mechanism of the inverter will kick in, especially for low and medium electricity supply network. A protection system must ensure proper operation for faults external to the inverter on the supply network. The special inverter must also be designed to synchronize its AC frequency with the grid, to ensure the correct integration of the inverter power flow into the grid according to the waveform.
Advantages
* Systems such as Net Metering and Feed-in Tariff which are offered by some system operators, can offset a customer's electricity usage costs. In some locations though, grid technologies cannot cope with distributed generation feeding into the grid, so the export of surplus electricity is not possible and that surplus is earthed.
* Grid-connected PV systems are comparatively easier to install as they do not require a battery system.[
* Grid interconnection of photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems has the advantage of effective utilization of generated power because there are no storage losses involved.]
Disadvantages
* Grid-connected PV can cause issues with voltage regulation. The traditional grid operates under the assumption of one-way, or radial, flow. But electricity injected into the grid increases voltage, and can drive levels outside the acceptable bandwidth of ±5%.power quality
Electric power quality is the degree to which the voltage, frequency, and waveform of a power supply system conform to established specifications. Good power quality can be defined as a steady supply voltage that stays within the prescribed range, ...
. PV's intermittent nature means rapid changes in voltage. This not only wears out voltage regulators due to frequent adjusting, but also can result in voltage flicker.
* Connecting to the grid poses many protection-related challenges. In addition to islanding, as mentioned above, too high levels of grid-connected PV result in problems like relay desensitization, nuisance tripping, interference with automatic reclosers, and ferroresonance.
Islanding
Islanding is the condition in which a distributed generator continues to power a location even though power from the electric utility grid is no longer present. Islanding can be dangerous to utility workers, who may not realize that a circuit is still powered, even though there is no power from the electrical grid. For that reason, distributed generators must detect islanding and immediately stop producing power; this is referred to as anti-islanding.
Anti-islanding
In the case of a utility blackout in a grid-connected PV system, the solar panels will continue to deliver power as long as the sun is shining. In this case, the supply line becomes an "island" with power surrounded by a "sea" of unpowered lines. For this reason, solar inverters that are designed to supply power to the grid are generally required to have automatic anti-islanding circuitry in them. In intentional islanding, the generator disconnects from the grid, and forces the distributed generator to power the local circuit. This is often used as a power backup system for buildings that normally sell their power to the grid.
There are two types of anti-islanding control techniques:
* ''Passive:'' The voltage and/or the frequency change during the grid failure is measured and a positive feedback loop is employed to push the voltage and/or the frequency further away from its nominal value. Frequency or voltage may not change if the load matches very well with the inverter output or the load has a very high quality factor (reactive to real power ratio). So there exists some ''Non Detection Zone'' (NDZ).
* ''Active:'' This method employs injecting some error in frequency or voltage. When grid fails, the error accumulates and pushes the voltage and/or frequency beyond the acceptable range.
See also
* Building-integrated photovoltaics
* Distributed generation
* Grid energy storage
*
* Photovoltaics
* Solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
* Renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
* Variable renewable energy
* Copper conductor
*Polyolefin
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More speciali ...
* Low smoke zero halogen
* MC4 connector
* Solar micro-inverter
*Tinning
Tinning is the process of thinly coating sheets of wrought iron or steel with tin, and the resulting product is known as tinplate. The term is also widely used for the different process of coating a metal with solder before soldering.
It is ...
* Energy demand management
* List of photovoltaic power stations
* List of rooftop photovoltaic installations
* Panel generation factor
* Photovoltaic power station
* Renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
* Rooftop photovoltaic power station
* Solar energy
Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's sunlight, light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating) and solar architecture. It is a ...
* Solar vehicle
References
External links
Summary of Photovoltaic Wire Requirements as Outlined in UL 4703
Photovoltaic Energy Factsheet
by the University of Michigan
The University of Michigan (U-M, U of M, or Michigan) is a public university, public research university in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest institution of higher education in the state. The University of Mi ...
'
Center for Sustainable Systems
Home Power Magazine
Solar project management
Best Practices for Siting Solar Photovoltaics on Municipal Solid Waste Landfills: A Study Prepared in Partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency for the RE-Powering America's Land Initiative: Siting Renewable Energy on Potentially Contaminated Land and Mine Sites
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
{{Authority control
Photovoltaics
 A grid connected system is connected to a larger independent grid (typically the public electricity grid) and feeds energy directly into the grid. This energy may be shared by a residential or commercial building before or after the revenue measurement point, depending on whether the credited energy production is calculated independently of the customer's energy consumption ( feed-in tariff) or only on the difference of energy ( net metering). These systems vary in size from residential (2–10 kWp) to solar power stations (up to tens of MWp). This is a form of decentralized electricity generation. Feeding electricity into the grid requires the transformation of DC into AC by a special, synchronizing grid-tie inverter. In kilowatt-sized installations the DC side system voltage is as high as permitted (typically 1000 V except US residential 600 V) to limit ohmic losses. Most modules (60 or 72 crystalline silicon cells) generate 160 W to 300 W at 36 volts. It is sometimes necessary or desirable to connect the modules partially in parallel rather than all in series. An individual set of modules connected in series is known as a 'string'. A set of series-connected "strings" is known as an "array."
A grid connected system is connected to a larger independent grid (typically the public electricity grid) and feeds energy directly into the grid. This energy may be shared by a residential or commercial building before or after the revenue measurement point, depending on whether the credited energy production is calculated independently of the customer's energy consumption ( feed-in tariff) or only on the difference of energy ( net metering). These systems vary in size from residential (2–10 kWp) to solar power stations (up to tens of MWp). This is a form of decentralized electricity generation. Feeding electricity into the grid requires the transformation of DC into AC by a special, synchronizing grid-tie inverter. In kilowatt-sized installations the DC side system voltage is as high as permitted (typically 1000 V except US residential 600 V) to limit ohmic losses. Most modules (60 or 72 crystalline silicon cells) generate 160 W to 300 W at 36 volts. It is sometimes necessary or desirable to connect the modules partially in parallel rather than all in series. An individual set of modules connected in series is known as a 'string'. A set of series-connected "strings" is known as an "array."
 Large utility-scale solar parks or farms are
Large utility-scale solar parks or farms are  A small PV system is capable of providing enough AC electricity to power a single home, or an isolated device in the form of AC or DC electric. Military and civilian Earth observation
A small PV system is capable of providing enough AC electricity to power a single home, or an isolated device in the form of AC or DC electric. Military and civilian Earth observation 
 Sunlight can be absorbed by dust, snow, or other impurities at the surface of the module (collectively referred to as soiling). Soiling reduces the light that strikes the cells, which in turn reduces the power output of the PV system. Soiling losses aggregate over time, and can become large without adequate cleaning. In 2018, the global annual energy loss due to soiling was estimated to at least 3–4%.
However, soiling losses vary significantly from region to region, and within regions.
Maintaining a clean module surface will increase output performance over the life of the PV system. In one study performed in a snow-rich area (
Sunlight can be absorbed by dust, snow, or other impurities at the surface of the module (collectively referred to as soiling). Soiling reduces the light that strikes the cells, which in turn reduces the power output of the PV system. Soiling losses aggregate over time, and can become large without adequate cleaning. In 2018, the global annual energy loss due to soiling was estimated to at least 3–4%.
However, soiling losses vary significantly from region to region, and within regions.
Maintaining a clean module surface will increase output performance over the life of the PV system. In one study performed in a snow-rich area ( Solar insolation is made up of direct, diffuse, and reflected
Solar insolation is made up of direct, diffuse, and reflected  A solar cable is the interconnection
A solar cable is the interconnection 
 A hybrid system combines PV with other forms of generation, usually a diesel generator. Biogas is also used. The other form of generation may be a type able to modulate power output as a function of demand. However more than one renewable form of energy may be used e.g. wind. The photovoltaic power generation serves to reduce the consumption of non renewable fuel. Hybrid systems are most often found on islands. Pellworm island in Germany and Kythnos island in Greece are notable examples (both are combined with wind). The Kythnos plant has reduced diesel consumption by 11.2%.
In 2015, a case-study conducted in seven countries concluded that in all cases generating costs can be reduced by hybridising mini-grids and isolated grids. However, financing costs for such hybrids are crucial and largely depend on the ownership structure of the power plant. While cost reductions for state-owned utilities can be significant, the study also identified economic benefits to be insignificant or even negative for non-public utilities, such as independent power producers.
There has also been work showing that the PV penetration limit can be increased by deploying a distributed network of PV+CHP hybrid systems in the U.S. The temporal distribution of solar flux, electrical and heating requirements for representative U.S. single family residences were analyzed and the results clearly show that hybridizing CHP with PV can enable additional PV deployment above what is possible with a conventional centralized electric generation system. This theory was reconfirmed with numerical simulations using per second solar flux data to determine that the necessary battery backup to provide for such a hybrid system is possible with relatively small and inexpensive battery systems. In addition, large PV+CHP systems are possible for institutional buildings, which again provide back up for intermittent PV and reduce CHP runtime.
* PVT system (hybrid PV/T), also known as photovoltaic thermal hybrid solar collectors, convert solar radiation into thermal and electrical energy. Such a system combines a solar (PV) module with a solar thermal collector in a complementary way.
* CPVT system. A ''concentrated photovoltaic thermal hybrid'' (CPVT) system is similar to a PVT system. It uses concentrated photovoltaics (CPV) instead of conventional PV technology, and combines it with a solar thermal collector.
* CPV/CSP system is a proposed novel solar hybrid system, combining concentrator photovoltaics with the non-PV technology of concentrated solar power (CSP), or also known as concentrated solar thermal.
* PV diesel system combines a photovoltaic system with a diesel generator. Combinations with other renewables are possible and include
A hybrid system combines PV with other forms of generation, usually a diesel generator. Biogas is also used. The other form of generation may be a type able to modulate power output as a function of demand. However more than one renewable form of energy may be used e.g. wind. The photovoltaic power generation serves to reduce the consumption of non renewable fuel. Hybrid systems are most often found on islands. Pellworm island in Germany and Kythnos island in Greece are notable examples (both are combined with wind). The Kythnos plant has reduced diesel consumption by 11.2%.
In 2015, a case-study conducted in seven countries concluded that in all cases generating costs can be reduced by hybridising mini-grids and isolated grids. However, financing costs for such hybrids are crucial and largely depend on the ownership structure of the power plant. While cost reductions for state-owned utilities can be significant, the study also identified economic benefits to be insignificant or even negative for non-public utilities, such as independent power producers.
There has also been work showing that the PV penetration limit can be increased by deploying a distributed network of PV+CHP hybrid systems in the U.S. The temporal distribution of solar flux, electrical and heating requirements for representative U.S. single family residences were analyzed and the results clearly show that hybridizing CHP with PV can enable additional PV deployment above what is possible with a conventional centralized electric generation system. This theory was reconfirmed with numerical simulations using per second solar flux data to determine that the necessary battery backup to provide for such a hybrid system is possible with relatively small and inexpensive battery systems. In addition, large PV+CHP systems are possible for institutional buildings, which again provide back up for intermittent PV and reduce CHP runtime.
* PVT system (hybrid PV/T), also known as photovoltaic thermal hybrid solar collectors, convert solar radiation into thermal and electrical energy. Such a system combines a solar (PV) module with a solar thermal collector in a complementary way.
* CPVT system. A ''concentrated photovoltaic thermal hybrid'' (CPVT) system is similar to a PVT system. It uses concentrated photovoltaics (CPV) instead of conventional PV technology, and combines it with a solar thermal collector.
* CPV/CSP system is a proposed novel solar hybrid system, combining concentrator photovoltaics with the non-PV technology of concentrated solar power (CSP), or also known as concentrated solar thermal.
* PV diesel system combines a photovoltaic system with a diesel generator. Combinations with other renewables are possible and include  A grid-connected photovoltaic system, or grid-connected PV system is an
A grid-connected photovoltaic system, or grid-connected PV system is an  Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers. They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed. Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers. They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed. Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.