|
Variable Renewable Energy
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or biomass, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power. The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also help. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andasol Guadix 4
The Andasol solar power station is a 150-megawatt (MW) concentrated solar power station and Europe's first commercial plant to use parabolic troughs. It is located near Guadix in Andalusia, Spain, and its name is a portmanteau of Andalusia and Sol (Sun in Spanish). The Andasol plant uses tanks of molten salt as thermal energy storage to continue generating electricity, irrespective of whether the sun is shining or not. Description Andasol is the first parabolic trough power plant in Europe, and Andasol 1 went online in March 2009. Because of the high altitude (1,100 m) and the semi-arid climate, the site has exceptionally high annual direct insolation of 2,200 kWh/m2 per year. Each plant has a gross electricity output of 50 megawatts (MWe) and 49.9 MWe net, producing around 165 gigawatt-hours (GW·h) per year. The collectors installed have a combined surface area of 51 hectares (equal to 70 soccer fields); it occupies about 200 ha of land. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
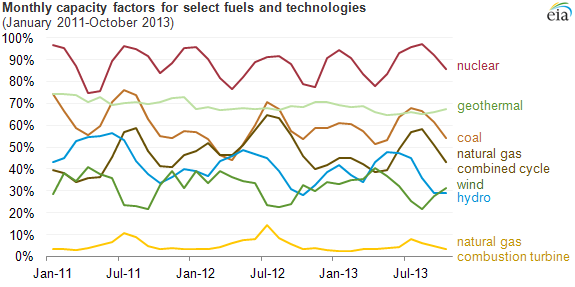
Capacity Factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production. The actual energy output during that period and the capacity factor vary greatly depending on a range of factors. The capacity factor can never exceed the availability factor, or uptime during the period. Uptime can be reduced due to, for example, reliability issues and maintenance, scheduled or unscheduled. Other fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Storage System
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide short-term energy storage, while others can endure for much longer. Bulk energy storage is currently dominated by hydroelectric dams, both conventional as well as pumped. Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Common examples of energy storage are the rechargeable battery, which stores chemical energy readily convertible to electricity to operate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air. The large magnitude of solar energy available makes it a highly appealing source of electricity. In 2020 solar energy has been the cheapest source of Electricity. In Saudi Arabia a power purchase agreemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance, repair and operations, maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoptic Scale Meteorology
The synoptic scale in meteorology (also known as large scale or cyclonic scale) is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1000 kilometers (about 620 miles) or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions (e.g., extratropical cyclones). Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps (such as surface weather analyses) are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word ''synoptic'' is derived from the Greek word ('), meaning ''seen together''. The Navier–Stokes equations applied to atmospheric motion can be simplified by scale analysis in the synoptic scale. It can be shown that the main terms in horizontal equations are Coriolis force and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aralvaimozhy Station
Aralvaimozhi is a panchayat town in Kanniyakumari District in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is a small town situated in southern India. The town was earlier called as ''Aramboly'' during colonial period. History Aralvaimozhi pass was a strategically important gap or mountain pass in the southernmost end of Western Ghats. It connected erstwhile Travancore with Madras Presidency. Many of the invasions faced by the Chera and the successor kingdoms came via this ghat. The name "Aral" was derived from the fort built and maintained by the rulers of Venad and later by the kingdom of Travancore to defend the kingdom from invasions from the east regions. It is also said that Aralvaimozhi means whispering wind. The whistling sound of wind in the region might have led to such a name. Aralvaimozhi Fort was one of the most important forts of Travancore. It was constructed around 1740 by Eustachius De Lannoy along with Udayagiri Fort, Vattakottai Fort and Travancore lines. The fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erie Shores Wind Farm Output Aug-Jul 2008
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 at the 2020 census. The estimated population in 2021 had decreased to 93,928. The Erie metropolitan area, equivalent to all of Erie County, consists of 266,096 residents. The Erie-Meadville combined statistical area had a population of 369,331 at the 2010 census. Erie is roughly equidistant from Buffalo and Cleveland, each being about 100 miles (160 kilometers) away. Erie's manufacturing sector remains prominent in the local economy, though insurance, healthcare, higher education, technology, service industries, and tourism are emerging as significant economic drivers. As with the other Great Lakes port cities, Erie is accessible to the oceans via the Lake Ontario and St. Lawrence River network in Canada. The local climate is humid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power Forecasting
A wind power forecast corresponds to an estimate of the expected production of one or more wind turbines (referred to as a wind farm) in the near future, up to a year. Forecast are usually expressed in terms of the available power of the wind farm, occasionally in units of energy, indicating the power production potential over a time interval. Time scales of forecasts Forecasting of the wind power generation may be considered at different time scales, depending on the intended application: * ''very short-term'' forecasts (from seconds up to minutes) are used for the real-time turbine control and electrical grid management, as well as for market clearing; * ''short-term'' forecasts (from 30 minutes up to hours) are used for dispatch planning, intelligent load shedding decisions; * ''medium-term'' forecasts (from 6 hours up to a day) are used for to make decisions for switching the turbine on or off for safety or conditions on the market; * ''long-term'' forecasts (from a day up t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |