Sleep Surgery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sleep surgery is a
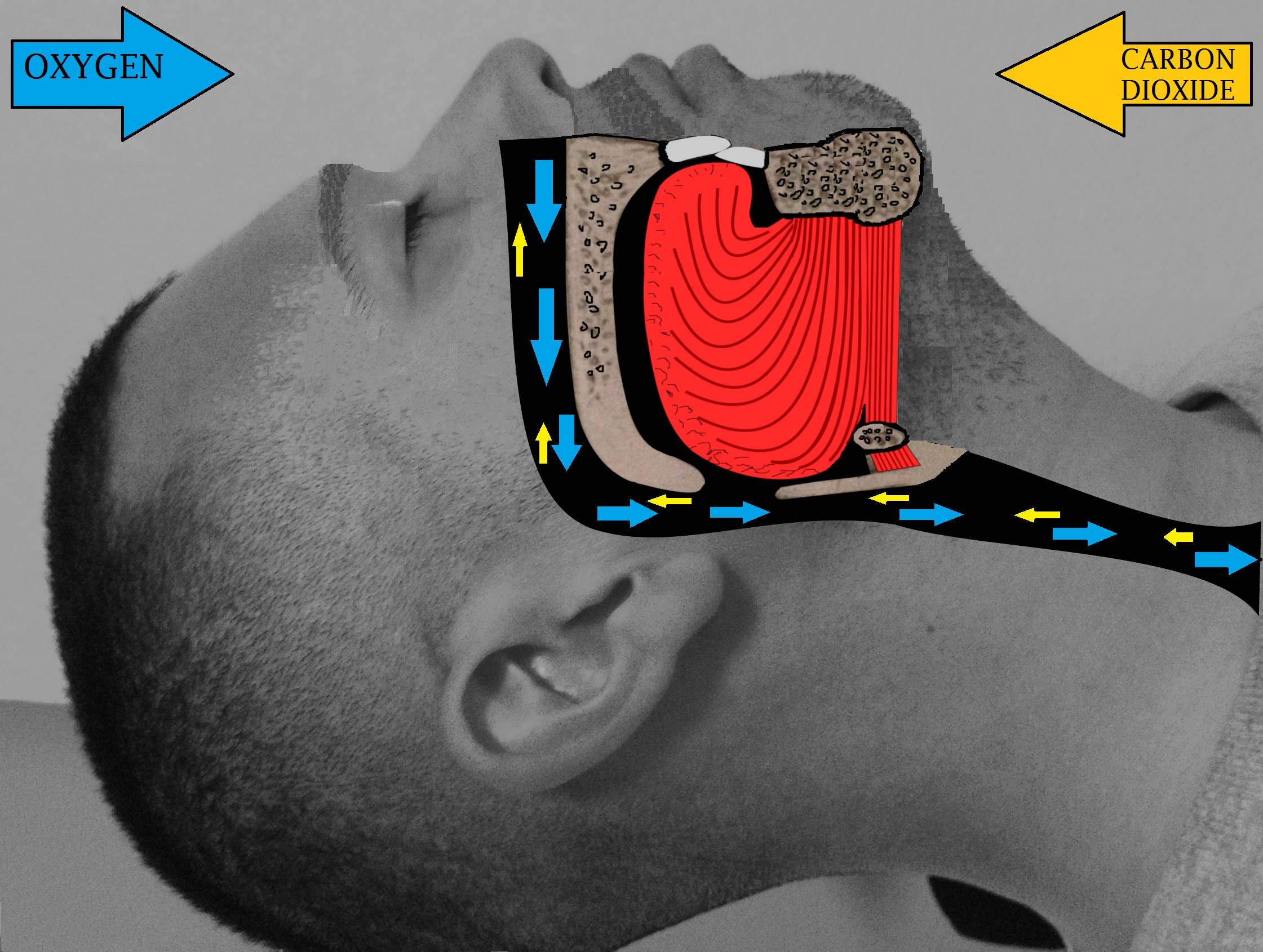



 Tongue muscles (
Tongue muscles (
 Currently, surgeons often perform maxillomandibular advancement surgery simultaneously with genioglossus advancement (tongue advancement). The genioglossus advancement pulls the tongue forward to decrease the amount of tongue blockage during sleep. MMA is one of the most effective surgical treatments for sleep apnea, with a high success rate. Nonetheless, the procedure is often used after other forms of treatment have failed (nasal surgeries, tonsillectomy, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, tongue reduction surgeries). There is a longer recovery when compared to other sleep apnea surgeries, since the bones of the face have to heal into their new position.
Currently, surgeons often perform maxillomandibular advancement surgery simultaneously with genioglossus advancement (tongue advancement). The genioglossus advancement pulls the tongue forward to decrease the amount of tongue blockage during sleep. MMA is one of the most effective surgical treatments for sleep apnea, with a high success rate. Nonetheless, the procedure is often used after other forms of treatment have failed (nasal surgeries, tonsillectomy, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, tongue reduction surgeries). There is a longer recovery when compared to other sleep apnea surgeries, since the bones of the face have to heal into their new position.

surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
performed to treat sleep disordered breathing. Sleep disordered breathing is a spectrum of disorders that includes snoring
Snoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. The sound may be soft or loud and unpleasant. Snoring during sleep may be a sign, or first alarm, of obs ...
, upper airway resistance syndrome, and obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial obstruction of the upper airway leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep. These episod ...
. These surgeries are performed by surgeons trained in otolaryngology, oral maxillofacial surgery, and craniofacial surgery.
Definitions
Obstructive sleep apnea orsleep apnea
Sleep apnea, also spelled sleep apnoea, is a sleep disorder in which pauses in breathing or periods of shallow breathing during sleep occur more often than normal. Each pause can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and they happen many times ...
is defined as either cessation of breathing (apnea) for 10 seconds, or a decrease in normal breathing (hypopnea) with an associated desaturation in oxygen and arousal during sleep that lasts at least 10 seconds. In adults, it is typical to have up to 4.9 events per hour. In obstructive sleep apnea, affected individuals are categorized based on how many apneas or hypopneas ( apnea-hypopnea index or AHI) or events they have per hour.
* Normal: <5 events per hour
* Mild: 5 to <15 events per hour
* Moderate: 15 to 30 events per hour
* Severe: >30 events per hour
The Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study, a longitudinal study
A longitudinal study (or longitudinal survey, or panel study) is a research design that involves repeated observations of the same variables (e.g., people) over short or long periods of time (i.e., uses longitudinal data). It is often a type of obs ...
of the natural history of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), found that of a random sample (602 employed men and women, 30–60 years old) the prevalence of OSA (5 or more events/hr) was 9% for women and 24% for men. However, the study found that among sleepy patients in this group, 2% of women and 4% of men met criteria for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). Those who snored habitually, were more likely to have an AHI of 15 or more.


Clinical results
Most obstructive sleep apnea sufferers have multiple points of obstruction in their airway and therefore require multilevel sleep surgery in order to maximize the efficacy of treatment. Asystematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
of the literature and meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
showed that multilevel sleep surgery achieves a 60.3% apnea hypopnea index (AHI) reduction. This reduction in sleep apnea severity via surgical means compares well against the AHI reduction for best case CPAP patients where an overall AHI reduction of 66% was achieved. Even single level surgical intervention in sleep apnea, which demonstrates a lesser degree of AHI reduction, showed a 31% survival benefit when compared against those using CPAP as therapy.
In children
Children with obstructive sleep apnea typically have enlarged tonsils and adenoid tissue. Surgery on children is over 80% successful by simply performing anadenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoid for reasons which include impaired breathing through the nose, chronic infections, or recurrent earaches. The effectiveness of removing the adenoids in children to improve recurrent nasal sympto ...
and tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a list of surgical procedures, surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat. The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent tonsillitis, throat infections and obstructive sleep ...
. Those less likely to benefit from an adenotonsillectomy are obese children and those with other medical problems, such as Down Syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual dis ...
.
A sub-group of children may have occult laryngomalacia, where the tissue directly above the vocal cord
In humans, vocal cords, also known as vocal folds or voice reeds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. Open when breathing and vibrating for speech ...
s (epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food int ...
, arytenoids
The arytenoid cartilages () are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoid ...
) collapses into the airway during sleep. These children may benefit from a supraglottoplasty to help prevent that tissue from collapsing into the airway.
Surgical procedures
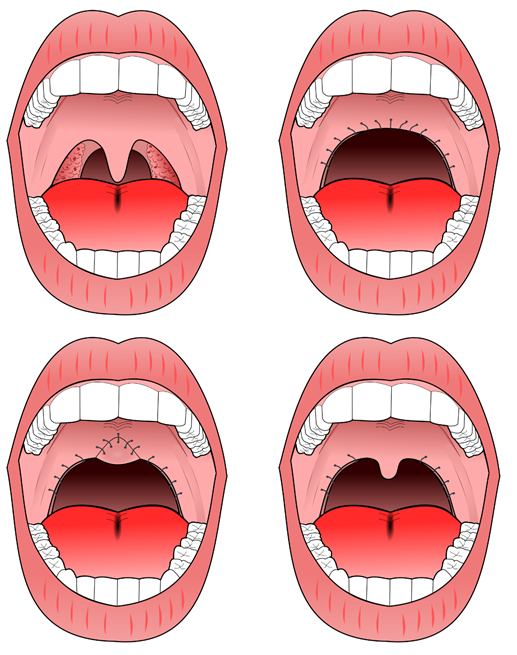
In adults, various surgeries treat specific causes for nasal and soft palate. Obstruction in adults is most often multiple level, so the most successful surgeries involve multi-level surgery.Tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy
Some adults with large tonsils may be candidates for having their tonsils and/or adenoids removed either alone or in combination with other procedures, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or nasal surgery.Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
The procedure most commonly performed for sleep apnea is theuvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (also known by the abbreviations UPPP and UP3) is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery used to remove tissue and/or remodel tissue in the throat. This could be because of sleep issues. Tissues which may typically be remov ...
(UPPP). This involves removal of the tonsils if still present, and a subsequent palatal procedure. The tonsil pillars are often sutured closed—and the uvula is either trimmed, cut, folded, reshaped, or sutured to the soft palate. Studies have shown that treatment effect of UPPP with tonsillectomy increases with tonsil size.

Hyoid suspension
Hyoid suspension Hyoid suspension, also known as hyoid myotomy and suspension or hyoid advancement, is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the hyoid bone and its muscle attachments to the tongue and airway are pulled forward with the aim of increasing ai ...
, also known as hyoid myotomy and suspension or hyoid advancement, is a surgical procedure in which the hyoid bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebr ...
and its muscle attachments to the tongue and airway are pulled forward in order to increase airway size and improve airway stability behind and below the base of tongue (retrolingual and hypopharyngeal region).
Genioglossus advancement
''Genioglossus advancement
Genioglossus advancement (GA), also known as genial tubercle advancement (GTA), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the base of the tongue is pulled forward, usually to increase airway size due to deformity or a sleep breathing di ...
(GA)'' also known as ''genial tubercle advancement (GTA)'', is a procedure that pulls the base of the tongue forward, usually to increase airway size due to deformity or a sleep breathing disorder. This procedure is frequently performed with either uvulopalatopharyngoplasty or maxillomandibular advancement surgeries.

 Tongue muscles (
Tongue muscles (genioglossus
The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding (or sticking out) the tongue.
Structure
Genioglossus is the fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the ma ...
, geniohyoid
The geniohyoid muscle is a narrow muscle situated superior to the medial border of the mylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from the chin ("genio-" is a standard prefix for "chin") to the hyoid bone.
Structure
It arises from the infe ...
and others) are attached to the lower jaw below the teeth. During a genioglossus advancement procedure, the surgeon cuts a small window or bone cut in the front part of the lower jaw (mandible) at the level of the geniotubercle where the genioglossus muscle attaches. This piece of bone, along with the attachment for the tongue (genial tubercle) is pulled forward and subsequently secured to the lower jaw, usually with a single screw or with a plate and screws.
This procedure is often combined with other surgeries such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasties or maxillomandibular advancement surgeries. It is rare to have this procedure performed as the only surgical treatment for sleep apnea, as obstruction in sleep apnea is most often at multiple levels (nose, palate, tongue, etc.).
Maxillomandibular advancement
''Maxillomandibular advancement
Maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) or orthognathic surgery, also sometimes called bimaxillary advancement (Bi-Max), or maxillomandibular osteotomy (MMO), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery which moves the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower j ...
'' (MMA) or orthognathic surgery
Orthognathic surgery (), also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion ...
, also sometimes called ''bimaxillary advancement'' (''bi-max''), or ''maxillomandibular osteotomy (MMO)'', is a procedure that moves the upper jaw (maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
) and the lower jaw (mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movabl ...
) forward.
The procedure was first used to correct deformities of the facial skeleton, including malocclusion
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-1930), ...
. In the late 1970s, advancement of the lower jaw (mandibular advancement) improved sleepiness in three patients. Subsequently, maxillomandibular advancement was used for patients with obstructive sleep apnea
Sleep apnea, also spelled sleep apnoea, is a sleep disorder in which pauses in breathing or periods of shallow breathing during sleep occur more often than normal. Each pause can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and they happen many times ...
.
 Currently, surgeons often perform maxillomandibular advancement surgery simultaneously with genioglossus advancement (tongue advancement). The genioglossus advancement pulls the tongue forward to decrease the amount of tongue blockage during sleep. MMA is one of the most effective surgical treatments for sleep apnea, with a high success rate. Nonetheless, the procedure is often used after other forms of treatment have failed (nasal surgeries, tonsillectomy, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, tongue reduction surgeries). There is a longer recovery when compared to other sleep apnea surgeries, since the bones of the face have to heal into their new position.
Currently, surgeons often perform maxillomandibular advancement surgery simultaneously with genioglossus advancement (tongue advancement). The genioglossus advancement pulls the tongue forward to decrease the amount of tongue blockage during sleep. MMA is one of the most effective surgical treatments for sleep apnea, with a high success rate. Nonetheless, the procedure is often used after other forms of treatment have failed (nasal surgeries, tonsillectomy, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, tongue reduction surgeries). There is a longer recovery when compared to other sleep apnea surgeries, since the bones of the face have to heal into their new position.
Tracheostomy
Tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the Vertebrate trachea, trache ...
is the only surgical procedure that completely bypasses the upper airway. This procedure was commonly performed in the 1960-1980's for obstructive sleep apnea, until other procedures such as the uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (also known by the abbreviations UPPP and UP3) is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery used to remove tissue and/or remodel tissue in the throat. This could be because of sleep issues. Tissues which may typically be remov ...
, hyoid suspension Hyoid suspension, also known as hyoid myotomy and suspension or hyoid advancement, is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the hyoid bone and its muscle attachments to the tongue and airway are pulled forward with the aim of increasing ai ...
, genioglossus advancement
Genioglossus advancement (GA), also known as genial tubercle advancement (GTA), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the base of the tongue is pulled forward, usually to increase airway size due to deformity or a sleep breathing di ...
, and maxillomandibular advancement
Maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) or orthognathic surgery, also sometimes called bimaxillary advancement (Bi-Max), or maxillomandibular osteotomy (MMO), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery which moves the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower j ...
surgeries were described as alternative surgical modalities for OSA.

Therapy alternatives
Continuous positive airway pressure
In 1981, Dr. Sullivan and colleagues introducedcontinuous positive airway pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The ap ...
(CPAP), which replaced tracheostomy as the gold standard treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. CPAP machines are specially designed to deliver a constant flow or pressure. Some CPAP machines have other features as well, such as heated humidifiers. CPAP is the most effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial obstruction of the upper airway leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep. These episod ...
, in which the pressure from CPAP prevents the airway from collapsing or becoming blocked.
Mandibular advancement device
A mandibular advancement device ormandibular advancement splint
A mandibular splint or mandibular advancement splint is a prescription custom-made medical device worn in the mouth used to treat sleep-related breathing disorders including: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), snoring, and TMJ disorders. These devi ...
may be used in select patients as treatment for mild or moderate OSA. Where appropriate, they are considered a good therapy choice as they are non-invasive, easily reversible, quiet, and generally well accepted by the patient. The focus of improvement in appliance design is in reducing bulk, permitting free jaw movement (i.e., yawning, speaking, and drinking), and allowing the user to breathe through their mouth (early "welded gum shield"-type devices prevented oral breathing).
Over the last decade, there has been a significant expansion in the evidence base supporting the use of oral devices in the treatment of OSA. Robust studies demonstrating their efficacy have been underpinned by increasing recognition of the importance of upper airway anatomy in the pathophysiology of OSA. Oral devices have been shown to have a beneficial effect in targeting a number of significant clinical end points. These include the polysomnographic indexes of OSA, subjective and objective measures of sleepiness, blood pressure, aspects of neuropsychological functioning, and quality of life. Elucidation of the mechanism of action of oral devices has provided insight into the factors that predict treatment response and may improve the selection of patients for this treatment modality
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
. A further study by Dr. Edmund Rose, University of Freiburg (2004), successfully treated ( AHI < 5) 88% of patients with MAS and proposes optimum patient selection to include AHI < 25, BMI < 30, and good dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiolo ...
.
Another study published in ''Sleep'' (2008) on the influence of nasal resistance (NAR) on oral device treatment outcome in OSA demonstrates the need for an interdisciplinary approach between ENT surgeons and sleep physicians to treating OSA. The study suggests that higher levels of NAR may negatively affect outcome with MAS and subsequently methods to lower nasal resistance may improve the outcome of oral device treatment.
Tongue retaining device
Tongue retaining devices are devices that can be placed in a manner such that the tongue is kept in a forward position. These devices have been used for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Tongue retaining devices hold the tongue in place by either suction, a fixed bar, or a custom dental impression. Hybrid devices combine mandibular advancement with the tongue restraint. Tongue retaining devices have not been well-received as a therapy choice since they are invasive, and the acclimation period is long. The devices have shown high success rates for therapy in studies published in ''Behaviour Research and Therapy'' and the '' Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine''.References
{{Reflist, 30em Treatment of sleep disorders