|
Sleep Surgery
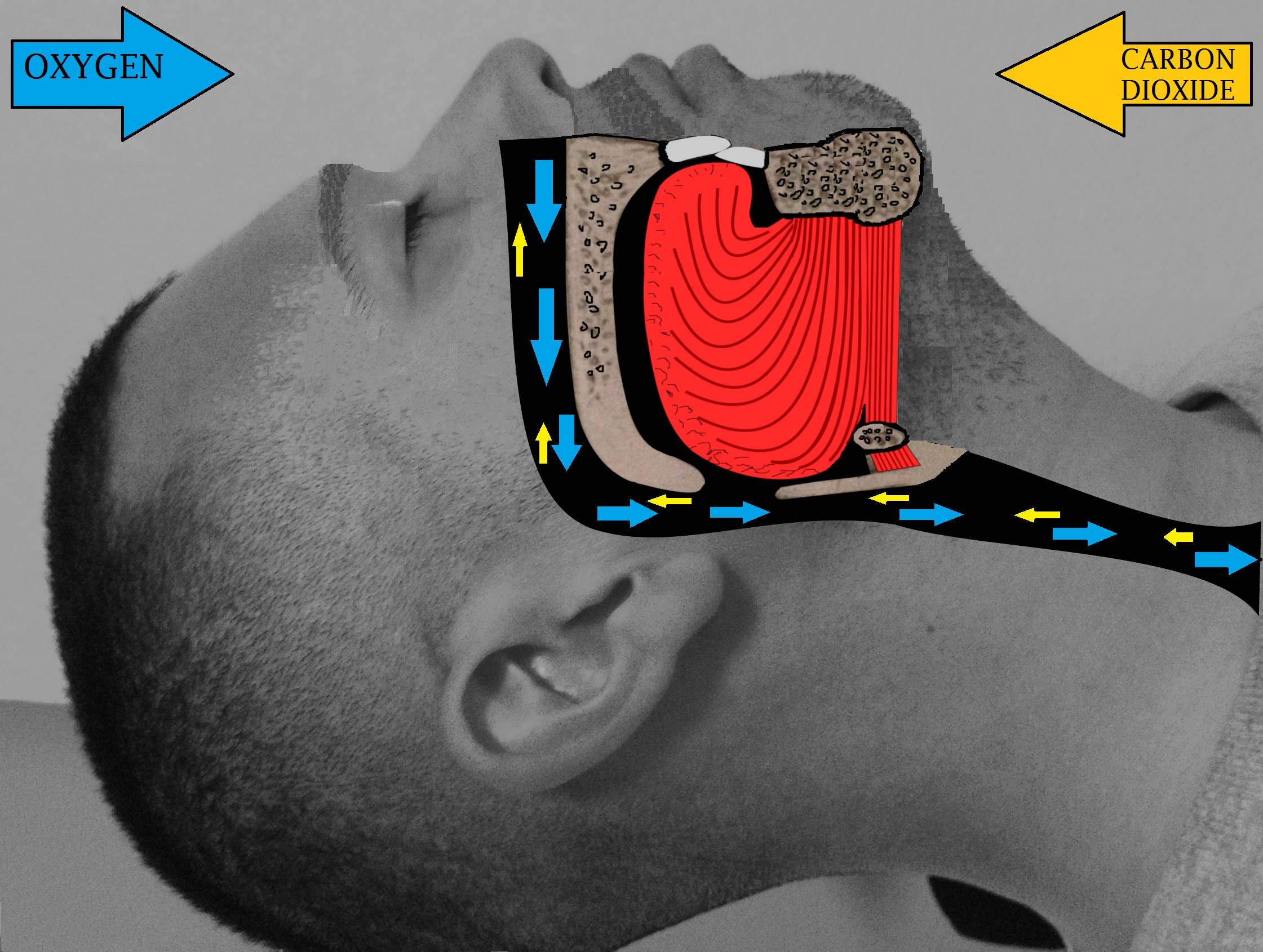
Sleep surgery is a surgery performed to treat sleep disordered breathing. Sleep disordered breathing is a spectrum of disorders that includes snoring, upper airway resistance syndrome, and obstructive sleep apnea. These surgeries are performed by surgeons trained in otolaryngology, oral maxillofacial surgery, and craniofacial surgery. Definitions Obstructive sleep apnea or sleep apnea is defined as either cessation of breathing (apnea) for 10 seconds, or a decrease in normal breathing (hypopnea) with an associated desaturation in oxygen and arousal during sleep that lasts at least 10 seconds. In adults, it is typical to have up to 4.9 events per hour. In obstructive sleep apnea, affected individuals are categorized based on how many apneas or hypopneas ( apnea-hypopnea index or AHI) or events they have per hour. * Normal: <5 events per hour * Mild: 5 to <15 events per hour * Moderate: 15 to 30 events per hour * Severe: >30 events per hour The Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study, a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food into the lungs, forcing the swallowed liquids or food to go along the oesophagus toward the stomach instead. It is thus the valve that diverts passage to either the trachea or the oesophagus. The epiglottis is made of elastic cartilage covered with a mucous membrane, attached to the entrance of the larynx. It projects upwards and backwards behind the tongue and the hyoid bone. The epiglottis may be inflamed in a condition called epiglottitis, which is most commonly due to the vaccine-preventable bacteria ''Haemophilus influenzae''. Dysfunction may cause the inhalation of food, called aspiration, which may lead to pneumonia or airway obstruction. The epiglottis is also an important landmark for intubation. The epiglottis has been identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
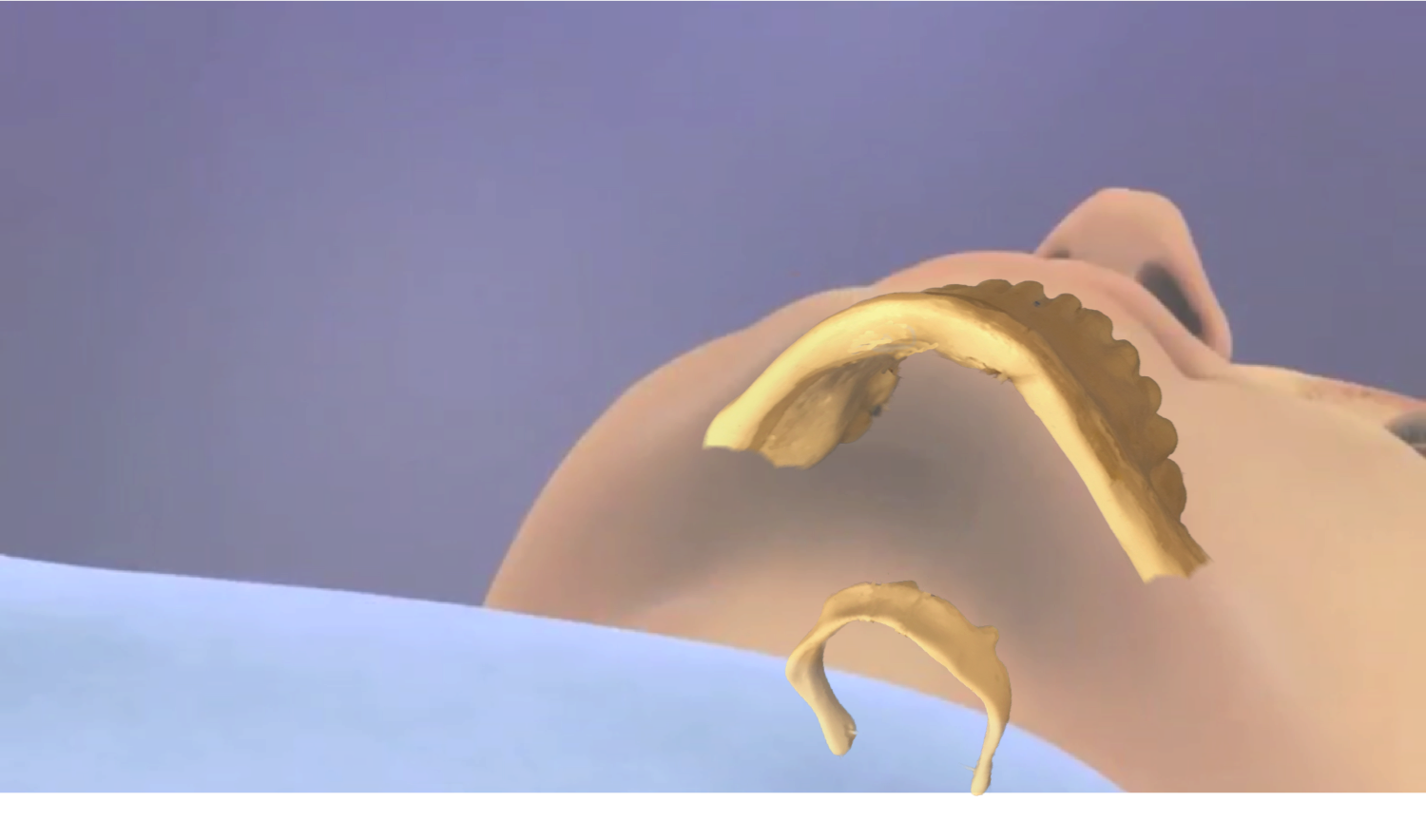
Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery (), also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems primarily arising from skeletal disharmonies, other orthodontic dental bite problems that cannot be easily treated with braces, as well as the broad range of facial imbalances, disharmonies, asymmetries and malproportions where correction can be considered to improve facial aesthetics and self esteem. The origins of orthognathic surgery belong in oral surgery, and the basic operations related to the surgical removal of impacted or displaced teeth – especially where indicated by orthodontics to enhance dental treatments of malocclusion and dental crowding. One of the first published cases of orthognathic surgery was the one from Dr. Simon P. Hullihen in 1849. Originally coined by Harold Hargis, it was more widely popularised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillomandibular Advancement
Maxillomandibular advancement (MMA) or orthognathic surgery, also sometimes called bimaxillary advancement (Bi-Max), or maxillomandibular osteotomy (MMO), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery which moves the upper jaw (maxilla) and the lower jaw (mandible) forward. The procedure was first used to correct deformities of the facial skeleton to include malocclusion. In the late 1970s advancement of the lower jaw (mandibular advancement) was noted to improve sleepiness in three patients. Subsequently, maxillomandibular advancement was used for patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Currently, maxillomandibular advancement surgery is often performed simultaneously with genioglossus advancement (tongue advancement). The genioglossus advancement pulls the tongue forward in a manner that decreases the amount of tongue blockage during sleep. MMA has been demonstrated to be one of the most effective surgical treatments for sleep apnea, due to its high success rate. Nonetheless, the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
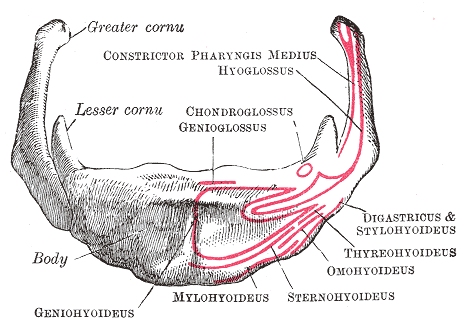
Geniohyoid
The geniohyoid muscle is a narrow muscle situated superior to the medial border of the mylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from the chin ("genio-" is a standard prefix for "chin") to the hyoid bone. Structure It arises from the inferior mental spine, on the back of the mandibular symphysis, and runs backward and slightly downward, to be inserted into the anterior surface of the body of the hyoid bone. It lies in contact with its fellow of the opposite side. It thus belongs to the suprahyoid muscles. The muscle is supplied by branches of the lingual artery. Innervation The geniohyoid muscle is innervated by fibres from the first cervical spinal nerve travelling alongside the hypoglossal nerve. Although the first three cervical nerves give rise to the ansa cervicalis, the geniohyoid muscle is said to be innervated by the first cervical nerve, as some of its efferent fibers do not contribute to ansa cervicalis. Variations It may be blended with the one on opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genioglossus
The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding (or sticking out) the tongue. Structure Genioglossus is the fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the majority of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible and its insertions are the hyoid bone and the bottom of the tongue. The genioglossus is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve, as are all muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus. Blood is supplied to the sublingual branch of the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The canine genioglossus muscle has been divided into horizontal and oblique compartments. Function The left and right genioglossus muscles protrude the tongue and deviate it towards the opposite side. When acting together, the muscles depress the center of the tongue at its back. Clinical significance Contraction of the genioglossus stabilizes and enlarges the porti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genioglossus Advancement After Osteotomy
The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding (or sticking out) the tongue. Structure Genioglossus is the fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the majority of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible and its insertions are the hyoid bone and the bottom of the tongue. The genioglossus is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve, as are all muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus. Blood is supplied to the sublingual branch of the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The canine genioglossus muscle has been divided into horizontal and oblique compartments. Function The left and right genioglossus muscles protrude the tongue and deviate it towards the opposite side. When acting together, the muscles depress the center of the tongue at its back. Clinical significance Contraction of the genioglossus stabilizes and enlarges the portio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genioglossus Advancement Before Surgery
The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding (or sticking out) the tongue. Structure Genioglossus is the fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the majority of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible and its insertions are the hyoid bone and the bottom of the tongue. The genioglossus is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve, as are all muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus. Blood is supplied to the sublingual branch of the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The canine genioglossus muscle has been divided into horizontal and oblique compartments. Function The left and right genioglossus muscles protrude the tongue and deviate it towards the opposite side. When acting together, the muscles depress the center of the tongue at its back. Clinical significance Contraction of the genioglossus stabilizes and enlarges the portio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genioglossus Advancement
Genioglossus advancement (GA), also known as genial tubercle advancement (GTA), is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the base of the tongue is pulled forward, usually to increase airway size due to deformity or a sleep breathing disorder. This procedure is frequently performed with either uvulopalatopharyngoplasty Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (also known by the abbreviations UPPP and UP3) is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery used to remove tissue and/or remodel tissue in the throat. This could be because of sleep issues. Tissues which may typically be remov ... or maxillomandibular advancement surgeries. Tongue muscles (genioglossus, geniohyoid and others) are attached to the lower jaw below the teeth. During a genioglossus advancement procedure, a small window or bone cut is made in the front part of the lower jaw (mandible) at the level of the geniotubercle which is where the genioglossus muscle is attached. This piece of bone along with the attachment for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Suspension
Hyoid suspension, also known as hyoid myotomy and suspension or hyoid advancement, is a surgical procedure or sleep surgery in which the hyoid bone and its muscle attachments to the tongue and airway are pulled forward with the aim of increasing airway size and improving airway stability in the retrolingual and hypopharyngeal airway (airway behind and below the base of tongue). The horseshoe shaped hyoid bone sits directly below the base of tongue with the arms of the bone flanking the airway. Hyoid suspension is typically performed as a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This procedure is frequently performed with a uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) which targets sites of obstruction higher in the airway. Typically, a hyoid suspension is considered successful when the patient's apnea-hypopnea index is significantly reduced after surgery. Background The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery position statement considers hyoid suspension "effective and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.png)