
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as
property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, r ...
. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as
race
Race, RACE or "The Race" may refer to:
* Race (biology), an informal taxonomic classification within a species, generally within a sub-species
* Race (human categorization), classification of humans into groups based on physical traits, and/or s ...
. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be
granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people
voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to
poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
. In the course of
human history
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied throug ...
, slavery was a typical feature of
civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
Ci ...
,
and was legal in most societies, but it is now
outlawed
An outlaw, in its original and legal meaning, is a person declared as outside the protection of the law. In pre-modern societies, all legal protection was withdrawn from the criminal, so that anyone was legally empowered to persecute or kill them ...
in most countries of the world, except as a
punishment for a crime.
In ''chattel slavery'', the slave is legally rendered the
personal property
property is property that is movable. In common law systems, personal property may also be called chattels or personalty. In civil law systems, personal property is often called movable property or movables—any property that can be moved fr ...
(chattel) of the slave owner. In economics, the term ''de facto slavery'' describes the conditions of
unfree labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
and
forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
that most slaves endure.
In 2019, approximately 40 million people, of whom 26 percent were children, were enslaved throughout the world despite it being illegal. In the modern world, more than 50 percent of slaves provide
forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
, usually in the factories and sweatshops of the
private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The ...
of a country's economy. In industrialised countries,
human trafficking
Human trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labour, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker or others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extrac ...
is a modern variety of slavery; in non-industrialised countries, enslavement by
debt bondage
Debt bondage, also known as debt slavery, bonded labour, or peonage, is the pledge of a person's services as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation. Where the terms of the repayment are not clearly or reasonably stated, the pe ...
is a common form of enslaving a person,
such as captive
domestic servants
A domestic worker or domestic servant is a person who works within the scope of a residence. The term "domestic service" applies to the equivalent occupational category. In traditional English contexts, such a person was said to be "in service ...
,
forced marriage
Forced marriage is a marriage in which one or more of the parties is married without their consent or against their will. A marriage can also become a forced marriage even if both parties enter with full consent if one or both are later force ...
, and
child soldiers
Children (defined by the Convention on the Rights of the Child as people under the age of 18) have been recruited for participation in military operations and campaigns throughout history and in many cultures.
Children in the military, includ ...
.
Terminology
The word arrived in modern English from
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
, from
Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligib ...
, from Late
Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. High ...
, from
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned ...
, from
Late Latin
Late Latin ( la, Latinitas serior) is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the , and continuing into the 7th century in t ...
, from
Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman co ...
'Sklábos'' 'Ésklabḗnos''
According to the widespread view, which has been known since the 18th century, Byzantine
'Sklábinoi'' 'Ésklabēnoí'' borrowed from Slavic gen self-name turned into , (
Late Latin
Late Latin ( la, Latinitas serior) is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the , and continuing into the 7th century in t ...
) in the meaning 'prisoner of war Slave', 'slave' in 8th/9th century, because they often became captured and enslaved.
['']Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a com ...
'', 2nd edition 1989, ''s.v.'' ''slave'' However this version has been disputed since the 19th century.
Alternative contemporary hypothesis states that
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned ...
via derives from Byzantine
'skūláō'', ''skyláō'' 'skūleúō'', ''skyleúō''- "to strip the enemy (killed in a battle)", "to make booty / extract spoils of war". This version is criticized as well.
There is a dispute among historians about whether terms such as "
unfree labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
er" or "enslaved person", rather than "slave", should be used when describing the victims of slavery. According to those proposing a change in terminology, ''slave'' perpetuates the crime of slavery in language by reducing its victims to a nonhuman noun instead of "carry
ngthem forward as people, not the property that they were" (see also ''
People-first language
People-first language (PFL), also called person-first language, is a type of linguistic prescription which puts a person before a diagnosis, describing what condition a person "has" rather than asserting what a person "is". It is intended to av ...
''). Other historians prefer ''slave'' because the term is familiar and shorter, or because it accurately reflects the inhumanity of slavery, with ''person'' implying a degree of autonomy that slavery does not allow.
Chattel slavery



As a social institution, chattel slavery classes slaves as ''chattels'' (
personal property
property is property that is movable. In common law systems, personal property may also be called chattels or personalty. In civil law systems, personal property is often called movable property or movables—any property that can be moved fr ...
) owned by the enslaver; like livestock, they can be bought and sold at will. While it was not present at all times and places in the classical world, chattel slavery did exist in ancient times and was practiced in places such as the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
. Chattel slavery reached its modern extreme in the Americas during European colonization. Beginning in the 18th century, a series of
abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
movements saw slavery as a violation of the slaves' rights as people ("
all men are created equal
The quotation "all men are created equal" is part of the sentence in the U.S. Declaration of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronounc ...
"), and sought to abolish it. Abolitionism encountered extreme resistance but was eventually successful; the last Western country to abolish slavery, Brazil,
did so in 1888. The last
third-world
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " Firs ...
country to abolish slavery,
Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
,
did not do so until 1981.
Bonded labour
Indenture, also known as bonded labour or debt bondage, is a form of unfree labour in which a person works to pay off a debt by pledging himself or herself as collateral. The services required to repay the debt, and their duration, may be undefined. Debt bondage can be passed on from generation to generation, with children required to pay off their progenitors' debt. It is the most widespread form of slavery today. Debt bondage is most prevalent in South Asia.
Money marriage refers to a marriage where a girl, usually, is married off to a man to settle debts owed by her parents. The
Chukri system is a
debt bondage
Debt bondage, also known as debt slavery, bonded labour, or peonage, is the pledge of a person's services as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation. Where the terms of the repayment are not clearly or reasonably stated, the pe ...
system found in parts of
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
where a female can be coerced into
prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
in order to pay off debts.
Dependents
The word "slavery" has also been used to refer to a legal state of dependency to somebody else.
For example, in
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the situations and lives of such slaves could be better than those of common citizens.
Forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is sometimes used to describe an individual who is forced to work against their own will, under threat of violence or other punishment, but the generic term "unfree labour" is also used to describe chattel slavery, as well as any other situation in which a person is obliged to work against their own will, and a person's ability to work productively is under the complete control of another person. This may also include institutions not commonly classified as slavery, such as
serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which develop ...
,
conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
and
penal labour. While some unfree labourers, such as
serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
s, have substantive, ''de jure'' legal or traditional rights, they also have no ability to terminate the arrangements under which they work and are frequently subject to forms of coercion, violence, and restrictions on their activities and movement outside their place of work.
Human trafficking primarily involves women and children forced into
prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
and is the fastest growing form of forced labour, with Thailand, Cambodia, India, Brazil and Mexico having been identified as leading hotspots of
commercial sexual exploitation of children
Commercial sexual exploitation of children (CSEC) is a commercial transaction that involves the sexual exploitation of a child, or person under the age of consent. CSEC involves a range of abuses, including but not limited to: the prostitution ...
.
Child soldiers and child labor
In 2007,
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
estimated that 200,000 to 300,000 children served as soldiers in then-current conflicts. More girls under 16 work as
domestic workers
A domestic worker or domestic servant is a person who works within the scope of a residence. The term "domestic service" applies to the equivalent occupational category. In traditional English contexts, such a person was said to be "in service ...
than any other category of child labour, often sent to cities by parents living in rural poverty as with the Haitian
restavek
A restavek (or restavec) is a child in Haiti who is sold by their parents to work for a host household as a domestic servant because the parents lack the resources required to support the child. The term comes from the French language ''rester a ...
s.
Forced marriage
Forced marriage
Forced marriage is a marriage in which one or more of the parties is married without their consent or against their will. A marriage can also become a forced marriage even if both parties enter with full consent if one or both are later force ...
s or early marriages are often considered types of slavery. Forced marriage continues to be practiced in parts of the world including some parts of Asia and Africa and in immigrant communities in the West.
Sacred prostitution
Sacred prostitution, temple prostitution, cult prostitution, and religious prostitution are Ritual, rites consisting of Prostitution, paid intercourse performed in the context of religious worship, possibly as a form of fertility rite or divine m ...
is where girls and women are pledged to priests or those of higher castes, such as the practice of
Devadasi
In India, a devadasi was a female artist who was dedicated to the worship and service of a deity or a temple for the rest of her life. The dedication took place in a ceremony that was somewhat similar to a marriage ceremony. In addition to taki ...
in South Asia or
fetish slaves in West Africa.
Marriage by abduction
Bride kidnapping, also known as marriage by abduction or marriage by capture, is a practice in which a man abducts the woman he wishes to marry.
Bride kidnapping (hence the portmanteau bridenapping) has been practiced around the world and ...
occurs in many places in the world today, with a 2003 study finding a national average of 69% of marriages in Ethiopia being through abduction.
Other uses of the term
The word ''slavery'' is often used as a pejorative to describe any activity in which one is coerced into performing. Some argue that
military drafts and other forms of coerced government labour constitute "state-operated slavery." Some
libertarians
Libertarianism (from french: libertaire, "libertarian"; from la, libertas, "freedom") is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, and minimize the state's enc ...
and
anarcho-capitalists
Anarcho-capitalism (or, colloquially, ancap) is an anti-statist, libertarian, and anti-political philosophy and economic theory that seeks to abolish centralized states in favor of stateless societies with systems of private property enfor ...
view government taxation as a form of slavery.
"Slavery" has been used by some
anti-psychiatry
Anti-psychiatry is a movement based on the view that psychiatric treatment is often more damaging than helpful to patients, highlighting controversies about psychiatry. Objections include the reliability of psychiatric diagnosis, the questionabl ...
proponents to define involuntary psychiatric patients, claiming there are no unbiased physical tests for mental illness and yet the psychiatric patient must follow the orders of the psychiatrist. They assert that instead of chains to control the slave, the psychiatrist uses drugs to control the mind.
Drapetomania
Drapetomania was a supposed mental illness that, in 1851, American physician Samuel A. Cartwright hypothesized as the cause of enslaved Africans fleeing captivity. This hypothesis centered around the belief that slavery was such an improvement up ...
was a pseudoscientific psychiatric diagnosis for a slave who desired freedom; "symptoms" included laziness and the tendency to flee captivity.
Some proponents of
animal rights
Animal rights is the philosophy according to which many or all sentient animals have moral worth that is independent of their utility for humans, and that their most basic interests—such as avoiding suffering—should be afforded the sa ...
have applied the term ''slavery'' to the condition of some or all human-owned animals, arguing that their status is comparable to that of human slaves.
The labour market, as institutionalized under contemporary capitalist systems, has been criticized by mainstream
socialists
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the eco ...
and by
anarcho-syndicalists
Anarcho-syndicalism is a political philosophy and anarchist school of thought that views revolutionary industrial unionism or syndicalism as a method for workers in capitalist society to gain control of an economy and thus control influence in ...
, who utilise the term
wage slavery
Wage slavery or slave wages refers to a person's dependence on wages (or a salary) for their livelihood, especially when wages are low, treatment and conditions are poor, and there are few chances of upward mobility.
The term is often used ...
as a
pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a ...
or
dysphemism
A dysphemism is an expression with connotations that are derogatory either about the subject matter or to the audience. Dysphemisms contrast with neutral or euphemistic expressions. Dysphemism may be motivated by fear, distaste, hatred, contempt, ...
for
wage labour
Wage labour (also wage labor in American English), usually referred to as paid work, paid employment, or paid labour, refers to the socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer in which the worker sells their labour power under ...
.
Socialists draw parallels between the trade of labour as a commodity and slavery.
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the estab ...
is also known to have suggested such parallels.
Characteristics
Private versus state-owned slaves
Slaves have been owned privately by individuals but have also been under state ownership. For example, the
kisaeng
Kisaeng (Hangul: 기생, Hanja: 妓生, RR: ''Gisaeng''), also called ginyeo (Hangul: 기녀, Hanja: 妓女), were women from outcast or slave families who were trained to be courtesans, providing artistic entertainment and conversation to men ...
were women from low castes in pre modern Korea, who were owned by the state under government officials known as ''hojang'' and were required to provide entertainment to the aristocracy; in the 2020s some are denoted ''
Kippumjo
The ''Kippumjo'' or ''Gippeumjo'' (translated variously as ''Pleasure Group'', ''Pleasure Groups'', ''Pleasure Squad'', or ''Pleasure Brigade'') is a collection of groups of approximately 2,000 women and girls reportedly maintained by t ...
'' (the pleasure brigades of North Korea — serving as the concubines of the rulers of the state). "Tribute labor" is compulsory labor for the state and has been used in various iterations such as
corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid, forced labour, that is intermittent in nature lasting for limited periods of time: typically for only a certain number of days' work each year.
Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state for the purposes of ...
,
mit'a
Mit'a () was mandatory service in the society of the Inca Empire. Its close relative, the regionally mandatory Minka is still in use in Quechua communities today and known as ''faena'' in Spanish.
Historians use the Hispanicized term ''mita'' to ...
and
repartimiento
The ''Repartimiento'' () (Spanish, "distribution, partition, or division") was a colonial labor system imposed upon the indigenous population of Spanish America. In concept, it was similar to other tribute-labor systems, such as the ''mit'a'' of t ...
. The
internment camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
s of
totalitarian
Totalitarianism is a form of government and a political system that prohibits all opposition parties, outlaws individual and group opposition to the state and its claims, and exercises an extremely high if not complete degree of control and regul ...
regimes such as the Nazis and the Soviet Union placed increasing importance on the labor provided in those camps, leading to a growing tendency among historians to designate such systems as slavery.
Economics
Economists have modeled the circumstances under which slavery (and variants such as
serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which develop ...
) appear and disappear. One observation is that slavery becomes more desirable for
landowners
In common law systems, land tenure, from the French verb "tenir" means "to hold", is the legal regime in which land owned by an individual is possessed by someone else who is said to "hold" the land, based on an agreement between both individual ...
where land is abundant but labour is scarce, such that rent is depressed and paid workers can demand high wages. If the opposite holds true, then it is more costly for landowners to guard the slaves than to employ paid workers who can demand only low wages because of the degree of competition. Thus, first slavery and then serfdom gradually decreased in Europe as the population grew. They were reintroduced in the Americas and in Russia as large areas of land with few inhabitants became available.
Slavery is more common when the tasks are relatively simple and thus easy to supervise, such as large-scale
monocrops such as
sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
and
cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
, in which output depended on
economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables ...
. This enables systems of labour, such as the
gang system
The gang system is a system of division of labor within slavery on a plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a ...
in the United States, to become prominent on large plantations where field hands toiled with factory-like precision. Then, each work gang was based on an internal division of labour that assigned every member of the gang to a task and made each worker's performance dependent on the actions of the others. The slaves chopped out the weeds that surrounded the cotton plants as well as excess sprouts. Plow gangs followed behind, stirring the soil near the plants and tossing it back around the plants. Thus, the gang system worked like an
assembly line
An assembly line is a manufacturing process (often called a ''progressive assembly'') in which parts (usually interchangeable parts) are added as the semi-finished assembly moves from workstation to workstation where the parts are added in seq ...
.
Since the 18th century, critics have argued that slavery retards technological advancement because the focus is on increasing the number of slaves doing simple tasks rather than upgrading their efficiency. For example, it is sometimes argued that, because of this narrow focus, technology in Greece – and later in Rome – was not applied to ease physical labour or improve manufacturing.

Scottish economist
Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——— ...
stated that free labour was economically better than slave labour, and that it was nearly impossible to end slavery in a free, democratic, or republican form of government since many of its legislators or political figures were slave owners, and would not punish themselves. He further stated that slaves would be better able to gain their freedom under centralized government, or a central authority like a king or church. Similar arguments appeared later in the works of
Auguste Comte
Isidore Marie Auguste François Xavier Comte (; 19 January 1798 – 5 September 1857) was a French philosopher and writer who formulated the doctrine of positivism. He is often regarded as the first philosopher of science in the modern sense ...
, especially given Smith's belief in the
separation of powers
Separation of powers refers to the division of a state's government into branches, each with separate, independent powers and responsibilities, so that the powers of one branch are not in conflict with those of the other branches. The typic ...
, or what Comte called the "separation of the spiritual and the temporal" during the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and the end of slavery, and Smith's criticism of masters, past and present. As Smith stated in the ''
Lectures on Jurisprudence'', "The great power of the clergy thus concurring with that of the king set the slaves at liberty. But it was absolutely necessary both that the authority of the king and of the clergy should be great. Where ever any one of these was wanting, slavery still continues..."

Even after slavery became a criminal offense, slave owners could get high returns. According to researcher
Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 were $91.2 billion. That was second only to drug trafficking, in terms of global criminal enterprises. At the time the weighted average global sales price of a slave was estimated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labour and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave. Approximately 40% of slave profits each year were generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4% of the world's 29 million slaves.
Identification
Throughout history, slaves were clothed in a distinctive fashion, particularly with respect to the frequent lack of footwear, as they were rather commonly forced to go
barefoot
Barefoot is the state of not wearing any footwear.
There are health benefits and some risks associated with going barefoot. Shoes, while they offer protection, can limit the flexibility, strength, and mobility of the foot and can lead to ...
. This was partly for economic reasons, but also served as a distinguishing feature, especially in South Africa and South America. For example, the
Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
slave code stated that "Slaves must go barefoot and must carry passes."
It also puts slaves at a physical disadvantage because of the lack of protection against environmental conditions and in confrontations, thereby making it more difficult to escape or to rebel against their owners.
This was the case in the majority of states. Most images from the respective historical period suggest that slaves were barefoot.
Brother Riemer stated, "
he slaves
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
are, even in their most beautiful suit, obliged to go barefoot. Slaves were forbidden to wear shoes. This was a prime mark of distinction between the free and the bonded and no exceptions were permitted."
According to the Bible, shoes have been considered badges of freedom since antiquity: "But the father said to his servants, Bring forth the best robe, and put
ton him; and put a ring on his hand, and shoes on
isfeet" (). This aspect can be viewed as an informal law in areas where slavery existed as any person sighted barefoot in public was assumed to be a slave.
In certain societies this rule continues. The
Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern A ...
still unofficially practice slavery and force their slaves to remain barefoot.
Another widespread practice was
branding
Branding may refer to:
Physical markings
* Making a mark, typically by charring:
** Wood branding, permanently marking, by way of heat, typically of wood (also applied to plastic, cork, leather, etc.)
** Livestock branding, the marking of animals ...
, either to explicitly mark slaves as property or as punishment.
Legal rights
Depending upon the era and the country, slaves sometimes had a limited set of legal rights. For example, in the
Province of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the Uni ...
, people who deliberately killed slaves were punishable under a 1686 statute. And, as already mentioned, certain legal rights attached to the nobi in Korea, to slaves in various African societies, and to black female slaves in the
French colony of Louisiana. Giving slaves legal rights has sometimes been a matter of morality, but also sometimes a matter of self-interest. For example, in
ancient Athens
Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achieve ...
, protecting slaves from mistreatment simultaneously protected people who might be mistaken for slaves, and giving slaves limited property rights incentivized slaves to work harder to get more property. In the southern United States prior to
the extirpation of slavery in 1865, a proslavery legal treatise reported that slaves accused of crimes typically had a legal right to counsel, freedom from
double jeopardy
In jurisprudence, double jeopardy is a procedural defence (primarily in common law jurisdictions) that prevents an accused person from being tried again on the same (or similar) charges following an acquittal or conviction and in rare case ...
, a right to trial by jury in graver cases, and the right to grand jury indictment, but they lacked many other rights such as white adults’ ability to control their own lives.
History
Some scholars differentiate ancient forms of slavery from the largely race-based slavery. The first type of slavery, sometimes called "just title servitude", was inflicted on
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
, debtors, and other vulnerable people. Race-based slavery grew to immense proportions starting in the 14th century. It was argued even by some contemporary writers to be intrinsically immoral.
Early history

Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures.
Slavery is rare among
hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
populations because it requires economic surpluses and a substantial population density. Thus, although it has existed among unusually resource-rich hunter gatherers, such as the
American Indian peoples of the
salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
-rich rivers of the
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
coast, slavery became widespread only with the invention of agriculture during the
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
about 11,000 years ago.
In the earliest known records, slavery is treated as an established institution. The
Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organised, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian, purportedly by Hamm ...
(c. 1760 BC), for example, prescribed death for anyone who helped a slave escape or who sheltered a fugitive.
The Bible
mentions slavery as an established institution.
Slavery was practiced in almost every ancient civilization.
Such institutions included debt bondage, punishment for crime, the enslavement of
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
,
child abandonment
Child abandonment is the practice of relinquishing interests and claims over one's offspring in an illegal way, with the intent of never resuming or reasserting guardianship. The phrase is typically used to describe the physical abandonment of a ...
, and the enslavement of slaves' offspring.
Classical antiquity
Africa
Slavery existed in
Pharaonic Egypt, but studying it is complicated by terminology used by the
Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
to refer to different classes of servitude over the course of history. Interpretation of the textual evidence of classes of slaves in
ancient Egypt has been difficult to differentiate by word usage alone. The three apparent types of enslavement in Ancient Egypt: chattel slavery, bonded labour, and forced labour.
Asia
Slavery existed in ancient China as early as the
Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and ...
. Slavery was employed largely by governments as a means of maintaining a public labour force.
Europe
=Ancient Greece and Rome
=
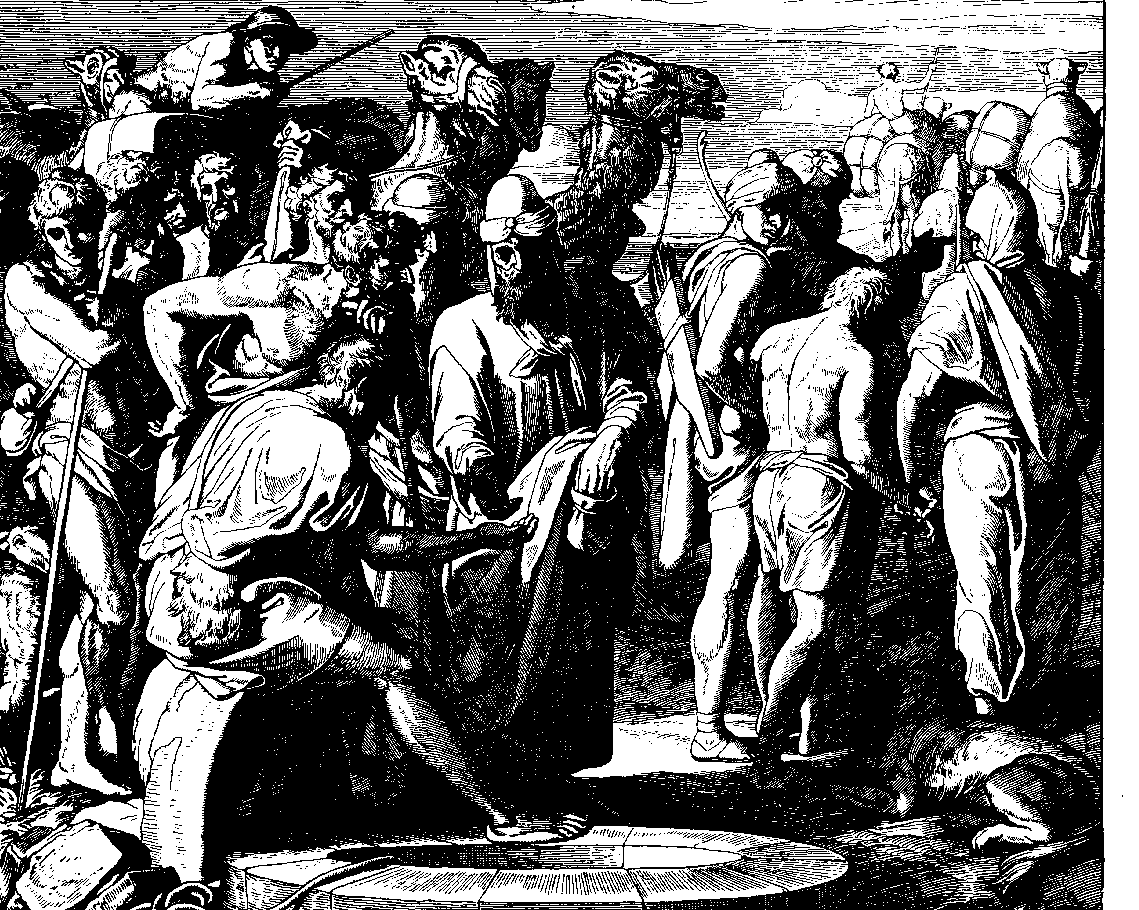

Records of
slavery in Ancient Greece
Slavery was an accepted practice in ancient Greece, as in other societies of the time. Some Ancient Greek writers (including, most notably, Aristotle) described slavery as natural and even necessary.[Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...]
.
Classical Athens
The city of Athens ( grc, Ἀθῆναι, ''Athênai'' .tʰɛ̂ː.nai̯ Modern Greek: Αθήναι, ''Athine'' or, more commonly and in singular, Αθήνα, ''Athina'' .'θi.na during the classical period of ancient Greece (480–323 BC) wa ...
had the largest slave population, with as many as 80,000 in the 6th and 5th centuries BC. As the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
expanded outward, entire populations were enslaved, across Europe and the Mediterranean. Slaves were used for labour, as well as for amusement (e.g.
gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
s and
sex slaves
Sexual slavery and sexual exploitation is an attachment of any ownership right over one or more people with the intent of coercing or otherwise forcing them to engage in sexual activities. This includes forced labor, reducing a person to a s ...
). This oppression by an elite minority eventually led to
slave revolts
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedo ...
(see
Roman Servile Wars
The Servile Wars were a series of three slave revolts ("servile" is derived from "''servus''", Latin for "slave") in the late Roman Republic.
Wars
* First Servile War (135−132 BC) — in Sicily, led by Eunus, a former slave claiming to be a p ...
); the
Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directly ...
was led by
Spartacus
Spartacus ( el, Σπάρτακος '; la, Spartacus; c. 103–71 BC) was a Thracian gladiator who, along with Crixus, Gannicus, Castus, and Oenomaus, was one of the escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major slave uprising ...
.

By the late Republican era, slavery had become an economic pillar of Roman wealth, as well as Roman society. It is estimated that 25% or more of the population of
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
was enslaved, although the actual percentage is debated by scholars and varied from region to region.
Slaves represented 15–25% of
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
's population,
mostly war captives,
especially from
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and
Epirus
sq, Epiri rup, Epiru
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Historical region
, image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg
, map_alt =
, map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by Heinrich ...
. Estimates of the number of slaves in the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
suggest that the majority were scattered throughout the
provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
outside of Italy.
Generally, slaves in Italy were indigenous Italians. Foreigners (including both slaves and freedmen) born outside of Italy were estimated to have peaked at 5% of the total in the capital, where their number was largest. Those from outside of Europe were predominantly of Greek descent. Jewish slaves never fully assimilated into Roman society, remaining an identifiable minority. These slaves (especially the foreigners) had higher death rates and lower birth rates than natives and were sometimes subjected to mass expulsions. The average recorded age at death for the slaves in Rome was seventeen and a half years (17.2 for males; 17.9 for females).
Middle Ages
Africa
Slavery was widespread in Africa, which pursued both internal and external slave trade. In the
Senegambia
The Senegambia (other names: Senegambia region or Senegambian zone,Barry, Boubacar, ''Senegambia and the Atlantic Slave Trade'', (Editors: David Anderson, Carolyn Brown; trans. Ayi Kwei Armah; contributors: David Anderson, American Council of Le ...
region, between 1300 and 1900, close to one-third of the population was enslaved. In early Islamic states of the western
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
, including
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
,
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
,
Segou, and
Songhai, about a third of the population were enslaved.
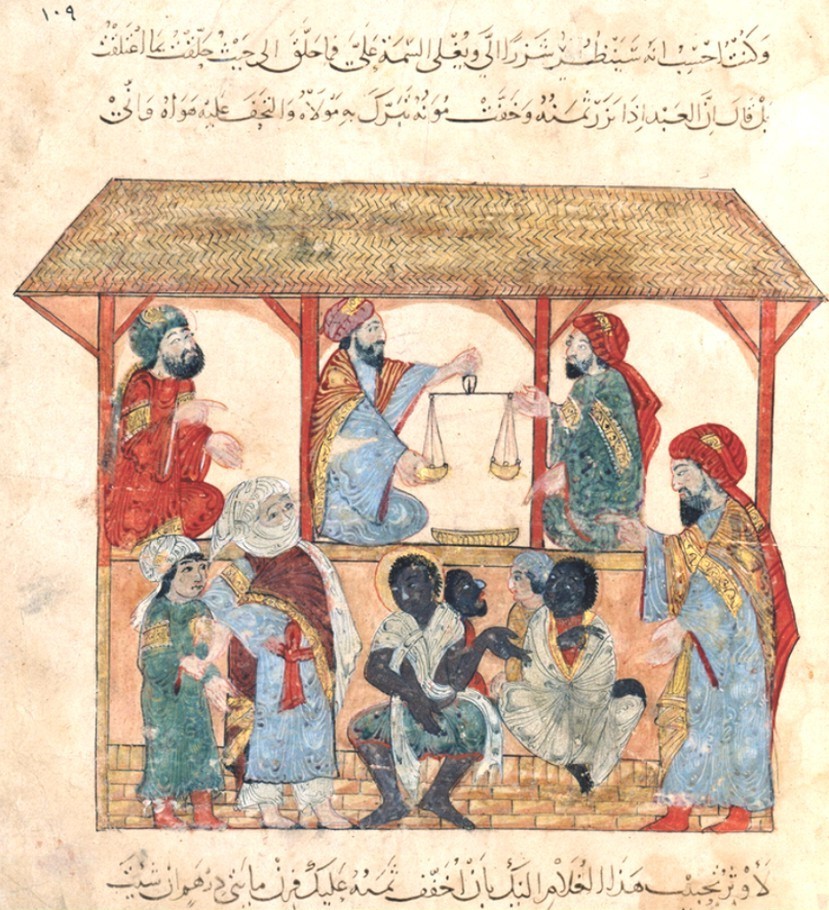

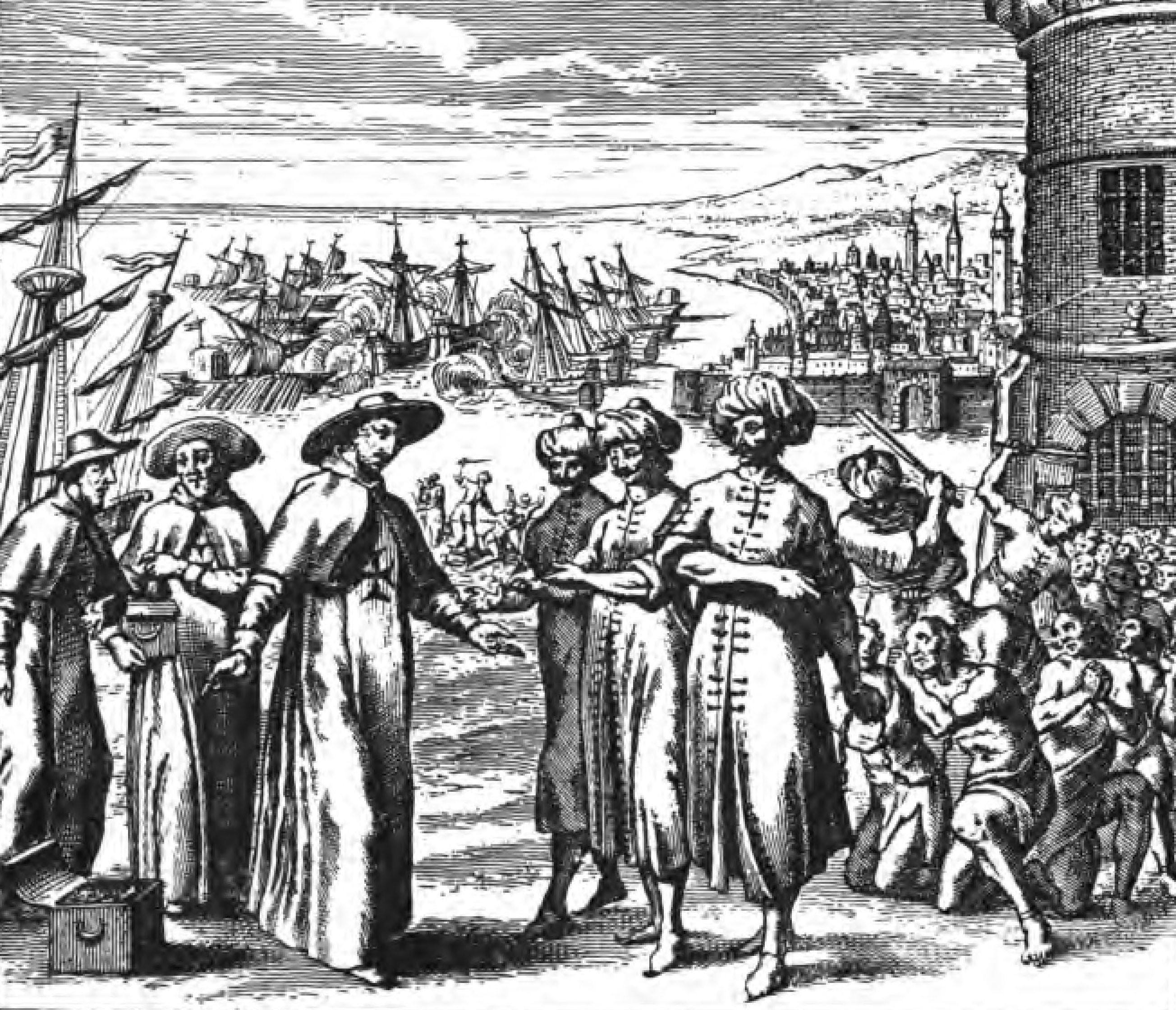
During the
trans-Saharan slave trade
During the Trans-Saharan slave trade, slaves were transported across the Sahara desert. Most were moved from Sub-Saharan Africa to North Africa to be sold to Mediterranean and Middle eastern civilizations; a small percentage went the other ...
, slaves from
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
were transported across the
Sahara desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
to
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
to be sold to
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
and
Middle eastern
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European ...
civilizations. The
Indian Ocean slave trade
The Indian Ocean slave trade, sometimes known as the East African slave trade or Arab slave trade, was multi-directional slave trade and has changed over time. Africans were sent as slaves to the Middle East, to Indian Ocean islands (including Ma ...
, sometimes known as the east African slave trade, was multi-directional. Africans were sent as slaves to the
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, to
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
islands (including
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
), to the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, and later to the Americas. These traders captured
Bantu peoples
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern A ...
(
Zanj
Zanj ( ar, زَنْج, adj. , ''Zanjī''; fa, زنگی, Zangi) was a name used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa (primarily the Swahili Coast) and to its Bantu inhabitants. This word is also ...
) from the interior in present-day
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
,
Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
and
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
and brought them to the coast.
There, the slaves gradually assimilated in rural areas, particularly on
Unguja
Unguja (also referred to as "Zanzibar Island" or simply "Zanzibar", in grc, Μενουθιάς, Menuthias – as mentioned in The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'') is the largest and most populated island of the Zanzibar archipelago, in Tanza ...
and
Pemba Pemba may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Places
* Pemba Island, in Tanzania
* Pemba, Mozambique, the capital of Cabo Delgado Province
* Pemba, Zambia, a small town
Individuals
* George Pemba, South African painter
* Pemba (panda), a red panda
* Tsewang Yishe ...
islands.
Americas
Slavery in Mexico can be traced back to the
Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
. Other
Amerindians
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Ame ...
, such as the
Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The admin ...
of the Andes, the
Tupinambá of Brazil, the
Creek of Georgia, and the
Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in La ...
of Texas, also practiced slavery.
Slavery in Canada
Slavery in Canada includes both that practised by First Nations from earliest times and that under European colonization.
Britain banned the institution of slavery in present-day Canada (and British colonies) in 1833, though the practice of sl ...
was practiced by
First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
and by
European settlers
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
.
Slave-owning people of what became Canada were, for example, the fishing societies, such as the
Yurok
The Yurok (Karuk language: Yurúkvaarar / Yuru Kyara - "downriver Indian; i.e. Yurok Indian") are an Indigenous people from along the Klamath River and Pacific coast, whose homelands are located in present-day California stretching from Trinidad ...
, that lived along the Pacific coast from Alaska to California, on what is sometimes described as the Pacific or Northern Northwest Coast. Some of the
indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast are composed of many nations and tribal affiliations, each with distinctive cultural and political identities. They share certain beliefs, traditions and prac ...
, such as the
Haida
Haida may refer to:
Places
* Haida, an old name for Nový Bor
* Haida Gwaii, meaning "Islands of the People", formerly called the Queen Charlotte Islands
* Haida Islands, a different archipelago near Bella Bella, British Columbia
Ships
* , a 1 ...
and
Tlingit
The Tlingit ( or ; also spelled Tlinkit) are indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America. Their language is the Tlingit language (natively , pronounced ), , were traditionally known as fierce warriors and slave-traders, raiding as far as California. Slavery was hereditary, the slaves being
prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
and their descendants were slaves. Some nations in British Columbia continued to segregate and ostracize the descendants of slaves as late as the 1970s.
[
]
Asia
Slavery also existed in
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
,
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
and
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
.
= China
=
Many
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
were enslaved in the process of the
Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
of
China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions popu ...
. According to Japanese historians Sugiyama Masaaki (杉山正明) and Funada Yoshiyuki (舩田善之), Mongolian slaves were owned by
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
during the
Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth ...
.
=Korea
=
Slavery in Korea
Slavery in Korea formally existed from antiquity up to the 20th century. Slavery was very important in medieval Korea; it was a major institution. The importance of slavery in Korea fluctuated over time. The Korean "''nobi''" system of slavery peak ...
existed since before the
Three Kingdoms of Korea
Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea () refers to the three kingdoms of Goguryeo (고구려, 高句麗), Baekje (백제, 百濟), and Silla (신라, 新羅). Goguryeo was later known as Goryeo (고려, 高麗), from which the modern name ''Kor ...
period, in the first century BCE. Slavery has been described as "very important in medieval Korea, probably more important than in any other
East Asian
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea a ...
country, but by the 16th century, population growth was making
tunnecessary".
Slavery went into decline around the 10th century but came back in the late
Goryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean kingdom founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korean Peninsula until 1392. Goryeo achieved what has been called a "true national unificati ...
period when Korea also experienced multiple
slave rebellion
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedo ...
s.
In the
Joseon
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and re ...
period of Korea, members of the slave class were known as ''nobi''. The nobi were socially indistinct from freemen (i.e., the
middle and
common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally com ...
classes) other than the ruling
yangban
The ''yangban'' () were part of the traditional ruling class or gentry of dynastic Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. The ''yangban'' were mainly composed of highly educated civil servants and military officers—landed or unlanded aristocrats ...
class, and some possessed property rights, and legal and civil rights. Hence, some scholars argue that it is inappropriate to call them "slaves", while some scholars describe them as
serfs
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
. The nobi population could fluctuate up to about one-third of the total, but on average the nobi made up about 10% of the total population. In 1801, the majority of government nobi were emancipated, and by 1858, the nobi population stood at about 1.5 percent of the Korean population.
Europe

Large-scale trading in slaves was mainly confined to the South and East of
early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
Europe: the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and the
Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
were the destinations, while
pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
(along with the
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
and
Tartary
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounde ...
) were important sources.
Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
,
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
,
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, and
Radhanite
The Radhanites or Radanites (; ar, الرذنية, ''ar-Raðaniyya'') were early medieval Jewish merchants, active in the trade between Christendom and the Muslim world during roughly the 8th to 10th centuries.
Many trade routes previously esta ...
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
merchants were all involved in the slave trade during the Early Middle Ages. The trade in European slaves reached a peak in the 10th century following the
Zanj Rebellion
The Zanj Rebellion ( ar, ثورة الزنج ) was a major revolt against the Abbasid Caliphate, which took place from 869 until 883. Begun near the city of Basra in present-day southern Iraq and led by one Ali ibn Muhammad, the insurrection invol ...
which dampened the use of African slaves in the Arab world.
Slavery in early medieval Europe was so common that the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
repeatedly prohibited it, or at least the export of Christian slaves to non-Christian lands, as for example at the
Council of Koblenz (922), the
Council of London (1102)
__NOTOC__
The Council of London was a Catholic church council convened by Anselm, archbishop of Canterbury, on Michaelmas in 1102. It marked the first major council of his episcopate, as he had been prohibited from convening any during the reign ...
(which aimed mainly at the sale of English slaves to Ireland)
and the Council of Armagh (1171).
Serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which develop ...
, on the contrary, was widely accepted. In 1452,
Pope Nicholas V
Pope Nicholas V ( la, Nicholaus V; it, Niccolò V; 13 November 1397 – 24 March 1455), born Tommaso Parentucelli, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 6 March 1447 until his death in March 1455. Pope Eugene IV, Po ...
issued the
papal bull ''
Dum Diversas'', granting the kings of Spain and Portugal the right to reduce any "Saracens (Muslims), pagans and any other unbelievers" to perpetual slavery, legitimizing the slave trade as a result of war. The approval of slavery under these conditions was reaffirmed and extended in his ''
Romanus Pontifex
(from Latin: "The Roman Pontiff") are papal bulls issued in 1436 by Pope Eugenius IV and in 1455 by Pope Nicholas V praising catholic King Afonso V of Portugal for his battles against the Muslims, endorsing his military expeditions into Western ...
'' bull of 1455.
=Britain
=
In Britain, slavery continued to be practiced following the fall of Rome, and sections of
Hywel the Good
Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell (died 949/950) was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubarth ...
's
laws
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. ...
dealt with slaves in
medieval Wales {{Commons category
Period
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Ce ...
. The trade particularly picked up after the Viking invasions, with major markets at
Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
and
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
supplied by Danish, Mercian, and Welsh raiding of one another's borderlands. At the time of the ''
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
'', nearly 10% of the
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
population were slaves.
William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
introduced a law preventing the sale of slaves overseas. According to historian
John Gillingham
John Bennett Gillingham (born 3 August 1940) is Emeritus Professor of Medieval History at the London School of Economics and Political Science. On 19 July 2007 he was elected a Fellow of the British Academy.
Gillingham is renowned as an expert on ...
, by 1200 slavery in the British Isles was non-existent.
Slavery had never been authorized by statute within England and Wales, and in 1772, in the case
Somerset v Stewart
''Somerset v Stewart'' (177298 ER 499(also known as ''Somersett's case'', ''v. XX Sommersett v Steuart and the Mansfield Judgment)'' is a judgment of the English Court of King's Bench in 1772, relating to the right of an enslaved person on En ...
, Lord Mansfield declared that it was also unsupported within England by the common law. The slave trade was abolished by the
Slave Trade Act 1807
The Slave Trade Act 1807, officially An Act for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom prohibiting the slave trade in the British Empire. Although it did not abolish the practice of slavery, it ...
, although slavery remained legal in possessions outside Europe until the passage of the
Slavery Abolition Act 1833
The Slavery Abolition Act 1833 (3 & 4 Will. IV c. 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which provided for the gradual abolition of slavery in most parts of the British Empire. It was passed by Earl Grey's reforming administrati ...
and the
Indian Slavery Act, 1843
The Indian Slavery Act, 1843, also known as Act V of 1843, was an act passed in British India under East India Company rule, which outlawed many economic transactions associated with slavery.
The act states how the sale of any person as a slav ...
.
However, when England began to have colonies in the Americas, and particularly from the 1640s, African slaves began to make their appearance in England and remained a presence until the eighteenth century. In Scotland, slaves continued to be sold as chattels until late in the eighteenth century (on the second May, 1722, an advertisement appeared in the ''
Edinburgh Evening Courant
The ''Edinburgh Courant'' was a broadsheet newspaper from the 18th century. It was published out of Edinburgh, Midlothian, Scotland. Its first issue was dated February 14–19, 1705 and was sold for a penny. It was Scotland's first regional newsp ...
'', announcing that a stolen slave had been found, who would be sold to pay expenses, unless claimed within two weeks).
For nearly two hundred years in the
history of coal mining in Scotland, miners were bonded to their "maisters" by a 1606 Act "Anent Coalyers and Salters". The
Colliers and Salters (Scotland) Act 1775
The Colliers and Salters (Scotland) Act 1775 is an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain
The Parliament of Great Britain was formed in May 1707 following the ratification of the Acts of Union by both the Parliament of England and the Parl ...
stated that "many colliers and salters are in a state of slavery and bondage" and announced emancipation; those starting work after 1 July 1775 would not become slaves, while those already in a state of slavery could, after 7 or 10 years depending on their age, apply for a decree of the Sheriff's Court granting their freedom. Few could afford this, until a further law in 1799 established their freedom and made this slavery and bondage illegal.
=Ottoman Empire
=

The
Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the
Ottoman wars in Europe
A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in ...
brought large numbers of slaves into the Islamic world. To staff its bureaucracy, the Ottoman Empire established a
janissary system which seized hundreds of thousands of Christian boys through the
devşirme
Devshirme ( ota, دوشیرمه, devşirme, collecting, usually translated as "child levy"; hy, Մանկահավաք, Mankahavak′. or "blood tax"; hbs-Latn-Cyrl, Danak u krvi, Данак у крви, mk, Данок во крв, Danok vo krv ...
system. They were well cared for but were legally slaves owned by the government and were not allowed to marry. They were never bought or sold. The empire gave them significant administrative and military roles. The system began about 1365; there were 135,000 janissaries in 1826, when the system ended.
After the
Battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states (comprising Spain and its Italian territories, several independent Italian states, and the Soverei ...
, 12,000 Christian galley slaves were recaptured and freed from the
Ottoman fleet. Eastern Europe suffered a series of
Tatar invasions
This article lists conflicts in Europe during the invasions of and subsequent occupations by the Mongol Empire and its successor states. The Mongol invasion of Europe took place in the 13th century. This resulted in the occupation of much of Easter ...
, the goal of which was to loot and capture slaves for selling them to Ottomans as
jasyr
Slavery in the Ottoman Empire was a lawful institution and a significant part of the Ottoman Empire's economy and traditional society. The main sources of slaves were wars and politically organized enslavement expeditions in the Caucasus, Easte ...
.
Seventy-five Crimean Tatar raids were recorded into
Poland–Lithuania between 1474 and 1569.
=Poland
=
Slavery in Poland was forbidden in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588; they were replaced by the second serfdom.
=Spain and Portugal
=

Medieval Spain
Spain in the Middle Ages is a period in the History of Spain that began in the 5th Century following the Fall of the Western Roman Empire and ended with the beginning of the Early modern period in 1492.
The history of Spain is marked by waves ...
and
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
were the scene of almost constant Muslim invasion of the predominantly Christian area. Periodic raiding expeditions were sent from
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus DIN 31635, translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label=Berber languages, Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, ...
to ravage the Iberian Christian kingdoms, bringing back booty and slaves. In a raid against Lisbon in 1189, for example, the
Almohad
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the Tawhid, unity of God) was a North African Berbers, Berber M ...
caliph
Yaqub al-Mansur
Abū Yūsuf Yaʿqūb ibn Yūsuf ibn Abd al-Muʾmin al-Manṣūr (; c. 1160 – 23 January 1199 Marrakesh), commonly known as Yaqub al-Mansur () or Moulay Yacoub (), was the third Almohad Caliph. Succeeding his father, al-Mansur reigned from 118 ...
took 3,000 female and child captives, while his governor of
Córdoba, in a subsequent attack upon
Silves Silves may refer to :
Europe
* Silves, Portugal, municipality and former bishopric in Algarve, southern Portugal
** Silves (parish), a civil parish in the municipality of Silves
** Castle of Silves, a medieval castle in civil parish of Silves
...
, Portugal, in 1191, took 3,000 Christian slaves. From the 11th to the 19th century, North African
Barbary Pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
engaged in raids on European coastal towns to capture Christian slaves to sell at
slave markets in places such as Algeria and Morocco.
The maritime town of
Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the List of cities in Africa by population, second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national ca ...
was the first slave market created in Portugal (one of the earliest colonizers of the Americas) for the sale of imported African slaves – the ''
Mercado de Escravos
The ''Mercado de Escravos'' (Slave Market) is a historical building in Lagos, in the Faro District of Portugal. It is located on the site where the first slave market in Europe of the modern era took place, in 1444. The building was first used ...
'', opened in 1444.
In 1441, the first slaves were brought to Portugal from northern Mauritania.
By 1552, black African slaves made up 10% of the population of
Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
. In the second half of the 16th century, the Crown gave up the monopoly on slave trade, and the focus of European trade in African slaves shifted from import to Europe to slave transports directly to tropical colonies in the Americas – especially Brazil.
In the 15th century one-third of the slaves were resold to the African market in exchange of gold.
=Russia
=
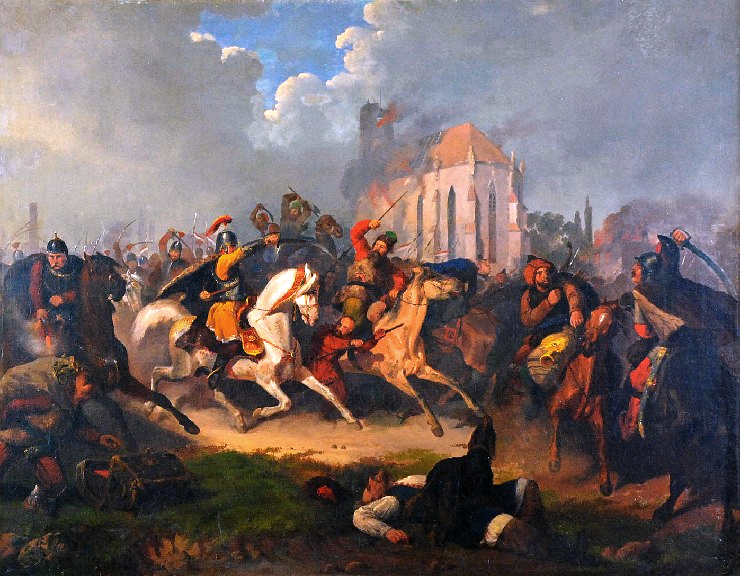

In
Kievan Rus
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
and
Muscovy Muscovy is an alternative name for the Grand Duchy of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
* Muscovy duck (''Cairina moschata'') and Domes ...
, slaves were usually classified as
kholop
A kholop ( rus, холо́п, p=xɐˈlop) was a type of feudal serf in Kievan Rus', then in Russia between the 10th and early 18th centuries. Their legal status was close to that of slaves.
Etymology
The word ''kholop'' was first mentioned in ...
s. According to David P. Forsythe, "In 1649 up to three-quarters of Muscovy's peasants, or 13 to 14 million people, were serfs whose material lives were barely distinguishable from slaves. Perhaps another 1.5 million were formally enslaved, with Russian slaves serving Russian masters."
Slavery remained a major institution in
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
until 1723, when
Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
converted the household slaves into house serfs. Russian agricultural slaves were formally converted into serfs earlier in 1679.
=Scandinavia
=
In Scandinavia,
thrall
A thrall ( non, þræll, is, þræll, fo, trælur, no, trell, træl, da, træl, sv, träl) was a slave or serf in Scandinavian lands during the Viking Age. The corresponding term in Old English was . The status of slave (, ) contrasts with ...
dom was abolished in the mid-14th century.
Early modern period
Africa

As recently as the early 1960s, Saudi Arabia's slave population was estimated at 300,000. Along with Yemen, the Saudis abolished slavery in 1962.
Historically, slaves in the
Arab World
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
came from many different regions, including
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
(mainly ''
Zanj
Zanj ( ar, زَنْج, adj. , ''Zanjī''; fa, زنگی, Zangi) was a name used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa (primarily the Swahili Coast) and to its Bantu inhabitants. This word is also ...
''), the
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
(mainly
Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia in ...
), Central Asia (mainly
Tartars
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounde ...
), and
Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Europe (mainly Slavs
'Saqaliba''.html" ;"title="Saqaliba.html" ;"title="'Saqaliba">'Saqaliba''">Saqaliba.html" ;"title="'Saqaliba">'Saqaliba''.
Some historians assert that as many as 17 million people were sold into slavery on the coast of the Indian Ocean, the Middle East, and North Africa, and approximately 5 million African slaves were bought by Muslim slave traders and taken from Africa across the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara desert between 1500 and 1900. The captives were sold throughout the Middle East. This trade accelerated as superior ships led to more trade and greater demand for labour on plantations in the region. Eventually, tens of thousands of captives were being taken every year.
The Indian Ocean slave trade was multi-directional and changed over time. To meet the demand for menial labour, Bantu slaves bought by east African slave traders from southeastern Africa were sold in cumulatively large numbers over the centuries to customers in Egypt, Arabia, the Persian Gulf, India, European colonies in the Far East, the
Indian Ocean islands
The islands of the Indian Ocean are part of either the eastern, western, or southern areas. Some prominently large islands include Madagascar, Sri Lanka, and the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Java.
Eastern Indian Ocean
* Andaman Islands (I ...
, Ethiopia and Somalia.
According to the ''
Encyclopedia of African History
The ''Encyclopedia of African History'' is a three-volume work dedicated to African history. It was edited by Kevin Shillington and published in New York City by Routledge in November 2004. The Library of Congress subjects for this work are ''Af ...
'', "It is estimated that by the 1890s the largest slave population of the world, about 2 million people, was concentrated in the territories of the
Sokoto Caliphate
The Sokoto Caliphate (), also known as the Fulani Empire or the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fulani jihads after defeating the Hausa Kingdoms in the Ful ...
. The use of slave labour was extensive, especially in agriculture." The Anti-Slavery Society estimated there were 2 million slaves in Ethiopia in the early 1930s out of an estimated population of 8 to 16 million.
Slave labour in East Africa was drawn from the ''Zanj,'' Bantu peoples that lived along the East African coast.
The Zanj were for centuries shipped as slaves by Arab traders to all the countries bordering the Indian Ocean. The Umayyad and Abbasid caliphs recruited many Zanj slaves as soldiers and, as early as 696, there were slave revolts of the Zanj against their Arab enslavers in Iraq. The
Zanj Rebellion
The Zanj Rebellion ( ar, ثورة الزنج ) was a major revolt against the Abbasid Caliphate, which took place from 869 until 883. Begun near the city of Basra in present-day southern Iraq and led by one Ali ibn Muhammad, the insurrection invol ...
, a series of uprisings that took place between 869 and 883 near
Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is hand ...
(also known as Basara), situated in present-day Iraq, is believed to have involved enslaved Zanj that had originally been captured from the
African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in the ...
region and areas further south in
East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
. It grew to involve over 500,000 slaves and free men who were imported from across the
Muslim empire
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and contin ...
and claimed over "tens of thousands of lives in lower Iraq".
The Zanj who were taken as slaves to the Middle East were often used in strenuous agricultural work. As the
plantation economy
A plantation economy is an economy based on agricultural mass production, usually of a few commodity crops, grown on large farms worked by laborers or slaves. The properties are called plantations. Plantation economies rely on the export of cas ...
boomed and the Arabs became richer, agriculture and other manual labour work was thought to be demeaning. The resulting labour shortage led to an increased slave market.

In
Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
, the capital of Algeria, captured Christians and Europeans were forced into slavery. In about 1650, there were as many as 35,000 Christian slaves in Algiers. By one estimate, raids by
Barbary slave trade
The Barbary slave trade involved slave markets on the Barbary Coast of North Africa, which included the Ottoman states of Algeria, Tunisia and Tripolitania and the independent sultanate of Morocco, between the 16th and 19th century. The Ottom ...
rs on coastal villages and ships extending from Italy to Iceland, enslaved an estimated 1 to 1.25 million Europeans between the 16th and 19th centuries.
However, this estimate is the result of an extrapolation which assumes that the number of European slaves captured by Barbary pirates was constant for a 250-year period:
Davis' numbers have been refuted by other historians, such as David Earle, who cautions that true picture of Europeans slaves is clouded by the fact the corsairs also seized non-Christian whites from eastern Europe.
[ In addition, the number of slaves traded was hyperactive, with exaggerated estimates relying on peak years to calculate averages for entire centuries, or millennia. Hence, there were wide fluctuations year-to-year, particularly in the 18th and 19th centuries, given slave imports, and also given the fact that, prior to the 1840s, there are no consistent records. Middle East expert, John Wright, cautions that modern estimates are based on back-calculations from human observation.]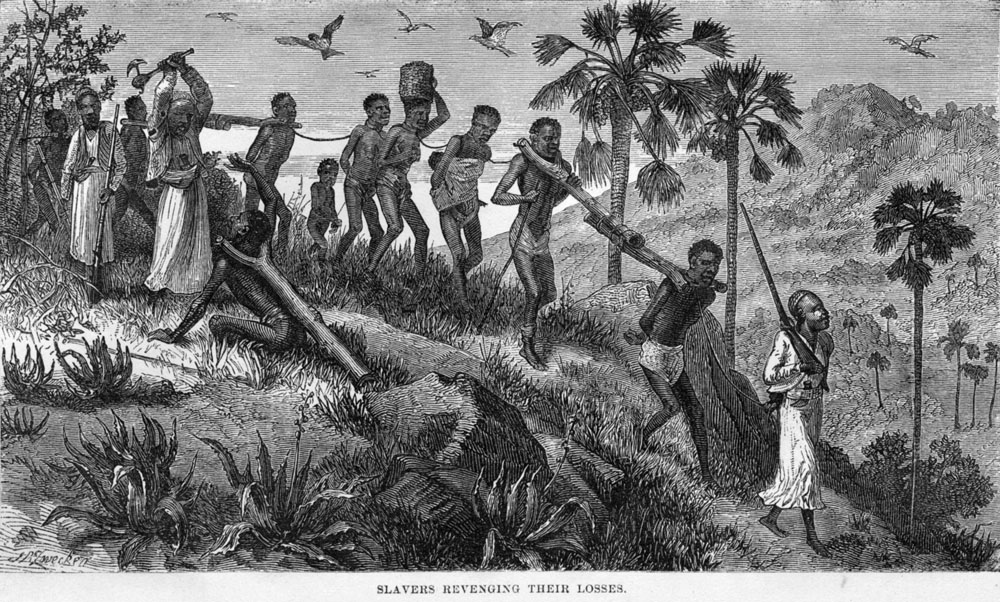 Under Omani Arabs, Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 African slaves passing through every year during the 19th century. Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 to 1900 AD.
Under Omani Arabs, Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 African slaves passing through every year during the 19th century. Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 to 1900 AD.Eduard Rüppell
Wilhelm Peter Eduard Simon Rüppell (20 November 1794 – 10 December 1884) was a German Natural history, naturalist and List of explorers, explorer. Rüppell is occasionally transliterated to "Rueppell" for the English alphabet, due to german ort ...
described the losses of Sudanese slaves being transported on foot to Egypt: "after the Daftardar bey's 1822 campaign in the southern Nuba mountains, nearly 40,000 slaves were captured. However, through bad treatment, disease and desert travel barely 5,000 made it to Egypt." W.A. Veenhoven wrote: "The German doctor, Gustav Nachtigal
Gustav Nachtigal (; born 23 February 1834 – 20 April 1885) was a German military surgeon and explorer of Central and West Africa. He is further known as the German Empire's consul-general for Tunisia and Commissioner for West Africa. His missio ...
, an eye-witness, believed that for every slave who arrived at a market three or four died on the way ... Keltie (''The Partition of Africa'', London, 1920) believes that for every slave the Arabs brought to the coast at least six died on the way or during the slavers' raid. Livingstone puts the figure as high as ten to one."
Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the ancient world
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cove ...
. In many African societies where slavery was prevalent, the slaves were not treated as chattel slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and were given certain rights in a system similar to indentured servitude
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, ...
elsewhere in the world. The forms of slavery in Africa were closely related to kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
structures. In many African communities, where land could not be owned, enslavement of individuals was used as a means to increase the influence a person had and expand connections.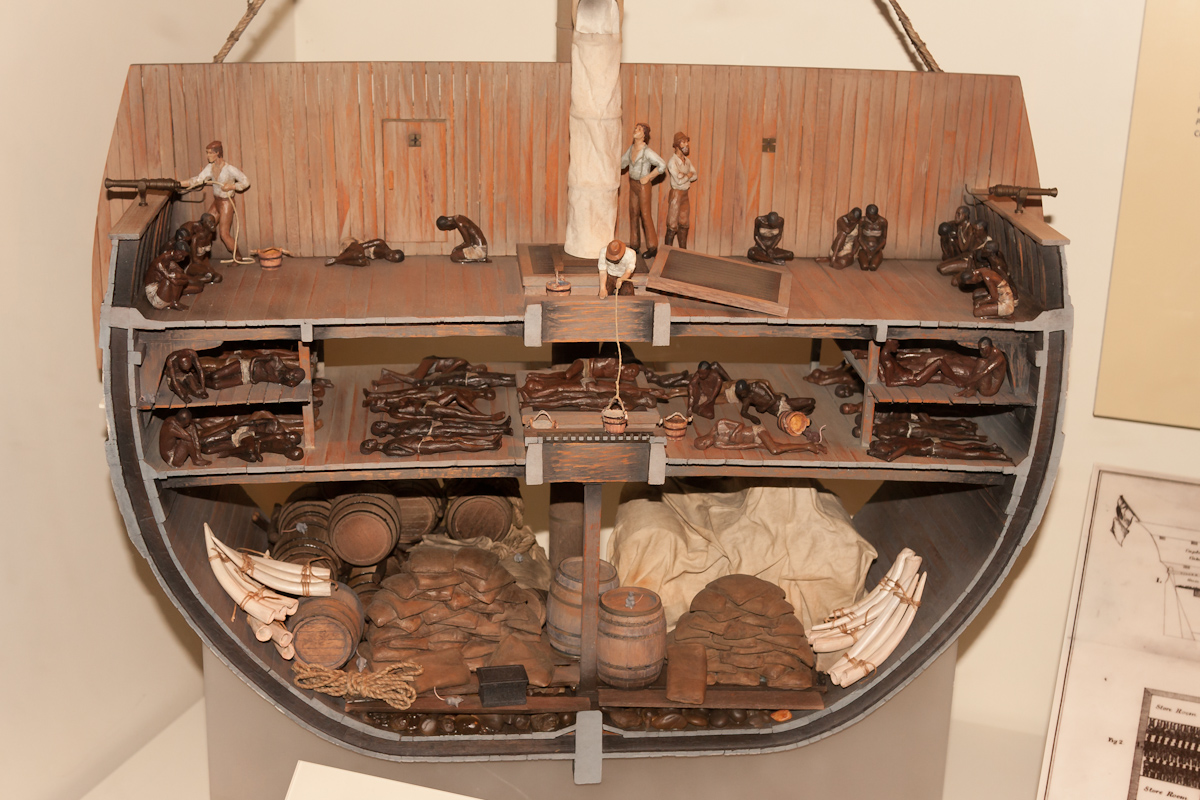 When the
When the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
began, many of the local slave systems began supplying captives for chattel slave markets outside Africa. Although the Atlantic slave trade was not the only slave trade from Africa, it was the largest in volume and intensity. As Elikia M’bokolo wrote in ''Le Monde diplomatique
''Le Monde diplomatique'' (meaning "The Diplomatic World" in French) is a French monthly newspaper offering analysis and opinion on politics, culture, and current affairs.
The publication is owned by Le Monde diplomatique SA, a subsidiary com ...
'':
The trans-Atlantic slave trade peaked in the late 18th century, when the largest number of slaves were captured on raiding expeditions into the interior of West Africa. These expeditions were typically carried out by African kingdoms, such as the Oyo Empire
The Oyo Empire was a powerful Yoruba empire of West Africa made up of parts of present-day eastern Benin and western Nigeria (including Southwest zone and the western half of Northcentral zone). It grew to become the largest Yoruba language, ...
(Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
), the Ashanti Empire
The Asante Empire (Asante Twi: ), today commonly called the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted between 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana as well as parts of Iv ...
,Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. Dahomey developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in the early 17th century and became a region ...
, and the Aro Confederacy
The Aro Confederacy (1690–1902) was a political union orchestrated by the Aro people, Igbo subgroup, centered in Arochukwu in present-day southeastern Nigeria. Their influence and presence was all over Eastern Nigeria, lower Middle Belt, and ...
. It is estimated that about 15 percent of slaves died during the voyage
Voyage(s) or The Voyage may refer to:
Literature
*''Voyage : A Novel of 1896'', Sterling Hayden
* ''Voyage'' (novel), a 1996 science fiction novel by Stephen Baxter
*''The Voyage'', Murray Bail
* "The Voyage" (short story), a 1921 story by ...
, with mortality rates considerably higher in Africa itself in the process of capturing and transporting indigenous peoples to the ships.
Americas
Slavery in America remains a contentious issue and played a major role in the history and evolution of some countries, triggering a revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
, a civil war, and numerous rebellions.
In order to establish itself as an American empire, Spain had to fight against the relatively powerful civilizations of the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
. The Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
conquest of the indigenous peoples in the Americas included using the Natives as forced labour. The Spanish colonies
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
were the first Europeans to use African slaves in the New World on islands such as Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
and Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
. Bartolomé de las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP ( ; ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a 16th-century Spanish landowner, friar, priest, and bishop, famed as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman then became a Dominican friar ...
, a 16th-century Dominican friar
A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders founded in the twelfth or thirteenth century; the term distinguishes the mendicants' itinerant apostolic character, exercised broadly under the jurisdiction of a superior general, from the ol ...
and Spanish historian, participated in campaigns in Cuba (at Bayamo
Bayamo is the capital city of the Granma Province of Cuba and one of the largest cities in the Oriente region.
Overview
The community of Bayamo lies on a plain by the Bayamo River. It is affected by the violent Bayamo wind.
One of the most ...
and Camagüey
Camagüey () is a city and municipality in central Cuba and is the nation's third-largest city with more than 321,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of the Camagüey Province.
It was founded as Santa María del Puerto del Príncipe in 1514, by S ...
) and was present at the massacre of Hatuey
Hatuey (), also Hatüey (; died 2 February 1512) was a Taíno ''Cacique'' (chief) of the Hispaniola province of Guahaba (present-day La Gonave, Haiti). He lived from the late 15th until the early 16th century. One day Chief Hatuey and many of ...
; his observation of that massacre led him to fight for a social movement away from the use of natives as slaves. Also, the alarming decline in the native
Native may refer to:
People
* Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Native Americans (disambiguation)
In arts and entert ...
population had spurred the first royal laws protecting the native population. The first African slaves arrived in Hispaniola in 1501. England played a prominent role in the Atlantic slave trade. The " slave triangle" was pioneered by Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
and his associates.
Many whites who arrived in North America during the 17th and 18th centuries came under contract as indentured servants. The transformation from indentured servitude to slavery was a gradual process in Virginia. The earliest legal documentation of such a shift was in 1640 where a Black man, John Punch, was sentenced to lifetime slavery, forcing him to serve his master, Hugh Gwyn, for the remainder of his life, for attempting to run away. This case was significant because it established the disparity between his sentence as a black man and that of the two white indentured servants who escaped with him (one described as Dutch and one as a Scotchman). It is the first documented case of a black man sentenced to lifetime servitude and is considered one of the first legal cases to make a racial distinction between black and white indentured servants.John Casor
John Casor (surname also recorded as Cazara and Corsala), a servant in Northampton County in the Virginia Colony, in 1655 became the first person of African descent in the Thirteen Colonies to be declared as a slave for life as a result of a civ ...
, as the result of a civil case.Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
holding that a person who had committed no crime could be held in servitude for life.
=Barbados
=
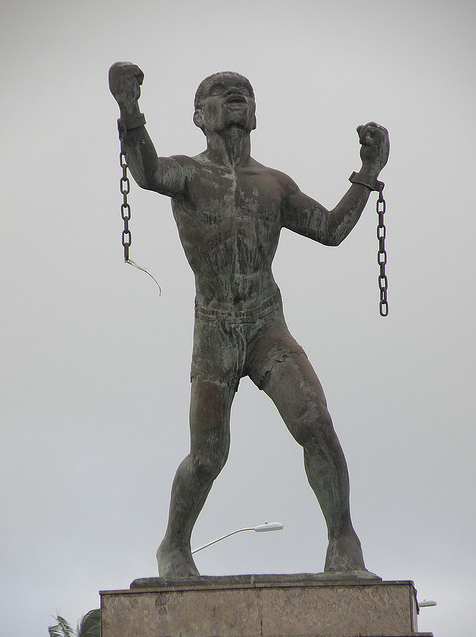 In the early 17th century, the majority of the labour in Barbados was provided by European indentured servants, mainly
In the early 17th century, the majority of the labour in Barbados was provided by European indentured servants, mainly English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
and Scottish, with African
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
and native American slaves providing little of the workforce. The introduction of sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks t ...
from Dutch Brazil
Dutch Brazil ( nl, Nederlands-Brazilië), also known as New Holland ( nl, Nieuw-Holland), was a colony of the Dutch Republic in the northeastern portion of modern-day Brazil, controlled from 1630 to 1654 during Dutch colonization of the Americas ...
in 1640 completely transformed society and the economy. Barbados eventually had one of the world's largest sugar industries.slave codes
The slave codes were laws relating to slavery and enslaved people, specifically regarding the Atlantic slave trade and chattel slavery in the Americas.
Most slave codes were concerned with the rights and duties of free people in regards to ensla ...
, which created differential treatment between Africans and the white workers and ruling planter class, the island became increasingly unattractive to poor whites
Poor White is a sociocultural classification used to describe economically disadvantaged Whites in the English-speaking world, especially White Americans with low incomes.
In the United States, Poor White (or Poor Whites of the South for ...
. Black or slave codes were implemented in 1661, 1676, 1682, and 1688. In response to these codes, several slave rebellions were attempted or planned during this time, but none succeeded. Nevertheless, poor whites who had or acquired the means to emigrate often did so. Planters expanded their importation of African slaves to cultivate sugar cane.
=Brazil
=


Slavery in Brazil
Slavery in Brazil began long before the first Portuguese settlement was established in 1516, with members of one tribe enslaving captured members of another. Later, colonists were heavily dependent on indigenous labor during the initial phases ...
began long before the first Portuguese settlement was established in 1532, as members of one tribe would enslave captured members of another.Luanda
Luanda () is the capital and largest city in Angola. It is Angola's primary port, and its major industrial, cultural and urban centre. Located on Angola's northern Atlantic coast, Luanda is Angola's administrative centre, its chief seaport ...
(in present-day Angola). Today, with the exception of Nigeria, the country with the largest population of people of African descent is Brazil.sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
economy in Brazil, and sugar was the primary export of the colony from 1600 to 1650. Gold and diamond deposits were discovered in Brazil in 1690, which sparked an increase in the importation of African slaves to power this newly profitable market. Transportation systems were developed for the mining infrastructure, and population boomed from immigrants seeking to take part in gold and diamond mining. Demand for African slaves did not wane after the decline of the mining industry in the second half of the 18th century. Cattle ranching and foodstuff production proliferated after the population growth, both of which relied heavily on slave labour. 1.7 million slaves were imported to Brazil from Africa from 1700 to 1800, and the rise of coffee in the 1830s further enticed expansion of the slave trade.
Brazil was the last country in the Western world to abolish slavery. Forty percent of the total number of slaves brought to the Americas were sent to Brazil. For reference, the United States received 10 percent. Despite being abolished, there are still people working in slavery-like conditions in Brazil in the 21st century.
=Cuba
=
In 1789 the Spanish Crown led an effort to reform slavery, as the demand for slave labour in Cuba was growing. The Crown issued a decree, ''Código Negro Español'' (Spanish Black Codex), that specified food and clothing provisions, put limits on the number of work hours
Working(laboring) time is the period of time that a person spends at paid labor. Unpaid labor such as personal housework or caring for children or pets is not considered part of the working week.
Many countries regulate the work week by law, s ...
, limited punishments, required religious instruction, and protected marriages, forbidding the sale of young children away from their mothers. The British made other changes to the institution of slavery in Cuba. But planters often flouted the laws and protested against them, considering them a threat to their authority and an intrusion into their personal lives.[
Those slaves who worked on sugar plantations and in sugar mills were often subject to the harshest of conditions. The field work was rigorous manual labour which the slaves began at an early age. The work days lasted close to 20 hours during harvest and processing, including cultivating and cutting the crops, hauling wagons, and processing sugarcane with dangerous machinery. The slaves were forced to reside in barracoons, where they were crammed in and locked in by a padlock at night, getting about three to four hours of sleep. The conditions of the barracoons were harsh; they were highly unsanitary and extremely hot. Typically there was no ventilation; the only window was a small barred hole in the wall.] Cuba's slavery system was gendered in a way that some duties were performed only by male slaves, some only by female slaves. Female slaves in
Cuba's slavery system was gendered in a way that some duties were performed only by male slaves, some only by female slaves. Female slaves in Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center. from the 16th century onwards performed duties such as operating the town taverns, eating houses, and lodges, as well as being laundresses and domestic labourers and servants. Female slaves also served as the town prostitutes.
Some Cuban women could gain freedom by having children with white men. As in other Latin cultures, there were looser borders with the mulatto
(, ) is a racial classification to refer to people of mixed African and European ancestry. Its use is considered outdated and offensive in several languages, including English and Dutch, whereas in languages such as Spanish and Portuguese is ...
or mixed-race population. Sometimes men who took slaves as wives or concubines freed both them and their children. As in New Orleans and Saint-Domingue, mulattos began to be classified as a third group between the European colonists and African slaves. Freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), abolitionism, emancipation (gra ...
, generally of mixed race, came to represent 20% of the total Cuban population and 41% of the non-white Cuban population.[Knight pp. 144–145]
Planters encouraged Afro-Cuban slaves to have children in order to reproduce their work force. The masters wanted to pair strong and large-built black men with healthy black women. They were placed in the barracoons and forced to have sex and create offspring of "breed stock" children, who would sell for around 500 pesos. The planters needed children to be born to replace slaves who died under the harsh regime. Sometimes if the overseers did not like the quality of children, they separate the parents and sent the mother back to working in the fields.arth
Arth is a village, a List of towns in Switzerland, town, and a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in Schwyz District in the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The municipality consists of the villages Arth, Oberarth, and Goldau. The four ...
to protect their bellies."
=Haiti
=
Slavery in Haiti
Slavery in Haiti began after the arrival of Christopher Columbus on the island in 1492 with the European colonists that followed from Portugal, Spain and France. The practice was devastating to the native population. Following the indigenous Ta ...
started with the arrival of Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
on the island in 1492. The practice was devastating to the native population. Following the indigenous Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
's near decimation from forced labour, disease and war, the Spanish, under advisement of the Catholic priest Bartolomeu de las Casas, and with the blessing of the Catholic church began engaging in earnest in the kidnapped and forced labour of African slaves. During the French colonial period beginning in 1625, the economy of Haiti (then known as Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer ...
) was based on slavery, and the practice there was regarded as the most brutal in the world.

 Following the
Following the Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance, which included England, ...
of 1697, Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
was divided between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. France received the western third and subsequently named it Saint-Domingue. To develop it into sugarcane plantations, the French imported thousands of slaves from Africa. Sugar was a lucrative commodity crop throughout the 18th century. By 1789, approximately 40,000 white colonists lived in Saint-Domingue. The whites were vastly outnumbered by the tens of thousands of African slaves they had imported to work on their plantations, which were primarily devoted to the production of sugarcane. In the north of the island, slaves were able to retain many ties to African cultures, religion and language; these ties were continually being renewed by newly imported Africans. Blacks outnumbered whites by about ten to one.
The French-enacted ''Code Noir
The (, ''Black code'') was a decree passed by the French King Louis XIV in 1685 defining the conditions of slavery in the French colonial empire. The decree restricted the activities of free people of color, mandated the conversion of all e ...
'' ("Black Code"), prepared by Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the countr ...
and ratified by Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
, had established rules on slave treatment and permissible freedoms. Saint-Domingue has been described as one of the most brutally efficient slave colonies; one-third of newly imported Africans died within a few years.smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
and typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
. They had birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
s around 3 percent, and there is evidence that some women aborted
Aborted is a Belgian death metal band formed in 1995 in Waregem. The group currently consists of vocalist, founder and only constant member Sven de Caluwé, guitarist Ian Jekelis, bassist Stefano Franceschini and drummer Ken Bedene. Although th ...
fetuses, or committed infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose is the prevention of reso ...
, rather than allow their children to live within the bonds of slavery.French colonial
French colonial architecture includes several styles of architecture used by the French during colonization. Many former French colonies, especially those in Southeast Asia, have previously been reluctant to promote their colonial architecture ...
government allowed some rights to free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (French: ''gens de couleur libres''; Spanish: ''gente de color libre'') were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not ...
: the mixed-race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
descendants of white male colonists and black female slaves (and later, mixed-race women). Over time, many were released from slavery. They established a separate social class. White French Creole fathers frequently sent their mixed-race sons to France for their education. Some men of color were admitted into the military. More of the free people of color lived in the south of the island, near Port-au-Prince
Port-au-Prince ( , ; ht, Pòtoprens ) is the capital and most populous city of Haiti. The city's population was estimated at 987,311 in 2015 with the metropolitan area estimated at a population of 2,618,894. The metropolitan area is define ...
, and many intermarried within their community. They frequently worked as artisans and tradesmen, and began to own some property. Some became slave holders. The free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (French: ''gens de couleur libres''; Spanish: ''gente de color libre'') were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not ...
petitioned the colonial government to expand their rights.
Slaves that made it to Haiti from the trans-Atlantic journey and slaves born in Haiti were first documented in Haiti's archives and transferred to France's Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. , these records are in The National Archives of France. According to the 1788 Census, Haiti's population consisted of nearly 40,000 whites, 30,000 free coloureds and 450,000 slaves.
The Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution (french: révolution haïtienne ; ht, revolisyon ayisyen) was a successful insurrection by slave revolt, self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolt ...
of 1804, the only successful slave revolt
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freed ...
in human history, precipitated the end of slavery in all French colonies.
=Jamaica
=
Jamaica was colonized by the Taino tribes prior to the arrival of Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
in 1494. The Spanish enslaved many of the Taino; some escaped, but most died from European diseases and overwork. The Spaniards also introduced the first African slaves.mestizo
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed Ethnic groups in Europe, European and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also r ...
children. Sexual violence with the Taíno women by the Spanish was also common.
Although the African slave population in the 1670s and 1680s never exceeded 10,000, by 1800 it had increased to over 300,000.
=Mexico
=
In 1519, Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
brought the first modern slave to the area.Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those g ...
. A labour shortage resulted as the Aztecs were either killed or died from disease. This led to the African slaves being imported, as they were not susceptible to smallpox. In exchange, many Africans were afforded the opportunity to buy their freedom, while eventually others were granted their freedom by their masters.[
]
=Puerto Rico
=
When Ponce de León
Ponce may refer to:
*Ponce (surname)
*
*Ponce, Puerto Rico, a city in Puerto Rico
** Ponce High School
** Ponce massacre, 1937
* USS ''Ponce'', several ships of the US Navy
*Manuel Ponce, a Mexican composer active in the 20th century
* British sla ...
and the Spaniards arrived on the island of Borikén (Puerto Rico), they enslaved Taíno tribes on the island, forcing them to work in the gold mines and in the construction of forts. Many Taíno died, particularly from smallpox, of which they had no immunity
Immunity may refer to:
Medicine
* Immunity (medical), resistance of an organism to infection or disease
* ''Immunity'' (journal), a scientific journal published by Cell Press
Biology
* Immune system
Engineering
* Radiofrequence immunity desc ...
. Other Taínos committed suicide or left the island after the failed Taíno revolt of 1511. The Spanish colonists, fearing the loss of their labour force, complained to the courts that they needed manpower. As an alternative, Las Casas suggested the importation and use of African slaves. In 1517, the Spanish Crown permitted its subjects to import twelve slaves each, thereby beginning the slave trade on the colonies.
African slaves were legally branded with a hot iron on the forehead, prevented their "theft" or lawsuits that challenged their captivity.Luquillo
Luquillo () is a town and municipality of Puerto Rico located in the northeast coast, northwest of Fajardo; and east of Rio Grande. Luquillo is spread over 5 barrios and Luquillo Pueblo (the downtown area and the administrative center of the ci ...
. Some became slave owners themselves.
=Suriname
=
 The planters of the Dutch colony relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate, harvest and process the commodity crops of coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Planters' treatment of the slaves was notoriously bad. Historian
The planters of the Dutch colony relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate, harvest and process the commodity crops of coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Planters' treatment of the slaves was notoriously bad. Historian C. R. Boxer
Sir Charles Ralph Boxer FBA GCIH (8 March 1904 – 27 April 2000) was a British historian of Dutch and Portuguese maritime and colonial history, especially in relation to South Asia and the Far East. In Hong Kong he was the chief spy for the ...
wrote that "man's inhumanity to man just about reached its limits in Surinam."
Many slaves escaped the plantations. With the help of the native South Americans living in the adjoining rain forests, these runaway slaves established a new and unique culture in the interior that was highly successful in its own right. They were known collectively in English as Maroons
Maroons are descendants of African diaspora in the Americas, Africans in the Americas who escaped from slavery and formed their own settlements. They often mixed with indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples, eventually ethnogenesi ...
, in French as ''Nèg'Marrons'' (literally meaning "brown negroes", that is "pale-skinned negroes"), and in Dutch as ''Marrons.'' The Maroons gradually developed several independent tribes through a process of ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introdu ...
, as they were made up of slaves from different African ethnicities. These tribes include the Saramaka
The Saramaka, Saamaka or Saramacca are one of six Maroon peoples (formerly called "Bush Negroes") in the Republic of Suriname and one of the Maroon peoples in French Guiana. In 2007, the Saramaka won a ruling by the Inter-American Court of Hum ...
, Paramaka, Ndyuka or Aukan, Kwinti
The Kwinti are a Maroon people, descendants of runaway African slaves, living in the forested interior of Suriname on the bank of the Coppename River, and the eponymous term for their language, which has fewer than 300 speakers. Their language i ...
, Aluku
The Aluku are a Bushinengue ethnic group living mainly on the riverbank in Maripasoula in southwest French Guiana. The group are sometimes called Boni, referring to the 18th-century leader, Bokilifu Boni.
History
The Aluku are an ethnic gro ...
or Boni, and Matawai.
The Maroons often raided plantations to recruit new members from the slaves and capture women, as well as to acquire weapons, food and supplies. They sometimes killed planters and their families in the raids. The colonists also mounted armed campaigns against the Maroons, who generally escaped through the rain forest, which they knew much better than did the coloniss. To end hostilities, in the 18th century the European colonial authorities signed several peace treaties with different tribes. They granted the Maroons sovereign status and trade rights in their inland territories, giving them autonomy.
In 1861–63, President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
of the United States and his administration looked abroad for places to relocate freed slaves who wanted to leave the United States. It opened negotiations with the Dutch government regarding African-American emigration to and colonization of the Dutch colony of Suriname in South America. Nothing came of it and after 1864, the proposal was dropped.
The Netherlands abolished slavery in Suriname, in 1863, under a gradual process that required slaves to work on plantations for 10 transition years for minimal pay, which was considered as partial compensation for their masters. Besides that, the Dutch government in 1863 also compensated each slave-owner for the loss of the working force of each slave 300 Dutch florins - in 2021 worth about 3,500 euros. After 1873, most freedmen largely abandoned the plantations where they had worked for several generations in favor of the capital city, Paramaribo
Paramaribo (; ; nicknamed Par'bo) is the capital and largest city of Suriname, located on the banks of the Suriname River in the Paramaribo District. Paramaribo has a population of roughly 241,000 people (2012 census), almost half of Suriname's ...
.
=United States
=

Slavery in the United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Sl ...
was the legal institution of human chattel enslavement, primarily of Africans and African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, that existed in the United States of America in the 18th and 19th centuries, after it gained independence from the British and before the end of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
. Slavery had been practiced in British America
British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, which became the British Empire after the 1707 union of the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, in the Americas from 16 ...
from early colonial days and was legal in all Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, at the time of the Declaration of Independence in 1776. By the time of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
, the status of slave had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. The United States became polarized over the issue of slavery, represented by the slave and free states
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
divided by the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, also called the Mason and Dixon line or Mason's and Dixon's line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (part of Virginia ...
, which separated free Pennsylvania from slave Maryland and Delaware.
Congress, during the Jefferson Jefferson may refer to:
Names
* Jefferson (surname)
* Jefferson (given name)
People
* Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), third president of the United States
* Jefferson (footballer, born 1970), full name Jefferson Tomaz de Souza, Brazilian foo ...
administration, prohibited the importation of slaves, effective 1808, although smuggling (illegal importing) was not unusual.hanging
Hanging is the suspension of a person by a noose or ligature around the neck.Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd ed. Hanging as method of execution is unknown, as method of suicide from 1325. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' states that hanging i ...
, beating, burning, mutilation, branding and imprisonment. Punishment was most often meted out in response to disobedience or perceived infractions, but sometimes abuse was carried out to re-assert the dominance of the master or overseer of the slave.William Wells Brown
William Wells Brown (c. 1814 – November 6, 1884) was a prominent abolitionist lecturer, novelist, playwright, and historian in the United States. Born into slavery in Montgomery County, Kentucky, near the town of Mount Sterling, Brown escape ...
, who escaped to freedom, reported that on one plantation, slave men were required to pick of cotton per day, while women were required to pick per day; if any slave failed in their quota, they were subject to whip lashes for each pound they were short. The whipping post stood next to the cotton scales. A New York man who attended a slave auction in the mid-19th century reported that at least three-quarters of the male slaves he saw at sale had scars on their backs from whipping.[
More than one million slaves were sold from the ]Upper South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern and lower Midwestern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, econom ...
, which had a surplus of labour, and taken to the Deep South in a forced migration, splitting up many families. New communities of African-American culture were developed in the Deep South, and the total slave population in the South eventually reached 4 million before liberation.[ Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas".] In the 19th century, proponents of slavery often defended the institution as a "necessary evil". White people of that time feared that emancipation of black slaves would have more harmful social and economic consequences than the continuation of slavery. The French writer and traveler Alexis de Tocqueville
Alexis Charles Henri Clérel, comte de Tocqueville (; 29 July 180516 April 1859), colloquially known as Tocqueville (), was a French aristocrat, diplomat, political scientist, political philosopher and historian. He is best known for his works ...
, in ''Democracy in America
(; published in two volumes, the first in 1835 and the second in 1840) is a classic French text by Alexis de Tocqueville. Its title literally translates to ''On Democracy in America'', but official English translations are usually simply entitl ...
'' (1835), expressed opposition to slavery while observing its effects on American society. He felt that a multiracial society without slavery was untenable, as he believed that prejudice against black people increased as they were granted more rights. Others, like James Henry Hammond
James Henry Hammond (November 15, 1807 – November 13, 1864) was an attorney, politician, and planter from South Carolina. He served as a United States representative from 1835 to 1836, the 60th Governor of South Carolina from 1842 to 1844, and ...
argued that slavery was a "positive good" stating: "Such a class you must have, or you would not have that other class which leads progress, civilization, and refinement."
The Southern state governments wanted to keep a balance between the number of slave and free states to maintain a political balance of power in Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
. The new territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
acquired from Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and Mexico were the subject of major political compromises. By 1850, the newly rich cotton-growing South was threatening to secede from the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
, and tensions continued to rise. Many white Southern Christians, including church ministers, attempted to justify their support for slavery as modified by Christian paternalism. The largest denominations, the Baptist, Methodist, and Presbyterian churches, split over the slavery issue into regional organizations of the North and South.
 When
When Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
won the 1860 election on a platform of halting the expansion of slavery, according to the 1860 U.S. census, roughly 400,000 individuals, representing 8% of all U.S. families, owned nearly 4,000,000 slaves. One-third of Southern families owned slaves. The South was heavily invested in slavery. As such, upon Lincoln's election, seven states broke away to form the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
. The first six states to secede held the greatest number of slaves in the South. Shortly after, over the issue of slavery, the United States erupted into an all out Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, with slavery legally ceasing as an institution following the war in December 1865.
Asia
Slavery has existed all throughout Asia, and forms of slavery still exist today.
=China
=
 Slavery has taken various forms throughout China's history. It was reportedly abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 law
Slavery has taken various forms throughout China's history. It was reportedly abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 lawTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
purchased Western slaves from the Radhanite
The Radhanites or Radanites (; ar, الرذنية, ''ar-Raðaniyya'') were early medieval Jewish merchants, active in the trade between Christendom and the Muslim world during roughly the 8th to 10th centuries.
Many trade routes previously esta ...
Jews. Tang Chinese soldiers and pirates enslaved Koreans, Turks, Persians, Indonesians, and people from Inner Mongolia, central Asia, and northern India. The greatest source of slaves came from southern tribes, including Thais and aboriginals from the southern provinces of Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Guizhou. Malays, Khmers, Indians, and "black skinned" peoples (who were either Austronesian Negrito
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the Onge, ...
s of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands, or Africans, or both) were also purchased as slaves in the Tang dynasty.
In the 17th century Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
, there was a hereditarily servile people called ''Booi Aha'' (Manchu:booi niyalma; Chinese transliteration: 包衣阿哈), which is a Manchu word literally translated as "household person" and sometimes rendered as "nucai
''Nucai'' (; Manchu: , Mölendroff: ''aha'') is a Chinese term that can be translated as, 'lackey', 'yes-man', 'servant', 'slave', or a 'person of unquestioning obedience'. It originated in the tribes of northeastern China as a negative and der ...
." The Manchu was establishing close personal and paternalist relationship between masters and their slaves, as Nurhachi said, "The Master should love the slaves and eat the same food as him". However, booi aha "did not correspond exactly to the Chinese category of "bond-servant slave" (Chinese:奴僕); instead, it was a relationship of personal dependency on a master which in theory guaranteed close personal relationships and equal treatment, even though many western scholars would directly translate "booi" as "bond-servant" (some of the "booi" even had their own servant).
Chinese Muslim
Islam has been practiced in China since the 7th century CE.. Muslims are a minority group in China, representing 1.6-2 percent of the total population (21,667,000- 28,210,795) according to various estimates. Though Hui Muslims are the most nume ...
(Tungans) Sufis who were charged with practicing xiejiao (heterodox religion), were punished by exile to Xinjiang and being sold as a slave to other Muslims, such as the Sufi begs. Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
who committed crimes such as those dealing with opium became slaves to the begs, this practice was administered by Qing law. Most Chinese in Altishahr
Altishahr (, , ; romanized: ''Altä-şähär'' or ''Alti-şähär''), also known as Kashgaria, is a historical name for the Tarim Basin region used in the 18th and 19th centuries. The term means 'Six Cities' in Turkic languages, referring to oasis ...
were exile slaves to Turkestani Begs. While free Chinese merchants generally did not engage in relationships with East Turkestani women, some of the Chinese slaves belonging to begs, along with Green Standard soldiers, Bannermen, and Manchus, engaged in affairs with the East Turkestani women that were serious in nature.
=India
=
Slavery in India
The early history of slavery in the Indian subcontinent is contested because it depends on the translations of terms such as ''dasa'' and ''dasyu''. Greek writer Megasthenes in his work Indika, while describing the Maurya Empire states that slav ...
was widespread by the 6th century BC, and perhaps even as far back as the Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betw ...
. Slavery intensified during the Muslim domination of northern India after the 11th-century. Slavery existed in Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
after the 16th century. The Dutch, too, largely dealt in Abyssian slaves, known in India as Habshis or Sheedes.Coromandel
Coromandel may refer to:
Places India
*Coromandel Coast, India
**Presidency of Coromandel and Bengal Settlements
** Dutch Coromandel
*Coromandel, KGF, Karnataka, India
New Zealand
*Coromandel, New Zealand, a town on the Coromandel Peninsula
*Coro ...
remained the largest sources of forced labour until the 1660s.
Between 1626 and 1662, the Dutch exported on an average 150–400 slaves annually from the Arakan-Bengal coast. During the first 30 years of Batavia's existence, Indian and Arakanese slaves provided the main labour force of the Dutch East India Company, Asian headquarters. An increase in Coromandel slaves occurred during a famine following the revolt of the Nayaka Indian rulers of South India (Tanjavur, Senji, and Madurai) against Bijapur overlordship (1645) and the subsequent devastation of the Tanjavur countryside by the Bijapur army. Reportedly, more than 150,000 people were taken by the invading Deccani Muslim armies to Bijapur and Golconda. In 1646, 2,118 slaves were exported to Batavia, the overwhelming majority from southern Coromandel. Some slaves were also acquired further south at Tondi, Adirampatnam, and Kayalpatnam. Another increase in slaving took place between 1659 and 1661 from Tanjavur as a result of a series of successive Bijapuri raids. At Nagapatnam, Pulicat, and elsewhere, the company purchased 8,000–10,000 slaves, the bulk of whom were sent to Ceylon, while a small portion were exported to Batavia and Malacca. Finally, following a long drought in Madurai and southern Coromandel, in 1673, which intensified the prolonged Madurai-Maratha struggle over Tanjavur and punitive fiscal practices, thousands of people from Tanjavur, mostly children, were sold into slavery and exported by Asian traders from Nagapattinam to Aceh, Johor, and other slave markets.
In September 1687, 665 slaves were exported by the English from Fort St. George, Madras. And, in 1694–96, when warfare once more ravaged South India, a total of 3,859 slaves were imported from Coromandel by private individuals into Ceylon. The volume of the total Dutch Indian Ocean slave trade has been estimated to be about 15–30% of the Atlantic slave trade, slightly smaller than the trans-Saharan slave trade, and one-and-a-half to three times the size of the Swahili and Red Sea coast and the Dutch West India Company slave trades.
According to Sir Henry Bartle Frere
Sir Henry Bartle Edward Frere, 1st Baronet, (29 March 1815 – 29 May 1884) was a Welsh British colonial administrator. He had a successful career in India, rising to become Governor of Bombay (1862–1867). However, as High Commissioner for ...
(who sat on the Viceroy's Council), there were an estimated 8 or 9 million slaves in India in 1841. About 15% of the population of Malabar
Malabar may refer to the following:
People
* Malabars, people originating from the Malabar region of India
* Malbars or Malabars, people of Tamil origin in Réunion
Places
* Malabar Coast, or Malabar, a region of the southwestern shoreline o ...
were slaves. Slavery was legally abolished in the possessions of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
by the Indian Slavery Act, 1843
The Indian Slavery Act, 1843, also known as Act V of 1843, was an act passed in British India under East India Company rule, which outlawed many economic transactions associated with slavery.
The act states how the sale of any person as a slav ...
.
=Indochina
=
The hill tribe people in Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
were "hunted incessantly and carried off as slaves by the Siamese (Thai), the Anamites (Vietnamese), and the Cambodians".Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
sultanate of Perak
Perak () is a state of Malaysia on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula. Perak has land borders with the Malaysian states of Kedah to the north, Penang to the northwest, Kelantan and Pahang to the east, and Selangor to the south. Thailand's ...
were slaves.North Borneo
North Borneo (usually known as British North Borneo, also known as the State of North Borneo) was a British Protectorate, British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo, which is present day Sabah. The territory of North Borneo ...
in the 1880s.
=Japan
=
After the Portuguese first made contact with Japan in 1543, slave trade developed in which Portuguese purchased Japanese as slaves in Japan and sold them to various locations overseas, including Portugal, throughout the 16th and 17th centuries. Many documents mention the slave trade along with protests against the enslavement of Japanese. Japanese slaves are believed to be the first of their nation to end up in Europe, and the Portuguese purchased numbers of Japanese slave girls to bring to Portugal for sexual purposes, as noted by the Church in 1555. Japanese slave women were even sold as concubine
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive.
Concubi ...
s to Asian lascar
A lascar was a sailor or militiaman from the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, the Arab world, British Somaliland, or other land east of the Cape of Good Hope, who was employed on European ships from the 16th century until the middle of the 2 ...
and African crew members, along with their European counterparts serving on Portuguese ships trading in Japan, mentioned by Luis Cerqueira, a Portuguese Jesuit, in a 1598 document. Japanese slaves were brought by the Portuguese to Macau
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a pop ...
, where they were enslaved to Portuguese or became slaves to other slaves.
Some Korean slaves were bought by the Portuguese and brought back to Portugal from Japan, where they had been among the tens of thousands of Korean prisoners of war transported to Japan during the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
. Historians pointed out that at the same time Hideyoshi expressed his indignation and outrage at the Portuguese trade in Japanese slaves, he was engaging in a mass slave trade of Korean prisoners of war in Japan.
Fillippo Sassetti saw some Chinese and Japanese slaves in Lisbon among the large slave community in 1578, although most of the slaves were black.Sebastian of Portugal
Sebastian ( pt, Sebastião I ; 20 January 1554 – 4 August 1578) was King of Portugal from 11 June 1557 to 4 August 1578 and the penultimate Portuguese monarch of the House of Aviz.
He was the son of João Manuel, Prince of Portugal, and hi ...
feared rampant slavery was having a negative effect on Catholic proselytization, so he commanded that it be banned in 1571. Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
was so disgusted that his own Japanese people were being sold ''en masse'' into slavery on Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surroun ...
, that he wrote a letter to Jesuit Vice-Provincial Gaspar Coelho on July 24, 1587, to demand the Portuguese, Siamese (Thai), and Cambodians stop purchasing and enslaving Japanese and return Japanese slaves who ended up as far as India. Hideyoshi blamed the Portuguese and Jesuits for this slave trade and banned Christian proselytizing as a result. In 1595, a law was passed by Portugal banning the selling and buying of Chinese and Japanese slaves.
=Korea
=
 During the
During the Joseon
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and re ...
period, the nobi
''Nobi'' were members of the slave class during the Korean dynasties of Goryeo and Joseon. Legally, they held the lowest rank in medieval Korean society. Like the slaves, serfs, and indentured servants of the Western Hemisphere, ''nobi'' wer ...
population could fluctuate up to about one-third of the population, but on average the nobi made up about 10% of the total population. The nobi system declined beginning in the 18th century. Since the outset of the Joseon dynasty and especially beginning in the 17th century, there was harsh criticism among prominent thinkers in Korea about the nobi system. Even within the Joseon government, there were indications of a shift in attitude toward the nobi.King Yeongjo
Yeongjo of Joseon (31 October 1694 – 22 April 1776), personal name Yi Geum (Korean: 이금, Hanja: 李昑), was the 21st monarch of the Joseon dynasty of Korea. He was the second son of King Sukjong, by his concubine Royal Noble Consort Suk ...
implemented a policy of gradual emancipation
Emancipation generally means to free a person from a previous restraint or legal disability. More broadly, it is also used for efforts to procure economic and social rights, political rights or equality, often for a specifically disenfranchis ...
in 1775,King Jeongjo
Jeongjo of Joseon (28 October 1752 – 18 August 1800), personal name Yi San (Korean language, Korean: 이산; Hanja: 李祘), sometimes called Jeongjo the Great (Korean language, Korean: 정조대왕; Hanja: 正祖大王), was the 22nd monarc ...
made many proposals and developments that lessened the burden on nobi, which led to the emancipation of the vast majority of government nobi in 1801.Gabo Reform
The Gabo Reform, also known as the Kabo Reform, describes a series of sweeping reforms suggested to the government of Korea, beginning in 1894 and ending in 1896 during the reign of Gojong of Korea in response to the Donghak Peasant Revolution. ...
of 1894. However, slavery did not completely disappear in Korea until 1930, during Imperial Japanese rule.
During the Imperial Japanese occupation of Korea around World War II, some Koreans were used in forced labour by the Imperial Japanese, in conditions which have been compared to slavery.comfort women
Comfort women or comfort girls were women and girls forced into sexual slavery by the Imperial Japanese Army in occupied countries and territories before and during World War II. The term "comfort women" is a translation of the Japanese '' ia ...
".
Oceania
Slaves (''he mōkai'') had a recognised social role in traditional Māori society
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
in New Zealand.
Blackbirding
Blackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant from their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people in ...
occurred on islands in the Pacific Ocean and Australia, especially in the 19th century.
Ottoman Empire and Black Sea
In Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, about one-fifth of the population consisted of slaves.Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia in ...
– were imported into the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
between 1800 and 1909.Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to ...
(a Muslim Tatar state) maintained a massive slave trade with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East.Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
, Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and so ...
, and Circassia
Circassia (; also known as Cherkessia in some sources; ady, Адыгэ Хэку, Адыгей, lit=, translit=Adıgə Xəku, Adıgey; ; ota, چرکسستان, Çerkezistan; ) was a country and a historical region in the along the northeast ...
by Tatar
The Tatars ()[Tatar]
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different horsemen and sold in the Crimean port of Kaffa. About 2 million mostly Christian slaves were exported over the 16th and 17th centuries until the Crimean Khanate was destroyed by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
in 1783. A slave market for captured Russian and
A slave market for captured Russian and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
slaves was centred in the Central Asian khanate of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva ( chg, ''Khivâ Khânligi'', fa, ''Khânât-e Khiveh'', uz, Xiva xonligi, tk, Hywa hanlygy) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm in Central Asia from 1511 to 1920, except fo ...
. In the early 1840s, the population of the Uzbek states of Bukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
and Khiva included about 900,000 slaves.
Late modern period
United States
In 1865, the United States ratified the 13th Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
, which banned slavery and involuntary servitude "except as punishment for a crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted," providing a legal basis for slavery, now referred to as penal labor, to continue in the country. This led to the system of convict leasing
Convict leasing was a system of forced penal labor which was practiced historically in the Southern United States, the laborers being mainly African-American men; it was ended during the 20th century. (Convict labor in general continues; f ...
, which affected primarily African Americans. The Prison Policy Initiative
The Prison Policy Initiative (PPI) is a criminal justice oriented American public policy think tank based in Easthampton, Massachusetts. It is a non-profit organization, designated 501(c)(3) by the IRS.
It is the "leading public critic" of the ...
, an American criminal justice think tank, cites the 2020 US prison population as 2.3 million, and nearly all able-bodied inmates work in some fashion. In Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
and Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage ...
, prisoners are not paid at all for their work. In other states, prisoners are paid between $0.12 and $1.15 per hour. Federal Prison Industries
Federal Prison Industries, Inc. (FPI), doing business as UNICOR (stylized as unicor) since 1977, is a wholly owned United States government corporation created in 1934 as a prison labor program for inmates within the Federal Bureau of Prisons, a ...
paid inmates an average of $0.90 per hour in 2017. Inmates who refuse to work may be indefinitely remanded into solitary confinement
Solitary confinement is a form of imprisonment in which the inmate lives in a single cell with little or no meaningful contact with other people. A prison may enforce stricter measures to control contraband on a solitary prisoner and use additi ...
, or have family visitation revoked. From 2010 to 2015 and again in 2016 and in 2018, some prisoners in the US refused to work, protesting for better pay, better conditions, and for the end of forced labor. Strike leaders were punished with indefinite solitary confinement. Forced prison labor occurs in both government-run prisons and private prisons
A private prison, or for-profit prison, is a place where people are imprisoned by a third party that is contracted by a government agency. Private prison companies typically enter into contractual agreements with governments that commit p ...
. CoreCivic
CoreCivic, formerly the Corrections Corporation of America (CCA), is a company that owns and manages private prisons and detention centers and operates others on a concession basis. Co-founded in 1983 in Nashville, Tennessee
Nashville is the ...
and GEO Group
The GEO Group, Inc. (GEO) is a publicly traded C corporation that invests in private prisons and mental health facilities in North America, Australia, South Africa, and the United Kingdom. Headquartered in Boca Raton, Florida, the company's f ...
constitute half the market share of private prisons, and they made a combined revenue of $3.5 billion in 2015. The value of all labor by inmates in the United States is estimated to be in the billions. In California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, 2,500 incarcerated workers fought wildfires for only $1 per hour through the CDCR's Conservation Camp Program, which saves the state as much as $100 million a year.
Soviet Union
 Between 1930 and 1960, the
Between 1930 and 1960, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
created a system of, according to Anne Applebaum
Anne Elizabeth Applebaum (born July 25, 1964) is an American journalist and historian. She has written extensively about the history of Communism and the development of civil society in Central and Eastern Europe.
She has worked at ''The Econo ...
and the "perspective of the Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty, Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of th ...
", slave labor camps called the ''Gulag'' (russian: ГУЛаг, GULag).
Prisoners in these camps were worked to death by a combination of extreme production quotas, physical and psychological brutality, hunger, lack of medical care, and the harsh environment. Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn
Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn. (11 December 1918 – 3 August 2008) was a Russian novelist. One of the most famous Soviet dissidents, Solzhenitsyn was an outspoken critic of communism and helped to raise global awareness of political repress ...
, who survived eight years of Gulag incarceration, provided firsthand testimony about the camps with the publication of ''The Gulag Archipelago
''The Gulag Archipelago: An Experiment in Literary Investigation'' (russian: Архипелаг ГУЛАГ, ''Arkhipelag GULAG'') is a three-volume non-fiction text written between 1958 and 1968 by Russian writer and Soviet dissident Aleksandr So ...
'', after which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901
, ...
. Fatality rate was as high as 80% during the first months in many camps. Hundreds of thousands of people, possibly millions, died as a direct result of forced labour under the Soviets.
Golfo Alexopoulos suggests comparing labor in the Gulag with ''"other forms of slave labor"'' and notes its ''"violence of human exploitation"'' in ''Illness and Inhumanity in Stalin's Gulag'':
Stalin's Gulag was, in many ways, less a concentration camp than a forced labor camp and less a prison system than a system of slavery. The image of the slave appears often in Gulag memoir literature. As Varlam Shalamov wrote: ''"Hungry and exhausted, we leaned into a horse collar, raising blood blisters on our chests and pulling a stone-filled cart up the slanted mine floor. The collar was the same device used long ago by the ancient Egyptians."'' Thoughtful and rigorous historical comparisons of Soviet forced labor and other forms of slave labor would be worthy of scholarly attention, in my view. For as in the case of global slavery, the Gulag found legitimacy in an elaborate narrative of difference that involved the presumption of dangerousness and guilt. This ideology of difference and the violence of human exploitation have left lasting legacies in contemporary Russia.
Historian Anne Applebaum
Anne Elizabeth Applebaum (born July 25, 1964) is an American journalist and historian. She has written extensively about the history of Communism and the development of civil society in Central and Eastern Europe.
She has worked at ''The Econo ...
writes in the introduction of her book that the word ''GULAG'' has come to represent ''"the system of Soviet slave labor itself, in all its forms and varieties"'':
The word ''"GULAG"'' is an acronym for ''Glavnoe Upravlenie Lagerei'', or Main Camp Administration, the institution which ran the Soviet camps. But over time, the word has also come to signify the system of Soviet slave labor itself, in all its forms and varieties: labor camps, punishment camps, criminal and political camps, women's camps, children's camps, transit camps. Even more broadly, "Gulag" has come to mean the Soviet repressive system itself, the set of procedures that Alexander Solzhenitsyn once called "our meat grinder": the arrests, the interrogations, the transport in unheated cattle cars, the forced labor, the destruction of families, the years spent in exile, the early and unnecessary deaths.
Applebaum's introduction has been criticized by Gulag researcher Wilson Bell, stating that her book "is, ''aside from the introduction'', a well-done overview of the Gulag, but it did not offer an interpretative framework much beyond Solzhenitsyn
Aleksandr Isayevich Solzhenitsyn. (11 December 1918 – 3 August 2008) was a Russian novelist. One of the most famous Soviet dissidents, Solzhenitsyn was an outspoken critic of communism and helped to raise global awareness of political repress ...
's paradigms".
Nazi Germany
 During the
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Nazi Germany effectively enslaved about 12 million people, both those considered undesirable and citizens of conquered countries, with the avowed intention of treating these ''Untermenschen
''Untermensch'' (, ; plural: ''Untermenschen'') is a Nazi term for non-Aryan "inferior people" who were often referred to as "the masses from the East", that is Jews, Roma, and Slavs (mainly ethnic Poles, Serbs, and later also Russians). The ...
'' (sub-humans) as a permanent slave-class of inferior beings who could be worked until they died, and who possessed neither the rights nor the legal status of members of the Aryan race
The Aryan race is an obsolete historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people of Proto-Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping. The terminology derives from the historical usage of Aryan, used by modern I ...
.
Besides Jews, the harshest deportation and forced labour policies were applied to the populations of Belarus, Ukraine, and Russia. By the end of the war, half of Belarus' population had been killed or deported.
Contemporary slavery
 Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today is estimated as between 12 million and 29.8 million.
Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today is estimated as between 12 million and 29.8 million.bonded labour
Debt bondage, also known as debt slavery, bonded labour, or peonage, is the pledge of a person's services as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation. Where the terms of the repayment are not clearly or reasonably stated, the pe ...
/debt bondage
Debt bondage, also known as debt slavery, bonded labour, or peonage, is the pledge of a person's services as security for the repayment for a debt or other obligation. Where the terms of the repayment are not clearly or reasonably stated, the pe ...
(18.1 million), forced labour (7.6 million), and trafficked slaves (2.7 million). According to a 2003 report by
According to a 2003 report by Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
, an estimated 15 million children in debt bondage in India
Debt bondage in India or Bandhua Mazdoori (बंधुआ मज़दूरी) was legally abolished in 1976 but remains prevalent due to weak enforcement by the government. Bonded labour is a system in which lenders force their borrowers to ...
work in slavery-like conditions to pay off their family's debts.
Slavoj Žižek
Slavoj Žižek (, ; ; born 21 March 1949) is a Slovenian philosopher, cultural theorist and public intellectual. He is international director of the Birkbeck Institute for the Humanities at the University of London, visiting professor at New Y ...
asserts that new forms of contemporary slavery have been created in the post-Cold War era of global capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, pric ...
, including migrant workers deprived of basic civil rights on the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, the total control of workers in Asian sweatshops
A sweatshop or sweat factory is a crowded workplace with very poor, socially unacceptable or illegal working conditions. Some illegal working conditions include poor ventilation, little to no breaks, inadequate work space, insufficient lighting, o ...
and the use of forced labor in the exploitation of natural resources in Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, ...
.
Distribution
In June 2013, U.S. State Department released a report on slavery. It placed Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and Uzbekistan in the worst offenders category. Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, Syria, and Zimbabwe were at the lowest level. The list also included Algeria, Libya, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait among a total of 21 countries.
In Kuwait, there are more than 600,000 migrant domestic workers who are vulnerable to forced labor and legally tied to their employers, who often illegally take their passports. In 2019, online slave markets on apps such as Instagram were uncovered.
In the preparations for the 2022 World Cup in Qatar, thousands of Nepalese, the largest group of labourers, faced slavery in the form of denial of wages, confiscation of documents, and inability to leave the workplace. In 2016, the United Nations gave Qatar 12 months to end migrant worker slavery or face investigation.
The Walk Free Foundation
Minderoo Foundation's Walk Free initiative is an independent, privately funded international human rights organisation based in Perth, Western Australia. Walk Free works towards ending modern slavery in all its forms by taking a multifaceted and g ...
reported in 2018 that slavery in wealthy Western societies is much more prevalent than previously known, in particular the United States and Great Britain, which have 403,000 (one in 800) and 136,000 slaves respectively. Andrew Forrest, founder of the organization, said that "The United States is one of the most advanced countries in the world yet has more than 400,000 modern slaves working under forced labour conditions." An estimated 40.3 million are enslaved globally, with North Korea having the most slaves at 2.6 million (one in 10). Of the estimated 40.3 million people in contemporary slavery, 71% are women and 29% are men. The report found of the 40.3 million in modern slavery, 15.4 million are in forced marriages and 24.9 million are in forced labor
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
. The foundation defines contemporary slavery as "situations of exploitation that a person cannot refuse or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, abuse of power, or deception."
China
The Chinese government has a history of imprisoning citizens for political reasons. Article 73 of China's Criminal Procedure
Criminal procedure is the adjudication process of the criminal law. While criminal procedure differs dramatically by jurisdiction, the process generally begins with a formal criminal charge with the person on trial either being free on bail or ...
Law was adopted in 2012 and allow the authorities to detain people for reasons of "state security" or "terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
". In this regard, detainees can be held for as long as six months in "designated locations" such as secret prisons.
In March 2020, the Chinese government was found to be using the Uyghur minority for forced labour, inside sweat shops. According to a report published then by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI), no fewer than around 80,000 Uyghurs were forcibly removed from the region of Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
and used for forced labour in at least twenty-seven corporate factories. According to the Business and Human Rights resource center, corporations such as Abercrombie & Fitch
Abercrombie & Fitch (A&F) is an American lifestyle retailer that focuses on casual wear. Its headquarters are in New Albany, Ohio. The company operates three other offshoot brands: Abercrombie Kids, Hollister Co., and Gilly Hicks. As of Februar ...
, Adidas
Adidas AG (; stylized as adidas since 1949) is a German multinational corporation, founded and headquartered in Herzogenaurach, Bavaria, that designs and manufactures shoes, clothing and accessories. It is the largest sportswear manufactur ...
, Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology c ...
, Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
, BMW, Fila
Fila Holdings Corp. is a sportswear brand of shoes and apparel. The company was founded by Ettore and Giansevero Fila in 1911 in Coggiola, near Biella, Piedmont, Italy. In 2003, it was sold to United States-based Sports Brand International. Sub ...
, Gap, H&M, Inditex
Industria de Diseño Textil, S.A. (Inditex; , ; ) is a Spanish multinational clothing company headquartered in Arteixo, Galicia, in Spain. Inditex, the biggest fast fashion group in the world, operates over 7,200 stores in 93 markets worldwide. ...
, Marks & Spencer
Marks and Spencer Group plc (commonly abbreviated to M&S and colloquially known as Marks's or Marks & Sparks) is a major British multinational retailer with headquarters in Paddington, London that specialises in selling clothing, beauty, home ...
, Nike
Nike often refers to:
* Nike (mythology), a Greek goddess who personifies victory
* Nike, Inc., a major American producer of athletic shoes, apparel, and sports equipment
Nike may also refer to:
People
* Nike (name), a surname and feminine give ...
, North Face North face or Northface or The North Face may refer to:
* North face (Eiger), in the Bernese Alps in Switzerland
* North Face (Everest), in Himalaya, usually traversed ascending Everest from the north
* North face (Fairview Dome), a climbing route ...
, Puma, PVH, Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
, and UNIQLO each have each sourced products from these factories prior to the publication of the ASPI report.
Libya
During the Second Libyan Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Second Libyan Civil War
, partof = the Arab Winter, Libyan Crisis (2011–present), Libyan Crisis, Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, War on terror, and Qatar–Saudi Arabia diplomat ...
, Libyans started capturing Sub-Saharan African migrants trying to get to Europe through Libya and selling them on slave markets or holding them hostage for ransom
Ransom is the practice of holding a prisoner or item to extort money or property to secure their release, or the sum of money involved in such a practice.
When ransom means "payment", the word comes via Old French ''rançon'' from Latin ''red ...
Women are often raped, used as sex slave
Sexual slavery and sexual exploitation is an attachment of any ownership right over one or more people with the intent of coercing or otherwise forcing them to engage in sexual activities. This includes forced labor, reducing a person to a s ...
s, or sold to brothel
A brothel, bordello, ranch, or whorehouse is a place where people engage in sexual activity with prostitutes. However, for legal or cultural reasons, establishments often describe themselves as massage parlors, bars, strip clubs, body rub par ...
s. Child migrants suffer from abuse and child rape
Child sexual abuse (CSA), also called child molestation, is a form of child abuse in which an adult or older adolescent uses a child for sexual stimulation. Forms of child sexual abuse include engaging in sexual activities with a child (wheth ...
in Libya.
Mauritania
In Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, the last country to abolish slavery (in 1981), it is estimated that 20% of its 3 million population, are enslaved as bonded labourers.
North Korea
North Korea's human rights record is often considered to be the worst in the world and has been globally condemned, with the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
and groups such as Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
all critical of the country's record. With forms of torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts c ...
, forced labour and abuses all being widespread. Most international human rights organizations consider North Korea to have no contemporary parallel with respect to violations of liberty.
Economics
While American slaves in 1809 were sold for around $40,000 (in inflation adjusted dollars), a slave nowadays can be bought for just $90, making replacement more economical than providing long-term care.
Trafficking
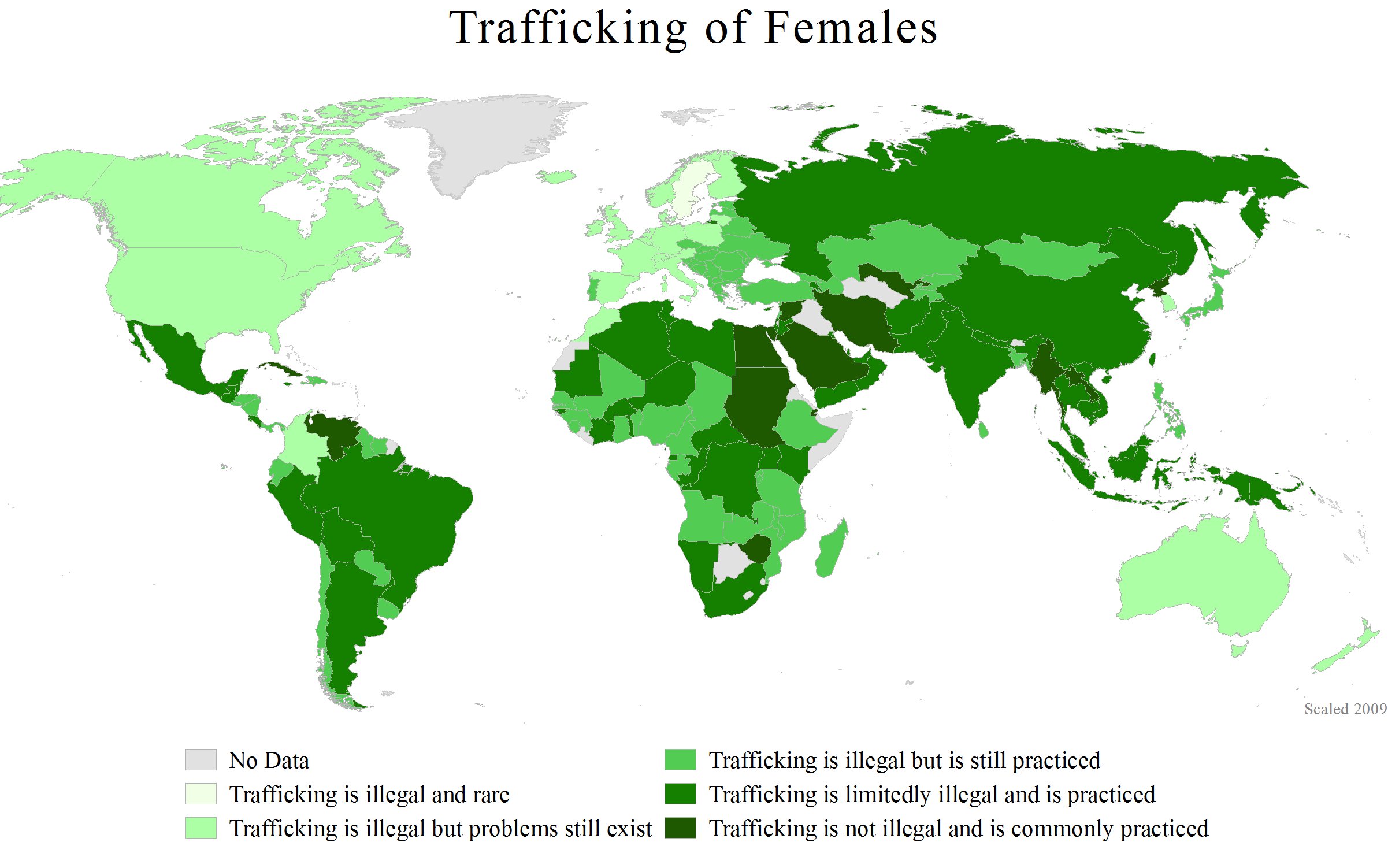 Victims of
Victims of human trafficking
Human trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labour, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker or others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extrac ...
are typically recruited through deceit or trickery (such as a false job offer, false migration offer, or false marriage offer), sale by family members, recruitment by former slaves, or outright abduction. Victims are forced into a "debt slavery" situation by coercion, deception, fraud, intimidation, isolation, threat, physical force, debt bondage or even force-feeding
Force-feeding is the practice of feeding a human or animal against their will. The term ''gavage'' (, , ) refers to supplying a substance by means of a small plastic feeding tube passed through the nose ( nasogastric) or mouth (orogastric) into t ...
with drugs to control their victims. "Annually, according to U.S. government-sponsored research completed in 2006, approximately 800,000 people are trafficked across national borders, which does not include millions trafficked within their own countries. Approximately 80% of transnational victims are women and girls, and up to 50% are minors, reports the U.S. State Department in a 2008 study.
While the majority of trafficking victims are women who are forced into prostitution
Forced prostitution, also known as involuntary prostitution or compulsory prostitution, is prostitution or sexual slavery that takes place as a result of coercion by a third party. The terms "forced prostitution" or "enforced prostitution" appea ...
(in which case the practice is called sex trafficking), victims also include men, women and children who are forced into manual labour
Manual labour (in Commonwealth English, manual labor in American English) or manual work is physical work done by humans, in contrast to labour by machines and working animals. It is most literally work done with the hands (the word ''manual'' ...
.
Abolitionism
Slavery has existed, in one form or another, throughout recorded human history – as have, in various periods, movements to free large or distinct groups of slaves.
In antiquity

Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, ...
, who ruled the Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
from 269 to 232 BCE, abolished the slave trade but not slavery. The Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), ...
, which ruled China from 221 to 206 BC, abolished slavery and discouraged serfdom. However, many of its laws were overturned when the dynasty was overthrown. Slavery was again abolished by Wang Mang
Wang Mang () (c. 45 – 6 October 23 CE), courtesy name Jujun (), was the founder and the only Emperor of China, emperor of the short-lived Chinese Xin dynasty. He was originally an official and consort kin of the Han dynasty and later ...
in China in 17 CE but was reinstituted after his assassination.
Americas
The Spanish colonization of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions ...
sparked a discussion about the right to enslave Native Americans. A prominent critic of slavery in the Spanish New World colonies
Slavery in the Spanish American colonies was an economic and social institution which existed throughout the Spanish Empire including Spain itself. In its American territories, Spain displayed an early abolitionist stance towards indigenous peopl ...
was the Spanish missionary and bishop, Bartolomé de las Casas
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP ( ; ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a 16th-century Spanish landowner, friar, priest, and bishop, famed as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman then became a Dominican friar ...
, who was "the first to expose the oppression of indigenous peoples by Europeans in the Americas and to call for the abolition of slavery there."
One of the first protests against slavery came from German and Dutch Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abil ...
in Pennsylvania in 1688. In 1777, Vermont, at the time an independent nation, became the first portion of what would become the United States to abolish slavery.
In the United States, all of the northern states had abolished slavery by 1804, with New Jersey being the last to act. Abolitionist pressure produced a series of small steps towards emancipation. After the Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves
The Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves of 1807 (, enacted March 2, 1807) is a United States federal law that provided that no new slaves were permitted to be imported into the United States. It took effect on January 1, 1808, the earliest dat ...
went into effect on January 1, 1808, the importation of slaves into the United States was prohibited, but not the internal slave trade, nor involvement in the international slave trade externally. Legal slavery persisted outside the northern states; most of those slaves already in the U.S. were legally emancipated only in 1863. Many American abolitionists took an active role in opposing slavery by supporting the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. T ...
. Violent clashes between anti-slavery and pro-slavery Americans included Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the ...
, a series of political and armed disputes in 1854–1861 as to whether Kansas would join the United States as a slave or free state. By 1860, the total number of slaves reached almost four million, and the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, beginning in 1861, led to the end of slavery in the United States. In 1863, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation, officially Proclamation 95, was a presidential proclamation and executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the Civil War. The Proclamation changed the legal sta ...
, which freed slaves held in the Confederate States; the 13th Amendment to the U. S. Constitution prohibited most forms of slavery throughout the country.
Many of the freed slaves became sharecroppers and indentured servants. In this manner, some became tied to the very parcel of land into which they had been born a slave having little freedom or economic opportunity because of Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
which perpetuated discrimination, limited education, promoted persecution without due process and resulted in continued poverty. Fear of reprisals such as unjust incarcerations and lynchings deterred upward mobility further.


Europe
France abolished slavery in 1794 during the Revolution, but it was restored in 1802 under Napoleon.Lord Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to Lond ...
, whose opinion in Somersett's Case
''Somerset v Stewart'' (177298 ER 499(also known as ''Somersett's case'', ''v. XX Sommersett v Steuart and the Mansfield Judgment)'' is a judgment of the English Court of King's Bench in 1772, relating to the right of an enslaved person on En ...
was widely taken to have held that slavery was illegal in England. This judgement also laid down the principle that slavery contracted in other jurisdictions could not be enforced in England.
Sons of Africa
The Sons of Africa were a late 18th-century group in Britain that campaigned to end African chattel slavery. The "corresponding society" has been called the Britain's first black political organisation. Its members were educated Africans in Lond ...
was a late 18th-century British group that campaigned to end slavery. Its members were Africans in London, freed slaves who included Ottobah Cugoano
Ottobah Cugoano, also known as John Stuart (c. 1757 – after 1791), was an abolitionist, political activist, and natural rights philosopher from West Africa who was active in Britain in the latter half of the eighteenth century. Captured in th ...
, Olaudah Equiano
Olaudah Equiano (; c. 1745 – 31 March 1797), known for most of his life as Gustavus Vassa (), was a writer and abolitionist from, according to his memoir, the Eboe (Igbo) region of the Kingdom of Benin (today southern Nigeria). Enslaved as ...
and other leading members of London's black community. It was closely connected to the Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade
The Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade, also known as the Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, and sometimes referred to as the Abolition Society or Anti-Slavery Society, was a British abolitionist group formed on ...
, a non-denominational group founded in 1787, whose members included Thomas Clarkson
Thomas Clarkson (28 March 1760 – 26 September 1846) was an English abolitionist, and a leading campaigner against the slave trade in the British Empire. He helped found The Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade (also known ...
. British Member of Parliament William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 175929 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist and leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, eventually becom ...
led the anti-slavery movement in the United Kingdom, although the groundwork was an anti-slavery essay by Clarkson. Wilberforce was urged by his close friend, Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
, to make the issue his own and was also given support by reformed Evangelical John Newton
John Newton (; – 21 December 1807) was an English evangelical Anglican cleric and slavery abolitionist. He had previously been a captain of slave ships and an investor in the slave trade. He served as a sailor in the Royal Navy (after forc ...
. The Slave Trade Act
Slave Trade Act is a stock short title used for legislation in the United Kingdom and the United States that relates to the slave trade.
The "See also" section lists other Slave Acts, laws, and international conventions which developed the conce ...
was passed by the British Parliament on March 25, 1807, making the slave trade illegal throughout the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, Wilberforce also campaigned for abolition of slavery in the British Empire, which he lived to see in the Slavery Abolition Act 1833
The Slavery Abolition Act 1833 (3 & 4 Will. IV c. 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which provided for the gradual abolition of slavery in most parts of the British Empire. It was passed by Earl Grey's reforming administrati ...
.
After the 1807 act abolishing the slave trade was passed, these campaigners switched to encouraging other countries to follow suit, notably France and the British colonies. Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron
The West Africa Squadron, also known as the Preventative Squadron, was a squadron of the British Royal Navy whose goal was to suppress the Atlantic slave trade by patrolling the coast of West Africa. Formed in 1808 after the British Parliame ...
seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard. Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers.
Worldwide
In 1839, the world's oldest international human rights organization, Anti-Slavery International
Anti-Slavery International, founded as the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society in 1839, is an international non-governmental organisation, registered charity and advocacy group, based in the United Kingdom. It is the world's oldest interna ...
, was formed in Britain by Joseph Sturge
Joseph Sturge (1793 – 14 May 1859) was an English Quaker, abolitionist and activist. He founded the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society (now Anti-Slavery International). He worked throughout his life in Radical political actions support ...
, which campaigned to outlaw slavery in other countries. There were celebrations in 2007 to commemorate the 200th anniversary of the abolition of the slave trade in the United Kingdom through the work of the British Anti-Slavery Society.
In the 1860s, David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, and pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, an explorer in Africa, and one of the most popular British heroes of t ...
's reports of atrocities within the Arab slave trade in Africa stirred up the interest of the British public, reviving the flagging abolitionist movement. The Royal Navy throughout the 1870s attempted to suppress "this abominable Eastern trade", at Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islands ...
in particular. In 1905, the French abolished indigenous slavery in most of French West Africa
French West Africa (french: Afrique-Occidentale française, ) was a federation of eight French colonial territories in West Africa: Mauritania, Senegal, French Sudan (now Mali), French Guinea (now Guinea), Ivory Coast, Upper Volta (now Burki ...
.
On December 10, 1948, the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal De ...
, which declared freedom from slavery is an internationally recognized human right
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
. Article 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal De ...
states:
In 2014, for the first time in history, major leaders of many religions, Buddhist, Hindu, Christian, Jewish, and Muslim met to sign a shared commitment against modern-day slavery; the declaration they signed calls for the elimination of slavery and human trafficking by 2020.Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013. ...
, Mātā Amṛtānandamayī, Bhikkhuni Thich Nu Chân Không
Chân Không (born 1938) is an expatriate Vietnamese Buddhist Bhikkhunī ( nun) and peace activist who has worked closely with Thích Nhất Hạnh in starting the Plum Village Tradition and helping conduct spiritual retreats internationally. ...
(representing Zen Master Thích Nhất Hạnh
Thích Nhất Hạnh ( ; ; born Nguyễn Xuân Bảo; 11 October 1926 – 22 January 2022) was a Vietnamese Thiền Buddhist monk, peace activist, prolific author, poet and teacher, who founded the Plum Village Tradition, historically recogni ...
), Datuk K Sri Dhammaratana, Chief High Priest of Malaysia, Rabbi Abraham Skorka
Abraham Skorka (born July 5, 1950, in Buenos Aires) is an Argentine biophysicist, rabbi and book author. Abraham Skorka is rector emeritus of the Seminario Rabínico Latinoamericano in Buenos Aires, the rabbi of the Jewish community Benei Tikva ...
, Rabbi David Rosen, Abbas Abdalla Abbas Soliman, Undersecretary of State of Al Azhar Alsharif (representing Mohamed Ahmed El-Tayeb, Grand Imam of Al-Azhar), Grand Ayatollah Mohammad Taqi al-Modarresi, Sheikh Naziyah Razzaq Jaafar, Special advisor of Grand Ayatollah (representing Grand Ayatollah Sheikh Basheer Hussain al Najafi), Sheikh Omar Abboud, Justin Welby, Archbishop of Canterbury, and Metropolitan Emmanuel of France (representing Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew.)American Anti-Slavery Group
The American Anti-Slavery Group (AASG) is a non-profit coalition of abolitionist organizations that engages in political activism to abolish slavery in the world. It raises awareness of contemporary slavery, particularly among the chattel slaves ...
, Anti-Slavery International
Anti-Slavery International, founded as the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society in 1839, is an international non-governmental organisation, registered charity and advocacy group, based in the United Kingdom. It is the world's oldest interna ...
, Free the Slaves
Free the Slaves is an international non-governmental organization and lobby group, established to campaign against the modern practice of slavery around the world. It was formed as the sister organization of Anti-Slavery International but has si ...
, the Anti-Slavery Society, and the Norwegian Anti-Slavery Society continue to campaign to eliminate slavery.
Apologies
On May 21, 2001, the National Assembly of France
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known a ...
passed the Taubira
Christiane Marie Taubira (; born 2 February 1952) is a French politician who served as Minister of Justice of France in the governments of Prime Ministers Jean-Marc Ayrault and Manuel Valls under President François Hollande from 2012 until 20 ...
law, recognizing slavery as a crime against humanity
Crimes against humanity are widespread or systemic acts committed by or on behalf of a ''de facto'' authority, usually a state, that grossly violate human rights. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity do not have to take place within the c ...
. Apologies on behalf of African nations, for their role in trading their countrymen into slavery, remain an open issue since slavery was practiced in Africa even before the first Europeans arrived and the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
was performed with a high degree of involvement of several African societies. The black slave market was supplied by well-established slave trade networks controlled by local African societies and individuals.
There is adequate evidence citing case after case of African control of segments of the trade. Several African nations such as the Calabar and other southern parts of Nigeria had economies depended solely on the trade. African peoples such as the Imbangala of Angola and the Nyamwezi of Tanzania would serve as middlemen or roving bands warring with other African nations to capture Africans for Europeans.
Several historians have made important contributions to the global understanding of the African side of the Atlantic slave trade. By arguing that African merchants determined the assemblage of trade goods accepted in exchange for slaves, many historians argue for African agency and ultimately a shared responsibility for the slave trade.
In 1999, President Mathieu Kérékou
Mathieu Kérékou (; 2 September 1933 – 14 October 2015) was a Beninese politician who served as President of Benin from 1972 to 1991 and again from 1996 to 2006.
After seizing power in a military coup, he ruled the country for 19 years, for ...
of Benin issued a national apology for the central role Africans played in the Atlantic slave trade.Luc Gnacadja
Luc-Marie Constant Gnacadja or simply Luc Gnacadja is a Beninese politician and architect. He was Executive Secretary of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification from 2007 to 2013.
Political career
Gnacadja served in the government ...
, minister of environment and housing for Benin, later said: "The slave trade is a shame, and we do repent for it."Slave Coast Slave Coast can mean:
* the Slave Coast of West Africa
* the Dutch Slave Coast
The Dutch Slave Coast ( Dutch: ''Slavenkust'') refers to the trading posts of the Dutch West India Company on the Slave Coast, which lie in contemporary Ghana, Ben ...
bordering the Bight of Benin
The Bight of Benin or Bay of Benin is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.
Geography
It extends eastward for about from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of t ...
.Jerry Rawlings
Jerry John Rawlings (22 June 194712 November 2020) was a Ghanaian military officer and politician who led the country for a brief period in 1979, and then from 1981 to 2001. He led a military junta until 1992, and then served two terms as the de ...
of Ghana also apologized for his country's involvement in the slave trade.reparations for slavery
Reparations for slavery is the application of the concept of reparations to victims of slavery and/or their descendants. There are concepts for reparations in legal philosophy and reparations in transitional justice. Reparations can take numer ...
and is still being pursued by entities across the world. For example, the Jamaican Reparations Movement approved its declaration and action plan. In 2007, British Prime Minister Tony Blair
Sir Anthony Charles Lynton Blair (born 6 May 1953) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007. He previously served as Leader of th ...
made a formal apology for Great Britain's involvement in slavery.
On February 25, 2007, the Commonwealth of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States, Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United Stat ...
resolved to 'profoundly regret' and apologize for its role in the institution of slavery. Unique and the first of its kind in the U.S., the apology was unanimously passed in both Houses as Virginia approached the 400th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown.
On August 24, 2007, Mayor of London
The mayor of London is the chief executive of the Greater London Authority. The role was created in 2000 after the 1998 Greater London Authority referendum, Greater London devolution referendum in 1998, and was the first Directly elected may ...
Ken Livingstone
Kenneth Robert Livingstone (born 17 June 1945) is an English politician who served as the Leader of the Greater London Council (GLC) from 1981 until the council was abolished in 1986, and as Mayor of London from the creation of the office i ...
issued a public apology for London's role in Atlantic slave trade, which took place at an event commemorating the 200th anniversary of the British slave trade's abolition. In his speech, Livingstone described the slave trade as "the racial murder of not just those who were transported but generations of enslaved African men, women and children. To justify this murder and torture black people had to be declared inferior or not human... We live with the consequences today."Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
, which was a large slave trading port, apologized in 1999.
On July 30, 2008, the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the Lower house, lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States Senate, Senate being ...
passed a resolution apologizing for American slavery and subsequent discriminatory laws. In June 2009, the U.S. Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and powe ...
passed a resolution apologizing to African-Americans for the "fundamental injustice, cruelty, brutality, and inhumanity of slavery". The news was welcomed by President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
, the nation's first president of African descent. Some of President Obama's ancestors may have been slave owners.
In 2010, Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi
Muammar Muhammad Abu Minyar al-Gaddafi, . Due to the lack of standardization of transcribing written and regionally pronounced Arabic, Gaddafi's name has been romanized in various ways. A 1986 column by ''The Straight Dope'' lists 32 spellin ...
apologized for Arab involvement in the slave trade, saying: "I regret the behavior of the Arabs... They brought African children to North Africa, they made them slaves, they sold them like animals, and they took them as slaves and traded them in a shameful way."
Reparations
There have been movements to achieve reparations for those formerly held as slaves or for their descendants. Claims for reparations for being held in slavery are handled as a civil law matter in almost every country. This is often decried as a serious problem, since former slaves' relatives lack of money means they often have limited access to a potentially expensive and futile legal process
Legal process (sometimes simply process) is any formal notice or writ by a court obtaining jurisdiction over a person or property. Common forms of process include a summons, subpoena, mandate, and warrant. Process normally takes effect by ...
. Mandatory systems of fines and reparations paid to an as yet undetermined group of claimants from fines, paid by unspecified parties, and collected by authorities have been proposed by advocates to alleviate this "civil court problem." Since in almost all cases there are no living ex-slaves or living ex-slave owners these movements have gained little traction. In nearly all cases the judicial system has ruled that the statute of limitations
A statute of limitations, known in civil law systems as a prescriptive period, is a law passed by a legislative body to set the maximum time after an event within which legal proceedings may be initiated. ("Time for commencing proceedings") In m ...
on these possible claims has long since expired.
Media
 Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world. The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as ''
Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world. The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as ''The Birth of a Nation
''The Birth of a Nation'', originally called ''The Clansman'', is a 1915 American silent epic drama film directed by D. W. Griffith and starring Lillian Gish. The screenplay is adapted from Thomas Dixon Jr.'s 1905 novel and play ''The Cla ...
'' (1915) and ''Gone with the Wind
Gone with the Wind most often refers to:
* ''Gone with the Wind'' (novel), a 1936 novel by Margaret Mitchell
* ''Gone with the Wind'' (film), the 1939 adaptation of the novel
Gone with the Wind may also refer to:
Music
* ''Gone with the Wind'' ...
'' (1939) became controversial because they gave a favourable depiction. In 1940 '' The Santa Fe Trail'' gave a liberal but ambiguous interpretation of John Brown John Brown most often refers to:
*John Brown (abolitionist) (1800–1859), American who led an anti-slavery raid in Harpers Ferry, Virginia in 1859
John Brown or Johnny Brown may also refer to:
Academia
* John Brown (educator) (1763–1842), Ir ...
's attacks on slavery. ''Song of the South
''Song of the South'' is a 1946 American Live-action animated film, live-action/animated musical film, musical drama film directed by Harve Foster and Wilfred Jackson; produced by Walt Disney and released by RKO Pictures, RKO Radio Pictures. ...
'' gave a favorable outlook on slavery in the United States in 1946.
The Civil Rights Movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
in the 1950s made defiant slaves into heroes. The question of slavery in American memory necessarily involves its depictions in feature films.
Most Hollywood films used American settings, although ''Spartacus'' (1960), dealt with an actual revolt in the Roman Empire known as the Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directly ...
. The revolt failed, and all the rebels were executed, but their spirit lived on according to the film. ''Spartacus'' stays surprisingly close to the historical record.
''The Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
'' (''La última cena'' in Spanish) was a 1976 film directed by Cuban Tomás Gutiérrez Alea
Tomás Gutiérrez Alea (; December 11, 1928 – April 16, 1996) was a Cuban film director and screenwriter. He wrote and directed more than twenty features, documentaries, and short films, which are known for his sharp insight into post-Revolu ...
about the teaching of Christianity to slaves in Cuba, and emphasizes the role of ritual and revolt. ''Burn!
''Burn!'' (original title: ''Queimada'') is a 1969 historical war drama film directed by Gillo Pontecorvo. Set in the mid-19th century, the film stars Marlon Brando as a British ''agent provocateur'' sent to overthrow a Portuguese colony in th ...
'' takes place on the imaginary Portuguese island of Queimada (where the locals speak Spanish) and it merges historical events that took place in Brazil, Cuba, Santo Domingo, Jamaica, and elsewhere.
Historians agree that films have largely shaped historical memories, but they debate issues of accuracy, plausibility, moralism, sensationalism, how facts are stretched in search of broader truths, and suitability for the classroom. Berlin argues that critics complain if the treatment emphasizes historical brutality, or if it glosses over the harshness to highlight the emotional impact of slavery.
See also
* Bodmin manumissions
The Bodmin manumissions are records included in a manuscript Gospel book, the Bodmin Gospels or St Petroc Gospels, British Library, Add MS 9381. The manuscript is mostly in Latin, but with elements in Old English and the earliest written example ...
, the names and details of slaves freed in Medieval Bodmin
Bodmin () is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated south-west of Bodmin Moor.
The extent of the civil parish corresponds fairly closely to that of the town so is mostly urban in character. It is bordere ...
* International Day for the Abolition of Slavery
* International Slavery Museum
The International Slavery Museum is a museum located in Liverpool, England that focuses on the history and legacy of the transatlantic slave trade. The museum which forms part of the Merseyside Maritime Museum, consists of three main galleries ...
* Involuntary servitude
Involuntary servitude or involuntary slavery is a legal and constitutional term for a person laboring against that person's will to benefit another, under some form of coercion, to which it may constitute slavery. While laboring to benefit another ...
* List of slaves
Slavery is a social-economic system under which people are enslaved: deprived of personal freedom and forced to perform labor or services without compensation. These people are referred to as slaves, or as enslaved people.
The following is a ...
* List of slave owners
The following is a list of slave owners, for which there is a consensus of historical evidence of slave ownership, in alphabetical order by last name.
A
* Adelicia Acklen (1817–1887), at one time the wealthiest woman in Tennessee, she in ...
* Mukataba
In Islamic law, a ''mukataba''مكاتبة is a contract of manumission between a master and a slave according to which the slave is required to pay a certain sum of money during a specific time period in exchange for freedom. In the legal li ...
* Slave rebellion
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedo ...
* Subjugate Subjugate or subjugation is the action of enslave, enslaving using force or coercion on other humans. It could include forced labour such as slavery, serfdom, Penal labour, Labor camps; or Wage, paid voluntary labor that is Taxation as theft, involu ...
* Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery
The Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery, the full title of which is the Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery, the Slave Trade, and Institutions and Practices Similar to Slavery, is a 1956 United Nations treaty wh ...
*
References
Bibliography
Surveys and reference
; Books
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
; Journal articles and reviews
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
United States
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
online review
* [
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
]
Slavery in the modern era
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
External links
Historical
Slavery in America: A Resource Guide
at the Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The library is ...
Digital Library on American Slavery
at University of North Carolina at Greensboro
The University of North Carolina at Greensboro (UNCG or UNC Greensboro) is a public research university in Greensboro, North Carolina. It is part of the University of North Carolina system. UNCG, like all members of the UNC system, is a stand-al ...
*
The West African Squadron and slave trade
history of the Victorian Royal Navy
Slavery and the Making of America
at WNET
WNET (channel 13), branded on-air as "Thirteen" (stylized as "THIRTEEN"), is a primary PBS member television station licensed to Newark, New Jersey, United States, serving the New York City area. Owned by The WNET Group (formerly known as the ...
*
Slavery archival sources
University of London, Senate House Library
Senate House is the administrative centre of the University of London, situated in the heart of Bloomsbury, London, immediately to the north of the British Museum.
The Art Deco building was constructed between 1932 and 1937 as the first phase ...
Mémoire St Barth (archives & history of slavery, slave trade and their abolition)
Comité de Liaison et d'Application des Sources Historiques 2010
Archives of the Middelburgsche Commercie Compagnie (MCC), 1720-1889 'Trade Company of Middelburg'
Inventory of the archives of the Dutch slave trade across the Atlantic
Slave Ships and the Middle Passage
at ''Encyclopedia Virginia Virginia Humanities (VH), formerly the Virginia Foundation for the Humanities, is a humanities council whose stated mission is to develop the civic, cultural, and intellectual life of the Commonwealth of Virginia by creating learning opportunities f ...
''
The Trans-Atlantic and Intra-American slave trade databases
at Emory University
Emory University is a private research university in Atlanta, Georgia. Founded in 1836 as "Emory College" by the Methodist Episcopal Church and named in honor of Methodist bishop John Emory, Emory is the second-oldest private institution of ...
Modern
2018 Global Slavery Index
at the Walk Free Foundation
What is Modern Slavery?
Office To Monitor And Combat Trafficking In Persons, U.S. Department of State.
{{Authority control
Business ethics
Employment
Human rights abuses
Labor
Social classes
 Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as 

 As a social institution, chattel slavery classes slaves as ''chattels'' (
As a social institution, chattel slavery classes slaves as ''chattels'' ( Scottish economist
Scottish economist  Even after slavery became a criminal offense, slave owners could get high returns. According to researcher Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 were $91.2 billion. That was second only to drug trafficking, in terms of global criminal enterprises. At the time the weighted average global sales price of a slave was estimated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labour and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave. Approximately 40% of slave profits each year were generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4% of the world's 29 million slaves.
Even after slavery became a criminal offense, slave owners could get high returns. According to researcher Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 were $91.2 billion. That was second only to drug trafficking, in terms of global criminal enterprises. At the time the weighted average global sales price of a slave was estimated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labour and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave. Approximately 40% of slave profits each year were generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4% of the world's 29 million slaves.
 Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures. Slavery is rare among
Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures. Slavery is rare among  Records of
Records of  By the late Republican era, slavery had become an economic pillar of Roman wealth, as well as Roman society. It is estimated that 25% or more of the population of
By the late Republican era, slavery had become an economic pillar of Roman wealth, as well as Roman society. It is estimated that 25% or more of the population of  During the
During the  Large-scale trading in slaves was mainly confined to the South and East of
Large-scale trading in slaves was mainly confined to the South and East of  The Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the
The Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the 
 As recently as the early 1960s, Saudi Arabia's slave population was estimated at 300,000. Along with Yemen, the Saudis abolished slavery in 1962. Historically, slaves in the
As recently as the early 1960s, Saudi Arabia's slave population was estimated at 300,000. Along with Yemen, the Saudis abolished slavery in 1962. Historically, slaves in the  In
In  Under Omani Arabs, Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 African slaves passing through every year during the 19th century. Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 to 1900 AD.
Under Omani Arabs, Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 African slaves passing through every year during the 19th century. Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 to 1900 AD.  When the
When the  In the early 17th century, the majority of the labour in Barbados was provided by European indentured servants, mainly
In the early 17th century, the majority of the labour in Barbados was provided by European indentured servants, mainly 

 Cuba's slavery system was gendered in a way that some duties were performed only by male slaves, some only by female slaves. Female slaves in
Cuba's slavery system was gendered in a way that some duties were performed only by male slaves, some only by female slaves. Female slaves in 
 Following the
Following the  The planters of the Dutch colony relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate, harvest and process the commodity crops of coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Planters' treatment of the slaves was notoriously bad. Historian
The planters of the Dutch colony relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate, harvest and process the commodity crops of coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Planters' treatment of the slaves was notoriously bad. Historian 
 When
When  Slavery has taken various forms throughout China's history. It was reportedly abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 law fully enacted in 1910, although the practice continued until at least 1949.
The
Slavery has taken various forms throughout China's history. It was reportedly abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 law fully enacted in 1910, although the practice continued until at least 1949.
The  During the
During the  A slave market for captured Russian and
A slave market for captured Russian and  Between 1930 and 1960, the
Between 1930 and 1960, the  During the
During the  Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today is estimated as between 12 million and 29.8 million. According to a broad definition of slavery, there were 27 million people in slavery in 1999, spread all over the world. In 2005, the International Labour Organization provided an estimate of 12.3 million forced labourers. Siddharth Kara has also provided an estimate of 28.4 million slaves at the end of 2006 divided into three categories:
Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today is estimated as between 12 million and 29.8 million. According to a broad definition of slavery, there were 27 million people in slavery in 1999, spread all over the world. In 2005, the International Labour Organization provided an estimate of 12.3 million forced labourers. Siddharth Kara has also provided an estimate of 28.4 million slaves at the end of 2006 divided into three categories:  According to a 2003 report by
According to a 2003 report by  Victims of
Victims of 


 Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world. The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as ''
Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world. The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as ''