 Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as Terminology
The word arrived in modern English fromChattel slavery


 As a social institution, chattel slavery classes slaves as ''chattels'' (
As a social institution, chattel slavery classes slaves as ''chattels'' (Bonded labour
Indenture, also known as bonded labour or debt bondage, is a form of unfree labour in which a person works to pay off a debt by pledging himself or herself as collateral. The services required to repay the debt, and their duration, may be undefined. Debt bondage can be passed on from generation to generation, with children required to pay off their progenitors' debt. It is the most widespread form of slavery today. Debt bondage is most prevalent in South Asia. Money marriage refers to a marriage where a girl, usually, is married off to a man to settle debts owed by her parents. The Chukri system is aDependents
The word "slavery" has also been used to refer to a legal state of dependency to somebody else. For example, inForced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is sometimes used to describe an individual who is forced to work against their own will, under threat of violence or other punishment, but the generic term "unfree labour" is also used to describe chattel slavery, as well as any other situation in which a person is obliged to work against their own will, and a person's ability to work productively is under the complete control of another person. This may also include institutions not commonly classified as slavery, such asChild soldiers and child labor
In 2007,Forced marriage
Other uses of the term
The word ''slavery'' is often used as a pejorative to describe any activity in which one is coerced into performing. Some argue that military drafts and other forms of coerced government labour constitute "state-operated slavery." SomeCharacteristics
Private versus state-owned slaves
Slaves have been owned privately by individuals but have also been under state ownership. For example, theEconomics
Economists have modeled the circumstances under which slavery (and variants such as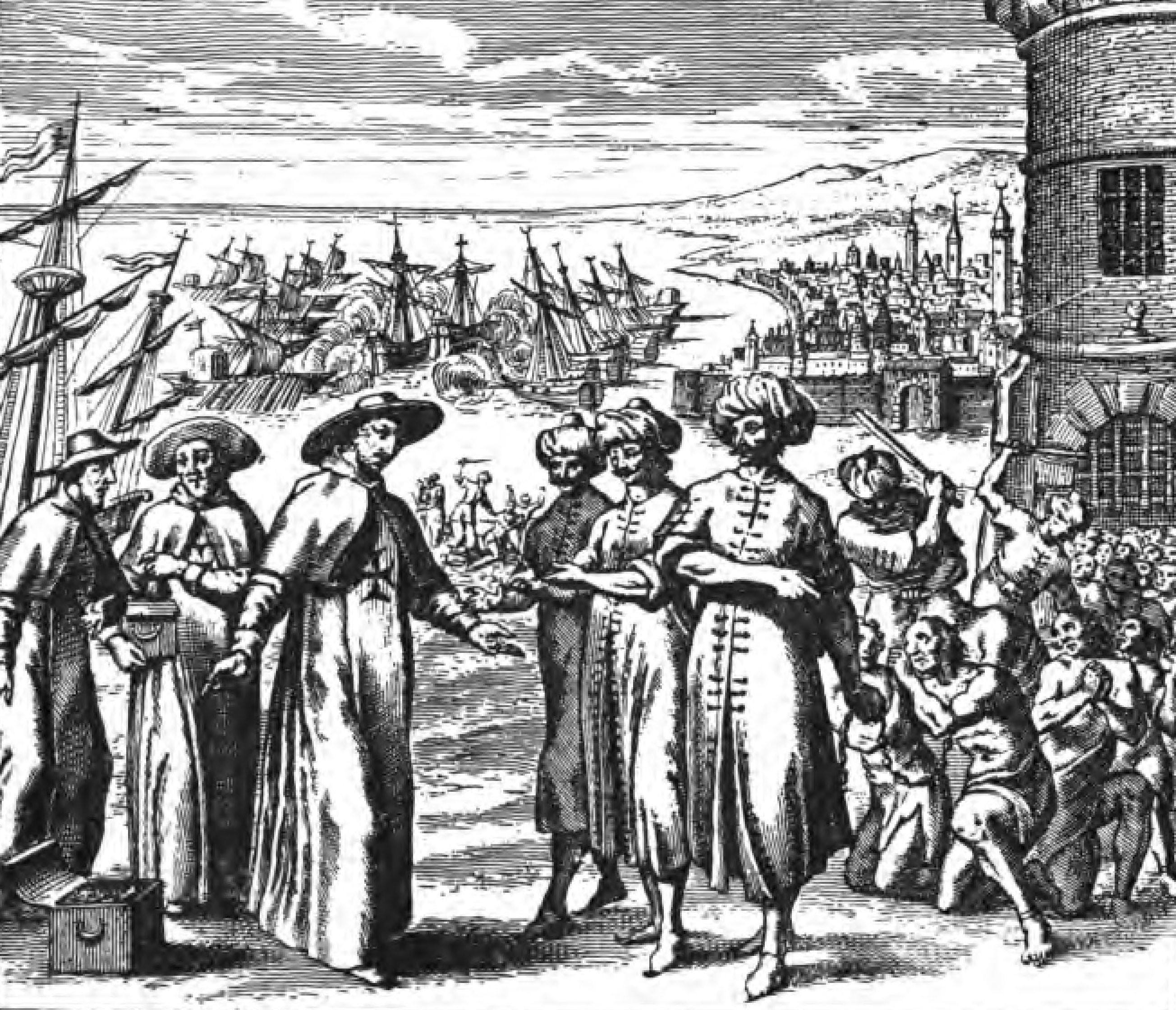 Scottish economist
Scottish economist  Even after slavery became a criminal offense, slave owners could get high returns. According to researcher Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 were $91.2 billion. That was second only to drug trafficking, in terms of global criminal enterprises. At the time the weighted average global sales price of a slave was estimated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labour and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave. Approximately 40% of slave profits each year were generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4% of the world's 29 million slaves.
Even after slavery became a criminal offense, slave owners could get high returns. According to researcher Siddharth Kara, the profits generated worldwide by all forms of slavery in 2007 were $91.2 billion. That was second only to drug trafficking, in terms of global criminal enterprises. At the time the weighted average global sales price of a slave was estimated to be approximately $340, with a high of $1,895 for the average trafficked sex slave, and a low of $40 to $50 for debt bondage slaves in part of Asia and Africa. The weighted average annual profits generated by a slave in 2007 was $3,175, with a low of an average $950 for bonded labour and $29,210 for a trafficked sex slave. Approximately 40% of slave profits each year were generated by trafficked sex slaves, representing slightly more than 4% of the world's 29 million slaves.
Identification
Throughout history, slaves were clothed in a distinctive fashion, particularly with respect to the frequent lack of footwear, as they were rather commonly forced to goLegal rights
Depending upon the era and the country, slaves sometimes had a limited set of legal rights. For example, in theHistory
Some scholars differentiate ancient forms of slavery from the largely race-based slavery. The first type of slavery, sometimes called "just title servitude", was inflicted onEarly history
 Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures. Slavery is rare among
Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures. Slavery is rare among Classical antiquity
Africa
Slavery existed in Ancient Egypt, Pharaonic Egypt, but studying it is complicated by terminology used by the Egyptians to refer to different classes of servitude over the course of history. Interpretation of the textual evidence of classes of slaves in ancient Egypt has been difficult to differentiate by word usage alone. The three apparent types of enslavement in Ancient Egypt: chattel slavery, bonded labour, and forced labour.Asia
Slavery existed in ancient China as early as the Shang dynasty. Slavery was employed largely by governments as a means of maintaining a public labour force.Europe
=Ancient Greece and Rome
=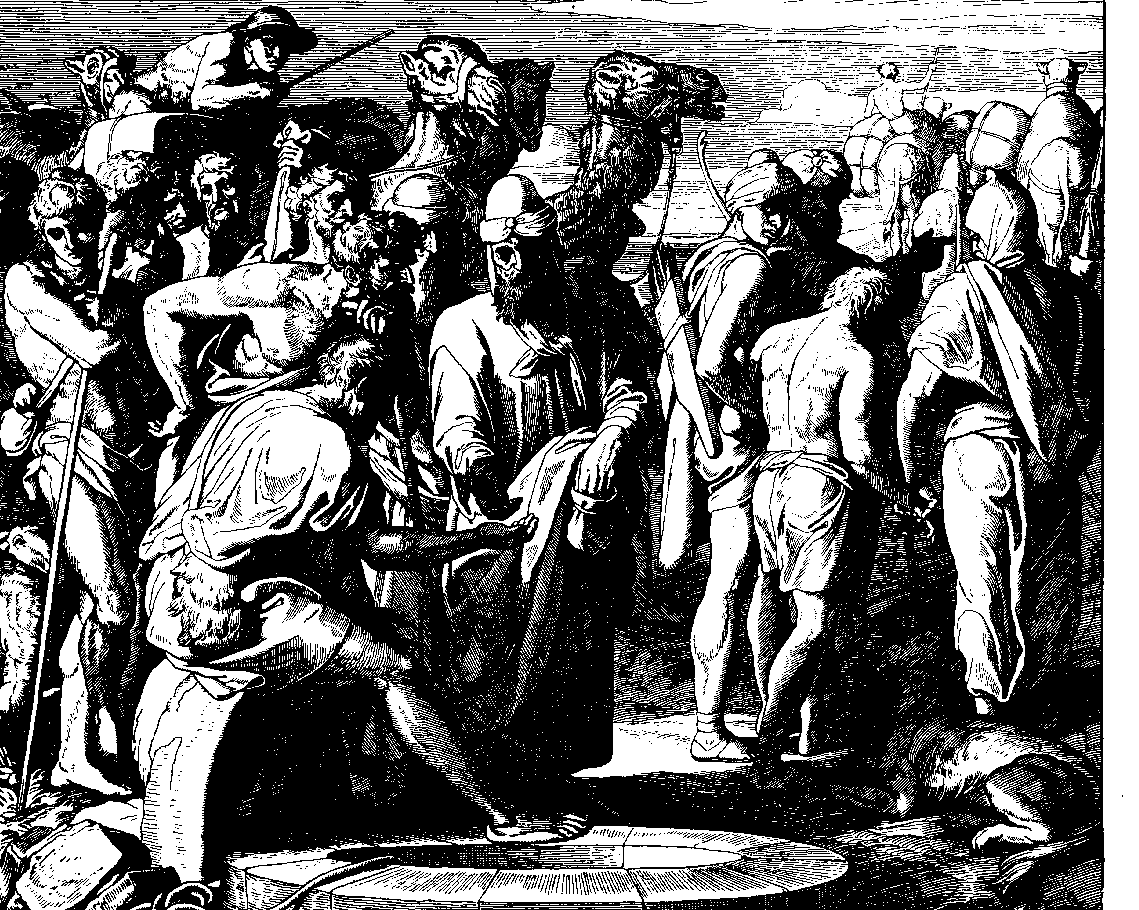 Records of slavery in Ancient Greece begin with Mycenaean Greece. Classical Athens had the largest slave population, with as many as 80,000 in the 6th and 5th centuries BC. As the Roman Republic expanded outward, entire populations were enslaved, across Europe and the Mediterranean. Slaves were used for labour, as well as for amusement (e.g. gladiators and sexual slavery, sex slaves). This oppression by an elite minority eventually led to slave rebellion, slave revolts (see Roman Servile Wars); the Third Servile War was led by Spartacus.
Records of slavery in Ancient Greece begin with Mycenaean Greece. Classical Athens had the largest slave population, with as many as 80,000 in the 6th and 5th centuries BC. As the Roman Republic expanded outward, entire populations were enslaved, across Europe and the Mediterranean. Slaves were used for labour, as well as for amusement (e.g. gladiators and sexual slavery, sex slaves). This oppression by an elite minority eventually led to slave rebellion, slave revolts (see Roman Servile Wars); the Third Servile War was led by Spartacus.
 By the late Republican era, slavery had become an economic pillar of Roman wealth, as well as Roman society. It is estimated that 25% or more of the population of Ancient Rome was enslaved, although the actual percentage is debated by scholars and varied from region to region. Slaves represented 15–25% of Roman Italy, Italy's population, mostly war captives, especially from Gaul and Epirus. Estimates of the number of slaves in the Roman Empire suggest that the majority were scattered throughout the Roman Province, provinces outside of Italy. Generally, slaves in Italy were indigenous Italians. Foreigners (including both slaves and freedmen) born outside of Italy were estimated to have peaked at 5% of the total in the capital, where their number was largest. Those from outside of Europe were predominantly of Greek descent. Jewish slaves never fully assimilated into Roman society, remaining an identifiable minority. These slaves (especially the foreigners) had higher death rates and lower birth rates than natives and were sometimes subjected to mass expulsions. The average recorded age at death for the slaves in Rome was seventeen and a half years (17.2 for males; 17.9 for females).
By the late Republican era, slavery had become an economic pillar of Roman wealth, as well as Roman society. It is estimated that 25% or more of the population of Ancient Rome was enslaved, although the actual percentage is debated by scholars and varied from region to region. Slaves represented 15–25% of Roman Italy, Italy's population, mostly war captives, especially from Gaul and Epirus. Estimates of the number of slaves in the Roman Empire suggest that the majority were scattered throughout the Roman Province, provinces outside of Italy. Generally, slaves in Italy were indigenous Italians. Foreigners (including both slaves and freedmen) born outside of Italy were estimated to have peaked at 5% of the total in the capital, where their number was largest. Those from outside of Europe were predominantly of Greek descent. Jewish slaves never fully assimilated into Roman society, remaining an identifiable minority. These slaves (especially the foreigners) had higher death rates and lower birth rates than natives and were sometimes subjected to mass expulsions. The average recorded age at death for the slaves in Rome was seventeen and a half years (17.2 for males; 17.9 for females).
Middle Ages
Africa
Slavery was widespread in Africa, which pursued both internal and external slave trade. In the Senegambia (geography), Senegambia region, between 1300 and 1900, close to one-third of the population was enslaved. In early Islamic states of the western Sahel, including Ghana Empire, Ghana, Mali Empire, Mali, Bamana Empire, Segou, and Songhai Empire, Songhai, about a third of the population were enslaved.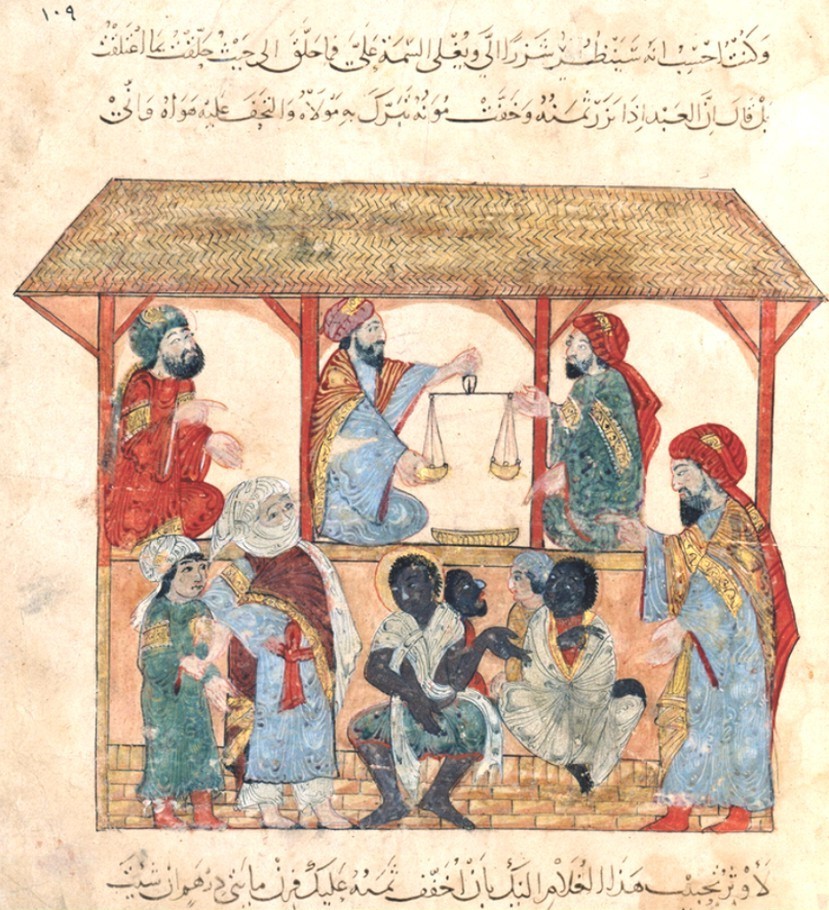 During the trans-Saharan slave trade, slaves from West Africa were transported across the Sahara, Sahara desert to North Africa to be sold to Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Middle East, Middle eastern civilizations. The Indian Ocean slave trade, sometimes known as the east African slave trade, was multi-directional. Africans were sent as slaves to the Arabian Peninsula, to Indian Ocean islands (including Madagascar), to the Indian subcontinent, and later to the Americas. These traders captured Bantu peoples (Zanj) from the interior in present-day Kenya, Mozambique and Tanzania and brought them to the coast. There, the slaves gradually assimilated in rural areas, particularly on Unguja and Pemba Island, Pemba islands.
During the trans-Saharan slave trade, slaves from West Africa were transported across the Sahara, Sahara desert to North Africa to be sold to Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Middle East, Middle eastern civilizations. The Indian Ocean slave trade, sometimes known as the east African slave trade, was multi-directional. Africans were sent as slaves to the Arabian Peninsula, to Indian Ocean islands (including Madagascar), to the Indian subcontinent, and later to the Americas. These traders captured Bantu peoples (Zanj) from the interior in present-day Kenya, Mozambique and Tanzania and brought them to the coast. There, the slaves gradually assimilated in rural areas, particularly on Unguja and Pemba Island, Pemba islands.
Americas
Aztec slavery, Slavery in Mexico can be traced back to the Aztecs. Other Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Amerindians, such as the Inca Empire, Inca of the Andes, the Tupí people, Tupinambá of Brazil, the Muscogee people, Creek of Georgia, and the Comanche of Texas, also practiced slavery. Slavery in Canada was practiced by First Nations in Canada, First Nations and by European colonization of the Americas, European settlers. Slave-owning people of what became Canada were, for example, the fishing societies, such as the Yurok tribe, Yurok, that lived along the Pacific coast from Alaska to California, on what is sometimes described as the Pacific or Northern Northwest Coast. Some of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, such as the Haida people, Haida and Tlingit people, Tlingit, were traditionally known as fierce warriors and slave-traders, raiding as far as California. Slavery was hereditary, the slaves beingAsia
Slavery also existed in Slavery in India, India, Slavery in Japan, Japan and Slavery in Vietnam, Vietnam.= China
= Many Han Chinese were enslaved in the process of the Mongol conquest of China, Mongol invasion of China proper. According to Japanese historians Sugiyama Masaaki (杉山正明) and Funada Yoshiyuki (舩田善之), Mongolian slaves were owned by Han Chinese during the Yuan dynasty.=Korea
= Slavery in Korea existed since before the Three Kingdoms of Korea period, in the first century BCE. Slavery has been described as "very important in medieval Korea, probably more important than in any other East Asian country, but by the 16th century, population growth was making tunnecessary". Slavery went into decline around the 10th century but came back in the late Goryeo period when Korea also experienced multiple slave rebellions. In the Joseon period of Korea, members of the slave class were known as ''nobi''. The nobi were socially indistinct from freemen (i.e., the Chungin, middle and Sangmin, common classes) other than the ruling yangban class, and some possessed property rights, and legal and civil rights. Hence, some scholars argue that it is inappropriate to call them "slaves", while some scholars describe them as serfs. The nobi population could fluctuate up to about one-third of the total, but on average the nobi made up about 10% of the total population. In 1801, the majority of government nobi were emancipated, and by 1858, the nobi population stood at about 1.5 percent of the Korean population.Europe
 Large-scale trading in slaves was mainly confined to the South and East of Early Middle Ages, early medieval Europe: the Byzantine Empire and the Muslim world were the destinations, while paganism, pagan Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe (along with the Caucasus and Tartary) were important sources. Viking, Arab people, Arab, Greeks, Greek, and Radhanite Jews, Jewish merchants were all involved in the slave trade during the Early Middle Ages. The trade in European slaves reached a peak in the 10th century following the Zanj Rebellion which dampened the use of African slaves in the Arab world.
Slavery in medieval Europe, Slavery in early medieval Europe was so common that the Catholic Church repeatedly prohibited it, or at least the export of Christian slaves to non-Christian lands, as for example at the Koblenz#Middle Ages, Council of Koblenz (922), the Council of London (1102) (which aimed mainly at the sale of English slaves to Ireland) and the Council of Armagh (1171). Serfdom, on the contrary, was widely accepted. In 1452, Pope Nicholas V issued the papal bull ''Dum Diversas'', granting the kings of Spain and Portugal the right to reduce any "Saracens (Muslims), pagans and any other unbelievers" to perpetual slavery, legitimizing the slave trade as a result of war. The approval of slavery under these conditions was reaffirmed and extended in his ''Romanus Pontifex'' bull of 1455.
Large-scale trading in slaves was mainly confined to the South and East of Early Middle Ages, early medieval Europe: the Byzantine Empire and the Muslim world were the destinations, while paganism, pagan Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe (along with the Caucasus and Tartary) were important sources. Viking, Arab people, Arab, Greeks, Greek, and Radhanite Jews, Jewish merchants were all involved in the slave trade during the Early Middle Ages. The trade in European slaves reached a peak in the 10th century following the Zanj Rebellion which dampened the use of African slaves in the Arab world.
Slavery in medieval Europe, Slavery in early medieval Europe was so common that the Catholic Church repeatedly prohibited it, or at least the export of Christian slaves to non-Christian lands, as for example at the Koblenz#Middle Ages, Council of Koblenz (922), the Council of London (1102) (which aimed mainly at the sale of English slaves to Ireland) and the Council of Armagh (1171). Serfdom, on the contrary, was widely accepted. In 1452, Pope Nicholas V issued the papal bull ''Dum Diversas'', granting the kings of Spain and Portugal the right to reduce any "Saracens (Muslims), pagans and any other unbelievers" to perpetual slavery, legitimizing the slave trade as a result of war. The approval of slavery under these conditions was reaffirmed and extended in his ''Romanus Pontifex'' bull of 1455.
=Britain
= In Britain, slavery continued to be practiced following the fall of Rome, and sections of Hywel the Good's Welsh law, laws dealt with slaves in medieval Wales. The trade particularly picked up after the Viking invasions, with major markets at Chester and Bristol supplied by Danish, Mercian, and Welsh raiding of one another's borderlands. At the time of the ''Domesday Book'', nearly 10% of the Norman England, English population were slaves. William the Conqueror introduced a law preventing the sale of slaves overseas. According to historian John Gillingham, by 1200 slavery in the British Isles was non-existent. Slavery had never been authorized by statute within England and Wales, and in 1772, in the case Somerset v Stewart, Lord Mansfield declared that it was also unsupported within England by the common law. The slave trade was abolished by the Slave Trade Act 1807, although slavery remained legal in possessions outside Europe until the passage of the Slavery Abolition Act 1833 and the Indian Slavery Act, 1843. However, when England began to have colonies in the Americas, and particularly from the 1640s, African slaves began to make their appearance in England and remained a presence until the eighteenth century. In Scotland, slaves continued to be sold as chattels until late in the eighteenth century (on the second May, 1722, an advertisement appeared in the ''Edinburgh Evening Courant'', announcing that a stolen slave had been found, who would be sold to pay expenses, unless claimed within two weeks). For nearly two hundred years in the history of coal mining in Scotland, miners were bonded to their "maisters" by a 1606 Act "Anent Coalyers and Salters". The Colliers and Salters (Scotland) Act 1775 stated that "many colliers and salters are in a state of slavery and bondage" and announced emancipation; those starting work after 1 July 1775 would not become slaves, while those already in a state of slavery could, after 7 or 10 years depending on their age, apply for a decree of the Sheriff's Court granting their freedom. Few could afford this, until a further law in 1799 established their freedom and made this slavery and bondage illegal.=Ottoman Empire
= The Byzantine–Ottoman Wars, Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the Ottoman wars in Europe brought large numbers of slaves into the Islamic world. To staff its bureaucracy, the Ottoman Empire established a Janissaries, janissary system which seized hundreds of thousands of Christian boys through the devşirme system. They were well cared for but were legally slaves owned by the government and were not allowed to marry. They were never bought or sold. The empire gave them significant administrative and military roles. The system began about 1365; there were 135,000 janissaries in 1826, when the system ended.
After the Battle of Lepanto (1571), Battle of Lepanto, 12,000 Christian galley slaves were recaptured and freed from the Ottoman fleet. Eastern Europe suffered a series of Mongol and Tatar states in Europe, Tatar invasions, the goal of which was to loot and capture slaves for selling them to Ottomans as jasyr. Seventy-five Crimean Tatar raids were recorded into Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland–Lithuania between 1474 and 1569.
The Byzantine–Ottoman Wars, Byzantine-Ottoman wars and the Ottoman wars in Europe brought large numbers of slaves into the Islamic world. To staff its bureaucracy, the Ottoman Empire established a Janissaries, janissary system which seized hundreds of thousands of Christian boys through the devşirme system. They were well cared for but were legally slaves owned by the government and were not allowed to marry. They were never bought or sold. The empire gave them significant administrative and military roles. The system began about 1365; there were 135,000 janissaries in 1826, when the system ended.
After the Battle of Lepanto (1571), Battle of Lepanto, 12,000 Christian galley slaves were recaptured and freed from the Ottoman fleet. Eastern Europe suffered a series of Mongol and Tatar states in Europe, Tatar invasions, the goal of which was to loot and capture slaves for selling them to Ottomans as jasyr. Seventy-five Crimean Tatar raids were recorded into Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland–Lithuania between 1474 and 1569.
=Poland
= Slavery in Poland was forbidden in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588; they were replaced by the second serfdom.=Spain and Portugal
= Spain in the Middle Ages, Medieval Spain and History of Portugal, Portugal were the scene of almost constant Muslim invasion of the predominantly Christian area. Periodic raiding expeditions were sent from Al-Andalus to ravage the Iberian Christian kingdoms, bringing back booty and slaves. In a raid against Lisbon in 1189, for example, the Almohad dynasty, Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur took 3,000 female and child captives, while his governor of Córdoba, Spain, Córdoba, in a subsequent attack upon Silves Municipality, Portugal, Silves, Portugal, in 1191, took 3,000 Christian slaves. From the 11th to the 19th century, North African Barbary corsairs, Barbary Pirates engaged in raids on European coastal towns to capture Christian slaves to sell at Barbary slave trade, slave markets in places such as Algeria and Morocco.
The maritime town of Lagos, Portugal, Lagos was the first slave market created in Portugal (one of the earliest colonizers of the Americas) for the sale of imported African slaves – the ''Mercado de Escravos'', opened in 1444. In 1441, the first slaves were brought to Portugal from northern Mauritania.
By 1552, black African slaves made up 10% of the population of Lisbon. In the second half of the 16th century, the Crown gave up the monopoly on slave trade, and the focus of European trade in African slaves shifted from import to Europe to slave transports directly to tropical colonies in the Americas – especially Brazil. In the 15th century one-third of the slaves were resold to the African market in exchange of gold.
Spain in the Middle Ages, Medieval Spain and History of Portugal, Portugal were the scene of almost constant Muslim invasion of the predominantly Christian area. Periodic raiding expeditions were sent from Al-Andalus to ravage the Iberian Christian kingdoms, bringing back booty and slaves. In a raid against Lisbon in 1189, for example, the Almohad dynasty, Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur took 3,000 female and child captives, while his governor of Córdoba, Spain, Córdoba, in a subsequent attack upon Silves Municipality, Portugal, Silves, Portugal, in 1191, took 3,000 Christian slaves. From the 11th to the 19th century, North African Barbary corsairs, Barbary Pirates engaged in raids on European coastal towns to capture Christian slaves to sell at Barbary slave trade, slave markets in places such as Algeria and Morocco.
The maritime town of Lagos, Portugal, Lagos was the first slave market created in Portugal (one of the earliest colonizers of the Americas) for the sale of imported African slaves – the ''Mercado de Escravos'', opened in 1444. In 1441, the first slaves were brought to Portugal from northern Mauritania.
By 1552, black African slaves made up 10% of the population of Lisbon. In the second half of the 16th century, the Crown gave up the monopoly on slave trade, and the focus of European trade in African slaves shifted from import to Europe to slave transports directly to tropical colonies in the Americas – especially Brazil. In the 15th century one-third of the slaves were resold to the African market in exchange of gold.
=Russia
==Scandinavia
= In Scandinavia, thralldom was abolished in the mid-14th century.Early modern period
Africa
 As recently as the early 1960s, Saudi Arabia's slave population was estimated at 300,000. Along with Yemen, the Saudis abolished slavery in 1962. Historically, slaves in the Arab World came from many different regions, including Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly ''Zanj''), the Caucasus (mainly Circassians), Central Asia (mainly Tartary, Tartars), and Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe (mainly Slavs [''Saqaliba'']).
Some historians assert that as many as 17 million people were sold into slavery on the coast of the Indian Ocean, the Middle East, and North Africa, and approximately 5 million African slaves were bought by Muslim slave traders and taken from Africa across the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara desert between 1500 and 1900. The captives were sold throughout the Middle East. This trade accelerated as superior ships led to more trade and greater demand for labour on plantations in the region. Eventually, tens of thousands of captives were being taken every year. The Indian Ocean slave trade was multi-directional and changed over time. To meet the demand for menial labour, Bantu slaves bought by east African slave traders from southeastern Africa were sold in cumulatively large numbers over the centuries to customers in Egypt, Arabia, the Persian Gulf, India, European colonies in the Far East, the List of islands in the Indian Ocean, Indian Ocean islands, Ethiopia and Somalia.
According to the ''Encyclopedia of African History'', "It is estimated that by the 1890s the largest slave population of the world, about 2 million people, was concentrated in the territories of the Sokoto Caliphate. The use of slave labour was extensive, especially in agriculture." The Anti-Slavery Society estimated there were 2 million slaves in Ethiopia in the early 1930s out of an estimated population of 8 to 16 million.
Slave labour in East Africa was drawn from the ''Zanj,'' Bantu peoples that lived along the East African coast. The Zanj were for centuries shipped as slaves by Arab traders to all the countries bordering the Indian Ocean. The Umayyad and Abbasid caliphs recruited many Zanj slaves as soldiers and, as early as 696, there were slave revolts of the Zanj against their Arab enslavers in Iraq. The Zanj Rebellion, a series of uprisings that took place between 869 and 883 near Basra (also known as Basara), situated in present-day Iraq, is believed to have involved enslaved Zanj that had originally been captured from the African Great Lakes region and areas further south in East Africa. It grew to involve over 500,000 slaves and free men who were imported from across the Muslim empire and claimed over "tens of thousands of lives in lower Iraq".
The Zanj who were taken as slaves to the Middle East were often used in strenuous agricultural work. As the plantation economy boomed and the Arabs became richer, agriculture and other manual labour work was thought to be demeaning. The resulting labour shortage led to an increased slave market.
As recently as the early 1960s, Saudi Arabia's slave population was estimated at 300,000. Along with Yemen, the Saudis abolished slavery in 1962. Historically, slaves in the Arab World came from many different regions, including Sub-Saharan Africa (mainly ''Zanj''), the Caucasus (mainly Circassians), Central Asia (mainly Tartary, Tartars), and Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe (mainly Slavs [''Saqaliba'']).
Some historians assert that as many as 17 million people were sold into slavery on the coast of the Indian Ocean, the Middle East, and North Africa, and approximately 5 million African slaves were bought by Muslim slave traders and taken from Africa across the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara desert between 1500 and 1900. The captives were sold throughout the Middle East. This trade accelerated as superior ships led to more trade and greater demand for labour on plantations in the region. Eventually, tens of thousands of captives were being taken every year. The Indian Ocean slave trade was multi-directional and changed over time. To meet the demand for menial labour, Bantu slaves bought by east African slave traders from southeastern Africa were sold in cumulatively large numbers over the centuries to customers in Egypt, Arabia, the Persian Gulf, India, European colonies in the Far East, the List of islands in the Indian Ocean, Indian Ocean islands, Ethiopia and Somalia.
According to the ''Encyclopedia of African History'', "It is estimated that by the 1890s the largest slave population of the world, about 2 million people, was concentrated in the territories of the Sokoto Caliphate. The use of slave labour was extensive, especially in agriculture." The Anti-Slavery Society estimated there were 2 million slaves in Ethiopia in the early 1930s out of an estimated population of 8 to 16 million.
Slave labour in East Africa was drawn from the ''Zanj,'' Bantu peoples that lived along the East African coast. The Zanj were for centuries shipped as slaves by Arab traders to all the countries bordering the Indian Ocean. The Umayyad and Abbasid caliphs recruited many Zanj slaves as soldiers and, as early as 696, there were slave revolts of the Zanj against their Arab enslavers in Iraq. The Zanj Rebellion, a series of uprisings that took place between 869 and 883 near Basra (also known as Basara), situated in present-day Iraq, is believed to have involved enslaved Zanj that had originally been captured from the African Great Lakes region and areas further south in East Africa. It grew to involve over 500,000 slaves and free men who were imported from across the Muslim empire and claimed over "tens of thousands of lives in lower Iraq".
The Zanj who were taken as slaves to the Middle East were often used in strenuous agricultural work. As the plantation economy boomed and the Arabs became richer, agriculture and other manual labour work was thought to be demeaning. The resulting labour shortage led to an increased slave market.
 In Algiers, the capital of Algeria, captured Christians and Europeans were forced into slavery. In about 1650, there were as many as 35,000 Christian slaves in Algiers. By one estimate, raids by Barbary slave traders on coastal villages and ships extending from Italy to Iceland, enslaved an estimated 1 to 1.25 million Europeans between the 16th and 19th centuries. However, this estimate is the result of an extrapolation which assumes that the number of European slaves captured by Barbary pirates was constant for a 250-year period:
Davis' numbers have been refuted by other historians, such as David Earle, who cautions that true picture of Europeans slaves is clouded by the fact the corsairs also seized non-Christian whites from eastern Europe. In addition, the number of slaves traded was hyperactive, with exaggerated estimates relying on peak years to calculate averages for entire centuries, or millennia. Hence, there were wide fluctuations year-to-year, particularly in the 18th and 19th centuries, given slave imports, and also given the fact that, prior to the 1840s, there are no consistent records. Middle East expert, John Wright, cautions that modern estimates are based on back-calculations from human observation. Such observations, across the late 16th and early 17th century observers, account for around 35,000 European Christian slaves held throughout this period on the Barbary Coast, across Tripoli, Tunis, but mostly in Algiers. The majority were sailors (particularly those who were English), taken with their ships, but others were fishermen and coastal villagers. However, most of these captives were people from lands close to Africa, particularly Spain and Italy. This eventually led to the Bombardment of Algiers (1816), bombardment of Algiers by an Anglo-Dutch fleet in 1816.
In Algiers, the capital of Algeria, captured Christians and Europeans were forced into slavery. In about 1650, there were as many as 35,000 Christian slaves in Algiers. By one estimate, raids by Barbary slave traders on coastal villages and ships extending from Italy to Iceland, enslaved an estimated 1 to 1.25 million Europeans between the 16th and 19th centuries. However, this estimate is the result of an extrapolation which assumes that the number of European slaves captured by Barbary pirates was constant for a 250-year period:
Davis' numbers have been refuted by other historians, such as David Earle, who cautions that true picture of Europeans slaves is clouded by the fact the corsairs also seized non-Christian whites from eastern Europe. In addition, the number of slaves traded was hyperactive, with exaggerated estimates relying on peak years to calculate averages for entire centuries, or millennia. Hence, there were wide fluctuations year-to-year, particularly in the 18th and 19th centuries, given slave imports, and also given the fact that, prior to the 1840s, there are no consistent records. Middle East expert, John Wright, cautions that modern estimates are based on back-calculations from human observation. Such observations, across the late 16th and early 17th century observers, account for around 35,000 European Christian slaves held throughout this period on the Barbary Coast, across Tripoli, Tunis, but mostly in Algiers. The majority were sailors (particularly those who were English), taken with their ships, but others were fishermen and coastal villagers. However, most of these captives were people from lands close to Africa, particularly Spain and Italy. This eventually led to the Bombardment of Algiers (1816), bombardment of Algiers by an Anglo-Dutch fleet in 1816.
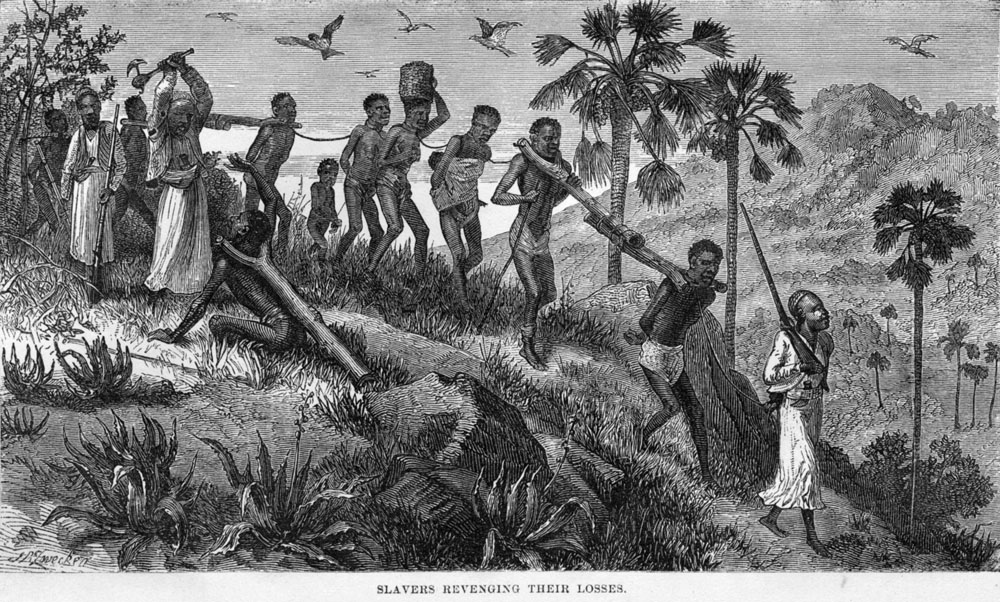 Under Omani Arabs, Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 African slaves passing through every year during the 19th century. Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 to 1900 AD. Eduard Rüppell described the losses of Sudanese slaves being transported on foot to Egypt: "after the Daftardar bey's 1822 campaign in the southern Nuba mountains, nearly 40,000 slaves were captured. However, through bad treatment, disease and desert travel barely 5,000 made it to Egypt." W.A. Veenhoven wrote: "The German doctor, Gustav Nachtigal, an eye-witness, believed that for every slave who arrived at a market three or four died on the way ... John Scott Keltie, Keltie (''The Partition of Africa'', London, 1920) believes that for every slave the Arabs brought to the coast at least six died on the way or during the slavers' raid. David Livingstone, Livingstone puts the figure as high as ten to one."
Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the Ancient history, ancient world. In many African societies where slavery was prevalent, the slaves were not treated as #Chattel slavery, chattel slaves and were given certain rights in a system similar to indentured servitude elsewhere in the world. The forms of slavery in Africa were closely related to kinship structures. In many African communities, where land could not be owned, enslavement of individuals was used as a means to increase the influence a person had and expand connections. This made slaves a permanent part of a master's lineage and the children of slaves could become closely connected with the larger family ties. Children of slaves born into families could be integrated into the master's kinship group and rise to prominent positions within society, even to the level of chief in some instances. However, stigma often remained attached and there could be strict separations between slave members of a kinship group and those related to the master. Slavery was practiced in many different forms: debt slavery, enslavement of war captives, military slavery, and criminal slavery were all practiced in various parts of Africa. Slavery for domestic and court purposes was widespread throughout Africa.
Under Omani Arabs, Zanzibar became East Africa's main slave port, with as many as 50,000 African slaves passing through every year during the 19th century. Some historians estimate that between 11 and 18 million African slaves crossed the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and Sahara Desert from 650 to 1900 AD. Eduard Rüppell described the losses of Sudanese slaves being transported on foot to Egypt: "after the Daftardar bey's 1822 campaign in the southern Nuba mountains, nearly 40,000 slaves were captured. However, through bad treatment, disease and desert travel barely 5,000 made it to Egypt." W.A. Veenhoven wrote: "The German doctor, Gustav Nachtigal, an eye-witness, believed that for every slave who arrived at a market three or four died on the way ... John Scott Keltie, Keltie (''The Partition of Africa'', London, 1920) believes that for every slave the Arabs brought to the coast at least six died on the way or during the slavers' raid. David Livingstone, Livingstone puts the figure as high as ten to one."
Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa, as they were in much of the Ancient history, ancient world. In many African societies where slavery was prevalent, the slaves were not treated as #Chattel slavery, chattel slaves and were given certain rights in a system similar to indentured servitude elsewhere in the world. The forms of slavery in Africa were closely related to kinship structures. In many African communities, where land could not be owned, enslavement of individuals was used as a means to increase the influence a person had and expand connections. This made slaves a permanent part of a master's lineage and the children of slaves could become closely connected with the larger family ties. Children of slaves born into families could be integrated into the master's kinship group and rise to prominent positions within society, even to the level of chief in some instances. However, stigma often remained attached and there could be strict separations between slave members of a kinship group and those related to the master. Slavery was practiced in many different forms: debt slavery, enslavement of war captives, military slavery, and criminal slavery were all practiced in various parts of Africa. Slavery for domestic and court purposes was widespread throughout Africa.
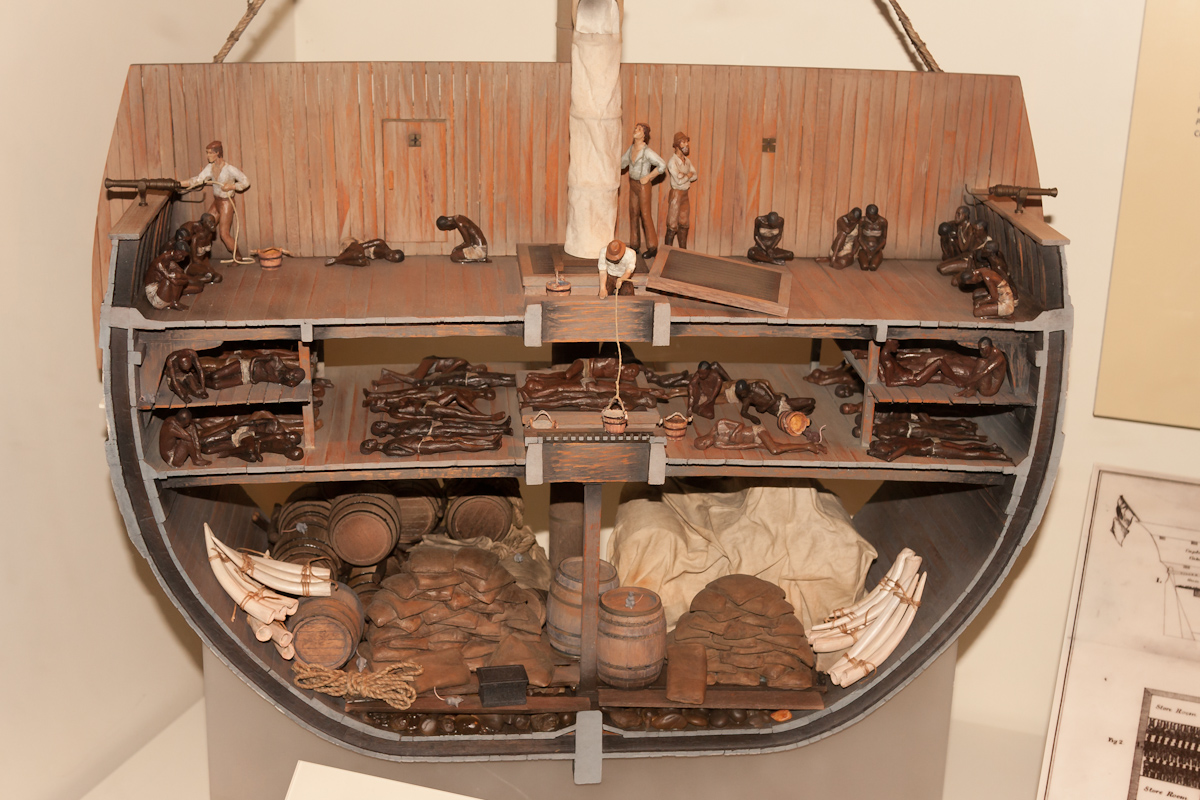 When the Atlantic slave trade began, many of the local slave systems began supplying captives for chattel slave markets outside Africa. Although the Atlantic slave trade was not the only slave trade from Africa, it was the largest in volume and intensity. As Elikia M’bokolo wrote in ''Le Monde diplomatique'':
The trans-Atlantic slave trade peaked in the late 18th century, when the largest number of slaves were captured on raiding expeditions into the interior of West Africa. These expeditions were typically carried out by List of kingdoms in pre-colonial Africa, African kingdoms, such as the Oyo Empire (Yoruba people, Yoruba), the Ashanti Empire, the kingdom of Dahomey, and the Aro Confederacy. It is estimated that about 15 percent of slaves died during the Middle Passage, voyage, with mortality rates considerably higher in Africa itself in the process of capturing and transporting indigenous peoples to the ships.
When the Atlantic slave trade began, many of the local slave systems began supplying captives for chattel slave markets outside Africa. Although the Atlantic slave trade was not the only slave trade from Africa, it was the largest in volume and intensity. As Elikia M’bokolo wrote in ''Le Monde diplomatique'':
The trans-Atlantic slave trade peaked in the late 18th century, when the largest number of slaves were captured on raiding expeditions into the interior of West Africa. These expeditions were typically carried out by List of kingdoms in pre-colonial Africa, African kingdoms, such as the Oyo Empire (Yoruba people, Yoruba), the Ashanti Empire, the kingdom of Dahomey, and the Aro Confederacy. It is estimated that about 15 percent of slaves died during the Middle Passage, voyage, with mortality rates considerably higher in Africa itself in the process of capturing and transporting indigenous peoples to the ships.
Americas
Slavery in America remains a contentious issue and played a major role in the history and evolution of some countries, triggering a Haitian Revolution, revolution, American Civil War, a civil war, and numerous rebellions. In order to establish itself as an American empire, Spain had to fight against the relatively powerful civilizations of the New World. The Spanish people, Spanish conquest of the indigenous peoples in the Americas included using the Natives as forced labour. The Slavery in the Spanish New World colonies, Spanish colonies were the first Europeans to use African slaves in the New World on islands such as Cuba and Hispaniola. Bartolomé de las Casas, a 16th-century Dominican Order, Dominican friar and Spanish historian, participated in campaigns in Cuba (at Bayamo and Camagüey) and was present at the massacre of Hatuey; his observation of that massacre led him to fight for a social movement away from the use of natives as slaves. Also, the alarming decline in the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, native population had spurred the first Laws of Burgos, royal laws protecting the native population. The first African slaves arrived in Hispaniola in 1501. England played a prominent role in the Atlantic slave trade. The "Triangular trade#Atlantic triangular slave trade, slave triangle" was pioneered by Francis Drake and his associates. Many whites who arrived in North America during the 17th and 18th centuries came under contract as indentured servants. The transformation from indentured servitude to slavery was a gradual process in Virginia. The earliest legal documentation of such a shift was in 1640 where a Black man, John Punch (slave), John Punch, was sentenced to lifetime slavery, forcing him to serve his master, Hugh Gwyn, for the remainder of his life, for attempting to run away. This case was significant because it established the disparity between his sentence as a black man and that of the two white indentured servants who escaped with him (one described as Dutch and one as a Scotchman). It is the first documented case of a black man sentenced to lifetime servitude and is considered one of the first legal cases to make a racial distinction between black and white indentured servants. After 1640, planters started to ignore the expiration of indentured contracts and keep their servants as slaves for life. This was demonstrated by the 1655 case ''Johnson v. Parker'', where the court ruled that a black man, Anthony Johnson (colonist), Anthony Johnson of Virginia, was granted ownership of another black man, John Casor, as the result of a civil case. This was the first instance of a judicial determination in the Thirteen Colonies holding that a person who had committed no crime could be held in servitude for life.=Barbados
= In the early 17th century, the majority of the labour in Barbados was provided by European indentured servants, mainly English people, English, Irish people, Irish and Scottish people, Scottish, with Atlantic slave trade, African and native American slaves providing little of the workforce. The introduction of sugar cane from Dutch Brazil in 1640 completely transformed society and the economy. Barbados eventually had one of the world's largest sugar industries.
As the effects of the new crop increased, so did the shift in the ethnic composition of Barbados and surrounding islands. The workable sugar plantation required a large investment and a great deal of heavy labour. At first, Dutch traders supplied the equipment, financing, and African slaves, in addition to transporting most of the sugar to Europe. In 1644, the population of Barbados was estimated at 30,000, of which about 800 were of African descent, with the remainder mainly of English descent. These English smallholders were eventually bought out, and the island filled up with large sugar plantations worked by African slaves. By 1660, there was near parity with 27,000 blacks and 26,000 whites. By 1666, at least 12,000 white smallholders had been bought out, died, or left the island. Many of the remaining whites were increasingly poor. By 1680, there were 17 slaves for every indentured servant. By 1700, there were 15,000 free whites and 50,000 enslaved Africans.
Because of the increased implementation of Barbados Slave Code, slave codes, which created differential treatment between Africans and the white workers and ruling planter class, the island became increasingly unattractive to redlegs, poor whites. Black or slave codes were implemented in 1661, 1676, 1682, and 1688. In response to these codes, several slave rebellions were attempted or planned during this time, but none succeeded. Nevertheless, poor whites who had or acquired the means to emigrate often did so. Planters expanded their importation of African slaves to cultivate sugar cane.
In the early 17th century, the majority of the labour in Barbados was provided by European indentured servants, mainly English people, English, Irish people, Irish and Scottish people, Scottish, with Atlantic slave trade, African and native American slaves providing little of the workforce. The introduction of sugar cane from Dutch Brazil in 1640 completely transformed society and the economy. Barbados eventually had one of the world's largest sugar industries.
As the effects of the new crop increased, so did the shift in the ethnic composition of Barbados and surrounding islands. The workable sugar plantation required a large investment and a great deal of heavy labour. At first, Dutch traders supplied the equipment, financing, and African slaves, in addition to transporting most of the sugar to Europe. In 1644, the population of Barbados was estimated at 30,000, of which about 800 were of African descent, with the remainder mainly of English descent. These English smallholders were eventually bought out, and the island filled up with large sugar plantations worked by African slaves. By 1660, there was near parity with 27,000 blacks and 26,000 whites. By 1666, at least 12,000 white smallholders had been bought out, died, or left the island. Many of the remaining whites were increasingly poor. By 1680, there were 17 slaves for every indentured servant. By 1700, there were 15,000 free whites and 50,000 enslaved Africans.
Because of the increased implementation of Barbados Slave Code, slave codes, which created differential treatment between Africans and the white workers and ruling planter class, the island became increasingly unattractive to redlegs, poor whites. Black or slave codes were implemented in 1661, 1676, 1682, and 1688. In response to these codes, several slave rebellions were attempted or planned during this time, but none succeeded. Nevertheless, poor whites who had or acquired the means to emigrate often did so. Planters expanded their importation of African slaves to cultivate sugar cane.
=Brazil
=
 Slavery in Brazil began long before the Colonial Brazil, first Portuguese settlement was established in 1532, as members of one tribe would enslave captured members of another.
Later, Portuguese colonists were heavily dependent on indigenous labour during the initial phases of settlement to maintain the subsistence economy, and natives were often captured by expeditions called '. The importation of African slaves began midway through the 16th century, but the enslavement of indigenous peoples continued well into the 17th and 18th centuries.
During the Atlantic slave trade era, Brazil imported more African slaves than any other country. Nearly 5 million slaves were brought from Africa to Brazil during the period from 1501 to 1866. Until the early 1850s, most African slaves who arrived on Brazilian shores were forced to embark at West Central African ports, especially in Luanda (in present-day Angola). Today, with the exception of Nigeria, the country with the largest population of people of African descent is Brazil.
Slave labour was the driving force behind the growth of the Sugarcane, sugar economy in Brazil, and sugar was the primary export of the colony from 1600 to 1650. Gold and diamond deposits were discovered in Brazil in 1690, which sparked an increase in the importation of African slaves to power this newly profitable market. Transportation systems were developed for the mining infrastructure, and population boomed from immigrants seeking to take part in gold and diamond mining. Demand for African slaves did not wane after the decline of the mining industry in the second half of the 18th century. Cattle ranching and foodstuff production proliferated after the population growth, both of which relied heavily on slave labour. 1.7 million slaves were imported to Brazil from Africa from 1700 to 1800, and the rise of coffee in the 1830s further enticed expansion of the slave trade.
Brazil was the last country in the Western world to abolish slavery. Forty percent of the total number of slaves brought to the Americas were sent to Brazil. For reference, the United States received 10 percent. Despite being abolished, there are still people working in slavery-like conditions in Brazil in the 21st century.
Slavery in Brazil began long before the Colonial Brazil, first Portuguese settlement was established in 1532, as members of one tribe would enslave captured members of another.
Later, Portuguese colonists were heavily dependent on indigenous labour during the initial phases of settlement to maintain the subsistence economy, and natives were often captured by expeditions called '. The importation of African slaves began midway through the 16th century, but the enslavement of indigenous peoples continued well into the 17th and 18th centuries.
During the Atlantic slave trade era, Brazil imported more African slaves than any other country. Nearly 5 million slaves were brought from Africa to Brazil during the period from 1501 to 1866. Until the early 1850s, most African slaves who arrived on Brazilian shores were forced to embark at West Central African ports, especially in Luanda (in present-day Angola). Today, with the exception of Nigeria, the country with the largest population of people of African descent is Brazil.
Slave labour was the driving force behind the growth of the Sugarcane, sugar economy in Brazil, and sugar was the primary export of the colony from 1600 to 1650. Gold and diamond deposits were discovered in Brazil in 1690, which sparked an increase in the importation of African slaves to power this newly profitable market. Transportation systems were developed for the mining infrastructure, and population boomed from immigrants seeking to take part in gold and diamond mining. Demand for African slaves did not wane after the decline of the mining industry in the second half of the 18th century. Cattle ranching and foodstuff production proliferated after the population growth, both of which relied heavily on slave labour. 1.7 million slaves were imported to Brazil from Africa from 1700 to 1800, and the rise of coffee in the 1830s further enticed expansion of the slave trade.
Brazil was the last country in the Western world to abolish slavery. Forty percent of the total number of slaves brought to the Americas were sent to Brazil. For reference, the United States received 10 percent. Despite being abolished, there are still people working in slavery-like conditions in Brazil in the 21st century.
=Cuba
= In 1789 the Spanish Crown led an effort to reform slavery, as the demand for slave labour in Cuba was growing. The Crown issued a decree, ''Código Negro Español'' (Spanish Black Codex), that specified food and clothing provisions, put limits on the number of work hours, limited punishments, required religious instruction, and protected marriages, forbidding the sale of young children away from their mothers. The British made other changes to the institution of slavery in Cuba. But planters often flouted the laws and protested against them, considering them a threat to their authority and an intrusion into their personal lives. The slaveowners did not protest against all the measures of the codex, many of which they argued were already common practices. They objected to efforts to set limits on their ability to apply physical punishment. For instance, the Black Codex limited Flagellation, whippings to 25 and required the whippings "not to cause serious bruises or bleeding". The slave-owners thought that the slaves would interpret these limits as weaknesses, ultimately leading to resistance. Another contested issue was the work hours that were restricted "from sunrise to sunset"; plantation owners responded by explaining that cutting and processing of cane needed 20-hour days during the harvest season. Those slaves who worked on sugar plantations and in sugar mills were often subject to the harshest of conditions. The field work was rigorous manual labour which the slaves began at an early age. The work days lasted close to 20 hours during harvest and processing, including cultivating and cutting the crops, hauling wagons, and processing sugarcane with dangerous machinery. The slaves were forced to reside in barracoons, where they were crammed in and locked in by a padlock at night, getting about three to four hours of sleep. The conditions of the barracoons were harsh; they were highly unsanitary and extremely hot. Typically there was no ventilation; the only window was a small barred hole in the wall. Cuba's slavery system was gendered in a way that some duties were performed only by male slaves, some only by female slaves. Female slaves in Havana from the 16th century onwards performed duties such as operating the town taverns, eating houses, and lodges, as well as being laundresses and domestic labourers and servants. Female slaves also served as the town prostitutes.
Some Cuban women could gain freedom by having children with white men. As in other Latin cultures, there were looser borders with the mulatto or mixed-race population. Sometimes men who took slaves as wives or concubines freed both them and their children. As in New Orleans and Saint-Domingue, mulattos began to be classified as a third group between the European colonists and African slaves. Freedmen, generally of mixed race, came to represent 20% of the total Cuban population and 41% of the non-white Cuban population.Knight pp. 144–145
Planters encouraged Afro-Cuban slaves to have children in order to reproduce their work force. The masters wanted to pair strong and large-built black men with healthy black women. They were placed in the barracoons and forced to have sex and create offspring of "breed stock" children, who would sell for around 500 pesos. The planters needed children to be born to replace slaves who died under the harsh regime. Sometimes if the overseers did not like the quality of children, they separate the parents and sent the mother back to working in the fields.
Both women and men were subject to the punishments of violence and humiliating abuse. Slaves who misbehaved or disobeyed their masters were often placed in stocks in the depths of the boiler houses where they were abandoned for days at a time, and oftentimes two to three months. These wooden stocks were made in two types: lying-down or stand-up types. women were punished, even when pregnant. They were subjected to whippings: they had to lie "face down over a scooped-out piece of round [earth] to protect their bellies." Some masters reportedly whipped pregnant women in the belly, often causing miscarriages. The wounds were treated with "compresses of tobacco leaves, urine and salt."
Cuba's slavery system was gendered in a way that some duties were performed only by male slaves, some only by female slaves. Female slaves in Havana from the 16th century onwards performed duties such as operating the town taverns, eating houses, and lodges, as well as being laundresses and domestic labourers and servants. Female slaves also served as the town prostitutes.
Some Cuban women could gain freedom by having children with white men. As in other Latin cultures, there were looser borders with the mulatto or mixed-race population. Sometimes men who took slaves as wives or concubines freed both them and their children. As in New Orleans and Saint-Domingue, mulattos began to be classified as a third group between the European colonists and African slaves. Freedmen, generally of mixed race, came to represent 20% of the total Cuban population and 41% of the non-white Cuban population.Knight pp. 144–145
Planters encouraged Afro-Cuban slaves to have children in order to reproduce their work force. The masters wanted to pair strong and large-built black men with healthy black women. They were placed in the barracoons and forced to have sex and create offspring of "breed stock" children, who would sell for around 500 pesos. The planters needed children to be born to replace slaves who died under the harsh regime. Sometimes if the overseers did not like the quality of children, they separate the parents and sent the mother back to working in the fields.
Both women and men were subject to the punishments of violence and humiliating abuse. Slaves who misbehaved or disobeyed their masters were often placed in stocks in the depths of the boiler houses where they were abandoned for days at a time, and oftentimes two to three months. These wooden stocks were made in two types: lying-down or stand-up types. women were punished, even when pregnant. They were subjected to whippings: they had to lie "face down over a scooped-out piece of round [earth] to protect their bellies." Some masters reportedly whipped pregnant women in the belly, often causing miscarriages. The wounds were treated with "compresses of tobacco leaves, urine and salt."
=Haiti
= Slavery in Haiti started with the arrival of Christopher Columbus on the island in 1492. The practice was devastating to the native population. Following the indigenous Taíno's near decimation from forced labour, disease and war, the Spanish, under advisement of the Catholic priest Bartolomeu de las Casas, and with the blessing of the Catholic church began engaging in earnest in the kidnapped and forced labour of African slaves. During the French colonial empire, French colonial period beginning in 1625, the economy of Haiti (then known as Saint-Domingue) was based on slavery, and the practice there was regarded as the most brutal in the world.
 Following the Treaty of Ryswick of 1697, Hispaniola was divided between Kingdom of France, France and Imperial Spain, Spain. France received the western third and subsequently named it Saint-Domingue. To develop it into sugarcane plantations, the French imported thousands of slaves from Africa. Sugar was a lucrative commodity crop throughout the 18th century. By 1789, approximately 40,000 white colonists lived in Saint-Domingue. The whites were vastly outnumbered by the tens of thousands of African slaves they had imported to work on their plantations, which were primarily devoted to the production of sugarcane. In the north of the island, slaves were able to retain many ties to African cultures, religion and language; these ties were continually being renewed by newly imported Africans. Blacks outnumbered whites by about ten to one.
The French-enacted ''Code Noir'' ("Black Code"), prepared by Jean-Baptiste Colbert and ratified by Louis XIV, had established rules on slave treatment and permissible freedoms. Saint-Domingue has been described as one of the most brutally efficient slave colonies; one-third of newly imported Africans died within a few years. Many slaves died from diseases such as smallpox and typhoid fever. They had birth rates around 3 percent, and there is evidence that some women abortion, aborted fetuses, or committed infanticide, rather than allow their children to live within the bonds of slavery.
As in its Louisiana (New France), Louisiana colony, the New France, French colonial government allowed some rights to free people of color: the mixed-race descendants of white male colonists and black female slaves (and later, mixed-race women). Over time, many were released from slavery. They established a separate social class. White French Creole peoples, Creole fathers frequently sent their mixed-race sons to France for their education. Some men of color were admitted into the military. More of the free people of color lived in the south of the island, near Port-au-Prince, and many intermarried within their community. They frequently worked as artisans and tradesmen, and began to own some property. Some became slave holders. The free people of color petitioned the colonial government to expand their rights.
Slaves that made it to Haiti from the trans-Atlantic journey and slaves born in Haiti were first documented in Haiti's archives and transferred to France's Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. , these records are in The National Archives of France. According to the 1788 Census, Haiti's population consisted of nearly 40,000 whites, 30,000 free coloureds and 450,000 slaves.
The Haitian Revolution of 1804, the only successful slave rebellion, slave revolt in human history, precipitated the end of slavery in all French colonies.
Following the Treaty of Ryswick of 1697, Hispaniola was divided between Kingdom of France, France and Imperial Spain, Spain. France received the western third and subsequently named it Saint-Domingue. To develop it into sugarcane plantations, the French imported thousands of slaves from Africa. Sugar was a lucrative commodity crop throughout the 18th century. By 1789, approximately 40,000 white colonists lived in Saint-Domingue. The whites were vastly outnumbered by the tens of thousands of African slaves they had imported to work on their plantations, which were primarily devoted to the production of sugarcane. In the north of the island, slaves were able to retain many ties to African cultures, religion and language; these ties were continually being renewed by newly imported Africans. Blacks outnumbered whites by about ten to one.
The French-enacted ''Code Noir'' ("Black Code"), prepared by Jean-Baptiste Colbert and ratified by Louis XIV, had established rules on slave treatment and permissible freedoms. Saint-Domingue has been described as one of the most brutally efficient slave colonies; one-third of newly imported Africans died within a few years. Many slaves died from diseases such as smallpox and typhoid fever. They had birth rates around 3 percent, and there is evidence that some women abortion, aborted fetuses, or committed infanticide, rather than allow their children to live within the bonds of slavery.
As in its Louisiana (New France), Louisiana colony, the New France, French colonial government allowed some rights to free people of color: the mixed-race descendants of white male colonists and black female slaves (and later, mixed-race women). Over time, many were released from slavery. They established a separate social class. White French Creole peoples, Creole fathers frequently sent their mixed-race sons to France for their education. Some men of color were admitted into the military. More of the free people of color lived in the south of the island, near Port-au-Prince, and many intermarried within their community. They frequently worked as artisans and tradesmen, and began to own some property. Some became slave holders. The free people of color petitioned the colonial government to expand their rights.
Slaves that made it to Haiti from the trans-Atlantic journey and slaves born in Haiti were first documented in Haiti's archives and transferred to France's Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. , these records are in The National Archives of France. According to the 1788 Census, Haiti's population consisted of nearly 40,000 whites, 30,000 free coloureds and 450,000 slaves.
The Haitian Revolution of 1804, the only successful slave rebellion, slave revolt in human history, precipitated the end of slavery in all French colonies.
=Jamaica
= Jamaica was colonized by the Taino tribes prior to the arrival of Christopher Columbus, Columbus in 1494. The Spanish enslaved many of the Taino; some escaped, but most died from European diseases and overwork. The Spaniards also introduced the first African slaves. The Spanish colonists did not bring women in the first expeditions and took Taíno women for their common-law wives, resulting in mestizo children. Sexual violence with the Taíno women by the Spanish was also common. Although the African slave population in the 1670s and 1680s never exceeded 10,000, by 1800 it had increased to over 300,000.=Mexico
= In 1519, Hernán Cortés brought the first Afro-Mexican#African slavery in Mexico, modern slave to the area. In the mid-16th century, the second viceroy to Mexico, Luis de Velasco, prohibited slavery of the Aztecs. A labour shortage resulted as the Aztecs were either killed or died from disease. This led to the African slaves being imported, as they were not susceptible to smallpox. In exchange, many Africans were afforded the opportunity to buy their freedom, while eventually others were granted their freedom by their masters.=Puerto Rico
= When Ponce de León and the Spaniards arrived on the island of Puerto Rico, Borikén (Puerto Rico), they enslaved Taíno tribes on the island, forcing them to work in the gold mines and in the construction of forts. Many Taíno died, particularly from smallpox, of which they had no immunity (medical), immunity. Other Taínos committed suicide or left the island after the failed Taíno revolt of 1511. The Spanish colonists, fearing the loss of their labour force, complained to the courts that they needed manpower. As an alternative, Las Casas suggested the importation and use of African slaves. In 1517, the Spanish Crown permitted its subjects to import twelve slaves each, thereby beginning the slave trade on the colonies. African slaves were legally branded with a hot iron on the forehead, prevented their "theft" or lawsuits that challenged their captivity. The colonists continued this branding practice for more than 250 years. They were sent to work in the gold mines, or in the island's ginger and sugar fields. They were allowed to live with their families in a hut on the master's land, and given a patch of land where they could farm, but otherwise were subjected to harsh treatment; including sexual abuse as the majority of colonists had arrived without women; many of them intermarried with the Africans or Taínos. Their mixed-race descendants formed the first generations of the early Puerto Rican population. The slaves faced heavy discrimination and had no opportunity for advancement, though they were educated by their masters. The Spaniards considered the Africans superior to the Taíno, since the latter were unwilling to assimilate. The slaves, in contrast, had little choice but to adapt. Many converted to Christianity and were given their masters' surnames. By 1570, the colonists found that the gold mines were depleted, relegating the island to a garrison for passing ships. The cultivation of crops such as tobacco, cotton, cocoa, and ginger became the cornerstone of the economy. With rising demand for sugar on the international market, major planters increased their labour-intensive cultivation and processing of sugar cane. Sugar plantations supplanted mining as Puerto Rico's main industry and kept demand high for African slavery. After 1784, Spain provided five ways by which slaves could obtain freedom. Five years later, the Spanish Crown issued the "Royal Decree of Graces of 1789", which set new rules related to the slave trade and added restrictions to the granting of freedman status. The decree granted its subjects the right to purchase slaves and to participate in the flourishing slave trade in the Caribbean. Later that year a new slave code, also known as ''El Código Negro'' (The Black Code), was introduced. Under "El Código Negro", a slave could buy his freedom, in the event that his master was willing to sell, by paying the price sought in installments. Slaves were allowed to earn money during their spare time by working as shoemakers, cleaning clothes, or selling the produce they grew on their own plots of land. For the freedom of their newborn child, not yet baptized, they paid at half the going price for a baptized child. Many of these freedmen started settlements in the areas which became known as Cangrejos (Santurce, San Juan, Puerto Rico, Santurce), Carolina, Puerto Rico, Carolina, Canóvanas, Puerto Rico, Canóvanas, Loíza, Puerto Rico, Loíza, and Luquillo, Puerto Rico, Luquillo. Some became slave owners themselves. Despite these paths to freedom, from 1790 onwards, the number of slaves more than doubled in Puerto Rico as a result of the dramatic expansion of the sugar industry in the island. On March 22, 1873, slavery was legally abolished in Puerto Rico. However, slaves were not emancipated but rather had to buy their own freedom, at whatever price was set by their last masters. They were also required to work for another three years for their former masters, for other colonists interested in their services, or for the state in order to pay some compensation. Between 1527 and 1873, slaves in Puerto Rico had carried out more than twenty revolts.=Suriname
= The planters of the Dutch colony relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate, harvest and process the commodity crops of coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Planters' treatment of the slaves was notoriously bad. Historian C. R. Boxer wrote that "man's inhumanity to man just about reached its limits in Surinam."
Many slaves escaped the plantations. With the help of the native South Americans living in the adjoining rain forests, these runaway slaves established a new and unique culture in the interior that was highly successful in its own right. They were known collectively in English as Maroon (people), Maroons, in French as ''Nèg'Marrons'' (literally meaning "brown negroes", that is "pale-skinned negroes"), and in Dutch as ''Marrons.'' The Maroons gradually developed several independent tribes through a process of ethnogenesis, as they were made up of slaves from different African ethnicities. These tribes include the Saramaka, Paramaka, Ndyuka people, Ndyuka or Aukan, Kwinti, Aluku or Boni, and Matawai.
The Maroons often raided plantations to recruit new members from the slaves and capture women, as well as to acquire weapons, food and supplies. They sometimes killed planters and their families in the raids. The colonists also mounted armed campaigns against the Maroons, who generally escaped through the rain forest, which they knew much better than did the coloniss. To end hostilities, in the 18th century the European colonial authorities signed several peace treaties with different tribes. They granted the Maroons sovereign status and trade rights in their inland territories, giving them autonomy.
In 1861–63, President Abraham Lincoln of the United States and his administration looked abroad for places to relocate freed slaves who wanted to leave the United States. It opened negotiations with the Dutch government regarding African-American emigration to and colonization of the Dutch colony of Suriname in South America. Nothing came of it and after 1864, the proposal was dropped.
The Netherlands abolished slavery in Suriname, in 1863, under a gradual process that required slaves to work on plantations for 10 transition years for minimal pay, which was considered as partial compensation for their masters. Besides that, the Dutch government in 1863 also compensated each slave-owner for the loss of the working force of each slave 300 Dutch florins - in 2021 worth about 3,500 euros. After 1873, most freedmen largely abandoned the plantations where they had worked for several generations in favor of the capital city, Paramaribo.
The planters of the Dutch colony relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate, harvest and process the commodity crops of coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Planters' treatment of the slaves was notoriously bad. Historian C. R. Boxer wrote that "man's inhumanity to man just about reached its limits in Surinam."
Many slaves escaped the plantations. With the help of the native South Americans living in the adjoining rain forests, these runaway slaves established a new and unique culture in the interior that was highly successful in its own right. They were known collectively in English as Maroon (people), Maroons, in French as ''Nèg'Marrons'' (literally meaning "brown negroes", that is "pale-skinned negroes"), and in Dutch as ''Marrons.'' The Maroons gradually developed several independent tribes through a process of ethnogenesis, as they were made up of slaves from different African ethnicities. These tribes include the Saramaka, Paramaka, Ndyuka people, Ndyuka or Aukan, Kwinti, Aluku or Boni, and Matawai.
The Maroons often raided plantations to recruit new members from the slaves and capture women, as well as to acquire weapons, food and supplies. They sometimes killed planters and their families in the raids. The colonists also mounted armed campaigns against the Maroons, who generally escaped through the rain forest, which they knew much better than did the coloniss. To end hostilities, in the 18th century the European colonial authorities signed several peace treaties with different tribes. They granted the Maroons sovereign status and trade rights in their inland territories, giving them autonomy.
In 1861–63, President Abraham Lincoln of the United States and his administration looked abroad for places to relocate freed slaves who wanted to leave the United States. It opened negotiations with the Dutch government regarding African-American emigration to and colonization of the Dutch colony of Suriname in South America. Nothing came of it and after 1864, the proposal was dropped.
The Netherlands abolished slavery in Suriname, in 1863, under a gradual process that required slaves to work on plantations for 10 transition years for minimal pay, which was considered as partial compensation for their masters. Besides that, the Dutch government in 1863 also compensated each slave-owner for the loss of the working force of each slave 300 Dutch florins - in 2021 worth about 3,500 euros. After 1873, most freedmen largely abandoned the plantations where they had worked for several generations in favor of the capital city, Paramaribo.
=United States
= Slavery in the United States was the legal institution of human chattel enslavement, primarily of Africans and African Americans, that existed in the United States of America in the 18th and 19th centuries, after it gained independence from the British and before the end of the American Civil War. Slavery had been practiced in British America from Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, early colonial days and was legal in all Thirteen Colonies, at the time of the Declaration of Independence in 1776. By the time of the American Revolution, the status of slave had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. The United States became polarized over the issue of slavery, represented by the slave and free states divided by the Mason–Dixon line, which separated free Pennsylvania from slave Maryland and Delaware.
Congress, during the Thomas Jefferson, Jefferson administration, Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves, prohibited the importation of slaves, effective 1808, although smuggling (illegal importing) was not unusual. Domestic slave trading, however, continued at a rapid pace, driven by labour demands from the development of cotton Plantations in the American South, plantations in the Deep South. Those states attempted to extend slavery into the new western territories to keep their share of political power in the nation. Such laws proposed to Congress to continue the spread of slavery into newly ratified states include the Kansas–Nebraska Act, Kansas-Nebraska Act.
The treatment of slaves in the United States varied widely depending on conditions, times, and places. The power relationships of slavery corrupted many whites who had authority over slaves, with children showing their own cruelty. Masters and overseers resorted to physical punishments to impose their wills. Slaves were punished by whipping, shackling, Lynching in the United States, hanging, beating, burning, mutilation, branding and imprisonment. Punishment was most often meted out in response to disobedience or perceived infractions, but sometimes abuse was carried out to re-assert the dominance of the master or overseer of the slave. Treatment was usually harsher on large plantations, which were often managed by overseers and owned by absentee slaveholders.
William Wells Brown, who escaped to freedom, reported that on one plantation, slave men were required to pick of cotton per day, while women were required to pick per day; if any slave failed in their quota, they were subject to whip lashes for each pound they were short. The whipping post stood next to the cotton scales. A New York man who attended a slave auction in the mid-19th century reported that at least three-quarters of the male slaves he saw at sale had scars on their backs from whipping. By contrast, small slave-owning families had closer relationships between the owners and slaves; this sometimes resulted in a more humane environment but was not a given.
More than one million slaves were sold from the Upper South, which had a surplus of labour, and taken to the Deep South in a forced migration, splitting up many families. New communities of African-American culture were developed in the Deep South, and the total slave population in the South eventually reached 4 million before liberation. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". In the 19th century, proponents of slavery often defended the institution as a "necessary evil". White people of that time feared that emancipation of black slaves would have more harmful social and economic consequences than the continuation of slavery. The French writer and traveler Alexis de Tocqueville, in ''Democracy in America'' (1835), expressed opposition to slavery while observing its effects on American society. He felt that a multiracial society without slavery was untenable, as he believed that prejudice against black people increased as they were granted more rights. Others, like James Henry Hammond argued that slavery was a "positive good" stating: "Such a class you must have, or you would not have that other class which leads progress, civilization, and refinement."
The Southern state governments wanted to keep a balance between the number of slave and free states to maintain a political balance of power in United States Congress, Congress. The new Territories of the United States, territories acquired from British Empire, Britain, French colonial empire, France, and Mexico were the subject of major political compromises. By 1850, the newly rich cotton-growing South was threatening to secede from the Union (American Civil War), Union, and tensions continued to rise. Many white Southern Christians, including church ministers, attempted to justify their support for slavery as modified by Christian paternalism. The largest denominations, the Baptist, Methodist, and Presbyterian churches, split over the slavery issue into regional organizations of the North and South.
Slavery in the United States was the legal institution of human chattel enslavement, primarily of Africans and African Americans, that existed in the United States of America in the 18th and 19th centuries, after it gained independence from the British and before the end of the American Civil War. Slavery had been practiced in British America from Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, early colonial days and was legal in all Thirteen Colonies, at the time of the Declaration of Independence in 1776. By the time of the American Revolution, the status of slave had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. The United States became polarized over the issue of slavery, represented by the slave and free states divided by the Mason–Dixon line, which separated free Pennsylvania from slave Maryland and Delaware.
Congress, during the Thomas Jefferson, Jefferson administration, Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves, prohibited the importation of slaves, effective 1808, although smuggling (illegal importing) was not unusual. Domestic slave trading, however, continued at a rapid pace, driven by labour demands from the development of cotton Plantations in the American South, plantations in the Deep South. Those states attempted to extend slavery into the new western territories to keep their share of political power in the nation. Such laws proposed to Congress to continue the spread of slavery into newly ratified states include the Kansas–Nebraska Act, Kansas-Nebraska Act.
The treatment of slaves in the United States varied widely depending on conditions, times, and places. The power relationships of slavery corrupted many whites who had authority over slaves, with children showing their own cruelty. Masters and overseers resorted to physical punishments to impose their wills. Slaves were punished by whipping, shackling, Lynching in the United States, hanging, beating, burning, mutilation, branding and imprisonment. Punishment was most often meted out in response to disobedience or perceived infractions, but sometimes abuse was carried out to re-assert the dominance of the master or overseer of the slave. Treatment was usually harsher on large plantations, which were often managed by overseers and owned by absentee slaveholders.
William Wells Brown, who escaped to freedom, reported that on one plantation, slave men were required to pick of cotton per day, while women were required to pick per day; if any slave failed in their quota, they were subject to whip lashes for each pound they were short. The whipping post stood next to the cotton scales. A New York man who attended a slave auction in the mid-19th century reported that at least three-quarters of the male slaves he saw at sale had scars on their backs from whipping. By contrast, small slave-owning families had closer relationships between the owners and slaves; this sometimes resulted in a more humane environment but was not a given.
More than one million slaves were sold from the Upper South, which had a surplus of labour, and taken to the Deep South in a forced migration, splitting up many families. New communities of African-American culture were developed in the Deep South, and the total slave population in the South eventually reached 4 million before liberation. Based on "records for 27,233 voyages that set out to obtain slaves for the Americas". In the 19th century, proponents of slavery often defended the institution as a "necessary evil". White people of that time feared that emancipation of black slaves would have more harmful social and economic consequences than the continuation of slavery. The French writer and traveler Alexis de Tocqueville, in ''Democracy in America'' (1835), expressed opposition to slavery while observing its effects on American society. He felt that a multiracial society without slavery was untenable, as he believed that prejudice against black people increased as they were granted more rights. Others, like James Henry Hammond argued that slavery was a "positive good" stating: "Such a class you must have, or you would not have that other class which leads progress, civilization, and refinement."
The Southern state governments wanted to keep a balance between the number of slave and free states to maintain a political balance of power in United States Congress, Congress. The new Territories of the United States, territories acquired from British Empire, Britain, French colonial empire, France, and Mexico were the subject of major political compromises. By 1850, the newly rich cotton-growing South was threatening to secede from the Union (American Civil War), Union, and tensions continued to rise. Many white Southern Christians, including church ministers, attempted to justify their support for slavery as modified by Christian paternalism. The largest denominations, the Baptist, Methodist, and Presbyterian churches, split over the slavery issue into regional organizations of the North and South.
 When Abraham Lincoln won the 1860 United States presidential election, 1860 election on a platform of halting the expansion of slavery, according to the 1860 United States Census, 1860 U.S. census, roughly 400,000 individuals, representing 8% of all U.S. families, owned nearly 4,000,000 slaves. One-third of Southern families owned slaves. The South was heavily invested in slavery. As such, upon Lincoln's election, seven states broke away to form the Confederate States of America. The first six states to secede held the greatest number of slaves in the South. Shortly after, over the issue of slavery, the United States erupted into an all out American Civil War, Civil War, with slavery legally ceasing as an institution following the war in December 1865.
When Abraham Lincoln won the 1860 United States presidential election, 1860 election on a platform of halting the expansion of slavery, according to the 1860 United States Census, 1860 U.S. census, roughly 400,000 individuals, representing 8% of all U.S. families, owned nearly 4,000,000 slaves. One-third of Southern families owned slaves. The South was heavily invested in slavery. As such, upon Lincoln's election, seven states broke away to form the Confederate States of America. The first six states to secede held the greatest number of slaves in the South. Shortly after, over the issue of slavery, the United States erupted into an all out American Civil War, Civil War, with slavery legally ceasing as an institution following the war in December 1865.
Asia
Slavery has existed all throughout Asia, and forms of slavery still exist today.=China
= Slavery has taken various forms throughout China's history. It was reportedly abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 law fully enacted in 1910, although the practice continued until at least 1949.
The Tang dynasty purchased Western slaves from the Radhanite Jews. Tang Chinese soldiers and pirates enslaved Koreans, Turks, Persians, Indonesians, and people from Inner Mongolia, central Asia, and northern India. The greatest source of slaves came from southern tribes, including Thais and aboriginals from the southern provinces of Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Guizhou. Malays, Khmers, Indians, and "black skinned" peoples (who were either Austronesian Negritos of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands, or Africans, or both) were also purchased as slaves in the Tang dynasty.
In the 17th century Qing Dynasty, there was a hereditarily servile people called ''Booi Aha'' (Manchu:booi niyalma; Chinese transliteration: 包衣阿哈), which is a Manchu word literally translated as "household person" and sometimes rendered as "nucai." The Manchu was establishing close personal and paternalist relationship between masters and their slaves, as Nurhachi said, "The Master should love the slaves and eat the same food as him". However, booi aha "did not correspond exactly to the Chinese category of "bond-servant slave" (Chinese:奴僕); instead, it was a relationship of personal dependency on a master which in theory guaranteed close personal relationships and equal treatment, even though many western scholars would directly translate "booi" as "bond-servant" (some of the "booi" even had their own servant).
Hui people, Chinese Muslim (Tungans) Sufis who were charged with practicing xiejiao (heterodox religion), were punished by exile to Xinjiang and being sold as a slave to other Muslims, such as the Sufi Baig, begs. Han Chinese who committed crimes such as those dealing with opium became slaves to the begs, this practice was administered by Qing law. Most Chinese in Altishahr were exile slaves to Turkestani Begs. While free Chinese merchants generally did not engage in relationships with East Turkestani women, some of the Chinese slaves belonging to begs, along with Green Standard soldiers, Bannermen, and Manchus, engaged in affairs with the East Turkestani women that were serious in nature.
Slavery has taken various forms throughout China's history. It was reportedly abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 law fully enacted in 1910, although the practice continued until at least 1949.
The Tang dynasty purchased Western slaves from the Radhanite Jews. Tang Chinese soldiers and pirates enslaved Koreans, Turks, Persians, Indonesians, and people from Inner Mongolia, central Asia, and northern India. The greatest source of slaves came from southern tribes, including Thais and aboriginals from the southern provinces of Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Guizhou. Malays, Khmers, Indians, and "black skinned" peoples (who were either Austronesian Negritos of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands, or Africans, or both) were also purchased as slaves in the Tang dynasty.
In the 17th century Qing Dynasty, there was a hereditarily servile people called ''Booi Aha'' (Manchu:booi niyalma; Chinese transliteration: 包衣阿哈), which is a Manchu word literally translated as "household person" and sometimes rendered as "nucai." The Manchu was establishing close personal and paternalist relationship between masters and their slaves, as Nurhachi said, "The Master should love the slaves and eat the same food as him". However, booi aha "did not correspond exactly to the Chinese category of "bond-servant slave" (Chinese:奴僕); instead, it was a relationship of personal dependency on a master which in theory guaranteed close personal relationships and equal treatment, even though many western scholars would directly translate "booi" as "bond-servant" (some of the "booi" even had their own servant).
Hui people, Chinese Muslim (Tungans) Sufis who were charged with practicing xiejiao (heterodox religion), were punished by exile to Xinjiang and being sold as a slave to other Muslims, such as the Sufi Baig, begs. Han Chinese who committed crimes such as those dealing with opium became slaves to the begs, this practice was administered by Qing law. Most Chinese in Altishahr were exile slaves to Turkestani Begs. While free Chinese merchants generally did not engage in relationships with East Turkestani women, some of the Chinese slaves belonging to begs, along with Green Standard soldiers, Bannermen, and Manchus, engaged in affairs with the East Turkestani women that were serious in nature.
=India
= Slavery in India was widespread by the 6th century BC, and perhaps even as far back as the Vedic period. Slavery intensified during the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim domination of northern India after the 11th-century. Slavery existed in Portuguese India after the 16th century. The Dutch, too, largely dealt in Abyssian slaves, known in India as Habshis or Sheedes. Arakan/Bengal, Malabar, and Coromandel Coast, Coromandel remained the largest sources of forced labour until the 1660s. Between 1626 and 1662, the Dutch exported on an average 150–400 slaves annually from the Arakan-Bengal coast. During the first 30 years of Batavia's existence, Indian and Arakanese slaves provided the main labour force of the Dutch East India Company, Asian headquarters. An increase in Coromandel slaves occurred during a famine following the revolt of the Nayaka Indian rulers of South India (Tanjavur, Senji, and Madurai) against Bijapur overlordship (1645) and the subsequent devastation of the Tanjavur countryside by the Bijapur army. Reportedly, more than 150,000 people were taken by the invading Deccani Muslim armies to Bijapur and Golconda. In 1646, 2,118 slaves were exported to Batavia, the overwhelming majority from southern Coromandel. Some slaves were also acquired further south at Tondi, Adirampatnam, and Kayalpatnam. Another increase in slaving took place between 1659 and 1661 from Tanjavur as a result of a series of successive Bijapuri raids. At Nagapatnam, Pulicat, and elsewhere, the company purchased 8,000–10,000 slaves, the bulk of whom were sent to Ceylon, while a small portion were exported to Batavia and Malacca. Finally, following a long drought in Madurai and southern Coromandel, in 1673, which intensified the prolonged Madurai-Maratha struggle over Tanjavur and punitive fiscal practices, thousands of people from Tanjavur, mostly children, were sold into slavery and exported by Asian traders from Nagapattinam to Aceh, Johor, and other slave markets. In September 1687, 665 slaves were exported by the English from Fort St. George, Madras. And, in 1694–96, when warfare once more ravaged South India, a total of 3,859 slaves were imported from Coromandel by private individuals into Ceylon. The volume of the total Dutch Indian Ocean slave trade has been estimated to be about 15–30% of the Atlantic slave trade, slightly smaller than the trans-Saharan slave trade, and one-and-a-half to three times the size of the Swahili and Red Sea coast and the Dutch West India Company slave trades. According to Sir Henry Bartle Frere (who sat on the Viceroy's Council), there were an estimated 8 or 9 million slaves in India in 1841. About 15% of the population of Malabar District, Malabar were slaves. Slavery was legally abolished in the possessions of the East India Company by the Indian Slavery Act, 1843.=Indochina
= The hill tribe people in Indochina were "hunted incessantly and carried off as slaves by the Siamese (Thai), the Anamites (Vietnamese), and the Cambodians". A Siamese military campaign in Laos in 1876 was described by a British observer as having been "transformed into slave-hunting raids on a large scale". The census, taken in 1879, showed that 6% of the population in the Monarchies of Malaysia, Malay sultanate of Perak were slaves. Enslaved people made up about two-thirds of the population in part of North Borneo in the 1880s.=Japan
= After Japan–Portugal relations#History, the Portuguese first made contact with Japan in 1543, slave trade developed in which Portuguese purchased Japanese as slaves in Japan and sold them to various locations overseas, including Portugal, throughout the 16th and 17th centuries. Many documents mention the slave trade along with protests against the enslavement of Japanese. Japanese slaves are believed to be the first of their nation to end up in Europe, and the Portuguese purchased numbers of Japanese slave girls to bring to Portugal for sexual purposes, as noted by the Church in 1555. Japanese slave women were even sold as concubines to Asian lascar and African crew members, along with their European counterparts serving on Portuguese ships trading in Japan, mentioned by Luis Cerqueira, a Portuguese Jesuit, in a 1598 document. Japanese slaves were brought by the Portuguese to Macau, where they were enslaved to Portuguese or became slaves to other slaves. Some Korean slaves were bought by the Portuguese and brought back to Portugal from Japan, where they had been among the tens of thousands of Korean prisoners of war transported to Japan during the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98). Historians pointed out that at the same time Hideyoshi expressed his indignation and outrage at the Portuguese trade in Japanese slaves, he was engaging in a mass slave trade of Korean prisoners of war in Japan. Fillippo Sassetti saw some Chinese and Japanese slaves in Lisbon among the large slave community in 1578, although most of the slaves were black. The Portuguese "highly regarded" Asian slaves from the East much more "than slaves from sub-Saharan Africa". The Portuguese attributed qualities like intelligence and industriousness to Chinese and Japanese slaves. King King Sebastian, Sebastian of Portugal feared rampant slavery was having a negative effect on Catholic proselytization, so he commanded that it be banned in 1571. Hideyoshi was so disgusted that his own Japanese people were being sold ''en masse'' into slavery on Kyushu, that he wrote a letter to Jesuit Vice-Provincial Gaspar Coelho on July 24, 1587, to demand the Portuguese, Siamese (Thai), and Cambodians stop purchasing and enslaving Japanese and return Japanese slaves who ended up as far as India. Hideyoshi blamed the Portuguese and Jesuits for this slave trade and banned Christian proselytizing as a result. In 1595, a law was passed by Portugal banning the selling and buying of Chinese and Japanese slaves.=Korea
= During the Joseon period, the nobi population could fluctuate up to about one-third of the population, but on average the nobi made up about 10% of the total population. The nobi system declined beginning in the 18th century. Since the outset of the Joseon dynasty and especially beginning in the 17th century, there was harsh criticism among prominent thinkers in Korea about the nobi system. Even within the Joseon government, there were indications of a shift in attitude toward the nobi. Yeongjo of Joseon, King Yeongjo implemented a policy of gradual emancipation in 1775, and he and his successor Jeongjo of Joseon, King Jeongjo made many proposals and developments that lessened the burden on nobi, which led to the emancipation of the vast majority of government nobi in 1801. In addition, population growth, numerous escaped slaves, growing commercialization of agriculture, and the rise of the independent small farmer class contributed to the decline in the number of nobi to about 1.5% of the total population by 1858. The hereditary nobi system was officially abolished around 1886–87, and the rest of the nobi system was abolished with the Gabo Reform of 1894. However, slavery did not completely disappear in Korea until 1930, during Imperial Japanese rule.
During the Korea under Japanese rule, Imperial Japanese occupation of Korea around World War II, some Koreans were used in forced labour by the Imperial Japanese, in conditions which have been compared to slavery. These included women forced into sexual slavery by the Imperial Japanese Army before and during World War II, known as "comfort women".
During the Joseon period, the nobi population could fluctuate up to about one-third of the population, but on average the nobi made up about 10% of the total population. The nobi system declined beginning in the 18th century. Since the outset of the Joseon dynasty and especially beginning in the 17th century, there was harsh criticism among prominent thinkers in Korea about the nobi system. Even within the Joseon government, there were indications of a shift in attitude toward the nobi. Yeongjo of Joseon, King Yeongjo implemented a policy of gradual emancipation in 1775, and he and his successor Jeongjo of Joseon, King Jeongjo made many proposals and developments that lessened the burden on nobi, which led to the emancipation of the vast majority of government nobi in 1801. In addition, population growth, numerous escaped slaves, growing commercialization of agriculture, and the rise of the independent small farmer class contributed to the decline in the number of nobi to about 1.5% of the total population by 1858. The hereditary nobi system was officially abolished around 1886–87, and the rest of the nobi system was abolished with the Gabo Reform of 1894. However, slavery did not completely disappear in Korea until 1930, during Imperial Japanese rule.
During the Korea under Japanese rule, Imperial Japanese occupation of Korea around World War II, some Koreans were used in forced labour by the Imperial Japanese, in conditions which have been compared to slavery. These included women forced into sexual slavery by the Imperial Japanese Army before and during World War II, known as "comfort women".
Oceania
Slaves (''he mōkai'') had a recognised social role in traditional Māori people, Māori society in New Zealand. Blackbirding occurred on islands in the Pacific Ocean and Australia, especially in the 19th century.Ottoman Empire and Black Sea
In Constantinople, about one-fifth of the population consisted of slaves. The city was a major centre of the slave trade in the 15th and later centuries. Slaves were provided by Tatar raids on Slavic villages but also by conquest and the suppression of rebellions, in the aftermath of which entire populations were sometimes enslaved and sold across the Empire, reducing the risk of future rebellion. The Ottomans also purchased slaves from traders who brought slaves into the Empire from Europe and Africa. It has been estimated that some 200,000 slaves – mainly Circassians – were imported into the Ottoman Empire between 1800 and 1909. As late as 1908, women slaves were still sold in the Ottoman Empire. Until the late 18th century, the Crimean Khanate (a Muslim Tatar state) maintained a massive slave trade with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East. The slaves were captured in southern Russia, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland-Lithuania, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Circassia by Tatars, Tatar horsemen and sold in the Crimean port of Feodosiya, Kaffa. About 2 million mostly Christian slaves were exported over the 16th and 17th centuries until the Crimean Khanate was destroyed by the Russian Empire in 1783. A slave market for captured Russian and Persian people, Persian slaves was centred in the Central Asian khanate of Khiva. In the early 1840s, the population of the Uzbek states of Emirate of Bukhara, Bukhara and Khiva included about 900,000 slaves.
A slave market for captured Russian and Persian people, Persian slaves was centred in the Central Asian khanate of Khiva. In the early 1840s, the population of the Uzbek states of Emirate of Bukhara, Bukhara and Khiva included about 900,000 slaves.
Late modern period
United States In 1865, the United States ratified the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 13th Amendment to the United States Constitution, which banned slavery and involuntary servitude "except as punishment for a crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted," providing a legal basis for slavery, now referred to as penal labor, to continue in the country. This led to the system of convict leasing, which affected primarily African Americans. The Prison Policy Initiative, an American criminal justice think tank, cites the 2020 US prison population as 2.3 million, and nearly all able-bodied inmates work in some fashion. In Texas, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, Alabama and Arkansas, prisoners are not paid at all for their work. In other states, prisoners are paid between $0.12 and $1.15 per hour. Federal Prison Industries paid inmates an average of $0.90 per hour in 2017. Inmates who refuse to work may be indefinitely remanded into solitary confinement, or have family visitation revoked. From 2010 to 2015 and 2016 U.S. prison strike, again in 2016 and 2018 U.S. prison strike, in 2018, some prisoners in the US Strike action, refused to work, protesting for better pay, better conditions, and for the end of forced labor. Strike leaders were punished with indefinite solitary confinement. Forced prison labor occurs in both government-run prisons and Private prisons in the United States, private prisons. CoreCivic and GEO Group constitute half the market share of private prisons, and they made a combined revenue of $3.5 billion in 2015. The value of all labor by inmates in the United States is estimated to be in the billions. In California, 2,500 incarcerated workers fought wildfires for only $1 per hour through the CDCR's California fire camps, Conservation Camp Program, which saves the state as much as $100 million a year.Soviet Union
 Between 1930 and 1960, the Soviet Union created a system of, according to Anne Applebaum and the "perspective of the Moscow Kremlin, Kremlin", slave labor camps called the ''Gulag'' (russian: ГУЛаг, GULag).
Prisoners in these camps were worked to death by a combination of extreme production quotas, physical and psychological brutality, hunger, lack of medical care, and the harsh environment. Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, who survived eight years of Gulag incarceration, provided firsthand testimony about the camps with the publication of ''The Gulag Archipelago'', after which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature. Fatality rate was as high as 80% during the first months in many camps. Hundreds of thousands of people, possibly millions, died as a direct result of forced labour under the Soviets.
Golfo Alexopoulos suggests comparing labor in the Gulag with ''"other forms of slave labor"'' and notes its ''"violence of human exploitation"'' in ''Illness and Inhumanity in Stalin's Gulag'':
Between 1930 and 1960, the Soviet Union created a system of, according to Anne Applebaum and the "perspective of the Moscow Kremlin, Kremlin", slave labor camps called the ''Gulag'' (russian: ГУЛаг, GULag).
Prisoners in these camps were worked to death by a combination of extreme production quotas, physical and psychological brutality, hunger, lack of medical care, and the harsh environment. Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, who survived eight years of Gulag incarceration, provided firsthand testimony about the camps with the publication of ''The Gulag Archipelago'', after which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature. Fatality rate was as high as 80% during the first months in many camps. Hundreds of thousands of people, possibly millions, died as a direct result of forced labour under the Soviets.
Golfo Alexopoulos suggests comparing labor in the Gulag with ''"other forms of slave labor"'' and notes its ''"violence of human exploitation"'' in ''Illness and Inhumanity in Stalin's Gulag'':
Stalin's Gulag was, in many ways, less a concentration camp than a forced labor camp and less a prison system than a system of slavery. The image of the slave appears often in Gulag memoir literature. As Varlam Shalamov wrote: ''"Hungry and exhausted, we leaned into a horse collar, raising blood blisters on our chests and pulling a stone-filled cart up the slanted mine floor. The collar was the same device used long ago by the ancient Egyptians."'' Thoughtful and rigorous historical comparisons of Soviet forced labor and other forms of slave labor would be worthy of scholarly attention, in my view. For as in the case of global slavery, the Gulag found legitimacy in an elaborate narrative of difference that involved the presumption of dangerousness and guilt. This ideology of difference and the violence of human exploitation have left lasting legacies in contemporary Russia.Historian Anne Applebaum writes in the introduction of her book that the word ''GULAG'' has come to represent ''"the system of Soviet slave labor itself, in all its forms and varieties"'':
The word ''"GULAG"'' is an acronym for ''Glavnoe Upravlenie Lagerei'', or Main Camp Administration, the institution which ran the Soviet camps. But over time, the word has also come to signify the system of Soviet slave labor itself, in all its forms and varieties: labor camps, punishment camps, criminal and political camps, women's camps, children's camps, transit camps. Even more broadly, "Gulag" has come to mean the Soviet repressive system itself, the set of procedures that Alexander Solzhenitsyn once called "our meat grinder": the arrests, the interrogations, the transport in unheated cattle cars, the forced labor, the destruction of families, the years spent in exile, the early and unnecessary deaths.Applebaum's introduction has been criticized by Gulag researcher Wilson Bell, stating that her book "is, ''aside from the introduction'', a well-done overview of the Gulag, but it did not offer an interpretative framework much beyond Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, Solzhenitsyn's paradigms".
Nazi Germany
 During the Second World War, Forced labour under German rule during World War II, Nazi Germany effectively enslaved about 12 million people, both those considered undesirable and citizens of conquered countries, with the avowed intention of treating these ''Untermenschen'' (sub-humans) as a permanent slave-class of inferior beings who could be worked until they died, and who possessed neither the rights nor the legal status of members of the Aryan race.
Besides Jews, the harshest deportation and forced labour policies were applied to the populations of Belarus, Ukraine, and Russia. By the end of the war, half of Belarus' population had been killed or deported.
During the Second World War, Forced labour under German rule during World War II, Nazi Germany effectively enslaved about 12 million people, both those considered undesirable and citizens of conquered countries, with the avowed intention of treating these ''Untermenschen'' (sub-humans) as a permanent slave-class of inferior beings who could be worked until they died, and who possessed neither the rights nor the legal status of members of the Aryan race.
Besides Jews, the harshest deportation and forced labour policies were applied to the populations of Belarus, Ukraine, and Russia. By the end of the war, half of Belarus' population had been killed or deported.
Contemporary slavery
 Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today is estimated as between 12 million and 29.8 million. According to a broad definition of slavery, there were 27 million people in slavery in 1999, spread all over the world. In 2005, the International Labour Organization provided an estimate of 12.3 million forced labourers. Siddharth Kara has also provided an estimate of 28.4 million slaves at the end of 2006 divided into three categories: bonded labour/
Even though slavery is now outlawed in every country, the number of slaves today is estimated as between 12 million and 29.8 million. According to a broad definition of slavery, there were 27 million people in slavery in 1999, spread all over the world. In 2005, the International Labour Organization provided an estimate of 12.3 million forced labourers. Siddharth Kara has also provided an estimate of 28.4 million slaves at the end of 2006 divided into three categories: bonded labour/ According to a 2003 report by
According to a 2003 report by Distribution
In June 2013, United States Department of State, U.S. State Department released a report on slavery. It placed Slavery in Russia, Russia, Laogai, China, and Uzbekistan in the worst offenders category. Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Slavery in Sudan, Sudan, Syria, and Zimbabwe were at the lowest level. The list also included Algeria, Libya, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait among a total of 21 countries. In Kuwait, there are more than 600,000 migrant domestic workers who are vulnerable to forced labor and legally tied to their employers, who often illegally take their passports. In 2019, online slave markets on apps such as Instagram were uncovered. In the preparations for the 2022 FIFA World Cup, 2022 World Cup in Qatar, thousands of Nepalese, the largest group of labourers, faced slavery in the form of denial of wages, confiscation of documents, and inability to leave the workplace. In 2016, the United Nations gave Qatar 12 months to end migrant worker slavery or face investigation. The Walk Free Foundation reported in 2018 that slavery in wealthy Western societies is much more prevalent than previously known, in particular the United States and Great Britain, which have 403,000 (one in 800) and 136,000 slaves respectively. Andrew Forrest, founder of the organization, said that "The United States is one of the most advanced countries in the world yet has more than 400,000 modern slaves working under forced labour conditions." An estimated 40.3 million are enslaved globally, with North Korea having the most slaves at 2.6 million (one in 10). Of the estimated 40.3 million people in contemporary slavery, 71% are women and 29% are men. The report found of the 40.3 million in modern slavery, 15.4 million are in Forced marriage, forced marriages and 24.9 million are in Forced labour, forced labor. The foundation defines contemporary slavery as "situations of exploitation that a person cannot refuse or leave because of threats, violence, coercion, abuse of power, or deception."China
The Chinese government has a history of imprisoning citizens for political reasons. Article 73 of China's Criminal procedure, Criminal Procedure Law was adopted in 2012 and allow the authorities to detain people for reasons of "state security" or "terrorism". In this regard, detainees can be held for as long as six months in "designated locations" such as secret prisons. In March 2020, the Chinese government was found to be using the Uyghurs, Uyghur minority for forced labour, inside sweat shops. According to a report published then by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI), no fewer than around 80,000 Uyghurs were Uyghur genocide, forcibly removed from the region of Xinjiang and used for forced labour in at least twenty-seven corporate factories. According to the Business and Human Rights resource center, corporations such as Abercrombie & Fitch, Adidas, Amazon (company), Amazon, Apple Inc., Apple, BMW, Fila (company), Fila, Gap Inc., Gap, H&M, Inditex, Marks & Spencer, Nike, Inc., Nike, The North Face, North Face, Puma (brand), Puma, PVH (company), PVH, Samsung, and Uniqlo, UNIQLO each have each sourced products from these factories prior to the publication of the ASPI report.Libya
During the Second Libyan Civil War, Libyans started capturing Slavery in Libya, Sub-Saharan African migrants trying to get to Europe through Libya and selling them on slave markets or holding them hostage for ransom Women are often raped, used as sex slaves, or sold to brothels. Child migrants suffer from abuse and child rape in Libya.Mauritania
In Slavery in Mauritania, Mauritania, the last country to abolish slavery (in 1981), it is estimated that 20% of its 3 million population, are enslaved as bonded labourers. Slavery in Mauritania was criminalized in August 2007. However, although slavery, as a practice, was legally banned in 1981, it was not a crime to own a slave until 2007. Although many slaves have escaped or have been freed since 2007, , only one slave owner had been sentenced to serve time in prison.North Korea
North Korea's human rights record is often considered to be the worst in the world and has been globally condemned, with the United Nations, the European Union and groups such asEconomics
While American slaves in 1809 were sold for around $40,000 (in inflation adjusted dollars), a slave nowadays can be bought for just $90, making replacement more economical than providing long-term care. Slavery is a multibillion-dollar industry with estimates of up to $35 billion generated annually.Trafficking
 Victims of
Victims of Abolitionism
Slavery has existed, in one form or another, throughout recorded human history – as have, in various periods, movements to free large or distinct groups of slaves.In antiquity
 Ashoka, who ruled the Maurya Empire in the Indian subcontinent from 269 to 232 BCE, abolished the slave trade but not slavery. The Qin dynasty, which ruled China from 221 to 206 BC, abolished slavery and discouraged serfdom. However, many of its laws were overturned when the dynasty was overthrown. Slavery was again abolished by Wang Mang in China in 17 CE but was reinstituted after his assassination.
Ashoka, who ruled the Maurya Empire in the Indian subcontinent from 269 to 232 BCE, abolished the slave trade but not slavery. The Qin dynasty, which ruled China from 221 to 206 BC, abolished slavery and discouraged serfdom. However, many of its laws were overturned when the dynasty was overthrown. Slavery was again abolished by Wang Mang in China in 17 CE but was reinstituted after his assassination.
Americas
The Spanish colonization of the Americas sparked a discussion about the right to enslave Native Americans. A prominent critic of slavery in the Spanish New World colonies was the Spanish missionary and bishop, Bartolomé de las Casas, who was "the first to expose the oppression of indigenous peoples by Europeans in the Americas and to call for the abolition of slavery there." One of the first protests against slavery came from German and Dutch Religious Society of Friends, Quakers in Pennsylvania in 1688. In 1777, Vermont, Vermont Republic, at the time an independent nation, History of slavery in Vermont, became the first portion of what would become the United States to abolish slavery. In the United States, all of the northern states had abolished slavery by 1804, with New Jersey being the last to act. Abolitionist pressure produced a series of small steps towards emancipation. After the Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves went into effect on January 1, 1808, the importation of slaves into the United States was prohibited, but not the Slavery in the United States#Internal slave trade, internal slave trade, nor involvement in the international slave trade externally. Legal slavery persisted outside the northern states; most of those slaves already in the U.S. were Emancipation Proclamation, legally emancipated only in 1863. Many American abolitionists took an active role in opposing slavery by supporting the Underground Railroad. Violent clashes between anti-slavery and pro-slavery Americans included Bleeding Kansas, a series of political and armed disputes in 1854–1861 as to whether Kansas would join the United States as a Slave and free states, slave or free state. By 1860, the total number of slaves reached almost four million, and the American Civil War, beginning in 1861, led to the end of slavery in the United States. In 1863, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which freed slaves held in the Confederate States; the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, 13th Amendment to the U. S. Constitution prohibited most forms of slavery throughout the country. Many of the freed slaves became sharecroppers and indentured servants. In this manner, some became tied to the very parcel of land into which they had been born a slave having little freedom or economic opportunity because of Jim Crow laws which perpetuated discrimination, limited education, promoted persecution without due process and resulted in continued poverty. Fear of reprisals such as unjust incarcerations and lynchings deterred upward mobility further.

Europe
France abolished slavery in 1794 during the Revolution, but it was restored in 1802 under Napoleon. It has been asserted that, before the Revolution, slavery was illegal in metropolitan France (as opposed to its colonies), but this has been refuted. One of the most significant milestones in the campaign to abolish slavery throughout the world occurred in England in 1772, with British Judge William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, Lord Mansfield, whose opinion in Somersett's Case was widely taken to have held that slavery was illegal in England. This judgement also laid down the principle that slavery contracted in other jurisdictions could not be enforced in England. Sons of Africa was a late 18th-century British group that campaigned to end slavery. Its members were Africans in London, freed slaves who included Ottobah Cugoano, Olaudah Equiano and other leading members of London's black community. It was closely connected to the Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade, a non-denominational group founded in 1787, whose members included Thomas Clarkson. British Member of Parliament William Wilberforce led the anti-slavery movement in the United Kingdom, although the groundwork was an anti-slavery essay by Clarkson. Wilberforce was urged by his close friend, Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger, to make the issue his own and was also given support by reformed Evangelical John Newton. The Slave Trade Act 1807, Slave Trade Act was passed by the British Parliament on March 25, 1807, making the slave trade illegal throughout the British Empire, Wilberforce also campaigned for abolition of slavery in the British Empire, which he lived to see in the Slavery Abolition Act 1833. After the 1807 act abolishing the slave trade was passed, these campaigners switched to Blockade of Africa, encouraging other countries to follow suit, notably France and the British colonies. Between 1808 and 1860, the British West Africa Squadron seized approximately 1,600 slave ships and freed 150,000 Africans who were aboard. Action was also taken against African leaders who refused to agree to British treaties to outlaw the trade, for example against "the usurping King of Lagos", deposed in 1851. Anti-slavery treaties were signed with over 50 African rulers.Worldwide
In 1839, the world's oldest international human rights organization, Anti-Slavery International, was formed in Britain by Joseph Sturge, which campaigned to outlaw slavery in other countries. There were celebrations in 2007 to commemorate the 200th anniversary of the abolition of the slave trade in the United Kingdom through the work of the British Anti-Slavery International, Anti-Slavery Society. In the 1860s, David Livingstone's reports of atrocities within the Arab slave trade in Africa stirred up the interest of the British public, reviving the flagging abolitionist movement. The Royal Navy throughout the 1870s attempted to suppress "this abominable Eastern trade", at Zanzibar in particular. In 1905, the French abolished indigenous slavery in most of French West Africa. On December 10, 1948, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which declared freedom from slavery is an internationally recognized human rights, human right. Article 4 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states: In 2014, for the first time in history, major leaders of many religions, Buddhist, Hindu, Christian, Jewish, and Muslim met to sign a shared commitment against modern-day slavery; the declaration they signed calls for the elimination of slavery and human trafficking by 2020. The signatories were: Pope Francis, Mata Amritanandamayi, Mātā Amṛtānandamayī, Bhikkhuni Thich Nu Chân Không (representing Zen Master Thích Nhất Hạnh), Datuk K Sri Dhammaratana, Chief High Priest of Malaysia, Rabbi Abraham Skorka, Rabbi David Rosen, Abbas Abdalla Abbas Soliman, Undersecretary of State of Al Azhar Alsharif (representing Mohamed Ahmed El-Tayeb, Grand Imam of Al-Azhar), Grand Ayatollah Mohammad Taqi al-Modarresi, Sheikh Naziyah Razzaq Jaafar, Special advisor of Grand Ayatollah (representing Grand Ayatollah Sheikh Basheer Hussain al Najafi), Sheikh Omar Abboud, Justin Welby, Archbishop of Canterbury, and Metropolitan Emmanuel of France (representing Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew.) Groups such as the American Anti-Slavery Group, Anti-Slavery International, Free the Slaves, the Anti-Slavery Society, and the Norwegian Anti-Slavery Society continue to campaign to eliminate slavery.Apologies
On May 21, 2001, the National Assembly of France passed the Christiane Taubira, Taubira law, recognizing slavery as a crime against humanity. Apologies on behalf of African nations, for their role in trading their countrymen into slavery, remain an open issue since slavery was practiced in Africa even before the first Europeans arrived and the Atlantic slave trade was performed with a high degree of involvement of several African societies. The black slave market was supplied by well-established slave trade networks controlled by local African societies and individuals.There is adequate evidence citing case after case of African control of segments of the trade. Several African nations such as the Calabar and other southern parts of Nigeria had economies depended solely on the trade. African peoples such as the Imbangala of Angola and the Nyamwezi of Tanzania would serve as middlemen or roving bands warring with other African nations to capture Africans for Europeans.Several historians have made important contributions to the global understanding of the African side of the Atlantic slave trade. By arguing that African merchants determined the assemblage of trade goods accepted in exchange for slaves, many historians argue for African agency and ultimately a shared responsibility for the slave trade. In 1999, President Mathieu Kérékou of Benin issued a national apology for the central role Africans played in the Atlantic slave trade. Luc Gnacadja, minister of environment and housing for Benin, later said: "The slave trade is a shame, and we do repent for it." Researchers estimate that 3 million slaves were exported out of the Slave Coast of West Africa, Slave Coast bordering the Bight of Benin. President Jerry Rawlings of Ghana also apologized for his country's involvement in the slave trade. The issue of an apology is linked to reparations for slavery and is still being pursued by entities across the world. For example, the Jamaican Reparations Movement approved its declaration and action plan. In 2007, British Prime Minister Tony Blair made a formal apology for Great Britain's involvement in slavery. On February 25, 2007, the Virginia, Commonwealth of Virginia resolved to 'profoundly regret' and apologize for its role in the institution of slavery. Unique and the first of its kind in the U.S., the apology was unanimously passed in both Houses as Virginia approached the 400th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown. On August 24, 2007, Mayor of London Ken Livingstone issued a public apology for London's role in Atlantic slave trade, which took place at an event commemorating the 200th anniversary of the British slave trade's abolition. In his speech, Livingstone described the slave trade as "the racial murder of not just those who were transported but generations of enslaved African men, women and children. To justify this murder and torture black people had to be declared inferior or not human... We live with the consequences today." City officials in Liverpool, which was a large slave trading port, apologized in 1999. On July 30, 2008, the United States House of Representatives passed a resolution apologizing for American slavery and subsequent discriminatory laws. In June 2009, the U.S. Senate passed a resolution apologizing to African-Americans for the "fundamental injustice, cruelty, brutality, and inhumanity of slavery". The news was welcomed by President Barack Obama, the nation's first president of African descent. Some of President Obama's ancestors may have been slave owners. In 2010, Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi apologized for Arab involvement in the slave trade, saying: "I regret the behavior of the Arabs... They brought African children to North Africa, they made them slaves, they sold them like animals, and they took them as slaves and traded them in a shameful way."
Reparations
There have been movements to achieve reparations for those formerly held as slaves or for their descendants. Claims for reparations for being held in slavery are handled as a Private law, civil law matter in almost every country. This is often decried as a serious problem, since former slaves' relatives lack of money means they often have limited access to a potentially expensive and futile Service of process, legal process. Mandatory systems of fines and reparations paid to an as yet undetermined group of claimants from fines, paid by unspecified parties, and collected by authorities have been proposed by advocates to alleviate this "civil court problem." Since in almost all cases there are no living ex-slaves or living ex-slave owners these movements have gained little traction. In nearly all cases the judicial system has ruled that the statute of limitations on these possible claims has long since expired.Media
 Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world. The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as ''The Birth of a Nation'' (1915) and ''Gone with the Wind (film), Gone with the Wind'' (1939) became controversial because they gave a favourable depiction. In 1940 ''Santa Fe Trail (film), The Santa Fe Trail'' gave a liberal but ambiguous interpretation of John Brown (abolitionist), John Brown's attacks on slavery. ''Song of the South'' gave a favorable outlook on slavery in the United States in 1946.
The Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s made defiant slaves into heroes. The question of slavery in American memory necessarily involves its depictions in feature films.
Most Hollywood films used American settings, although Spartacus (film), ''Spartacus'' (1960), dealt with an actual revolt in the Roman Empire known as the Third Servile War. The revolt failed, and all the rebels were executed, but their spirit lived on according to the film. ''Spartacus'' stays surprisingly close to the historical record.
''The Last Supper (1976 film), The Last Supper'' (''La última cena'' in Spanish) was a 1976 film directed by Cuban Tomás Gutiérrez Alea about the teaching of Christianity to slaves in Cuba, and emphasizes the role of ritual and revolt. ''Burn!'' takes place on the imaginary Portuguese island of Queimada (where the locals speak Spanish) and it merges historical events that took place in Brazil, Cuba, Santo Domingo, Jamaica, and elsewhere.
Historians agree that films have largely shaped historical memories, but they debate issues of accuracy, plausibility, moralism, sensationalism, how facts are stretched in search of broader truths, and suitability for the classroom. Berlin argues that critics complain if the treatment emphasizes historical brutality, or if it glosses over the harshness to highlight the emotional impact of slavery.
Film has been the most influential medium in the presentation of the history of slavery to the general public around the world. The American film industry has had a complex relationship with slavery and until recent decades often avoided the topic. Films such as ''The Birth of a Nation'' (1915) and ''Gone with the Wind (film), Gone with the Wind'' (1939) became controversial because they gave a favourable depiction. In 1940 ''Santa Fe Trail (film), The Santa Fe Trail'' gave a liberal but ambiguous interpretation of John Brown (abolitionist), John Brown's attacks on slavery. ''Song of the South'' gave a favorable outlook on slavery in the United States in 1946.
The Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s made defiant slaves into heroes. The question of slavery in American memory necessarily involves its depictions in feature films.
Most Hollywood films used American settings, although Spartacus (film), ''Spartacus'' (1960), dealt with an actual revolt in the Roman Empire known as the Third Servile War. The revolt failed, and all the rebels were executed, but their spirit lived on according to the film. ''Spartacus'' stays surprisingly close to the historical record.
''The Last Supper (1976 film), The Last Supper'' (''La última cena'' in Spanish) was a 1976 film directed by Cuban Tomás Gutiérrez Alea about the teaching of Christianity to slaves in Cuba, and emphasizes the role of ritual and revolt. ''Burn!'' takes place on the imaginary Portuguese island of Queimada (where the locals speak Spanish) and it merges historical events that took place in Brazil, Cuba, Santo Domingo, Jamaica, and elsewhere.
Historians agree that films have largely shaped historical memories, but they debate issues of accuracy, plausibility, moralism, sensationalism, how facts are stretched in search of broader truths, and suitability for the classroom. Berlin argues that critics complain if the treatment emphasizes historical brutality, or if it glosses over the harshness to highlight the emotional impact of slavery.
See also
* Bodmin manumissions, the names and details of slaves freed in Medieval Bodmin * International Day for the Abolition of Slavery * International Slavery Museum * Involuntary servitude * List of slaves * List of slave owners * Mukataba * Slave rebellion * Subjugate * Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery * Wilberforce Institute for the Study of Slavery and EmancipationReferences
Bibliography
Surveys and reference
; Books * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ; Journal articles and reviews * * * * * * * *United States
* * * * * * * * * * * *online review
* * * * * * * *
Slavery in the modern era
* * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * *External links
Historical
Slavery in America: A Resource Guide
at the Library of Congress
Digital Library on American Slavery
at University of North Carolina at Greensboro *
The West African Squadron and slave trade
history of the Victorian Royal Navy
Slavery and the Making of America
at WNET *
Slavery archival sources
University of London, Senate House Library
Mémoire St Barth (archives & history of slavery, slave trade and their abolition)
Comité de Liaison et d'Application des Sources Historiques 2010
Archives of the Middelburgsche Commercie Compagnie (MCC), 1720-1889 'Trade Company of Middelburg'
Inventory of the archives of the Dutch slave trade across the Atlantic
Slave Ships and the Middle Passage
at ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
The Trans-Atlantic and Intra-American slave trade databases
at Emory University
Modern
2018 Global Slavery Index
at the Walk Free Foundation
What is Modern Slavery?
Office To Monitor And Combat Trafficking In Persons, U.S. Department of State. {{Authority control Slavery, Business ethics Employment Human rights abuses Labor Social classes