Skåne Market on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Scania market (Danish ''Skånemarkedet'', Swedish ''Skånemarknaden'') was a major
The Great Herring Market in Scania"
. Brill, , pp. 39–44. The Scania Market continued to be an important trade center for 250 years and was a cornerstone of the
. Terra Scaniae, 2007. In Swedish. Retrieved 27 August 2008.
 The basis for the market's popularity was the rich herring
The basis for the market's popularity was the rich herring
 The fishing trade was closely regulated by the Danish crown, with special rules regarding issues such as the fishing nets' mesh size, enforced by special bailiffs who policed the trade. Royal governors were installed in castles at Skanør and Falsterbo to collect customs and act as judicial and administrative leaders.
Apart from the fishermen and the local fish traders, merchants from Lübeck and other Hanseatic towns, as well as from
The fishing trade was closely regulated by the Danish crown, with special rules regarding issues such as the fishing nets' mesh size, enforced by special bailiffs who policed the trade. Royal governors were installed in castles at Skanør and Falsterbo to collect customs and act as judicial and administrative leaders.
Apart from the fishermen and the local fish traders, merchants from Lübeck and other Hanseatic towns, as well as from
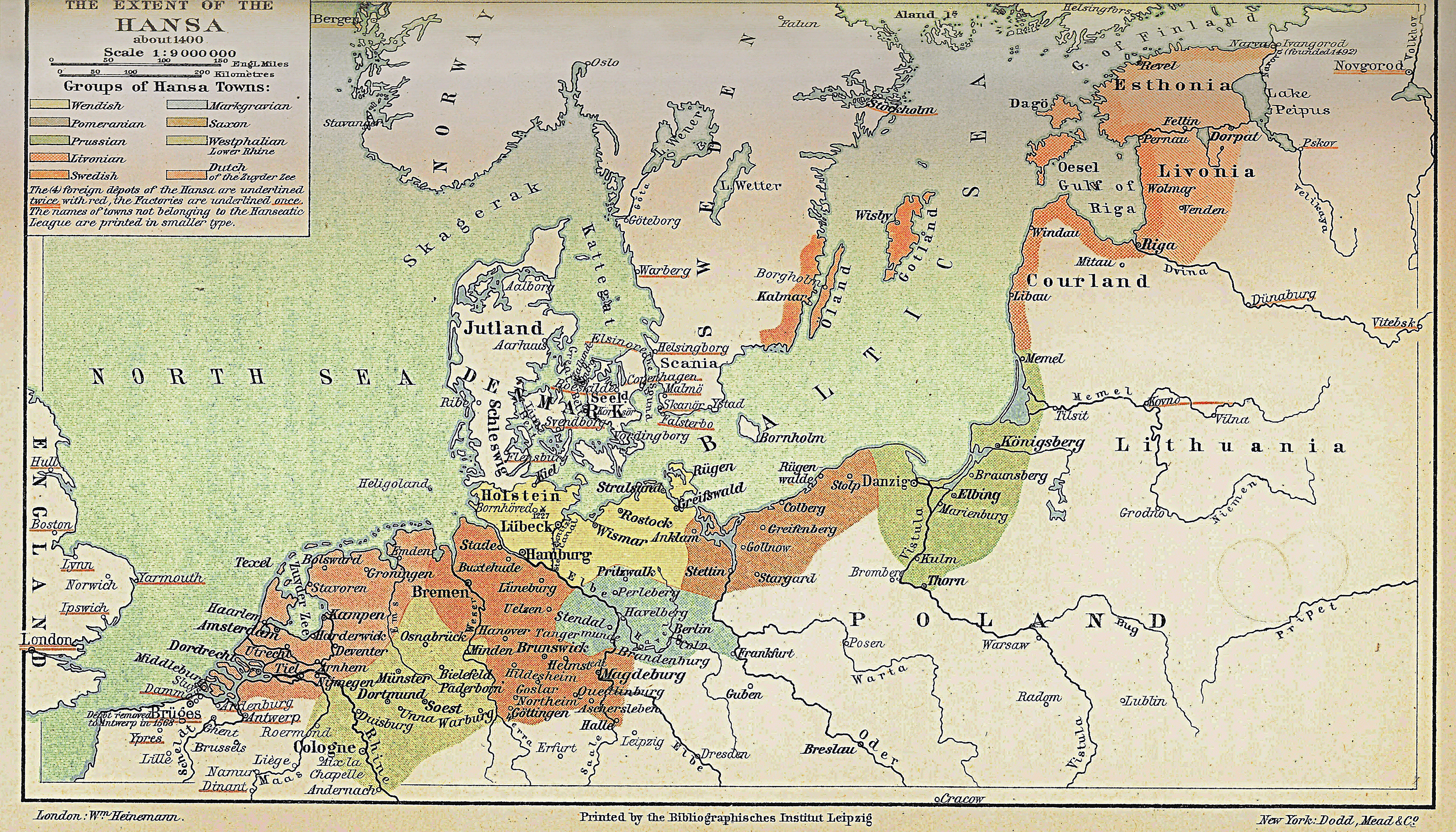 Most of the 14th century was characterized by strife and wars between Danish kings and the Hansa. According to a German view, the Danes got herring "for nothing from God"—only to sell it dearly. As opposed to
Most of the 14th century was characterized by strife and wars between Danish kings and the Hansa. According to a German view, the Danes got herring "for nothing from God"—only to sell it dearly. As opposed to
The German Hansa
Routledge, 1999. , p. 70. The Danish-Hanseatic War resulted in a Hanseatic victory. With the Treaty of Stralsund in 1370, a peace was settled that left the Hanseatic League in control of the fortifications at the Scania Market and along the rest of Öresund for 15 years.Pulsiano, Phillip and Kirsten Wolf (1993)
Medieval Scandinavia
Taylor & Francis, , p. 652. The abundance of herring around Scania abruptly ceased in the beginning of the 15th century and the region lost its importance as a trading place.
Scanian Market
- by Oresundstid {{DEFAULTSORT:Skane Market Trading posts of the Hanseatic League History of Lübeck Scania Fish markets Skanör med Falsterbo
fish market
A fish market is a marketplace for selling Fish as food, fish and fish products. It can be dedicated to wholesale trade between Fisherman, fishermen and fish merchants, or to the sale of seafood to individual consumers, or to both. Retail fish ma ...
for herring
Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the Order (biology), order Clupeiformes.
Herring often move in large Shoaling and schooling, schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate wate ...
which took place annually in Scania
Scania ( ), also known by its native name of Skåne (), is the southernmost of the historical provinces of Sweden, provinces () of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous w ...
during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. From around 1200, it became one of the most important events for trade around the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
and made Scania into a major distribution center for West-Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
an goods bound for eastern Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
.Etting, Vivian (2004). ''Queen Margrete I, 1353-1412, and the Founding of the Nordic Union'' (Chapter 5:The Great Herring Market in Scania"
. Brill, , pp. 39–44. The Scania Market continued to be an important trade center for 250 years and was a cornerstone of the
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
's wealth.
The fair took place from August 24 to October 9, mainly in locations between the two Scanian towns of Skanör
Skanör is a town in Vellinge Municipality and part of the conurbation Skanör med Falsterbo in southwestern Scania, Sweden. City facilities include hotels, restaurants, a harbour, a medieval church and an elementary school. A greenbelt calle ...
and Falsterbo
Falsterbo (, outdatedly ) is a town located at the south-western tip of Sweden in Vellinge Municipality in Skåne. Falsterbo is situated in the southern part of the Falsterbo peninsula. It is part of Skanör med Falsterbo, one of Sweden's histori ...
at the southern mouth of Öresund, with much of the connected industry spread out on the surrounding peninsula, but Køge
Køge (, older spelling ''Kjøge'') is a Danish seaport on the coast of Køge Bugt (''Bay of Køge'') 39 km southwest of Copenhagen. It is the principal town and seat of Køge Municipality, Region Sjælland (Zealand), Denmark. In 2025, the ...
, Dragør
Dragør () is the main town of Dragør Municipality, (Denmark), which includes the village of Store Magleby. The city hall and seat of the municipal council lies on Kirkevej 7 (postal code 2791 Dragør) in Store Magleby, which has enough space ...
, Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
, Malmö
Malmö is the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, third-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm and Gothenburg, and the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, sixth-largest city in Nordic countries, the Nordic region. Located on ...
, Helsingborg
Helsingborg (, , ), is a Urban areas in Sweden, city and the seat of Helsingborg Municipality, Scania County, Scania (Skåne), Sweden. It is the second-largest city in Scania (after Malmö) and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, ninth ...
, Simrishamn
Simrishamn is a Urban areas in Sweden, locality and the seat of Simrishamn Municipality, Skåne County, Sweden with 6,527 inhabitants in 2010. Despite its small population, Simrishamn is, for historical reasons, usually still referred to as a Stad ...
, Ystad
Ystad () is a town and the seat of Ystad Municipality, in Scania County, Sweden. Ystad had 18,350 inhabitants in 2010. The settlement dates from the 11th century and has become a busy ferryport, local administrative centre, and tourist attracti ...
, and Trelleborg
Trelleborg () is a town in Skåne County, Sweden, with 43,359 inhabitants as of 31 December 2015. It is the southernmost town in Sweden located some west from the Smygehuk, southernmost point of Sweden and the Scandinavian Peninsula. It is one ...
were also part of the Scania Market. Since the fishermen erected their trading booths and temporary shops close to the area where the herring was spawning
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is ...
, the exact locations of the Scania Market changed from year to year.Skånemarknaden. Terra Scaniae, 2007. In Swedish. Retrieved 27 August 2008.
Herring trade and salt import
 The basis for the market's popularity was the rich herring
The basis for the market's popularity was the rich herring fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
around the Falsterbo Peninsula. Legend tells that the herring fishery off the Scanian coast was so rich, that one could scoop up the fish with one's hands. After a visit to the region in 1364, the French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
crusader
Crusader or Crusaders may refer to:
Military
* Crusader, a participant in one of the Crusades
* Convair NB-36H Crusader, an experimental nuclear-powered bomber
* Crusader tank, a British cruiser tank of World War II
* Crusaders (guerrilla), a C ...
Philippe de Mezieres wrote: "Two months a year, that is in September and October, the herring travel from one sea to the other through the Sound, by order of God, in such large numbers that it is a great wonder, and so many pass through the sound in these months, that at several places one can cut them with a dagger."Qtd. in Etting, Vivian (2004). ''Queen Margrete I, 1353-1412, and the Founding of the Nordic Union''. Brill, , p. 39. Mezieres further went on to estimate that no less than 300,000 people were active in the trade during these months. As early as the 12th century the peninsula had become a centre for the herring trade; the Scanian name for the town Falsterbo
Falsterbo (, outdatedly ) is a town located at the south-western tip of Sweden in Vellinge Municipality in Skåne. Falsterbo is situated in the southern part of the Falsterbo peninsula. It is part of Skanör med Falsterbo, one of Sweden's histori ...
was ''Falsterbothe'', which meant "the booths for fish from Falster". The 13th-century German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
chronicler
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, ...
Arnold of Lübeck
Arnold of Lübeck (died 1211–1214) was a Benedictine abbot, a chronicler, the author of the '' Chronica Slavorum'' and advocate of the papal cause in the Hohenstaufen conflict. He was a monk at St. Ägidien monastery in Braunschweig, then from 11 ...
, author of Chronicon Slavorum
The ''Chronica Sclavorum'' or ''Chronicle of the Slavs'' is a medieval chronicle which recounts the pre-Christian culture and religion of the Polabian Slavs, written by Helmold ( – after 1177), a Saxon priest and historian. It describes event ...
, wrote that the Danes had wealth and an abundance of everything thanks to the yearly catches of herring at the Scanian coast. The laws of the city of Leiden
Leiden ( ; ; in English language, English and Archaism, archaic Dutch language, Dutch also Leyden) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Nethe ...
in the 15th century stated that all herring sellers selling herring other than from Scania, should warn their customers with a clear marking.
The demand for herring during this period was great; it was a fairly inexpensive source of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
for the populations around the Baltic during the winter and the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
demanded fasting
Fasting is the act of refraining from eating, and sometimes drinking. However, from a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (before "breakfast"), or to the metabolic sta ...
(from meat), in Christ
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Christianity, central figure of Christianity, the M ...
's following, in connection with Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, t ...
. Due to the large production and the great demand, the Scania Market became the most important North European market in the 14th century.
During the fishing season, the necessary salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
and barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden stave (wood), staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers ...
s for conservation came from Hanseatic Lüneburg
Lüneburg, officially the Hanseatic City of Lüneburg and also known in English as Lunenburg, is a town in the German Bundesland (Germany), state of Lower Saxony. It is located about southeast of another Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city, Hambur ...
and were provided by Hanseatic traders mainly from Lübeck
Lübeck (; or ; Latin: ), officially the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City of Lübeck (), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 220,000 inhabitants, it is the second-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and the second-larg ...
. Lübeck also, to some extent, provided the Scanians with an additional work force, so called "gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
-women" who cleaned the fish, ensuring a swift salting of the landed fish.
Danish taxation
 The fishing trade was closely regulated by the Danish crown, with special rules regarding issues such as the fishing nets' mesh size, enforced by special bailiffs who policed the trade. Royal governors were installed in castles at Skanør and Falsterbo to collect customs and act as judicial and administrative leaders.
Apart from the fishermen and the local fish traders, merchants from Lübeck and other Hanseatic towns, as well as from
The fishing trade was closely regulated by the Danish crown, with special rules regarding issues such as the fishing nets' mesh size, enforced by special bailiffs who policed the trade. Royal governors were installed in castles at Skanør and Falsterbo to collect customs and act as judicial and administrative leaders.
Apart from the fishermen and the local fish traders, merchants from Lübeck and other Hanseatic towns, as well as from England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, and Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, came to the herring market to buy and sell herring, but also to trade in other goods with the Scandinavian merchants, landowners and peasants. Traders arrived from Denmark, eastern Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, as well as the rest of the Baltic. A wide variety of goods were traded, among them horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s, butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of Churning (butter), churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 81% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black b ...
, grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
, and handicraft
A handicraft is a traditional main sector of craft making and applies to a wide range of creative and design activities that are related to making things with one's hands and skill, including work with textiles, moldable and rigid material ...
products from the North, Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, and Livonia
Livonia, known in earlier records as Livland, is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century, the name was extende ...
.
The fishing and the Scania Market yielded a large income to the Danish Crown, and made together with the Sound Toll the state virtually independent of tax
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax co ...
incomes for extended periods of time. A good fishing year in the 14th century could mean an export of 300,000 barrels of herring; and it is estimated that one third of the Danish king's income came from the Scania Market.
Strife between Denmark and the Hanseatic League
 Most of the 14th century was characterized by strife and wars between Danish kings and the Hansa. According to a German view, the Danes got herring "for nothing from God"—only to sell it dearly. As opposed to
Most of the 14th century was characterized by strife and wars between Danish kings and the Hansa. According to a German view, the Danes got herring "for nothing from God"—only to sell it dearly. As opposed to Stockholm
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately ...
and Bergen
Bergen (, ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, second-largest city in Norway after the capital Oslo.
By May 20 ...
, which had Scandinavia's largest Hanseatic colonies, the Danish towns of the Scania Market did not encourage large permanent settlements of Hansa merchants; most of the merchants arrived in the summer and went back home after the end of the market.
In 1367, the Hansa towns allied themselves with Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow. ...
, and Holstein
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider (river), Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost States of Germany, state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 8 ...
, and the Confederation of Cologne
The Confederation of Cologne () was a medieval military alliance formed to combat the Kingdom of Denmark. It was established on 19 November, 1367 by several Hanseatic cities and other towns from Holland, Zeeland and Zuiderzee.
Though originally o ...
went to war against Denmark and Norway.Dollinger, Phillipe et al. (1999)The German Hansa
Routledge, 1999. , p. 70. The Danish-Hanseatic War resulted in a Hanseatic victory. With the Treaty of Stralsund in 1370, a peace was settled that left the Hanseatic League in control of the fortifications at the Scania Market and along the rest of Öresund for 15 years.Pulsiano, Phillip and Kirsten Wolf (1993)
Medieval Scandinavia
Taylor & Francis, , p. 652. The abundance of herring around Scania abruptly ceased in the beginning of the 15th century and the region lost its importance as a trading place.
See also
*History of Scania
For hundreds of years up until the 18th century, the history of the province of Scania was marked by the struggle between the two Scandinavian kingdoms of Denmark and Sweden over the hegemony in the Baltic area.
Viking age
It was previously ...
* Old Salt Route
References
External links
Scanian Market
- by Oresundstid {{DEFAULTSORT:Skane Market Trading posts of the Hanseatic League History of Lübeck Scania Fish markets Skanör med Falsterbo