Skulls Rainbow Room on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The skull is a

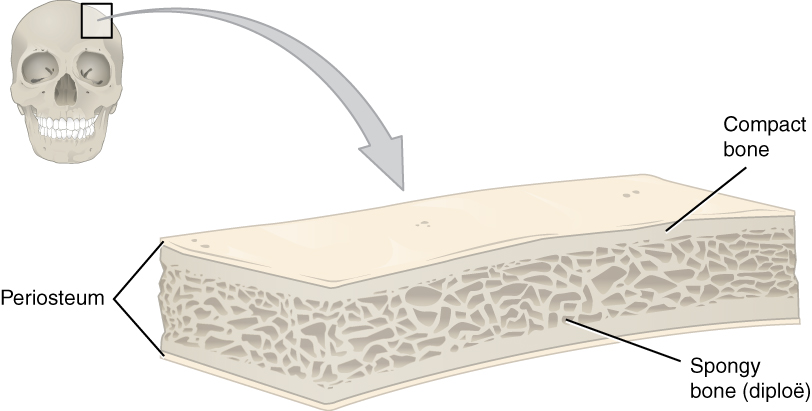

 The human skull is the bone structure that forms the head in the human skeleton. It supports the structures of the
The human skull is the bone structure that forms the head in the human skeleton. It supports the structures of the
 The skull also contains
The skull also contains


 The temporal fenestrae are anatomical features of the skulls of several types of amniotes, characterised by bilaterally symmetrical holes (fenestrae) in the temporal bone. Depending on the lineage of a given animal, two, one, or no pairs of temporal fenestrae may be present, above or below the
The temporal fenestrae are anatomical features of the skulls of several types of amniotes, characterised by bilaterally symmetrical holes (fenestrae) in the temporal bone. Depending on the lineage of a given animal, two, one, or no pairs of temporal fenestrae may be present, above or below the
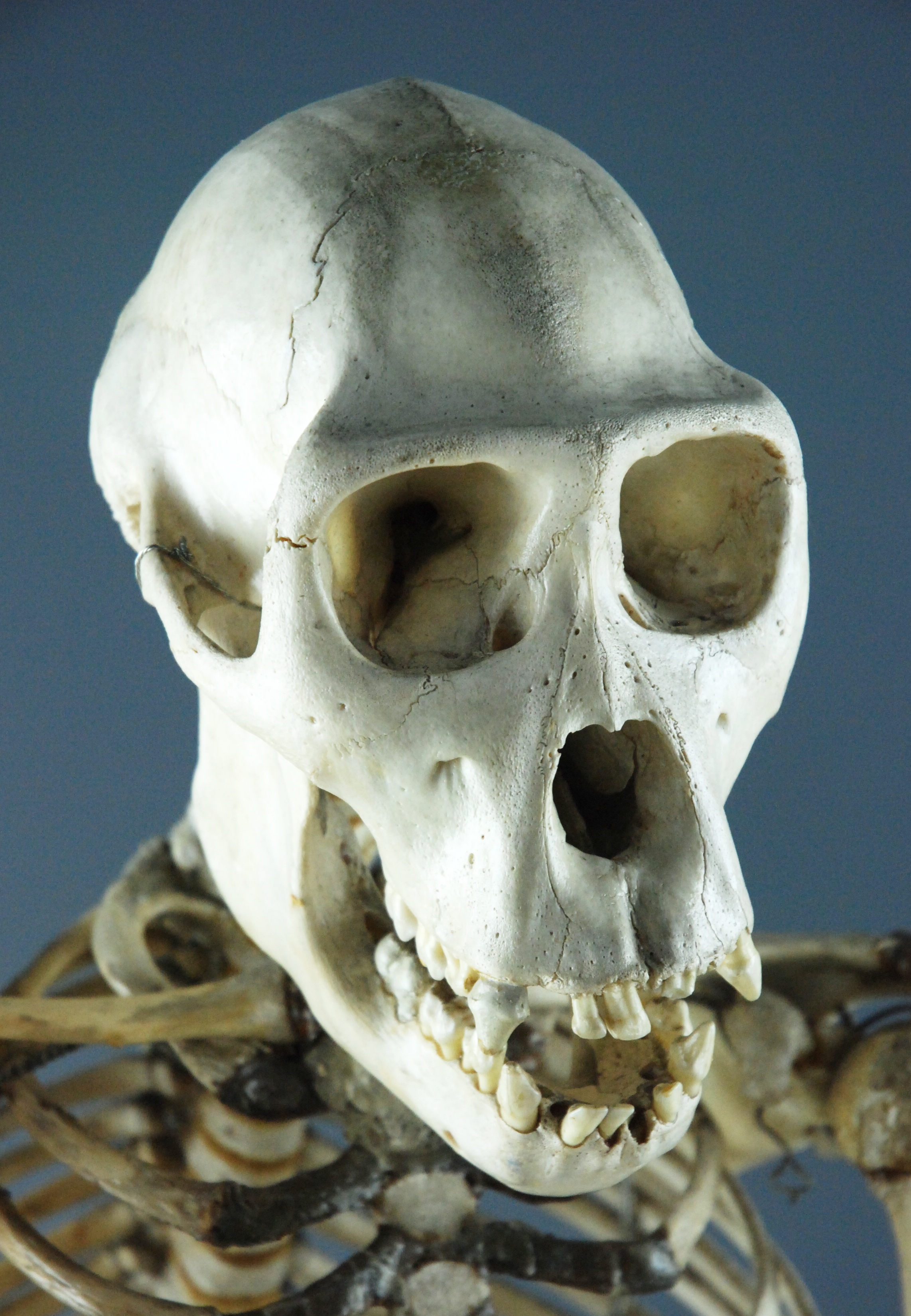

 There are four types of amniote skull, classified by the number and location of their temporal fenestrae. These are:
*
There are four types of amniote skull, classified by the number and location of their temporal fenestrae. These are:
*
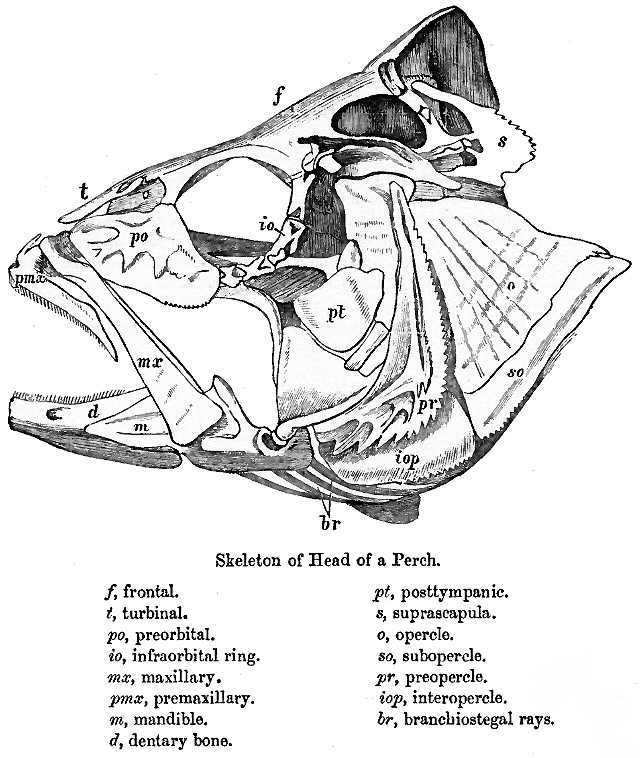
 The skull of fishes is formed from a series of only loosely connected bones.
The skull of fishes is formed from a series of only loosely connected bones.
 The skulls of the earliest
The skulls of the earliest
 Living amphibians typically have greatly reduced skulls, with many of the bones either absent or wholly or partly replaced by cartilage. In mammals and birds, in particular, modifications of the skull occurred to allow for the expansion of the brain. The fusion between the various bones is especially notable in birds, in which the individual structures may be difficult to identify.
Living amphibians typically have greatly reduced skulls, with many of the bones either absent or wholly or partly replaced by cartilage. In mammals and birds, in particular, modifications of the skull occurred to allow for the expansion of the brain. The fusion between the various bones is especially notable in birds, in which the individual structures may be difficult to identify.
 The skull is a complex structure; its bones are formed both by intramembranous and endochondral ossification. The skull roof bones, comprising the bones of the facial skeleton and the sides and roof of the neurocranium, are
The skull is a complex structure; its bones are formed both by intramembranous and endochondral ossification. The skull roof bones, comprising the bones of the facial skeleton and the sides and roof of the neurocranium, are
WPATH Clarification on Medical Necessity of Treatment, Sex Reassignment, and Insurance Coverage in the U.S.A.
(2008).World Professional Association for Transgender Health.
Standards of Care for the Health of Transsexual, Transgender, and Gender Nonconforming People, Version 7.
'' pg. 58 (2011).
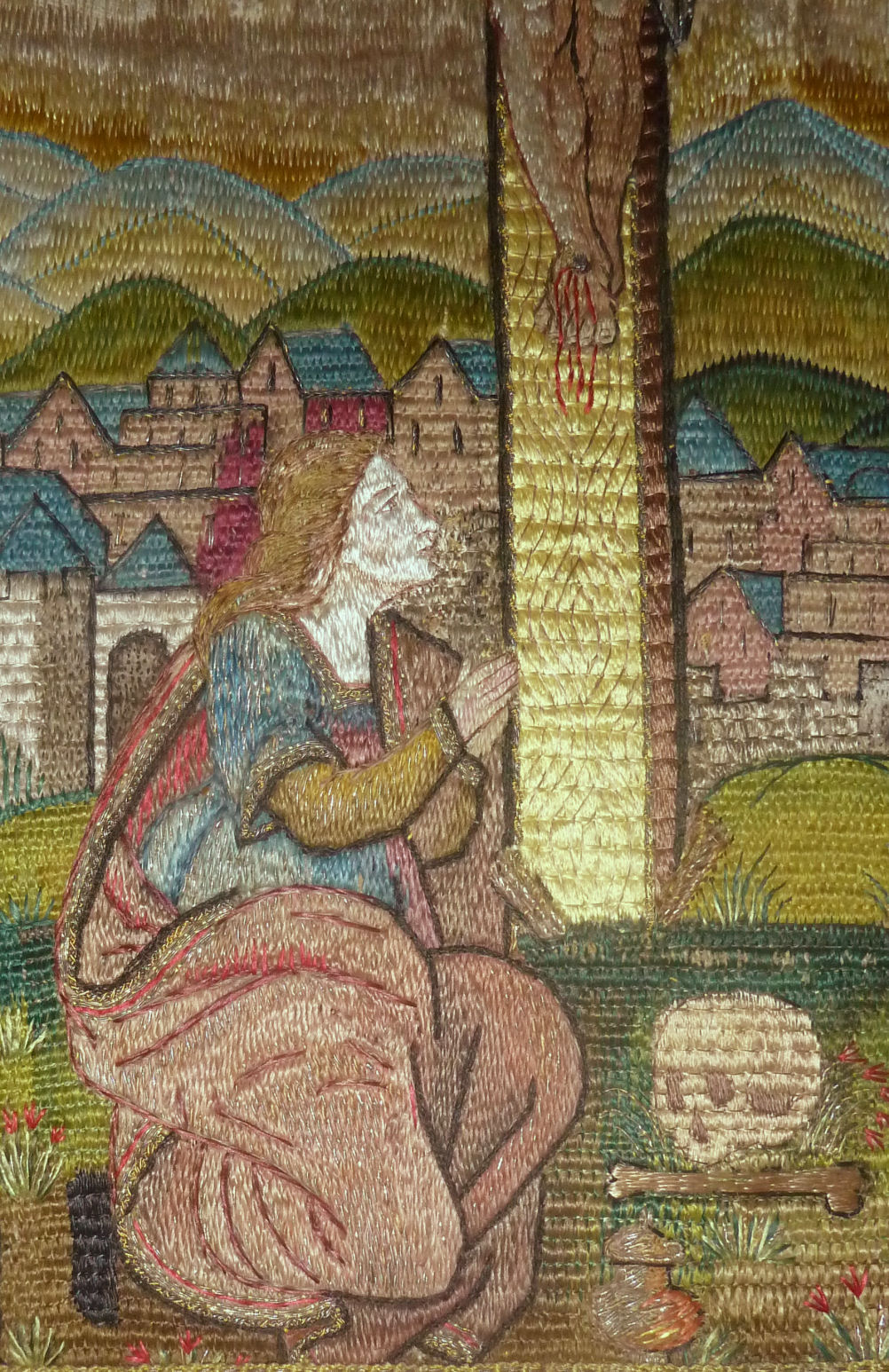 Artificial cranial deformation is a largely historical practice of some cultures. Cords and wooden boards would be used to apply pressure to an infant's skull and alter its shape, sometimes quite significantly. This procedure would begin just after birth and would be carried on for several years.
Artificial cranial deformation is a largely historical practice of some cultures. Cords and wooden boards would be used to apply pressure to an infant's skull and alter its shape, sometimes quite significantly. This procedure would begin just after birth and would be carried on for several years.
Skull Module
(California State University Department of Anthology)
Skull Anatomy Tutorial.
(GateWay Community College)
Bird Skull Collection
Bird skull database with very large collection of skulls (Agricultural University of Wageningen)
(in German)
Human Skulls / Anthropological Skulls / Comparison of Skulls of Vertebrates
(PDF; 502 kB) {{Portal bar, Anatomy Skull, Vertebrate anatomy Flat bones Bones of the head and neck Human head and neck
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
. In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s, these two parts are the neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.
Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision
Stereopsis () is the component of depth perception retrieved through binocular vision.
Stereopsis is not the only contributor to depth perception, but it is a major one. Binocular vision happens because each eye receives a different image becaus ...
, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance.
The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system us ...
of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ...
s (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
) for the horns Horns or The Horns may refer to:
* Plural of Horn (instrument), a group of musical instruments all with a horn-shaped bells
* The Horns (Colorado), a summit on Cheyenne Mountain
* ''Horns'' (novel), a dark fantasy novel written in 2010 by Joe Hill ...
.
The English word ''skull'' is probably derived from Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
, while the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word comes from the Greek root
The English language uses many Greek and Latin roots, stems, and prefixes. These roots are listed alphabetically on three pages:
* Greek and Latin roots from A to G
* Greek and Latin roots from H to O
* Greek and Latin roots from P to Z.
Some ...
(). The human skull fully develops two years after birth.The junctions of the skull bones are joined by structures called sutures.
The skull is made up of a number of fused flat bone
Flat bones are bones whose principal function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates,''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). (See infobox) as in the cranium ...
s, and contains many foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
, fossae, processes, and several cavities or in
sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
. In zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and ...
there are openings in the skull called fenestra
A fenestra (fenestration; plural fenestrae or fenestrations) is any small opening or pore, commonly used as a term in the biological sciences. It is the Latin word for "window", and is used in various fields to describe a pore in an anatomical st ...
e.
Structure
Humans



face
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
and forms a cavity for the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
. Like the skulls of other vertebrates, it protects the brain from injury.
The skull consists of three parts, of different embryological
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and ...
origin—the neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
, the sutures, and the facial skeleton (also called the ''membraneous viscerocranium''). The neurocranium (or ''braincase'') forms the protective cranial cavity that surrounds and houses the brain and brainstem. The upper areas of the cranial bones
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
form the calvaria (skullcap). The membranous viscerocranium includes the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
.
The sutures are fairly rigid joints between bones of the neurocranium.
The facial skeleton is formed by the bones supporting the face.
Bones
Except for themandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
, all of the bones of the skull are joined by sutures— synarthrodial (immovable) joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
formed by bony ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in ...
, with Sharpey's fibres permitting some flexibility. Sometimes there can be extra bone pieces within the suture known as wormian bone
Wormian bones, also known as intrasutural bones or sutural bones, are extra bone pieces that can occur within a suture (joint) in the skull. These are irregular isolated bones that can appear in addition to the usual centres of ossification of the ...
s or ''sutural bones''. Most commonly these are found in the course of the lambdoid suture
The lambdoid suture (or lambdoidal suture) is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.
Structure
T ...
.
The human skull is generally considered to consist of twenty-two bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s—eight cranial bones and fourteen facial skeleton bones. In the neurocranium these are the occipital bone, two temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. ...
s, two parietal bone
The parietal bones () are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is nam ...
s, the sphenoid, ethmoid
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a ...
and frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
s.
The bones of the facial skeleton (14) are the vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right max ...
, two inferior nasal concha
The inferior nasal concha (inferior turbinated bone or inferior turbinal/turbinate) is one of the three paired nasal conchae in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, c ...
e, two nasal bones, two maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
, the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
, two palatine bones, two zygomatic bone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from grc, ζῠγόν, zugón, yoke), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is s ...
s, and two lacrimal bone
The lacrimal bone is a small and fragile bone of the facial skeleton; it is roughly the size of the little fingernail. It is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders. Several bony landmarks of ...
s. Some sources count a paired bone as one, or the maxilla as having two bones (as its parts); some sources include the hyoid bone or the three ossicles of the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the ...
but the overall general consensus of the number of bones in the human skull is the stated twenty-two.
Some of these bones—the occipital, parietal, frontal, in the neurocranium, and the nasal, lacrimal, and vomer, in the facial skeleton are flat bone
Flat bones are bones whose principal function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates,''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). (See infobox) as in the cranium ...
s.
Cavities and foramina
 The skull also contains
The skull also contains sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
, air-filled cavities known as paranasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
, and numerous foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
. The sinuses are lined with in
respiratory epithelium
Respiratory epithelium, or airway epithelium, is a type of ciliated columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract as respiratory mucosa, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It is not present in the vocal cords o ...
. Their known functions are the lessening of the weight of the skull, the aiding of resonance to the voice and the warming and moistening of the air drawn into the nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the human nose, nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. ...
.
The foramina are openings in the skull. The largest of these is the foramen magnum that allows the passage of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
as well as nerves and blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s.
Processes
The many processes of the skull include themastoid process
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, ...
and the zygomatic process
The zygomatic processes are three processes (protrusions) from other bones of the skull which each articulate with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are:
* Zygomatic process of frontal bone from the frontal bone
* Zygomatic process of max ...
es.
Other vertebrates
Fenestrae
 The temporal fenestrae are anatomical features of the skulls of several types of amniotes, characterised by bilaterally symmetrical holes (fenestrae) in the temporal bone. Depending on the lineage of a given animal, two, one, or no pairs of temporal fenestrae may be present, above or below the
The temporal fenestrae are anatomical features of the skulls of several types of amniotes, characterised by bilaterally symmetrical holes (fenestrae) in the temporal bone. Depending on the lineage of a given animal, two, one, or no pairs of temporal fenestrae may be present, above or below the postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ...
and squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral co ...
bones. The upper temporal fenestrae are also known as the supratemporal fenestrae, and the lower temporal fenestrae are also known as the infratemporal fenestra
An infratemporal fenestra, also called the lateral temporal fenestra or simply temporal fenestra, is an opening in the skull behind the orbit in some animals. It is ventrally bordered by a zygomatic arch. An opening in front of the eye sockets ...
e. The presence and morphology of the temporal fenestra are critical for taxonomic classification of the synapsids, of which mammals are part.
Physiological speculation associates it with a rise in metabolic rates and an increase in jaw musculature. The earlier amniotes of the Carboniferous did not have temporal fenestrae but two more advanced lines did: the synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ...
s (mammal-like reptiles) and the diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years a ...
s (most reptiles and later birds). As time progressed, diapsids' and synapsids' temporal fenestrae became more modified and larger to make stronger bites and more jaw muscles. Dinosaurs, which are diapsids, have large advanced openings, and their descendants, the birds, have temporal fenestrae which have been modified. Synapsids, possess one fenestral opening in the skull, situated to the rear of the orbit. In their descendants, the cynodonts, the orbit fused with the fenestral opening after the latter had started expanding within the therapsids
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented mo ...
. Thus most mammals also have this. Later, primates separated their orbit from ''temporal fossa
The temporal fossa is a fossa (shallow depression) on the side of the skull bounded by the temporal lines and terminating below the level of the zygomatic arch.
Boundaries
* Medial: frontal bone, parietal bone, temporal bone, and sphenoid bon ...
'' by the postorbital bar The postorbital bar (or postorbital bone) is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most strep ...
with haplorhines later evolving the postorbital septum.
=Classification
=
 There are four types of amniote skull, classified by the number and location of their temporal fenestrae. These are:
*
There are four types of amniote skull, classified by the number and location of their temporal fenestrae. These are:
* Anapsida
An anapsid is an amniote whose skull lacks one or more skull openings (fenestra, or fossae) near the temples. Traditionally, the Anapsida are the most primitive subclass of amniotes, the ancestral stock from which Synapsida and Diapsida evolved ...
– no openings
* Synapsida – one low opening (beneath the postorbital and squamosal bones)
* Euryapsida
__NOTOC__
Euryapsida is a polyphyletic (unnatural, as the various members are not closely related) group of sauropsids that are distinguished by a single temporal fenestra, an opening behind the orbit, under which the post-orbital and squamosal b ...
– one high opening (above the postorbital and squamosal bones); euryapsids actually evolved from a diapsid configuration, losing their lower temporal fenestra.
* Diapsida
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years ag ...
– two openings
Evolutionarily, they are related as follows:
*Amniota
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are dis ...
**Class Synapsida
***Order Therapsida
****Class Mammalia
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
– mammals
**(Unranked) Sauropsida – reptiles and birds
***Class Reptilia
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
****Subclass Parareptilia
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids (reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near th ...
*****Infraclass Anapsida
An anapsid is an amniote whose skull lacks one or more skull openings (fenestra, or fossae) near the temples. Traditionally, the Anapsida are the most primitive subclass of amniotes, the ancestral stock from which Synapsida and Diapsida evolved ...
****Subclass Eureptilia
Eureptilia ("true reptiles") is one of the two major subgroups of the clade Sauropsida, the other one being Parareptilia. Eureptilia includes Diapsida (the clade containing all modern reptiles and birds), as well as a number of primitive Permo ...
*****Infraclass Diapsida
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years ag ...
******Class Aves
*****Infraclass Euryapsida
__NOTOC__
Euryapsida is a polyphyletic (unnatural, as the various members are not closely related) group of sauropsids that are distinguished by a single temporal fenestra, an opening behind the orbit, under which the post-orbital and squamosal b ...
Bones
Thejugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the zygomatic bone
In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from grc, ζῠγόν, zugón, yoke), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is s ...
or malar bone.
The prefrontal bone
The prefrontal bone is a bone separating the lacrimal and frontal bones in many tetrapod skulls. It first evolved in the sarcopterygian clade Rhipidistia, which includes lungfish and the Tetrapodomorpha. The prefrontal is found in most modern a ...
is a bone separating the lacrimal and frontal bones in many tetrapod skulls.
Fish

 The skull of fishes is formed from a series of only loosely connected bones.
The skull of fishes is formed from a series of only loosely connected bones. Lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like s ...
s and sharks only possess a cartilaginous endocranium, with both the upper and lower jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serv ...
s being separate elements. Bony fishes have additional dermal bone
A dermal bone or investing bone or membrane bone is a bony structure derived from intramembranous ossification forming components of the vertebrate skeleton including much of the skull, jaws, gill covers, shoulder girdle and fin spines rays ( le ...
, forming a more or less coherent skull roof in lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
and holost fish. The lower jaw defines a chin.
The simpler structure is found in jawless fish
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present ( cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclosto ...
, in which the cranium is normally represented by a trough-like basket of cartilaginous elements only partially enclosing the brain, and associated with the capsules for the inner ears and the single nostril. Distinctively, these fish have no jaws.
Cartilaginous fish, such as shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s and rays, have also simple, and presumably primitive, skull structures. The cranium is a single structure forming a case around the brain, enclosing the lower surface and the sides, but always at least partially open at the top as a large fontanelle. The most anterior part of the cranium includes a forward plate of cartilage, the rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
, and capsules to enclose the olfactory organs. Behind these are the orbits, and then an additional pair of capsules enclosing the structure of the inner ear. Finally, the skull tapers towards the rear, where the foramen magnum lies immediately above a single condyle
A condyle (;Entry "condyle"
in
vertebra The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
. There are, in addition, at various points throughout the cranium, smaller in
vertebra The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
foramina
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (;Entry "foramen"
in
for the cranial nerves. The jaws consist of separate hoops of cartilage, almost always distinct from the cranium proper.
In in
ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species.
The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or h ...
, there has also been considerable modification from the primitive pattern. The roof of the skull is generally well formed, and although the exact relationship of its bones to those of tetrapods is unclear, they are usually given similar names for convenience. Other elements of the skull, however, may be reduced; there is little cheek region behind the enlarged orbits, and little, if any bone in between them. The upper jaw is often formed largely from the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
, with the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
itself located further back, and an additional bone, the symplectic, linking the jaw to the rest of the cranium.
Although the skulls of fossil lobe-finned fish resemble those of the early tetrapods, the same cannot be said of those of the living lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
es. The skull roof is not fully formed, and consists of multiple, somewhat irregularly shaped bones with no direct relationship to those of tetrapods. The upper jaw is formed from the pterygoid Pterygoid, from the Greek for 'winglike', may refer to:
* Pterygoid bone, a bone of the palate of many vertebrates
* Pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bone
** Lateral pterygoid plate
** Medial pterygoid plate
* Lateral pterygoid muscle
* Medi ...
s and vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right max ...
s alone, all of which bear teeth. Much of the skull is formed from cartilage, and its overall structure is reduced.
Tetrapods
 The skulls of the earliest
The skulls of the earliest tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s closely resembled those of their ancestors amongst the lobe-finned fish
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass includ ...
es. The skull roof is formed of a series of plate-like bones, including the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
, frontals, parietals, and lacrimals, among others. It is overlaying the endocranium, corresponding to the cartilaginous skull in sharks
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimorp ...
and rays
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (gra ...
. The various separate bones that compose the temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. ...
of humans are also part of the skull roof series. A further plate composed of four pairs of bones forms the roof of the mouth; these include the vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right max ...
and palatine bones. The base of the cranium is formed from a ring of bones surrounding the foramen magnum and a median bone lying further forward; these are homologous with the occipital bone and parts of the sphenoid in mammals. Finally, the lower jaw is composed of multiple bones, only the most anterior of which (the dentary) is homologous with the mammalian mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
.
In living tetrapods, a great many of the original bones have either disappeared or fused into one another in various arrangements.
Birds

Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s have a diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years a ...
skull, as in reptiles, with a prelacrimal fossa (present in some reptiles). The skull has a single occipital condyle. The skull consists of five major bones: the frontal (top of head), parietal (back of head), premaxillary and nasal (top beak), and the mandible (bottom beak). The skull of a normal bird usually weighs about 1% of the bird's total bodyweight. The eye occupies a considerable amount of the skull and is surrounded by a sclerotic eye-ring, a ring of tiny bones. This characteristic is also seen in reptiles.
Amphibians
 Living amphibians typically have greatly reduced skulls, with many of the bones either absent or wholly or partly replaced by cartilage. In mammals and birds, in particular, modifications of the skull occurred to allow for the expansion of the brain. The fusion between the various bones is especially notable in birds, in which the individual structures may be difficult to identify.
Living amphibians typically have greatly reduced skulls, with many of the bones either absent or wholly or partly replaced by cartilage. In mammals and birds, in particular, modifications of the skull occurred to allow for the expansion of the brain. The fusion between the various bones is especially notable in birds, in which the individual structures may be difficult to identify.
Development
 The skull is a complex structure; its bones are formed both by intramembranous and endochondral ossification. The skull roof bones, comprising the bones of the facial skeleton and the sides and roof of the neurocranium, are
The skull is a complex structure; its bones are formed both by intramembranous and endochondral ossification. The skull roof bones, comprising the bones of the facial skeleton and the sides and roof of the neurocranium, are dermal bone
A dermal bone or investing bone or membrane bone is a bony structure derived from intramembranous ossification forming components of the vertebrate skeleton including much of the skull, jaws, gill covers, shoulder girdle and fin spines rays ( le ...
s formed by intramembranous ossification, though the temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. ...
s are formed by endochondral ossification. The endocranium, the bones supporting the brain (the occipital
The occipital bone () is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cereb ...
, sphenoid, and ethmoid
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a ...
) are largely formed by endochondral ossification. Thus frontal and parietal bones are purely membranous. The geometry of the skull base
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
Structures found at the base of the skull are for ...
and its fossae, the anterior cranial fossa, anterior, middle cranial fossa, middle and posterior cranial fossae changes rapidly. The anterior cranial fossa changes especially during the pregnancy, first trimester of pregnancy and skull defects can often develop during this time.
At birth, the human skull is made up of 44 separate bony elements. During development, many of these bony elements gradually fuse together into solid bone (for example, the frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
). The bones of the skull roof, roof of the skull are initially separated by regions of dense connective tissue called fontanelles. There are six fontanelles: one anterior (or frontal), one posterior (or occipital), two sphenoid (or anterolateral), and two mastoid (or posterolateral). At birth, these regions are fibrous and moveable, necessary for birth and later growth. This growth can put a large amount of tension on the "obstetrical hinge", which is where the Squama occipitalis, squamous and Lateral parts of occipital bone, lateral parts of the occipital bone meet. A possible complication of this tension is rupture of the great cerebral vein. As growth and ossification progress, the connective tissue of the fontanelles is invaded and replaced by bone creating Suture (anatomical), sutures. The five sutures are the two squamosal suture, squamous sutures, one coronal suture, coronal, one lambdoid suture, lambdoid, and one sagittal suture. The posterior fontanelle usually closes by eight weeks, but the anterior fontanel can remain open up to eighteen months. The anterior fontanelle is located at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones; it is a "soft spot" on a baby's forehead. Careful observation will show that you can count a baby's heart rate by observing the pulse pulsing softly through the anterior fontanelle.
The skull in the neonate is large in proportion to other parts of the body. The facial skeleton is one seventh of the size of the calvaria. (In the adult it is half the size). The base of the skull is short and narrow, though the inner ear is almost adult size.
Clinical significance
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous Suture (joint), sutures in an infant skull prematurely fuses, and changes the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it grows more in the parallel direction. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development. A copper beaten skull is a phenomenon wherein intense intracranial pressure disfigures the internal surface of the skull. The name comes from the fact that the inner skull has the appearance of having been beaten with a ball-peen hammer, such as is often used by coppersmiths. The condition is most common in children.Injuries and treatment
Injuries to the brain can be life-threatening. Normally the skull protects the brain from damage through its hard unyieldingness; the skull is one of the least deformable structures found in nature with it needing the force of about 1 ton to reduce the diameter of the skull by 1 cm. In some cases, however, of head injury, there can be raised intracranial pressure through mechanisms such as a subdural haematoma. In these cases the raised intracranial pressure can cause herniation of the brain out of the foramen magnum ("coning") because there is no space for the brain to expand; this can result in significant brain damage or death unless an urgent operation is performed to relieve the pressure. This is why patients with concussion must be watched extremely carefully. Repeated concussions can activate the structure of skull bones as the brain's protective covering. Dating back to Neolithic times, a skull operation called trepanning was sometimes performed. This involved drilling a ''burr'' hole in the cranium. Examination of skulls from this period reveals that the patients sometimes survived for many years afterward. It seems likely that trepanning was also performed purely for ritualistic or religious reasons. Nowadays this procedure is still used but is normally called a craniectomy. In March 2013, for the first time in the U.S., researchers replaced a large percentage of a patient's skull with a precision, 3D printing, 3D-printed polymer Implant (medicine), implant. About 9 months later, the first complete cranium replacement with a 3D-printed plastic insert was performed on a Dutch woman. She had been suffering from hyperostosis, which increased the thickness of her skull and compressed her brain. A study conducted in 2018 by the researchers of Harvard Medical School in Boston, funded by National Institutes of Health (NIH), suggested that instead of travelling via blood, there are "tiny channels" in the skull through which the White blood cell, immune cells combined with the bone marrow reach the areas of inflammation after an injury to the brain tissues.Transgender procedures
Surgical alteration of sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic skull features may be carried out as a part of facial feminization surgery, a set of reconstructive surgical procedures that can alter male facial features to bring them closer in shape and size to typical female facial features. These procedures can be an important part of the treatment of transgender people for gender dysphoria.World Professional Association for Transgender HealthWPATH Clarification on Medical Necessity of Treatment, Sex Reassignment, and Insurance Coverage in the U.S.A.
(2008).World Professional Association for Transgender Health.
Standards of Care for the Health of Transsexual, Transgender, and Gender Nonconforming People, Version 7.
'' pg. 58 (2011).
Society and culture
Osteology
Like the face, the skull and teeth can also indicate a person's life history and origin. Forensics, Forensic scientists and archeology, archaeologists use quantitative and qualitative traits to estimate what the bearer of the skull looked like. When a significant amount of bones are found, such as at Spitalfields in the UK and Jōmon shell mounds in Japan, Osteology, osteologists can use traits, such as the proportions of length, height and width, to know the relationships of the population of the study with other living or extinct populations. The German physician Franz Joseph Gall in around 1800 formulated the theory of phrenology, which attempted to show that specific features of the skull are associated with certain personality traits or intellectual capabilities of its owner. His theory is now considered to be pseudoscience, pseudoscientific.Sexual dimorphism
In the mid-nineteenth century, anthropologists found it crucial to distinguish between male and female skulls. An anthropologist of the time, James McGrigor Allan, argued that the female brain was similar to that of an animal. This allowed anthropologists to declare that women were in fact more emotional and less rational than men. McGrigor then concluded that women's brains were more analogous to infants, thus deeming them inferior at the time. To further these claims of female inferiority and silence the feminists of the time, other anthropologists joined in on the studies of the female skull. These cranial measurements are the basis of what is known as craniology. These cranial measurements were also used to draw a connection between women and black people. Research has shown that while in early life there is little difference between male and female skulls, in adulthood male skulls tend to be larger and more robust than female skulls, which are lighter and smaller, with a cranial capacity about 10 percent less than that of the male. However, later studies show that women's skulls are slightly thicker and thus men may be more susceptible to head injury than women. However, other studies shows that men's skulls are slightly thicker in certain areas. As well as some studies showing that females are more susceptible to head injury (concussion) than males. Men's skulls have also been shown to maintain density with age, which may aid in preventing head injury, while women's skull density slightly decreases with age. Male skulls can have more prominent supraorbital ridges, a more prominent glabella, and more prominent parietal bone, temporal lines. Female skulls generally have rounder Orbit (anatomy), orbits, and narrower jaws. Male skulls on average have larger, broader palates, squarer orbits, largermastoid process
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, ...
es, larger Paranasal sinus, sinuses, and larger occipital condyles than those of females. Male Human mandible, mandibles typically have squarer chins and thicker, rougher muscle attachments than female mandibles.
Craniometry
The cephalic index is the ratio of the width of the head, multiplied by 100 and divided by its length (front to back). The index is also used to categorize animals, especially dogs and cats. The width is usually measured just below the parietal eminence, and the length from the glabella to the occipital point. Humans may be: * ''Dolichocephalic'' — long-headed * ''Mesaticephalic'' — medium-headed * ''Brachycephalic'' — short-headedTerminology
* Chondrocranium, a primitive cartilaginous skeletal structure * Endocranium * Epicranium * Pericranium, a membrane that lines the outer surface of the craniumHistory
Trepanning, a practice in which a hole is created in the skull, has been described as the oldest surgical procedure for which there is archaeological evidence, found in the forms of cave paintings and human remains. At one burial site in France dated to 6500 BCE, 40 out of 120 prehistoric France, prehistoric skulls found had trepanation holes.Additional images
See also
*Craniometry *Crystal skull *Head and neck anatomy *Human skull symbolism *Memento mori *Plagiocephaly, the abnormal flattening of one side of the skull *Skull and crossbones (disambiguation) *Teshik-Tash#The skull, Teshik-Tash *Totenkopf *Yorick *Overmodelled skull *DiploëReferences
External links
Skull Module
(California State University Department of Anthology)
Skull Anatomy Tutorial.
(GateWay Community College)
Bird Skull Collection
Bird skull database with very large collection of skulls (Agricultural University of Wageningen)
(in German)
Human Skulls / Anthropological Skulls / Comparison of Skulls of Vertebrates
(PDF; 502 kB) {{Portal bar, Anatomy Skull, Vertebrate anatomy Flat bones Bones of the head and neck Human head and neck