Sinus Headache on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Sinus infections can also cause middle-ear problems due to the congestion of the nasal passages. This can be demonstrated by dizziness, "a pressurized or heavy head", or vibrating sensations in the head.
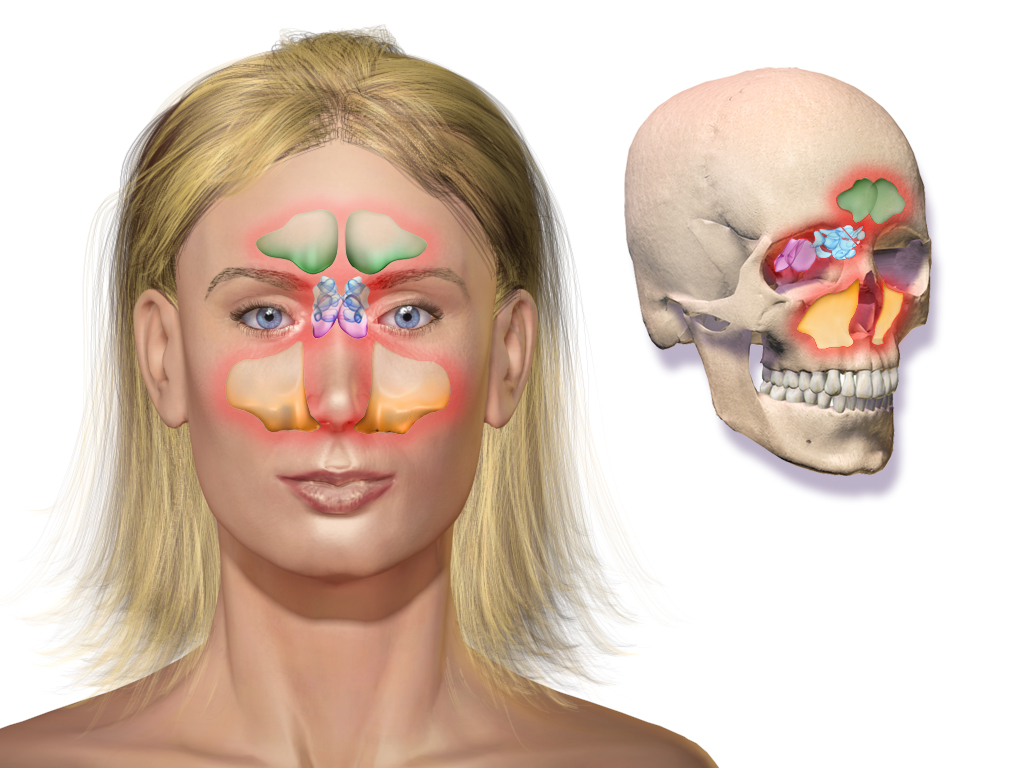 Sinusitis (or rhinosinusitis) is defined as an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the
Sinusitis (or rhinosinusitis) is defined as an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the
Image:Sinuses and Sinusitis (5937085231).jpg, CT of chronic sinusitis
File:CT of chronic sinuitis.jpg,
inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
s, a poor sense of smell, sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. Usually, causes of sore throat include
* viral infections
* group A streptococcal infection (GAS) bacterial infection
* pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat)
* tonsi ...
, a feeling that phlegm is oozing out from the back of the nose to the throat along with a necessity to clear the throat frequently and frequent attacks of cough.
Generally sinusitis starts off as a common viral infection like common cold. This infection generally subsides within 5 to 7 days. During this time the nasal structures can swell and facilitate the stagnation of fluids in sinuses that leads to acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
sinusitis which lasts from 6th day of the infection to 15th day. From the 15th day to 45th day of the infection comes the subacute stage followed by chronic stage. Whenever a chronic stage patient's immunity takes a hit the infection moves to "acute on sinusitis" stage and moves back to chronic when the immunity is up.
Sinusitis occurs only in individuals with underlying conditions like allergies, or structural problems in the nose and in people with lesser immunity against bacteria by birth. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Recurrent episodes are more likely in persons with asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
, cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
, and poor immune function
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
. In early stages an ENT doctor confirms sinusitis using nasal endoscopy. Diagnostic imaging is not usually needed in acute stage unless complications are suspected. In chronic cases, confirmatory testing is recommended by either direct visualization or computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
.
Some cases may be prevented by hand washing, avoiding smoking, and immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen).
When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-sel ...
. Pain killers
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It i ...
such as naproxen, nasal steroids, and nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation (also called nasal lavage, nasal toilet, or nasal douche) is a personal hygiene practice in which the nasal cavity is washed to flush out mucus and debris from the nose and sinuses, in order to enhance nasal breathing. Nasal ir ...
may be used to help with symptoms. Recommended initial treatment for acute sinusitis is watchful waiting. If symptoms do not improve in 7–10 days or get worse, then an antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
may be used or changed. In those in whom antibiotics are used, either amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate is recommended first line. Surgery may occasionally be used in people with chronic disease or in someone who is not responding to medicines as per doctor's expectation.
Sinusitis is a common condition. It affects between about 10 and 30 percent of people each year in the United States and Europe. Chronic sinusitis affects about 12.5% of people. Treatment of sinusitis in the United States results in more than 11 billion in costs. The unnecessary and ineffective treatment of viral sinusitis with antibiotics is common.
Signs and symptoms
Headache, facial pain, or pressure of a dull, constant, or aching sort over the affected sinuses is common with both acute and chronic stages of sinusitis. This pain is usually localized to the involved sinus and may worsen when the affected person bends over or lies down. Pain often starts on one side of the head and progresses to both sides. Acute sinusitis may be accompanied by a thicknasal discharge
Rhinorrhea, rhinorrhoea, or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is a common condition. It is a common symptom of allergies (hay fever) or certain viral infections, such as the common cold or COVID-1 ...
that is usually green in color, and may contain pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
or blood. Often, a localized headache or toothache is present, and these symptoms distinguish a sinus-related headache from other types of headaches, such as tension and migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
headaches. Another way to distinguish between toothache and sinusitis is that the pain in sinusitis is usually worsened by tilting the head forward and with the Valsalva maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air out as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can ...
.
Other symptoms associated with acute rhinosinusitis include cough, fatigue, hyposmia, anosmia and ear fullness or pressure.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Sinus infections can also cause middle-ear problems due to the congestion of the nasal passages. This can be demonstrated by dizziness, "a pressurized or heavy head", or vibrating sensations in the head.
Postnasal drip
Post-nasal drip (PND), also known as upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), occurs when excessive mucus is produced by the nasal mucosa. The excess mucus accumulates in the back of the nose, and eventually in the throat once it drips down the back of ...
is also a symptom of chronic rhinosinusitis.
Halitosis
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a symptom in which a noticeably unpleasant breath odour is present. It can result in anxiety among those affected. It is also associated with depression and symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder.
Th ...
(bad breath) is often stated to be a symptom of chronic rhinosinusitis; however, gold-standard breath analysis techniques have not been applied. Theoretically, several possible mechanisms of both objective and subjective halitosis may be involved.
A 2005 review suggested that most "sinus headaches" are migraines. The confusion occurs in part because migraine involves activation of the trigeminal nerves
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; ...
, which innervate both the sinus region and the meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in th ...
surrounding the brain. As a result, accurately determining the site from which the pain originates is difficult. People with migraines do not typically have the thick nasal discharge that is a common symptom of a sinus infection.
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis may include nasal congestion, facial pain, headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
, night-time coughing, an increase in previously minor or controlled asthma symptoms, general malaise
As a medical term, malaise is a feeling of general discomfort, uneasiness or lack of wellbeing and often the first sign of an infection or other disease. The word has existed in French since at least the 12th century.
The term is often used ...
, thick green or yellow discharge
Discharge may refer to
Expel or let go
* Discharge, the act of firing a gun
* Discharge, or termination of employment, the end of an employee's duration with an employer
* Military discharge, the release of a member of the armed forces from serv ...
, feeling of facial fullness or tightness that may worsen when bending over, dizziness, aching teeth, and bad breath. Often, chronic sinusitis can lead to anosmia, the loss of the sense of smell
Smell may refer to;
* Odor, airborne molecules perceived as a scent or aroma
* Sense of smell, the scent also known scientifically as olfaction
* "Smells" (''Bottom''), an episode of ''Bottom''
* The Smell, a music venue in Los Angeles, Californ ...
.By location
The four pairedparanasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
are the frontal, ethmoidal, maxillary, and sphenoidal sinuses. The ethmoidal sinuses are further subdivided into anterior and posterior ethmoid sinuses, the division of which is defined as the basal lamella of the middle nasal concha
The medial surface of the labyrinth of ethmoid consists of a thin lamella, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and ends below in a free, convoluted margin, the middle nasal concha (middle nasal turbinate).
It is rough, a ...
. In addition to the severity of disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
, discussed below, sinusitis can be classified by the sinus cavity it affects:
* Maxillary – can cause pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
or pressure in the maxillary ( cheek) area (''e.g.,'' toothache, or headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.
Headaches can occur as a result ...
) (J01.0/J32.0)
* Frontal
Front may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film
* ''The Front'', 1976 film
Music
*The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and ea ...
– can cause pain or pressure in the frontal sinus cavity (located above the eyes), headache, particularly in the forehead (J01.1/J32.1)
* Ethmoidal – can cause pain or pressure pain between/behind the eyes, the sides of the upper part of the nose (the medial canthi), and headaches (J01.2/J32.2)
* Sphenoidal – can cause pain or pressure behind the eyes, but is often felt
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile or wood ...
in the top of the head, over the mastoid process
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, t ...
es, or the back of the head.
Complications
Complications are thought to be rare (1 case per 10,000). The proximity of the brain to the sinuses makes the most dangerous complication of sinusitis, particularly involving the frontal and sphenoid sinuses, infection of the brain by the invasion ofanaerobic bacteria
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
through the bones or blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s. Abscesses, meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
, and other life-threatening conditions may result. In extreme cases, the patient may experience mild personality changes, headache, altered consciousness, visual problems, seizures, coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
, and possibly death.
Sinus infection can spread through anastomosing veins or by direct extension to close structures. Orbital complications were categorized by Chandler et al. into five stages according to their severity (see table). Contiguous spread to the orbit may result in periorbital cellulitis, subperiosteal abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b ...
, orbital cellulitis, and abscess. Orbital cellulitis can complicate acute ethmoiditis if anterior and posterior ethmoidal veins thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following s ...
enables the spread of the infection to the lateral or orbital side of the ethmoid labyrinth
The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone ...
. Sinusitis may extend to the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
, where it may cause cavernous sinus thrombosis
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
Structure
The cave ...
, retrograde meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
, and epidural, subdural, and brain abscesses. Orbital symptoms frequently precede intracranial spread of the infection . Other complications include sinobronchitis, maxillary osteomyelitis, and frontal bone osteomyelitis. Osteomyelitis of the frontal bone often originates from a spreading thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following s ...
. A periostitis of the frontal sinus causes an osteitis
Osteitis is inflammation of bone. More specifically, it can refer to one of the following conditions:
* Osteomyelitis, or ''infectious osteitis'', mainly ''bacterial osteitis''
* Alveolar osteitis or "dry socket"
* Condensing osteitis (or Osteitis ...
and a periostitis of the outer membrane, which produces a tender, puffy swelling of the forehead.
The diagnosis of these complications can be assisted by noting local tenderness and dull pain, and can be confirmed by CT and nuclear isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
scanning. The most common microbial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
causes are anaerobic bacteria and '' S. aureus''. Treatment includes performing surgical drainage and administration of antimicrobial therapy. Surgical debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
In p ...
is rarely required after an extended course of parenteral
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
antimicrobial therapy. Chronic sinus infections may lead to mouth breathing, which can result in mouth dryness and an increased risk of gingivitis. Decongestants may also cause mouth dryness.
If an odontogenic infection involves the maxillary sinus, odontogenic sinusitis (ODS) may ensue. Odontogenic sinusitis can often spread to other sinuses such as the ethmoid, frontal
Front may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''The Front'' (1943 film), a 1943 Soviet drama film
* ''The Front'', 1976 film
Music
*The Front (band), an American rock band signed to Columbia Records and active in the 1980s and ea ...
and (less frequently) sphenoid sinus, and even to the contralateral nasal cavity. In rare instances, these infections may involve the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
, causing orbital cellulitis, which may in turn result in blindness, or determine central nervous system complications such as meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
, subdural empyema, brain abscess and life-threatening cavernous sinus thrombosis.
Infection of the eye socket is a rare complication of ethmoid sinusitis, which may result in the loss of sight and is accompanied by fever and severe illness. Another possible complication is the infection of the bones ( osteomyelitis) of the forehead and other facial bones – Pott's puffy tumor.
Causes
Acute
Acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
sinusitis is usually precipitated by an earlier upper respiratory tract infection, generally of viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
origin, mostly caused by rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the grc, ῥίς, rhis "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the la, vīrus) is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in tem ...
es (with RVA and RVC giving more severe infection than RVB), coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the com ...
es, and influenza viruses
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek language, Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus, negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genus, genera: ''Influenza ...
, others caused by adenoviruses, human parainfluenza viruses, human respiratory syncytial virus, enteroviruses other than rhinoviruses, and metapneumovirus
''Metapneumovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family ''Pneumoviridae''.
The genus contains two species:
* Avian metapneumovirus (aMPV)
* Human metapneumovirus
''Human metapneumovirus'' (HMPV) is a negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus ...
. If the infection is of bacterial origin, the most common three causative agents are '' Streptococcus pneumoniae (38%)'', ''Haemophilus influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria ...
(36%)'', and '' Moraxella catarrhalis (16%)''. Until recently, ''H. influenzae'' was the most common bacterial agent to cause sinus infections. However, introduction of the ''H. influenzae'' type B (Hib) vaccine has dramatically decreased these infections and now non-typable ''H. influenzae'' (NTHI) is predominantly seen in clinics. Other sinusitis-causing bacterial
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s include '' S. aureus'' and other streptococci
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs ...
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
, anaerobic bacteria
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
and, less commonly, Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
bacteria. Viral sinusitis typically lasts for 7 to 10 days.
Acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
episodes of sinusitis can also result from fungal
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
invasion. These infections are typically seen in people with diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
or other immune deficiencies (such as AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
or transplant
Transplant or Transplantation may refer to:
Sciences
*Transplanting a plant from one location to another
*Organ transplantation, moving an organ from one body to another
*Transplant thought experiment, an experiment similar to Trolley problem
*Tra ...
on immunosuppressive antirejection medications) and can be life-threatening. In type I diabetics, ketoacidosis can be associated with sinusitis due to mucormycosis
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a serious fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the ...
.
Chronic
By definition, chronic sinusitis lasts longer than 12 weeks and can be caused by many different diseases that share chronic inflammation of the sinuses as a common symptom. It is subdivided into cases with and without polyps. When polyps are present, the condition is called chronic hyperplastic sinusitis; however, the causes are poorly understood. It may develop with anatomic derangements, including deviation of the nasal septum and the presence of concha bullosa (pneumatization of the middle concha) that inhibit the outflow of mucus, or with allergic rhinitis, asthma, cystic fibrosis, and dental infections. Chronic rhinosinusitis represents a multifactorial inflammatory disorder, rather than simply a persistent bacterial infection. The medical management of chronic rhinosinusitis is now focused upon controlling the inflammation that predisposes people to obstruction, reducing the incidence of infections. Surgery may be needed if medications are not working. Attempts have been made to provide a more consistent nomenclature for subtypes of chronic sinusitis. The presence of eosinophils in the mucous lining of the nose and paranasal sinuses has been demonstrated for many people, and this has been termed eosinophilic mucin rhinosinusitis (EMRS). Cases of EMRS may be related to an allergic response, but allergy is not often documented, resulting in further subcategorization into allergic and nonallergic EMRS. A more recent, and still debated, development in chronic sinusitis is the role thatfungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
play in this disease. Whether fungi are a definite factor in the development of chronic sinusitis remains unclear, and if they are, what is the difference between those who develop the disease and those who remain free of symptoms. Trials of antifungal treatments have had mixed results.
Recent theories of sinusitis indicate that it often occurs as part of a spectrum of diseases that affect the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to th ...
(''i.e.'', the "one airway" theory) and is often linked to asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
.
Both smoking and secondhand smoke
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called secondhand smoke (SHS), or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by persons other than the intended "active" smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke enters an environment, causing its inhalat ...
are associated with chronic rhinosinusitis.
Other diseases such as cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
and granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), previously known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), is a rare long-term systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis). It is a form of vasculitis ...
can also cause chronic sinusitis.
Maxillary sinus
Maxillary sinusitis may also develop from problems with the teeth, and these cases were calculated to be about 40% in one study and 50% in another. The cause of this situation is usually a periapical or periodontal infection of a maxillary posterior tooth, where the inflammatoryexudate
An exudate is a fluid emitted by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation.
''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin ''exsūdāre'' 'to (ooze out) sweat' (''ex-'' 'out' and ''sūdāre'' 'to ...
has eroded through the bone superiorly to drain into the maxillary sinus.
An estimated 0.5 to 2.0% of viral rhinosinusitis (VRS) will develop into bacterial infections in adults and 5 to 10% in children.
Pathophysiology
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
bacterial infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
s may account for many cases of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
-refractory chronic sinusitis. Biofilms are complex aggregates of extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide stru ...
and interdependent microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s from multiple species, many of which may be difficult or impossible to isolate
Isolate may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Isolate'' (film), a 2013 Australian film
* ''Isolate'' (Circus Maximus album), 2007
* ''Isolate'' (Gary Numan album), 1992
Language
* Isolating language, with near-unity morpheme/word ...
using standard clinical laboratory techniques. Bacteria found in biofilms have their antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
increased up to 1000 times when compared to free-living bacteria of the same species. A recent study found that biofilms were present on the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
of 75% of people undergoing surgery for chronic sinusitis.
Diagnosis
Classification
 Sinusitis (or rhinosinusitis) is defined as an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the
Sinusitis (or rhinosinusitis) is defined as an inflammation of the mucous membrane that lines the paranasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoid ...
and is classified chronologically into several categories:
* Acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
sinusitis – A new infection that may last up to four weeks and can be subdivided symptomatically into severe and nonsevere. Some use definitions up to 12 weeks.
* Recurrent acute sinusitis – Four or more full episodes of acute sinusitis that occur within one year
* Subacute
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotes that it is of short duration and, as a corollary of that, of recent onset. The quantification of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core deno ...
sinusitis – An infection that lasts between four and 12 weeks, and represents a transition between acute and chronic infection.
* Chronic sinusitis – When the signs and symptoms last for more than 12 weeks.
* Acute exacerbation of chronic sinusitis – When the signs and symptoms of chronic sinusitis exacerbate, but return to baseline after treatment.
Roughly 90% of adults have had sinusitis at some point in their lives.
Acute
Health care providers distinguish bacterial and viral sinusitis by watchful waiting. If a person has had sinusitis for fewer than 10 days without the symptoms becoming worse, then the infection is presumed to be viral. When symptoms last more than 10 days or get worse in that time, then the infection is considered bacterial sinusitis. Pain in the teeth and bad breath are also more indicative of bacterial disease. Imaging by either X-ray, CT or MRI is generally not recommended unless complications develop. Pain caused by sinusitis is sometimes confused for pain caused by pulpitis (toothache) of the maxillary teeth, and vice versa. Classically, the increased pain when tilting the head forwards separates sinusitis from pulpitis. For cases of maxillary sinusitis, limited field CBCT imaging, as compared to periapical radiographs, improves the ability to detect the teeth as the sources for sinusitis. A coronal CT picture may also be useful.Chronic
For sinusitis lasting more than 12 weeks, aCT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
is recommended. On a CT scan, acute sinus secretions have a radiodensity of 10 to 25 Hounsfield units (HU), but in a more chronic state they become more viscous
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inter ...
, with a radiodensity of 30 to 60 HU.
Nasal endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
and clinical symptoms are also used to make a positive diagnosis. A tissue sample for histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
and cultures can also be collected and tested.Harrison's Manual of Medicine 16/e Nasal endoscopy involves inserting a flexible fiber-optic tube with a light and camera at its tip into the nose to examine the nasal passages and sinuses.
Sinus infections, if they result in tooth pain, usually present with pain involving more than one of the upper teeth, whereas a toothache usually involves a single tooth. Dental examination and appropriate radiography aid in ruling out pain arises from a tooth.
CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
of chronic sinusitis, showing a filled right maxillary sinus with sclerotic thickened bone.
File:Brain MRI 112010 rgbca.png, MRI image showing sinusitis. Edema and mucosal thickening appears in both maxillary sinuses.
File:RtmaxobitinfectteethCT.png, Maxillary sinusitis caused by a dental infection associated with periorbital cellulitis
Periorbital cellulitis, or preseptal cellulitis (not to be confused with orbital cellulitis, which is posterior to the orbital septum), is an inflammation and infection of the eyelid and portions of skin around the eye anterior to the orbital sept ...
File:FrontalSinusitisMark.png, Frontal sinusitis
File:Maxilar sinusites.jpg, X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
of left-sided maxillary sinusitis marked by an arrow. There is lack of the air transparency indicating fluid in contrast to the other side.
Treatment
Recommended treatments for most cases of sinusitis include rest and drinking enough water to thin the mucus. Antibiotics are not recommended for most cases. Breathing low-temperature steam such as from a hot shower orgargling
Gargling is the act of bubbling liquid in the mouth. It is also the washing of one's mouth and throat with a liquid, such as mouthwash, that is kept in motion by breathing through it with a gurgling sound.
A traditional home remedy of gargling ...
can relieve symptoms. There is tentative evidence for nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation (also called nasal lavage, nasal toilet, or nasal douche) is a personal hygiene practice in which the nasal cavity is washed to flush out mucus and debris from the nose and sinuses, in order to enhance nasal breathing. Nasal ir ...
in acute sinusitis, for example during upper respiratory infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the human nose, nose, Paranasal sinus, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal ...
s. Decongestant nasal spray
Nasal sprays are used to deliver medications locally in the nasal cavities or systemically. They are used locally for conditions such as nasal congestion and allergic rhinitis. In some situations, the nasal delivery route is preferred for syste ...
s containing oxymetazoline may provide relief, but these medications should not be used for more than the recommended period. Longer use may cause rebound sinusitis. It is unclear if nasal irrigation, antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides re ...
s, or decongestants work in children with acute sinusitis. There is no clear evidence that plant extracts such as '' Cyclamen europaeum'' are effective as an intranasal wash to treat acute sinusitis. Evidence is inconclusive on whether anti-fungal treatments improve symptoms or quality of life.
Antibiotics
Most sinusitis cases are caused by viruses and resolve without antibiotics. However, if symptoms do not resolve within 10 days, amoxicillin/clavulanate is a reasonable antibiotic association for first treatment. A 2018 Cochrane review, however, found no evidence that people with symptoms lasting seven days or more before consulting their physician are more likely to have bacterial sinusitis as one study found that about 80% of patients have symptoms lasting more than 7 days and another about 70%. Antibiotics are specifically not recommended in those with mild / moderate disease during the first week of infection due to risk of adverse effects,antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. ...
, and cost.
Fluoroquinolones
A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic molecule, bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-Quinolone, 4-quinolone. They are used in human and ...
, and a newer macrolide antibiotic such as clarithromycin or a tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including Acne vulgaris, acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague (disease), plague, malaria, and sy ...
like doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, an ...
, are used in those who have severe allergies to penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
s. Because of increasing resistance to amoxicillin the 2012 guideline of the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends amoxicillin-clavulanate as the initial treatment of choice for bacterial sinusitis. The guidelines also recommend against other commonly used antibiotics, including azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumon ...
, clarithromycin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, because of growing antibiotic resistance. The FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
recommends against the use of fluoroquinolones when other options are available due to higher risks of serious side effects.
A short-course (3–7 days) of antibiotics seems to be just as effective as the typical longer-course (10–14 days) of antibiotics for those with clinically diagnosed acute bacterial sinusitis without any other severe disease or complicating factors. The IDSA guideline suggest five to seven days of antibiotics is long enough to treat a bacterial infection without encouraging resistance. The guidelines still recommend children receive antibiotic treatment for ten days to two weeks.
Corticosteroids
For unconfirmed acute sinusitis,nasal sprays
Nasal is an adjective referring to the nose, part of human or animal anatomy. It may also be shorthand for the following uses in combination:
* With reference to the human nose:
** Nasal administration, a method of pharmaceutical drug delivery
** ...
using corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
s have not been found to be better than a placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general ...
either alone or in combination with antibiotics. For cases confirmed by radiology or nasal endoscopy, treatment with intranasal corticosteroids alone or in combination with antibiotics is supported. The benefit, however, is small.
For confirmed chronic rhinosinusitis, there is limited evidence that intranasal steroids improve symptoms and insufficient evidence that one type of steroid is more effective.
There is only limited evidence to support short treatment with corticosteroids by mouth for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. There is limited evidence to support corticosteroids by mouth in combination with antibiotics for acute sinusitis; it has only short-term effect improving the symptoms.
Surgery
For sinusitis of dental origin, treatment focuses on removing the infection and preventing reinfection, by removal of themicroorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s, their byproducts, and pulpal debris from the infected root canal. Systemic antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
s are ineffective as a definitive solution, but may afford temporary relief of symptoms by improving sinus clearing, and may be appropriate for rapidly spreading infections, but debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
In p ...
and disinfection of the root canal system at the same time is necessary. Treatment options include non-surgical root canal treatment, periradicular surgery
In the dental specialty of endodontics, periradicular surgery is surgery to the external root surface. Examples of periradicular surgery include apicoectomy, root resection, repair of root perforation or resorption defects, removal of broken frag ...
, tooth replantation
Tooth replantation is a form of restorative dentistry in which an avulsed or luxated tooth is reinserted and secured into its socket through a combination of dental procedures. The purposes of tooth replantation is to resolve tooth loss and prese ...
, or extraction of the infected tooth.
For chronic or recurring sinusitis, referral to an otolaryngologist may be indicated, and treatment options may include nasal surgery. Surgery should only be considered for those people who do not benefit with medication. It is unclear how benefits of surgery compare to medical treatments in those with nasal polyps as this has been poorly studied.
A number of surgical approaches can be used to access the sinuses and these have generally shifted from external/extranasal approaches to intranasal endoscopic
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
ones. The benefit of functional endoscopic sinus surgery
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS), or functional endoscopic sinus surgery, is a procedure that is used to treat sinusitis and other conditions that affect the sinuses. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses that can cause symptoms su ...
(FESS) is its ability to allow for a more targeted approach to the affected sinuses, reducing tissue disruption, and minimizing post-operative complications. The use of drug eluting stents
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a peripheral or coronary stent (a scaffold) placed into narrowed, diseased peripheral or coronary arteries that slowly release a drug to block cell proliferation. This prevents fibrosis that, together with clots (t ...
such as propel mometasone furoate implant may help in recovery after surgery.
Another recently developed treatment is balloon sinuplasty. This method, similar to balloon angioplasty
Angioplasty, is also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclero ...
used to "unclog" arteries of the heart, utilizes balloons in an attempt to expand the openings of the sinuses in a less invasive manner. The effectiveness of the functional endoscopic balloon dilation approach compared to conventional FESS is not known.
Treatments directed to rhinovirus infection
A study has shown that patients given spray formulation of 0.73 mg of Tremacamra (a soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1CAM-1
Qikiqtaryuaq, formerly Jenny Lind Island, for the Swedish born opera singer, Jenny Lind, is a small island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. The island is located in the Queen Maud Gulf, about southeast of Cambridge Bay.
The isla ...
receptor) reduced the severity of illness.
Prognosis
A 2018 review has found that without the use of antibiotics, about 46% were cured after one week and 64% after two weeks.Epidemiology
Sinusitis is a common condition, with between 24 and 31 million cases occurring in the United States annually. Chronic sinusitis affects approximately 12.5% of people.Research
Based on recent theories on the role thatfungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
may play in the development of chronic sinusitis, antifungal treatments have been used, on a trial basis. These trials have had mixed results.
See also
*Fungal sinusitis
Fungal sinusitis is the inflammation of the lining mucosa of the paranasal sinuses due to fungal infection. It occurs in people with reduced immunity. The maxillary sinus is the most commonly involved. Fungi responsible for fungal sinusitis are ...
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Nose disorders Headaches Inflammations Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate