|
Hyperplastic
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition of excessive proliferation of the cells of the endometrium, or inner lining of the uterus. Most cases of endometrial hyperplasia result from high levels of estrogens, combined with insufficient levels of the progesterone-like hormones which ordinarily counteract estrogen's proliferative effects on this tissue. This may occur in a number of settings, including obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, estrogen producing tumours (e.g. granulosa cell tumour) and certain formulations of estrogen replacement therapy. Endometrial hyperplasia with atypia is a significant risk factor for the development or even co-existence of endometrial cancer, so careful monitoring and treatment of women with this disorder is essential. Classification Like other hyperplastic disorders, endometrial hyperplasia initially represents a physiological response of endometrial tissue to the growth-promoting actions of estrogen. However, the gland-forming cells of a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss of bladder control. Complications can include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and chronic kidney problems. The cause is unclear. Risk factors include a family history, obesity, type 2 diabetes, not enough exercise, and erectile dysfunction. Medications like pseudoephedrine, anticholinergics, and calcium channel blockers may worsen symptoms. The underlying mechanism involves the prostate pressing on the urethra and thereby making it difficult to pass urine out of the bladder. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and examination after ruling out other possible causes. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, a number of procedures, and surgery. In those with mild symptoms, weight loss, exercise, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasia
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Tumor
A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize (spread throughout the body). Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface (fibrous sheath of connective tissue) or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids. Some forms of benign tumors may be harmful to health. Benign tumor growth causes a mass effect that can compress neighboring tissues. This can lead to nerve damage, blood flow reduction ( ischemia), tissue death (necrosis), or organ damage. The health effects of benign tumor growth may be more prominent if the tumor is contained within an enclosed space such as the cranium, respiratory tract, sinus, or bones. For example, unlike most benign tumors elsewhere in the body, benign brain tumors can be life-thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number.Updated by Linda J. Vorvick. 8/14/1Hyperplasia/ref> Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally-induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery File:*+ * Photographic documentation on sexual education - Hypertrophy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
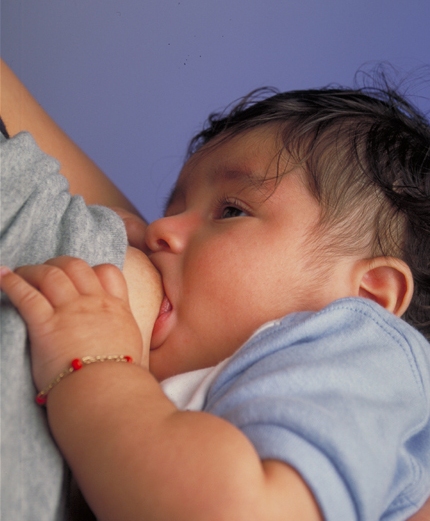
Breast Feeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfeeding has a number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex. Most of these disorders involve excessive or deficient production of hormones such as glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, or sex steroids, and can alter development of primary or secondary sex characteristics in some affected infants, children, or adults. It is one of the most common autosomal recessive disorders in humans. Types CAH can occur in various forms. The clinical presentation of each form is different and depends to a large extent on the underlying enzyme defect, its precursor retention, and deficient products. Classical forms appear in infancy, and nonclassical forms appear in late childhood. The presentation in patients with classic CAH can be further subdivided into two forms: salt-wasting and simple-virilizing, depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cushing's Disease
Cushing's disease is one cause of Cushing's syndrome characterised by increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary (secondary hypercortisolism). This is most often as a result of a pituitary adenoma (specifically pituitary basophilism) or due to excess production of hypothalamus CRH ( corticotropin releasing hormone) (tertiary hypercortisolism/hypercorticism) that stimulates the synthesis of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Pituitary adenomas are responsible for 80% of endogenous Cushing's syndrome, when excluding Cushing's syndrome from exogenously administered corticosteroids. The equine version of this disease is Pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction. This should not be confused with ectopic Cushing syndrome or exogenous steroid use. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of Cushing's disease are similar to those seen in other causes of Cushing's syndrome. Patients with Cushing's disease usually present with one or more signs and sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of IGF-1 and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of hGH called somatropin (INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health care providers are prescribi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


