A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world.
In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with
model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided in ...
.
Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in which simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time.
Another way to distinguish between the terms is to define simulation as
experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
ation with the help of a model. This definition includes time-independent simulations. Often,
computers are used to execute the simulation.
Simulation is used in many contexts, such as simulation of technology for
performance tuning
Performance tuning is the improvement of system Computer performance, performance. Typically in computer systems, the motivation for such activity is called a performance problem, which can be either real or anticipated. Most systems will respond t ...
or optimizing,
safety engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering Branches of science, discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety en ...
, testing, training, education, and video games. Simulation is also used with
scientific modelling
Scientific modelling is an activity that produces models representing empirical objects, phenomena, and physical processes, to make a particular part or feature of the world easier to understand, define, quantify, visualize, or simulate. It ...
of natural systems or human systems to gain insight into their functioning, as in economics. Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may simply not exist.
Key issues in
modeling and simulation
Modeling and simulation (M&S) is the use of models (e.g., physical, mathematical, behavioral, or logical representation of a system, entity, phenomenon, or process) as a basis for simulations to develop data utilized for managerial or technica ...
include the acquisition of valid sources of information about the relevant selection of key characteristics and behaviors used to build the model, the use of simplifying approximations and assumptions within the model, and fidelity and validity of the simulation outcomes. Procedures and protocols for
model verification and validation are an ongoing field of academic study, refinement, research and development in simulations technology or practice, particularly in the work of computer simulation.
Classification and terminology

Historically, simulations used in different fields developed largely independently, but 20th-century studies of
systems theory
Systems theory is the Transdisciplinarity, transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, de ...
and
cybernetics
Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions (its outputs) return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with ...
combined with spreading use of computers across all those fields have led to some unification and a more systematic view of the concept.
''
Physical simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
'' refers to simulation in which physical objects are substituted for the real thing. These physical objects are often chosen because they are smaller or cheaper than the actual object or system. ()
Alternatively, ''physical simulation'' may refer to computer simulations considering selected laws of physics, as in
multiphysics simulation
In computational modelling, multiphysics simulation (often shortened to simply "multiphysics") is defined as the simultaneous simulation of different aspects of a physical system or systems and the interactions among them. For example, simultaneou ...
. ()
''Interactive simulation'' is a special kind of physical simulation, often referred to as a ''
human-in-the-loop
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) is used in multiple contexts. It can be defined as a model requiring human interaction. HITL is associated with modeling and simulation (M&S) in the live, virtual, and constructive taxonomy. HITL along with the related hum ...
'' simulation, in which physical simulations include human operators, such as in a
flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
,
sailing simulator, or
driving simulator
Driving simulators are used for entertainment as well as in training of driver's education courses taught in educational institutions and private businesses. They are also used for research purposes in the area of human factors and medical rese ...
.
''
Continuous simulation
Continuous Simulation refers to simulation approaches where a system is modeled with the help of variables that change continuously according to a set of differential equations.
History
It is notable as one of the first uses ever put to computers, ...
'' is a simulation based on
continuous-time rather than discrete-time steps, using numerical integration of
differential equations.
[McLeod, J. (1968) "Simulation: the Dynamic Modeling of Ideas And Systems with Computers", McGraw-Hill, NYC.]
''
Discrete-event simulation
A discrete-event simulation (DES) models the operation of a system as a ( discrete) sequence of events in time. Each event occurs at a particular instant in time and marks a change of state in the system. Between consecutive events, no change in t ...
'' studies systems whose states change their values only at discrete times. For example, a simulation of an epidemic could change the number of infected people at time instants when susceptible individuals get infected or when infected individuals recover.
''
Stochastic simulation A stochastic simulation is a simulation of a system that has variables that can change stochastically (randomly) with individual probabilities.DLOUHÝ, M.; FÁBRY, J.; KUNCOVÁ, M.. Simulace pro ekonomy. Praha : VŠE, 2005.
Realizations of these ...
'' is a simulation where some variable or process is subject to random variations and is projected using
Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo ( ; ; or colloquially ; , ; ) is an official administrative area of Monaco, specifically the Ward (country subdivision), ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is located. Informally, the name also refers to ...
techniques using pseudo-random numbers. Thus replicated runs with the same boundary conditions will each produce different results within a specific confidence band.
''
Deterministic simulation
Determinism is the metaphysical view that all events within the universe (or multiverse) can occur only in one possible way. Deterministic theories throughout the history of philosophy have developed from diverse and sometimes overlapping mo ...
'' is a simulation which is not stochastic: thus the variables are regulated by deterministic algorithms. So replicated runs from the same boundary conditions always produce identical results.
''Hybrid simulation'' (or combined simulation) corresponds to a mix between continuous and discrete event simulation and results in integrating numerically the differential equations between two sequential events to reduce the number of discontinuities.
A ''stand-alone simulation'' is a simulation running on a single workstation by itself.
A is one which uses more than one computer simultaneously, to guarantee access from/to different resources (e.g. multi-users operating different systems, or distributed data sets); a classical example is
Distributed Interactive Simulation
Distributed Interactive Simulation (DIS) is an IEEE standard for conducting real-time platform-level wargaming across multiple host computers and is used worldwide, especially by military organizations but also by other agencies such as those inv ...
(DIS).
''Parallel simulation'' speeds up a simulation's execution by concurrently distributing its workload over multiple processors, as in
high-performance computing
High-performance computing (HPC) is the use of supercomputers and computer clusters to solve advanced computation problems.
Overview
HPC integrates systems administration (including network and security knowledge) and parallel programming into ...
.
''Interoperable simulation'' is where multiple models, simulators (often defined as federates) interoperate locally, distributed over a network; a classical example is
High-Level Architecture
The High Level Architecture (HLA) is a standard for distributed simulation, used when building a simulation for a larger purpose by combining (federating) several simulations. The standard was developed in the 1990s under the leadership of the US ...
.
''Modeling and simulation as a service'' is where simulation is accessed as a service over the web.
''Modeling, interoperable simulation and serious games'' is where
serious game
A serious game or applied game is a game designed for a primary purpose other than pure entertainment. The "serious" adjective is generally prepended to refer to video games used by industries like defense, education, scientific exploration, he ...
approaches (e.g. game engines and engagement methods) are integrated with interoperable simulation.
''Simulation fidelity'' is used to describe the accuracy of a simulation and how closely it imitates the real-life counterpart. Fidelity is broadly classified as one of three categories: low, medium, and high. Specific descriptions of fidelity levels are subject to interpretation, but the following generalizations can be made:
* Low – the minimum simulation required for a system to respond to accept inputs and provide outputs
* Medium – responds automatically to stimuli, with limited accuracy
* High – nearly indistinguishable or as close as possible to the real system
A ''synthetic environment'' is a computer simulation that can be included in human-in-the-loop simulations.
''Simulation in failure analysis'' refers to simulation in which we create environment/conditions to identify the cause of equipment failure. This can be the best and fastest method to identify the failure cause.
Computer simulation
A computer simulation (or "sim") is an attempt to model a real-life or hypothetical situation on a computer so that it can be studied to see how the system works. By changing variables in the simulation,
prediction
A prediction (Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dictum'', "something said") or forecast is a statement about a future event or about future data. Predictions are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge of forecasters. There ...
s may be made about the behaviour of the system. It is a tool to virtually investigate the behaviour of the system under study.
Computer simulation has become a useful part of
modeling
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the Plan_(drawing), plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French language, French and Italian language, Italian ult ...
many natural systems in
physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
,
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
and
biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, and human systems in economics and
social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
(e.g.,
computational sociology
Computational sociology is a branch of sociology that uses computationally intensive methods to analyze and model social phenomena. Using computer simulations, artificial intelligence, complex statistical methods, and analytic approaches like soc ...
) as well as in engineering to gain insight into the operation of those systems. A good example of the usefulness of using computers to simulate can be found in the field of
network traffic simulation Network traffic simulation is a process used in telecommunications engineering to measure the efficiency of a communications network.
Overview
Telecommunications systems are complex real-world systems, containing many different components which in ...
. In such simulations, the
model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided in ...
behaviour will change each simulation according to the set of initial parameters assumed for the environment.
Traditionally, the formal modeling of systems has been via a
mathematical model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical m ...
, which attempts to find analytical solutions enabling the prediction of the behaviour of the system from a set of parameters and initial conditions. Computer simulation is often used as an adjunct to, or substitution for, modeling systems for which simple
closed form analytic solutions are not possible. There are many different types of computer simulation, the common feature they all share is the attempt to generate a sample of representative
scenario
In the performing arts, a scenario (, ; ; from Italian , "that which is pinned to the scenery") is a synoptical collage of an event or series of actions and events. In the ''commedia dell'arte'', it was an outline of entrances, exits, and actio ...
s for a model in which a complete enumeration of all possible states would be prohibitive or impossible.
Several software packages exist for running computer-based simulation modeling (e.g.
Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo ( ; ; or colloquially ; , ; ) is an official administrative area of Monaco, specifically the Ward (country subdivision), ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is located. Informally, the name also refers to ...
simulation,
stochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
modeling, multimethod modeling) that makes all the modeling almost effortless.
Modern usage of the term "computer simulation" may encompass virtually any computer-based representation.
Computer science
In
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, simulation has some specialized meanings:
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer ...
used the term ''simulation'' to refer to what happens when a
universal machine
In computer science, a universal Turing machine (UTM) is a Turing machine capable of computing any computable sequence, as described by Alan Turing in his seminal paper "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem". Co ...
executes a state transition table (in modern terminology, a computer runs a program) that describes the state transitions, inputs and outputs of a subject discrete-state machine. The computer simulates the subject machine. Accordingly, in
theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science is a subfield of computer science and mathematics that focuses on the Abstraction, abstract and mathematical foundations of computation.
It is difficult to circumscribe the theoretical areas precisely. The Associati ...
the term ''
simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
'' is a relation between
state transition system
In theoretical computer science, a transition system is a concept used in the study of computation. It is used to describe the potential behavior of discrete systems. It consists of states and transitions between states, which may be labeled wi ...
s, useful in the study of
operational semantics
Operational semantics is a category of formal programming language semantics in which certain desired properties of a program, such as correctness, safety or security, are verified by constructing proofs from logical statements about its exec ...
.
Less theoretically, an interesting application of computer simulation is to simulate computers using computers. In
computer architecture, a type of simulator, typically called an ''
emulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run sof ...
'', is often used to execute a program that has to run on some inconvenient type of computer (for example, a newly designed computer that has not yet been built or an obsolete computer that is no longer available), or in a tightly controlled testing environment (see
Computer architecture simulator
A computer architecture simulator is a program that simulates the execution of computer architecture.
Computer architecture simulators are used for the following purposes:
* Lowering cost by evaluating hardware designs without building physical ...
and
Platform virtualization
In computing, virtualization (abbreviated v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of Virtual machine, virtual machines, Operating system, operating systems, processes or containers.
Vir ...
). For example, simulators have been used to debug a
microprogram
In processor design, microcode serves as an intermediary layer situated between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer. It consists of a set of hardware-level instructions ...
or sometimes commercial application programs, before the program is downloaded to the target machine. Since the operation of the computer is simulated, all of the information about the computer's operation is directly available to the programmer, and the speed and execution of the simulation can be varied at will.
Simulators may also be used to interpret
fault tree
Fault tree analysis (FTA) is a type of failure analysis in which an undesired state of a system is examined. This analysis method is mainly used in safety engineering and reliability engineering to understand how systems can fail, to identify the ...
s, or test
VLSI logic designs before they are constructed.
Symbolic simulation
In computer science, a simulation is a computation of the execution of some appropriately modelled state-transition system. Typically this process models the complete state of the system at individual points in a discrete linear time frame, compu ...
uses variables to stand for unknown values.
In the field of
optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
, simulations of physical processes are often used in conjunction with
evolutionary computation
Evolutionary computation from computer science is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms ...
to optimize control strategies.
Simulation in education and training
Simulation is extensively used for educational purposes. It is used for cases where it is prohibitively expensive or simply too dangerous to allow trainees to use the real equipment in the real world. In such situations they will spend time learning valuable lessons in a "safe" virtual environment yet living a lifelike experience (or at least it is the goal). Often the convenience is to permit mistakes during training for a safety-critical system.
Simulations in education are somewhat like training simulations. They focus on specific tasks. The term 'microworld' is used to refer to educational simulations which model some abstract concept rather than simulating a realistic object or environment, or in some cases model a real-world environment in a simplistic way so as to help a learner develop an understanding of the key concepts. Normally, a user can create some sort of construction within the microworld that will behave in a way consistent with the concepts being modeled.
Seymour Papert
Seymour Aubrey Papert (; 29 February 1928 – 31 July 2016) was a South African-born American mathematician, computer scientist, and educator, who spent most of his career teaching and researching at MIT. He was one of the pioneers of artif ...
was one of the first to advocate the value of microworlds, and the
Logo
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name that it represents, as in ...
programming environment developed by Papert is one of the most well-known microworlds.
Project management simulation is increasingly used to train students and professionals in the art and science of project management. Using simulation for
project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
training improves learning retention and enhances the learning process.
''Social simulations'' may be used in social science classrooms to illustrate social and political processes in anthropology, economics, history, political science, or sociology courses, typically at the high school or university level. These may, for example, take the form of civics simulations, in which participants assume roles in a simulated society, or international relations simulations in which participants engage in negotiations, alliance formation, trade, diplomacy, and the use of force. Such simulations might be based on fictitious political systems, or be based on current or historical events. An example of the latter would be
Barnard College
Barnard College is a Private college, private Women's colleges in the United States, women's Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college affiliated with Columbia University in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a grou ...
's ''Reacting to the Past'' series of historical educational games. The
National Science Foundation
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is an Independent agencies of the United States government#Examples of independent agencies, independent agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that su ...
has also supported the creation of
reacting games
Reacting games are educational role-playing games set in the past, with a focus on student debates about great texts.
History
Reacting games developed as a genre of experiential education games in the United States in the late 1990s from work ...
that address science and math education. In social media simulations, participants train communication with critics and other stakeholders in a private environment.
In recent years, there has been increasing use of social simulations for staff training in aid and development agencies. The Carana simulation, for example, was first developed by the
United Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries eliminate poverty and achieve sustainable economic growth and human development. The UNDP emphasizes on developing local capacity towar ...
, and is now used in a very revised form by the
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development ...
for training staff to deal with fragile and conflict-affected countries.
Military uses for simulation often involve aircraft or armoured fighting vehicles, but can also target small arms and other weapon systems training. Specifically, virtual firearms ranges have become the norm in most military training processes and there is a significant amount of data to suggest this is a useful tool for armed professionals.
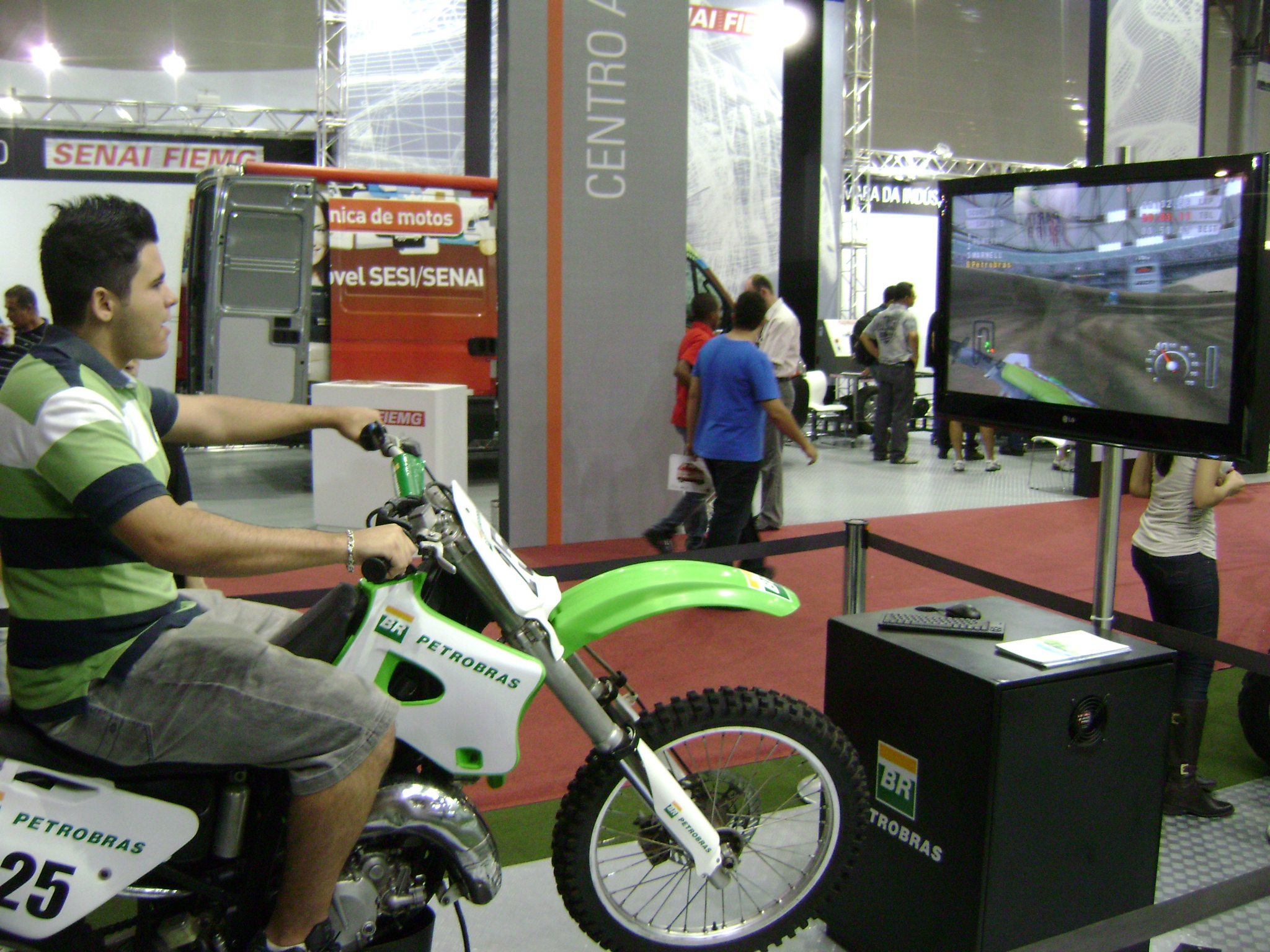
Virtual simulation
A virtual simulation is a category of simulation that uses simulation equipment to create a simulated world for the user. Virtual simulations allow users to interact with a
virtual world
A virtual world (also called a virtual space or spaces) is a Computer simulation, computer-simulated environment which may be populated by many simultaneous users who can create a personal Avatar (computing), avatar and independently explore th ...
. Virtual worlds operate on platforms of integrated software and hardware components. In this manner, the system can accept input from the user (e.g., body tracking, voice/sound recognition, physical controllers) and produce output to the user (e.g., visual display, aural display, haptic display) .
Virtual simulations use the aforementioned modes of interaction to produce a sense of
immersion
Immersion may refer to:
The arts
* "Immersion", a 2012 story by Aliette de Bodard
* ''Immersion'', a French comic book series by Léo Quievreux
* ''Immersion'' (album), the third album by Australian group Pendulum
* ''Immersion'' (film), a 2021 ...
for the user.
Virtual simulation input hardware

There is a wide variety of input hardware available to accept user input for virtual simulations. The following list briefly describes several of them:
* ''Body tracking'': The
motion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mocap or mo-cap, for short) is the process of recording high-resolution motion (physics), movement of objects or people into a computer system. It is used in Military science, military, entertainment, sports ...
method is often used to record the user's movements and translate the captured data into inputs for the virtual simulation. For example, if a user physically turns their head, the motion would be captured by the simulation hardware in some way and translated to a corresponding shift in view within the simulation.
**
Capture suits and/or gloves may be used to capture movements of users body parts. The systems may have sensors incorporated inside them to sense movements of different body parts (e.g., fingers). Alternatively, these systems may have exterior tracking devices or marks that can be detected by external ultrasound, optical receivers or electromagnetic sensors. Internal inertial sensors are also available on some systems. The units may transmit data either wirelessly or through cables.
**
Eye tracker
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research ...
s can also be used to detect eye movements so that the system can determine precisely where a user is looking at any given instant.
* ''Physical controllers'': Physical controllers provide input to the simulation only through direct manipulation by the user. In virtual simulations, tactile feedback from physical controllers is highly desirable in a number of simulation environments.
**
Omnidirectional treadmill
An omnidirectional treadmill (ODT) is a mechanical device, similar to a typical treadmill, that allows a person to perform locomotive motion in any direction, allowing for 360 degrees of movement. The ability to move in any direction is how thes ...
s can be used to capture the users locomotion as they walk or run.
** High fidelity instrumentation such as instrument panels in virtual aircraft cockpits provides users with actual controls to raise the level of immersion. For example, pilots can use the actual
global positioning system
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide ge ...
controls from the real device in a simulated cockpit to help them practice procedures with the actual device in the context of the integrated cockpit system.
* ''Voice/sound recognition'': This form of interaction may be used either to interact with agents within the simulation (e.g., virtual people) or to manipulate objects in the simulation (e.g., information). Voice interaction presumably increases the level of immersion for the user.
** Users may use headsets with boom microphones, lapel microphones or the room may be equipped with strategically located microphones.
Current research into user input systems
Research in future input systems holds a great deal of promise for virtual simulations. Systems such as
brain–computer interface
A brain–computer interface (BCI), sometimes called a brain–machine interface (BMI), is a direct communication link between the brain's electrical activity and an external device, most commonly a computer or robotic limb. BCIs are often dire ...
s (BCIs) offer the ability to further increase the level of immersion for virtual simulation users. Lee, Keinrath, Scherer, Bischof, Pfurtscheller proved that naïve subjects could be trained to use a BCI to navigate a virtual apartment with relative ease. Using the BCI, the authors found that subjects were able to freely navigate the virtual environment with relatively minimal effort. It is possible that these types of systems will become standard input modalities in future virtual simulation systems.
Virtual simulation output hardware
There is a wide variety of output hardware available to deliver a stimulus to users in virtual simulations. The following list briefly describes several of them:
*''Visual display'': Visual displays provide the visual stimulus to the user.
** Stationary displays can vary from a conventional desktop display to 360-degree wrap-around screens to stereo three-dimensional screens. Conventional desktop displays can vary in size from . Wrap around screens is typically used in what is known as a
cave automatic virtual environment
A cave automatic virtual environment (better known by the recursive acronym CAVE) is an immersive virtual reality environment where projectors are directed to between three and six of the walls of a room-sized cube. The name is also a referen ...
(CAVE). Stereo three-dimensional screens produce three-dimensional images either with or without special glasses—depending on the design.
**
Head-mounted display
A head-mounted display (HMD) is a display device, worn on the head or as part of a helmet (see helmet-mounted display for aviation applications), that has a small display optic in front of one (monocular HMD) or each eye (binocular vision, bi ...
s (HMDs) have small displays that are mounted on headgear worn by the user. These systems are connected directly into the virtual simulation to provide the user with a more immersive experience. Weight, update rates and field of view are some of the key variables that differentiate HMDs. Naturally, heavier HMDs are undesirable as they cause fatigue over time. If the update rate is too slow, the system is unable to update the displays fast enough to correspond with a quick head turn by the user. Slower update rates tend to cause simulation sickness and disrupt the sense of immersion. Field of view or the angular extent of the world that is seen at a given moment
field of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to elec ...
can vary from system to system and has been found to affect the user's sense of immersion.
* ''Aural display'': Several different types of audio systems exist to help the user hear and localize sounds spatially. Special software can be used to produce 3D audio effects
3D audio
3D audio effects are a group of sound effects that manipulate the sound produced by Stereophonic sound, stereo speakers, Surround sound, surround-sound speakers, speaker-arrays, or headphones. This frequently involves the virtual placement of sou ...
to create the illusion that sound sources are placed within a defined three-dimensional space around the user.
** Stationary conventional speaker systems may be used to provide dual or multi-channel surround sound. However, external speakers are not as effective as headphones in producing 3D audio effects.
** Conventional headphones offer a portable alternative to stationary speakers. They also have the added advantages of masking real-world noise and facilitate more effective 3D audio sound effects.
* ''Haptic display'': These displays provide a sense of touch to the user (
haptic technology
Haptic technology (also kinaesthetic communication or 3D touch) is technology that can create an experience of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user. These technologies can be used to create virtual objects in a computer s ...
). This type of output is sometimes referred to as force feedback.
** Tactile tile displays use different types of actuators such as inflatable bladders, vibrators, low-frequency sub-woofers, pin actuators and/or thermo-actuators to produce sensations for the user.
** End effector displays can respond to users inputs with resistance and force.
These systems are often used in medical applications for remote surgeries that employ robotic instruments.
* ''Vestibular display'': These displays provide a sense of motion to the user (
motion simulator
A motion simulator or motion platform is a mechanism that creates the feelings of being in a real motion environment. In a simulator, the movement is synchronised with a visual display of the outside world (OTW) scene. Motion platforms can provid ...
). They often manifest as motion bases for virtual vehicle simulation such as driving simulators or flight simulators. Motion bases are fixed in place but use actuators to move the simulator in ways that can produce the sensations pitching, yawing or rolling. The simulators can also move in such a way as to produce a sense of acceleration on all axes (e.g., the motion base can produce the sensation of falling).
Clinical healthcare simulators
Clinical healthcare simulators are increasingly being developed and deployed to teach therapeutic and diagnostic procedures as well as medical concepts and decision making to personnel in the health professions. Simulators have been developed for training procedures ranging from the basics such as
blood draw
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous blood sampling (also called ''phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by medical labor ...
, to
laparoscopic
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or human pelvis, pelvis using small Surgical incision, incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few ...
surgery and trauma care. They are also important to help on prototyping new devices for biomedical engineering problems. Currently, simulators are applied to research and develop tools for new therapies, treatments and early diagnosis in medicine.
Many medical simulators involve a computer connected to a plastic simulation of the relevant anatomy. Sophisticated simulators of this type employ a life-size mannequin that responds to injected drugs and can be programmed to create simulations of life-threatening emergencies.
In other simulations, visual components of the procedure are reproduced by
computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
techniques, while touch-based components are reproduced by
haptic feedback devices combined with physical simulation routines computed in response to the user's actions. Medical simulations of this sort will often use 3D
CT or
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
scans of patient data to enhance realism. Some medical simulations are developed to be widely distributed (such as web-enabled simulations and procedural simulations that can be viewed via standard web browsers) and can be interacted with using standard computer interfaces, such as the
keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Mus ...
and
mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
.
Placebo
An important medical application of a simulator—although, perhaps, denoting a slightly different meaning of ''simulator''—is the use of a
placebo
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
drug, a formulation that simulates the active drug in trials of drug efficacy.
Improving patient safety
Patient safety is a concern in the medical industry. Patients have been known to suffer injuries and even death due to management error, and lack of using best standards of care and training. According to Building a National Agenda for Simulation-Based Medical Education (Eder-Van Hook, Jackie, 2004), "a health care provider's ability to react prudently in an unexpected situation is one of the most critical factors in creating a positive outcome in medical emergency, regardless of whether it occurs on the battlefield, freeway, or hospital emergency room." Eder-Van Hook (2004) also noted that medical errors kill up to 98,000 with an estimated cost between $37 and $50 million and $17 to $29 billion for preventable adverse events dollars per year.
Simulation is being used to study patient safety, as well as train medical professionals.
Studying patient safety and safety interventions in healthcare is challenging, because there is a lack of experimental control (i.e., patient complexity, system/process variances) to see if an intervention made a meaningful difference (Groves & Manges, 2017). An example of innovative simulation to study patient safety is from nursing research. Groves et al. (2016) used a high-fidelity simulation to examine nursing safety-oriented behaviors during times such as
change-of-shift report
In healthcare, a change-of-shift report is a meeting between healthcare providers at the change of shift in which vital information about and responsibility for the patient is provided from the off-going provider to the on-coming provider (Groves, ...
.
However, the value of simulation interventions to translating to clinical practice are is still debatable.
As Nishisaki states, "there is good evidence that simulation training improves provider and team
self-efficacy
In psychology, self-efficacy is an individual's belief in their capacity to act in the ways necessary to reach specific goals. The concept was originally proposed by the psychologist Albert Bandura in 1977.
Self-efficacy affects every area of hum ...
and competence on manikins. There is also good evidence that procedural simulation improves actual operational performance in clinical settings."
However, there is a need to have improved evidence to show that
crew resource management training through simulation.
One of the largest challenges is showing that team simulation improves team operational performance at the bedside.
Although evidence that simulation-based training actually improves patient outcome has been slow to accrue, today the ability of simulation to provide hands-on experience that translates to the operating room is no longer in doubt.
One of the largest factors that might impact the ability to have training impact the work of practitioners at the bedside is the ability to empower frontline staff (Stewart, Manges, Ward, 2015).
Another example of an attempt to improve patient safety through the use of simulations training is patient care to deliver just-in-time service or/and just-in-place. This training consists of 20 minutes of simulated training just before workers report to shift. One study found that just in time training improved the transition to the bedside. The conclusion as reported in Nishisaki (2008) work, was that the simulation training improved resident participation in real cases; but did not sacrifice the quality of service. It could be therefore hypothesized that by increasing the number of highly trained residents through the use of simulation training, that the simulation training does, in fact, increase patient safety.
History of simulation in healthcare
The first medical simulators were simple models of human patients.
Since antiquity, these representations in clay and stone were used to demonstrate clinical features of disease states and their effects on humans. Models have been found in many cultures and continents. These models have been used in some cultures (e.g., Chinese culture) as a "
diagnostic
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
" instrument, allowing women to consult male physicians while maintaining social laws of modesty. Models are used today to help students learn the
anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
of the
musculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provid ...
system and organ systems.
In 2002, the
Society for Simulation in Healthcare (SSH) was formed to become a leader in international interprofessional advances the application of medical simulation in healthcare
The need for a "uniform mechanism to educate, evaluate, and certify simulation instructors for the health care profession" was recognized by McGaghie et al. in their critical review of simulation-based medical education research.
In 2012 the SSH piloted two new certifications to provide recognition to educators in an effort to meet this need.
Type of models
Active models
Active models that attempt to reproduce living anatomy or physiology are recent developments. The famous
"Harvey" mannequin was developed at the
University of Miami
The University of Miami (UM, UMiami, Miami, U of M, and The U) is a private university, private research university in Coral Gables, Florida, United States. , the university enrolled 19,852 students in two colleges and ten schools across over ...
and is able to recreate many of the physical findings of the
cardiology
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery di ...
examination, including
palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
,
auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory system, circulatory and resp ...
, and
electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles.
It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of t ...
.
Interactive models
More recently, interactive models have been developed that respond to actions taken by a student or physician.
[ Until recently, these simulations were two dimensional computer programs that acted more like a textbook than a patient. Computer simulations have the advantage of allowing a student to make judgments, and also to make errors. The process of iterative learning through assessment, evaluation, decision making, and error correction creates a much stronger learning environment than passive instruction.
]
Computer simulators
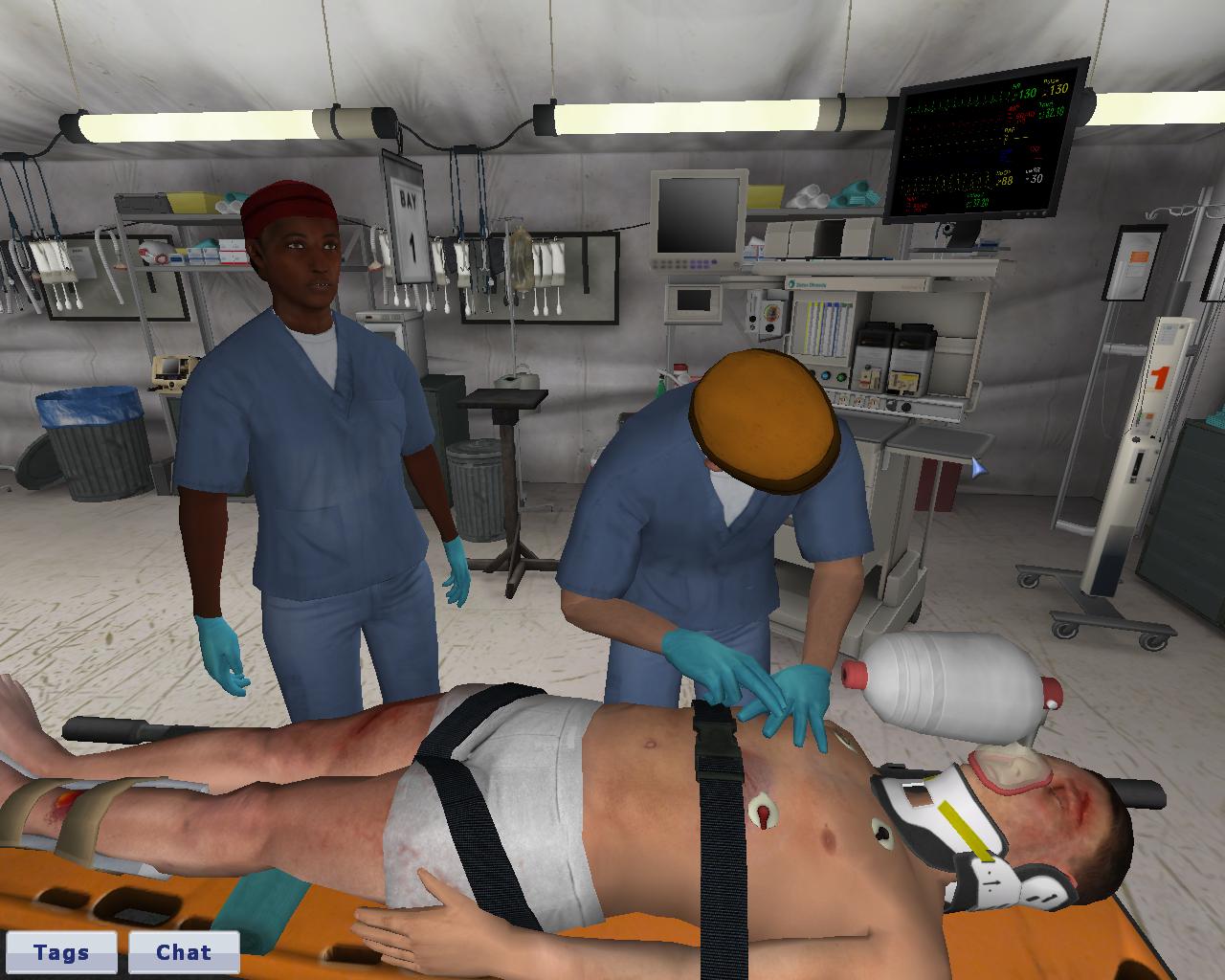 Simulators have been proposed as an ideal tool for assessment of students for clinical skills.
Simulators have been proposed as an ideal tool for assessment of students for clinical skills.
Simulation in entertainment
Simulation in entertainment encompasses many large and popular industries such as film, television, video games (including serious game
A serious game or applied game is a game designed for a primary purpose other than pure entertainment. The "serious" adjective is generally prepended to refer to video games used by industries like defense, education, scientific exploration, he ...
s) and rides in theme parks. Although modern simulation is thought to have its roots in training and the military, in the 20th century it also became a conduit for enterprises which were more hedonistic in nature.
History of visual simulation in film and games
Early history (1940s and 1950s)
The first simulation game may have been created as early as 1947 by Thomas T. Goldsmith Jr. and Estle Ray Mann. This was a straightforward game that simulated a missile being fired at a target. The curve of the missile and its speed could be adjusted using several knobs. In 1958, a computer game called ''Tennis for Two
''Tennis for Two'' (also known as ''Computer Tennis'') is a sports video game that simulates a game of tennis, and was one of the first games developed in the early history of video games. American physicist William Higinbotham designed the game ...
'' was created by Willy Higginbotham which simulated a tennis game between two players who could both play at the same time using hand controls and was displayed on an oscilloscope. This was one of the first electronic video games to use a graphical display.
1970s and early 1980s
Computer-generated imagery
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in Digital art, art, Publishing, printed media, Training simulation, simulators, videos and video games. These images ...
was used in the film to simulate objects as early as 1972 in ''A Computer Animated Hand
''A Computer Animated Hand'' is the title of a 1972 American List of computer-animated films, computer-animated short film produced by Edwin Catmull and Fred Parke. Produced during Catmull's tenure at the University of Utah, the short was created ...
'', parts of which were shown on the big screen in the 1976 film ''Futureworld
''Futureworld'' is a 1976 American science fiction thriller film directed by Richard T. Heffron and written by Mayo Simon and George Schenck. It is a sequel to the 1973 Michael Crichton film '' Westworld'', and is the second installment in ...
''. This was followed by the "targeting computer" that young Skywalker turns off in the 1977 film ''Star Wars
''Star Wars'' is an American epic film, epic space opera media franchise created by George Lucas, which began with the Star Wars (film), eponymous 1977 film and Cultural impact of Star Wars, quickly became a worldwide popular culture, pop cu ...
''.
The film ''Tron
''Tron'' (stylized as ''TRON'') is a 1982 American science fiction action adventure film written and directed by Steven Lisberger from a story by Lisberger and Bonnie MacBird. The film stars Jeff Bridges as Kevin Flynn, a computer programmer ...
'' (1982) was the first film to use computer-generated imagery for more than a couple of minutes.
Advances in technology in the 1980s caused 3D simulation to become more widely used and it began to appear in movies and in computer-based games such as Atari's '' Battlezone'' (1980) and Acornsoft
Acornsoft was the software arm of Acorn Computers, and a major publisher of software for the BBC Micro and Acorn Electron. As well as games, it also produced a large number of educational titles, extra computer languages and business and util ...
's ''Elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (, from , to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful or wealthy people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. Defined by the ...
'' (1984), one of the first wire-frame 3D graphics games for home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
s.
Pre-virtual cinematography era (early 1980s to 1990s)
Advances in technology in the 1980s made the computer more affordable and more capable than they were in previous decades, which facilitated the rise of computer such as the Xbox gaming. The first video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that Input/output, outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can typically be played with a game controller. These may be home video game console, home consoles, which are generally ...
s released in the 1970s and early 1980s fell prey to the industry crash in 1983, but in 1985, Nintendo
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto. It develops, publishes, and releases both video games and video game consoles.
The history of Nintendo began when craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi ...
released the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) which became one of the best selling consoles in video game history. In the 1990s, computer games became widely popular with the release of such game as ''The Sims
''The Sims'' is a series of life simulation video games developed by Maxis and Video game publisher, published by Electronic Arts. The franchise has sold nearly 200 million copies worldwide, and is one of the List of best-selling video game fran ...
'' and ''Command & Conquer
''Command & Conquer'' (''C&C'') is a real-time strategy (RTS) video game franchise created and originally developed by Westwood Studios and currently owned by Electronic Arts. The first game was one of the earliest of the RTS genre, itself ba ...
'' and the still increasing power of desktop computers. Today, computer simulation games such as ''World of Warcraft
''World of Warcraft'' (''WoW'') is a 2004 massively multiplayer online role-playing (MMORPG) video game developed and published by Blizzard Entertainment for Windows and Mac OS X. Set in the '' Warcraft'' fantasy universe, ''World of War ...
'' are played by millions of people around the world.
In 1993, the film ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton, centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of De-extinction#Cloning, cloned dinosaurs. It bega ...
'' became the first popular film to use computer-generated graphics extensively, integrating the simulated dinosaurs almost seamlessly into live action scenes.
This event transformed the film industry; in 1995, the film ''Toy Story
''Toy Story'' is a 1995 American animated adventure comedy film produced by Pixar Animation Studios for Walt Disney Pictures. It is the first installment in the Toy Story (franchise), ''Toy Story'' franchise and the Firsts in animation, firs ...
'' was the first film to use only computer-generated images and by the new millennium computer generated graphics were the leading choice for special effects in films.
Virtual cinematography (early 2000s–present)
The advent of virtual cinematography in the early 2000s has led to an explosion of movies that would have been impossible to shoot without it. Classic examples are the Virtual actor, digital look-alikes of Neo, Smith and other characters in the The Matrix (franchise), ''Matrix'' sequels and the extensive use of physically impossible camera runs in The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''The Lord of the Rings'' trilogy.
The terminal in the Pan Am (TV series) no longer existed during the filming of this 2011–2012 aired series, which was no problem as they created it in virtual cinematography using automation, automated camera angle, viewpoint finding and matching in conjunction with compositing real and simulated footage, which has been the bread and butter of the movie artist in and around film studios since the early 2000s.
Computer-generated imagery
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a specific-technology or application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in Digital art, art, Publishing, printed media, Training simulation, simulators, videos and video games. These images ...
is "the application of the field of 3D computer graphics to special effects". This technology is used for visual effects because they are high in quality, controllable, and can create effects that would not be feasible using any other technology either because of cost, resources or safety. Computer-generated graphics can be seen in many live-action movies today, especially those of the action genre. Further, computer-generated imagery has almost completely supplanted hand-drawn animation in children's movies which are increasingly computer-generated only. Examples of movies that use computer-generated imagery include ''Finding Nemo'', ''300 (film), 300'' and ''Iron Man (2008 film), Iron Man''.
Examples of non-film entertainment simulation
Simulation games
Simulation games, as opposed to other genres of video and computer games, represent or simulate an environment accurately. Moreover, they represent the interactions between the playable characters and the environment realistically. These kinds of games are usually more complex in terms of gameplay. Simulation games have become incredibly popular among people of all ages. Popular simulation games include ''SimCity'' and ''Tiger Woods PGA Tour''. There are also flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
and driving simulator
Driving simulators are used for entertainment as well as in training of driver's education courses taught in educational institutions and private businesses. They are also used for research purposes in the area of human factors and medical rese ...
games.
Theme park rides
Simulators have been used for entertainment since the Link Trainer in the 1930s. The first modern simulator ride to open at a theme park was Disney's Star Tours in 1987 soon followed by Universal's The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera (ride), The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera in 1990 which was the first ride to be done entirely with computer graphics.[simulatr.](_blank)
/ref>
Simulator rides are the progeny of military training simulators and commercial simulators, but they are different in a fundamental way. While military training simulators react realistically to the input of the trainee in real time, ride simulators only feel like they move realistically and move according to prerecorded motion scripts.
Simulation and manufacturing
Manufacturing simulation represents one of the most important applications of simulation. This technique represents a valuable tool used by engineers when evaluating the effect of capital investment in equipment and physical facilities like factory plants, warehouses, and distribution centers. Simulation can be used to predict the performance of an existing or planned system and to compare alternative solutions for a particular design problem.
Another important goal of simulation in manufacturing systems is to quantify system performance. Common measures of system performance include the following:
* Throughput under average and peak loads
* System cycle time (how long it takes to produce one part)
* Use of resource, labor, and machines
* Bottlenecks and choke points
* Queuing at work locations
* Queuing and delays caused by material-handling devices and systems
* WIP storages needs
* Staffing requirements
* Effectiveness of scheduling systems
* Effectiveness of control systems
More examples of simulation
Automobiles
An automobile simulator provides an opportunity to reproduce the characteristics of real vehicles in a virtual environment. It replicates the external factors and conditions with which a vehicle interacts enabling a driver to feel as if they are sitting in the cab of their own vehicle. Scenarios and events are replicated with sufficient reality to ensure that drivers become fully immersed in the experience rather than simply viewing it as an educational experience.
The simulator provides a constructive experience for the novice driver and enables more complex exercises to be undertaken by the more mature driver. For novice drivers, truck simulators provide an opportunity to begin their career by applying best practice. For mature drivers, simulation provides the ability to enhance good driving or to detect poor practice and to suggest the necessary steps for remedial action. For companies, it provides an opportunity to educate staff in the driving skills that achieve reduced maintenance costs, improved productivity and, most importantly, to ensure the safety of their actions in all possible situations.
File:Car racing simulator - SBR Racing, Construma, 2015.04.17.JPG, Car racing simulator
File:Vehicle simulator.jpg, A soldier tests out a heavy-wheeled-vehicle driving simulator.
Biomechanics
A biomechanics simulator is a simulation platform for creating dynamic mechanical models built from combinations of rigid and deformable bodies, joints, constraints, and various force actuators. It is specialized for creating biomechanical models of human anatomical structures, with the intention to study their function and eventually assist in the design and planning of medical treatment.
A biomechanics simulator is used to analyze walking dynamics, study sports performance, simulate surgical procedures, analyze joint loads, design medical devices, and animate human and animal movement.
A neuromechanical simulator that combines biomechanical and biologically realistic neural network simulation. It allows the user to test hypotheses on the neural basis of behavior in a physically accurate 3-D virtual environment.
City and urban
A city simulator can be a city-building game but can also be a tool used by urban planners to understand how cities are likely to evolve in response to various policy decisions. AnyLogic is an example of modern, large-scale urban simulators designed for use by urban planners. City simulators are generally Agent (economics), agent-based simulations with explicit representations for land use and transportation. UrbanSim and Land Use Evolution and Impact Assessment Model, LEAM are examples of large-scale urban simulation models that are used by metropolitan planning agencies and military bases for land use and transportation planning.
Christmas
Several Christmas-themed simulations exist, many of which are centred around Santa Claus. An example of these simulations are websites which claim to allow the user to track Santa Claus. Due to the fact that Santa is a legendary character and not a real, living person, it is impossible to provide actual information on his location, and services such as NORAD Tracks Santa and the Google Santa Tracker (the former of which claims to use radar and other technologies to track Santa) display fake, predetermined location information to users. Another example of these simulations are websites that claim to allow the user to email or send messages to Santa Claus. Websites such as emailSanta.com or Santa's former page on the now-defunct Windows Live Spaces by Microsoft use automated Computer program, programs or scripts to generate personalized replies claimed to be from Santa himself based on user input.
Classroom of the future
The classroom of the future will probably contain several kinds of simulators, in addition to textual and visual learning tools. This will allow students to enter the clinical years better prepared, and with a higher skill level. The advanced student or postgraduate will have a more concise and comprehensive method of retraining—or of incorporating new clinical procedures into their skill set—and regulatory bodies and medical institutions will find it easier to assess the proficiency and Competence (human resources), competency of individuals.
The classroom of the future will also form the basis of a clinical skills unit for continuing education of medical personnel; and in the same way that the use of periodic flight training assists airline pilots, this technology will assist practitioners throughout their career.
The simulator will be more than a "living" textbook, it will become an integral a part of the practice of medicine. The simulator environment will also provide a standard platform for curriculum development in institutions of medical education.
Communication satellites
Modern satellite communications systems (Satcom (satellite), SATCOM) are often large and complex with many interacting parts and elements. In addition, the need for broadband connectivity on a moving vehicle has increased dramatically in the past few years for both commercial and military applications. To accurately predict and deliver high quality of service, SATCOM system designers have to factor in terrain as well as atmospheric and meteorological conditions in their planning. To deal with such complexity, system designers and operators increasingly turn towards computer models of their systems to simulate real-world operating conditions and gain insights into usability and requirements prior to final product sign-off. Modeling improves the understanding of the system by enabling the SATCOM system designer or planner to simulate real-world performance by injecting the models with multiple hypothetical atmospheric and environmental conditions. Simulation is often used in the training of civilian and military personnel. This usually occurs when it is prohibitively expensive or simply too dangerous to allow trainees to use the real equipment in the real world. In such situations, they will spend time learning valuable lessons in a "safe" virtual environment yet living a lifelike experience (or at least it is the goal). Often the convenience is to permit mistakes during training for a safety-critical system.
Digital lifecycle
Simulation solutions are being increasingly integrated with computer-aided solutions and processes (computer-aided design or CAD, computer-aided manufacturing or CAM, computer-aided engineering or CAE, etc.). The use of simulation throughout the product lifecycle, especially at the earlier concept and design stages, has the potential of providing substantial benefits. These benefits range from direct cost issues such as reduced prototyping and shorter time-to-market to better performing products and higher margins. However, for some companies, simulation has not provided the expected benefits.
The successful use of simulation, early in the lifecycle, has been largely driven by increased integration of simulation tools with the entire set of CAD, CAM and product-lifecycle management solutions. Simulation solutions can now function across the extended enterprise in a CAD data exchange, multi-CAD environment, and include solutions for managing simulation data and processes and ensuring that simulation results are made part of the product lifecycle history.
Disaster preparedness
Simulation training has become a method for preparing people for disasters. Simulations can replicate emergency situations and track how learners respond thanks to a lifelike experience. Disaster preparedness simulations can involve training on how to handle terrorism attacks, natural disasters, pandemic outbreaks, or other life-threatening emergencies.
One organization that has used simulation training for disaster preparedness is CADE (Center for Advancement of Distance Education). CADE has used a video game to prepare emergency workers for multiple types of attacks. As reported by News-Medical.Net, "The video game is the first in a series of simulations to address bioterrorism, pandemic flu, smallpox, and other disasters that emergency personnel must prepare for." Developed by a team from the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), the game allows learners to practice their emergency skills in a safe, controlled environment.
The Emergency Simulation Program (ESP) at the British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT), Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada is another example of an organization that uses simulation to train for emergency situations. ESP uses simulation to train on the following situations: forest fire fighting, oil or chemical spill response, earthquake response, law enforcement, municipal firefighting, hazardous material handling, military training, and response to terrorist attack
Economics
Simulations in economics and especially in macroeconomics, judge the desirability of the effects of proposed policy actions, such as fiscal policy changes or monetary policy changes. A mathematical model of the economy, having been fitted to historical economic data, is used as a proxy for the actual economy; proposed values of government spending, taxation, open market operations, etc. are used as inputs to the simulation of the model, and various variables of interest such as the inflation rate, the unemployment rate, the balance of trade deficit, the government budget deficit, etc. are the outputs of the simulation. The simulated values of these variables of interest are compared for different proposed policy inputs to determine which set of outcomes is most desirable.
Engineering, technology, and processes
Simulation is an important feature in engineering systems or any system that involves many processes. For example, in electrical engineering, delay lines may be used to simulate propagation delay and Phase (waves)#Phase shift, phase shift caused by an actual transmission line. Similarly, dummy loads may be used to simulate Electrical impedance, impedance without simulating propagation and is used in situations where propagation is unwanted. A simulator may imitate only a few of the operations and functions of the unit it simulates. ''Contrast with'': emulator, emulate.[Federal Standard 1037C]
Most engineering simulations entail mathematical modeling and computer-assisted investigation. There are many cases, however, where mathematical modeling is not reliable. Simulation of fluid dynamics problems often require both mathematical and physical simulations. In these cases the physical models require similitude (model), dynamic similitude. Physical and chemical simulations have also direct realistic uses, rather than research uses; in chemical engineering, for example, process simulations are used to give the process parameters immediately used for operating chemical plants, such as oil refineries. Simulators are also used for plant operator training. It is called Operator Training Simulator (OTS) and has been widely adopted by many industries from chemical to oil&gas and to the power industry. This created a safe and realistic virtual environment to train board operators and engineers. MiMiC Simulation Software, Mimic is capable of providing high fidelity dynamic models of nearly all chemical plants for operator training and control system testing.
Ergonomics
Ergonomic simulation involves the analysis of virtual products or manual tasks within a virtual environment. In the engineering process, the aim of ergonomics is to develop and to improve the design of products and work environments.[Reed, M. P., Faraway, J., Chaffin, D. B., & Martin, B. J. (2006). The HUMOSIM Ergonomics Framework: A new approach to digital human simulation for ergonomic analysis. SAE Technical Paper, 01-2365] Ergonomic simulation utilizes an anthropometric virtual representation of the human, commonly referenced as a mannequin or Digital Human Models (DHMs), to mimic the postures, mechanical loads, and performance of a human operator in a simulated environment such as an airplane, automobile, or manufacturing facility. DHMs are recognized as evolving and valuable tool for performing proactive ergonomics analysis and design. The simulations employ 3D-graphics and physics-based models to animate the virtual humans. Ergonomics software uses inverse kinematics (IK) capability for posing the DHMs.
Finance
In finance, computer simulations are often used for scenario planning. Risk-adjusted net present value, for example, is computed from well-defined but not always known (or fixed) inputs. By imitating the performance of the project under evaluation, simulation can provide a distribution of NPV over a range of discounts and allowances, discount rates and other variables. Simulations are also often used to test a financial theory or the ability of a financial model.
Simulations are frequently used in financial training to engage participants in experiencing various historical as well as fictional situations. There are stock market simulations, portfolio simulations, risk management simulations or models and forex simulations. Such simulations are typically based on stochastic asset models. Using these simulations in a training program allows for the application of theory into a something akin to real life. As with other industries, the use of simulations can be technology or case-study driven.
Flight
 Flight simulation is mainly used to train pilots outside of the aircraft.
Flight simulation is mainly used to train pilots outside of the aircraft.
Marine
 Bearing resemblance to
Bearing resemblance to flight simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they rea ...
s, a marine simulator is meant for training of ship personnel. The most common marine simulators include:
Military
Military simulations, also known informally as war games, are models in which theories of warfare can be tested and refined without the need for actual hostilities. They exist in many different forms, with varying degrees of realism. In recent times, their scope has widened to include not only military but also political and social factors (for example, the Nationlab series of strategic exercises in Latin America). While many governments make use of simulation, both individually and collaboratively, little is known about the model's specifics outside professional circles.
Network and distributed systems
Network and distributed systems have been extensively simulated in other to understand the impact of new protocols and algorithms before their deployment in the actual systems. The simulation can focus on different levels (physical layer, network layer, application layer), and evaluate different metrics (network bandwidth, resource consumption, service time, dropped packets, system availability). Examples of simulation scenarios of network and distributed systems are:
* Content delivery networks
* Smart cities
* Internet of things
Payment and securities settlement system
Simulation techniques have also been applied to payment and securities settlement systems. Among the main users are central banks who are generally responsible for the oversight of market infrastructure and entitled to contribute to the smooth functioning of the payment systems.
Central banks have been using payment system simulations to evaluate things such as the adequacy or sufficiency of liquidity available ( in the form of account balances and intraday credit limits) to participants (mainly banks) to allow efficient settlement of payments. The need for liquidity is also dependent on the availability and the type of netting procedures in the systems, thus some of the studies have a focus on system comparisons.
Another application is to evaluate risks related to events such as communication network breakdowns or the inability of participants to send payments (e.g. in case of possible bank failure). This kind of analysis falls under the concepts of stress testing or scenario analysis.
A common way to conduct these simulations is to replicate the settlement logics of the real payment or securities settlement systems under analysis and then use real observed payment data. In case of system comparison or system development, naturally, also the other settlement logics need to be implemented.
To perform stress testing and scenario analysis, the observed data needs to be altered, e.g. some payments delayed or removed. To analyze the levels of liquidity, initial liquidity levels are varied. System comparisons (benchmarking) or evaluations of new netting algorithms or rules are performed by running simulations with a fixed set of data and varying only the system setups.
An inference is usually done by comparing the benchmark simulation results to the results of altered simulation setups by comparing indicators such as unsettled transactions or settlement delays.
Power systems
Project management
Project management simulation is simulation used for project management training and analysis. It is often used as a training simulation for project managers. In other cases, it is used for what-if analysis and for supporting decision-making in real projects. Frequently the simulation is conducted using software tools.
Robotics
A robotics simulator is used to create embedded applications for a specific (or not) robot without being dependent on the 'real' robot. In some cases, these applications can be transferred to the real robot (or rebuilt) without modifications. Robotics simulators allow reproducing situations that cannot be 'created' in the real world because of cost, time, or the 'uniqueness' of a resource. A simulator also allows fast robot prototyping. Many robot simulators feature physics engines to simulate a robot's dynamics.
Production
Simulation of production systems is used mainly to examine the effect of improvements or investments in a Operations management#Production systems, production system. Most often this is done using a static spreadsheet with process times and transportation times. For more sophisticated simulations Discrete Event Simulation (DES) is used with the advantages to simulate dynamics in the production system. A production system is very much dynamic depending on variations in manufacturing processes, assembly times, machine set-ups, breaks, breakdowns and small stoppages. There is much List of discrete event simulation software, software commonly used for discrete event simulation. They differ in usability and markets but do often share the same foundation.
Sales process
Simulations are useful in modeling the flow of transactions through business processes, such as in the field of sales process engineering, to study and improve the flow of customer orders through various stages of completion (say, from an initial proposal for providing goods/services through order acceptance and installation). Such simulations can help predict the impact of how improvements in methods might impact variability, cost, labor time, and the number of transactions at various stages in the process. A full-featured computerized process simulator can be used to depict such models, as can simpler educational demonstrations using spreadsheet software, pennies being transferred between cups based on the roll of a die, or dipping into a tub of colored beads with a scoop.
Sports
In sports, computer simulations are often done to predict the outcome of events and the performance of individual sportspeople. They attempt to recreate the event through models built from statistics. The increase in technology has allowed anyone with knowledge of programming the ability to run simulations of their models. The simulations are built from a series of mathematical algorithms, or models, and can vary with accuracy. Accuscore, which is licensed by companies such as ESPN, is a well-known simulation program for all major sports. It offers a detailed analysis of games through simulated betting lines, projected point totals and overall probabilities.
With the increased interest in fantasy sports simulation models that predict individual player performance have gained popularity. Companies like What If Sports and StatFox specialize in not only using their simulations for predicting game results but how well individual players will do as well. Many people use models to determine whom to start in their fantasy leagues.
Another way simulations are helping the sports field is in the use of biomechanics. Models are derived and simulations are run from data received from sensors attached to athletes and video equipment. Sports biomechanics aided by simulation models answer questions regarding training techniques such as the effect of fatigue on throwing performance (height of throw) and biomechanical factors of the upper limbs (reactive strength index; hand contact time).
Computer simulations allow their users to take models which before were too complex to run, and give them answers. Simulations have proven to be some of the best insights into both play performance and team predictability.
Space shuttle countdown
 Simulation was used at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) to train and certify Space Shuttle engineers during simulated launch countdown operations. The Space Shuttle engineering community would participate in a launch countdown integrated simulation before each Shuttle flight. This simulation is a virtual simulation where real people interact with simulated Space Shuttle vehicle and Ground Support Equipment (GSE) hardware. The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, also known as S0044, involved countdown processes that would integrate many of the Space Shuttle vehicle and GSE systems. Some of the Shuttle systems integrated in the simulation are the main propulsion system, RS-25, Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster, solid rocket boosters, ground liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, external tank, flight controls, navigation, and avionics. The high-level objectives of the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation are:
* To demonstrate Firing room#Firing room, firing room final countdown phase operations.
* To provide training for system engineers in recognizing, reporting and evaluating system problems in a time critical environment.
* To exercise the launch team's ability to evaluate, prioritize and respond to problems in an integrated manner within a time critical environment.
* To provide procedures to be used in performing failure/recovery testing of the operations performed in the final countdown phase.
The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation took place at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Control Center Firing room#Firing room, firing rooms. The firing room used during the simulation is the same control room where real launch countdown operations are executed. As a result, equipment used for real launch countdown operations is engaged. Command and control computers, application software, engineering plotting and trending tools, launch countdown procedure documents, launch commit criteria documents, hardware requirement documents, and any other items used by the engineering launch countdown teams during real launch countdown operations are used during the simulation.
The Space Shuttle vehicle hardware and related GSE hardware is simulated by mathematical models (written in Shuttle Ground Operations Simulator (SGOS) modeling language) that behave and react like real hardware. During the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, engineers command and control hardware via real application software executing in the control consoles – just as if they were commanding real vehicle hardware. However, these real software applications do not interface with real Shuttle hardware during simulations. Instead, the applications interface with mathematical model representations of the vehicle and GSE hardware. Consequently, the simulations bypass sensitive and even dangerous mechanisms while providing engineering measurements detailing how the hardware would have reacted. Since these math models interact with the command and control application software, models and simulations are also used to debug and verify the functionality of application software.
Simulation was used at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) to train and certify Space Shuttle engineers during simulated launch countdown operations. The Space Shuttle engineering community would participate in a launch countdown integrated simulation before each Shuttle flight. This simulation is a virtual simulation where real people interact with simulated Space Shuttle vehicle and Ground Support Equipment (GSE) hardware. The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, also known as S0044, involved countdown processes that would integrate many of the Space Shuttle vehicle and GSE systems. Some of the Shuttle systems integrated in the simulation are the main propulsion system, RS-25, Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster, solid rocket boosters, ground liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, external tank, flight controls, navigation, and avionics. The high-level objectives of the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation are:
* To demonstrate Firing room#Firing room, firing room final countdown phase operations.
* To provide training for system engineers in recognizing, reporting and evaluating system problems in a time critical environment.
* To exercise the launch team's ability to evaluate, prioritize and respond to problems in an integrated manner within a time critical environment.
* To provide procedures to be used in performing failure/recovery testing of the operations performed in the final countdown phase.
The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation took place at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Control Center Firing room#Firing room, firing rooms. The firing room used during the simulation is the same control room where real launch countdown operations are executed. As a result, equipment used for real launch countdown operations is engaged. Command and control computers, application software, engineering plotting and trending tools, launch countdown procedure documents, launch commit criteria documents, hardware requirement documents, and any other items used by the engineering launch countdown teams during real launch countdown operations are used during the simulation.
The Space Shuttle vehicle hardware and related GSE hardware is simulated by mathematical models (written in Shuttle Ground Operations Simulator (SGOS) modeling language) that behave and react like real hardware. During the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, engineers command and control hardware via real application software executing in the control consoles – just as if they were commanding real vehicle hardware. However, these real software applications do not interface with real Shuttle hardware during simulations. Instead, the applications interface with mathematical model representations of the vehicle and GSE hardware. Consequently, the simulations bypass sensitive and even dangerous mechanisms while providing engineering measurements detailing how the hardware would have reacted. Since these math models interact with the command and control application software, models and simulations are also used to debug and verify the functionality of application software.
Satellite navigation
The only true way to test GNSS receivers (commonly known as Sat-Nav's in the commercial world) is by using an RF Constellation Simulator. A receiver that may, for example, be used on an aircraft, can be tested under dynamic conditions without the need to take it on a real flight. The test conditions can be repeated exactly, and there is full control over all the test parameters. this is not possible in the 'real-world' using the actual signals. For testing receivers that will use the new Galileo (satellite navigation) there is no alternative, as the real signals do not yet exist.
Trains
Weather
Predicting weather conditions by extrapolating/interpolating previous data is one of the real use of simulation. Most of the weather forecasts use this information published by Weather bureaus. This kind of simulations helps in predicting and forewarning about extreme weather conditions like the path of an active hurricane/cyclone. Numerical weather prediction for forecasting involves complicated numeric computer models to predict weather accurately by taking many parameters into account.
Simulation games
Strategy games—both traditional and modern—may be viewed as simulations of abstracted decision-making for the purpose of training military and political leaders (see History of Go for an example of such a tradition, or Kriegsspiel (wargame), Kriegsspiel for a more recent example).
Many other video games are simulators of some kind. Such games can simulate various aspects of reality, from business simulation game, business, to Government simulation, government, to Construction and management simulation games, construction, to Vehicle simulation game, piloting vehicles (see above).
Historical usage
Historically, the word had negative connotations:
However, the connection between simulation and dissembling later faded out and is now only of linguistic interest.[South, in the passage quoted, was speaking of the differences between a falsehood and an honestly mistaken statement; the difference being that for the statement to be a lie the truth must be known, and the opposite of the truth must have been knowingly uttered. And, from this, to the extent to which a ''lie'' involves deceptive ''words'', a ''simulation'' involves deceptive ''actions'', deceptive ''gestures'', or deceptive ''behavior''. Thus, it would seem, if a simulation is ''false'', then the truth must be known (for ''something other than the truth'' to be presented in its stead); and, for the ''simulation'' to ''simulate''. Because, otherwise, one would not know what to offer up in a simulation. Bacon's essay ''s:The Works of Francis Bacon, Volume 1/Essays/Of Simulation and Dissimulation, Of Simulation and Dissimulation'' expresses somewhat similar views. Samuel Johnson thought so highly of South's definition, that he used it in the entry for simulation in his ''A Dictionary of the English Language, Dictionary of the English Language''.]
See also
* Computer experiment
* Grey box model
* ''In silico''
* List of computer simulation software
* List of discrete event simulation software
* Merger simulation
* Microarchitecture simulation
* Mining simulator
* Monte Carlo algorithm
* Network simulation
* Pharmacokinetics simulation
* Roleplay simulation
* Rule-based modeling
* Simulated reality
* Simulation language
* Training simulation
* Web-based simulation
* Virtual reality
* Simulation hypothesis
Fields of study
* Computational astrophysics
* Computational chemistry
* Computational fluid dynamics
* Computational physics
* Futures studies
* Molecular dynamics
* System identification
Specific examples & literature
* Illustris project
* Planet Simulator
* UltraHLE
* Simulacra and Simulation
References
External links
Bibliographies containing more references
to be found on the website of the journa
''Simulation & Gaming''
{{Authority control
Simulation,
Mathematical and quantitative methods (economics)

 Historically, simulations used in different fields developed largely independently, but 20th-century studies of
Historically, simulations used in different fields developed largely independently, but 20th-century studies of  There is a wide variety of input hardware available to accept user input for virtual simulations. The following list briefly describes several of them:
* ''Body tracking'': The
There is a wide variety of input hardware available to accept user input for virtual simulations. The following list briefly describes several of them:
* ''Body tracking'': The  Flight simulation is mainly used to train pilots outside of the aircraft. In comparison to training in flight, simulation-based training allows for practicing maneuvers or situations that may be impractical (or even dangerous) to perform in the aircraft while keeping the pilot and instructor in a relatively low-risk environment on the ground. For example, electrical system failures, instrument failures, hydraulic system failures, and even flight control failures can be simulated without risk to the crew or equipment.
Instructors can also provide students with a higher concentration of training tasks in a given period of time than is usually possible in the aircraft. For example, conducting multiple instrument approaches in the actual aircraft may require significant time spent repositioning the aircraft, while in a simulation, as soon as one approach has been completed, the instructor can immediately reposition the simulated aircraft to a location from which the next approach can be begun.
Flight simulation also provides an economic advantage over training in an actual aircraft. Once fuel, maintenance, and insurance costs are taken into account, the operating costs of an FSTD are usually substantially lower than the operating costs of the simulated aircraft. For some large transport category airplanes, the operating costs may be several times lower for the FSTD than the actual aircraft. Another advantage is reduced environmental impact, as simulators don't contribute directly to carbon or noise emissions.
There also exist "engineering flight simulators" which are a key element of the aircraft design process. Many benefits that come from a lower number of test flights like cost and safety improvements are described above, but there are some unique advantages. Having a simulator available allows for faster design iteration cycle or using more test equipment than could be fit into a real aircraft.
Flight simulation is mainly used to train pilots outside of the aircraft. In comparison to training in flight, simulation-based training allows for practicing maneuvers or situations that may be impractical (or even dangerous) to perform in the aircraft while keeping the pilot and instructor in a relatively low-risk environment on the ground. For example, electrical system failures, instrument failures, hydraulic system failures, and even flight control failures can be simulated without risk to the crew or equipment.
Instructors can also provide students with a higher concentration of training tasks in a given period of time than is usually possible in the aircraft. For example, conducting multiple instrument approaches in the actual aircraft may require significant time spent repositioning the aircraft, while in a simulation, as soon as one approach has been completed, the instructor can immediately reposition the simulated aircraft to a location from which the next approach can be begun.
Flight simulation also provides an economic advantage over training in an actual aircraft. Once fuel, maintenance, and insurance costs are taken into account, the operating costs of an FSTD are usually substantially lower than the operating costs of the simulated aircraft. For some large transport category airplanes, the operating costs may be several times lower for the FSTD than the actual aircraft. Another advantage is reduced environmental impact, as simulators don't contribute directly to carbon or noise emissions.
There also exist "engineering flight simulators" which are a key element of the aircraft design process. Many benefits that come from a lower number of test flights like cost and safety improvements are described above, but there are some unique advantages. Having a simulator available allows for faster design iteration cycle or using more test equipment than could be fit into a real aircraft.
 Bearing resemblance to
Bearing resemblance to  Simulation was used at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) to train and certify Space Shuttle engineers during simulated launch countdown operations. The Space Shuttle engineering community would participate in a launch countdown integrated simulation before each Shuttle flight. This simulation is a virtual simulation where real people interact with simulated Space Shuttle vehicle and Ground Support Equipment (GSE) hardware. The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, also known as S0044, involved countdown processes that would integrate many of the Space Shuttle vehicle and GSE systems. Some of the Shuttle systems integrated in the simulation are the main propulsion system, RS-25, Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster, solid rocket boosters, ground liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, external tank, flight controls, navigation, and avionics. The high-level objectives of the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation are:
* To demonstrate Firing room#Firing room, firing room final countdown phase operations.
* To provide training for system engineers in recognizing, reporting and evaluating system problems in a time critical environment.
* To exercise the launch team's ability to evaluate, prioritize and respond to problems in an integrated manner within a time critical environment.
* To provide procedures to be used in performing failure/recovery testing of the operations performed in the final countdown phase.
The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation took place at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Control Center Firing room#Firing room, firing rooms. The firing room used during the simulation is the same control room where real launch countdown operations are executed. As a result, equipment used for real launch countdown operations is engaged. Command and control computers, application software, engineering plotting and trending tools, launch countdown procedure documents, launch commit criteria documents, hardware requirement documents, and any other items used by the engineering launch countdown teams during real launch countdown operations are used during the simulation.
The Space Shuttle vehicle hardware and related GSE hardware is simulated by mathematical models (written in Shuttle Ground Operations Simulator (SGOS) modeling language) that behave and react like real hardware. During the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, engineers command and control hardware via real application software executing in the control consoles – just as if they were commanding real vehicle hardware. However, these real software applications do not interface with real Shuttle hardware during simulations. Instead, the applications interface with mathematical model representations of the vehicle and GSE hardware. Consequently, the simulations bypass sensitive and even dangerous mechanisms while providing engineering measurements detailing how the hardware would have reacted. Since these math models interact with the command and control application software, models and simulations are also used to debug and verify the functionality of application software.
Simulation was used at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) to train and certify Space Shuttle engineers during simulated launch countdown operations. The Space Shuttle engineering community would participate in a launch countdown integrated simulation before each Shuttle flight. This simulation is a virtual simulation where real people interact with simulated Space Shuttle vehicle and Ground Support Equipment (GSE) hardware. The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, also known as S0044, involved countdown processes that would integrate many of the Space Shuttle vehicle and GSE systems. Some of the Shuttle systems integrated in the simulation are the main propulsion system, RS-25, Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster, solid rocket boosters, ground liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, external tank, flight controls, navigation, and avionics. The high-level objectives of the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation are:
* To demonstrate Firing room#Firing room, firing room final countdown phase operations.
* To provide training for system engineers in recognizing, reporting and evaluating system problems in a time critical environment.
* To exercise the launch team's ability to evaluate, prioritize and respond to problems in an integrated manner within a time critical environment.
* To provide procedures to be used in performing failure/recovery testing of the operations performed in the final countdown phase.
The Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation took place at the Kennedy Space Center Launch Control Center Firing room#Firing room, firing rooms. The firing room used during the simulation is the same control room where real launch countdown operations are executed. As a result, equipment used for real launch countdown operations is engaged. Command and control computers, application software, engineering plotting and trending tools, launch countdown procedure documents, launch commit criteria documents, hardware requirement documents, and any other items used by the engineering launch countdown teams during real launch countdown operations are used during the simulation.
The Space Shuttle vehicle hardware and related GSE hardware is simulated by mathematical models (written in Shuttle Ground Operations Simulator (SGOS) modeling language) that behave and react like real hardware. During the Shuttle Final Countdown Phase Simulation, engineers command and control hardware via real application software executing in the control consoles – just as if they were commanding real vehicle hardware. However, these real software applications do not interface with real Shuttle hardware during simulations. Instead, the applications interface with mathematical model representations of the vehicle and GSE hardware. Consequently, the simulations bypass sensitive and even dangerous mechanisms while providing engineering measurements detailing how the hardware would have reacted. Since these math models interact with the command and control application software, models and simulations are also used to debug and verify the functionality of application software.