Silver Slugger Award winners on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Silver is a
 Silver is similar in its physical and chemical properties to its two vertical neighbours in group 11 of the
Silver is similar in its physical and chemical properties to its two vertical neighbours in group 11 of the
 Silver and gold have rather low chemical affinity, chemical affinities for oxygen, lower than copper, and it is therefore expected that silver oxides are thermally quite unstable. Soluble silver(I) salts precipitate dark-brown silver(I) oxide, Ag2O, upon the addition of alkali. (The hydroxide AgOH exists only in solution; otherwise it spontaneously decomposes to the oxide.) Silver(I) oxide is very easily reduced to metallic silver, and decomposes to silver and oxygen above 160 °C.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1181–82 This and other silver(I) compounds may be oxidized by the strong oxidizing agent peroxodisulfate to black AgO, a mixed silver(I,III) oxide of formula AgIAgIIIO2. Some other mixed oxides with silver in non-integral oxidation states, namely Ag2O3 and Ag3O4, are also known, as is Ag3O which behaves as a metallic conductor.
Silver(I) sulfide, Ag2S, is very readily formed from its constituent elements and is the cause of the black tarnish on some old silver objects. It may also be formed from the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with silver metal or aqueous Ag+ ions. Many non-stoichiometric selenides and telluride (chemistry), tellurides are known; in particular, AgTe~3 is a low-temperature superconductor.
Silver and gold have rather low chemical affinity, chemical affinities for oxygen, lower than copper, and it is therefore expected that silver oxides are thermally quite unstable. Soluble silver(I) salts precipitate dark-brown silver(I) oxide, Ag2O, upon the addition of alkali. (The hydroxide AgOH exists only in solution; otherwise it spontaneously decomposes to the oxide.) Silver(I) oxide is very easily reduced to metallic silver, and decomposes to silver and oxygen above 160 °C.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1181–82 This and other silver(I) compounds may be oxidized by the strong oxidizing agent peroxodisulfate to black AgO, a mixed silver(I,III) oxide of formula AgIAgIIIO2. Some other mixed oxides with silver in non-integral oxidation states, namely Ag2O3 and Ag3O4, are also known, as is Ag3O which behaves as a metallic conductor.
Silver(I) sulfide, Ag2S, is very readily formed from its constituent elements and is the cause of the black tarnish on some old silver objects. It may also be formed from the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with silver metal or aqueous Ag+ ions. Many non-stoichiometric selenides and telluride (chemistry), tellurides are known; in particular, AgTe~3 is a low-temperature superconductor.
 Silver complexes tend to be similar to those of its lighter homologue copper. Silver(III) complexes tend to be rare and very easily reduced to the more stable lower oxidation states, though they are slightly more stable than those of copper(III). For instance, the square planar periodate [Ag(IO5OH)2]5− and tellurate [Ag2]5− complexes may be prepared by oxidising silver(I) with alkaline peroxodisulfate. The yellow diamagnetic [AgF4]− is much less stable, fuming in moist air and reacting with glass.
Silver(II) complexes are more common. Like the valence isoelectronic copper(II) complexes, they are usually square planar and paramagnetic, which is increased by the greater field splitting for 4d electrons than for 3d electrons. Aqueous Ag2+, produced by oxidation of Ag+ by ozone, is a very strong oxidising agent, even in acidic solutions: it is stabilized in phosphoric acid due to complex formation. Peroxodisulfate oxidation is generally necessary to give the more stable complexes with heterocyclic amines, such as [Ag(py)4]2+ and [Ag(bipy)2]2+: these are stable provided the counterion cannot reduce the silver back to the +1 oxidation state. [AgF4]2− is also known in its violet barium salt, as are some silver(II) complexes with ''N''- or ''O''-donor ligands such as pyridine carboxylates.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1189
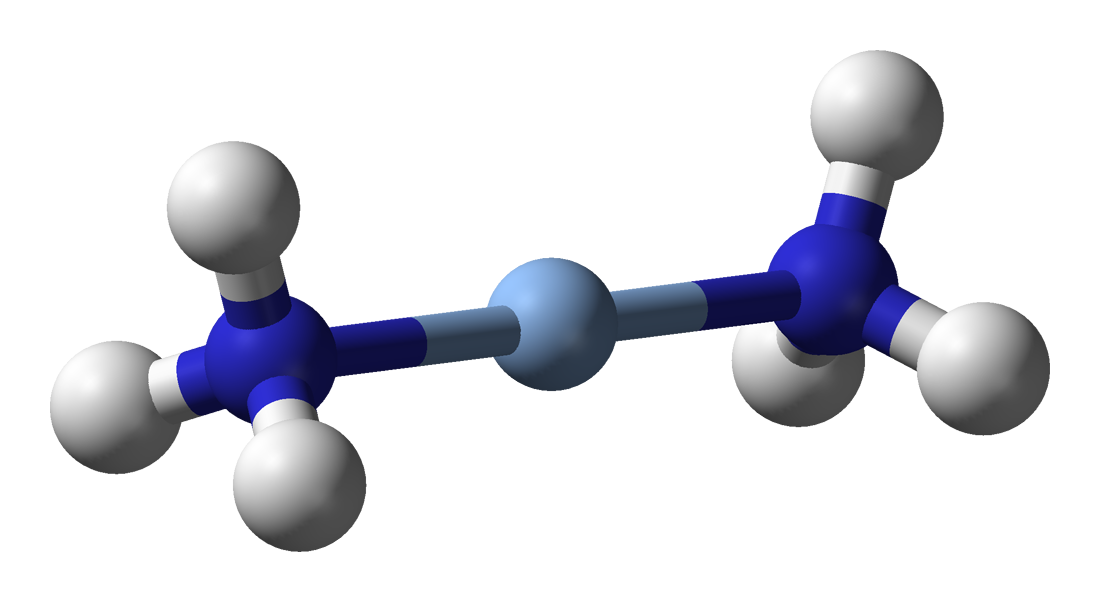
By far the most important oxidation state for silver in complexes is +1. The Ag+ cation is diamagnetic, like its homologues Cu+ and Au+, as all three have closed-shell electron configurations with no unpaired electrons: its complexes are colourless provided the ligands are not too easily polarized such as I−. Ag+ forms salts with most anions, but it is reluctant to coordinate to oxygen and thus most of these salts are insoluble in water: the exceptions are the nitrate, perchlorate, and fluoride. The tetracoordinate tetrahedral aqueous ion [Ag(H2O)4]+ is known, but the characteristic geometry for the Ag+ cation is 2-coordinate linear. For example, silver chloride dissolves readily in excess aqueous ammonia to form [Ag(NH3)2]+; silver salts are dissolved in photography due to the formation of the thiosulfate complex [Ag(S2O3)2]3−; and cyanide extraction for silver (and gold) works by the formation of the complex [Ag(CN)2]−. Silver cyanide forms the linear polymer ; silver thiocyanate has a similar structure, but forms a zigzag instead because of the sp3-orbital hybridization, hybridized sulfur atom. Chelating ligands are unable to form linear complexes and thus silver(I) complexes with them tend to form polymers; a few exceptions exist, such as the near-tetrahedral diphosphine and diarsine complexes [Ag(L–L)2]+.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1195–96
Silver complexes tend to be similar to those of its lighter homologue copper. Silver(III) complexes tend to be rare and very easily reduced to the more stable lower oxidation states, though they are slightly more stable than those of copper(III). For instance, the square planar periodate [Ag(IO5OH)2]5− and tellurate [Ag2]5− complexes may be prepared by oxidising silver(I) with alkaline peroxodisulfate. The yellow diamagnetic [AgF4]− is much less stable, fuming in moist air and reacting with glass.
Silver(II) complexes are more common. Like the valence isoelectronic copper(II) complexes, they are usually square planar and paramagnetic, which is increased by the greater field splitting for 4d electrons than for 3d electrons. Aqueous Ag2+, produced by oxidation of Ag+ by ozone, is a very strong oxidising agent, even in acidic solutions: it is stabilized in phosphoric acid due to complex formation. Peroxodisulfate oxidation is generally necessary to give the more stable complexes with heterocyclic amines, such as [Ag(py)4]2+ and [Ag(bipy)2]2+: these are stable provided the counterion cannot reduce the silver back to the +1 oxidation state. [AgF4]2− is also known in its violet barium salt, as are some silver(II) complexes with ''N''- or ''O''-donor ligands such as pyridine carboxylates.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1189
By far the most important oxidation state for silver in complexes is +1. The Ag+ cation is diamagnetic, like its homologues Cu+ and Au+, as all three have closed-shell electron configurations with no unpaired electrons: its complexes are colourless provided the ligands are not too easily polarized such as I−. Ag+ forms salts with most anions, but it is reluctant to coordinate to oxygen and thus most of these salts are insoluble in water: the exceptions are the nitrate, perchlorate, and fluoride. The tetracoordinate tetrahedral aqueous ion [Ag(H2O)4]+ is known, but the characteristic geometry for the Ag+ cation is 2-coordinate linear. For example, silver chloride dissolves readily in excess aqueous ammonia to form [Ag(NH3)2]+; silver salts are dissolved in photography due to the formation of the thiosulfate complex [Ag(S2O3)2]3−; and cyanide extraction for silver (and gold) works by the formation of the complex [Ag(CN)2]−. Silver cyanide forms the linear polymer ; silver thiocyanate has a similar structure, but forms a zigzag instead because of the sp3-orbital hybridization, hybridized sulfur atom. Chelating ligands are unable to form linear complexes and thus silver(I) complexes with them tend to form polymers; a few exceptions exist, such as the near-tetrahedral diphosphine and diarsine complexes [Ag(L–L)2]+.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1195–96

 Silver forms
Silver forms
 Silver was one of the seven
Silver was one of the seven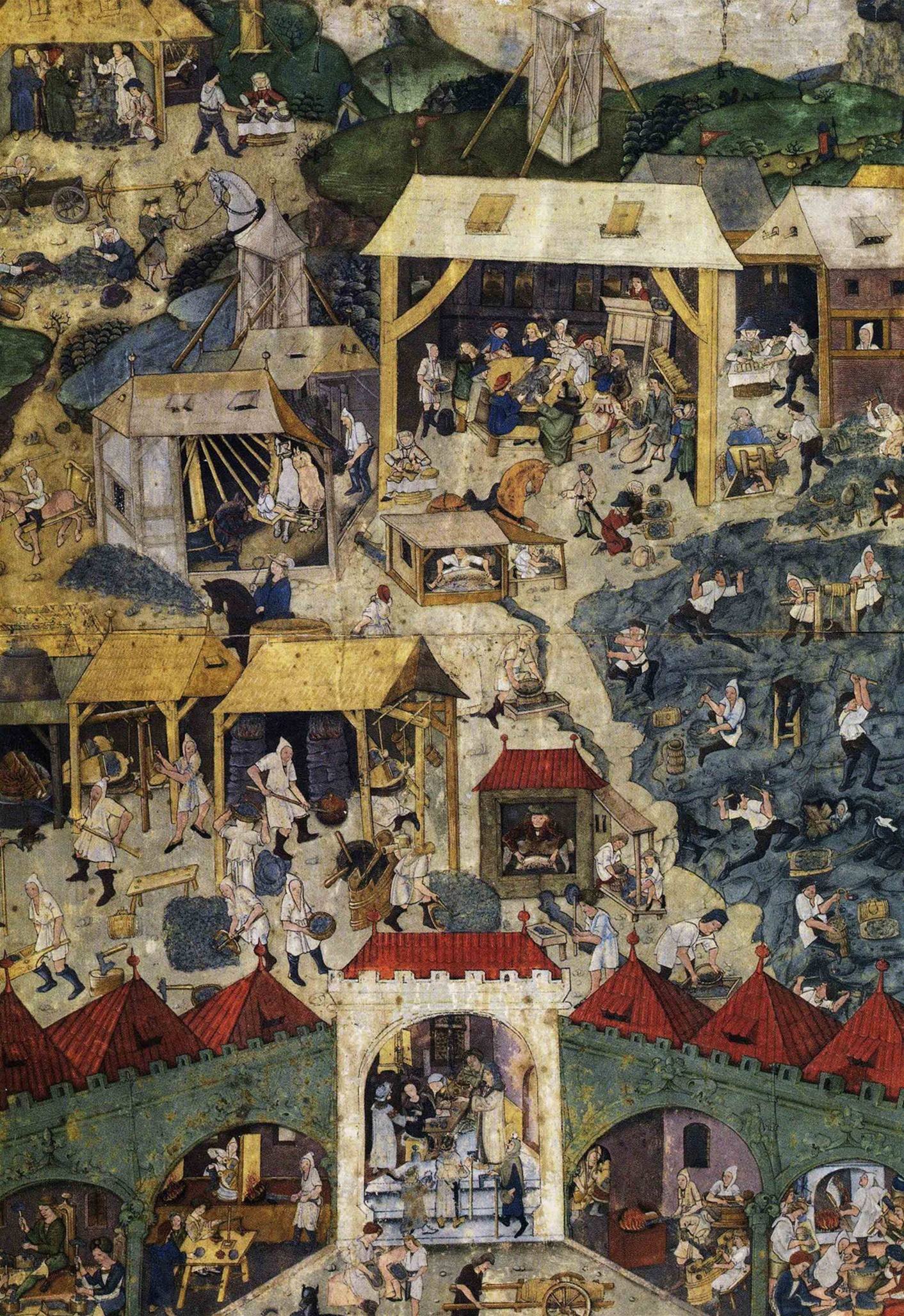  When the Phoenicians first came to what is now Spain, they obtained so much silver that they could not fit it all on their ships, and as a result used silver to weight their anchors instead of lead. By the time of the Greek and Roman civilizations, silver coins were a staple of the economy: the Greeks were already extracting silver from galena by the 7th century BC, and the rise of Athens was partly made possible by the nearby silver mines at Laurium, from which they extracted about 30 tonnes a year from 600 to 300 BC. The stability of the Roman currency relied to a high degree on the supply of silver bullion, mostly from Spain, which Roman metallurgy, Roman miners produced on a scale unparalleled before the discovery of the New World. Reaching a peak production of 200 tonnes per year, an estimated silver stock of 10,000 tonnes circulated in the Roman economy in the middle of the second century AD, five to ten times larger than the combined amount of silver available to Early Middle Ages, medieval Europe and the Abbasid Caliphate around AD 800. The Romans also recorded the extraction of silver in central and northern Europe in the same time period. This production came to a nearly complete halt with the fall of the Roman Empire, not to resume until the time of Charlemagne: by then, tens of thousands of tonnes of silver had already been extracted.Ullmann, pp. 16–19
Central Europe became the centre of silver production during the Middle Ages, as the Mediterranean deposits exploited by the ancient civilisations had been exhausted. Silver mines were opened in Bohemia, Saxony, Erzgebirge, Alsace, the Lahn region, Siegerland, Silesia, Hungary, Norway, Steiermark, Schwaz, and the southern Black Forest. Most of these ores were quite rich in silver and could simply be separated by hand from the remaining rock and then smelted; some deposits of native silver were also encountered. Many of these mines were soon exhausted, but a few of them remained active until the Industrial Revolution, before which the world production of silver was around a meagre 50 tonnes per year. In the Americas, high temperature silver-lead cupellation technology was developed by pre-Inca civilizations as early as AD 60–120; silver deposits in India, China, Japan, and pre-Columbian America continued to be mined during this time.
With the discovery of America and the plundering of silver by the Spanish conquistadors, Central and South America became the dominant producers of silver until around the beginning of the 18th century, particularly Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina: the last of these countries later took its name from that of the metal that composed so much of its mineral wealth. The silver trade gave way to a Global silver trade from the 16th to 19th centuries, global network of exchange. As one historian put it, silver "went round the world and made the world go round." Much of this silver ended up in the hands of the Chinese. A Portuguese merchant in 1621 noted that silver "wanders throughout all the world... before flocking to China, where it remains as if at its natural center." Still, much of it went to Spain, allowing Spanish rulers to pursue military and political ambitions in both Europe and the Americas. "New World mines," concluded several historians, "supported the Spanish empire."
In the 19th century, primary production of silver moved to North America, particularly Canada, Mexico, and Nevada in the United States: some secondary production from lead and zinc ores also took place in Europe, and deposits in Siberia and the Russian Far East as well as in Australia were mined. Poland emerged as an important producer during the 1970s after the discovery of copper deposits that were rich in silver, before the centre of production returned to the Americas the following decade. Today, Peru and Mexico are still among the primary silver producers, but the distribution of silver production around the world is quite balanced and about one-fifth of the silver supply comes from recycling instead of new production.
When the Phoenicians first came to what is now Spain, they obtained so much silver that they could not fit it all on their ships, and as a result used silver to weight their anchors instead of lead. By the time of the Greek and Roman civilizations, silver coins were a staple of the economy: the Greeks were already extracting silver from galena by the 7th century BC, and the rise of Athens was partly made possible by the nearby silver mines at Laurium, from which they extracted about 30 tonnes a year from 600 to 300 BC. The stability of the Roman currency relied to a high degree on the supply of silver bullion, mostly from Spain, which Roman metallurgy, Roman miners produced on a scale unparalleled before the discovery of the New World. Reaching a peak production of 200 tonnes per year, an estimated silver stock of 10,000 tonnes circulated in the Roman economy in the middle of the second century AD, five to ten times larger than the combined amount of silver available to Early Middle Ages, medieval Europe and the Abbasid Caliphate around AD 800. The Romans also recorded the extraction of silver in central and northern Europe in the same time period. This production came to a nearly complete halt with the fall of the Roman Empire, not to resume until the time of Charlemagne: by then, tens of thousands of tonnes of silver had already been extracted.Ullmann, pp. 16–19
Central Europe became the centre of silver production during the Middle Ages, as the Mediterranean deposits exploited by the ancient civilisations had been exhausted. Silver mines were opened in Bohemia, Saxony, Erzgebirge, Alsace, the Lahn region, Siegerland, Silesia, Hungary, Norway, Steiermark, Schwaz, and the southern Black Forest. Most of these ores were quite rich in silver and could simply be separated by hand from the remaining rock and then smelted; some deposits of native silver were also encountered. Many of these mines were soon exhausted, but a few of them remained active until the Industrial Revolution, before which the world production of silver was around a meagre 50 tonnes per year. In the Americas, high temperature silver-lead cupellation technology was developed by pre-Inca civilizations as early as AD 60–120; silver deposits in India, China, Japan, and pre-Columbian America continued to be mined during this time.
With the discovery of America and the plundering of silver by the Spanish conquistadors, Central and South America became the dominant producers of silver until around the beginning of the 18th century, particularly Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina: the last of these countries later took its name from that of the metal that composed so much of its mineral wealth. The silver trade gave way to a Global silver trade from the 16th to 19th centuries, global network of exchange. As one historian put it, silver "went round the world and made the world go round." Much of this silver ended up in the hands of the Chinese. A Portuguese merchant in 1621 noted that silver "wanders throughout all the world... before flocking to China, where it remains as if at its natural center." Still, much of it went to Spain, allowing Spanish rulers to pursue military and political ambitions in both Europe and the Americas. "New World mines," concluded several historians, "supported the Spanish empire."
In the 19th century, primary production of silver moved to North America, particularly Canada, Mexico, and Nevada in the United States: some secondary production from lead and zinc ores also took place in Europe, and deposits in Siberia and the Russian Far East as well as in Australia were mined. Poland emerged as an important producer during the 1970s after the discovery of copper deposits that were rich in silver, before the centre of production returned to the Americas the following decade. Today, Peru and Mexico are still among the primary silver producers, but the distribution of silver production around the world is quite balanced and about one-fifth of the silver supply comes from recycling instead of new production.
File:Proto-Elamite kneeling bull holding a spouted vessel.jpg, Proto-Elamite kneeling bull holding a spouted vessel; 3100–2900 BC; 16.3 x 6.3 x 10.8 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
Horus as falcon god with Egyptian crown from the 27th dynasty (05).jpg, Ancient Egyptian figurine of Horus as falcon god with an Egyptian crown; circa 500 BC; silver and electrum; height: 26.9 cm; Staatliche Sammlung für Ägyptische Kunst (Munich, Germany)
Silver tetradrachm MET DP139641.jpg, Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek tetradrachm; 315–308 BC; diameter: 2.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Silver-gilt bowl MET DP105813.jpg, Ancient Greek gilded bowl; 2nd–1st century BC; height: 7.6 cm, dimeter: 14.8 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Silver plate MET DP231273.jpg, Roman Empire, Roman plate; 1st–2nd century AD; height: 0.1 cm, diameter: 12.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Silver bust of Serapis MET DT6658.jpg, Roman bust of Serapis; 2nd century; 15.6 x 9.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Schaal met voorstellingen uit de geschiedenis van Diana en Actaeon door Paulus Willemsz van Vianen in 1613.jpg, Auricular style, Auricular basin with scenes from the story of Diana and Actaeon; 1613; length: 50 cm, height: 6 cm, width: 40 cm; Rijksmuseum (Amsterdam, the Netherlands)
Silver Tureen (a), lid (b) -pair with 1975.1.2560a-c- MET SLP2561a b-1.jpg, French Rococo tureen; 1749; height: 26.3 cm, width: 39 cm, depth: 24 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Coffeepot MET DP103144 (cropped),.jpg, French Rococo coffeepot; 1757; height: 29.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ewer MET DT236853.jpg, French Neoclassicism, Neoclassical ewer; 1784–1785; height: 32.9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Elkington & Co. - Neo-Rococo Coffee Pot - 2003.243 - Cleveland Museum of Art.jpg, Rococo revival, Neo-Rococo coffeepot; 1845; overall: 32 x 23.8 x 15.4 cm; Cleveland Museum of Art (Cleveland, Ohio, USA)
Dessert Spoon (France), ca. 1890 (CH 18653899-2).jpg, French Art Nouveau dessert spoons; circa 1890; Cooper Hewitt, Smithsonian Design Museum (New York City)
Jardiniere And Liner (Germany), ca. 1905–10 (CH 18444035) (cropped).jpg, Art Nouveau jardinière; circa 1905–1910; height: 22 cm, width: 47 cm, depth: 22.5 cm; Cooper Hewitt, Smithsonian Design Museum
Handspiegel met gedreven Jugendstilornament, BK-1967-10.jpg, Hand mirror; 1906; height: 20.7 cm, weight: 88 g; Rijksmuseum (Amsterdam, the Netherlands)
Mystery watch.jpg, Mystery watch; ca. 1889; diameter: 5.4 cm, depth: 1.8 cm; Watch Museum of Le Locle, Musée d'Horlogerie of Le Locle, (Switzerland)
 Silver plays a certain role in mythology and has found various usage as a metaphor and in folklore. The Greek poet Hesiod's ''Works and Days'' (lines 109–201) lists different ages of man named after metals like gold, silver, bronze and iron to account for successive ages of humanity. Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'' contains another retelling of the story, containing an illustration of silver's metaphorical use of signifying the second-best in a series, better than bronze but worse than gold:
In folklore, silver was commonly thought to have mystic powers: for example, a silver bullet, bullet cast from silver is often supposed in such folklore the only weapon that is effective against a werewolf, witch, or other monsters. From this the idiom of a silver bullet developed into figuratively referring to any simple solution with very high effectiveness or almost miraculous results, as in the widely discussed software engineering paper ''No Silver Bullet''. Other powers attributed to silver include detection of poison and facilitation of passage into the Fairyland, mythical realm of fairies.
Silver production has also inspired figurative language. Clear references to cupellation occur throughout the Old Testament of the Bible, such as in Jeremiah's rebuke to Judah: "The bellows are burned, the lead is consumed of the fire; the founder melteth in vain: for the wicked are not plucked away. Reprobate silver shall men call them, because the Lord hath rejected them." (Jeremiah 6:19–20) Jeremiah was also aware of sheet silver, exemplifying the malleability and ductility of the metal: "Silver spread into plates is brought from Tarshish, and gold from Uphaz, the work of the workman, and of the hands of the founder: blue and purple is their clothing: they are all the work of cunning men." (Jeremiah 10:9)
Silver also has more negative cultural meanings: the idiom wikt:thirty pieces of silver, thirty pieces of silver, referring to a reward for betrayal, references the bribe Judas Iscariot is said in the New Testament to have taken from Jewish leaders in Jerusalem to turn Jesus, Jesus of Nazareth over to soldiers of the high priest Caiaphas. Ethically, silver also symbolizes greed and degradation of consciousness; this is the negative aspect, the perverting of its value.
Silver plays a certain role in mythology and has found various usage as a metaphor and in folklore. The Greek poet Hesiod's ''Works and Days'' (lines 109–201) lists different ages of man named after metals like gold, silver, bronze and iron to account for successive ages of humanity. Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'' contains another retelling of the story, containing an illustration of silver's metaphorical use of signifying the second-best in a series, better than bronze but worse than gold:
In folklore, silver was commonly thought to have mystic powers: for example, a silver bullet, bullet cast from silver is often supposed in such folklore the only weapon that is effective against a werewolf, witch, or other monsters. From this the idiom of a silver bullet developed into figuratively referring to any simple solution with very high effectiveness or almost miraculous results, as in the widely discussed software engineering paper ''No Silver Bullet''. Other powers attributed to silver include detection of poison and facilitation of passage into the Fairyland, mythical realm of fairies.
Silver production has also inspired figurative language. Clear references to cupellation occur throughout the Old Testament of the Bible, such as in Jeremiah's rebuke to Judah: "The bellows are burned, the lead is consumed of the fire; the founder melteth in vain: for the wicked are not plucked away. Reprobate silver shall men call them, because the Lord hath rejected them." (Jeremiah 6:19–20) Jeremiah was also aware of sheet silver, exemplifying the malleability and ductility of the metal: "Silver spread into plates is brought from Tarshish, and gold from Uphaz, the work of the workman, and of the hands of the founder: blue and purple is their clothing: they are all the work of cunning men." (Jeremiah 10:9)
Silver also has more negative cultural meanings: the idiom wikt:thirty pieces of silver, thirty pieces of silver, referring to a reward for betrayal, references the bribe Judas Iscariot is said in the New Testament to have taken from Jewish leaders in Jerusalem to turn Jesus, Jesus of Nazareth over to soldiers of the high priest Caiaphas. Ethically, silver also symbolizes greed and degradation of consciousness; this is the negative aspect, the perverting of its value.
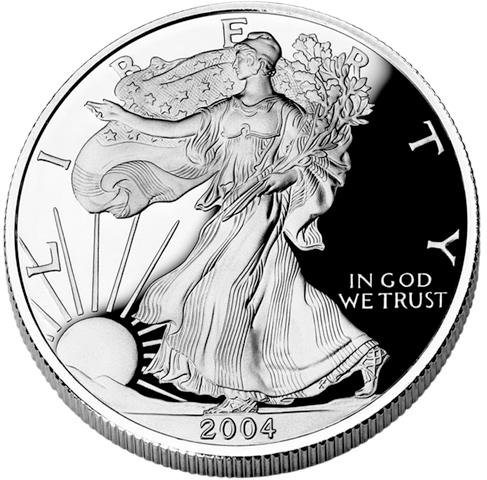 The earliest known coins were minted in the kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia, Asia Minor around 600 BC. The coins of Lydia were made of electrum, which is a naturally occurring
The earliest known coins were minted in the kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia, Asia Minor around 600 BC. The coins of Lydia were made of electrum, which is a naturally occurring
s.v. 'dirhem'
the karshapana from ancient India and rupee from the time of the Mughal Empire (grouped with copper and gold coins to create a trimetallic standard), and the Spanish dollar. The ratio between the amount of silver used for coinage and that used for other purposes has fluctuated greatly over time; for example, in wartime, more silver tends to have been used for coinage to finance the war.Ullmann, pp. 63–65 Today, silver bullion has the ISO 4217 currency code XAG, one of only four
 Silver prices are normally quoted in Troy weight, troy ounces. One troy ounce is equal to . The London silver fix is published every working day at noon London time. This price is determined by several major international banks and is used by London bullion market members for trading that day. Prices are most commonly shown as the United States dollar (USD), the Pound sterling (GBP), and the Euro (EUR).
Silver prices are normally quoted in Troy weight, troy ounces. One troy ounce is equal to . The London silver fix is published every working day at noon London time. This price is determined by several major international banks and is used by London bullion market members for trading that day. Prices are most commonly shown as the United States dollar (USD), the Pound sterling (GBP), and the Euro (EUR).
 The major use of silver besides coinage throughout most of history was in the manufacture of
The major use of silver besides coinage throughout most of history was in the manufacture of
European Union Observatory for Nanomaterials (EUON)
silver nanoparticles are used both in pigments, as well as cosmetics.
 Pure silver metal is used as a food colouring. It has the E number, E174 designation and is approved in the European Union. Traditional Indian and Pakistani dishes sometimes include decorative silver foil known as ''vark'', and in various other cultures, silver ''dragée'' are used to decorate cakes, cookies, and other dessert items.
Photochromic lenses include silver halides, so that ultraviolet light in natural daylight liberates metallic silver, darkening the lenses. The silver halides are reformed in lower light intensities. Colourless silver chloride films are used in Particle detector, radiation detectors. Zeolite sieves incorporating Ag+ ions are used to Desalination, desalinate seawater during rescues, using silver ions to precipitate chloride as silver chloride. Silver is also used for its antibacterial properties for water sanitisation, but the application of this is limited by limits on silver consumption. Colloidal silver is similarly used to disinfect closed swimming pools; while it has the advantage of not giving off a smell like hypochlorite treatments do, colloidal silver is not effective enough for more contaminated open swimming pools. Small silver iodide crystals are used in cloud seeding to cause rain.Ullmann, pp. 83–84
The Texas Legislature designated silver the official precious metal of Texas in 2007.
Pure silver metal is used as a food colouring. It has the E number, E174 designation and is approved in the European Union. Traditional Indian and Pakistani dishes sometimes include decorative silver foil known as ''vark'', and in various other cultures, silver ''dragée'' are used to decorate cakes, cookies, and other dessert items.
Photochromic lenses include silver halides, so that ultraviolet light in natural daylight liberates metallic silver, darkening the lenses. The silver halides are reformed in lower light intensities. Colourless silver chloride films are used in Particle detector, radiation detectors. Zeolite sieves incorporating Ag+ ions are used to Desalination, desalinate seawater during rescues, using silver ions to precipitate chloride as silver chloride. Silver is also used for its antibacterial properties for water sanitisation, but the application of this is limited by limits on silver consumption. Colloidal silver is similarly used to disinfect closed swimming pools; while it has the advantage of not giving off a smell like hypochlorite treatments do, colloidal silver is not effective enough for more contaminated open swimming pools. Small silver iodide crystals are used in cloud seeding to cause rain.Ullmann, pp. 83–84
The Texas Legislature designated silver the official precious metal of Texas in 2007.
Silver
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Society of American Silversmiths
The Silver Institute
A silver industry website
Samples of silver
Transport, Fate and Effects of Silver in the Environment
Bloomberg – Markets Precious and Industrial Metals – Silver
{{good article Silver, Chemical elements Transition metals Noble metals Precious metals Cubic minerals Minerals in space group 225 Electrical conductors Native element minerals E-number additives Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements canno ...
with the symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Ag (from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
', derived from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of ever ...
47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
, thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
, and reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic ...
of any metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductili ...
with gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite
In mineralogy, argentite (from the Latin ''argentum'', silver) is cubic silver sulfide (Ag2S), which can only exist at temperatures above 173 °C, 177 °C or 179 °C. When it cools to ordinary temperatures it turns into its monocli ...
and chlorargyrite
Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric - hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to colum ...
. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, gold, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
refining
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
.
Silver has long been valued as a precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value.
Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements (see noble metal). They are usually ductile and have a high lu ...
. Silver metal is used in many bullion coin
Bullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes fro ...
s, sometimes alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal
A native metal is any metal that is found pure in its metallic form in nature. Metals that can be found as native deposits singly or in alloys include aluminium, antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, indium, iron, manganese, m ...
. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille
Per mille (from Latin , "in each thousand") is an expression that means parts per thousand. Other recognised spellings include per mil, per mill, permil, permill, or permille.
The associated sign is written , which looks like a percent si ...
basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity
The metals of antiquity are the seven metals which humans had identified and found use for in prehistoric times in Europe and the Middle East: gold, silver, copper, tin, lead, iron, and mercury. These seven are the metals from which the mode ...
, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures.
Other than in currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general ...
and as an investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing is ...
medium (coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
and bullion
Bullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes fro ...
), silver is used in solar panels
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
, water filtration
A water filter removes impurities by lowering contamination of water using a fine physical barrier, a chemical process, or a biological process. Filters cleanse water to different extents, for purposes such as: providing agricultural irrigation ...
, jewellery
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
, ornaments, high-value tableware and utensils (hence the term "silverware
Silverware may refer to:
* Household silver including
**Tableware
**Cutlery
**Candlesticks
*The work of a silversmith
* Silverware is also a slang term for a collection of trophies
A trophy is a tangible, durable reminder of a specific achievem ...
"), in electrical contact
An electrical contact is an electrical circuit component found in electrical switches, relays, connectors and circuit breakers. Each contact is a piece of electrically conductive material, typically metal. When a pair of contacts touch, they c ...
s and conductors, in specialized mirrors, window coatings, in catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
of chemical reactions, as a colorant in stained glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
, and in specialized confectionery. Its compounds are used in photographic
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed ...
and X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
film. Dilute solutions of silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
and other silver compounds are used as disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than s ...
s and microbiocides (oligodynamic effect
The oligodynamic effect (from Greek ''oligos'', "few", and ''dynamis'', "force") is a biocidal effect of metals, especially heavy metals, that occurs even in low concentrations.
In modern times, the effect was observed by Carl Nägeli, although ...
), added to bandage
A bandage is a piece of material used either to support a medical device such as a dressing or splint, or on its own to provide support to or to restrict the movement of a part of the body. When used with a dressing, the dressing is applie ...
s, wound-dressings, catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgi ...
s, and other medical instrument
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assura ...
s.
Characteristics
 Silver is similar in its physical and chemical properties to its two vertical neighbours in group 11 of the
Silver is similar in its physical and chemical properties to its two vertical neighbours in group 11 of the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of ch ...
: copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
. Its 47 electrons are arranged in the configuration
Configuration or configurations may refer to:
Computing
* Computer configuration or system configuration
* Configuration file, a software file used to configure the initial settings for a computer program
* Configurator, also known as choice bo ...
rd105s1, similarly to copper ( rd104s1) and gold ( ef145d106s1); group 11 is one of the few groups in the d-block
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ...
which has a completely consistent set of electron configurations. This distinctive electron configuration, with a single electron in the highest occupied s subshell over a filled d subshell, accounts for many of the singular properties of metallic silver.
Silver is a relatively soft and extremely ductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
and malleable
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...
, though it is slightly less malleable than gold. Silver crystallizes in a face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
lattice with bulk coordination number 12, where only the single 5s electron is delocalized, similarly to copper and gold.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1178 Unlike metals with incomplete d-shells, metallic bonds in silver are lacking a covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
character and are relatively weak. This observation explains the low hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard ...
and high ductility of single crystals
In materials science, a single crystal (or single-crystal solid or monocrystalline solid) is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no grain boundaries.RIWD. "Re ...
of silver.
Silver has a brilliant, white, metallic luster that can take a high polish, and which is so characteristic that the name of the metal itself has become a colour name.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1177 Unlike copper and gold, the energy required to excite an electron from the filled d band to the s-p conduction band in silver is large enough (around 385 kJ/mol) that it no longer corresponds to absorption in the visible region of the spectrum, but rather in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
; hence, silver is not a coloured metal. Protected silver has greater optical reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic ...
than aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
at all wavelengths longer than ~450 nm. At wavelengths shorter than 450 nm, silver's reflectivity is inferior to that of aluminium and drops to zero near 310 nm.
Very high electrical and thermal conductivity are common to the elements in group 11, because their single s electron is free and does not interact with the filled d subshell, as such interactions (which occur in the preceding transition metals) lower electron mobility. The thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa.
Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal ...
of silver is among the highest of all materials, although the thermal conductivity of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
(in the diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, b ...
allotrope
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical State of matter, state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications o ...
) and superfluid helium-4
Superfluid helium-4 is the superfluid form of helium-4, an isotope of the element helium. A superfluid is a state of matter in which matter behaves like a fluid with zero viscosity. The substance, which looks like a normal liquid, flows wit ...
are higher. The electrical conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows ...
of silver is the highest of all metals, greater even than copper. Silver also has the lowest contact resistance
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance of a system which can be attributed to the contacting interfaces of electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance. This effect is describe ...
of any metal. Silver is rarely used for its electrical conductivity, due to its high cost, although an exception is in radio-frequency engineering
Radio-frequency (RF) engineering is a subset of electronic engineering involving the application of transmission line, waveguide, antenna and electromagnetic field principles to the design and application of devices that produce or use sign ...
, particularly at VHF
Very high frequency (VHF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) from 30 to 300 megahertz (MHz), with corresponding wavelengths of ten meters to one meter.
Frequencies immediately below VHF ...
and higher frequencies where silver plating improves electrical conductivity because those currents tend to flow on the surface of conductors rather than through the interior. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
in the US, tons of silver were used for the electromagnets
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in ...
in calutron
A calutron is a mass spectrometer originally designed and used for separating the isotopes of uranium. It was developed by Ernest Lawrence during the Manhattan Project and was based on his earlier invention, the cyclotron. Its name was deri ...
s for enriching uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, mainly because of the wartime shortage of copper.
Silver readily forms alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductili ...
s with copper, gold, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
. Zinc-silver alloys with low zinc concentration may be considered as face-centred cubic solid solutions of zinc in silver, as the structure of the silver is largely unchanged while the electron concentration rises as more zinc is added. Increasing the electron concentration further leads to body-centred cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
(electron concentration 1.5), complex cubic (1.615), and hexagonal close-packed
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occu ...
phases (1.75).
Isotopes
Naturally occurring silver is composed of two stableisotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass num ...
s, 107Ag and 109Ag, with 107Ag being slightly more abundant (51.839% natural abundance). This almost equal abundance is rare in the periodic table. The atomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
is 107.8682(2) u; this value is very important because of the importance of silver compounds, particularly halides, in gravimetric analysis
Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass. The principle of this type of analysis is that once an ion's mass has been ...
. Both isotopes of silver are produced in stars via the s-process
The slow neutron-capture process, or ''s''-process, is a series of reactions in nuclear astrophysics that occur in stars, particularly asymptotic giant branch stars. The ''s''-process is responsible for the creation ( nucleosynthesis) of approxim ...
(slow neutron capture), as well as in supernovas via the r-process
In nuclear astrophysics, the rapid neutron-capture process, also known as the ''r''-process, is a set of nuclear reactions that is responsible for the creation of approximately half of the atomic nuclei heavier than iron, the "heavy elements", ...
(rapid neutron capture).
Twenty-eight radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
s have been characterized, the most stable being 105Ag with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
of 41.29 days, 111Ag with a half-life of 7.45 days, and 112Ag with a half-life of 3.13 hours. Silver has numerous nuclear isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have ...
s, the most stable being 108mAg (''t''1/2 = 418 years), 110mAg (''t''1/2 = 249.79 days) and 106mAg (''t''1/2 = 8.28 days). All of the remaining radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
isotopes have half-lives of less than an hour, and the majority of these have half-lives of less than three minutes.
Isotopes of silver range in relative atomic mass
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a ...
from 92.950 u (93Ag) to 129.950 u (130Ag); the primary decay mode
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
before the most abundant stable isotope, 107Ag, is electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. ...
and the primary mode after is beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For ...
. The primary decay product
In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope, radio-daughter, or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps ( ...
s before 107Ag are palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself ...
(element 46) isotopes, and the primary products after are cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Li ...
(element 48) isotopes.
The palladium isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass num ...
107Pd decays by beta emission to 107Ag with a half-life of 6.5 million years. Iron meteorite
Iron meteorites, also known as siderites, or ferrous meteorites, are a type of meteorite that consist overwhelmingly of an iron–nickel alloy known as meteoric iron that usually consists of two mineral phases: kamacite and taenite. Most i ...
s are the only objects with a high-enough palladium-to-silver ratio to yield measurable variations in 107Ag abundance. Radiogenic 107Ag was first discovered in the Santa Clara meteorite in 1978. 107Pd–107Ag correlations observed in bodies that have clearly been melted since the accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
of the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
must reflect the presence of unstable nuclides in the early Solar System.
Chemistry
Silver is a rather unreactive metal. This is because its filled 4d shell is not very effective in shielding the electrostatic forces of attraction from the nucleus to the outermost 5s electron, and hence silver is near the bottom of theelectrochemical series
The data values of standard electrode potentials (''E''°) are given in the table below, in volts relative to the standard hydrogen electrode, and are for the following conditions:
* A temperature of .
* An effective concentration of 1 mol ...
(''E''0(Ag+/Ag) = +0.799 V). In group 11, silver has the lowest first ionization energy (showing the instability of the 5s orbital), but has higher second and third ionization energies than copper and gold (showing the stability of the 4d orbitals), so that the chemistry of silver is predominantly that of the +1 oxidation state, reflecting the increasingly limited range of oxidation states along the transition series as the d-orbitals fill and stabilize.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1180 Unlike copper, for which the larger hydration energy of Cu2+ as compared to Cu+ is the reason why the former is the more stable in aqueous solution and solids despite lacking the stable filled d-subshell of the latter, with silver this effect is swamped by its larger second ionisation energy. Hence, Ag+ is the stable species in aqueous solution and solids, with Ag2+ being much less stable as it oxidizes water.
Most silver compounds have significant covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
character due to the small size and high first ionization energy (730.8 kJ/mol) of silver. Furthermore, silver's Pauling electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the ...
of 1.93 is higher than that of lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
(1.87), and its electron affinity of 125.6 kJ/mol is much higher than that of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
(72.8 kJ/mol) and not much less than that of oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
(141.0 kJ/mol).Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1176 Due to its full d-subshell, silver in its main +1 oxidation state exhibits relatively few properties of the transition metals proper from groups 4 to 10, forming rather unstable organometallic compound
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and s ...
s, forming linear complexes showing very low coordination number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central io ...
s like 2, and forming an amphoteric oxide as well as Zintl phase
In chemistry, a Zintl phase is a product of a reaction between a group 1 (alkali metal) or group 2 ( alkaline earth metal) and main group metal or metalloid (from groups 13, 14, 15, or 16). It is characterized by intermediate metallic/ ionic bond ...
s like the post-transition metal
The metallic elements in the periodic table located between the transition metals and the chemically weak nonmetallic metalloids have received many names in the literature, such as ''post-transition metals'', ''poor metals'', ''other metals'', ...
s. Unlike the preceding transition metals, the +1 oxidation state of silver is stable even in the absence of π-acceptor ligands.
Silver does not react with air, even at red heat, and thus was considered by alchemist
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim ...
s as a noble metal
A noble metal is ordinarily regarded as a metallic chemical element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its raw form. Gold, platinum, and the other platinum group metals ( ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, o ...
, along with gold. Its reactivity is intermediate between that of copper (which forms copper(I) oxide when heated in air to red heat) and gold. Like copper, silver reacts with sulfur and its compounds; in their presence, silver tarnishes in air to form the black silver sulfide (copper forms the green sulfate instead, while gold does not react). Unlike copper, silver will not react with the halogens, with the exception of fluorine gas, with which it forms the silver(II) fluoride, difluoride. While silver is not attacked by non-oxidizing acids, the metal dissolves readily in hot concentrated sulfuric acid, as well as dilute or concentrated nitric acid. In the presence of air, and especially in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, silver dissolves readily in aqueous solutions of cyanide.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1179
The three main forms of deterioration in historical silver artifacts are tarnishing, formation of silver chloride due to long-term immersion in salt water, as well as reaction with nitrate ions or oxygen. Fresh silver chloride is pale yellow, becoming purplish on exposure to light; it projects slightly from the surface of the artifact or coin. The precipitation of copper in ancient silver can be used to date artifacts, as copper is nearly always a constituent of silver alloys.
Silver metal is attacked by strong oxidizers such as potassium permanganate () and potassium dichromate (), and in the presence of potassium bromide (). These compounds are used in photography to bleach silver images, converting them to silver bromide that can either be fixed with thiosulfate or redeveloped to potassium dichromate#photography, intensify the original image. Silver forms cyanide complexes (silver cyanide) that are soluble in water in the presence of an excess of cyanide ions. Silver cyanide solutions are used in electroplating of silver.
The common oxidation states of silver are (in order of commonness): +1 (the most stable state; for example, silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
, AgNO3); +2 (highly oxidising; for example, silver(II) fluoride, AgF2); and even very rarely +3 (extreme oxidising; for example, potassium tetrafluoroargentate(III), KAgF4). The +3 state requires very strong oxidising agents to attain, such as fluorine or peroxodisulfate, and some silver(III) compounds react with atmospheric moisture and attack glass.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1188 Indeed, silver(III) fluoride is usually obtained by reacting silver or silver monofluoride with the strongest known oxidizing agent, krypton difluoride.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 903
Compounds
Oxides and chalcogenides
Halides
The only known dihalide of silver is silver(II) fluoride, the difluoride, AgF2, which can be obtained from the elements under heat. A strong yet thermally stable and therefore safe fluorinating agent, silver(II) fluoride is often used to synthesize hydrofluorocarbons.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1183–85 In stark contrast to this, all four silver(I) halides are known. The silver(I) fluoride, fluoride, silver chloride, chloride, and silver bromide, bromide have the sodium chloride structure, but the silver iodide, iodide has three known stable forms at different temperatures; that at room temperature is the cubic zinc blende structure. They can all be obtained by the direct reaction of their respective elements. As the halogen group is descended, the silver halide gains more and more covalent character, solubility decreases, and the color changes from the white chloride to the yellow iodide as the energy required for charge-transfer complex, ligand-metal charge transfer (X−Ag+ → XAg) decreases. The fluoride is anomalous, as the fluoride ion is so small that it has a considerable solvation energy and hence is highly water-soluble and forms di- and tetrahydrates. The other three silver halides are highly insoluble in aqueous solutions and are very commonly used in gravimetric Wet chemistry, analytical methods. All four are photosensitive (though the monofluoride is so only toultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light), especially the bromide and iodide which photodecompose to silver metal, and thus were used in Monochrome photography, traditional photography. The reaction involved is:Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1185–87
:X− + ''hν'' → X + e− (excitation of the halide ion, which gives up its extra electron into the conduction band)
:Ag+ + e− → Ag (liberation of a silver ion, which gains an electron to become a silver atom)
The process is not reversible because the silver atom liberated is typically found at a crystal defect or an impurity site, so that the electron's energy is lowered enough that it is "trapped".
Other inorganic compounds
Whitesilver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
, AgNO3, is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, especially the halides, and is much less sensitive to light. It was once called ''lunar caustic'' because silver was called ''luna'' by the ancient alchemists, who believed that silver was associated with the Moon. It is often used for gravimetric analysis, exploiting the insolubility of the heavier silver halides which it is a common precursor to. Silver nitrate is used in many ways in organic synthesis, e.g. for deprotection and oxidations. Ag+ binds alkenes reversibly, and silver nitrate has been used to separate mixtures of alkenes by selective absorption. The resulting adduct can be decomposed with ammonia to release the free alkene.
Yellow silver carbonate, Ag2CO3 can be easily prepared by reacting aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate with a deficiency of silver nitrate. Its principal use is for the production of silver powder for use in microelectronics. It is reduced with formaldehyde, producing silver free of alkali metals:Andreas Brumby et al. "Silver, Silver Compounds, and Silver Alloys" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008.
:Ag2CO3 + CH2O → 2 Ag + 2 CO2 + H2
Silver carbonate is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis such as the Koenigs-Knorr reaction. In the Fétizon oxidation, silver carbonate on celite acts as an oxidising agent to form lactones from diols. It is also employed to convert alkyl bromides into Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols.
Silver fulminate, AgCNO, a powerful, touch-sensitive explosive used in percussion caps, is made by reaction of silver metal with nitric acid in the presence of ethanol. Other dangerously explosive silver compounds are silver azide, AgN3, formed by reaction of silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
with sodium azide, and silver acetylide, Ag2C2, formed when silver reacts with acetylene gas in ammonia solution. In its most characteristic reaction, silver azide decomposes explosively, releasing nitrogen gas: given the photosensitivity of silver salts, this behaviour may be induced by shining a light on its crystals.
: 2 (s) → 3 (g) + 2 Ag (s)
Coordination compounds
 Silver complexes tend to be similar to those of its lighter homologue copper. Silver(III) complexes tend to be rare and very easily reduced to the more stable lower oxidation states, though they are slightly more stable than those of copper(III). For instance, the square planar periodate [Ag(IO5OH)2]5− and tellurate [Ag2]5− complexes may be prepared by oxidising silver(I) with alkaline peroxodisulfate. The yellow diamagnetic [AgF4]− is much less stable, fuming in moist air and reacting with glass.
Silver(II) complexes are more common. Like the valence isoelectronic copper(II) complexes, they are usually square planar and paramagnetic, which is increased by the greater field splitting for 4d electrons than for 3d electrons. Aqueous Ag2+, produced by oxidation of Ag+ by ozone, is a very strong oxidising agent, even in acidic solutions: it is stabilized in phosphoric acid due to complex formation. Peroxodisulfate oxidation is generally necessary to give the more stable complexes with heterocyclic amines, such as [Ag(py)4]2+ and [Ag(bipy)2]2+: these are stable provided the counterion cannot reduce the silver back to the +1 oxidation state. [AgF4]2− is also known in its violet barium salt, as are some silver(II) complexes with ''N''- or ''O''-donor ligands such as pyridine carboxylates.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1189
By far the most important oxidation state for silver in complexes is +1. The Ag+ cation is diamagnetic, like its homologues Cu+ and Au+, as all three have closed-shell electron configurations with no unpaired electrons: its complexes are colourless provided the ligands are not too easily polarized such as I−. Ag+ forms salts with most anions, but it is reluctant to coordinate to oxygen and thus most of these salts are insoluble in water: the exceptions are the nitrate, perchlorate, and fluoride. The tetracoordinate tetrahedral aqueous ion [Ag(H2O)4]+ is known, but the characteristic geometry for the Ag+ cation is 2-coordinate linear. For example, silver chloride dissolves readily in excess aqueous ammonia to form [Ag(NH3)2]+; silver salts are dissolved in photography due to the formation of the thiosulfate complex [Ag(S2O3)2]3−; and cyanide extraction for silver (and gold) works by the formation of the complex [Ag(CN)2]−. Silver cyanide forms the linear polymer ; silver thiocyanate has a similar structure, but forms a zigzag instead because of the sp3-orbital hybridization, hybridized sulfur atom. Chelating ligands are unable to form linear complexes and thus silver(I) complexes with them tend to form polymers; a few exceptions exist, such as the near-tetrahedral diphosphine and diarsine complexes [Ag(L–L)2]+.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1195–96
Silver complexes tend to be similar to those of its lighter homologue copper. Silver(III) complexes tend to be rare and very easily reduced to the more stable lower oxidation states, though they are slightly more stable than those of copper(III). For instance, the square planar periodate [Ag(IO5OH)2]5− and tellurate [Ag2]5− complexes may be prepared by oxidising silver(I) with alkaline peroxodisulfate. The yellow diamagnetic [AgF4]− is much less stable, fuming in moist air and reacting with glass.
Silver(II) complexes are more common. Like the valence isoelectronic copper(II) complexes, they are usually square planar and paramagnetic, which is increased by the greater field splitting for 4d electrons than for 3d electrons. Aqueous Ag2+, produced by oxidation of Ag+ by ozone, is a very strong oxidising agent, even in acidic solutions: it is stabilized in phosphoric acid due to complex formation. Peroxodisulfate oxidation is generally necessary to give the more stable complexes with heterocyclic amines, such as [Ag(py)4]2+ and [Ag(bipy)2]2+: these are stable provided the counterion cannot reduce the silver back to the +1 oxidation state. [AgF4]2− is also known in its violet barium salt, as are some silver(II) complexes with ''N''- or ''O''-donor ligands such as pyridine carboxylates.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 1189
By far the most important oxidation state for silver in complexes is +1. The Ag+ cation is diamagnetic, like its homologues Cu+ and Au+, as all three have closed-shell electron configurations with no unpaired electrons: its complexes are colourless provided the ligands are not too easily polarized such as I−. Ag+ forms salts with most anions, but it is reluctant to coordinate to oxygen and thus most of these salts are insoluble in water: the exceptions are the nitrate, perchlorate, and fluoride. The tetracoordinate tetrahedral aqueous ion [Ag(H2O)4]+ is known, but the characteristic geometry for the Ag+ cation is 2-coordinate linear. For example, silver chloride dissolves readily in excess aqueous ammonia to form [Ag(NH3)2]+; silver salts are dissolved in photography due to the formation of the thiosulfate complex [Ag(S2O3)2]3−; and cyanide extraction for silver (and gold) works by the formation of the complex [Ag(CN)2]−. Silver cyanide forms the linear polymer ; silver thiocyanate has a similar structure, but forms a zigzag instead because of the sp3-orbital hybridization, hybridized sulfur atom. Chelating ligands are unable to form linear complexes and thus silver(I) complexes with them tend to form polymers; a few exceptions exist, such as the near-tetrahedral diphosphine and diarsine complexes [Ag(L–L)2]+.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1195–96
Organometallic
Under standard conditions, silver does not form simple carbonyls, due to the weakness of the Ag–C bond. A few are known at very low temperatures around 6–15 K, such as the green, planar paramagnetic Ag(CO)3, which dimerizes at 25–30 K, probably by forming Ag–Ag bonds. Additionally, the silver carbonyl [Ag(CO)] [B(OTeF5)4] is known. Polymeric AgLX complexes with alkenes and alkynes are known, but their bonds are thermodynamically weaker than even those of the platinum complexes (though they are formed more readily than those of the analogous gold complexes): they are also quite unsymmetrical, showing the weak ''π'' bonding in group 11. Ag–C ''σ'' bonds may also be formed by silver(I), like copper(I) and gold(I), but the simple alkyls and aryls of silver(I) are even less stable than those of copper(I) (which tend to explode under ambient conditions). For example, poor thermal stability is reflected in the relative decomposition temperatures of AgMe (−50 °C) and CuMe (−15 °C) as well as those of PhAg (74 °C) and PhCu (100 °C).Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1199–200 The C–Ag bond is stabilized by perfluoroalkane, perfluoroalkyl ligands, for example in AgCF(CF3)2. Alkenylsilver compounds are also more stable than their alkylsilver counterparts. Silver-Transition metal carbene complex, NHC complexes are easily prepared, and are commonly used to prepare other NHC complexes by displacing labile ligands. For example, the reaction of the bis(NHC)silver(I) complex with bis(acetonitrile)palladium dichloride or chlorido(dimethyl sulfide)gold(I): :
Intermetallic
alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductili ...
s with most other elements on the periodic table. The elements from groups 1–3, except for hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
, lithium, and beryllium, are very miscible with silver in the condensed phase and form intermetallic compounds; those from groups 4–9 are only poorly miscible; the elements in groups 10–14 (except boron and carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
) have very complex Ag–M phase diagrams and form the most commercially important alloys; and the remaining elements on the periodic table have no consistency in their Ag–M phase diagrams. By far the most important such alloys are those with copper: most silver used for coinage and jewellery is in reality a silver–copper alloy, and the eutectic mixture is used in vacuum brazing. The two metals are completely miscible as liquids but not as solids; their importance in industry comes from the fact that their properties tend to be suitable over a wide range of variation in silver and copper concentration, although most useful alloys tend to be richer in silver than the eutectic mixture (71.9% silver and 28.1% copper by weight, and 60.1% silver and 28.1% copper by atom).Ullmann, pp. 54–61
Most other binary alloys are of little use: for example, silver–gold alloys are too soft and silver–cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Li ...
alloys too toxic. Ternary alloys have much greater importance: dental amalgam (dentistry), amalgams are usually silver–tin–mercury alloys, silver–copper–gold alloys are very important in jewellery (usually on the gold-rich side) and have a vast range of hardnesses and colours, silver–copper–zinc alloys are useful as low-melting brazing alloys, and silver–cadmium–indium (involving three adjacent elements on the periodic table) is useful in nuclear reactors because of its high thermal neutron capture Cross section (physics), cross-section, good conduction of heat, mechanical stability, and resistance to corrosion in hot water.
Etymology
The word "silver" appears in Old English in various spellings, such as ''seolfor'' and ''siolfor''. It is cognate with Old High German ''silabar''; Gothic language, Gothic ''silubr''; or Old Norse ''silfr'', all ultimately deriving from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*silubra''. The Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic words for silver are rather similar to the Germanic ones (e.g. Russian language, Russian серебро [''serebró''], Polish language, Polish ''srebro'', Lithuanian language, Lithuanian ''sidãbras''), as is the Celtiberians, Celtiberian form ''silabur''. They may have a common Indo-European origin, although their morphology rather suggest a non-Indo-European ''Wanderwort''. Some scholars have thus proposed a Paleo-Hispanic languages, Paleo-Hispanic origin, pointing to the Basque language, Basque form ''zilharr'' as an evidence. The chemical symbol Ag is from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
word for "silver", ''argentum'' (compare Ancient Greek ἄργυρος, ''árgyros''), from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
root *''h₂erǵ-'' (formerly reconstructed as ''*arǵ-''), meaning "white" or "shining". This was the usual Proto-Indo-European word for the metal, whose reflexes are missing in Germanic and Balto-Slavic.
History
 Silver was one of the seven
Silver was one of the seven metals of antiquity
The metals of antiquity are the seven metals which humans had identified and found use for in prehistoric times in Europe and the Middle East: gold, silver, copper, tin, lead, iron, and mercury. These seven are the metals from which the mode ...
that were known to prehistoric humans and whose discovery is thus lost to history.Weeks, p. 4 In particular, the three metals of group 11, copper, silver, and gold, occur in the native metal, elemental form in nature and were probably used as the first primitive forms of money as opposed to simple bartering.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1173–74 However, unlike copper, silver did not lead to the growth of metallurgy on account of its low structural strength, and was more often used ornamentally or as money. Since silver is more reactive than gold, supplies of native silver were much more limited than those of gold. For example, silver was more expensive than gold in Egypt until around the fifteenth century BC:Weeks, pp. 14–19 the Egyptians are thought to have separated gold from silver by heating the metals with salt, and then reducing the silver chloride produced to the metal.
The situation changed with the discovery of cupellation, a technique that allowed silver metal to be extracted from its ores. While slag heaps found in Asia Minor and on the islands of the Aegean Sea indicate that silver was being separated from lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
as early as the 4th millennium BC, and one of the earliest silver extraction centres in Europe was Sardinia in the early Chalcolithic period, these techniques did not spread widely until later,
when it spread throughout the region and beyond. The origins of silver production in India, China, and Japan were almost certainly equally ancient, but are not well-documented due to their great age.
 When the Phoenicians first came to what is now Spain, they obtained so much silver that they could not fit it all on their ships, and as a result used silver to weight their anchors instead of lead. By the time of the Greek and Roman civilizations, silver coins were a staple of the economy: the Greeks were already extracting silver from galena by the 7th century BC, and the rise of Athens was partly made possible by the nearby silver mines at Laurium, from which they extracted about 30 tonnes a year from 600 to 300 BC. The stability of the Roman currency relied to a high degree on the supply of silver bullion, mostly from Spain, which Roman metallurgy, Roman miners produced on a scale unparalleled before the discovery of the New World. Reaching a peak production of 200 tonnes per year, an estimated silver stock of 10,000 tonnes circulated in the Roman economy in the middle of the second century AD, five to ten times larger than the combined amount of silver available to Early Middle Ages, medieval Europe and the Abbasid Caliphate around AD 800. The Romans also recorded the extraction of silver in central and northern Europe in the same time period. This production came to a nearly complete halt with the fall of the Roman Empire, not to resume until the time of Charlemagne: by then, tens of thousands of tonnes of silver had already been extracted.Ullmann, pp. 16–19
Central Europe became the centre of silver production during the Middle Ages, as the Mediterranean deposits exploited by the ancient civilisations had been exhausted. Silver mines were opened in Bohemia, Saxony, Erzgebirge, Alsace, the Lahn region, Siegerland, Silesia, Hungary, Norway, Steiermark, Schwaz, and the southern Black Forest. Most of these ores were quite rich in silver and could simply be separated by hand from the remaining rock and then smelted; some deposits of native silver were also encountered. Many of these mines were soon exhausted, but a few of them remained active until the Industrial Revolution, before which the world production of silver was around a meagre 50 tonnes per year. In the Americas, high temperature silver-lead cupellation technology was developed by pre-Inca civilizations as early as AD 60–120; silver deposits in India, China, Japan, and pre-Columbian America continued to be mined during this time.
With the discovery of America and the plundering of silver by the Spanish conquistadors, Central and South America became the dominant producers of silver until around the beginning of the 18th century, particularly Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina: the last of these countries later took its name from that of the metal that composed so much of its mineral wealth. The silver trade gave way to a Global silver trade from the 16th to 19th centuries, global network of exchange. As one historian put it, silver "went round the world and made the world go round." Much of this silver ended up in the hands of the Chinese. A Portuguese merchant in 1621 noted that silver "wanders throughout all the world... before flocking to China, where it remains as if at its natural center." Still, much of it went to Spain, allowing Spanish rulers to pursue military and political ambitions in both Europe and the Americas. "New World mines," concluded several historians, "supported the Spanish empire."
In the 19th century, primary production of silver moved to North America, particularly Canada, Mexico, and Nevada in the United States: some secondary production from lead and zinc ores also took place in Europe, and deposits in Siberia and the Russian Far East as well as in Australia were mined. Poland emerged as an important producer during the 1970s after the discovery of copper deposits that were rich in silver, before the centre of production returned to the Americas the following decade. Today, Peru and Mexico are still among the primary silver producers, but the distribution of silver production around the world is quite balanced and about one-fifth of the silver supply comes from recycling instead of new production.
When the Phoenicians first came to what is now Spain, they obtained so much silver that they could not fit it all on their ships, and as a result used silver to weight their anchors instead of lead. By the time of the Greek and Roman civilizations, silver coins were a staple of the economy: the Greeks were already extracting silver from galena by the 7th century BC, and the rise of Athens was partly made possible by the nearby silver mines at Laurium, from which they extracted about 30 tonnes a year from 600 to 300 BC. The stability of the Roman currency relied to a high degree on the supply of silver bullion, mostly from Spain, which Roman metallurgy, Roman miners produced on a scale unparalleled before the discovery of the New World. Reaching a peak production of 200 tonnes per year, an estimated silver stock of 10,000 tonnes circulated in the Roman economy in the middle of the second century AD, five to ten times larger than the combined amount of silver available to Early Middle Ages, medieval Europe and the Abbasid Caliphate around AD 800. The Romans also recorded the extraction of silver in central and northern Europe in the same time period. This production came to a nearly complete halt with the fall of the Roman Empire, not to resume until the time of Charlemagne: by then, tens of thousands of tonnes of silver had already been extracted.Ullmann, pp. 16–19
Central Europe became the centre of silver production during the Middle Ages, as the Mediterranean deposits exploited by the ancient civilisations had been exhausted. Silver mines were opened in Bohemia, Saxony, Erzgebirge, Alsace, the Lahn region, Siegerland, Silesia, Hungary, Norway, Steiermark, Schwaz, and the southern Black Forest. Most of these ores were quite rich in silver and could simply be separated by hand from the remaining rock and then smelted; some deposits of native silver were also encountered. Many of these mines were soon exhausted, but a few of them remained active until the Industrial Revolution, before which the world production of silver was around a meagre 50 tonnes per year. In the Americas, high temperature silver-lead cupellation technology was developed by pre-Inca civilizations as early as AD 60–120; silver deposits in India, China, Japan, and pre-Columbian America continued to be mined during this time.
With the discovery of America and the plundering of silver by the Spanish conquistadors, Central and South America became the dominant producers of silver until around the beginning of the 18th century, particularly Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina: the last of these countries later took its name from that of the metal that composed so much of its mineral wealth. The silver trade gave way to a Global silver trade from the 16th to 19th centuries, global network of exchange. As one historian put it, silver "went round the world and made the world go round." Much of this silver ended up in the hands of the Chinese. A Portuguese merchant in 1621 noted that silver "wanders throughout all the world... before flocking to China, where it remains as if at its natural center." Still, much of it went to Spain, allowing Spanish rulers to pursue military and political ambitions in both Europe and the Americas. "New World mines," concluded several historians, "supported the Spanish empire."
In the 19th century, primary production of silver moved to North America, particularly Canada, Mexico, and Nevada in the United States: some secondary production from lead and zinc ores also took place in Europe, and deposits in Siberia and the Russian Far East as well as in Australia were mined. Poland emerged as an important producer during the 1970s after the discovery of copper deposits that were rich in silver, before the centre of production returned to the Americas the following decade. Today, Peru and Mexico are still among the primary silver producers, but the distribution of silver production around the world is quite balanced and about one-fifth of the silver supply comes from recycling instead of new production.
Symbolic role
Occurrence and production
The abundance of silver in the Earth's crust is 0.08 parts per million, almost exactly the same as that of mercury (element), mercury. It mostly occurs in sulfide ores, especially acanthite andargentite
In mineralogy, argentite (from the Latin ''argentum'', silver) is cubic silver sulfide (Ag2S), which can only exist at temperatures above 173 °C, 177 °C or 179 °C. When it cools to ordinary temperatures it turns into its monocli ...
, Ag2S. Argentite deposits sometimes also contain native metal, native silver when they occur in reducing environments, and when in contact with salt water they are converted to chlorargyrite
Chlorargyrite is the mineral form of silver chloride (AgCl). Chlorargyrite occurs as a secondary mineral phase in the oxidation of silver mineral deposits. It crystallizes in the isometric - hexoctahedral crystal class. Typically massive to colum ...
(including horn silver), AgCl, which is prevalent in Chile and New South Wales.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 1174–67 Most other silver minerals are silver pnictides or chalcogenides; they are generally lustrous semiconductors. Most true silver deposits, as opposed to argentiferous deposits of other metals, came from Tertiary period vulcanism.Ullmann, pp. 21–22
The principal sources of silver are the ores of copper, copper-nickel, lead, and lead-zinc obtained from Peru, Bolivia, Mexico, China, Australia, Chile, Poland and Serbia. Peru, Bolivia and Mexico have been mining silver since 1546, and are still major world producers. Top silver-producing mines are Cannington Mine, Cannington (Australia), Mina Proaño, Fresnillo (Mexico), San Cristóbal mine (Bolivia), San Cristóbal (Bolivia), Antamina mine, Antamina (Peru), Rudna mine, Rudna (Poland), and Peñasquito Polymetallic Mine, Penasquito (Mexico). Top near-term mine development projects through 2015 are Pascua Lama (Chile), Navidad (Argentina), Jaunicipio (Mexico), Malku Khota (Bolivia), and Hackett River (Canada). In Central Asia, Mining in Tajikistan#Silver, Tajikistan is known to have some of the largest silver deposits in the world.
Silver is usually found in nature combined with other metals, or in minerals that contain silver compounds, generally in the form of sulfides such as galena (lead sulfide) or cerussite (lead carbonate). So the primary production of silver requires the smelting and then cupellation of argentiferous lead ores, a historically important process.Kassianidou, V. 2003. Early Extraction of Silver from Complex Polymetallic Ores, in Craddock, P.T. and Lang, J (eds) Mining and Metal production through the Ages. London, British Museum Press: 198–206 Lead melts at 327 °C, lead oxide at 888 °C and silver melts at 960 °C. To separate the silver, the alloy is melted again at the high temperature of 960 °C to 1000 °C in an oxidizing environment. The lead oxidises to Lead(II) oxide, lead monoxide, then known as litharge, which captures the oxygen from the other metals present. The liquid lead oxide is removed or absorbed by capillary action into the hearth linings.
Bayley, J., Crossley, D. and Ponting, M. (eds). 2008. "Metals and Metalworking. A research framework for archaeometallurgy". Historical Metallurgy Society 6.
: (s) + 2(s) + (g) → 2(absorbed) + Ag(l)
Today, silver metal is primarily produced instead as a secondary byproduct of Refining_(metallurgy)#Electrolytic_refining, electrolytic refining of copper, lead, and zinc, and by application of the Parkes process on lead bullion from ore that also contains silver. In such processes, silver follows the non-ferrous metal in question through its concentration and smelting, and is later purified out. For example, in copper production, purified copper is electrolysis, electrolytically deposited on the cathode, while the less reactive precious metals such as silver and gold collect under the anode as the so-called "anode slime". This is then separated and purified of base metals by treatment with hot aerated dilute sulfuric acid and heating with lime or silica flux, before the silver is purified to over 99.9% purity via electrolysis in nitrate solution.
Commercial-grade fine silver is at least 99.9% pure, and purities greater than 99.999% are available. In 2014, Mexico was the top producer of silver (5,000 tonnes or 18.7% of the world's total of 26,800 t), followed by China (4,060 t) and Peru (3,780 t).
In marine environments
Silver concentration is low in seawater (pmol/L). Levels vary by depth and between water bodies. Dissolved silver concentrations range from 0.3 pmol/L in coastal surface waters to 22.8 pmol/L in pelagic deep waters. Analyzing the presence and dynamics of silver in marine environments is difficult due to these particularly low concentrations and complex interactions in the environment. Although a rare trace metal, concentrations are greatly impacted by fluvial, aeolian, atmospheric, and upwelling inputs, as well as anthropogenic inputs via discharge, waste disposal, and emissions from industrial companies. Other internal processes such as decomposition of organic matter may be a source of dissolved silver in deeper waters, which feeds into some surface waters through upwelling and vertical mixing. In the Atlantic and Pacific, silver concentrations are minimal at the surface but rise in deeper waters. Silver is taken up by plankton in the photic zone, remobilized with depth, and enriched in deep waters. Silver is transported from the Atlantic to the other oceanic water masses. In North Pacific waters, silver is remobilized at a slower rate and increasingly enriched compared to deep Atlantic waters. Silver has increasing concentrations that follow the major oceanic conveyor belt that cycles water and nutrients from the North Atlantic to the South Atlantic to the North Pacific. There is not an extensive amount of data focused on how marine life is affected by silver despite the likely deleterious effects it could have on organisms through bioaccumulation, association with particulate matters, and sorption. Not until about 1984 did scientists begin to understand the chemical characteristics of silver and the potential toxicity. In fact, Mercury (element), mercury is the only other trace metal that surpasses the toxic effects of silver; however, the full extent of silver toxicity is not expected in oceanic conditions because of its ability to transfer into nonreactive biological compounds. In one study, the presence of excess ionic silver and silver nanoparticles caused bioaccumulation effects on zebrafish organs and altered the chemical pathways within their gills. In addition, very early experimental studies demonstrated how the toxic effects of silver fluctuate with salinity and other parameters, as well as between life stages and different species such as finfish, molluscs, and crustaceans. Another study found raised concentrations of silver in the muscles and liver of dolphins and whales, indicating pollution of this metal within recent decades. Silver is not an easy metal for an organism to eliminate and elevated concentrations can cause death.Monetary use
 The earliest known coins were minted in the kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia, Asia Minor around 600 BC. The coins of Lydia were made of electrum, which is a naturally occurring
The earliest known coins were minted in the kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia, Asia Minor around 600 BC. The coins of Lydia were made of electrum, which is a naturally occurring alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductili ...
of gold and silver, that was available within the territory of Lydia. Since that time, silver standards, in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver, have been widespread throughout the world until the 20th century. Notable silver coins through the centuries include the Greek drachma, the Roman denarius, the Islamic dirham,''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st editions.v. 'dirhem'
the karshapana from ancient India and rupee from the time of the Mughal Empire (grouped with copper and gold coins to create a trimetallic standard), and the Spanish dollar. The ratio between the amount of silver used for coinage and that used for other purposes has fluctuated greatly over time; for example, in wartime, more silver tends to have been used for coinage to finance the war.Ullmann, pp. 63–65 Today, silver bullion has the ISO 4217 currency code XAG, one of only four
precious metal
Precious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value.
Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements (see noble metal). They are usually ductile and have a high lu ...
s to have one (the others being palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself ...
, platinum, and gold). Silver coins are produced from cast rods or ingots, rolled to the correct thickness, heat-treated, and then used to cut planchet, blanks from. These blanks are then milled and minted in a coining press; modern coining presses can produce 8000 silver coins per hour.
Price
 Silver prices are normally quoted in Troy weight, troy ounces. One troy ounce is equal to . The London silver fix is published every working day at noon London time. This price is determined by several major international banks and is used by London bullion market members for trading that day. Prices are most commonly shown as the United States dollar (USD), the Pound sterling (GBP), and the Euro (EUR).
Silver prices are normally quoted in Troy weight, troy ounces. One troy ounce is equal to . The London silver fix is published every working day at noon London time. This price is determined by several major international banks and is used by London bullion market members for trading that day. Prices are most commonly shown as the United States dollar (USD), the Pound sterling (GBP), and the Euro (EUR).
Applications
Jewellery and silverware
 The major use of silver besides coinage throughout most of history was in the manufacture of
The major use of silver besides coinage throughout most of history was in the manufacture of jewellery
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
and other general-use items, and this continues to be a major use today. Examples include household silver, table silver for cutlery, for which silver is highly suited due to its antibacterial properties. Western concert flutes are usually plated with or made out of sterling silver;Ullmann, pp. 65–67 in fact, most silverware is only silver-plated rather than made out of pure silver; the silver is normally put in place by electroplating. Silver-plated glass (as opposed to metal) is used for mirrors, vacuum flasks, and Christmas tree decorations.
Because pure silver is very soft, most silver used for these purposes is alloyed with copper, with finenesses of 925/1000, 835/1000, and 800/1000 being common. One drawback is the easy tarnishing of silver in the presence of hydrogen sulfide and its derivatives. Including precious metals such as palladium, platinum, and gold gives resistance to tarnishing but is quite costly; base metals like zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12 element, group 12, zinc and mercury (element), mercury. Li ...
, silicon, and germanium do not totally prevent corrosion and tend to affect the lustre and colour of the alloy. Electrolytically refined pure silver plating is effective at increasing resistance to tarnishing. The usual solutions for restoring the lustre of tarnished silver are dipping baths that reduce the silver sulfide surface to metallic silver, and cleaning off the layer of tarnish with a paste; the latter approach also has the welcome side effect of polishing the silver concurrently.
Medicine
In medicine, silver is incorporated into wound dressings and used as an antibiotic coating in medical devices. Wound dressings containing silver sulfadiazine or Silver nanoparticles, silver nanomaterials are used to treat external infections. Silver is also used in some medical applications, such as urinary catheters (where tentative evidence indicates it reduces catheter-related urinary tract infections) and in endotracheal tube, endotracheal breathing tubes (where evidence suggests it reduces ventilator-associated pneumonia). The silver ion is Biological activity, bioactive and in sufficient concentration readily kills bacteria ''in vitro''. Silver ions interfere with enzymes in the bacteria that transport nutrients, form structures, and synthesise cell walls; these ions also bond with the bacteria's genetic material. Silver and silver nanoparticles are used as an antimicrobial in a variety of industrial, healthcare, and domestic application: for example, infusing clothing with nanosilver particles thus allows them to stay odourless for longer. Bacteria can, however, develop resistance to the antimicrobial action of silver. Silver compounds are taken up by the body like mercury (element), mercury compounds, but lack the toxicity of the latter. Silver and its alloys are used in cranial surgery to replace bone, and silver–tin–mercury amalgams are used in dentistry.Ullmann, pp. 67–71 Silver diammine fluoride, the fluoride salt of a coordination complex with the formula [Ag(NH3)2]F, is a topical medicament (drug) used to treat and prevent dental caries (cavities) and relieve dentinal hypersensitivity.Electronics
Silver is very important in electronics for conductors and electrodes on account of its high electrical conductivity even when tarnished. Bulk silver and silver foils were used to make vacuum tubes, and continue to be used today in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, circuits, and their components. For example, silver is used in high quality connectors for Radio frequency, RF, Very high frequency, VHF, and higher frequencies, particularly in tuned circuits such as RF and microwave filter#Cavity filters, cavity filters where conductors cannot be scaled by more than 6%. Printed circuit board, Printed circuits and RFID antennas are made with silver paints, Powdered silver and its alloys are used in paste preparations for conductor layers and electrodes, ceramic capacitors, and other ceramic components.Ullmann, pp. 71–78Brazing alloys
Silver-containing brazing alloys are used for brazing metallic materials, mostly cobalt, nickel, and copper-based alloys, tool steels, and precious metals. The basic components are silver and copper, with other elements selected according to the specific application desired: examples include zinc, tin, cadmium, palladium, manganese, and phosphorus. Silver provides increased workability and corrosion resistance during usage.Ullmann, pp. 78–81Chemical equipment
Silver is useful in the manufacture of chemical equipment on account of its low chemical reactivity, high thermal conductivity, and being easily workable. Silver crucibles (alloyed with 0.15% nickel to avoid recrystallisation of the metal at red heat) are used for carrying out alkaline fusion. Copper and silver are also used when doing chemistry with fluorine. Equipment made to work at high temperatures is often silver-plated. Silver and its alloys with gold are used as wire or ring seals for oxygen compressors and vacuum equipment.Ullmann, pp. 81–82Catalysis
Silver metal is a good catalyst for oxidation reactions; in fact it is somewhat too good for most purposes, as finely divided silver tends to result in complete oxidation of organic substances to carbon dioxide and water, and hence coarser-grained silver tends to be used instead. For instance, 15% silver supported on α-Al2O3 or silicates is a catalyst for the oxidation of ethylene to ethylene oxide at 230–270 °C. Dehydrogenation of methanol to formaldehyde is conducted at 600–720 °C over silver gauze or crystals as the catalyst, as is dehydrogenation of isopropanol to acetone. In the gas phase, glycol yields glyoxal and ethanol yields acetaldehyde, while organic amines are dehydrated to nitriles.Photography
The photosensitivity of the silver halides allowed for their use in traditional photography, although digital photography, which does not use silver, is now dominant. The Photographic emulsion, photosensitive emulsion used in black-and-white photography is a suspension of silver halide crystals in gelatin, possibly mixed in with some noble metal compounds for improved photosensitivity, Photographic processing, developing, and . Color photography, Colour photography requires the addition of special dye components and sensitisers, so that the initial black-and-white silver image couples with a different dye component. The original silver images are bleached off and the silver is then recovered and recycled. Silver nitrate is the starting material in all cases.Ullmann, p. 82 The use of silver nitrate and silver halides in photography has rapidly declined with the advent of digital technology. From the peak global demand for photographic silver in 1999 (267,000,000 troy ounces or 8,304.6 tonnes) the market contracted almost 70% by 2013.Nanoparticles
Nanosilver particles, between 10 and 100 nanometres in size, are used in many applications. They are used in conductive inks for printed electronics, and have a much lower melting point than larger silver particles of micrometre size. They are also used medicinally in antibacterials and antifungals in much the same way as larger silver particles. In addition, according to thEuropean Union Observatory for Nanomaterials (EUON)
silver nanoparticles are used both in pigments, as well as cosmetics.
Miscellanea
 Pure silver metal is used as a food colouring. It has the E number, E174 designation and is approved in the European Union. Traditional Indian and Pakistani dishes sometimes include decorative silver foil known as ''vark'', and in various other cultures, silver ''dragée'' are used to decorate cakes, cookies, and other dessert items.
Photochromic lenses include silver halides, so that ultraviolet light in natural daylight liberates metallic silver, darkening the lenses. The silver halides are reformed in lower light intensities. Colourless silver chloride films are used in Particle detector, radiation detectors. Zeolite sieves incorporating Ag+ ions are used to Desalination, desalinate seawater during rescues, using silver ions to precipitate chloride as silver chloride. Silver is also used for its antibacterial properties for water sanitisation, but the application of this is limited by limits on silver consumption. Colloidal silver is similarly used to disinfect closed swimming pools; while it has the advantage of not giving off a smell like hypochlorite treatments do, colloidal silver is not effective enough for more contaminated open swimming pools. Small silver iodide crystals are used in cloud seeding to cause rain.Ullmann, pp. 83–84
The Texas Legislature designated silver the official precious metal of Texas in 2007.
Pure silver metal is used as a food colouring. It has the E number, E174 designation and is approved in the European Union. Traditional Indian and Pakistani dishes sometimes include decorative silver foil known as ''vark'', and in various other cultures, silver ''dragée'' are used to decorate cakes, cookies, and other dessert items.
Photochromic lenses include silver halides, so that ultraviolet light in natural daylight liberates metallic silver, darkening the lenses. The silver halides are reformed in lower light intensities. Colourless silver chloride films are used in Particle detector, radiation detectors. Zeolite sieves incorporating Ag+ ions are used to Desalination, desalinate seawater during rescues, using silver ions to precipitate chloride as silver chloride. Silver is also used for its antibacterial properties for water sanitisation, but the application of this is limited by limits on silver consumption. Colloidal silver is similarly used to disinfect closed swimming pools; while it has the advantage of not giving off a smell like hypochlorite treatments do, colloidal silver is not effective enough for more contaminated open swimming pools. Small silver iodide crystals are used in cloud seeding to cause rain.Ullmann, pp. 83–84
The Texas Legislature designated silver the official precious metal of Texas in 2007.
Precautions
Silver compounds have low toxicity compared to those of most other heavy metals, as they are poorly absorbed by the human body when ingested, and that which does get absorbed is rapidly converted to insoluble silver compounds or complexed by metallothionein. However, silver fluoride and silver nitrate are caustic and can cause tissue damage, resulting in gastroenteritis, diarrhoea, falling blood pressure, cramps, paralysis, and respiratory arrest. Animals repeatedly dosed with silver salts have been observed to experience anaemia, slowed growth, necrosis of the liver, and fatty degeneration of the liver and kidneys; rats implanted with silver foil or injected with colloidal silver have been observed to develop localised tumours. Route of administration, Parenterally admistered colloidal silver causes acute silver poisoning.Ullmann, pp. 88–91 Some waterborne species are particularly sensitive to silver salts and those of the other precious metals; in most situations, however, silver does not pose serious environmental hazards. In large doses, silver and compounds containing it can be absorbed into the circulatory system and become deposited in various body tissues, leading to argyria, which results in a blue-grayish pigmentation of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Argyria is rare, and so far as is known, does not otherwise harm a person's health, though it is disfiguring and usually permanent. Mild forms of argyria are sometimes mistaken for cyanosis, a blue tint on skin, caused by lack of oxygen. Metallic silver, like copper, is an antibacterial agent, which was known to the ancients and first scientifically investigated and named theoligodynamic effect
The oligodynamic effect (from Greek ''oligos'', "few", and ''dynamis'', "force") is a biocidal effect of metals, especially heavy metals, that occurs even in low concentrations.
In modern times, the effect was observed by Carl Nägeli, although ...
by Carl Nägeli. Silver ions damage the metabolism of bacteria even at such low concentrations as 0.01–0.1 milligrams per litre; metallic silver has a similar effect due to the formation of silver oxide. This effect is lost in the presence of sulfur due to the extreme insolubility of silver sulfide.
Some silver compounds are very explosive, such as the nitrogen compounds silver azide, silver amide, and silver fulminate, as well as silver acetylide, silver oxalate, and silver(II) oxide. They can explode on heating, force, drying, illumination, or sometimes spontaneously. To avoid the formation of such compounds, ammonia and acetylene should be kept away from silver equipment. Salts of silver with strongly oxidising acids such as silver chlorate and silver nitrate can explode on contact with materials that can be readily oxidised, such as organic compounds, sulfur and soot.
See also
* Silver coin * Silver medal * Free silver * List of countries by silver production * :Silver compounds, List of silver compounds * Silver as an investment * Silverpoint drawingReferences
Sources used above
* * *Further reading
* William L. Silber, ''The Story of Silver: How the White Metal Shaped America and the Modern World.'' Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2019.External links
Silver
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Society of American Silversmiths
The Silver Institute
A silver industry website
Samples of silver
Transport, Fate and Effects of Silver in the Environment
Bloomberg – Markets Precious and Industrial Metals – Silver
{{good article Silver, Chemical elements Transition metals Noble metals Precious metals Cubic minerals Minerals in space group 225 Electrical conductors Native element minerals E-number additives Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure