Sikyon Ancient Theatre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sicyon (; el, ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į; ''gen''.: ╬Ż╬╣╬║Žģß┐Č╬Į╬┐Žé) or Sikyon was an
Sicyon (; el, ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į; ''gen''.: ╬Ż╬╣╬║Žģß┐Č╬Į╬┐Žé) or Sikyon was an
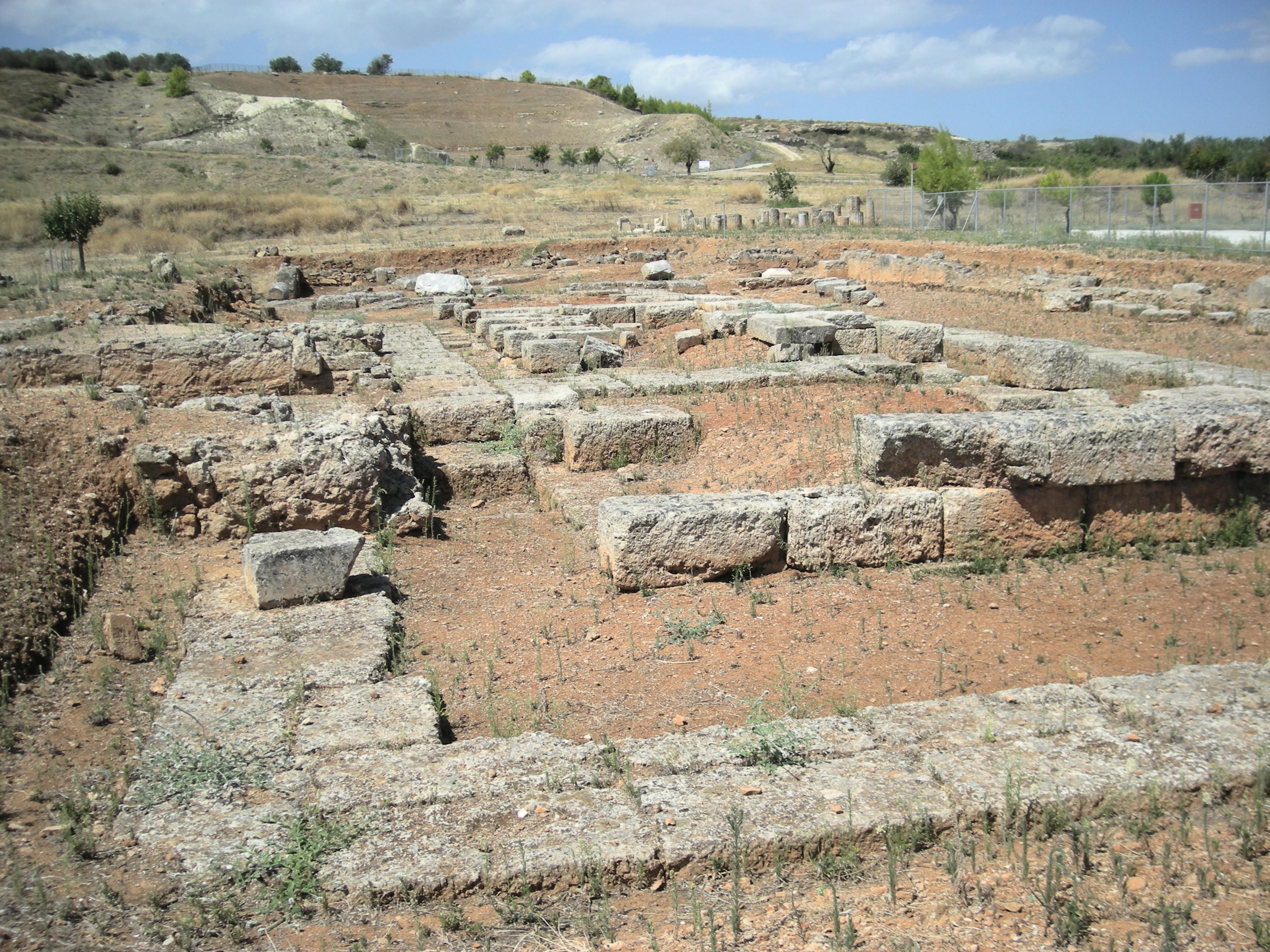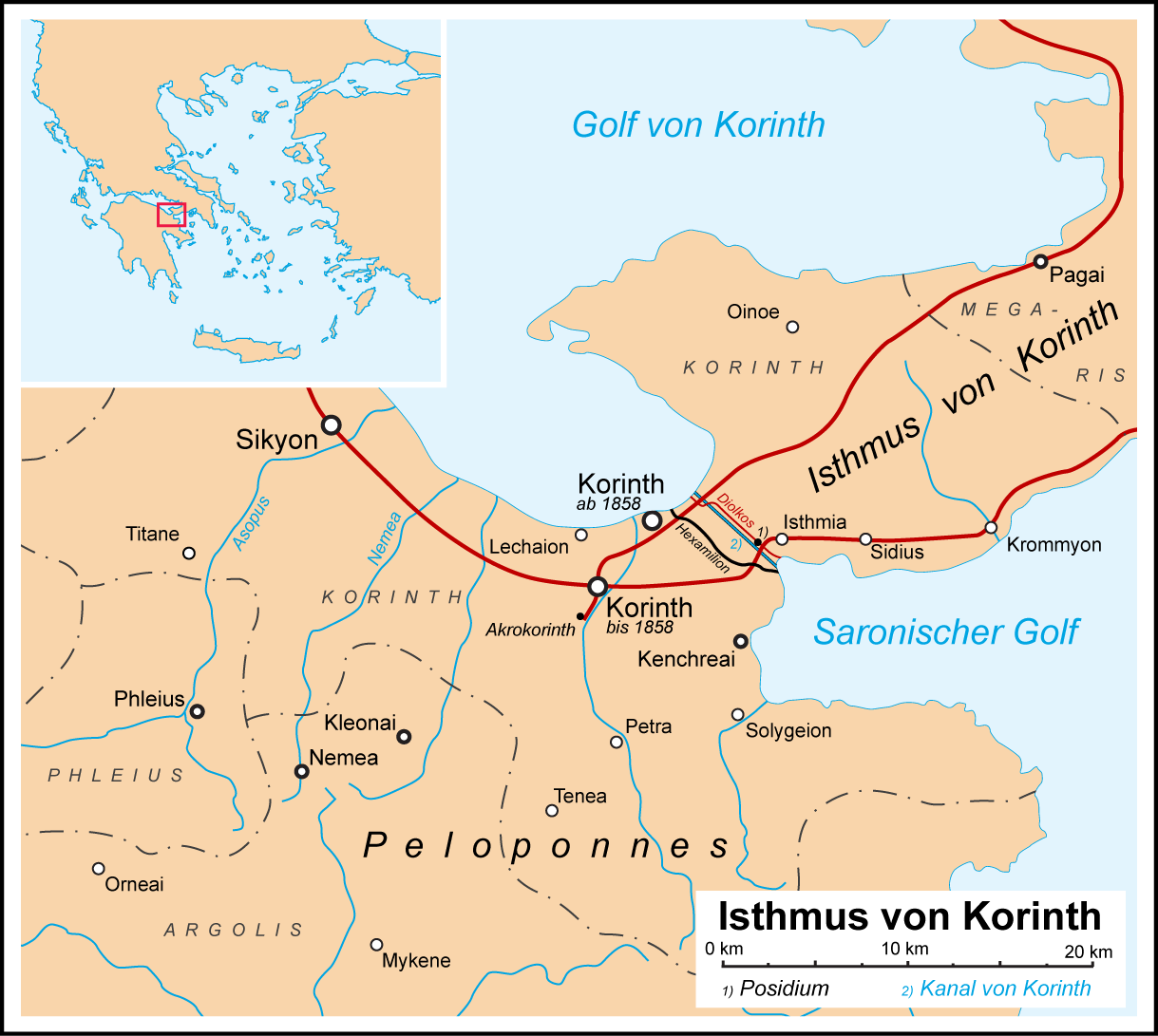

 Sicyon was built on a low triangular
Sicyon was built on a low triangular
"Sicyon: The most ancient Greek city-state (via archive.org)"
Ellen Papakyriakou/Anagnostou. Contains a great deal of information on ancient and present-day Sicyon.
The Ancient Theatre Archive. Theatre specifications and tour of the ancient theatre. {{Authority control Greek city-states Former populated places in Greece Cities in ancient Peloponnese Populated places in ancient Peloponnese Ancient Greek cities Locations in the Iliad
 Sicyon (; el, ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į; ''gen''.: ╬Ż╬╣╬║Žģß┐Č╬Į╬┐Žé) or Sikyon was an
Sicyon (; el, ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į; ''gen''.: ╬Ż╬╣╬║Žģß┐Č╬Į╬┐Žé) or Sikyon was an ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
city state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
situated in the northern Peloponnesus
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, ╬Ā╬Ą╬╗╬┐ŽĆŽī╬Į╬Į╬ĘŽā╬┐Žé, Pelop├│nn─ōsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which ...
between Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, ╬ÜŽīŽü╬╣╬Į╬Ė╬┐Žé, K├│rinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
and Achaea
Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaïa'' ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwestern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. The ...
on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia
Corinthia ( el, ╬Ü╬┐Žü╬╣╬Į╬Ė╬»╬▒ ''Korinth├Ła'') is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese. It is situated around the city of Corinth, in the north-eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula.
Geography
Cori ...
. An ancient monarchy at the times of the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has ...
, the city was ruled by a number of tyrants during the Archaic and Classical period and became a democracy in the 3rd century BC. Sicyon was celebrated for its contributions to ancient Greek art, producing many famous painters and sculptors. In Hellenistic times it was also the home of Aratus of Sicyon
Aratus of Sicyon (Ancient Greek: ß╝īŽü╬▒Žä╬┐Žé ßĮü ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į╬╣╬┐Žé; 271ŌĆō213 BC) was a politician and military commander of Hellenistic Greece. He was elected strategos of the Achaean League 17 times, leading the League through numerous mili ...
, the leader of the Achaean League
The Achaean League (Greek: , ''Koinon ton Akhaion'' "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern Pel ...
.
History


 Sicyon was built on a low triangular
Sicyon was built on a low triangular plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ha ...
about 3 kilometres (two miles) from the Corinthian Gulf
The Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf ( el, ╬Ü╬┐Žü╬╣╬Į╬Ė╬╣╬▒╬║ŽīŽé KŽī╬╗ŽĆ╬┐Žé, ''KorinthiakŽīs KŽīlpos'', ) is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea, separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. It is bounded in the east by the Isth ...
. Between the city and its port lay a fertile plain with olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
groves and orchards.
In Mycenean times Sicyon had been ruled by a line of twenty-six mythical kings and then seven priests of Apollo. The king-list given by Pausanias Pausanias ( el, ╬Ā╬▒ŽģŽā╬▒╬Į╬»╬▒Žé) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ...
comprises twenty-four kings, beginning with the autochthonous
Autochthon, autochthons or autochthonous may refer to:
Fiction
* Autochthon (Atlantis), a character in Plato's myth of Atlantis
* Autochthons, characters in the novel ''The Divine Invasion'' by Philip K. Dick
* Autochthon, a Primordial in the ...
Aegialeus. The penultimate king of the list, Agamemnon
In Greek mythology, Agamemnon (; grc-gre, ß╝ł╬│╬▒╬╝╬Ł╬╝╬ĮŽē╬Į ''Agam├®mn┼Źn'') was a king of Mycenae who commanded the Greeks during the Trojan War. He was the son, or grandson, of King Atreus and Queen Aerope, the brother of Menelaus, the husb ...
, compels the submission of Sicyon to Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, ╬£Žģ╬║ß┐å╬Į╬▒╬╣ or , ''Myk─ō╠énai'' or ''MykßĖŚn─ō'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. Th ...
; after him comes the Dorian usurper Phalces. Pausanias shares his source with Castor of Rhodes
Castor of Rhodes ( el, ╬Ü╬¼ŽāŽäŽēŽü ßĮü ß┐¼Žī╬┤╬╣╬┐Žé), also known as Castor of Massalia or Castor of Galatia according to the ''Suda'', or as Castor the Annalist, was a Greek grammarian and rhetorician. He was surnamed Philoromaeus (╬”╬╣╬╗╬┐ŽüŽÄ╬╝ ...
, who used the king-list in compiling tables of history; the common source was convincingly identified by Felix Jacoby
Felix Jacoby (; 19 March 1876 ŌĆō 10 November 1959) was a German classicist and philologist. He is best known among classicists for his highly important work ''Fragmente der griechischen Historiker'', a collection of text fragments of ancient Gr ...
as a lost ''Sicyonica'' by the late 4th-century poet Menaechmus of Sicyon :''There is also a Menaechmus in Plautus' play, ''The Menaechmi''.''
Menaechmus ( el, ╬£╬Ł╬Į╬▒╬╣Žć╬╝╬┐Žé, 380ŌĆō320 BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician, geometer and philosopher born in Alopeconnesus or Prokonnesos in the Thracian Chersonese, wh ...
.
After the Dorian invasion the city remained subject to Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
...
, whence its Dorian conquerors had come. The community was now divided into the ordinary three Dorian tribes and an equally privileged tribe of Ionians
The Ionians (; el, ß╝╝Žē╬Į╬ĄŽé, ''├Ź┼Źnes'', singular , ''├Ź┼Źn'') were one of the four major tribes that the Greeks considered themselves to be divided into during the ancient period; the other three being the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achae ...
, besides which a class of serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
s (, or , ) lived on and worked the land.
For some centuries the suzerainty of Argos remained, but after 676 BC Sicyon regained its independence under a line of tyrants called the Orthagorides after the name of the first ruler Orthagoras. The most important however was the founder's grandson Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes ( ; grc-gre, ╬Ü╬╗╬Ą╬╣Žā╬Ė╬Ł╬Į╬ĘŽé), or Clisthenes (c. 570c. 508 BC), was an ancient Athenian lawgiver credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508 BC. For these accomplishm ...
, the grandfather of the Athenian legislator Cleisthenes
Cleisthenes ( ; grc-gre, ╬Ü╬╗╬Ą╬╣Žā╬Ė╬Ł╬Į╬ĘŽé), or Clisthenes (c. 570c. 508 BC), was an ancient Athenian lawgiver credited with reforming the constitution of ancient Athens and setting it on a democratic footing in 508 BC. For these accomplishm ...
, who ruled from 600 to 560 BC. Besides reforming the city's constitution to the advantage of the Ionians and replacing Dorian cults with the worship of Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, ╬ö╬╣Žī╬ĮŽģŽā╬┐Žé ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
, Cleisthenes gained a reputation as the chief instigator and general of the First Sacred War
The First Sacred War, or Cirraean War, was fought between the Amphictyonic League of Delphi and the city of Kirrha. At the beginning of the 6th century BC the Pylaeo-Delphic Amphictyony, controlled by the Thessalians, attempted to take hold of the ...
(590 BC) in the interests of the Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (╬ĀŽģ╬ĖŽÄ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
ans.
His successor Aeschines was expelled by the Spartans in 556 BC and Sicyon became an ally of the Lacedaemonians for more than a century. During this time, the Sicyonians developed the various industries for which they were known in antiquity. As the abode of the sculptors Dipoenus and Scyllis it gained pre-eminence in woodcarving and bronze work such as is still to be seen in the archaic metal facings found at Olympia
The name Olympia may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Olympia'' (1938 film), by Leni Riefenstahl, documenting the Berlin-hosted Olympic Games
* ''Olympia'' (1998 film), about a Mexican soap opera star who pursues a career as an athlet ...
. Its pottery, which resembled Corinthian ware, was exported with the latter as far as Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria.
Etruscan Etruria
The ancient people of Etruria
are identified as Etruscan civiliza ...
. In Sicyon also the art of painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ...
was supposed to have been invented. After the fall of the tyrants their institutions survived until the end of the 6th century BC, when Dorian supremacy was re-established, perhaps by the agency of Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: ╬ŻŽĆ╬¼ŽüŽä╬▒, ''Sp├Īrt─ü''; Attic Greek: ╬ŻŽĆ╬¼ŽüŽä╬Ę, ''Sp├Īrt─ō'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
under the ephor Chilon, and the city was enrolled in the Peloponnesian League
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance of ancient Greek city-states, dominated by Sparta and centred on the Peloponnese, which lasted from c.550 to 366 BC. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431ŌĆō404 BC ...
. Henceforth, its policy was usually determined either by Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: ╬ŻŽĆ╬¼ŽüŽä╬▒, ''Sp├Īrt─ü''; Attic Greek: ╬ŻŽĆ╬¼ŽüŽä╬Ę, ''Sp├Īrt─ō'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
or Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, ╬ÜŽīŽü╬╣╬Į╬Ė╬┐Žé, K├│rinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
.
During the Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
, the Sicyonians participated with fifteen triremes in the Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
and with 3,000 hoplites in the Battle of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states (including Sparta, Athens, C ...
. On the Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (╬ĀŽģ╬ĖŽÄ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
c Serpent Column
The Serpent Column ( grc, ╬żŽü╬╣╬║╬¼Žü╬Ę╬Į╬┐Žé ßĮīŽå╬╣Žé ''╬żrikarenos ╬¤phis'' "Three-headed Serpent";, i.e. "the bronze three-headed serpent"; see
See also , . tr, Y─▒lanl─▒ S├╝tun "Serpentine Column"), also known as the Serpentine Column, ...
celebrating the victory Sicyon was named in fifth place after Sparta, Athens, Corinth and Tegea. In September 479 BC a Sicyonian contingent fought bravely in the Battle of Mycale, where they lost more men than any other city.
Later in the 5th century BC, Sicyon, like Corinth, suffered from the commercial rivalry of Athens
Athens ( ; el, ╬æ╬Ė╬«╬Į╬▒, Ath├Łna ; grc, ß╝ł╬Ėß┐å╬Į╬▒╬╣, Ath├¬nai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
in the western seas, and was repeatedly harassed by squadrons of Athenian ships. The Sicyonians fought two battles against the Athenians, first against their admiral Tolmides Tolmides, (Greek: ╬ż╬┐╬╗╬╝╬»╬┤╬ĘŽé), son of Tolmaeus, was a leading Athenian general of the First Peloponnesian War. He rivalled Pericles and Myronides for the military leadership of Athens during the 450s and early 440s BC.
In 455 BC, Tolmides was ...
in 455 BC and then in a land battle against Pericles
Pericles (; grc-gre, ╬Ā╬ĄŽü╬╣╬║╬╗ß┐åŽé; c. 495 ŌĆō 429 BC) was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Pelopo ...
with 1000 hoplites in 453 BC.
In the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431ŌĆō404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
Sicyon followed the lead of Sparta and Corinth. When these two powers quarrelled during the peace of Nicias
The Peace of Nicias was a peace treaty signed between the Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in March 421 BC that ended the first half of the Peloponnesian War.
In 425 BC, the Spartans had lost the battles of Pylos and Sphacteria, a severe d ...
, it remained loyal to the Spartans. At the reprise of the war, during the Athenian expedition in Sicily, the Sicyonians contributed 200 pressed hoplites under their commander Sargeus to the force that relieved Syracuse. At the beginning of the 4th century, in the Corinthian war
The Corinthian War (395ŌĆō387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with ...
, Sicyon sided again with Sparta and became its base of operations against the allied troops round Corinth.
In 369 BC Sicyon was captured and garrisoned by the Thebans in their successful attack on the Peloponnesian League. From 368 to 366 BC Sicyon was ruled by Euphron
Euphron was a tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of Sicyon between 368 and 364 BC.
Euphron was a citizen of Sicyon, who held the chief power during the period of its subjection to Sparta. In 368 BC the city was compelled by Epaminondas to ...
who first favoured democracy, but then made himself tyrant. Euphron was killed in Thebes by a group of Sicyonian aristocrats, but his compatriots buried him in his home town and continued to honour him like the second founder of the city.
During the 4th century BC, the city reached its zenith as a centre of art: its school of painting gained fame under Eupompus
Eupompus (Ancient Greek: ) was the founder of the great Sicyonic school of painting, which flourished in the 4th century BC at Sicyon in Ancient Greece. He was eclipsed by his successors, and is chiefly remembered for the advice which he is said ...
and attracted the great masters Pamphilus and Apelles
Apelles of Kos (; grc-gre, ß╝łŽĆ╬Ą╬╗╬╗ß┐åŽé; fl. 4th century BC) was a renowned painter of ancient Greece. Pliny the Elder, to whom much of modern scholars' knowledge of this artist is owed (''Naturalis Historia'' 35.36.79ŌĆō97 and ''passim'' ...
as students, while Lysippus
Lysippos (; grc-gre, ╬øŽŹŽā╬╣ŽĆŽĆ╬┐Žé) was a Greek sculptor of the 4th century BC. Together with Scopas and Praxiteles, he is considered one of the three greatest sculptors of the Classical Greek era, bringing transition into the Hellenistic p ...
and his pupils raised the Sicyonian sculpture to a level hardly surpassed anywhere else in Greece. The tyrant Aristratus, a friend of the Macedonian royal family, had himself portrayed by the painter Melanthius
Melanthius ( grc, ╬£╬Ą╬╗╬¼╬Į╬Ė╬╣╬┐Žé) was an ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the followin ...
aside the goddess of victory Nike
Nike often refers to:
* Nike (mythology), a Greek goddess who personifies victory
* Nike, Inc., a major American producer of athletic shoes, apparel, and sports equipment
Nike may also refer to:
People
* Nike (name), a surname and feminine give ...
on a chariot. In this period Sicyon was the undisputed center of Greek painting with its school attracting famous artists from all over Greece, including the celebrated Apelles
Apelles of Kos (; grc-gre, ß╝łŽĆ╬Ą╬╗╬╗ß┐åŽé; fl. 4th century BC) was a renowned painter of ancient Greece. Pliny the Elder, to whom much of modern scholars' knowledge of this artist is owed (''Naturalis Historia'' 35.36.79ŌĆō97 and ''passim'' ...
and Pausias
Pausias ( el, ╬Ā╬▒ŽģŽā╬»╬▒Žé) was an ancient Greek painter of the first half of the 4th century BCE, of the school of Sicyon.
Biography
Pausias introduced the custom of painting ceilings of houses. His great merit appears to have lain in the bet ...
.
In 323 BC Euphron the Younger
Euphron was a tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of Sicyon between 368 and 364 BC.
Euphron was a citizen of Sicyon, who held the chief power during the period of its subjection to Sparta. In 368 BC the city was compelled by Epaminondas to ...
, a grandson of the tyrant Euphron, reintroduced a democracy, but was soon conquered by the Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, ╬£╬▒╬║╬Ą╬┤╬┐╬Į╬»╬▒), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by ...
ians during the Lamian War
The Lamian War, or the Hellenic War (323ŌĆō322 BC) was fought by a coalition of cities including Athens and the Aetolian League against Macedon and its ally Boeotia. The war broke out after the death of the King of Macedon, Alexander the Great, ...
. When the Macedonian commander Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
was murdered in Sicyon in 314 BC, his wife Cratesipolis Cratesipolis ( el, KŽü╬▒Žä╬ĘŽā╬»ŽĆo╬╗╬╣Žé meaning "conqueror of the city") was the ruler of Sicyon and Corinth in 314-308 BC. She was the wife of Alexander (son of Polyperchon) and was highly distinguished for her beauty, talents, and energy.
In ...
took control of the city and ruled it for six years, until she was induced by king Ptolemy I
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, ╬ĀŽä╬┐╬╗╬Ą╬╝╬▒ß┐¢╬┐Žé ╬ŻŽēŽä╬«Žü, ''Ptolema├«os S┼ŹtßĖŚr'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC ŌĆō January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and companion of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedon ...
to hand it over to the Egyptians. Between 308 and 303 BC Sicyon was ruled by two Ptolemaic commanders, first Cleonides and then Philip.
In 303 BC Sicyon was conquered by Demetrius Poliorcetes
Demetrius I (; grc, ╬ö╬Ę╬╝╬«ŽäŽü╬╣╬┐Žé; 337ŌĆō283 BC), also called Poliorcetes (; el, ╬Ā╬┐╬╗╬╣╬┐Žü╬║╬ĘŽä╬«Žé, "The Besieger"), was a Macedonian nobleman, military leader, and king of Macedon (294ŌĆō288 BC). He belonged to the Antigonid dynasty ...
who razed the ancient city in the plain and built a new wall on the ruins of the old Acropolis on the high triangular plateau which resulted sufficient for the reduced populace. The new agora was adorned by a "Painted Stoa" attributed to the king's mistress Lamia
LaMia Corporation S.R.L., operating as LaMia (short for ''L├Łnea A├®rea M├®rida Internacional de Aviaci├│n''), was a Bolivian charter airline headquartered in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, as an EcoJet subsidiary. It had its origins from the failed ...
, a flute player. For a short time the town was now called "Demetrias", but eventually the old name prevailed.
Demetrius left a garrison in the castle to control the city, and the commander Cleon
Cleon (; grc-gre, ╬Ü╬╗╬ŁŽē╬Į, ; died 422 BC) was an Athenian general during the Peloponnesian War. He was the first prominent representative of the commercial class in Athenian politics, although he was an aristocrat himself. He strongly advocate ...
established another tyrannical regime. After some twenty years he was killed by two rivals, Euthydemus and Timocleidas
Timocleidas ( el, ╬ż╬╣╬╝╬┐╬║╬╗╬Ą╬»╬┤╬▒Žé) was a tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of Sicyon in the 3rd century BC. After the violent death of the previous tyrant Cleon, he ruled jointly with Euthydemus, until the two were deposed by the citi ...
, who became the new joint tyrants of Sicyon. Their rule ended, probably around the start of the Chremonidean War
The Chremonidean War (267ŌĆō261 BC) was fought by a coalition of some Greek city-states and Ptolemaic Egypt against Antigonid Macedonian domination. It ended in a Macedonian victory which confirmed Antigonid control over the city-states of Gre ...
in 267 BC, when they were expelled by the people who elected their leader Cleinias to govern the city on a democratic ground. Two magistrates of these years were the hieromnemoi Sosicles and Euthydamos, known from an inscription at Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (╬ĀŽģ╬ĖŽÄ), in ancient times was a sacred precinct that served as the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient classical world. The oracle ...
. The democratic government's most important achievement was the construction of the gymnasium which is attributed to Cleinias. During the same time Xenokrates of Sicyon published his history of art which contributed to spread the fame of Sicyion as an undisputed capital of ancient art.
Even this time democracy did not last more than a few years, and in 264 BC Cleinias was slain by his cognate Abantidas
Abantidas (in Greek ß╝ł╬▓╬▒╬ĮŽä╬»╬┤╬▒Žé), the son of Paseas, became tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of Sicyon in 264 BC after murdering Cleinias, the father of Aratus. After the assassination, Abantidas had the remaining friends and relati ...
, who established his tyranny for twelve years. In 252 BC Abantidas was murdered by two rhetoricians, Aristotle the Dialectician
Aristotle the Dialectician (or Aristoteles of Argos, el, ß╝łŽü╬╣ŽāŽä╬┐Žä╬Ł╬╗╬ĘŽé; fl. 3rd century BC), was an ancient Greek dialectic philosopher from Argos. In 252 BC, together with the historian Deinias of Argos, he contrived a plot to overthro ...
and Deinias of Argos
Deinias of Argos (╬ö╬Ą╬╣╬Į╬»╬▒Žé) was an ancient Greek philosopher and historian of the 3rd century BC. In 252 BC he joined with Aristotle the Dialectician in an attempt to overthrow the rule of the tyrant Abantidas of Sicyon. The two philosopher ...
, and his father Paseas
Paseas (╬Ā╬▒Žā╬Ł╬▒Žé) was a tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of Sicyon in the 3rd century BC. He succeeded his son, Abantidas
Abantidas (in Greek ß╝ł╬▓╬▒╬ĮŽä╬»╬┤╬▒Žé), the son of Paseas, became tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of S ...
took over, only to be murdered after a short rule by another rival named Nicocles.
In 251, Aratus of Sicyon
Aratus of Sicyon (Ancient Greek: ß╝īŽü╬▒Žä╬┐Žé ßĮü ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į╬╣╬┐Žé; 271ŌĆō213 BC) was a politician and military commander of Hellenistic Greece. He was elected strategos of the Achaean League 17 times, leading the League through numerous mili ...
, the 20-year-old son of Cleinias, conquered the city with a night assault and expelled the last tyrant. Aratus re-established democracy, called back the exiles and brought his city into the Achaean League
The Achaean League (Greek: , ''Koinon ton Akhaion'' "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern Pel ...
. This move ended the internal strife and Aratus remained the leading figure of Achaean politics until his death in 213 BC, during a period of great achievements. The prosperity and peaceful condition of Sicyon was only interrupted by an Aetolia
Aetolia ( el, ╬æß╝░ŽäŽē╬╗╬»╬▒, Aß╝░t┼Źl├Ła) is a mountainous region of Greece on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, forming the eastern part of the modern regional units of Greece, regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania.
Geography
The Achelous ...
n raid in 241 BC and an unsuccessful siege at the hands of king Cleomenes III
Cleomenes III ( grc, ╬Ü╬╗╬Ą╬┐╬╝╬Ł╬Į╬ĘŽé) was one of the two kings of Sparta from 235 to 222 BC. He was a member of the Agiad dynasty and succeeded his father, Leonidas II. He is known for his attempts to reform the Spartan state.
From 229 to ...
of Sparta in early 224 BC.
As a member of the Achaean federation Sicyon remained a stable democracy until the dissolution of the League by the Romans in 146 BC. In this period Sicyon was damaged by two disastrous earthquakes in 153 BC and 141 BC.
The destruction of Corinth (146 BC) brought Sicyon an acquisition of territory and the presidency over the Isthmian games
Isthmian Games or Isthmia (Ancient Greek: ß╝╝Žā╬Ė╬╝╬╣╬▒) were one of the Panhellenic Games of Ancient Greece, and were named after the Isthmus of Corinth, where they were held. As with the Nemean Games, the Isthmian Games were held both the year ...
; yet in Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC ŌĆō 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the estab ...
's time it had fallen deep into debt. Under the Roman empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ Žäß┐Č╬Į ß┐¼Žē╬╝╬▒╬»Žē╬Į, Basile├Ła t├┤n Rh┼Źma├Ł┼Źn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
it was quite obscured by the restored cities of Corinth and Patrae
)
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 =
, demographics1_info2 =
, timezone1 = EET
, utc_offset1 = +2
, ...
; in Pausanias Pausanias ( el, ╬Ā╬▒ŽģŽā╬▒╬Į╬»╬▒Žé) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ...
' age (150 AD) it was almost desolate. In Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
times it became a bishop's seat, and to judge by its later name Hellas it served as a refuge for the Greeks from the Slavonic invasions of the 8th century.
In the 4th century BC the people of Sicyon were the subject of a popular comedy by Menander
Menander (; grc-gre, ╬£╬Ł╬Į╬▒╬Į╬┤Žü╬┐Žé ''Menandros''; c. 342/41 ŌĆō c. 290 BC) was a Greek dramatist and the best-known representative of Athenian New Comedy. He wrote 108 comedies and took the prize at the Lenaia festival eight times. His rec ...
titled Sikyonioi.
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 ŌĆō 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
, in his 1606 play ''Antony and Cleopatra
''Antony and Cleopatra'' (First Folio title: ''The Tragedie of Anthonie, and Cleopatra'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. The play was first performed, by the King's Men, at either the Blackfriars Theatre or the Globe Theatre in around ...
'' (Act I, Scene 2), notes that Marc Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the aut ...
's wife, Fulvia
Fulvia (; c. 83 BC ŌĆō 40 BC) was an aristocratic Roman woman who lived during the Late Roman Republic. Fulvia's birth into an important political dynasty facilitated her relationships and, later on, marriages to Publius Clodius Pulcher, Gai ...
died in Sicyon. Historically, she died there in 40 BC while in rebellion against Octavius Caesar.
Friedrich H├Člderlin
Johann Christian Friedrich H├Člderlin (, ; ; 20 March 1770 ŌĆō 7 June 1843) was a German poet and philosopher. Described by Norbert von Hellingrath as "the most German of Germans", H├Člderlin was a key figure of German Romanticism. Part ...
's novel '' Hyperion'' from 1797 starts at the "paradisiac plain of Sicyon".
Monuments
* Temple of Apollo or Artemis * Theatre of Sikyon * Palaestra - Gymnasium * Stadium of Sikyon * Bouleuterion of Sikyon A village named until 1920 ''Vasiliko'' (described by the 1911 ''Encyclop├”dia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclop├”dia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclop├”dia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
'' as "insignificant") now occupies the site.Mythological Rulers
Rulers according to Eusebius's chronicle and other greek sources are: *1st: Aegialeus *2nd: Europs *3rd:Telchis :''"Telchis" is also the singular form of "Telchines".''
In Greek mythology, Telchis ( grc, ╬ż╬Ą╬╗Žć╬»Žé means "one of the Telchines") may refer to two different or the same characters:
* Telchis or Telchin, the third king of Sicyon who reigned for ...
*4th:Apis of Sicyon
In Greek mythology, Apis (; Ancient Greek: ß╝īŽĆ╬╣Žé derived from ''apios'' "far-off" or "of the pear-tree") was the fourth king of Sicyon who reigned for 25 years.
Family
Apis was the son and heir of King Telchis, descendant of the city's foun ...
*5th: Thelxion of Sicyon
In Greek mythology, Thelxion ( grc, ╬ś╬Ą╬╗╬Š╬»Žē╬Į) was the fifth king of Sicyon who reigned for 52 years.
Family
Thelxion was the son and heir of King Apis (Greek mythology), Apis, descendant of the city's founder Aegialeus (King of Sicyon), A ...
*6th:Aegyrus In Greek mythology, Aegyrus (Ancient Greek: ╬æß╝┤╬│ŽģŽü╬┐Žé) or Aegydrus was the sixth king of Sicyon who reigned for 34 years.
Family
Aegyrus was the son and heir of King Thelxion, descendant of the city's founder Aegialeus (an autochthon). ...
*7th:Thurimachus
In Greek mythology, Thurimachus (Ancient Greek: ╬ś╬┐ŽģŽü╬»╬╝╬▒Žć╬┐Žé) was the seventh king of Sicyon who reigned for 45 years.Eusebius, ''Chronographia'63/ref>
Family
Thurimachus was the son and heir of King Aegyrus, descendant of the city's fo ...
*8th:Leucippus
Leucippus (; el, ╬ø╬ĄŽŹ╬║╬╣ŽĆŽĆ╬┐Žé, ''Le├║kippos''; fl. 5th century BCE) is a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who has been credited as the first philosopher to develop a theory of atomism.
Leucippus' reputation, even in antiquity, was obscured ...
*9th:Messapus
Messapus, (Greek: ╬£╬ŁŽāŽā╬▒ŽĆ╬┐Žé, ''Messapos'') a character in Virgil's ''Aeneid'', appears in Books VII to XII of the Latin epic poem. He was a son of Neptune, a famous tamer of horses, and king of Etruria, known for being one "whom no one ca ...
or Peratus In Greek mythology, Peratus (Ancient Greek: ╬Ā╬ŁŽü╬▒Žä╬┐Žé means "wanderer, emigrant"), also called Eratus (ß╝£Žü╬▒Žä╬┐Žé means "lovely"), was the 10th king of Sicyon who reigned for 46 years.Eusebius, ''Chronographia'63/ref>
Family
Peratus was ...
*10th:Plemnaeus In Greek mythology, Plemnaeus (Ancient Greek: ╬Ā╬╗╬Ę╬╝╬Į╬▒ß┐¢╬┐╬Į or ╬Ā╬╗╬Ę╬╝╬Į╬▒╬»ß┐│) was the 11th king of Sicyon who reigned for 48 years.
Family
Plemnaeus was the son and heir of King Peratus, son of Poseidon. He was the father of Orthopoli ...
*11th:Orthopolis In Greek mythology, Orthopolis (Ancient Greek: ßĮłŽü╬Ė╬┐ŽĆŽī╬╗╬╣╬┤╬╣ or ßĮłŽü╬ĖŽīŽĆ╬┐╬╗╬╣╬Į means "upholding the city") was the 12th king of Sicyon who reigned for 63 years.Eusebius, ''Chronographia'63/ref>
Family
Orthopolis was the son and heir ...
*12th:Marathonius
In Greek mythology, Marathonius or Marathonios may refer to two distinct characters:
* Marathonius, the 13th king of Sicyon who reigned for 30 years. His predecessor was Orthopolis and himself was succeeded by Marathus. During his reign, Cecrop ...
or Coronus
*13th:Marathus
*14th:
*15th: Coronus or Echyreus
*16th: Corax
*17th :Epopeus of Sicyon
In Greek mythology, Epopeus (; Ancient Greek: ß╝śŽĆŽēŽĆ╬ĄŽŹŽé) was the 17th king of Sicyon, with an archaic bird-name that linked him to ''epops'' (ß╝öŽĆ╬┐Žł), the hoopoe, the "watcher". A fragment of Callimachus' ''Aitia'' ("Origins") appears to ...
*18th: Lamedon
*19th:Sicyon
Sicyon (; el, ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į; ''gen''.: ╬Ż╬╣╬║Žģß┐Č╬Į╬┐Žé) or Sikyon was an ancient Greek city state situated in the northern Peloponnesus between Corinth and Achaea on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia. An ancient mona ...
*20th:Polybus of Sicyon
In Greek mythology, Polybus (Ancient Greek: ╬ĀŽī╬╗Žģ╬▓╬┐Žé) was the 20th king of Sicyon who reigned for 40 years.Eusebius, ''Chronographia'63/ref>
Family
Polybus was the son of Hermes and Chthonophyle, daughter of the eponym of Sicyon. He h ...
*21st:Adrastus
In Greek mythology, Adrastus or Adrestus (Ancient Greek: ß╝ī╬┤Žü╬▒ŽāŽä╬┐Žé or ß╝ī╬┤Žü╬ĘŽāŽä╬┐Žé), (perhaps meaning "the inescapable"), was a king of Argos, and leader of the Seven against Thebes. He was the son of the Argive king Talaus, but was ...
*Before Agammemnon:Polypheides In Greek mythology, the name Polypheides or Polyphides (; Ancient Greek: ╬Ā╬┐╬╗ŽģŽå╬Ą╬»╬┤╬ĘŽé) may refer to:
*Polypheides, son of Mantius and brother of Cleitus. He was granted prophetic skills by Apollo and became the best seer among mortals afte ...
Notable people
Ancient * Aegialeus (21st century BC) legendary founder * Tellis (8th century BC), runner (Olympic victor 708 BC) *Butades
Butades of Sicyon ( grc, ╬Æ╬┐ŽģŽä╬¼╬┤╬ĘŽé ''Boutades''), sometimes mistakenly called Dibutades, was the reputed inventor of the art of modelling clay in relief, which an accident first led him to practise, in conjunction with his daughter, at Cor ...
(7th century BC) sculptor
*Canachus Canachus ( grc, ╬Ü╬¼╬Į╬▒Žć╬┐Žé ) was a sculptor of Sicyon in Corinthia, of the latter part of the 6th century . He was especially noted as the author of two great statues of Apollo, one in bronze made for the temple at Didyma near Miletus, and ...
(6th century BC) sculptor
* Aristocles (5th century BC) sculptor
*Praxilla
Praxilla of Sicyon ( grc-gre, ╬ĀŽü╬¼╬Š╬╣╬╗╬╗╬▒), was a Greek lyric poet of the 5th century BC, from Sicyon on the Gulf of Corinth. Eusebius dates her ''floruit'' to 451/450 BC (the second year of the 82nd Olympiad).
Little of Praxilla's work su ...
(5th century BC) poetess
*Ariphron Ariphron (; Gr. ) was the name of several people from ancient Greek history:
*Ariphron, the father of Xanthippus, and grandfather of Pericles, both prominent Athenian statesmen. He was associated with the Alcmaeonid family.
*Ariphron, the brother ...
(5th century BC) poet
*Alypus
Alypus ( grc-gre, ß╝ī╬╗ŽģŽĆ╬┐Žé) was a sculptor of ancient Greece, a native of Sicyon. He studied under Naucydes of Argos. His age may be fixed from his having executed bronze statues of some Spartans who shared in the victory of Lysander at Ae ...
(5th to 4th century BC) sculptor
*Alexis Alexis may refer to:
People Mononym
* Alexis (poet) ( ŌĆō ), a Greek comic poet
* Alexis (sculptor), an ancient Greek artist who lived around the 3rd or 4th century BC
* Alexis (singer) (born 1968), German pop singer
* Alexis (comics) (1946ŌĆō1977 ...
(5th or 4th century BC) sculptor
*Eupompus
Eupompus (Ancient Greek: ) was the founder of the great Sicyonic school of painting, which flourished in the 4th century BC at Sicyon in Ancient Greece. He was eclipsed by his successors, and is chiefly remembered for the advice which he is said ...
(4th century BC) painter
* Pamphilus (4th century BC) painter
*Melanthius
Melanthius ( grc, ╬£╬Ą╬╗╬¼╬Į╬Ė╬╣╬┐Žé) was an ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the followin ...
(4th century BC) painter
*Pausias
Pausias ( el, ╬Ā╬▒ŽģŽā╬»╬▒Žé) was an ancient Greek painter of the first half of the 4th century BCE, of the school of Sicyon.
Biography
Pausias introduced the custom of painting ceilings of houses. His great merit appears to have lain in the bet ...
(4th century BC) painter
*Eutychides
Eutychides ( grc, ╬ĢßĮÉŽäŽģŽć╬»╬┤╬ĘŽé, ) of Sicyon in Corinthia, Greek sculptor of the early part of the 3rd century BC, was a pupil of Lysippus.Ogden, ''The Legend of Seleucus'', p. 136. His most noted work was a statue of the Tyche of Antioch ...
(4th century BC) sculptor
*Lysippos
Lysippos (; grc-gre, ╬øŽŹŽā╬╣ŽĆŽĆ╬┐Žé) was a Ancient Greek sculpture, Greek sculptor of the 4th century BC. Together with Scopas and Praxiteles, he is considered one of the three greatest sculptors of the Ancient Greece, Classical Greek era, bri ...
(4th century BC) sculptor
* Lysistratus (4th century BC) sculptor
* Sostrates (4th century BC) pankratiast (thrice Olympic champion)
* Xenokrates (3rd century BC) sculptor and art historian
*Machon
Machon (Ancient Greek: ╬£╬¼ŽćŽē╬Į, fl. 3rd century BC) was a playwright of the New Comedy.
He was born in Corinth or Sicyon, and lived in Alexandria. It is said that he taught the grammarian Aristophanes of Byzantium. Two fragments from two o ...
(3rd century BC) playwright
*Timanthes
Timanthes of Cythnus ( el, ╬ż╬╣╬╝╬¼╬ĮŽæ╬ĘŽé) was an ancient Greek painter of the fourth century BC. The most celebrated of his works was a picture representing the sacrifice of Iphigenia, in which he finely depicted the emotions of those who to ...
(3rd century BC) painter
*Nealkes
Nealkes was an ancient Greek painter from Sicyon who flourished in the 3rd century BC.
He was a friend of Aratus of Sicyon and after the liberation of their city in 251 BC he interceded to save an artful painting by Melanthius showing the forme ...
(3rd century BC) painter
*Anaxandra
Anaxandra ( grc-gre, ß╝ł╬Į╬▒╬Š╬¼╬Į╬┤Žü╬▒; fl. 220s BC) was an ancient Greek female artist and painter from ancient Greece, Greece. She was the daughter and student of Nealkes, a painter of mythological and genre scenes. She painted circa 228 B.C. ...
(3rd century BC) female painter
* Pythocles (3rd century BC), runner (Olympic victor 236 BC)
*Aratus of Sicyon
Aratus of Sicyon (Ancient Greek: ß╝īŽü╬▒Žä╬┐Žé ßĮü ╬Ż╬╣╬║ŽģŽÄ╬Į╬╣╬┐Žé; 271ŌĆō213 BC) was a politician and military commander of Hellenistic Greece. He was elected strategos of the Achaean League 17 times, leading the League through numerous mili ...
(271ŌĆō213 BC) strategos of the Achaean League
* Baccheidas, a dancer and teacher of music
* Daetondas of Sicyon, sculptor
Modern
* Sotirios Krokidas, jurist and PM
Mythology: Identification with Mecone
Sicyon has been traditionally identified with the mythical Mecone or Mekone, site of thetrick at Mecone
The trick at Mecone or Mekone was an event in Greek mythology first attested by Hesiod in which Prometheus tricked Zeus for mankind's benefit, and thus incurred his wrath. It is unusual among Greek myths for being etiological, i.e. explaining the ...
carried out by Prometheus. Mecone is also described by Callimachus
Callimachus (; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works in a wide variety ...
as "the seat of the gods", and as the place where the gods Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, ╬öß┐ÉŽīŽé, ''Di├│s'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, ╬ö╬ĄŽŹŽé, De├║s ; grc, ╬ö╬Ł╬┐Žé, ''D├®os'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, ╬ö╬»╬▒Žé, ''D├ ...
Poseidon
Poseidon (; grc-gre, ╬Ā╬┐Žā╬Ą╬╣╬┤ß┐Č╬Į) was one of the Twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and myth, god of the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136ŌĆō139 In pre-Olympian Bronze Age Greece, he was venerated as a ch ...
and Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ߊŹ╬┤╬ĘŽé, H├Īid─ōs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
cast lots for what part of the world they ruled.Quoted st page 115, M.L. West, The Journal of Hellenic Studies Vol. 122 (2002), pp. 109-133
See also
*List of ancient Greek cities
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
References
External links
"Sicyon: The most ancient Greek city-state (via archive.org)"
Ellen Papakyriakou/Anagnostou. Contains a great deal of information on ancient and present-day Sicyon.
The Ancient Theatre Archive. Theatre specifications and tour of the ancient theatre. {{Authority control Greek city-states Former populated places in Greece Cities in ancient Peloponnese Populated places in ancient Peloponnese Ancient Greek cities Locations in the Iliad