|
Nealkes
Nealkes was an ancient Greek painter from Sicyon who flourished in the 3rd century BC. He was a friend of Aratus of Sicyon and after the liberation of their city in 251 BC he interceded to save an artful painting by Melanthius showing the former tyrant Aristratus of Sicyon with the goddess of victory Nike on a chariot. When Aratus insisted on the destruction of the portrait, Nealkes cried out in tears and finally offered to cancel the face by his own hand in order to save the rest of the artwork. He then painted a palm where the tyrant stood, but forgot his feet which remained visible underneath the chariot. The best known of his own paintings were a portrait of Aphrodite and a Battle on the Nile with a famous detail showing an ass on the bank of the river being attacked by a crocodile. His daughter was the painter Anaxandra, and his color-grinder was Erigonus, who was also a teacher of the modeller Aegineta. References * Plutarch, ''Aratus'' 13. * Pliny Pliny may refer to: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristratus Of Sicyon
Aristratus was a tyrant of the ancient Greek city-state of Sicyon who flourished in the years when Philipp II of Macedon established his hegemony over Greece, probably between 346 and 337 BC. Aristratus is named twice in Demosthenes speech ''On the Crown'' as one of the rulers who favoured the Macedonian king. In the first passage he is called an ''outcast'' by the orator. In the second passage he is mentioned together with another Sicyonian called Epichares, but it is not clear whether this man was an assistant, a colleague or a successor. The fact that Aristratus was a tyrant is established by Plutarch in his biography of Aratus of Sicyon, where the author narrates the destruction of the former tyrants' portraits in the town hall of Sicyon after the reintroduction of democracy in 251 BC. According to Aratus' own memoirs, the most artful painting showed Aristratus with the goddess of victory Nike on a chariot. Although the artwork was by the hand of the famous painter Melanthius w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegineta
Aegineta was an ancient Greek modeller (or ''fictor,'' one who sculpts with clay or other plastic material) mentioned by Pliny the Elder. Some scholars supposed that the word ''Aeginetae'' in the passage of Pliny denoted merely the country—Aegina—of some artist, whose real name was not given. The consensus of scholarly opinion is now against this hypothesis, however, and it is generally believed that "Aegineta" was the man's given name. Aegineta's brother Pasias, a painter of some distinction, was a pupil of Erigonus, who had been color-grinder to the artist Nealkes. Plutarch says that that Nealkes was a friend of Aratus of Sicyon, who was first elected strategos of the Achaean League The Achaean League ( Greek: , ''Koinon ton Akhaion'' "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern P ... in 243 BC. This would make it possible t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
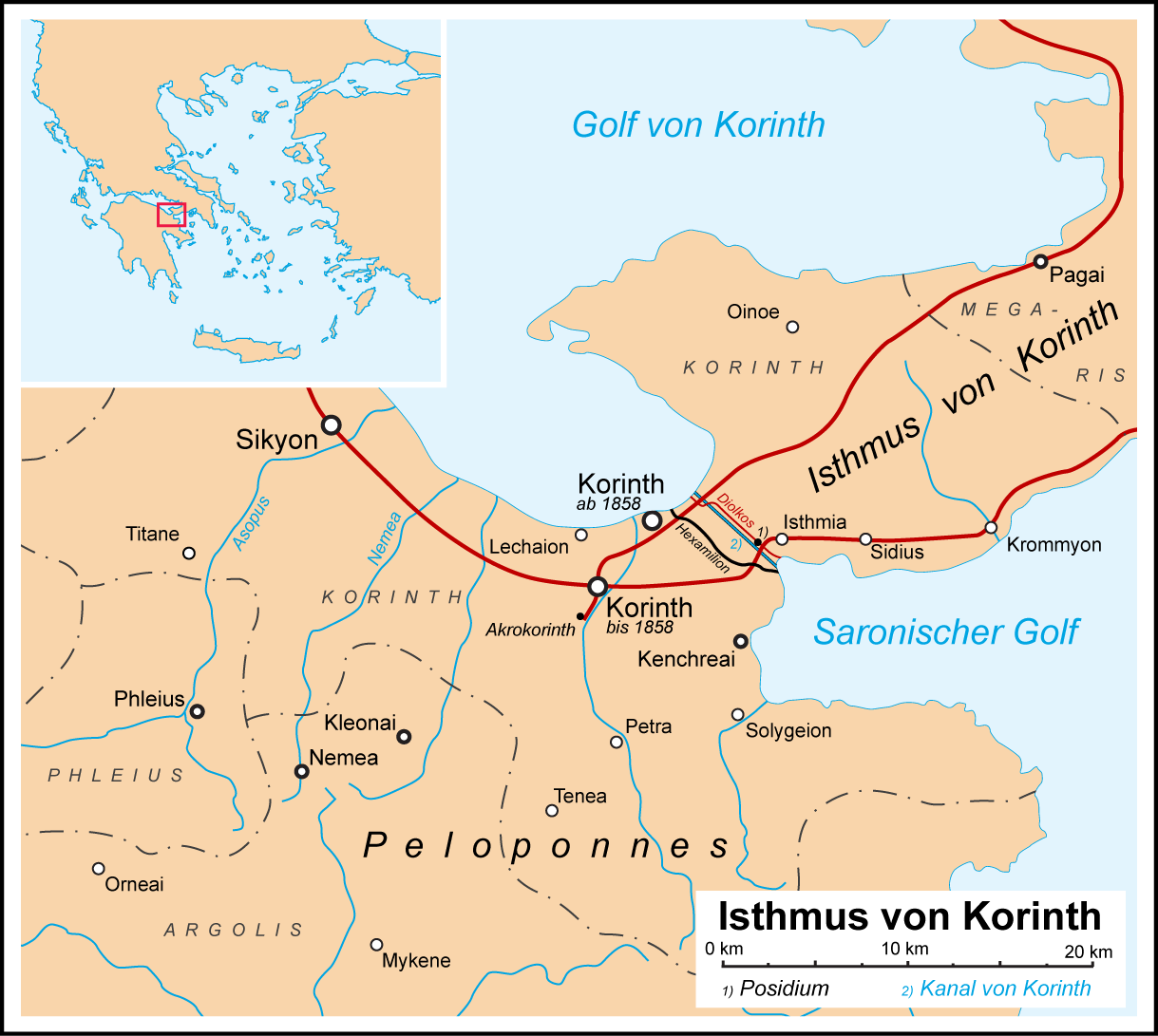
Sicyon
Sicyon (; el, Σικυών; ''gen''.: Σικυῶνος) or Sikyon was an ancient Greek city state situated in the northern Peloponnesus between Corinth and Achaea on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia. An ancient monarchy at the times of the Trojan War, the city was ruled by a number of tyrants during the Archaic and Classical period and became a democracy in the 3rd century BC. Sicyon was celebrated for its contributions to ancient Greek art, producing many famous painters and sculptors. In Hellenistic times it was also the home of Aratus of Sicyon, the leader of the Achaean League. History Sicyon was built on a low triangular plateau about 3 kilometres (two miles) from the Corinthian Gulf. Between the city and its port lay a fertile plain with olive groves and orchards. In Mycenean times Sicyon had been ruled by a line of twenty-six mythical kings and then seven priests of Apollo. The king-list given by Pausanias comprises twenty-four kings, beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaxandra
Anaxandra ( grc-gre, Ἀναξάνδρα; fl. 220s BC) was an ancient Greek female artist and painter from ancient Greece, Greece. She was the daughter and student of Nealkes, a painter of mythological and genre scenes. She painted circa 228 B.C. She is mentioned by Clement of Alexandria, the 2nd century Christian theologian, in a section of his Stromateis (Miscellanies) entitled "''Women as Well as Men Capable of Perfection''". Clement cites a lost work of the Hellenistic scholar Didymus Chalcenterus (1st century BC) as his source. Modern uses Her name was given by the International Astronomical Union in 1994 to a large 20 km diameter crater on Venus to commemorate the artist. The name was also used by the author Caroline B. Cooney for the principal character in her 2003 novel ''Goddess of Yesterday'', which is set during the Trojan War. See also *List of craters on Venus Notes ReferencesAnaxandra in the ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'' William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and airbrushes, can be used. In art, the term ''painting ''describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate multiple other materials, including sand, clay, paper, plaster, gold leaf, and even whole objects. Painting is an important form in the visual arts, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture (as in gestural painting), narration (as in narrative art), and abstraction (as in abstract art). Paintings can be naturalistic and representational (as in still life and landscape painting), photographic, abstract, nar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aratus Of Sicyon
Aratus of Sicyon (Ancient Greek: Ἄρατος ὁ Σικυώνιος; 271–213 BC) was a politician and military commander of Hellenistic Greece. He was elected strategos of the Achaean League 17 times, leading the League through numerous military campaigns including the Cleomenean War and the Social War. Aratus was exiled to Argos at the age of seven, after his father, the magistrate of Sicyon, was killed in a coup. In 251 BC, he led an expedition composed of other exiles which freed Sicyon from tyranny, and assumed power in the city. Sicyon joined the Achaean League, in which Aratus would later be elected ''strategos''. In his first major campaign as strategos, he seized the Macedonian-held citadel of Acrocorinth, previously believed impregnable. After conquering the Acrocorinth, Aratus pursued the Achaean League's expansion. When the Spartan king Cleomenes III conquered the Achaean cities of Argos and Corinth, Aratus succeeded in securing an alliance with his erstwhile e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanthius
Melanthius ( grc, Μελάνθιος) was an ancient Greek Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ... painter of the 4th century BC. He belonged to the school of Sicyon, which was noted for fine drawing. References * Ancient Greek painters 4th-century BC Greek people 4th-century BC painters {{Greece-painter-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nike (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Nike (; grc, Νίκη, lit=victory, ancient: , modern: ) was a goddess who personified victory in any field including art, music, war, and athletics. She is often portrayed in Greek art as Winged Victory in the motion of flight; however, she can also appear without wings as "Wingless Victory" when she is being portrayed as an attribute of another deity such as Athena.Suidas. ''The Suda on Line: Byzantine Lexicography''. Translated by Whitehead, David, et al. (2014). Accessed 9 December 2022. https://www.cs.uky.edu/~raphael/sol/sol-html/ In Greek literature Nike is described as both an attribute and attendant to the gods Zeus and Athena. Nike gained this honored role beside Zeus during the Titanomachy where she was one of the first gods to offer her allegiance to Zeus. At Athens, Nike became a servant to Athena as well as an attribute of her due to the prominent status Athena held in her patron city. The fusion of the two goddesses at Athens has contributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include myrtles, roses, doves, sparrows, and swans. The cult of Aphrodite was largely derived from that of the Phoenician goddess Astarte, a cognate of the East Semitic goddess Ishtar, whose cult was based on the Sumerian cult of Inanna. Aphrodite's main cult centers were Cythera, Cyprus, Corinth, and Athens. Her main festival was the Aphrodisia, which was celebrated annually in midsummer. In Laconia, Aphrodite was worshipped as a warrior goddess. She was also the patron goddess of prostitutes, an association which led early scholars to propose the concept of "sacred prostitution" in Greco-Roman culture, an idea which is now generally seen as erroneous. In Hesiod's ''Theogony'', Aphrodite is born off the coast of Cythera from the foam (, ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)