Signal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of
 Two main types of signals encountered in practice are '' analog'' and '' digital''. The figure shows a digital signal that results from approximating an analog signal by its values at particular time instants. Digital signals are '' quantized'', while analog signals are continuous.
Two main types of signals encountered in practice are '' analog'' and '' digital''. The figure shows a digital signal that results from approximating an analog signal by its values at particular time instants. Digital signals are '' quantized'', while analog signals are continuous.
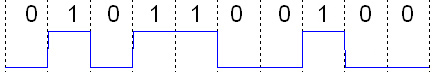 A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization of an optical or other electromagnetic field, acoustic pressure, the
A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization of an optical or other electromagnetic field, acoustic pressure, the
 A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
over some media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Means of communication, tools and channels used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Interactive media, media that is inter ...
accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
, information theory and biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
.
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video
Video is an Electronics, electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving picture, moving image, visual Media (communication), media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, whi ...
, speech, image
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ...
, sonar, and radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
as examples of signals. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. ...
), even if it does not carry information.
In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biol ...
. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biolo ...
, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typically provided by a sensor, and often the original form of a signal is converted to another form of energy using a transducer. For example, a microphone converts an acoustic signal to a voltage waveform, and a speaker does the reverse.
Another important property of a signal is its entropy or information content. Information theory serves as the formal study of signals and their content. The information of a signal is often accompanied by noise, which primarily refers to unwanted modifications of signals, but is often extended to include unwanted signals conflicting with desired signals ( crosstalk). The reduction of noise is covered in part under the heading of signal integrity. The separation of desired signals from background noise is the field of signal recovery, one branch of which is estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of Statistical parameter, parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such ...
, a probabilistic approach to suppressing random disturbances.
Engineering disciplines such as electrical engineering have advanced the design, study, and implementation of systems involving transmission, storage, and manipulation of information. In the latter half of the 20th century, electrical engineering itself separated into several disciplines: electronic engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flo ...
and computer engineering
Computer engineering (CE, CoE, or CpE) is a branch of engineering specialized in developing computer hardware and software.
It integrates several fields of electrical engineering, electronics engineering and computer science.
Computer engi ...
developed to specialize in the design and analysis of systems that manipulate physical signals, while design engineering developed to address the functional design of signals in user–machine interfaces.
Definitions
Definitions specific to sub-fields are common: * Inelectronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
and telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
, ''signal'' refers to any time-varying voltage, current, or electromagnetic wave that carries information.
* In signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
, signals are analog and digital representations of analog physical quantities.
* In information theory, a signal is a codified message, that is, the sequence of states in a communication channel that encodes a message.
* In a communication system, a ''transmitter'' encodes a ''message'' to create a signal, which is carried to a ''receiver'' by the communication channel. For example, the words " Mary had a little lamb" might be the message spoken into a telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most ...
. The telephone transmitter converts the sounds into an electrical signal. The signal is transmitted to the receiving telephone by wires; at the receiver it is reconverted into sounds.
* In telephone networks, signaling, for example common-channel signaling, refers to phone number and other digital control information rather than the actual voice signal.
Classification
Signals can be categorized in various ways. The most common distinction is between discrete and continuous spaces that the functions are defined over, for example, discrete and continuous-time domains. Discrete-time signals are often referred to as ''time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. ...
'' in other fields. Continuous-time signals are often referred to as ''continuous signals''.
A second important distinction is between discrete-valued and continuous-valued. Particularly in digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
, a digital signal may be defined as a sequence of discrete values, typically associated with an underlying continuous-valued physical process. In digital electronics, digital signals are the continuous-time waveform signals in a digital system, representing a bit-stream.
Signals may also be categorized by their spatial distributions as either point source signals (PSSs) or distributed source signals (DSSs).
In Signals and Systems, signals can be classified according to many criteria, mainly: according to the different feature of values, classified into analog signals and digital signals; according to the determinacy of signals, classified into deterministic signals and random signals; according to the strength of signals, classified into energy signals and power signals.
Analog and digital signals
Analog signal
An analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time-varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another time varying signal. For example, in an analogaudio signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals or a series of binary numbers for Digital signal (signal processing), digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies i ...
, the instantaneous voltage of the signal varies continuously with the sound pressure. It differs from a digital signal, in which the continuous quantity is a representation of a sequence of discrete values which can only take on one of a finite number of values.
The term ''analog signal'' usually refers to electrical signals; however, analog signals may use other mediums such as mechanical, pneumatic or hydraulic. An analog signal uses some property of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses rotary position as the signal to convey pressure information. In an electrical signal, the voltage, current, or frequency of the signal may be varied to represent the information.
Any information may be conveyed by an analog signal; often such a signal is a measured response to changes in physical phenomena, such as sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
, light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
, temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
, position, or pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
. The physical variable is converted to an analog signal by a transducer. For example, in sound recording, fluctuations in air pressure (that is to say, sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
) strike the diaphragm of a microphone which induces corresponding electrical fluctuations. The voltage or the current is said to be an ''analog'' of the sound.
Digital signal
 A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization of an optical or other electromagnetic field, acoustic pressure, the
A digital signal is a signal that is constructed from a discrete set of waveforms of a physical quantity so as to represent a sequence of discrete values. A ''logic signal'' is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics.
Alternatively, a digital signal may be considered to be the sequence of codes represented by such a physical quantity. The physical quantity may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization of an optical or other electromagnetic field, acoustic pressure, the magnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material. Accordingly, physicists and engineers usually define magnetization as the quanti ...
of a magnetic storage media, etc. Digital signals are present in all digital electronics, notably computing equipment and data transmission.
With digital signals, system noise, provided it is not too great, will not affect system operation whereas noise always degrades the operation of analog signals to some degree.
Digital signals often arise via sampling of analog signals, for example, a continually fluctuating voltage on a line that can be digitized by an analog-to-digital converter circuit, wherein the circuit will read the voltage level on the line, say, every 50 microseconds and represent each reading with a fixed number of bits. The resulting stream of numbers is stored as digital data on a discrete-time and quantized-amplitude signal. Computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
s and other digital devices are restricted to discrete time.
Energy and power
According to the strengths of signals, practical signals can be classified into two categories: energy signals and power signals. Energy signals: Those signals'energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
are equal to a finite positive value, but their average powers are 0;
Power signals: Those signals' average power are equal to a finite positive value, but their energy are infinite.
Deterministic and random
Deterministic signals are those whose values at any time are predictable and can be calculated by a mathematical equation. Random signals are signals that take on random values at any given time instant and must be modeledstochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
ally.
Even and odd
An even signal satisfies the condition or equivalently if the following equation holds for all and in the domain of : : An odd signal satisfies the condition or equivalently if the following equation holds for all and in the domain of : :Periodic
A signal is said to be periodic if it satisfies the condition: