Sidonians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sidon ( ; he, צִידוֹן, ''Ṣīḏōn'') known locally as Sayda or Saida ( ar, صيدا ''Ṣaydā''), is the third-largest city in
 Sidon was one of the most important
Sidon was one of the most important
 When Sidon fell under Roman domination, it continued to mint its own silver coins. The Romans also built a theater and other major monuments in the city. In the reign of
When Sidon fell under Roman domination, it continued to mint its own silver coins. The Romans also built a theater and other major monuments in the city. In the reign of
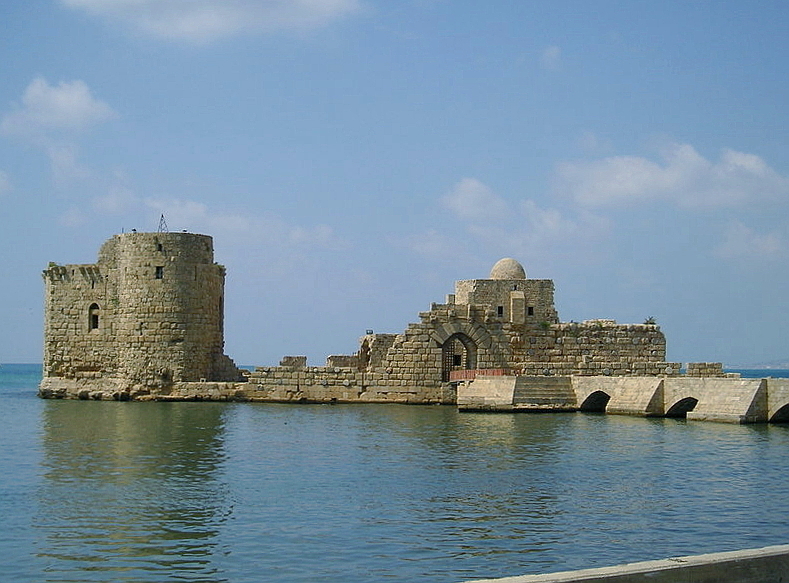 On 4 December 1110, Sidon was captured after the siege of Sidon, a decade after the
On 4 December 1110, Sidon was captured after the siege of Sidon, a decade after the
 After
After
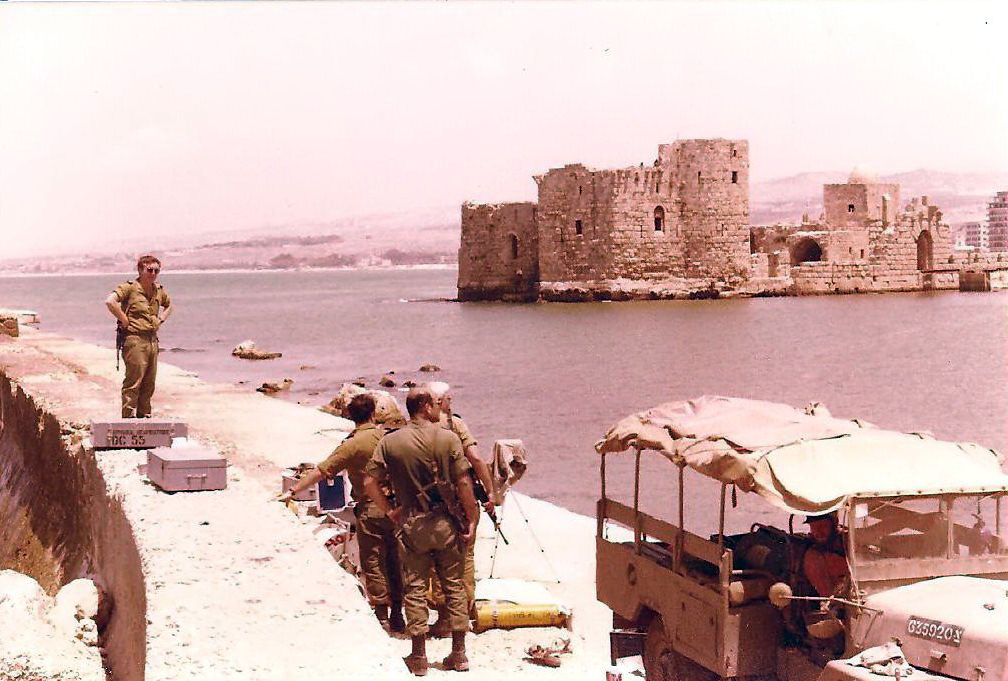 This sectarian and demographic division rose to the surface during the
This sectarian and demographic division rose to the surface during the

 * Sidon Sea Castle, a fortress built by the
* Sidon Sea Castle, a fortress built by the
"Tell el-Burak: A New Middle Bronze Age Site from Lebanon"
''Near Eastern Archaeology'', Vol. 73, No. 2/3 (2010), pp. 130–141. University of Chicago Press Archaeologists determined that Sidon was clearly the big power centre during MBA, controlling significant territory. So there appears to have been the "Kingdom of Sidon" that controlled el-Burak, and many other surrounding areas.

File:Port of Sidon 19th Century.jpg, Port of Sidon, 19th century
File:The castle and the harbour of Saida, the ancient Sidon-colored.jpg, The castle and the harbour of Saida, the ancient Sidon
File:Sidon Castle, Sidon, Lebanon.jpg, Sidon Castle
File:Sidon, Sarcophagus relief of a boat.jpg, Sidon, Sarcophagus relief of a boat
File:Sidon-coast.jpg, Sidon coast
File:Sidon College site.jpg, Sidon College site
File:Sidon Stadium.jpg, Sidon Stadium
File:Sidon, Lebanon, Panorama.jpg, Sidon, Lebanon, Panorama
File:Mosque, Sidon, Lebanon.jpg, Mosque, Sidon
File:Carpsaida.jpg, Saida Souks
File:صيدا - صورة جوية قديمة.tif, صيدا - صورة جوية قديمة
File:Sidon2009b.JPG, Mosque
File:5,Sidon, vue meridionale.jpg, Sidon, vue meridionale
File:Saida Map.jpg, alt=, Sidon District Map
Sidon On Google Maps Street View By Paul Saad
Sidonianews
(Sidon News Portal)
Lebanon, the Cedars' Land: Sidon
{{Authority control Sidon Mediterranean port cities and towns in Lebanon Populated coastal places in Lebanon Populated places in Sidon District Shia Muslim communities in Lebanon Sunni Muslim communities in Lebanon Archaeological sites in Lebanon 4th-millennium BC establishments Coloniae (Roman) Heavy Neolithic sites Hebrew Bible cities Hellenistic colonies Phoenician cities Phoenician sites in Lebanon Populated places established in the 4th millennium BC Torah cities Former kingdoms Tourist attractions in Lebanon Tourism in Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
. It is located in the South Governorate
South Governorate ( ar, الجنوب; transliterated: al-Janub) is one of the governorates of Lebanon. South Lebanon has a population of 500,000 inhabitants and an area of 929.6 km2. The capital is Sidon. The lowest elevation is sea-level ...
, of which it is the capital, on the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
coast. Tyre to the south and Lebanese capital Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
to the north are both about away. Sidon has a population of about 80,000 within city limits, while its metropolitan area has more than a quarter-million inhabitants.
Name
The Phoenician name ''Ṣīdūn'' (, ) probably meant "fishery" or "fishing town". It is mentioned inPapyrus Anastasi I {{More footnotes, date=March 2017
Papyrus Anastasi I (officially designated papyrus British Museum 10247) is an ancient Egyptian papyrus containing a satirical text used for the training of scribes during the Ramesside Period (i.e. Nineteenth and ...
as Djedouna. It appears in Biblical Hebrew as ''Ṣīḏōn'' ( he, צִידוֹן) and in Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
as ''Ṣidon'' (). This was Hellenised
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the H ...
as ''Sidṓn'' ( grc-gre, Σιδών), which was Latinised as '. The name appears in Classical Arabic as ''Ṣaydūn'' () and in Modern Arabic Modern Arabic may refer to:
*Modern Standard Arabic
*living varieties of Arabic
The varieties (or dialects or vernacular languages) of Arabic, a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family originating in the Arabian Peninsula, are the lingui ...
as ''Ṣaydā'' ().
As a Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Character ...
, it was notionally refounded and given the formal name ' to honour its imperial sponsor.
In the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
, Sidon was the first-born son of Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, who was a son of Ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 39. As a processed meat, the term "ham ...
, thereby making Sidon a great-grandson of Noah.
During the crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
, Sidon was known in Latin as and in French as , Sayette or Sagette.
History
In the years before Christianity, Sidon had many conquerors: Assyrians,Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
, Egyptians, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, and finally Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
visited Sidon. Both Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
and Saint Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
are said to have visited it, too (see '' Biblical Sidon'' below). The city was eventually conquered by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and then by the Ottoman Turks.
Prehistory
Sidon has been inhabited since very early in prehistory. The archaeological site of Sidon II shows a lithic assemblage dating to theAcheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped "hand axes" associated ...
, whilst finds at Sidon III include a Heavy Neolithic
Heavy Neolithic (alternatively, Gigantolithic) is a style of large stone and flint tools (or industry) associated primarily with the Qaraoun culture in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon, dating to the Epipaleolithic or early Pre-Pottery Neolithic at t ...
assemblage suggested to date just prior to the invention of pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
.
Phoenicia in early classical antiquity
 Sidon was one of the most important
Sidon was one of the most important Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n cities, and it may have been the oldest. From there and other ports, a great Mediterranean commercial empire was founded. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
praised the skill of its craftsmen in producing glass, purple dyes, and its women's skill at the art of embroidery. It was also from here that a colonising party went to found the city of Tyre. Tyre also grew into a great city, and in subsequent years there was competition between the two, each claiming to be the metropolis ('Mother City') of Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
.
Glass manufacturing, Sidon's most important enterprise in the Phoenician era, was conducted on a vast scale, and the production of purple dye was almost as important. The small shell of the Murex trunculus
''Hexaplex trunculus'' (previously known as ''Murex trunculus'', ''Phyllonotus trunculus'', or the banded dye-murex) is a medium-sized sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex shells or rock snails. It is included ...
was broken in order to extract the pigment that was so rare it became the mark of royalty.
In AD 1855, the sarcophagus of King Eshmun’azar II was discovered. From a Phoenician inscription on its lid, it appears that he was a "king of the Sidonians," probably in the 5th century BC, and that his mother was a priestess of ‘Ashtart, "the goddess of the Sidonians." In this inscription the gods Eshmun
Eshmun (or Eshmoun, less accurately Esmun or Esmoun; phn, 𐤀𐤔𐤌𐤍 '; akk, 𒅀𒋢𒈬𒉡 ''Yasumunu'') was a Phoenician god of healing and the tutelary god of Sidon.
History
This god was known at least from the Iron Age period at ...
and Ba‘al Sidon 'Lord of Sidon' (who may or may not be the same) are mentioned as chief gods of the Sidonians. ‘Ashtart is entitled ''‘Ashtart-Shem-Ba‘al,'' '‘Ashtart the name of the Lord', a title also found in an Ugaritic
Ugaritic () is an extinct Northwest Semitic language, classified by some as a dialect of the Amorite language and so the only known Amorite dialect preserved in writing. It is known through the Ugaritic texts discovered by French archaeologist ...
text.
Nebuchadnezzar II subjugated the city to be part of the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bei ...
. At the end of the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
era, in 351 BC, Phoenicia was invaded by Artaxerxes III
Ochus ( grc-gre, Ὦχος ), known by his dynastic name Artaxerxes III ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 359/58 to 338 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
.
Persian and Hellenistic periods
Like other Phoenician city-states, Sidon suffered from a succession of conquerors, first by thePersian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Achamenid empire in the 6th century BC, ending with its occupation by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 333 BC, and the start of the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
era of Sidon's history. The Persian influence seems to have been profound, as is observed in the change of the architectural style of the city. Under the successors of Alexander, it enjoyed relative autonomy and organised games and competitions in which the greatest athletes of the region participated. In the Hellenistic-period necropolis of Sidon, important finds such as the Alexander Sarcophagus
The Alexander Sarcophagus is a late 4th century BC Hellenistic stone sarcophagus from the necropolis near Sidon, Lebanon. It is adorned with bas-relief carvings of Alexander the Great and scrolling historical and mythological narratives. The ...
, the Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
n tomb and the Sarcophagus of the Crying Women were discovered, which are now on display at the Archaeological Museum of Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
.
Roman period
 When Sidon fell under Roman domination, it continued to mint its own silver coins. The Romans also built a theater and other major monuments in the city. In the reign of
When Sidon fell under Roman domination, it continued to mint its own silver coins. The Romans also built a theater and other major monuments in the city. In the reign of Elagabalus
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Sextus Varius Avitus Bassianus, 204 – 11/12 March 222), better known by his nickname "Elagabalus" (, ), was Roman emperor from 218 to 222, while he was still a teenager. His short reign was conspicuous for s ...
, a Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Character ...
was established there. During the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
period, when the great earthquake of AD 551 destroyed most of the cities of Phoenice
Phoenice or Phoenike ( el, Φοινίκη) was an ancient Greek city in Epirus and capital of the Chaonians.: "To the north the Chaonians had expelled the Corcyraeans from their holdings on the mainland and built fortifications at Buthrotum, K ...
, Beirut's School of Law took refuge in Sidon. The town continued quietly for the next century, until it was conquered by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
in AD 636.
Crusader-Ayyubid period
 On 4 December 1110, Sidon was captured after the siege of Sidon, a decade after the
On 4 December 1110, Sidon was captured after the siege of Sidon, a decade after the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic r ...
, by King Baldwin I of Jerusalem
Baldwin I, also known as Baldwin of Boulogne (1060s – 2April 1118), was the first count of Edessa from 1098 to 1100, and king of Jerusalem from 1100 to his death in 1118. He was the youngest son of Eustace II, Count of Boulogne, and Ida of Lor ...
and King Sigurd I of Norway
Sigurd Magnusson (1089 – 26 March 1130), also known as Sigurd the Crusader (Old Norse: ''Sigurðr Jórsalafari'', Norwegian: ''Sigurd Jorsalfar''), was King of Norway (being Sigurd I) from 1103 to 1130. His rule, together with his half-brothe ...
. It then became the center of the Lordship of Sidon, an important vassal-state of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
. Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
captured it from the Crusaders in 1187, but German Crusaders restored it to Christian control in the Crusade of 1197
The Crusade of 1197, also known as the Crusade of Henry VI (german: Kreuzzug Heinrichs VI.) or the German Crusade (''Deutscher Kreuzzug''), was a crusade launched by the Hohenstaufen emperor Henry VI in response to the aborted attempt of his fa ...
. It would remain an important Crusader stronghold until it was finally destroyed by the Ayyubids
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin ...
in 1249. In 1260, it was again destroyed by the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
led by Kitbuqa
Kitbuqa Noyan (died 1260), also spelled Kitbogha, Kitboga, or Ketbugha, was an Eastern Christian of the Naimans, a group that was subservient to the Mongol Empire. He was a lieutenant and confidant of the Mongol Ilkhan Hulagu, assisting him ...
. The remains of the original walls are still visible.
Ottoman period
After Sidon came under Ottoman Turkish rule in the early 16th century, it became the capital of theSidon Eyalet
ota, ایالت صیدا
, common_name = Eyalet of Sidon
, subdivision = Eyalet
, nation = the Ottoman Empire
, year_start = 1660
, year_end = 1864
, date_start =
, date_end =
, ev ...
(province) and regained a great deal of its earlier commercial importance. Starting in the 18th century the city was dominated by the Hammud family of notables, who monopolized the production and exporting of cotton in the region and built numerous palaces and public works in the city. The Hammuds also served as government customs agents and tax collectors for various Ottoman religious foundations.
During the Egyptian–Ottoman War, Sidon – like much of Ottoman Syria – was occupied by the forces of Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali Pasha al-Mas'ud ibn Agha, also known as Muhammad Ali of Egypt and the Sudan ( sq, Mehmet Ali Pasha, ar, محمد علي باشا, ; ota, محمد علی پاشا المسعود بن آغا; ; 4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849), was ...
. His ambitions were opposed by the British Empire, which backed the Ottomans. The British Admiral Charles Napier, commanding a mixed squadron of British, Turkish and Austrian ships, bombarded Sidon on 26 September 1840, and landed with the storming column. Sidon capitulated in two days, and the British went on to Acre. This action was recalled in two Royal Navy vessels being named .
From 1887 the Royal necropolis of Sido was extensively excavated by the Ottomans, and its treasured trasferred to Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
(like the Alexander sarcophagus
The Alexander Sarcophagus is a late 4th century BC Hellenistic stone sarcophagus from the necropolis near Sidon, Lebanon. It is adorned with bas-relief carvings of Alexander the Great and scrolling historical and mythological narratives. The ...
).
After World War I
 After
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
it became part of the French Mandate of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
the city, together with the rest of Lebanon, was captured by British forces fighting against the Vichy French
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its terr ...
, and following the war it became a major city of independent Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
.
Following the Palestinian exodus in 1948, a considerable number of Palestinian
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
refugees arrived in Sidon, as in other Lebanese cities, and were settled at the large refugee camps of Ein el-Hilweh and Mieh Mieh. At first these consisted of enormous rows of tents, but gradually houses were constructed. The refugee camps constituted de facto neighborhoods of Sidon, but had a separate legal and political status which made them into a kind of enclaves. At the same time, the remaining Jews of the city fled, and the Jewish cemetery fell into disrepair, threatened by coastal erosion.
On Easter Sunday
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the ''Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel P ...
, 19 April 1981, at least sixteen people were killed in Sidon after the (South Lebanon Army
The South Lebanon Army or South Lebanese Army (SLA; ar, جيش لبنان الجنوبي, Jayš Lubnān al-Janūbiyy), also known as the Lahad Army ( ar, جيش لحد, label=none) and referred to as the De Facto Forces (DFF) by the United Nat ...
) SLA’s long-range artillery indiscriminately shelled the city centre. It was reported that it was in response to a request from Bashir Gemayel
Bachir Pierre Gemayel ( ; 10 November 1947 – 14 September 1982) was a Lebanese militia commander who led the Lebanese Forces, the military wing of the Kataeb Party in the Lebanese Civil War and was elected President of Lebanon in 1982.
...
in connection with ongoing Syrian attacks on Phalangist positions around Zahle. Israel denied involvement.
After the 1982 Israeli invasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity aggressively enter territory (country subdivision), territory owned by another such entity, gen ...
of Lebanon Sidon was occupied by the Israeli army for almost two and a half years.
On 18 August 1997, following a roadside bomb near Jezzine which killed of two teenage members of a SLA leader’s family, SLA artillery shelled Sidon killing seven civilians and wounding thirty-five. Hizbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's paramili ...
responded the following day by firing 60–80 rockets into the security zone and northern Israel. According to UNIFIL observers the missiles appeared to be targeted at uninhabited areas. The attack on Sidon is credited with leading to a truce between Hizbollah and Amal Amal may refer to:
* Amal (given name)
* Åmål, a small town in Sweden
* Amal Movement, a Lebanese political party
** Amal Militia, Amal Movement's defunct militia
* Amal language of Papua New Guinea
* Amal (film), ''Amal'' (film), 2007, directed ...
and increased cooperation between the two groups and the Lebanese Army. This was evident in the Ansariya ambush the following month.
Sidon was a small fishing town of 10,000 inhabitants in 1900, but studies in 2000 showed a population of 65,000 in the city, and around 200,000 in the metropolitan area. The little level land around the city is used for cultivation of some wheat, vegetables, and fruits, especially citrus and bananas. The fishing in the city remains active with a newly opened fishery that sells fresh fish by bidding every morning. The ancient basin was transformed into a fishing port, while a small quay was constructed to receive small commercial vessels. (Refer to the ''"Old City"'' and the ''"Architecture and landscape"'' sections below.)
Saida Municipal Stadium
The Saida Municipal Stadium (), also known as the Martyr Rafic Hariri Stadium ( ar, ملعب الرئيس الشهيد رفيق الحريري, links=no), is a 22,600 capacity multi-purpose stadium in Sidon, Lebanon.
The stadium was built in 1 ...
was inaugurated in 2000 for the Asian Football Confederation's Cup 2000.
Politics
 This sectarian and demographic division rose to the surface during the
This sectarian and demographic division rose to the surface during the Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ar, الحرب الأهلية اللبنانية, translit=Al-Ḥarb al-Ahliyyah al-Libnāniyyah) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities a ...
, when armed clashes erupted between Sunni Muslims and Christians. The clashes ended with the surrender of the Christian front, and the Christians were forced to move to east Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
. After the war ended in 1990, the Christians have gradually returned to their hometowns and in the year 2000 many fled to Israel.
The local politics of Sidon in the 20th century was mainly dominated up till the 1980s by allegiances around two main families, the El-Bizri
El-Bizri (البزري—البزرة) is an Arabic name. Historically, its members settled in Sidon, Lebanon with a large branch also growing in Damascus, Syria, and a much smaller presence in Acre, Israel, Acre ('Akka) mainly in pre-1948 Palestin ...
and Saad. The El-Bizri politicians were known for their business connections, close ties with eminent Lebanese and Levantine leaders, and their bent on serving the Lebanese state as government ministers, officials and mayors. The Saad politicians tended to be populist and became engaged in violent protests in the 1940s, 1950s and then during the Lebanese civil war as Nasserites (populist followers of Nasser in Lebanon).
The local political conflict between these two families was always resolved through amicable means and ties of kinship. Their hold over the political aspects of the city was similar to that of Mediterranean families in Sicily or to being also influenced by the ties of Arab families, clans, and tribes in traditionalist forms. The most notable figures of the El-Bizri family in the first half of the 20th century were: Ahmad El-Bizri (born 1899), Salah El-Bizri, Eizeddine El-Bizri (commonly known as Eizzo) and Anwar El-Bizri (born 1910). These four brothers were businessmen and politicians who dominated the political life of the city up till the late 1940s, using traditional inherited forms of governance since Ottoman times. With intelligence and strength they maintained their power for over 50 years. It is from their ranks that Maarouf Saad started his public life, and their close cousins, Nazih El-Bizri, Amin El-Bizri, and Fouad El-Bizri became the next generation of politicians and statesmen in Lebanon; holding positions as ministers and members of parliament.
The El-Bizri and the Saad political practices were bent on social justice and on local service in public affairs. The El-Bizri were since the Ottoman rule bent on serving the state, and this continued with their loyalty and support to the successive governments of Lebanon since the times of independence. They also helped eminent politicians and statesmen from Sidonian descent such as the Prime Ministers Riad Solh
Riad Reda Al Solh ( ar, رياض الصلح; 17 August 1894 – 17 July 1951) was the first prime minister of Lebanon after the country's independence.
, Takieddine el-Solh and Rashid Solh, they also gave their support to former Prime Minister Saeb Salam
Saeb Salam (17 January 1905 – 21 January 2000) ( ar, صائب سلام) was a Lebanese politician, who served as Prime Minister six times between 1952 and 1973. Following his death, the Lebanese daily ''As-Safir'' described Salam as "most ...
, father of Tamam Salam, Prime Minister 2014–2016. The presence of the El-Bizris was at times intimidating on the local scene, but they were also known for their goodwill and dignified public service.
The Saad family developed their links with Nasserism in the 1950s and engaged in the uprising and armed protest of 1958 against the government of the Lebanese President Chamoun. They also became involved in the civil war as part of the left wing politics of the Lebanon (Al-Haraka al-Wataniyya) with PLO connections, and they actively contributed to resisting the Israeli occupation after 1982. The Saads remained populist in their politics and focused on the grassroots, while the El-Bizri were generally appealing to the middle and upper classes. In the middle 1980s, the Hariri family started to rise to prominence and it became the most influential in Sidon in political and financial terms, even though the presence of the Saad and the El-Bizri in local politics remained significant at the level of visibility and activism.
The politics of Sidon is similar to that of the traditional old cities of the Levant in the sense of being family-based. In broad terms one could say that the El-Bizri family had an influence since Ottoman times, and most significantly during the entirety of the 20th century. It was local in impact at first, but then the members of this family became influential within the Lebanese state and institutions, and they supported the Solh family that had successive Prime Ministers and that moved its power base from Sidon to Beirut. The Saad family developed its original politics from within the sphere of influence of the El-Bizri family and then became a power to reckon with on its own after 1948, and most powerfully in 1958, then in the civil war and up till today.
Maarouf Saad, the leader of his family, and a local influential politician, was assassinated at the eve of the Lebanese civil war in 1975. The Saads retained their populism and grassroots appeal, and attracted a core of loyal adherents since the middle of the 20th century. While the El-Bizri were Levantine in their Arabism (namely focused mainly on Bilad al-Shaam in regional politics), and the Solh being also similar to them in this, the Saad were leaning more towards a broader pan-Arabism (Nasserite, Libyan, and then Syrian). As for the Hariri family, they are regionally focused on Saudi orientations in politics. The Hariri family started to rise to political and economic prominence in the 1980s and became perhaps the most influential family in Lebanon by the middle 1990s. It is now one of the most organised in political terms and it follows modern forms of political practice through a large party (Future Movement) that cuts across various economic classes but that is usually seen as a Sunni political movement with regional weight due to its close ties with Saudi Arabia.
Impact on Sidon of regional underdevelopment
According to a recent United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) report "data also point to an increase in urban poverty especially in Lebanon's largest cities suburbs such as Beirut, Tripoli and Saida, as illustrated by poverty-driven symptoms (child labour, over-crowding and deteriorated environment conditions)." In another UNDP report, the author discusses the development predominance of Beirut over the rest of the regions of Lebanon (North, South and Beqaa) is a well-known imbalance that can be dated to the early 19th century. With the expansion of Beirut in the 1870s, urban growth in the future capital outpaced Tripoli and Saida. Transportation routes, missionary schools, universities and hospitals as well as the Beirut port development and the commerce of silk participated to the fortification of Beirut as a major trade center for Mediterranean exchange (ARNAUD 1993; LABAKI 1999: 23). However, the establishment of Great Lebanon in 1920, under the French mandate, added the poorer areas of the North (Akkar), Beqaa (Baalbak-Hermel) and the South (Jabal Aamel) to the relatively affluent cities of Mount Lebanon. This addition made of Lebanon a country composed of unequally developed regions. This legacy remains a heavy load to bear socially, culturally, economically and politically. Even though the public policies elaborated by the young Lebanese State were attempting to have regional perspectives, the early urban planning schemes reveal a development approach exclusively axed on Beirut and its suburbs. The post war development policy of the State, promoted by Hariri government (1992–1998), was centered around balanced development and is widely inspired by the 1943 Pact and the 1989 Taef agreement (LABAKI1993: 104). However the application of this policy aims mainly at the rehabilitation and construction of roads and infrastructures (electricity, telephone, sewage). Another of its components is the rehabilitation of government buildings (airport, port, schools, universities and hospitals). Transportation projects (mainly concentrated on the coastal line) constitute 25% of the budget of 10-year economic plan developed by the CDR (BAALBAKI 1994: 90). However, all these projects are predominantly concentrated around Beirut, ignoring the regions.The Former ''Makab'' (waste dump) and the Treatment Plant
Near the southern entrance to the city used to be a 'rubbish mountain' called at the time by the locals the ''Makab''; namely, a 600,000 cubic metre heap that reached the height of a four-story building. It was originally created to dispose of the remains of buildings destroyed in Israeli air strikes during the 1982 invasion, but it then became the main dump for the city. Growing out of the sea, it became an environmental hazard, with medical waste and plastic bags polluting nearby fishing grounds. Sidon politicians, including the Hariri family, failed for decades to resolve the ''Makab'' crisis—which has endangered residents health (especially during episodic burning). In 2004, Engineer Hamzi Moghrabi, a Sidon native, conceived the idea to establish a treatment plant for the city's decades-old chronic waste problem. He established the privately funded IBC Enviro and the treatment plant became operational in 2013. The Ministry of Environment came up with a $50,000+ plan to clean the whole area and transform the dump into a green space, along with other heaps in the country. Qamla beach in Sidon, a coast in close proximity to the Sea Castle, witnessed a large municipal cleanup in May 2011, as it was an easy target of rubbish being washed up by the Makab. These plans aim to revive the former glory of the city's coasts and attract tourists who avoided swimming in Sidon's sea before. The project of cleaning the region where the waste dump has already started, and currently a waves-barrier is being built, and the vast bulk of the waste dump being cleared.Local government
The city of Sidon is administrated by the Municipality of Sidon. The municipality is constituted of a council of 21 members including the City Mayor and his Deputy. It has administrative and financial independence but remains under the control and supervision of the central government, specifically the Ministry of Interior. The municipality's jurisdiction is limited to a region of 786 hectares in area and 5 meters in elevation, while each of the city's suburbs is administrated by its own independent municipal council. Sidon is the center of the Governorate of South Lebanon, and hosts the seat of the Governor of Southern Lebanon. The city is also the center of the Sidon District and the Union of Sidon and Zahrani Municipalities (founded in 1978 and contains 15 municipalities). Sidon hosts the southern regional headquarters of a series of governmental facilities like the Central Bank of Lebanon, Électricité du Liban, Central Telecommunications Station and others. It is also the home of the Justice Palace of South Lebanon in its new headquarters on East Boulevard (the old headquarters were an old Ottoman Saray that is currently occupied by the LSF and is planned to be transformed into a cultural center by the municipality). In the 2000 and 2005 parliamentary elections, the Sidon District along with the Tyre andBint Jbeil
Bint Jbeil () is the second largest town in the Nabatiye Governorate in Southern Lebanon.
The town has an estimated population of 30,000. Its exact population is unknown, because Lebanon has not conducted a population census since 1932.
Hist ...
districts formed the first electoral district of South Lebanon. However, in the 2009 elections – and due to the reactivation of the 1960 electoral law – the city of Sidon was separated from its district to form a separate electoral district.
Demographics
The overwhelming majority of Sidon's population belong to the Sunni sect of Islam, with few Shiites and Christians. Sidon is the seat of the Greek Melkite Catholic Archbishop of Sidon and Deir el Qamar, and has housed a significant Catholic population throughout its history. Sidon also hosts the seat of theShiite
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
Ayatollah
Ayatollah ( ; fa, آیتالله, āyatollāh) is an honorific title for high-ranking Twelver Shia clergy in Iran and Iraq that came into widespread usage in the 20th century.
Etymology
The title is originally derived from Arabic word p ...
of South Lebanon.
In the 1930s, when Lebanon was still under the French mandate, Sidon had the largest Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
population in Lebanon, estimated at 3,588, compared to 3,060 in Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
.
Main sights

 * Sidon Sea Castle, a fortress built by the
* Sidon Sea Castle, a fortress built by the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
in the early 13th century. It is located near the Port of Sidon.
* Sidon Soap Museum. It traces the history of the soap making in the region and its different manufacturing steps.
* Khan al-Franj (" Caravanserai of the French"), a complex built in the 16th century, though erroneously credited to Emir Fakhreddine in the 17th century. It gained its name for accommodating French merchants and goods in order to develop trade with Europe. This is a typical khan with a large rectangular courtyard and a central fountain surrounded by covered galleries.
* Debbane Palace
Debbane Palace, also Qasr Debbane, Dar Ali Agha al-Hammud, and Dar Debbané, is an Arab-Ottoman-style grand mansion in Sidon, Lebanon. The palace was built as a private residence in 1721 by Ali Agha al-Hammud, a Sidonian notable descending from ...
, a historical residence built in 1721, an example of Arab-Ottoman architecture. It is currently in the process of being transformed into the History Museum of Sidon. This villa was earlier occupied by the Hammoud family in the 18th century and also by members of the famous Ottoman aristocrats of the Abaza clan in the late 19th century and early 20th century. The vaults at the ground level being originally stables for the villa residents and then turned into shops as part of the old souks, and known until recent time by association to the Abazas.
* The Castle of St. Louis (''Qalaat Al Muizz''). It was built by the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
in the 13th century on top of the remains of a fortress built by the Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
caliph Al Muizz. It is located to the south of the Old Souks near Murex Hill.
* Eshmun Temple
The Temple of Eshmun ( ar, معبد أشمون) is an ancient place of worship dedicated to Eshmun, the Phoenician god of healing. It is located near the Awali river, northeast of Sidon in southwestern Lebanon. The site was occupied from the ...
, dedicated to the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n God of healing. Built in the 7th century BC, it is located in the north of Sidon near the Awali river.
* The British War Cemetery in Sidon. Opened in 1943 by units of His Majesty's (King George VI) British Forces occupying the Lebanon after the 1941 campaign against the Vichy French troops. It was originally used for the burial of men who died while serving with the occupation force, but subsequently the graves of a number of the casualties of the 1941 campaign were moved into the cemetery from other burial grounds or from isolated positions in the vicinity. The cemetery now contains 176 Commonwealth burials of the Second World War and nine war graves of other nationalities. It was designed by G. Vey. It is perhaps that only garden in modern Sidon that is elegantly kept and cared for. It is not a public garden but can be visited when the wardens have its gateways opened
*Khan Sacy in Sidon: Khan Sacy has undergone a series of modifications and tells part of the city's past. In its heart, it hides a much older story. It is composed of rooms of a majestic height with three water wells, three hammams and an oven.
Education
Sidon is home to numerous educational facilities ranging from public elementary schools to private universities. According to a 2006 study, the city is home to 29 schools that serve a total of 18,731 students: 37% are in public schools, 63% are in private schools. Sidon also contains 10 universities, 5 of which are private universities.Archaeology
The following archaeological sites in the area indicate settlements from the earliest prehistorical times. Sidon I is an archaeological site located to the east of the city, south of the road to Jezzine. An assemblage offlint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
tools was found by P. E. Gigues suggested to date between 3800 and 3200 BC. The collection included narrow axe
An axe ( sometimes ax in American English; see spelling differences) is an implement that has been used for millennia to shape, split and cut wood, to harvest timber, as a weapon, and as a ceremonial or heraldic symbol. The axe has ma ...
s or chisels that were polished on one side and flaked on the other, similar to ones found at Ain Cheikh, Nahr Zahrani and Gelal en Namous. The collection appears to have gone missing from the Archaeological Museum of the American University of Beirut
The Archaeology Museum of the American University of Beirut in Beirut, Lebanon is the third oldest museum in the Near East after Cairo and Constantinople.
History
The Archaeological Museum of the American University of Beirut (AUB Archaeological M ...
.
Sidon II is said to be "near the church" at approximately fifty meters above sea level. P. E. Gigues suggested that the industry found on the surface of this site dated to the Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped "hand axes" associated ...
.
Sidon III was found by E. Passemard in the 1920s, who made a collection of material that is now in the National Museum of Beirut
The National Museum of Beirut ( ar, متحف بيروت الوطنيّ, ''Matḥaf Bayrūt al-waṭanī'' or French: Musée national de Beyrouth) is the principal museum of archaeology in Lebanon. The collection begun after World War I, and the m ...
marked "Camp de l'Aviation". It includes large flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
and chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a ...
bifacials that may be of Heavy Neolithic
Heavy Neolithic (alternatively, Gigantolithic) is a style of large stone and flint tools (or industry) associated primarily with the Qaraoun culture in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon, dating to the Epipaleolithic or early Pre-Pottery Neolithic at t ...
origin.
Sidon IV is the tell mound of ancient Sidon with Early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
(c. 3200 BC) deposits, now located underneath the ruined Saint Louis Castle and what are also thought to be the ruins of a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
theater.
Bronze Age Sidon
In the area of this ruined Crusader castle, recent excavations uncovered a late Early Bronze Age I (EB I) settlement on bedrock. Here, an uninterrupted sequence from EB I to EB III was found. A modest third-millennium BC settlement consisting of domestic installations and tombs was also uncovered. Yet the following history of Sidon was not clarified. Very little has been known about the location, extent, and significance of Middle Bronze Age (MBA) Sidon until recently. Since the early 21st century, Tell el-Burak excavations have helped significantly in this area, because it was an active settlement during MBA, and quite well preserved. Tell el-Burak is located along the coast 9 km south from Sidon. Previously, there was a big gap in the history of this whole coastal area from the end of theEarly Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
until the middle of the 2nd millennium BC, when Sidon is first mentioned in the historical texts.Hélène Sader, Jens Kamlah (2010)"Tell el-Burak: A New Middle Bronze Age Site from Lebanon"
''Near Eastern Archaeology'', Vol. 73, No. 2/3 (2010), pp. 130–141. University of Chicago Press Archaeologists determined that Sidon was clearly the big power centre during MBA, controlling significant territory. So there appears to have been the "Kingdom of Sidon" that controlled el-Burak, and many other surrounding areas.
Excavation history
The area around Sidon contains a number of important necropoli (below in order of age, and noting their principal excavators): * Dakerman (Roger Saidah, 1968–1969) * Tambourit (Saidah, 1977) * Magharet Abloun (Aimé Péretié, 1855; Ernest Renan, 1864;Georges Contenau
Georges Contenau (April 9, 1877 – March 22, 1964) was a French archeologist, curator, orientalist and religious historian who was an expert in the field of culture and religion of the ancient civilizations of the Near and Middle East.
Life
Con ...
, 1920)
* Ayaa (William King Eddy, 1887; Osman Hamdi Bey
Osman Hamdi Bey (30 December 1842, in Istanbul 24 February 1910) was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administrator, intellectual, art expert and also a prominent and pioneering painter. He was also an accomplished archaeologist, and is regarded as th ...
, 1892; Contenau, 1920)
* Ain al-Hilweh
Ain al-Hilweh ( ar, عين الحلوة, lit. meaning "sweet natural spring"), also spelled as Ayn al-Hilweh and Ein al-Hilweh, is the largest Palestinian refugee camp in Lebanon. It had a population of over 70,000 Palestinian refugees but swell ...
( Charles Cutler Torrey, 1919–1920)
* El-Merah (Contenau, 1920)
* Qrayé (Contenau, 1920)
* Almoun, (Conenau, 1924)
* El-Harah ( Theodore Makridi, 1904; Contenau, 1924)
* Magharet Abloun, Greco-Roman part (Renan, 1864; Contenau, 1914–1924)
* Helalié/Baramié/Mar Elias (William John Bankes
William John Bankes (11 December 1786 – 15 April 1855) was an English politician, explorer, Egyptologist and adventurer.
The second, but first surviving, son of Henry Bankes MP, he was a member of the Bankes family of Dorset and he had Sir Ch ...
, 1816; Renan 1864; Contenau, 1914; M. Meurdrac & L. Albanèse, 1938–1939)
In indication of the high-profile of the old city of Sidon in archaeological expeditions, and mainly in the 19th century, in October 1860 the famous French scholar Ernest Renan was entrusted with an archaeological mission to Lebanon, which included the search for the antique parts of Sidon. The Phoenician inscriptions that he discovered, and his field data, were eventually published in his notebook the: ''Mission de Phénicie'' (1864–1874; ''Phoenician Expedition'').
The St. Louis land-castle grounds were excavated in 1914–1920 by a French team. Then eastwards a new site was also excavated by another generation of French expeditions in the 1960s. This same site received renewed attention in 1998 when the Directorate General of Antiquities in Lebanon authorized the British Museum to begin excavations on this area of land that was specifically demarcated for archaeological research. This has resulted in published papers, with a special focus on studying ceramics.
The archaeological fieldwork was not fully undertaken since the independence of the Lebanon. The main finds are displayed in the National Museum in Beirut. The fieldwork was also interrupted during the long civil war period, and it is now resumed but at a timid and slow scale, and not involving major international expeditions or expertise. Perhaps this is also indicative of the general lack in cultural interests among the authorities of this city, and almost of the non-existence of notable intellectual activities in its modern life. There are signs that the locals are beginning to recognize the value of the medieval quarters, but this remains linked to minor individual initiatives and not a coordinated collective effort to rehabilitate it like it has been the case with Byblos
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8 ...
, even though the old district of Sidon contains a great wealth in old and ancient architecture.
Biblical Sidon

Hebrew Bible/Old Testament
TheHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Canaan Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, the grandson of Noah (, ).
* The '' Canaan Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
Tribe of Zebulun
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Zebulun (alternatively rendered as ''Zabulon, Zabulin, Zabulun, Zebulon''; ) was one of the twelve tribes of Israel.
Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes in the Bo ...
has a frontier on Sidon ()
* It was the first home of the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns on the coast of Canaan, and from its extensive commercial relations became a "great" city (, ).
* It was the mother city of Tyre. It lay within the lot of the tribe of Asher, but was never subdued ().
* The Sidonians long oppressed Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
().
* From the time of David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
its glory began to wane, and Tyre, its "virgin daughter" (), rose to its place of pre-eminence.
* Solomon entered into a matrimonial alliance with the Sidonians, and thus their form of idolatrous worship found a place in the land of Israel (, ).
* Jezebel
Jezebel (;"Jezebel"
(US) and ) was the daughte ...
was a Sidonian princess ().
* It was famous for its manufactures and arts, as well as for its commerce (; ; ).
* It is frequently referred to by the prophets (, , ; , , ; , , , ; ).
* (US) and ) was the daughte ...
Elijah
Elijah ( ; he, אֵלִיָּהוּ, ʾĒlīyyāhū, meaning "My El (deity), God is Yahweh/YHWH"; Greek form: Elias, ''Elías''; syr, ܐܸܠܝܼܵܐ, ''Elyāe''; Arabic language, Arabic: إلياس or إليا, ''Ilyās'' or ''Ilyā''. ) w ...
sojourned in Sidon, performing miracles (; see also in the New Testament, ).
New Testament
* Jesus visited the region or "coasts" (King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an Bible translations into English, English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and publis ...
) of Tyre and Sidon (; ) and from this region many came forth to hear him preaching (; ), leading to the stark contrast in to Korazin
Chorazin ( gr, Χοραζίν ; also Chorazain) or Korazim ( he, כורזים; also Chorizim) was an ancient village in the Roman and Byzantine periods, best known from the Christian Gospels. It stood on the Korazim Plateau in the Upper Galilee on ...
and Bethsaida. See the exorcism of the Syrophoenician woman's daughter
The Exorcism of the Syrophoenician woman's daughter is one of the miracles of Jesus in the Gospels and is recounted in the Gospel of Mark in Chapter 7 () and in the Gospel of Matthew in Chapter 15 (). In Matthew, the story is recounted as the h ...
, which takes place on the coast, in the region of Sidon and Tyre.
* From Sidon, at which his ship put in after leaving Caesarea, Paul
Paul may refer to:
*Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
* Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chri ...
finally sailed for Rome (, ).
* Then he returned from the region of Tyre, and went by way of Sidon towards the Sea of Galilee, in the region of the Decapolis ()
Sanchuniathon
* The account ascribed to the Phoenician historian Sanchuniathon makes Sidon a daughter of Pontus, son ofNereus
In Greek mythology, Nereus ( ; ) was the eldest son of Pontus (the Sea) and Gaia ( the Earth), with Pontus himself being a son of Gaia. Nereus and Doris became the parents of 50 daughters (the Nereids) and a son ( Nerites), with whom Nereus ...
. She is said there to have first invented musical song from the sweetness of her voice.
Gallery
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Sidon is twinned with: * Constanța, Romania *Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
, Bulgaria
* Sochi, Russia
Notable people
In antiquity and the pre-modern era
Chronological list. *Eumaeus
In Greek mythology, Eumaeus (; Ancient Greek: Εὔμαιος ''Eumaios'' means 'searching well') was Odysseus' swineherd and friend. His father, Ktesios son of Ormenos was king of an island called Syra (present-day Syros in the Greek islands ...
, character from Greek mythology. In Homer, Eumaeus tells of having been kidnapped as child from Sidon, where his father was the king.
* Antipater of Sidon
Antipater of Sidon (Greek: Ἀντίπατρος ὁ Σιδώνιος, ''Antipatros ho Sidonios'') was an ancient Greek poet of the second half of the 2nd century BC.
Cicero mentions him living at Rome in the time of Crassus and Quintus Lutatius ...
(2nd century BC), poet
* Zeno of Sidon
Zeno of Sidon ( grc-gre, Ζήνων ὁ Σιδώνιος; c. 150 – c. 75 BC) was a Greek Epicurean philosopher from the Seleucid city of Sidon. His writings have not survived, but there are some epitomes of his lectures preserved among the wr ...
(c. 150 – c. 75 BC), Epicurean philosopher born in Sidon
* Dorotheus of Sidon
Dorotheus of Sidon ( grc-gre, Δωρόθεος Σιδώνιος, c. 75 CE - ?? CE) was a 1st-century Greek astrologer and astrological poet, who, during the Hellenistic Period, wrote a didactic poem on horoscopic astrology in Greek, known as the ...
(1st century BC) Greek astrologer associated with Sidon
* Boethus of Sidon
Boethus of Sidon ( grc-gre, Βόηθος, Bóēthos; – ) was a Peripatetic philosopher from Sidon, who lived towards the end of the 1st century BC. None of his work has been preserved and the complete collection of quotings and paraphrases appe ...
(c. 75 – c. 10 BC), peripatetic philosopher
* Tiberius Julius Abdes Pantera
Tiberius Julius Abdes Pantera (; c. 22 BC – AD 40) was a Roman- Phoenician soldier born in Sidon, whose tombstone was found in Bingerbrück, Germany, in 1859. A historical connection from this soldier to Jesus has long been hypothesized by nume ...
, Roman soldier who, according to his grave found in Germany in the 19th century, was born in Sidon
* Zenobius and his sister Zenobia, early-Christian martyrs executed around AD 290 under Diocletian
* Gymnasius (Γυμνάσιος), a sophist in the time of the Emperor Constantine
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterrane ...
* Euthymios Saifi
Euthymios Michael Saifi (or ''Aftimios Sayfi'', 1643–1723) was the Melkite Catholic bishop of Tyre and Sidon during the early 18th century. A leading proponent of re-establishing communion between the Orthodox Church of Antioch and the Ca ...
(1643–1723), Melkite Catholic Bishop of Sidon and Tyre
In the modern era
* Adel Osseiran, co-founder of modern Lebanon, was a prominent Lebanese statesman, a former Speaker of the Lebanese Parliament, and one of the founding fathers of the Lebanese Republic. * Raymond Audi, international banker, and former Minister of Refugees in the government of Lebanon (Originally Palestinian) * Ali Osseiran, Member of Parliament and Former Minister *Afif al-Bizri
Afif al-Bizri ( ar, عفيف البزري) (1914 – 28 January 1994) was a Syrian career military officer who served as the chief of staff of the Syrian Army between 1957–1959. He was known for his communist sympathies, and for spearheading the ...
, (Afif El-Bizri
El-Bizri (البزري—البزرة) is an Arabic name. Historically, its members settled in Sidon, Lebanon with a large branch also growing in Damascus, Syria, and a much smaller presence in Acre, Israel, Acre ('Akka) mainly in pre-1948 Palestin ...
) former Chief of Staff of the Syrian armed forces with a high-standing military rank and political profile during the Syria-Egypt republican union of the Nasser era.
* Mousbah Baalbaki, contemporary male belly dancer
*The Four Brothers - Riad El Bizri's Sons:
**Ahmad El-Bizri, Salah-Eddine El-Bizri (Mayor of Sidon from 1937 till 1951. Member of Parliament from 1951 till 1953), Ezzedine El-Bizri, Anwar El-Bizri.
* Hisham El-Bizri, filmmaker, producer, professor
* Nader El-Bizri
Nader El-Bizri ( ar, نادر البزري, ''nādir al-bizrĩ'') is the Dean of the College of Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences at the University of Sharjah. He served before as a tenured longstanding full Professor of philosophy and ci ...
, philosopher, architect
* Nazih El Bizri, longstanding politician: mayor of Sidon from 1952 till 1959, Member of Lebanese Parliament from 1953 till 1958 and from 1972 till 1992. Lebanese Minister of Health, and Minister of Social Affairs from 1955 till 1956, then from 1972 till 1973, and from 1980 till 1982.
* Rafic Hariri
Rafic Bahaa El Deen Al Hariri ( ar, رفيق بهاء الدين الحريري; 1 November 1944 – 14 February 2005) was a Lebanese business tycoon and politician who served as the Prime Minister of Lebanon from 1992 to 1998 and again from ...
, former Prime Minister, billionaire and international businessman
* Bahia Hariri, former Minister of Education in the governments of Lebanon and philanthropist
* Saad Hariri
Saad El-Din Rafik Al-Hariri ( ar, سعد الدين رفيق الحريري, translit=Saʿd ad-Dīn Rafīq al-Ḥarīrī; born 18 April 1970) is a Lebanese-Saudi politician who served as the prime minister of Lebanon from 2009 to 2011 and 2016 ...
, youngest former Prime Minister of Lebanon
* Bahaa Hariri
Bahaa El-Dine Rafic Al-Hariri ( ar, بهاء الدين رفيق الحريري; born 26 April 1966) is a Lebanese-Saudi billionaire business man. He is the eldest son of assassinated former Lebanese Prime Minister Rafic Hariri from his father ...
, international businessman and billionaire, son of Rafic Hariri
* Ahmad Hijazi (born 1994), Lebanese footballer
* Sheikh Mohamad Osseiran, Jaafari Mufti of Sidon
* Maarouf Saad, former deputy representing Sidon in the national parliament and founder of the Popular Nasserite Party
* Fouad Siniora, former Prime Minister of Lebanon, minister of finance, and member of parliament
* Riad Solh
Riad Reda Al Solh ( ar, رياض الصلح; 17 August 1894 – 17 July 1951) was the first prime minister of Lebanon after the country's independence.
, former Prime Minister of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
* Sami Solh, former Prime Minister of Lebanon
* Fayza Ahmed (Al-Rawwass), Arab singer formerly based in Egypt
* Paul Watkins (born 1950), former Manson family member lived in Sidon during his childhood (d.1990)
* Hussein Zein (born 1995), Lebanese footballer
See also
*Sidon Eyalet
ota, ایالت صیدا
, common_name = Eyalet of Sidon
, subdivision = Eyalet
, nation = the Ottoman Empire
, year_start = 1660
, year_end = 1864
, date_start =
, date_end =
, ev ...
(Ottoman era)
* Kfar Beit
* Kitbuqa
Kitbuqa Noyan (died 1260), also spelled Kitbogha, Kitboga, or Ketbugha, was an Eastern Christian of the Naimans, a group that was subservient to the Mongol Empire. He was a lieutenant and confidant of the Mongol Ilkhan Hulagu, assisting him ...
* Zimredda (Sidon mayor)
Zimredda, also Zimr-Edda or Zimr-Eddi ( ''Amorite'': ) was the mayor of Sidon, (i.e. the " King of Sidon") in the mid 14th century BC. He is mentioned in several of the Amarna letters, in the late Rib-Hadda series, and later. He authored letters E ...
* Amarna letter EA 144
* Tabnit sarcophagus
The Tabnit sarcophagus is the sarcophagus of the Phoenician King of Sidon Tabnit I (ruled c. 549–539 BC), the father of King Eshmunazar II. The sarcophagus is decorated with two separate and unrelated inscriptions – one in Egyptian hierogly ...
* Eshmunazar II sarcophagus
The Eshmunazar II sarcophagus is a 6th-century BC sarcophagus unearthed in 1855 in the "Phoenician Necropolis", a hypogeum (underground tomb) complex in the southern area of the city of Sidon in modern-day Lebanon. The sarcophagus was discov ...
* Abdashtart I
* Evagoras II
* Abdalonymus
References
Sources
* * Additional notes taken from ''Collier's Encyclopedia'' (1967 edition) * *Further reading
*Aubet, Maria Eugenia. ''The Phoenicians and the West: Politics, Colonies and Trade''. 2d ed. Translated by Mary Turton. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2001. *Markoe, Glenn. ''Phoenicians''. Vol. 2, ''Peoples of the Past''. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2000. *Moscati, Sabatino. ''The World of the Phoenicians''. London: Phoenix Giant, 1999.External links
Sidon On Google Maps Street View By Paul Saad
Sidonianews
(Sidon News Portal)
Lebanon, the Cedars' Land: Sidon
{{Authority control Sidon Mediterranean port cities and towns in Lebanon Populated coastal places in Lebanon Populated places in Sidon District Shia Muslim communities in Lebanon Sunni Muslim communities in Lebanon Archaeological sites in Lebanon 4th-millennium BC establishments Coloniae (Roman) Heavy Neolithic sites Hebrew Bible cities Hellenistic colonies Phoenician cities Phoenician sites in Lebanon Populated places established in the 4th millennium BC Torah cities Former kingdoms Tourist attractions in Lebanon Tourism in Lebanon