Shortest Remaining Time on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
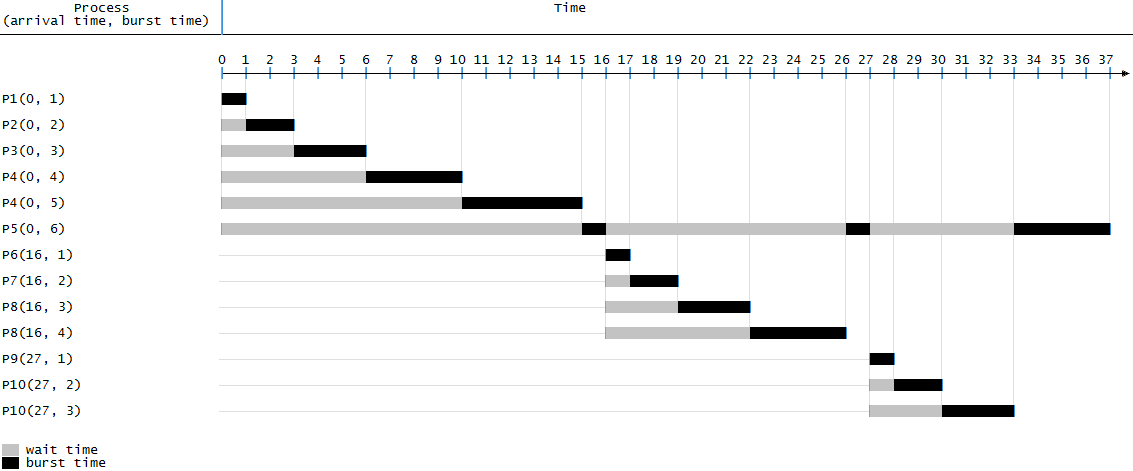 Shortest remaining time, also known as shortest remaining time first (SRTF), is a
Shortest remaining time, also known as shortest remaining time first (SRTF), is a
 Shortest remaining time, also known as shortest remaining time first (SRTF), is a
Shortest remaining time, also known as shortest remaining time first (SRTF), is a scheduling
A schedule or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such things are i ...
method that is a preemptive version of shortest job next scheduling. In this scheduling algorithm, the process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
*Business process, activities that produce a specific se ...
with the smallest amount of time remaining until completion is selected to execute. Since the currently executing process is the one with the shortest amount of time remaining by definition, and since that time should only reduce as execution progresses, the process will either run until it completes or get preempted if a new process is added that requires a smaller amount of time.
Shortest remaining time is advantageous because short processes are handled very quickly. The system also requires very little overhead since it only makes a decision when a process completes or a new process is added, and when a new process is added the algorithm only needs to compare the currently executing process with the new process, ignoring all other processes currently waiting to execute.
Like shortest job next, it has the potential for process starvation: long processes may be held off indefinitely if short processes are continually added. This threat can be minimal when process times follow a heavy-tailed distribution
In probability theory, heavy-tailed distributions are probability distributions whose tails are not exponentially bounded: that is, they have heavier tails than the exponential distribution. In many applications it is the right tail of the distrib ...
. A similar algorithm which avoids starvation at the cost of higher tracking overhead is highest response ratio next (HRRN).
Limitations
Like shortest job next scheduling, shortest remaining time scheduling is rarely used outside of specialized environments because it requires accurate estimates of the runtime of each process.References
{{Queueing theory Processor scheduling algorithms de:Prozess-Scheduler#Strategien