Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest
branch
A branch, sometimes called a ramus in botany, is a woody structural member connected to the central trunk of a tree (or sometimes a shrub). Large branches are known as boughs and small branches are known as twigs. The term '' twig'' usually ...
of
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
. It holds that the
Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God in Islam, God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. So ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
designated
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his
successor (''khalīfa'') and the
Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, ser ...
(spiritual and political leader) after him,
most notably at the
event of Ghadir Khumm,
but was prevented from succeeding Muhammad as the leader of the
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
as a result of the choice made by some of
Muhammad's other companions (''ṣaḥāba'') at
Saqifah. This view primarily contrasts with that of
Sunnī Islam, whose adherents believe that Muhammad did not appoint a successor before
his death and consider
Abū Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
, who was appointed
caliph by a group of senior Muslims at Saqifah, to be the first
rightful (''rāshidūn'') caliph after Muhammad. Adherents of Shīʿa Islam are called Shīʿa Muslims, Shīʿītes, or simply Shīʿa or Shia.
Shīʿa Islam is based on a
''ḥadīth'' report concerning Muhammad's pronouncement at Ghadir Khumm.
[Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam". Oxford University Press, 2002 , . p. 40] Shīʿa Muslims believe that
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib, Muhammad's cousin and son-in-law, should have been the designated successor to Muhammad as Islam's spiritual and political leader.
This belief later developed into the concept of
Imamah, the idea that certain descendants of Muhammad, the ''
Ahl al-Bayt'', are rightful rulers or Imams, whom Shīʿa Muslims believe possess special spiritual and political authority over the
Muslim community.
Although there are many
Shīʿa subsects, modern Shīʿa Islam has been divided into two main groupings:
Twelvers and
Ismāʿīlīs, with Twelver Shīʿas being the largest and most influential group among Shīʿa Muslims.
Shīʿa Islam is the
second largest branch of Islam, followed by 10–15% of all Muslims.
is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam,
comprising about 85% of all Shīʿa Muslims.
Terminology
Collectively, adherents of Shīʿa Islam are called the ''Shīʿah'' ( ar, شِيعَة; ), which is short for ''Shīʿatu ʿAlī'' ( ar, شِيعَة عَلِيّ; ) meaning "followers of Ali", "faction of Ali", or "partisans of Ali";
[The New Encyclopædia Britannica, Jacob E. Safra, Chairman of the Board, 15th Edition, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 1998, , Vol 10, p. 738] ''Shīʿī'' () denotes both the singular noun and the adjective form, while ''Shīyāʿ'' () refers to the plural noun.
''Shīʿa'' or ''Shia'' and ''Shīʿīsm''/''Shīʿīte'' or ''Shiism''/''Shiite'' are the forms used in
English and other
European languages for adherents, mosques, traditions, and things associated with the Shīʿa branch of Islam.
The term was first used during Muhammad's lifetime. At present, the word refers to the Muslims who believe that the leadership of the
Muslim community after Muhammad belongs to
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib, Muhammad's cousin and son-in-law, and his successors.
Nawbakhti states that the term ''Shīʿa'' refers to a group of Muslims who at the time of Muhammad and after him regarded ʿAlī as the
Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, ser ...
and
caliph.
expresses that the term ''Shīʿa'' refers to those who believe that ʿAlī is designated as the
heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Official ...
, Imam, and caliph by Muhammad
and that ʿAlī's authority is maintained through his descendants.
For the adherents of Shīʿa Islam, this conviction is implicit in the
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
and the
history of Islam. Shīʿa Muslim scholars emphasize that the notion of authority is linked to the family of the
Abrahamic prophets as the Quranic verses and show: ''"Indeed, God chose Adam and Noah and the family of Abraham and the family of 'Imran over the worlds – (33) Descendants, some of them from others. And God is Hearing and Knowing. (34)"''
Beliefs and practices
Theology
Shīʿa Islam is the
second largest branch of Islam, followed by 10–15% of all Muslims,
considered to be vast and
inclusive of many different denominations and subgroups.
Shīʿa Islam embodies a completely independent system of religious interpretation and political authority in the
Muslim world. The original Shīʿa identity referred to the followers of Imam ʿAlī, and Shīʿa theology was formulated after the ''
hijra'' (8th century CE). The first Shīʿa governments and societies were established by the end of the 9th century CE. The 10th century CE has been referred to by the scholar of Islamic studies
Louis Massignon as "the Shiite Ismaili century in the history of Islam".
Profession of faith (''Shahada'')

The Shīʿa version of the ''
Shahada'', the Islamic profession of faith, differs from that of the
Sunnīs.
The Sunnī version of the ''Shahada'' states "There is no god except God, Muhammad is the messenger of God", but to this declaration of faith Shīʿa Muslims append the phrase ''Ali-un-Waliullah'' (: "ʿAlī is the ''
Wali'' (custodian) of
God"). The basis for the Shīʿa belief in ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as the ''Wali'' of God is derived from the Quranic verse , the "
Verse of Wilayah".
This additional phrase to the declaration of faith embodies the Shīʿa emphasis on the inheritance of authority through
Muhammad's family and lineage. The three clauses of the Shīʿa version of the ''Shahada'' thus address the fundamental Islamic beliefs of ''
Tawḥīd
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanization of Arabic, romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion ...
'' (unity and oneness of God), ''
Nubuwwah'' (the
prophethood of Muhammad), and ''
Imamah'' (the Imamate, leadership of the faith).
Infallibility (''Ismah'')

''Ismah'' is the concept of
infallibility or "divinely bestowed freedom from error and sin" in Islam.
Muslims believe that Muhammad, along with
other prophets and messengers in Islam, possessed ''ismah''.
Twelver and
Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa Muslims also attribute the quality to
Imams as well as to
Fāṭimah, daughter of Muhammad, in contrast to the
Zaydī Shīʿas, who don't attribute ''ismah'' to the Imams. Though initially beginning as a political movement, infallibility and sinlessness of the Imams later evolved as a distinct belief of (non-Zaydī) Shīʿīsm.
According to
Shīʿa Muslim theologians, infallibility is considered a rational, necessary precondition for spiritual and religious guidance. They argue that since
God has commanded absolute obedience from these figures, they must only order that which is right. The state of infallibility is based on the Shīʿa interpretation of the
Verse of Purification. Thus, they are the most pure ones, the only immaculate ones preserved from, and immune to, all uncleanness. It doesn't mean that supernatural powers prevent them from committing a
sin, but due to the fact that they have absolute belief in God, they refrain from doing anything that is a sin.
They also have a complete knowledge of God's will. They are in possession of all knowledge brought by the
angels to the prophets (''nabī'') and the messengers (''rāsūl''). Their knowledge encompasses the totality of all times. Thus, they are believed to act without fault in religious matters. Shīʿa Muslims regard
ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as the
successor of Muhammad not only ruling over the entire
Muslim community in justice, but also interpreting the Islamic faith, practices, and its esoteric meaning. Hence he was regarded as being free from error and sin (infallible), and appointed by God by divine decree (''
nass'') to be the first Imam. ʿAlī is regarded as a "perfect man" (''al-insan al-kamil'') similar to Muhammad, according to the Shīʿa viewpoint.
Occultation (''Ghaybah'')
The
Occultation is an
eschatological belief held in various denominations of Shīʿa Islam concerning a
messianic figure, the hidden and last Imam known as "the
Mahdi", that one day shall return on Earth and fill the world with justice. According to the doctrine of
Twelver Shīʿīsm, the main goal of Imam Mahdi will be to establish an
Islamic state and to apply
Islamic laws
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
that were revealed to Muhammad. The Quran doesn't contain verses on the Imamate, which is the basic doctrine of Shīʿa Islam. Some Shīʿa subsects, such as the
Zaydī Shīʿas and
Nizārī Ismāʿīlīs, don't believe in the idea of the Occultation. The groups which do believe in it differ as to which lineage of the Imamate is valid, and therefore which individual has gone into Occultation. They believe there are many signs that will indicate the time of his return.
Twelver Shīʿa Muslims believe that the prophesied Mahdi and
twelfth Imam,
Hujjat Allah al-Mahdi
Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan al-Mahdī ( ar, محمد بن الحسن المهدي) is believed by the Twelver Shia to be the last of the Twelve Imams and the eschatological Mahdi, who will emerge in the end of time to establish peace and justic ...
, is already on Earth in Occultation, and
will return at the end of time.
Ṭayyibi Ismāʿīlīs and Fatimid/Bohra/
Dawoodi Bohra believe the same but for their 21st Ṭayyib,
At-Tayyib Abi l-Qasim, and also believe that a ''
Da'i al-Mutlaq'' ("Unrestricted Missionary") maintains contact with him.
Sunnī Muslims believe that the future Mahdi has not yet arrived on Earth.
''Ḥadīth'' tradition
Shīʿa Muslims believe that the status of ʿAlī is supported by numerous ''
ḥadīth
Ḥadīth ( or ; ar, حديث, , , , , , , literally "talk" or "discourse") or Athar ( ar, أثر, , literally "remnant"/"effect") refers to what the majority of Muslims believe to be a record of the words, actions, and the silent approval ...
'', including the
Hadith of the pond of Khumm,
Hadith of the two weighty things,
Hadith of the pen and paper,
Hadith of the invitation of the close families, and
Hadith of the Twelve Successors. In particular, the
Hadith of the Cloak is often quoted to illustrate Muhammad's feeling towards ʿAlī and his family by both Sunnī and Shīʿa scholars. Shīʿa Muslims prefer to study and read the ''ḥadīth'' attributed to the ''
Ahl al-Bayt'' and close associates, and most
have their own separate ''ḥadīth'' canon.
Holy Relics (''Tabarruk'')
It is believed that the armaments and sacred items of all of the prophets, including
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
, were handed down in succession to the Imams of the ''
Ahl al-Bayt''.
Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq, the
6th Shīʿīte Imam, in ''
Kitab al-Kafi'' mentions that "with me are the arms of the Messenger of Allah. It is not disputable."
Further, he claims that with him is the sword of the Messenger of God, his coat of arms, his Lamam (pennon) and his helmet. In addition, he mentions that with him is the flag of the Messenger of God, the victorious. With him is the Staff of
Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu ( Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pr ...
, the ring of
Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
, son of
David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
, and the tray on which Moses used to offer his offerings. With him is the name that whenever the Messenger of God would place it between the Muslims and pagans no arrow from the pagans would reach the Muslims. With him is the similar object that angels brought.
Al-Ṣādiq also narrated that the passing down of armaments is synonymous to receiving the ''Imamat'' (leadership), similar to how the
Ark of Covenant in the house of the
Israelites signaled prophethood.
Imam
Ali al-Ridha narrates that wherever the armaments among us would go, knowledge would also follow and the armaments would never depart from those with knowledge (''Imamat'').
Other doctrines
Doctrine about necessity of acquiring knowledge
According to
Muhammad Rida al-Muzaffar, God gives humans the faculty of reason and argument. Also, God orders humans to spend time thinking carefully on creation while he refers to all creations as his signs of power and glory. These signs encompass all of the universe. Furthermore, there is a similarity between humans as the little world and the universe as the large world. God does not accept the faith of those who follow him without thinking and only with imitation, but also God blames them for such actions. In other words, humans have to think about the universe with reason and intellect, a faculty bestowed on us by God. Since there is more insistence on the faculty of intellect among Shīʿa Muslims, even evaluating the claims of someone who claims prophecy is on the basis of intellect.
Doctrine concerning prayer
Praying in Shīʿa Islam has an important place, as Muhammad described it as a weapon of the
believer
Believer(s) or The Believer(s) may refer to:
Religion
* Believer, a person who holds a particular belief
** Believer, a person who holds a particular religious belief
*** Believers, Christians with a religious faith in the divine Christ
*** Bel ...
. In fact, Duʼa considered as something that is a feature of Shia community in a sense. Performing Duʼa in Shīʿa Islam has a special ritual. Because of this, there are many books written on the instructions and conditions of praying among Shīʿa Muslims.
Shīʿīte clergymen always invited their followers to recite Duʼa. For instance, ʿAlī has been considered with the subject of Duʼa because of his leadership in monotheism.
Practices

Shīʿa religious practices, such as prayers, differ only slightly from the Sunnīs. While all
Muslims pray five times daily, Shīʿa Muslims have the option of combining ''
Dhuhr'' with ''
Asr'' and ''
Maghrib'' with ''
Isha''', as there are three distinct times mentioned in the
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
. The Sunnīs tend to combine only under certain circumstances.
Holidays
Shīʿa Muslims celebrate the following annual holidays:
*
Eid ul-Fitr, which marks the end of fasting during the month of
Ramadan
, type = islam
, longtype = Islam, Religious
, image = Ramadan montage.jpg
, caption=From top, left to right: A crescent moon over Sarıçam, Turkey, marking the beginning of the Islamic month of Ramadan. Ramadan Quran reading in Bandar Torkaman, I ...
*
Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha () is the second and the larger of the two main holidays celebrated in Islam (the other being Eid al-Fitr). It honours the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to Allah's co ...
, which marks the end of the ''
Hajj
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carri ...
'' or pilgrimage to Mecca
*
Eid al-Ghadeer, which is the anniversary of the Ghadir Khum, the occasion when Muhammad announced Ali's Imamate before a multitude of Muslims. Eid al-Ghadeer is held on the 18th of Dhu al-Hijjah.
* The
Mourning of Muharram and the
Day of Ashura for Shīʿa Muslims commemorate the martyrdom of
Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, brother of
Ḥasan and grandson of Muhammad, who was killed by Yazid ibn Muawiyah in
Karbala
Karbala or Kerbala ( ar, كَرْبَلَاء, Karbalāʾ , , also ;) is a city in central Iraq, located about southwest of Baghdad, and a few miles east of Lake Milh, also known as Razzaza Lake. Karbala is the capital of Karbala Governorat ...
(central Iraq). Ashura is a day of deep mourning which occurs on the 10th of
Muharram.
*
Arba'een commemorates the suffering of the women and children of Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī's household. After Ḥusayn was killed, they were marched over the desert, from Karbala (central Iraq) to Shaam (
Damascus, Syria). Many children (some of whom were direct descendants of Muhammad) died of thirst and exposure along the route. Arbaein occurs on the 20th of
Safar
Ṣafar ( ar, صَفَر) also spelt as Safer in Turkish, is the second month of the lunar Islamic calendar. The Arabic word ''ṣafar'' means "travel, migration", corresponding to the pre-Islamic Arabian time period when muslims flee the oppr ...
, 40 days after Ashura.
*
Mawlid
Mawlid, Mawlid an-Nabi ash-Sharif or Eid Milad un Nabi ( ar, المولد النبوي, translit=mawlid an-nabawī, lit=Birth of the Prophet, sometimes simply called in colloquial Arabic , , among other vernacular pronunciations; sometimes , ) ...
, Muhammad's birth date. Unlike Sunnī Muslims, who celebrate the 12th of
Rabi' al-awwal as Muhammad's day of birth or death (because they assert that his birth and death both occur in this week), Shīʿa Muslims celebrate Muhammad's birthday on the 17th of the month, which coincides with the birth date of
Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq, the
6th Shīʿīte Imam.
*
Fāṭimah's birthday on 20th of
Jumada al-Thani. This day is also considered as the "'women and mothers' day"
*
ʿAlī's birthday on 13th of
Rajab.
*
Mid-Sha'ban is the birth date of the 12th and final Twelver imam,
Muhammad al-Mahdi
Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan al-Mahdī ( ar, محمد بن الحسن المهدي) is believed by the Twelver Shia to be the last of the Twelve Imams and the eschatological Mahdi, who will emerge in the end of time to establish peace and justic ...
. It is celebrated by Shia Muslims on the 15th of
Sha'aban.
*
Laylat al-Qadr, anniversary of the night of the revelation of the Quran.
*
Eid al-Mubahila celebrates a meeting between the ''
Ahl al-Bayt'' (household of Muhammad) and a Christian deputation from Najran. Al-Mubahila is held on the 24th of Dhu al-Hijjah.
Holy sites
After the
four holy cities of Islam (
Mecca,
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
,
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, and
Damascus), the cities of
Najaf,
Karbala
Karbala or Kerbala ( ar, كَرْبَلَاء, Karbalāʾ , , also ;) is a city in central Iraq, located about southwest of Baghdad, and a few miles east of Lake Milh, also known as Razzaza Lake. Karbala is the capital of Karbala Governorat ...
, and
Qom
Qom (also spelled as "Ghom", "Ghum", or "Qum") ( fa, قم ) is the seventh largest metropolis and also the seventh largest city in Iran. Qom is the capital of Qom Province. It is located to the south of Tehran. At the 2016 census, its popul ...
are the most revered by Shīʿa Muslims.
The
Sanctuary of Imām ʿAlī in Najaf, the
Shrine of Imam Ḥusayn in Karbala, and the
Shrine of Fāṭimah al-Maʿṣūmah in Qom are very essential for Shīʿa Muslims. Other venerated pilgrimage sites include the
Imam Reza shrine in
Mashhad
Mashhad ( fa, مشهد, Mašhad ), also spelled Mashad, is the List of Iranian cities by population, second-most-populous city in Iran, located in the relatively remote north-east of the country about from Tehran. It serves as the capital of R ...
, the
Kadhimiya Mosque in
Kadhimiya
Kadhimiya ( ar, ٱلْكَاظِمِيَّة, al-Kāẓimiyyah, ) or Kadhimayn (, ) is a northern neighbourhood of the city of Baghdad, Iraq. It is about from the city's center, on the west bank of the Tigris. 'Kadhimiya' is also the name of on ...
,
Al-Askari Mosque in
Samarra
Samarra ( ar, سَامَرَّاء, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The city of Samarra was founded by Abbasid Caliph Al-Mutasim for his Turkish professional army ...
, the
Sahla Mosque, the
Great Mosque of Kufa, the
Jamkaran Mosque in Qom, and the
Tomb of Daniel in
Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo-Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
.
Most of the
Shīʿa sacred places and heritage sites in Saudi Arabia have been destroyed by the
Al Saud-
Wahhabi armies of the
Ikhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
, the most notable being the tombs of the Imams located in the Al-Baqi' cemetery in 1925. In 2006, a bomb destroyed the shrine of Al-Askari Mosque. (''See'':
Anti-Shi'ism).
Demographics
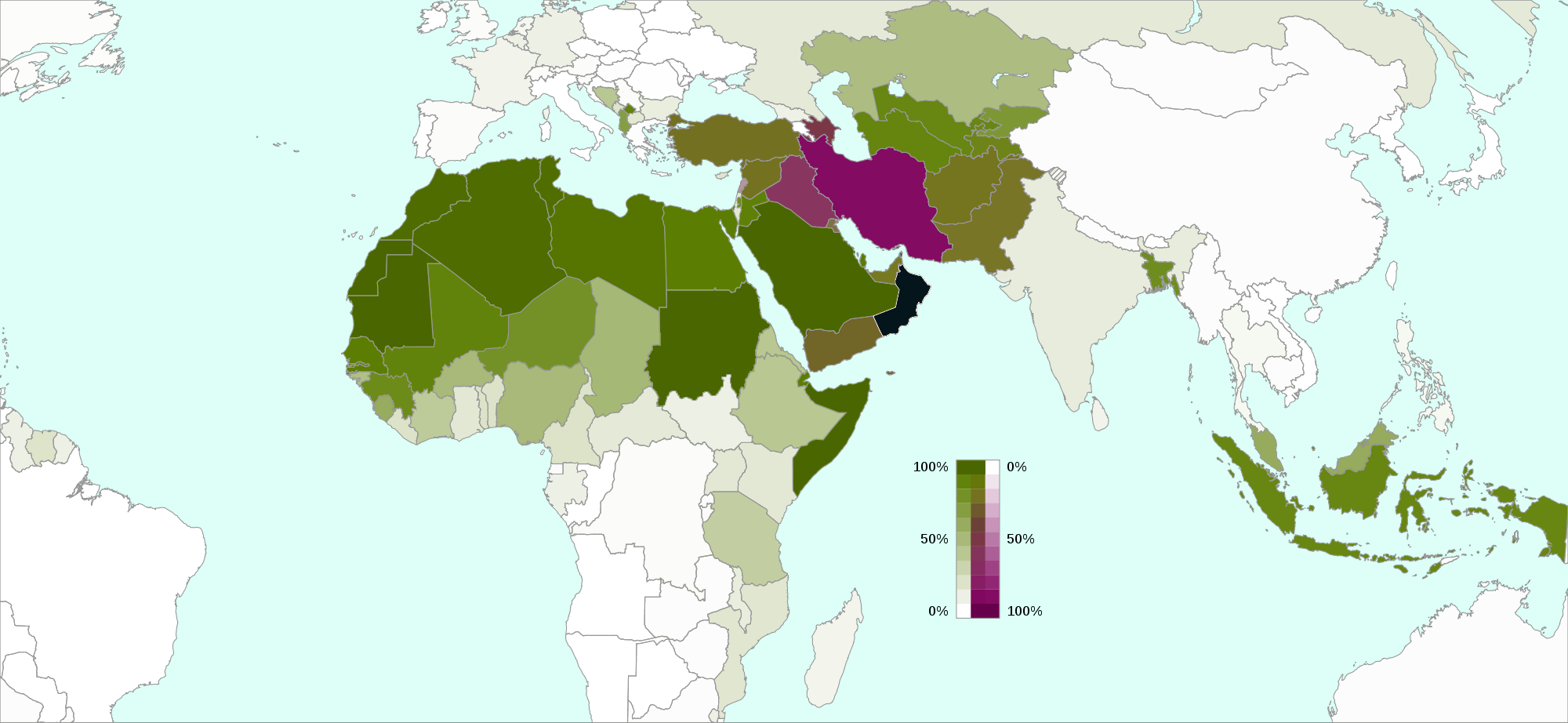

It is estimated that either 10–20%
or 10–13%
of the
global Muslim population are Shīʿas. They may number up to 200 million as of 2009.
As of 1985, Shīʿa Muslims are estimated to be 21% of the Muslim population in
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
, although the total number is difficult to estimate.
Shīʿa Muslims form a majority of the population in various regions of the
Muslim world, including
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
,
Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
,
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
, and
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
,
as well as a plurality in
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
. Shīʿa Muslims constitute 36.3% of the entire population (and 38.6% of the Muslim population) of the
Middle East.
Estimates have placed the proportion of Shīʿa Muslims in Lebanon between 27% and 45% of the population,
30%–35% of the citizen population in
Kuwait (no figures exist for the non-citizen population),
over 20% in
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
,
5–20% of the population in
Pakistan,
and 10–19% of
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
's population.
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
hosts a number of distinct Shīʿa communities, including the
Twelver Baharna in the
Eastern Province and
Nakhawila of Medina, and the
Ismāʿīlī Sulaymani
The Sulaymani branch of Tayyibi Isma'ilism is an Islamic community, of which around 70,000 members reside in Yemen, while a few thousand Sulaymani Bohras can be found in India. The Sulaymanis are sometimes headed by a ''Da'i al-Mutlaq'' from t ...
and
Zaydī Shīʿas of
Najran
Najran ( ar, نجران '), is a city in southwestern Saudi Arabia near the border with Yemen. It is the capital of Najran Province. Designated as a new town, Najran is one of the fastest-growing cities in the kingdom; its population has risen f ...
. Estimations put the number of Shīʿīte citizens at 2–4 million, accounting for roughly 15% of the local population. Approximately 40% of the population of Yemen are Shīʿa Muslims.
Significant Shīʿa communities also exist in the coastal regions of
West Sumatra and
Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
in Indonesia (see
Tabuik).
The Shīʿa presence is negligible elsewhere in Southeast Asia, where Muslims are predominantly
Shāfiʿī
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional Fiqh, schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunni Islam, Sunnī branch of Islam. I ...
Sunnīs.
A significant
Shīʿa minority is present in Nigeria, made up of modern-era converts to a
Shīʿīte movement centered around
Kano and
Sokoto states.
Several African countries like
Kenya,
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
,
, etc. hold small minority populations of various Shīʿa subsects, primarily descendants of immigrants from South Asia during the colonial period, such as the
Khoja.
Significant populations worldwide
Figures indicated in the first three columns below are based on the October 2009 demographic study by the
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
report, ''Mapping the Global Muslim Population''.
Major denominations or branches
The Shīʿa community throughout its history split over the issue of the Imamate. The largest branch are the
Twelvers, followed by the
Zaydīs and the
Ismāʿīlīs. Each subsect of Shīʿīsm follows its own line of Imamate. All mainstream Twelver and Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa Muslims follow the same school of thought, the
Jaʽfari jurisprudence, named after
Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq, the
6th Shīʿīte Imam.
Shīʿīte clergymen and
jurists usually carry the title of ''
mujtahid
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a le ...
'' (i.e., someone authorized to issue legal opinions in Shīʿa Islam).
Twelver
Twelver Shīʿīsm or Ithnāʿashariyyah is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, and the terms ''Shīʿa Muslim'' and ''Shīʿa'' often refer to the Twelvers by default. The designation ''Twelver'' is derived from the doctrine of believing in twelve divinely ordained leaders, known as "
the Twelve Imams". Twelver Shīʿas are otherwise known as ''Imami'' or ''Jaʿfari''; the latter term derives from
Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq, the
6th Shīʿīte Imam, who elaborated the Twelver jurisprudence. Twelver Shīʿas constitute the majority of the population in
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
(90%),
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
(85%),
Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
(70%),
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
(65%), and
Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
(65% of Muslims).
[Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam" Oxford University Press, 2002. . p. 45]
Doctrine

Twelver doctrine is based on
five principles. These five principles known as ''Usul ad-Din'' are as follow:
#
Monotheism:
God is one and unique;
#
Justice: the concept of moral rightness based on ethics, fairness, and equity, along with the punishment of the breach of these ethics;
#
Prophethood: the institution by which God sends emissaries, or prophets, to guide humankind;
#
Leadership: a divine institution which succeeded the institution of Prophethood. Its appointees (''Imams'') are divinely appointed;
#
Resurrection and Last Judgment: God's final assessment of humanity.
More specifically, these principles are known as ''Usul al-Madhhab'' (principles of the Shīʿa branch of Islam) according to Twelver Shīʿas, which differ from ''Daruriyat al-Din'' ("Necessities of Religion"), which are principles in order for one to be a Muslim. ''Daruriyat al-Din'' don't include leadership (''Imamah''), as it is not a requirement in order for one to be recognized as a Muslim. However, this category, according to Twelver scholars like
Ayatollah
Ayatollah ( ; fa, آیتالله, āyatollāh) is an Title of honor, honorific title for high-ranking Twelver Shia clergy in Iran and Iraq that came into widespread usage in the 20th century.
Etymology
The title is originally derived from ...
Abu al-Qasim al-Khoei, does include belief in God, prophethood, the Day of Resurrection, and other "necessities" (such as the
belief in angels). In this regard, Twelver Shīʿas draw a distinction in terms of believing in the
main principles of Islam on the one hand, and specifically Shīʿīte doctrines like the
Imamate
{{expand Arabic, date=April 2021
The term imamate or ''imamah'' ( ar, إمامة, ''imāmah'') means "leadership" and refers to the office of an ''imam'' or a state ruled by an ''imam''.
Theology
*Imamate, in Sunni doctrine the caliphate
:* Naqshb ...
on the other.
Books
Besides the
Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
, which is the
sacred text
Religious texts, including scripture, are texts which various religions consider to be of central importance to their religious tradition. They differ from literature by being a compilation or discussion of beliefs, mythologies, ritual prac ...
common to all Muslims, Twelver Shīʿas derive scriptural and authoritative guidance from
collections of sayings and traditions (
''ḥadīth'') attributed to Muhammad and the Twelve Imams. Below is a list of some of the most prominent of these books:
* ''
Nahj al-Balagha'' by
Ash-Sharif Ar-Radhi – the most famous collection of sermons, letters & narration attributed to Ali, the first Imam regarded by Shias
* ''
Kitab al-Kafi'' by
Muhammad ibn Ya'qub al-Kulayni
* ''
Wasa'il al-Shiʻah'' by
al-Hurr al-Amili
Muhammad bin al-Ḥasan bin Ali bin al-Ḥusayn al-Ḥurr al-ʿĀmili al-Mashghari ( ar, مُحَمَّد ٱبْن ٱلْحَسَن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱلْحُرّ ٱلْعَامِلِيّ ٱلْمَشْغَرِي ...
The Twelve Imams

The ''Twelve Imams'' are the
spiritual and political successors to Muhammad for the Twelvers. According to the theology of Twelvers, the successor of Muhammad is an
infallible human individual who not only rules over the
Muslim community with justice but also is able to keep and interpret the
divine law (''sharīʿa'') and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the Twelve Imams are a guide and model for the Muslim community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and
sin, and Imams must be chosen by
divine decree
''Qadar'' ( ar, قدر, transliterated ''qadar'', meaning literally "power",J. M. Cowan (ed.) (1976). ''The Hans Wehr Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic''. Wiesbaden, Germany: Spoken Language Services. but translated variously as: "Fate", "Di ...
(''nass'') through Muhammad.
In Twelver Shīʿīsm, each Imam was the son of the previous Imam, with the exception of
Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, who was the brother of
Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī. The twelfth and final Imam is
Hujjat Allah al-Mahdi
Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan al-Mahdī ( ar, محمد بن الحسن المهدي) is believed by the Twelver Shia to be the last of the Twelve Imams and the eschatological Mahdi, who will emerge in the end of time to establish peace and justic ...
, who is believed by Twelvers to be currently alive and hidden in
Occultation.
Jurisprudence
The Twelver jurisprudence is called ''
Jaʽfari jurisprudence''. In this
school of Islamic jurisprudence, the ''
sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and passed ...
'' is considered to be comprehensive of the oral traditions of Muhammad and their implementation and interpretation by the Twelve Imams. There are three schools of Jaʿfari jurisprudence: Usuli, Akhbari, and
Shaykhi
Shaykhism ( ar, الشيخية) is a Shi'a Islamic school founded by Shaykh Ahmad in early 19th-century Qajar Iran. While grounded in traditional Twelver Shiʻi doctrine, Shaykhism diverged from the Usuli school in its interpretation of key idea ...
; the Usuli school is by far the largest of the three. Twelver groups that don't follow the Jaʿfari jurisprudence include
Alevis,
Bektashi, and
Qizilbash.
The
five pillars of Islam to the Jaʿfari jurisprudence are known as ''Usul ad-Din'':
# ''
Tawḥīd
Tawhid ( ar, , ', meaning "unification of God in Islam (Allāh)"; also romanization of Arabic, romanized as ''Tawheed'', ''Tawhid'', ''Tauheed'' or ''Tevhid'') is the indivisible oneness concept of monotheism in Islam. Tawhid is the religion ...
'': unity and oneness of God;
# ''
Nubuwwah'': prophethood of Muhammad;
# ''
Muʿad'': resurrection and final judgment;
# ''
ʿAdl'': justice of God;
# ''
Imamah'': the rightful place of the Shīʿīte Imams.
In Jaʿfari jurisprudence, there are eight secondary pillars, known as ''Furu ad-Din'', which are as follows:
[
# '']Salat
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːh, ( or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːtʰin construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba wit ...
'' (prayer);
# '' Sawm'' (fasting);
# ''Hajj
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carri ...
'' (pilgrimage) to Mecca;
# '' Zakāt'' (alms giving to the poor);
# '' Jihād'' (struggle) for the righteous cause;
# Directing others towards good;
# Directing others away from evil;
# '' Khums'' (20% tax on savings yearly, after deduction of commercial expenses).
According to Twelvers, defining and interpretation of Islamic jurisprudence (''fiqh'') is the responsibility of Muhammad and the Twelve Imams. Since the 12th Imam is currently in Occultation, it is the duty of Shīʿīte clerics to refer to the Islamic literature, such as the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
and ''ḥadīth'', and identify legal decisions within the confines of Islamic law to provide means to deal with current issues from an Islamic perspective. In other words, clergymen in Twelver Shīʿīsm are believed to be the guardians of ''fiqh'', which is believed to have been defined by Muhammad and his twelve successors. This process is known as ''ijtihad
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a le ...
'' and the clerics are known as ''marjaʿ
Marji ( ar, مرجع, transliteration: ''marjiʿ''; plural: ''marājiʿ''), literally meaning "source to follow" or "religious reference", is a title given to the highest level of Twelver Shia authority, a Grand Ayatollah with the authority giv ...
'', meaning "reference"; the labels ''Allamah
''Allāmah'' ( ar, عَلَّامة, Urdu and , meaning "learned"), also spelled ''Allāma'' and ''Allama'' and “ Allameh “, is an Islamic honorary title for a profound scholar, a polymath, a man of vast reading and erudition, or a great ...
'' and ''Ayatollah
Ayatollah ( ; fa, آیتالله, āyatollāh) is an Title of honor, honorific title for high-ranking Twelver Shia clergy in Iran and Iraq that came into widespread usage in the 20th century.
Etymology
The title is originally derived from ...
'' are in use for Twelver clerics.
Islamists
Islamist Shīʿīsm ( fa, تشیع اخوانی) is a new denomination within Twelver Shīʿīsm greatly inspired by the political ideology of the Muslim Brotherhood
The Society of the Muslim Brothers ( ar, جماعة الإخوان المسلمين'' ''), better known as the Muslim Brotherhood ( ', is a transnational Sunni Islamist organization founded in Egypt by Islamic scholar and schoolteacher Hassan ...
and mysticism of Ibn Arabi. It sees Islam as a political system and differs from the other mainstream Usuli and Akhbari groups in favoring the idea of the establishment of an Islamic state in Occultation under the rule of the 12th Imam. Hadi Khosroshahi
Seyyed Hadi Khosroshahi ( fa, سید هادی خسروشاهی; – 27 February 2020) was an Iranian cleric and diplomat who served as Iran's first ambassador to the Vatican.
Career
When he was 15 years old, Khosroshahi joined the leader of m ...
was the first person to identify himself as '' ikhwani'' (Islamist) Shīʿa Muslim. Because of the concept of the hidden Imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi
Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan al-Mahdī ( ar, محمد بن الحسن المهدي) is believed by the Twelver Shia to be the last of the Twelve Imams and the eschatological Mahdi, who will emerge in the end of time to establish peace and justic ...
, Shīʿa Islam is inherently secular in the age of Occultation, therefore Islamist Shīʿa Muslims had to borrow ideas from Sunnī Islamists and adjust them in accordance with the doctrine of Shīʿīsm. Its foundations were laid during the Persian Constitutional Revolution
The Persian Constitutional Revolution ( fa, مشروطیت, Mashrūtiyyat, or ''Enghelāb-e Mashrūteh''), also known as the Constitutional Revolution of Iran, took place between 1905 and 1911. The revolution led to the establishment of a par ...
at the start of 20th century in Qajar Iran (1905–1911), when Fazlullah Nouri supported the Persian king Ahmad Shah Qajar against the will of Muhammad Kazim Khurasani, the Usuli ''marjaʿ
Marji ( ar, مرجع, transliteration: ''marjiʿ''; plural: ''marājiʿ''), literally meaning "source to follow" or "religious reference", is a title given to the highest level of Twelver Shia authority, a Grand Ayatollah with the authority giv ...
'' of the time.
Ismāʿīlī (''Sevener'')
Ismāʿīlīs, otherwise known as ''Sevener'', derive their name from their acceptance of Ismāʿīl ibn Jaʿfar as the divinely appointed spiritual successor (Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, ser ...
) to Jaʿfar al-Ṣādiq, the 6th Shīʿīte Imam, wherein they differ from the Twelvers, who recognize Mūsā al-Kāẓim, younger brother of Ismāʿīl, as the true Imam.
After the death or Occultation of Muhammad ibn Imam Ismāʿīl in the 8th century CE, the teachings of Ismāʿīlīsm further transformed into the belief system as it is known today, with an explicit concentration on the deeper, esoteric meaning ('' bāṭin'') of the Islamic faith. With the eventual development of Twelver Shīʿīsm into the more literalistic ''( zahīr)'' oriented Akhbari and later Usuli schools of thought, Shīʿīsm further developed in two separate directions: the metaphorical Ismāʿīlī group focusing on the mystical path and nature of God and the divine manifestation in the personage of the "Imam of the Time" as the "Face of God", with the more literalistic Twelver group focusing on divine law (''sharī'ah'') and the deeds and sayings (''sunnah'') attributed to Muhammad and his successors (the ''Ahl al-Bayt''), who as A'immah were guides and a light (''nūr'') to God.
 Though there are several subsects amongst the Ismāʿīlīs, the term in today's vernacular generally refers to the Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī Nizārī community, often referred to as the ''Ismāʿīlīs'' by default, who are followers of the Aga Khan and the largest group within Ismāʿīlīsm. Another Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī community are the Dawudi Bohras, led by a '' Da'i al-Mutlaq'' ("Unrestricted Missionary") as representative of a hidden Imam. While there are many other branches with extremely differing exterior practices, much of the spiritual theology has remained the same since the days of the faith's early Imams. In recent centuries, Ismāʿīlīs have largely been an Indo-Iranian community, but they can also be found in
Though there are several subsects amongst the Ismāʿīlīs, the term in today's vernacular generally refers to the Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī Nizārī community, often referred to as the ''Ismāʿīlīs'' by default, who are followers of the Aga Khan and the largest group within Ismāʿīlīsm. Another Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī community are the Dawudi Bohras, led by a '' Da'i al-Mutlaq'' ("Unrestricted Missionary") as representative of a hidden Imam. While there are many other branches with extremely differing exterior practices, much of the spiritual theology has remained the same since the days of the faith's early Imams. In recent centuries, Ismāʿīlīs have largely been an Indo-Iranian community, but they can also be found in India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, Pakistan, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
, Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Ri ...
, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
, East and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
, and in recent years several Ismāʿīlīs have emigrated to China, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
(primarily in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
), Australia, New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
, and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
.
Ismāʿīlī Imams
In the Nizārī
The Nizaris ( ar, النزاريون, al-Nizāriyyūn, fa, نزاریان, Nezāriyān) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent ...
Ismāʿīlī interpretation of Shīʿa Islam, the Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, ser ...
is the guide and the intercessor between humans and God, and the individual through whom God is recognized. He is also responsible for the esoteric interpretation of the Quran (''taʾwīl''). He is the possessor of divine knowledge and therefore the "Prime Teacher". According to the "Epistle of the Right Path", a Persian Ismāʿīlī prose text from the post- Mongol period of Ismāʿīlī history, by an anonymous author, there has been a chain of Imams since the beginning of time, and there will continue to be an Imam present on the Earth until the end of time. The worlds would not exist in perfection without this uninterrupted chain of Imams. The proof (''hujja
A term used in Shi'i terminology, "hujja" means "proof mplied: proof of God" It is usually used to refer to a single individual in any given human era who represents God's "proof" to humanity.http://iranica.com/articles/hojjat. The hujja is a ...
'') and gate ('' bāb'') of the Imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, ser ...
are always aware of his presence and are witness to this uninterrupted chain.
After the death of Ismāʿīl ibn Jaʿfar, many Ismāʿīlīs believed that one day the eschatological figure of Imam Mahdi, whom they believed to be Muhammad ibn Imam Ismāʿīl, would return and establish an age of justice. One group included the violent Qarmatians
The Qarmatians ( ar, قرامطة, Qarāmiṭa; ) were a militant Isma'ilism, Isma'ili Shia Islam, Shia movement centred in Al-Ahsa Oasis, al-Hasa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a Utopia#Religious utopias, religious-utopian Socialis ...
, who had a stronghold in Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
. In contrast, some Ismāʿīlīs believed the Imamate ''did'' continue, and that the Imams were in Occultation and still communicated and taught their followers through a network of '' Da'i'' ("Missionaries").
In 909 CE, Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah, a claimant to the Ismāʿīlī Imamate, established the Fatimid Caliphate. During this period, three lineages of Imams were formed. The first branch, known today as the Druze, began with Al-Ḥākim bi-Amr Allāh.monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
Abrahamic religion and ethno-religious group
An ethnoreligious group (or an ethno-religious group) is a grouping of people who are unified by a common religious and ethnic background.
Furthermore, the term ethno-religious group, along with ethno-regional and ethno-linguistic groups, is a s ...
with its own unique doctrines,Nizārī
The Nizaris ( ar, النزاريون, al-Nizāriyyūn, fa, نزاریان, Nezāriyān) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent ...
and Musta‘lī Ismāʿīlīs following the death of Ma'ad al-Mustansir Billah in 1094 CE. His rule was the longest of any caliph in any Islamic empire. Upon his passing away, his sons, Nizār (the older) and Al-Musta‘lī (the younger), fought for political and spiritual control of the dynasty. Nizār was defeated and jailed, but according to the Nizārī tradition his son escaped to Alamut, where the Iranian Ismāʿīlī had accepted his claim.
Pillars
Ismāʿīlīs have categorized their practices which are known as ''seven pillars Seven pillars may refer to:
* Seven Pillars for Prosperity, policy statement of the Progressive Canadian Party
*Seven Pillars Institute for Global Finance and Ethics (SPI) in Lawrence, Kansas
* Seven pillars of Ismailism in Shia Islam and in Nizari ...
'':
Contemporary leadership
The Nizārīs place importance on a scholarly institution because of the existence of a present Imam. The Imam of the Age defines the jurisprudence, and his guidance may differ with Imams previous to him because of different times and circumstances. For Nizārī Ismāʿīlīs, the current Imam is Karim al-Husayni Aga Khan IV. The Nizārī line of Imams has continued to this day as an uninterrupted chain.
Divine leadership has continued in the Bohra branch through the institution of the "Missionary" ('' Da'i''). According to the Bohra tradition, before the last Imam, At-Tayyib Abi l-Qasim, went into seclusion, his father, the 20th Al-Amir bi-Ahkami l-Lah, had instructed Al-Hurra Al-Malika the Malik
Malik, Mallik, Melik, Malka, Malek, Maleek, Malick, Mallick, or Melekh ( phn, 𐤌𐤋𐤊; ar, ملك; he, מֶלֶךְ) is the Semitic term translating to "king", recorded in East Semitic and Arabic, and as mlk in Northwest Semitic duri ...
a ( Queen consort) in Yemen to appoint a vicegerent after the seclusion—the '' Da'i al-Mutlaq'' ("Unrestricted Missionary"), who as the Imam's vicegerent has full authority to govern the community in all matters both spiritual and temporal while the lineage of Musta‘lī- Ṭayyibi Imams remains in seclusion (''Dawr-e-Satr''). The three branches of Musta‘lī Ismāʿīlīs ( Dawudi Bohras, Sulaymani Bohras, and Alavi Bohras) differ on who the current "Unrestricted Missionary" is.
Zaydī (''Fiver'')

 Zaydīsm, otherwise known as Zaydīyyah or Zaydī, is a branch of Shīʿa Islam named after Zayd ibn ʿAlī. Followers of the Zaydī school of jurisprudence are called Zaydīs or occasionally ''Fivers''. However, there is also a group called ''Zaydī Wasītīs'' who are Twelvers (see below). Zaydīs constitute roughly 42–47% of the population of Yemen.
Zaydīsm, otherwise known as Zaydīyyah or Zaydī, is a branch of Shīʿa Islam named after Zayd ibn ʿAlī. Followers of the Zaydī school of jurisprudence are called Zaydīs or occasionally ''Fivers''. However, there is also a group called ''Zaydī Wasītīs'' who are Twelvers (see below). Zaydīs constitute roughly 42–47% of the population of Yemen.
Doctrine
The Zaydīs, Twelvers, and Ismāʿīlīs all recognize the same first four Imams; however, the Zaydīs consider Zayd ibn ʿAlī as the 5th Imam. After the time of Zayd ibn ʿAlī, the Zaydīs believed that any descendant (''Sayyid'') of Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī or Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī could become the next Imam, after fulfilling certain conditions.
Jurisprudence
In matters of Islamic jurisprudence
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and e ...
, Zaydīs follow the teachings of Zayd ibn ʿAlī, which are documented in his book ''Majmu'l Fiqh'' (in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
: ). Al-Ḥādī ila'l-Ḥaqq Yaḥyā, the first Zaydī Imam and founder of the Zaydī State in Yemen, is regarded as the codifier of Zaydī jurisprudence, and as such most Zaydī Shīʿas today are known as ''Hadawis''.
Timeline
The Idrisids ( ar, ) were Arab Zaydī Shīʿas whose dynasty, named after its first sultan, Idris I, ruled in the western Maghreb from 788 to 985 CE. Another Zaydī State was established in the region of Gilan, Deylaman, and Tabaristan (northern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
) in 864 CE by the Alavids
Alid dynasties of northern Iran or Alavids (). In the 9th–14th centuries, the northern Iranian regions of Tabaristan, Daylam and Gilan, sandwiched between the Caspian Sea and the Alborz range, came under the rule of a number of Arab Alid ...
; it lasted until the death of its leader at the hand of the Samanids in 928 CE. Roughly forty years later, the Zaydī State was revived in Gilan and survived under Hasanid leaders until 1126 CE. Afterwards, from the 12th to 13th centuries, the Zaydī Shīʿas of Deylaman, Gilan, and Tabaristan then acknowledged the Zaydī Imams of Yemen or rival Zaydī Imams within Iran.
The Buyids were initially Zaydī Shīʿas, as were the Banu Ukhaidhir
The Banu 'l-Ukhaidhir ( ar, بنو الأخيضر), informally as Ukhaydhirites, was an Arab dynasty that ruled in Najd and al-Yamamah (central Arabia) from 867 to at least the mid-eleventh century. An Alid dynasty, they were descendants of Muha ...
rulers of al-Yamama in the 9th and 10th centuries. The leader of the Zaydī community took the title of caliph; thus, the ruler of Yemen was known by this title. Al-Hadi Yahya bin al-Hussain bin al-Qasim ar-Rassi, a descendant of Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī, founded the Zaydī Imamate at Sa'dah in 893–897 CE, and the Rassid dynasty continued to rule over Yemen until the middle of the 20th century, when the republican revolution of 1962 deposed the last Zaydī Imam. (''See'': Arab Cold War). The founding Zaydī branch in Yemen was the Jarudiyya; however, with increasing interaction with the Ḥanafī
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools (maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named afte ...
and Shāfiʿī
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional Fiqh, schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunni Islam, Sunnī branch of Islam. I ...
schools of Sunnī jurisprudence, there was a shift from the Jarudiyya group to the Sulaimaniyya, Tabiriyya, Butriyya, and Salihiyya. Zaydī Shīʿas form the second dominant religious group in Yemen. Currently, they constitute about 40–45% of the population in Yemen; Jaʿfaris and Ismāʿīlīs constitute the 2–5%. In Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia ...
, it is estimated that there are over 1 million Zaydī Shīʿas, primarily based in the western provinces.
Currently, the most prominent Zaydī political movement is the Houthi movement in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
,Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen Saudi may refer to:
* Saudi Arabia
* Saudis, people from Saudi Arabia
* Saudi culture, the culture of Saudi Arabia
* House of Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is c ...
seeking to restore Hadi in power.militant
The English word ''militant'' is both an adjective and a noun, and it is generally used to mean vigorously active, combative and/or aggressive, especially in support of a cause, as in "militant reformers". It comes from the 15th century Latin " ...
group and Salafi-jihadist terrorist organization ISIL/ISIS/IS/Daesh.
History
Succession of ʿAlī
Shīʿa Muslims believe that just as a prophet is appointed by God alone, only God has the prerogative to appoint the successor to his prophet. They believe God chose ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib to be Muhammad's successor, infallible, the first caliph (''khalīfa'', head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state (polity), state#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international p ...
) of Islam. Shīʿa Muslims believe that Muhammad designated Ali as his successor by God's command ( Eid Al Ghadir). ʿAlī was Muhammad's first-cousin and closest living male relative as well as his son-in-law, having married Muhammad's daughter, Fāṭimah.[Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of World Religions, Wendy Doniger, Consulting Editor, Merriam-Webster, Incorporated, Springfield, MA 1999, , LoC: BL31.M47 1999, p. 525]["Esposito, John. "What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam" Oxford University Press, 2002. . p. 46]
The Party of ʿAlī
Even during the time of Muhammad, there were signs of split among the companions with Salman al-Farsi, Abu Dharr al-Ghifari, Miqdad, and Ammar ibn Yasir amongst the most vehement and loyal supporters of ʿAlī.[
*]
The event of Dhul Asheera
During the revelation of Ash-Shu'ara
Ash-Shu‘ara’ ( ar, الشعراء, ; The Poets) is the 26th chapter (sūrah) of the Qurʾan with 227 verses ( āyāt). Many of these verses are very short. The chapter is named from the worAsh-Shu'arain ayat 224.
The chapter talks about v ...
, the twenty-sixth Surah of the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
, in 617 CE, Muhammad is said to have received instructions to warn his family members against adhering to their pre-Islamic religious practices. There are differing accounts of Muhammad's attempt to do this, with one version stating that he had invited his relatives to a meal (later termed the Feast of Dhul Asheera), during which he gave the pronouncement. According to Ibn Ishaq
Muḥammad ibn Isḥāq ibn Yasār ibn Khiyār (; according to some sources, ibn Khabbār, or Kūmān, or Kūtān, ar, محمد بن إسحاق بن يسار بن خيار, or simply ibn Isḥaq, , meaning "the son of Isaac"; died 767) was an 8 ...
, it consisted of the following speech:
Among those gathered, only ʿAlī offered his consent. Some sources, such as the '' Musnad Ahmad ibn Hanbal'', do not record Muhammad's reaction to this, though Ibn Ishaq continues that he then declared ʿAlī to be his brother, heir and successor. In another narration, when Muhammad accepted ʿAlī's offer, he "threw up his arms around the generous youth, and pressed him to his bosom" and said, "Behold my brother, my vizir, my vicegerent ... let all listen to his words, and obey him." The direct appointment of ʿAlī as heir in this version is notable in that it alleges that his right to succession was established at the very beginning of Muhammad's prophetic activity. The association with the revelation of a Quranic verse also serves the purpose of providing the nomination with authenticity as well as a divine authorization.
Event of Ghadir Khumm
The ''ḥadīth'' report of Ghadir Khumm has many different variations and is transmitted by both Sunnī and Shīʿa sources. The narrations generally state that in March 632, Muhammad, while returning from his Farewell Pilgrimage alongside a large number of followers and companions, stopped at the oasis of Ghadir Khumm. There, he took ʿAlī's hand and addressed the gathering. The point of contention between different sects arises when Muhammad, whilst giving his speech, gave the proclamation "Anyone who has me as his '' mawla'', has ʿAlī as his ''mawla.''" Some versions add the additional sentence "O God, befriend the friend of ʿAlī and be the enemy of his enemy."Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
, with interpretations of Muhammad's use here being split along sectarian lines between the Sunnī and Shīʿa Muslims. Among the former group, the word is translated as "friend" or "one who is loyal/close" and that Muhammad was advocating that ʿAlī was deserving of friendship and respect. Conversely, Shīʿa Muslims tend to view the meaning as being "master" or "ruler", and that the statement was a clear designation of ʿAlī being Muhammad's appointed successor. Shīʿa sources also record further details of the event, such as stating that those present congratulated ʿAlī and acclaimed him as ''Amir al-Mu'minin
Amir al-Mu'minin ( ar, أَمِير ٱلْمُؤْمِنِين, amīr al-muʾminīn) is an Arabic title designating the supreme leader of an Islamic community. It is usually translated as "Commander of the Faithful", though sometimes also as "Prin ...
'' ("commander of the believers").[
]
Caliphate of ʿAlī
 When Muhammad died in 632 CE, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib and Muhammad's closest relatives made the funeral arrangements. While they were preparing his body,
When Muhammad died in 632 CE, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib and Muhammad's closest relatives made the funeral arrangements. While they were preparing his body, Abū Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
, ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
, and Abu Ubaidah ibn al Jarrah met with the leaders of Medina and elected Abū Bakr as caliph. ʿAlī did not accept the caliphate of Abū Bakr and refused to pledge allegiance to him. This is indicated in a ''ḥadīth'' report which both Sunnī and Shīʿa Muslims regard as '' sahih'' (authentic).
Ibn Qutaybah, a 9th-century Sunnī Islamic scholar narrates of ʿAlī:I am the servant of God and the brother of the Messenger of God. I am thus more worthy of this office than you. I shall not give allegiance to you bu Bakr & Umarwhen it is more proper for you to give bayʼah to me. You have seized this office from the Ansar using your tribal relationship to the Prophet as an argument against them. Would you then seize this office from us, the ahl al-bayt by force? Did you not claim before the Ansar that you were more worthy than they of the caliphate because Muhammad came from among you (but Muhammad was never from Abu Bakr's family) – and thus they gave you leadership and surrendered command? I now contend against you with the same argument…It is we who are more worthy of the Messenger of God, living or dead. Give us our due right if you truly have faith in God, or else bear the charge of wilfully doing wrong... Umar, I will not yield to your commands: I shall not pledge loyalty to him.' Ultimately Abu Bakr said, "O 'Ali! If you do not desire to give your bay'ah, I am not going to force you for the same.
ʿAlī's wife and daughter of Muhammad, Fāṭimah, refused to pledge allegiance to Abū Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
and remained angry with him until she died due to the issues of Fadak
Fadak ( ar, فدك) was a village with fertile land in an oasis near Medina. The takeover of Fadak by Muslims in 629 CE was peaceful and a share of it thus belonged to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. After Muhammad died in 632, Fadak was confisc ...
, the inheritance from her father, and the situation of ʿUmar at Fāṭimah's house; this is stated in various Sunnī ''ḥadīth'' collections, including ''Sahih al-Bukhari
Sahih al-Bukhari ( ar, صحيح البخاري, translit=Ṣaḥīḥ al-Bukhārī), group=note is a ''hadith'' collection and a book of '' sunnah'' compiled by the Persian scholar Muḥammad ibn Ismā‘īl al-Bukhārī (810–870) around 846. Al ...
'' and '' Sahih Muslim''. Fāṭimah never pledged allegiance to Abū Bakr; neither did she acknowledge or accept his claim to the caliphate. Almost all members of Banu Hashim, the Quraysh
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qur ...
tribe to which Muhammad belonged, and many of his closest companions (the ''ṣaḥāba'') had supported ʿAlī's cause after the death of Muhammad, whilst others supported Abū Bakr.

 It was not until the murder of the third '' rāshidūn'' caliph, ʿUthmān (657 CE), that the Muslims of
It was not until the murder of the third '' rāshidūn'' caliph, ʿUthmān (657 CE), that the Muslims of Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
in desperation invited ʿAlī to become the fourth caliph as the last source,Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
).civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polic ...
between Muslims within the early Islamic empire. The First Fitna began as a series of revolts fought against ʿAlī, caused by the assassination of his political predecessor, ʿUthmān. While the rebels had previously affirmed the legitimacy of ʿAlī's ''khilafāʾ'' (caliphate), they later turned against ʿAlī and fought him.sujud
Sujūd ( ar, سُجود, ), or sajdah (, ), is the act of low bowing or prostration to God facing the ''qiblah'' (direction of the Kaaba at Mecca). It is usually done in standardized prayers (salah). The position involves kneeling and bowing t ...
''). ʿAlī's main rival, Muawiyah, then claimed the caliphate.
The connection between the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
and Shīʿa Islam was established through the early Muslim conquests. According to Derryl N. Maclean, a link between the Sindh region
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Shīʿas or proto-Shīʿas can be traced to Hakim ibn Jabalah al-Abdi, a companion of Muhammad
The Companions of the Prophet ( ar, اَلصَّحَابَةُ; ''aṣ-ṣaḥāba'' meaning "the companions", from the verb meaning "accompany", "keep company with", "associate with") were the disciples and followers of Muhammad who saw or ...
, who traveled across the Sindh to Makran
Makran ( fa, مكران), mentioned in some sources as Mecran and Mokrān, is the coastal region of Baluchistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in Balochistan, in Pakistan and Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, ...
in the year 649 CE, and presented a report on the area to the caliph. He supported ʿAlī, and died in the Battle of the Camel alongside Sindhi Jats
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subse ...
. He was also a poet and few couplets of his poem in praise of ʿAlī have survived, as reported in Chachnama:
During the caliphate of ʿAlī, many Jats came under the influence of Shīʿa Islam. Harith ibn Murrah Al-abdi and Sayfi ibn Fil' al-Shaybani, both officers of ʿAlī's army, attacked Sindhi bandits and chased them to Al-Qiqan (present-day Quetta) in the year 658 CE. Sayfi was one of the seven Shīʿa Muslims who were beheaded alongside Hujr ibn Adi al-Kindi in 660 CE, near Damascus.
Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī
Upon the death of ʿAlī, his elder son Ḥasan became leader of the Muslims of Kufa, and after a series of skirmishes between the Kufa Muslims and the army of Muawiyah, Ḥasan agreed to cede the caliphate to Muawiyah and maintain peace among Muslims upon certain conditions:
# The enforced public cursing of ʿAlī, e.g. during prayers, should be abandoned
# Muawiyah should not use tax money for his own private needs
# There should be peace, and followers of Ḥasan should be given security and their rights
# Muawiyah will never adopt the title of ''Amir al-Mu'minin
Amir al-Mu'minin ( ar, أَمِير ٱلْمُؤْمِنِين, amīr al-muʾminīn) is an Arabic title designating the supreme leader of an Islamic community. It is usually translated as "Commander of the Faithful", though sometimes also as "Prin ...
'' ("commander of the believers")
# Muawiyah will not nominate any successor
Ḥasan then retired to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, where in 670 CE he was poisoned by his wife Ja'da bint al-Ash'ath ibn Qays, after being secretly contacted by Muawiyah who wished to pass the caliphate to his own son Yazid
Yazīd ( ar, يزيد, links=no, "increasing", "adding more") is an Arabic name and may refer to:
Given name
* Yazid I (647–683), second Umayyad Caliph upon succeeding his father Muawiyah
* Yazid II (687–724), Umayyad caliph
* Yazid III (701� ...
and saw Ḥasan as an obstacle.
Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī
 Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, ʿAlī's younger son and brother to Ḥasan, initially resisted calls to lead the Muslims against Muawiyah and reclaim the caliphate. In 680 CE, Muawiyah died and passed the caliphate to his son
Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, ʿAlī's younger son and brother to Ḥasan, initially resisted calls to lead the Muslims against Muawiyah and reclaim the caliphate. In 680 CE, Muawiyah died and passed the caliphate to his son Yazid
Yazīd ( ar, يزيد, links=no, "increasing", "adding more") is an Arabic name and may refer to:
Given name
* Yazid I (647–683), second Umayyad Caliph upon succeeding his father Muawiyah
* Yazid II (687–724), Umayyad caliph
* Yazid III (701� ...
, and breaking the treaty with Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī. Yazid asked Husayn to swear allegiance ('' bay'ah'') to him. ʿAlī's faction, having expected the caliphate to return to ʿAlī's line upon Muawiyah's death, saw this as a betrayal of the peace treaty and so Ḥusayn rejected this request for allegiance. There was a groundswell of support in Kufa for Ḥusayn to return there and take his position as caliph and Imam, so Ḥusayn collected his family and followers in Medina and set off for Kufa. En route to Kufa, he was blocked by an army of Yazid's men, which included people from Kufa, near Karbala (modern Iraq); Ḥusayn and approximately 72 of his family members and followers were killed in the Battle of Karbala.
Shīʿa Muslims regard Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī as a martyr ('' shahid''), and count him as an Imam from the ''Ahl al-Bayt''. They view Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī as the defender of Islam from annihilation at the hands of Yazid I. Ḥusayn is the last Imam following ʿAlī mutually recognized by all branches of Shīʿa Islam. The Battle of Karbala and martyrdom of Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī is often cited as the definitive separation between the Shīʿa and Sunnī sects of Islam, and is commemorated each year by Shīʿa Muslims on the Day of Ashura.
Imamate of the ''Ahl al-Bayt''
 Later, most denominations of Shīʿa Islam, including Twelvers and Ismāʿīlīs, became Imamis. Imami Shīʿītes believe that Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad.
Later, most denominations of Shīʿa Islam, including Twelvers and Ismāʿīlīs, became Imamis. Imami Shīʿītes believe that Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad.divine decree
''Qadar'' ( ar, قدر, transliterated ''qadar'', meaning literally "power",J. M. Cowan (ed.) (1976). ''The Hans Wehr Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic''. Wiesbaden, Germany: Spoken Language Services. but translated variously as: "Fate", "Di ...
(''nass'') through Muhammad.[Nasr (1979), p. 10]Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God in Islam, God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. So ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
during his lifetime), and other areas of Islamic belief throughout the history of Islam. For instance, the ''ḥadīth'' collections venerated by Shīʿa Muslims are centered on narrations by members of the ''Ahl al-Bayt'' and their supporters, while some ''ḥadīth'' transmitted by narrators not belonging to or supporting the ''Ahl al-Bayt'' are not included. Those of Abu Hurairah, for example, Ibn Asakir in his ''Taʿrikh Kabir'', and Muttaqi in his ''Kanzuʿl-Umma'' report that ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate ...
lashed him, rebuked him, and forbade him to narrate ''ḥadīth'' from Muhammad. ʿUmar is reported to have said: "Because you narrate hadith in large numbers from the Holy Prophet, you are fit only for attributing lies to him. (That is, one expects a wicked man like you to utter only lies about the Holy Prophet.) So you must stop narrating hadith from the Prophet; otherwise, I will send you to the land of Dus." (An Arab clan in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast an ...
, to which Abu Hurairah belonged). According to Sunnī Muslims, ʿAlī was the fourth successor to Abū Bakr, while Shīʿa Muslims maintain that ʿAlī was the first divinely sanctioned "Imam", or successor of Muhammad. The seminal event in Shīʿa history is the martyrdom at the Battle of Karbala of ʿAlī's son, Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, and 71 of his followers in 680 CE, who led a non-allegiance movement against the defiant caliph.
 It is believed in Twelver and Ismāʿīlī branches of Shīʿa Islam that divine wisdom (''ʿaql'') was the source of the souls of the prophets and Imams, which bestowed upon them esoteric knowledge (''ḥikmah''), and that their sufferings were a means of divine grace to their devotees. Although the Imam was not the recipient of a divine revelation (''waḥy''), he had a close relationship with God, through which God guides him, and the Imam, in turn, guides the people.
It is believed in Twelver and Ismāʿīlī branches of Shīʿa Islam that divine wisdom (''ʿaql'') was the source of the souls of the prophets and Imams, which bestowed upon them esoteric knowledge (''ḥikmah''), and that their sufferings were a means of divine grace to their devotees. Although the Imam was not the recipient of a divine revelation (''waḥy''), he had a close relationship with God, through which God guides him, and the Imam, in turn, guides the people. Imamate
{{expand Arabic, date=April 2021
The term imamate or ''imamah'' ( ar, إمامة, ''imāmah'') means "leadership" and refers to the office of an ''imam'' or a state ruled by an ''imam''.
Theology
*Imamate, in Sunni doctrine the caliphate
:* Naqshb ...
, or belief in the divine guide, is a fundamental belief in the Twelver and Ismāʿīlī branches of Shīʿa Islam, and is based on the concept that God would not leave humanity without access to divine guidance.
Imam Mahdi, last Imam of the Shīʿa
 In Shīʿa Islam, Imam Mahdi is regarded as the prophesied eschatological redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine, or nineteen years (according to differing interpretations) before the Day of Judgment and will rid the world of evil. According to Islamic tradition, the Mahdi's tenure will coincide with the
In Shīʿa Islam, Imam Mahdi is regarded as the prophesied eschatological redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine, or nineteen years (according to differing interpretations) before the Day of Judgment and will rid the world of evil. According to Islamic tradition, the Mahdi's tenure will coincide with the Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messi ...
of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
(ʿĪsā), who is to assist the Mahdi against the Masih ad-Dajjal (literally, the "false Messiah" or Antichrist). Jesus, who is considered the ''Masih'' (" Messiah") in Islam, will descend at the point of a white arcade east of Damascus, dressed in yellow robes with his head anointed. He will then join the Mahdi in his war against the Dajjal, where it is believed the Mahdi will slay the Dajjal and unite humankind.
Historians dispute over the origins of Shīʿa Islam, with many Western scholars positing that Shīʿīsm began as a political faction rather than a truly religious movement.[Francis Robinson, ''Atlas of the Islamic World'', p. 23.] Other scholars disagree, considering this concept of religious-political separation to be an anachronistic application of a Western concept.
Dynasties
In the century following the Battle of Karbala (680 CE), as various Shia-affiliated groups diffused in the emerging Islamic world, several nations arose based on a Shia leadership or population.
* Idrisids (788–985 CE): a Zaydi dynasty in what is now Morocco
*Qarmatians
The Qarmatians ( ar, قرامطة, Qarāmiṭa; ) were a militant Isma'ilism, Isma'ili Shia Islam, Shia movement centred in Al-Ahsa Oasis, al-Hasa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a Utopia#Religious utopias, religious-utopian Socialis ...
(899–1077 CE): an Ismaili
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sa ...
Iranian dynasty. Their headquarters were in East Arabia and Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
. It was founded by Abu Sa'id al-Jannabi.
* Buyids (934–1055 CE): a Twelver Iranian dynasty. at its peak consisted of large portions of modern Iraq and Iran.
* Uqaylids (990–1096 CE): a Shia Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
dynasty with several lines that ruled in various parts of Al-Jazira, northern Syria and Iraq.
* Ilkhanate (1256–1335): a Persianate Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mong ...
established in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
in the 13th century, considered a part of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
. The Ilkhanate was based, originally, on Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr /> Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent) Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin ...
's campaigns in the Khwarezmid Empire in 1219–1224, and founded by Genghis's grandson, Hulagu, in territories which today comprise most of Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Turkey, and Pakistan. The Ilkhanate initially embraced many religions, but was particularly sympathetic to Buddhism and Christianity. Later Ilkhanate rulers, beginning with Ghazan in 1295, embraced Islam his brother Öljaitü promoted Shia Islam.
* Bahmanids (1347–1527): a Shia Muslim state of the Deccan in southern India and one of the great medieval Indian kingdoms. Bahmanid Sultanate was the first independent Islamic Kingdom in South India.
Fatimid Caliphate
 * Fatimids (909–1171 CE): Controlled much of North Africa, the
* Fatimids (909–1171 CE): Controlled much of North Africa, the Levant
The Levant () is an approximation, approximate historical geography, historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology an ...
, parts of Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
and Mecca and Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
. The group takes its name from Fatima, Muhammad's daughter, from whom they claim descent.
* In 909 CE the Shi'i military leader Abu Abdallah al-Shiʻi, overthrew the Sunni ruler in Northern Africa; which began the Fatimid regime.Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo met ...
and the great al-Azhar Mosque. A Greek slave by origin, he was freed by Al-Mu'izz.
Safavid Empire
 A major turning point in the history of Shīʿa Islam was the dominion of the
A major turning point in the history of Shīʿa Islam was the dominion of the Safavid dynasty
The Safavid dynasty (; fa, دودمان صفوی, Dudmâne Safavi, ) was one of Iran's most significant ruling dynasties reigning from 1501 to 1736. Their rule is often considered the beginning of modern Iranian history, as well as one of th ...
(1501–1736) in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkme ...
. This caused a number of changes in the Muslim world:
* The ending of the relative mutual tolerance between Sunnīs and Shīʿas that existed from the time of the Mongol conquests onwards and the resurgence of antagonism between the two groups.
* Initial dependence of Shīʿīte clerics on the state followed by the emergence of an independent body of '' ulama'' capable of taking a political stand different from official policies.
* The growth in importance of Persian centers of Islamic education and religious learning, which resulted in the change of Twelver Shīʿīsm from being a predominantly Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
phenomenon to become predominantly Persian.
* The growth of the Akhbari school of thought, which taught that only the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , sing.: ...
, ''ḥadīth'' literature, and ''sunnah
In Islam, , also spelled ( ar, سنة), are the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad that constitute a model for Muslims to follow. The sunnah is what all the Muslims of Muhammad's time evidently saw and followed and passed ...
'' (accounts of the sayings and living habits attributed to the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God in Islam, God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. So ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
during his lifetime) are to be bases for verdicts, rejecting the use of reasoning.
With the fall of the Safavids, the state in Persia—including the state system of courts with government-appointed judges (''qāḍī'')—became much weaker. This gave the ''sharīʿa'' courts of ''mujtahid
''Ijtihad'' ( ; ar, اجتهاد ', ; lit. physical or mental ''effort'') is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning by an expert in Islamic law, or the thorough exertion of a jurist's mental faculty in finding a solution to a le ...
'' an opportunity to fill the legal vacuum and enabled the ''ulama'' to assert their judicial authority. The Usuli school of thought also increased in strength at this time.
File:The declaration of Shi'ism as the state religion of Iran by Shah Ismail -Safavids dynasty.jpeg, The declaration of Twelver Shīʿīsm as the state religion of Safavid Persia
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
.
File:Battle of Chaldiran (1514).jpg, Battle of Chaldiran in 1514, was a major sectarian crisis between Muslims in the Middle East.
File:Chaldiran Battlefield Site in 2004.JPG, Monument commemorating the Battle of Chaldiran, where more than 7000 Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
of the Shīʿa and Sunnī sects killed each other.
Persecution of Shīʿa Muslims
 The history of Shīʿa—Sunnī relations has often involved religious discrimination,
The history of Shīʿa—Sunnī relations has often involved religious discrimination, persecution
Persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or group by another individual or group. The most common forms are religious persecution, racism, and political persecution, though there is naturally some overlap between these term ...
, and violence, dating back to the earliest development of the two competing sects.
At various times throughout the history of Islam, Shīʿa groups and minorities have faced persecution perpetrated by Sunnī Muslims.
Militarily established and holding control over the Umayyad government, many Sunnī rulers perceived the Shīʿas as a threat—both to their political and religious authority. The Sunnī rulers under the Umayyad dynasty sought to marginalize the Shīʿa minority, and later the Abbasids turned on their Shīʿa allies and imprisoned, persecuted, and killed them. The persecution of Shīʿa Muslims throughout history by their Sunnī co-religionists has often been characterized by brutal and genocidal
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Latin ...
acts. Comprising only about 10–15% of the global Muslim population,sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
Selim I (1512–1520) ordered the massacre of 40,000 Alevis and Bektashi (Anatolian Shīʿa Muslims). According to Jalal Al-e-Ahmad, "Sultan Selim I carried things so far that he announced that the killing of one Shīʿa had as much otherworldly reward as killing 70 Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
." In 1802, the Al Saud- Wahhabi armies of the Ikhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
from the First Saudi State (1727–1818) attacked and sacked the city of Karbala, the Shīʿa shrine in Najaf (eastern region of Iraq) that commemorates the martyrdom and death of Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī.
Under Saddam Hussein's Ba'athist regime in Iraq (1968–2003), Shīʿa Muslims were heavily persecuted, arrested, tortured, and killed. In March 2011, the Malaysian government declared Shīʿa Islam a "deviant" sect and banned Shīʿa Muslims from promoting their faith to other Muslims, but left them free to practice it themselves privately.
The most recent and grave attempt by Sunnī Muslims to entirely eradicate the Shīʿa community through violent means was the large-scale genocide of Shīʿa Muslims organized and perpetrated by ISIL/ISIS/IS/Daesh in Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Iraq between 2014 and 2018,
militant
The English word ''militant'' is both an adjective and a noun, and it is generally used to mean vigorously active, combative and/or aggressive, especially in support of a cause, as in "militant reformers". It comes from the 15th century Latin " ...
group and Salafi-jihadist terrorist organization.
See also
* Alawi Islam
* Anti-Shi'ism
* Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam dates from the initial ideological rift among early Muslims that led to the two primary denominations of Islam, the Sunnis and the Shias. The question of succession to Muhammad in Islam, the nature of the Imamat ...
* History of Shia Islam
* Imamate in Shia doctrine
** Imamate and guardianship of Ali ibn Abi Talib
** Imamate in Ismaili doctrine
** Imamate in Nizari doctrine
The Imamate in Nizari Isma'ili doctrine ( ar, إمامة) is a concept in Nizari Isma'ilism which defines the political, religious and spiritual dimensions of authority concerning Islamic leadership over the nation of believers. The primary fun ...
** Imamate in Twelver doctrine
Imāmah ( ar, إِمَامَة) means " leadership" and is a concept in Twelver theology. The Twelve Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad, the Prophet of Islam, in the Twelver branch of Shia Islam. According to Tw ...
* Intellectual proofs in Shia jurisprudence
* List of Shia books
* List of Shia Islamic dynasties
* List of Shia Muslim scholars of Islam
* List of Shia Muslims
* Shia clergy
* Shia crescent
* Shia genocide
* Shia Islam in the Indian subcontinent
* Shia nations
The Shia Crescent (or Shiite Crescent) is the notionally crescent-shaped region of the Middle East where the majority population is Shia or where there is a strong Shia minority in the population.
In recent years the term has come to identify are ...
* Shia Rights Watch
* Shia view of Ali
Ali was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a member of the ''Ahl al-Bayt''. According to Shias, Ali was the first Imam who is believed to be the rightful successor to Muhammad, divinely appointed successors of Mu ...
* Shia view of the Quran
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Shi'a Minorities in the Contemporary World: Migration, Transnationalism and Multilocality. United Kingdom, Edinburgh University Press, 2020.
*
*
External links
*
*
*
{{Authority control
 The Shīʿa version of the '' Shahada'', the Islamic profession of faith, differs from that of the Sunnīs. The Sunnī version of the ''Shahada'' states "There is no god except God, Muhammad is the messenger of God", but to this declaration of faith Shīʿa Muslims append the phrase ''Ali-un-Waliullah'' (: "ʿAlī is the '' Wali'' (custodian) of God"). The basis for the Shīʿa belief in ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as the ''Wali'' of God is derived from the Quranic verse , the " Verse of Wilayah".
This additional phrase to the declaration of faith embodies the Shīʿa emphasis on the inheritance of authority through Muhammad's family and lineage. The three clauses of the Shīʿa version of the ''Shahada'' thus address the fundamental Islamic beliefs of ''
The Shīʿa version of the '' Shahada'', the Islamic profession of faith, differs from that of the Sunnīs. The Sunnī version of the ''Shahada'' states "There is no god except God, Muhammad is the messenger of God", but to this declaration of faith Shīʿa Muslims append the phrase ''Ali-un-Waliullah'' (: "ʿAlī is the '' Wali'' (custodian) of God"). The basis for the Shīʿa belief in ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as the ''Wali'' of God is derived from the Quranic verse , the " Verse of Wilayah".
This additional phrase to the declaration of faith embodies the Shīʿa emphasis on the inheritance of authority through Muhammad's family and lineage. The three clauses of the Shīʿa version of the ''Shahada'' thus address the fundamental Islamic beliefs of '' ''Ismah'' is the concept of infallibility or "divinely bestowed freedom from error and sin" in Islam. Muslims believe that Muhammad, along with other prophets and messengers in Islam, possessed ''ismah''. Twelver and Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa Muslims also attribute the quality to Imams as well as to Fāṭimah, daughter of Muhammad, in contrast to the Zaydī Shīʿas, who don't attribute ''ismah'' to the Imams. Though initially beginning as a political movement, infallibility and sinlessness of the Imams later evolved as a distinct belief of (non-Zaydī) Shīʿīsm.
According to Shīʿa Muslim theologians, infallibility is considered a rational, necessary precondition for spiritual and religious guidance. They argue that since God has commanded absolute obedience from these figures, they must only order that which is right. The state of infallibility is based on the Shīʿa interpretation of the Verse of Purification. Thus, they are the most pure ones, the only immaculate ones preserved from, and immune to, all uncleanness. It doesn't mean that supernatural powers prevent them from committing a sin, but due to the fact that they have absolute belief in God, they refrain from doing anything that is a sin.
They also have a complete knowledge of God's will. They are in possession of all knowledge brought by the angels to the prophets (''nabī'') and the messengers (''rāsūl''). Their knowledge encompasses the totality of all times. Thus, they are believed to act without fault in religious matters. Shīʿa Muslims regard ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as the successor of Muhammad not only ruling over the entire Muslim community in justice, but also interpreting the Islamic faith, practices, and its esoteric meaning. Hence he was regarded as being free from error and sin (infallible), and appointed by God by divine decree ('' nass'') to be the first Imam. ʿAlī is regarded as a "perfect man" (''al-insan al-kamil'') similar to Muhammad, according to the Shīʿa viewpoint.
''Ismah'' is the concept of infallibility or "divinely bestowed freedom from error and sin" in Islam. Muslims believe that Muhammad, along with other prophets and messengers in Islam, possessed ''ismah''. Twelver and Ismāʿīlī Shīʿa Muslims also attribute the quality to Imams as well as to Fāṭimah, daughter of Muhammad, in contrast to the Zaydī Shīʿas, who don't attribute ''ismah'' to the Imams. Though initially beginning as a political movement, infallibility and sinlessness of the Imams later evolved as a distinct belief of (non-Zaydī) Shīʿīsm.
According to Shīʿa Muslim theologians, infallibility is considered a rational, necessary precondition for spiritual and religious guidance. They argue that since God has commanded absolute obedience from these figures, they must only order that which is right. The state of infallibility is based on the Shīʿa interpretation of the Verse of Purification. Thus, they are the most pure ones, the only immaculate ones preserved from, and immune to, all uncleanness. It doesn't mean that supernatural powers prevent them from committing a sin, but due to the fact that they have absolute belief in God, they refrain from doing anything that is a sin.
They also have a complete knowledge of God's will. They are in possession of all knowledge brought by the angels to the prophets (''nabī'') and the messengers (''rāsūl''). Their knowledge encompasses the totality of all times. Thus, they are believed to act without fault in religious matters. Shīʿa Muslims regard ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as the successor of Muhammad not only ruling over the entire Muslim community in justice, but also interpreting the Islamic faith, practices, and its esoteric meaning. Hence he was regarded as being free from error and sin (infallible), and appointed by God by divine decree ('' nass'') to be the first Imam. ʿAlī is regarded as a "perfect man" (''al-insan al-kamil'') similar to Muhammad, according to the Shīʿa viewpoint.
 Shīʿa religious practices, such as prayers, differ only slightly from the Sunnīs. While all Muslims pray five times daily, Shīʿa Muslims have the option of combining '' Dhuhr'' with '' Asr'' and '' Maghrib'' with '' Isha''', as there are three distinct times mentioned in the
Shīʿa religious practices, such as prayers, differ only slightly from the Sunnīs. While all Muslims pray five times daily, Shīʿa Muslims have the option of combining '' Dhuhr'' with '' Asr'' and '' Maghrib'' with '' Isha''', as there are three distinct times mentioned in the 
 It is estimated that either 10–20% or 10–13% of the global Muslim population are Shīʿas. They may number up to 200 million as of 2009. As of 1985, Shīʿa Muslims are estimated to be 21% of the Muslim population in
It is estimated that either 10–20% or 10–13% of the global Muslim population are Shīʿas. They may number up to 200 million as of 2009. As of 1985, Shīʿa Muslims are estimated to be 21% of the Muslim population in  Twelver doctrine is based on five principles. These five principles known as ''Usul ad-Din'' are as follow:
# Monotheism: God is one and unique;
# Justice: the concept of moral rightness based on ethics, fairness, and equity, along with the punishment of the breach of these ethics;
# Prophethood: the institution by which God sends emissaries, or prophets, to guide humankind;
# Leadership: a divine institution which succeeded the institution of Prophethood. Its appointees (''Imams'') are divinely appointed;
# Resurrection and Last Judgment: God's final assessment of humanity.
More specifically, these principles are known as ''Usul al-Madhhab'' (principles of the Shīʿa branch of Islam) according to Twelver Shīʿas, which differ from ''Daruriyat al-Din'' ("Necessities of Religion"), which are principles in order for one to be a Muslim. ''Daruriyat al-Din'' don't include leadership (''Imamah''), as it is not a requirement in order for one to be recognized as a Muslim. However, this category, according to Twelver scholars like
Twelver doctrine is based on five principles. These five principles known as ''Usul ad-Din'' are as follow:
# Monotheism: God is one and unique;
# Justice: the concept of moral rightness based on ethics, fairness, and equity, along with the punishment of the breach of these ethics;
# Prophethood: the institution by which God sends emissaries, or prophets, to guide humankind;
# Leadership: a divine institution which succeeded the institution of Prophethood. Its appointees (''Imams'') are divinely appointed;
# Resurrection and Last Judgment: God's final assessment of humanity.
More specifically, these principles are known as ''Usul al-Madhhab'' (principles of the Shīʿa branch of Islam) according to Twelver Shīʿas, which differ from ''Daruriyat al-Din'' ("Necessities of Religion"), which are principles in order for one to be a Muslim. ''Daruriyat al-Din'' don't include leadership (''Imamah''), as it is not a requirement in order for one to be recognized as a Muslim. However, this category, according to Twelver scholars like  The ''Twelve Imams'' are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad for the Twelvers. According to the theology of Twelvers, the successor of Muhammad is an infallible human individual who not only rules over the Muslim community with justice but also is able to keep and interpret the divine law (''sharīʿa'') and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the Twelve Imams are a guide and model for the Muslim community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin, and Imams must be chosen by
The ''Twelve Imams'' are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad for the Twelvers. According to the theology of Twelvers, the successor of Muhammad is an infallible human individual who not only rules over the Muslim community with justice but also is able to keep and interpret the divine law (''sharīʿa'') and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the Twelve Imams are a guide and model for the Muslim community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin, and Imams must be chosen by  Though there are several subsects amongst the Ismāʿīlīs, the term in today's vernacular generally refers to the Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī Nizārī community, often referred to as the ''Ismāʿīlīs'' by default, who are followers of the Aga Khan and the largest group within Ismāʿīlīsm. Another Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī community are the Dawudi Bohras, led by a '' Da'i al-Mutlaq'' ("Unrestricted Missionary") as representative of a hidden Imam. While there are many other branches with extremely differing exterior practices, much of the spiritual theology has remained the same since the days of the faith's early Imams. In recent centuries, Ismāʿīlīs have largely been an Indo-Iranian community, but they can also be found in
Though there are several subsects amongst the Ismāʿīlīs, the term in today's vernacular generally refers to the Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī Nizārī community, often referred to as the ''Ismāʿīlīs'' by default, who are followers of the Aga Khan and the largest group within Ismāʿīlīsm. Another Shīʿa Imami Ismāʿīlī community are the Dawudi Bohras, led by a '' Da'i al-Mutlaq'' ("Unrestricted Missionary") as representative of a hidden Imam. While there are many other branches with extremely differing exterior practices, much of the spiritual theology has remained the same since the days of the faith's early Imams. In recent centuries, Ismāʿīlīs have largely been an Indo-Iranian community, but they can also be found in 
 Zaydīsm, otherwise known as Zaydīyyah or Zaydī, is a branch of Shīʿa Islam named after Zayd ibn ʿAlī. Followers of the Zaydī school of jurisprudence are called Zaydīs or occasionally ''Fivers''. However, there is also a group called ''Zaydī Wasītīs'' who are Twelvers (see below). Zaydīs constitute roughly 42–47% of the population of Yemen.
Zaydīsm, otherwise known as Zaydīyyah or Zaydī, is a branch of Shīʿa Islam named after Zayd ibn ʿAlī. Followers of the Zaydī school of jurisprudence are called Zaydīs or occasionally ''Fivers''. However, there is also a group called ''Zaydī Wasītīs'' who are Twelvers (see below). Zaydīs constitute roughly 42–47% of the population of Yemen.
 When Muhammad died in 632 CE, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib and Muhammad's closest relatives made the funeral arrangements. While they were preparing his body,
When Muhammad died in 632 CE, ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib and Muhammad's closest relatives made the funeral arrangements. While they were preparing his body, 
 Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, ʿAlī's younger son and brother to Ḥasan, initially resisted calls to lead the Muslims against Muawiyah and reclaim the caliphate. In 680 CE, Muawiyah died and passed the caliphate to his son
Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī, ʿAlī's younger son and brother to Ḥasan, initially resisted calls to lead the Muslims against Muawiyah and reclaim the caliphate. In 680 CE, Muawiyah died and passed the caliphate to his son  Later, most denominations of Shīʿa Islam, including Twelvers and Ismāʿīlīs, became Imamis. Imami Shīʿītes believe that Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad. Imams are human individuals who not only rule over the Muslim community with justice, but also are able to keep and interpret the divine law and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the Imams are a guide and model for the community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin, and must be chosen by
Later, most denominations of Shīʿa Islam, including Twelvers and Ismāʿīlīs, became Imamis. Imami Shīʿītes believe that Imams are the spiritual and political successors to Muhammad. Imams are human individuals who not only rule over the Muslim community with justice, but also are able to keep and interpret the divine law and its esoteric meaning. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the Imams are a guide and model for the community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin, and must be chosen by  It is believed in Twelver and Ismāʿīlī branches of Shīʿa Islam that divine wisdom (''ʿaql'') was the source of the souls of the prophets and Imams, which bestowed upon them esoteric knowledge (''ḥikmah''), and that their sufferings were a means of divine grace to their devotees. Although the Imam was not the recipient of a divine revelation (''waḥy''), he had a close relationship with God, through which God guides him, and the Imam, in turn, guides the people.
It is believed in Twelver and Ismāʿīlī branches of Shīʿa Islam that divine wisdom (''ʿaql'') was the source of the souls of the prophets and Imams, which bestowed upon them esoteric knowledge (''ḥikmah''), and that their sufferings were a means of divine grace to their devotees. Although the Imam was not the recipient of a divine revelation (''waḥy''), he had a close relationship with God, through which God guides him, and the Imam, in turn, guides the people.  In Shīʿa Islam, Imam Mahdi is regarded as the prophesied eschatological redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine, or nineteen years (according to differing interpretations) before the Day of Judgment and will rid the world of evil. According to Islamic tradition, the Mahdi's tenure will coincide with the
In Shīʿa Islam, Imam Mahdi is regarded as the prophesied eschatological redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine, or nineteen years (according to differing interpretations) before the Day of Judgment and will rid the world of evil. According to Islamic tradition, the Mahdi's tenure will coincide with the  * Fatimids (909–1171 CE): Controlled much of North Africa, the
* Fatimids (909–1171 CE): Controlled much of North Africa, the  A major turning point in the history of Shīʿa Islam was the dominion of the
A major turning point in the history of Shīʿa Islam was the dominion of the