Delayed puberty is when a person lacks or has incomplete development of specific
sexual characteristics
Sexual characteristics are physical traits of an organism (typically of a sexually dimorphic organism) which are indicative of its biological sex. These can include sex organs used for reproduction and secondary sex characteristics which distingui ...
past the usual age of onset of
puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
.
The person may have no physical or
hormonal signs that puberty has begun. In the United States, girls are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack breast development by age 13 or have not started menstruating by age 15.
Boys are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack enlargement of the testicles by age 14.
Delayed puberty affects about 2% of adolescents.
Most commonly, puberty may be delayed for several years and still occur normally, in which case it is considered constitutional delay of growth and puberty, a common variation of healthy physical development.
Delay of puberty may also occur due to various causes such as
malnutrition, various
systemic diseases, or defects of the
reproductive system (
hypogonadism) or the body's responsiveness to
sex hormones.
Initial workup for delayed puberty not due to a chronic condition involves measuring serum
FSH,
LH,
testosterone/
estradiol, as well as bone age radiography.
If it becomes clear that there is a permanent defect of the reproductive system, treatment usually involves replacement of the appropriate hormones (
testosterone/
dihydrotestosterone for boys,
and
progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the m ...
for girls).
Timing and definitions
Puberty is considered delayed when the child has not begun puberty when two
standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while ...
s or about 95% of children from similar backgrounds have.
In North American girls, puberty is considered delayed when breast development has not begun by age 13, when they have not started menstruating by age 15,
and when there is no increased growth rate.
Furthermore, slowed progression through the
Tanner scale or lack of
menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility.
Gir ...
within 3 years of breast development may also be considered delayed puberty.
In the United States, the age of onset of puberty in girls depends heavily on their racial background. Delayed puberty means the lack of breast development by age 12.8 years for White girls, and by age 12.4 years for Black girls.
The lack of menstruation by age 15 in any ethnic background is considered delayed.
In North American boys, puberty is considered delayed when the testes remain less than 2.5 cm in diameter
or less than 4 mL in volume by the age of 14.
Delayed puberty is more common in males.
Although absence of pubic and/or axillary hair is common in children with delayed puberty, the presence of sexual hair is due to adrenal sex hormone secretion unrelated to the sex hormones produced by the ovaries or testes.
The age of onset of puberty is dependent on genetics, general health, socioeconomic status, and environmental exposures. Children residing closer to the equator, at lower altitudes, in cities and other urban areas generally begin the process of puberty earlier than their counterparts.
Mildly obese to morbidly obese children are also more likely to begin puberty earlier than children of normal weight.
Variation in genes related to obesity such as FTO or NEGRI have been associated with earlier onset of puberty.
Children whose parents started puberty at an earlier age were also more likely to experience it themselves, especially in women where onset of menstruation correlated well between mothers and daughters and between sisters.
Causes
Pubertal delay can be separated into four categories from most to least common:
Constitutional and physiologic delay
Children who are healthy but have a slower rate of physical development than average have a
constitutional delay
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty (CDGP) is a term describing a temporary delay in the skeletal growth and thus height of a child with no physical abnormalities causing the delay. Short stature may be the result of a growth pattern inher ...
with a subsequent delay in puberty. It is the most common cause of delayed puberty in girls
(30%)
and even more so in boys
(65%).
It is commonly inherited with as much as 80% of the variation in the age of onset of puberty due to genetic factors.
These children have a history of shorter stature than their age-matched peers throughout childhood, but their height is appropriate for
bone age, meaning that they have delayed skeletal maturation with potential for future growth.
It is often difficult to establish if it is a true constitutional delay of growth and puberty or if there is an underlying pathology because lab tests are not always discriminatory.
In absence of any other symptoms, short stature, delayed growth in height and weight, and/or delayed puberty may be the only clinical manifestations of certain chronic diseases including
coeliac disease.
Malnutrition or chronic disease
When underweight or sickly children present with pubertal delay, it is warranted to search for illnesses that cause a temporary and reversible delay in puberty.
Chronic conditions such as
sickle cell disease and
thalassemia
Thalassemias are inherited blood disorders characterized by decreased hemoglobin production. Symptoms depend on the type and can vary from none to severe. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin). Anemia can result ...
,
cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
,
HIV/AIDS,
hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
,
chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
,
and chronic gastroenteric disorders (such as
coeliac disease and
inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammation, inflammatory conditions of the colon (anatomy), colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine a ...
) cause a delayed activation of the
hypothalamic
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus i ...
region of the brain to send signals to start puberty.
Childhood cancer survivors can also present with delayed puberty secondary to their cancer treatments, especially males.
The type of treatment, amount of exposure/dosage of drugs, and age during treatment determine the level by which the
gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
s are affected with younger patients at a lower risk of negative reproductive effects.
Excessive physical exercise and physical stress, especially in athletes can also delay pubertal onset.
Eating disorders such as
bulimia nervosa and
anorexia nervosa can also impair puberty due to
undernutrition.
Carbohydrate-restricted diet
Low-carbohydrate diets restrict carbohydrate consumption relative to the average diet. Foods high in carbohydrates (e.g., sugar, bread, pasta) are limited, and replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of fat and protein (e.g., meat ...
s for weight loss has also been shown to decrease the stimulation of
insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
which in turn does not stimulate
kisspeptin neurons vital in the release of puberty-starting hormones. This shows that carbohydrate restricted children and children with
diabetes mellitus type 1 can have delayed puberty.
Primary failure of the ovaries or testes (hypergonadotropic hypogonadism)

Primary failure of the
ovaries or
testes (
gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
s) will cause delayed puberty due to the lack of hormonal response by the final receptors of the
HPG axis HPG may refer to:
* Huppuguda railway station, in Hyderabad, India
* Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis
* People's Defence Forces (Kurdish: '), the armed wing of the Kurdistan Workers' Party
* Shennongjia Hongping Airport, in Hubei, China
* ...
.
In this scenario, the brain sends a lot of hormonal signals (high
gonadotropin), but the gonads are unable to respond to said signals causing
hypergonadotropic hypogonadism.
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism can be caused by congenital defects or acquired defects.
Congenital disorders
Congenital diseases include untreated
cryptorchidism where the
testicles fail to descend from the abdomen.
Other congenital disorders are genetic in nature. In males, there can be deformities in the
seminiferous tubule as in
Klinefelter syndrome (most common cause in males),
defects in the production of testicular steroids, receptor mutations preventing testicular hormones from working, chromosomal abnormalities such as
Noonan syndrome, or problems with the cells making up the testes.
Females can also have chromosomal abnormalities such as
Turner syndrome (most common cause in girls),
, and
XY gonadal dysgenesis, problems in the ovarian hormone synthesis pathway such as
aromatase deficiency
Aromatase deficiency is an exceedingly rare condition characterized by extremely low levels or complete absence of the enzyme aromatase activity in the body. It is an autosomal recessive disease resulting from various mutations of gene CPY19 (P450 ...
or congenital anatomical deformities such as
Müllerian agenesis.
Acquired disorders
Acquired diseases include
mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts Gener ...
orchitis,
Coxsackievirus
Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the ''Picornaviridae'' family of viral envelope, nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus ''Enterovirus'', which also includes poliovi ...
B infection, irradiation,
chemotherapy, or trauma; all problems causing the gonads to fail.
Genetic or acquired defect of the hormonal pathway of puberty (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism)
The
hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis can also be affected at the level of the brain.
The brain does not send its hormonal signals to the gonads (low
gonadotropins) causing the gonads to never be activated in the first-place resulting in
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
The HPG axis can be altered in two places, at the hypothalamic or at the pituitary level.
CNS disorders such as childhood brain tumors (''e.g.''
craniopharyngioma,
prolactinoma,
germinoma
A germinoma is a type of germ-cell tumor, which is not differentiated upon examination. It may be benign or malignant.
Cause
Germinomas are thought to originate from an error of development, when certain primordial germ cells fail to migrate pro ...
,
glioma) can disrupt the communication between the hypothalamus and the pituitary.
Pituitary tumors, especially
prolactinomas, can increase the level of dopamine causing an inhibiting effect to the HPG axis.
Hypothalamic disorders include
Prader-Willi syndrome and
Kallmann syndrome,
but the most common cause of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is a functional deficiency in the hormone regulator produced by the hypothalamus,
the gonadotropin-releasing hormone or GnRH.
Diagnosis
Pediatric endocrinologists are the physicians with the most training and experience evaluating delayed puberty. A complete medical history, review of systems, growth pattern, and physical examination as well as laboratory testing and imaging will reveal most of the systemic diseases and conditions capable of arresting development or delaying puberty, as well as providing clues to some of the recognizable
syndromes affecting the reproductive system.
Timely medical assessment is a necessity since as many as half of girls with delayed puberty have an underlying pathology.
History and physical
Constitutional and physiologic delay
Children with constitutional delay are reported to be shorter than their peers, lacking a
growth spurt, and having an overall smaller build.
Their growth has begun to slow down years before the expected growth spurt secondary to puberty, which helps differentiate a constitutional delay from an HPG-axis related disorder.
A complete family history with the ages at which parents hit the pubertal milestones can also provide a reference point for the expected age of puberty.
Growth measurement parameters in children with suspected constitutional delay include a height, a weight, the rate of growth, and the calculated mid-parental height which represents the expected adult height for the child.
Malnutrition or chronic disease
Diet and physical activity habits, as well as history of previous serious illnesses and medication history can provide clues as to the cause of delayed puberty.
Delayed growth and puberty can be the first signs of severe chronic illnesses such as metabolic disorders including
inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammation, inflammatory conditions of the colon (anatomy), colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine a ...
and
hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
.
Symptoms such as fatigue, pain, and abnormal stooling pattern are suggestive of an underlying chronic condition.
Low
BMI can lead a physician to diagnose an eating disorder,
undernutrition, child abuse, or chronic gastrointestinal disorders.
Primary failure of the ovaries or testes
A
eunuchoid body shape where the arm span exceeds the height by more than 5 cm suggests a delay in growth plate closure secondary to
hypogonadism.
has unique diagnostic features including a webbed neck, short stature, shield chest, and low hairline.
presents with tall stature as well as small, firm testes.
Genetic or acquired defect of the hormonal pathway of puberty
Lacking the sense of smell (
anosmia) along with delayed puberty are strong clinical indications for
Kallmann syndrome.
[Male Hypogonadism. Friedrich Jockenhovel. Uni-Med Science. 2004. . Chapter 3. Diagnostic work up of hypogonadism.] Deficiencies in GnRH, the signalling hormone produced by the hypothalamus, can cause congenital malformations including cleft lip and scoliosis.
The presence of neurological symptoms including headaches and visual disturbances suggest a brain disorder such as a brain tumor causing
hypopituitarism.
The presence of neurological symptoms in addition to
lactation are signs of high prolactin levels and could indicate either a drug side effect or a
prolactinoma.
Imaging
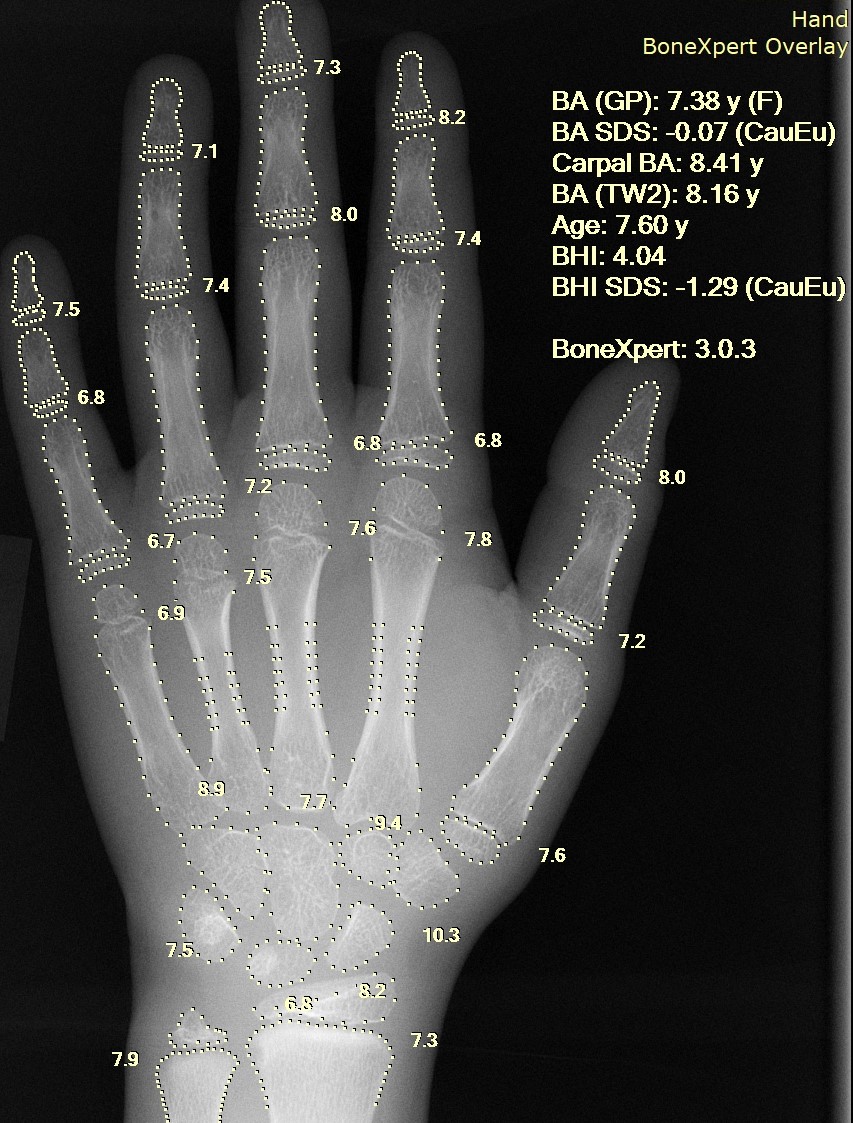
Since bone maturation is a good indicator of overall physical maturation, an
x-ray of the left hand and wrist to assess
bone age usually reveals whether the child has reached a stage of physical maturation at which puberty should be occurring.
X-ray displaying a bone age <11 years in girls or <13 years in boys (despite a higher chronological age) is most often consistent with constitutional delay of puberty.
An MRI of the brain should be considered if neurological symptoms are present in addition to delayed puberty, two findings suspicious for pituitary or hypothalamic tumors.
An MRI can also confirm the diagnosis of
Kallmann syndrome due to the absence or abnormal development of the olfactory tract.
However, in the absence of clear neurological symptoms, an MRI may not be the most cost-effective option.
A pelvic ultrasound can detect anatomical abnormalities including undescended testes and
müllerian agenesis.
Laboratory evaluation

The first step in evaluating children with delayed puberty involves differentiating between the different causes of delayed puberty. Constitutional delay can be evaluated with a thorough history, physical, and bone age.
Malnutrition and chronic diseases can be diagnosed through history and disease-specific testing.
Screening studies include a complete blood count, an
erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and thyroid studies.
can be differentiated between hyper- and hypo-gonadotropic hypogonadism by measuring serum
follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, an ...
(FSH) and
luteinizing hormone (LH) (
gonadotropins to measure pituitary output), and estradiol in girls (to measure gonadal output).
By the age of 10–12, children with failure of the ovaries or testes will have high LH and FSH because the brain is attempting to jump-start puberty, but the gonads are not responsive to these signals.
Stimulating the body by administering an artificial version of
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH, the hypothalamic hormone) can differentiate between constitutional delay of puberty and a GnRH deficiency in boys, although no studies have been done in girls to prove this.
It is often sufficient to simply measure the baseline gonadotrophin levels to differentiate between the two.
In girls with
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, a serum
prolactin level is measured to identify if they have the pituitary tumor
prolactinoma. High levels of prolactin would warrant further testing with MRI imaging, except if drugs inducing the production of prolactin can be identified.
If the child has any neurological symptoms, it is highly recommended that the physician obtains a head MRI to detect possible brain lesions.
In girls with
hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, a
karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
can identify chromosomal abnormalities, the most common of which is
Turner syndrome.
In boys, a karyotype is indicated if the child may have a congenital gonadal defect such as
Klinefelter syndrome.
In children with a normal karyotype, defects in the synthesis of the
adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
steroid sex hormones can be identified by measuring
17-hydroxylase
Cytochrome P450 17A1 (steroid 17α-monooxygenase, 17α-hydroxylase, 17-alpha-hydroxylase, 17,20-lyase, 17,20-desmolase) is an enzyme of the hydroxylase type that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP17A1'' gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expr ...
, an important enzyme involved in the production of sex hormones.
Management
The goals of short-term hormone therapy are to induce the beginning of sexual development and induce a growth spurt, but should be limited to children with severe distress or anxiety secondary to their delayed puberty.
Bone age must be monitored frequently to prevent precocious closure of the bone plates, thereby stunting growth.
Constitutional and physiologic delay
If a child is healthy with a constitutional delay of growth and puberty, reassurance and prediction based on the bone age can be provided.
No other intervention is usually necessary, but repeat evaluation by measuring serum testosterone or estrogen is recommended.
Furthermore, the diagnosis of
hypogonadism can be excluded once the adolescent has started puberty by age 16–18.
Boys aged >14 years old whose growth is severely stunted or are experiencing severe distress secondary to their lack of puberty can be started on
testosterone to increase their height.
Testosterone treatment can also be used to stimulate sexual development, but it can close bone plates prematurely stopping growth altogether if not carefully administered.
Another therapeutic option is the use of
aromatase inhibitors to inhibit the conversion of androgens to estrogens as estrogens are responsible for stopping bone growth plate development and thus growth.
However, due to side effects, therapy with testosterone alone is most often used.
Overall, neither growth hormone nor aromatase inhibitors are recommended for constitutional delay to increase growth.
Girls can be started on
estrogen with the same goals as their male counterparts.
Overall, studies have shown no significant difference in final adult height between adolescents treated with sex steroids and those who were only observed with no treatment.
Malnutrition or chronic disease
If the delay is due to systemic disease or
malnutrition, the therapeutic intervention is likely to focus direction on those conditions. In patients with
coeliac disease, an early diagnosis and the establishment of a
gluten-free diet prevents long-term complications and allows restoration of normal maturation.
Thyroid hormone therapy will be necessary in the case of hypothyroidism.
Primary failure of the ovaries or testes (hypergonadotropic hypogonadism)
Whereas children with constitutional delay will have normal levels of sex hormones post-puberty, gonadotropin deficiency or hypogonadism may require lifelong sex steroid replacement.
In girls with
primary ovarian failure
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) (also called premature ovarian insufficiency, premature menopause, and premature ovarian failure) is the partial or total loss of reproductive and hormonal function of the ovaries before age 40 because of foll ...
,
estrogen should be started when puberty is supposed to start.
Progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic co ...
s are usually added after there is acceptable breast development, about 12 to 24 months after starting estrogen, as starting treatment with progestin too early can negatively affect breast growth.
After acceptable breast growth, administering
estrogen and
progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic co ...
in a cyclical manner can help establish regular menses once puberty is started.
The goal is to complete sexual maturation over 2 to 3 years.
Once sexual maturation has been achieved, a trial period with no hormonal therapy can determine whether or not the child will require life-long treatment.
Girls with congenital GnRH deficiency require enough sex hormone supplementation to maintain body levels in the expected pubertal levels necessary to induce ovulation, especially when fertility is a concern.
Males with primary failure of the testes will be on lifelong
testosterone.
Pulsatile GnRH, weekly multi-LH, or hCG and FSH can be used to induce fertility in adulthood for both males and females.
Genetic or acquired defect of the hormonal pathway of puberty (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism)
Boys aged >12 years old with
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism are most often treated with short-term testosterone while males with testicular failure will be on life-long
testosterone.
Choice of formulation (topical vs injection) is dependent on the child's and family's preference as well as on how well they tolerate side effects.
Although testosterone therapy alone will result in the start of puberty, to increase fertility potential, they may need pulsatile GnRH or hCG with rFSH.
hCG can be used by itself in boys with spontaneous onset of puberty from non-permanent forms of
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and rFSH can be added in cases of low sperm count after 6 to 12 months of treatment.
If puberty has not started after 1 year of treatment, then permanent
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism should be considered.
Girls with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism are started on the same sex steroid therapy as their counterparts with a constitutional delay, however doses are gradually increased to reach full adult replacement levels.
Dosage of estrogen is titrated based on the woman's ability to have withdrawal bleeds and to maintain appropriate bone density.
Induction of fertility must also be done through pulsatile GnRH.
Others
Growth hormone is another option that has been described, however it should only be used in proven growth hormone deficiency
such as
idiopathic short stature.
Children with a constitutional delay have not been shown to benefit from growth hormone therapy.
Although serum growth hormone levels are low in constitutional delay of puberty, they increase after treatment with sex hormones and in those cases, growth hormone is not suggested to accelerate growth.
Subnormal
vitamin A intake is one of the etiological factors in delayed pubertal maturation. Supplementation of both vitamin A and
iron to normal constitutionally delayed children with subnormal vitamin A intake is as efficacious as hormonal therapy in the induction of growth and puberty.
More therapies are being developed to target the more discreet modulators of the
HPG axis HPG may refer to:
* Huppuguda railway station, in Hyderabad, India
* Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis
* People's Defence Forces (Kurdish: '), the armed wing of the Kurdistan Workers' Party
* Shennongjia Hongping Airport, in Hubei, China
* ...
including
kisspeptin and
neurokinin B.
In cases of severe delayed puberty secondary to
hypogonadism, evaluation by a psychologist or psychiatrist, as well as counseling and a supportive environment are an important supplemental therapy for the child.
Transition from pediatric to adult care is also vital as many children are lost during transition of care.
Outlook
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty is a variation of normal development with no long-term health consequences, however it can have lasting psychological effects.
Adolescent boys with delayed puberty have a higher level of anxiety and depression relative to their peers.
Children with delayed puberty also display decreased academic performance in their adolescent education, but changes in academic achievement in adulthood have not been determined.
There is conflicting evidence as to whether or not children with constitutional growth and pubertal delay reach their full height potential.
The conventional teaching is that these children catch up on their growth during the pubertal growth spurt and just remain shorter before their delayed puberty starts. However, some studies show that these children fall short of their target height from about 4 to 11 cm.
Factors that could affect final height include familial short stature and pre-pubertal growth development.
Pubertal delay can also affect bone mass and subsequent development of osteoporosis.
Men with delayed puberty often have low to normal
bone mineral density
Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone (relating to density in the physics sense), although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optica ...
unaffected by
androgen therapy.
Women are more likely to have lower bone mineral density and thus an increased risk of fractures as early as even before the onset of puberty.
Furthermore, delayed puberty is correlated with a higher risk in cardiovascular and metabolic disorders in women only, but also appears to be protective for breast and endometrial in women and testicular cancer in men.
See also
*
Developmental milestones
Child development stages are the theoretical milestones of child development, some of which are asserted in nativist theories. This article discusses the most widely accepted developmental stages in children. There exists a wide variation i ...
*
Endocrinology
*
Puberty
*
Constitutional growth delay
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty (CDGP) is a term describing a temporary delay in the skeletal growth and thus height of a child with no physical abnormalities causing the delay. Short stature may be the result of a growth pattern inher ...
*
Hypogonadism
*
Kallmann syndrome
*
Turner syndrome
*
Klinefelter syndrome
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Delayed Puberty
Puberty
Endocrine gonad disorders
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropins
Pediatrics
Sexuality and age
Sexual health
Human female endocrine system
Intersex variations
 Primary failure of the ovaries or testes (
Primary failure of the ovaries or testes ( Since bone maturation is a good indicator of overall physical maturation, an x-ray of the left hand and wrist to assess bone age usually reveals whether the child has reached a stage of physical maturation at which puberty should be occurring. X-ray displaying a bone age <11 years in girls or <13 years in boys (despite a higher chronological age) is most often consistent with constitutional delay of puberty. An MRI of the brain should be considered if neurological symptoms are present in addition to delayed puberty, two findings suspicious for pituitary or hypothalamic tumors. An MRI can also confirm the diagnosis of Kallmann syndrome due to the absence or abnormal development of the olfactory tract. However, in the absence of clear neurological symptoms, an MRI may not be the most cost-effective option. A pelvic ultrasound can detect anatomical abnormalities including undescended testes and müllerian agenesis.
Since bone maturation is a good indicator of overall physical maturation, an x-ray of the left hand and wrist to assess bone age usually reveals whether the child has reached a stage of physical maturation at which puberty should be occurring. X-ray displaying a bone age <11 years in girls or <13 years in boys (despite a higher chronological age) is most often consistent with constitutional delay of puberty. An MRI of the brain should be considered if neurological symptoms are present in addition to delayed puberty, two findings suspicious for pituitary or hypothalamic tumors. An MRI can also confirm the diagnosis of Kallmann syndrome due to the absence or abnormal development of the olfactory tract. However, in the absence of clear neurological symptoms, an MRI may not be the most cost-effective option. A pelvic ultrasound can detect anatomical abnormalities including undescended testes and müllerian agenesis.
 The first step in evaluating children with delayed puberty involves differentiating between the different causes of delayed puberty. Constitutional delay can be evaluated with a thorough history, physical, and bone age. Malnutrition and chronic diseases can be diagnosed through history and disease-specific testing. Screening studies include a complete blood count, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and thyroid studies. Hypogonadism can be differentiated between hyper- and hypo-gonadotropic hypogonadism by measuring serum
The first step in evaluating children with delayed puberty involves differentiating between the different causes of delayed puberty. Constitutional delay can be evaluated with a thorough history, physical, and bone age. Malnutrition and chronic diseases can be diagnosed through history and disease-specific testing. Screening studies include a complete blood count, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and thyroid studies. Hypogonadism can be differentiated between hyper- and hypo-gonadotropic hypogonadism by measuring serum