|
Noonan Syndrome
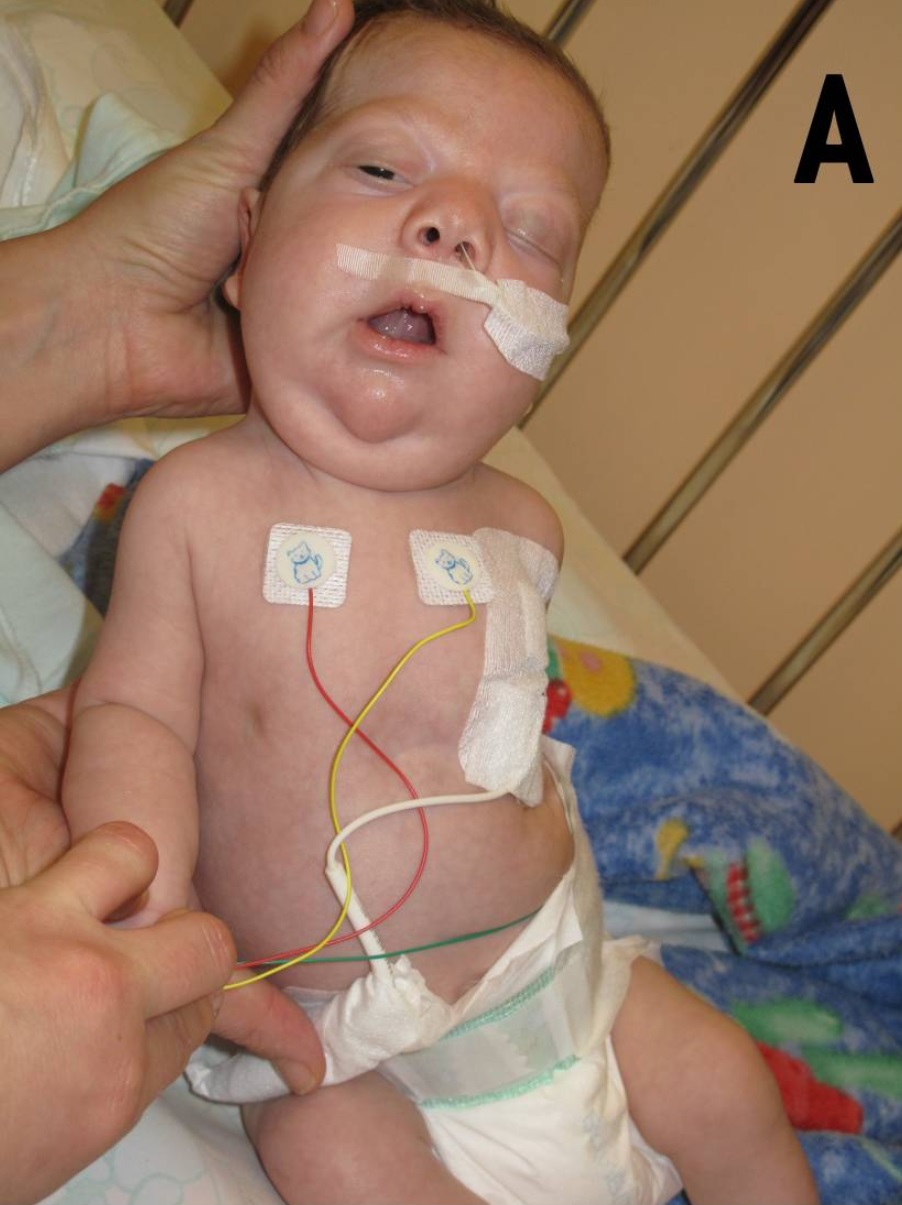
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited from a person's parents as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves overactivation within the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood tests. Confirmation may be achieved with genetic tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webbed Neck
A webbed neck, or pterygium colli, is a congenital skin fold that runs along the sides of the neck down to the shoulders. There are many variants. Signs and symptoms On babies, webbed neck may look like loose folds of skin on the neck. As the child grows, the skin may stretch out to look like there is little or no neck. Associated conditions It is a feature of Turner syndrome (only found in girls) and Noonan syndrome, as well as the rarer Klippel–Feil syndrome, or Diamond–Blackfan anemia Diamond–Blackfan anemia (DBA) is a congenital erythroid aplasia that usually presents in infancy. DBA causes low red blood cell counts (anemia), without substantially affecting the other blood components (the platelets and the white blood cel ... References External links {{Congenital malformations and deformations of ear, face and neck Congenital disorders of eye, ear, face and neck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrognathism
Micrognathism is a condition where the jaw is undersized. It is also sometimes called mandibular hypoplasia. It is common in infants, but is usually self-corrected during growth, due to the jaws' increasing in size. It may be a cause of abnormal tooth alignment and in severe cases can hamper feeding. It can also, both in adults and children, make intubation difficult, either during anesthesia or in emergency situations. Causes While not always pathological, it can present as a birth defect in multiple syndromes including: * Catel–Manzke syndrome * Bloom syndrome * Coffin–Lowry syndrome * Congenital rubella syndrome * Cri du chat syndrome * DiGeorge syndrome * Ehlers–Danlos syndrome * Fetal alcohol syndrome * Hallermann–Streiff syndrome * Hemifacial microsomia (as part of Goldenhar syndrome) * Incontinentia pigmenti * Juvenile idiopathic arthritis * Marfan syndrome * Möbius syndrome * Noonan syndrome * Pierre Robin syndrome * Prader–Willi syndrome * Progeria * Silve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat adult heart disease. Surgical aspects are not included in cardiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the age of 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, but some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults up to 25. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word ''pediatrics'' and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from the two Greek words: (''pais'' "child") and (''iatros'' "doctor, healer"). Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties (e.g. neonatology requires resources available in a NICU). History The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Therapy
Growth hormone therapy refers to the use of growth hormone (GH) as a prescription medication—it is one form of hormone therapy. Growth hormone is a peptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland that stimulates growth and cell reproduction. In the past, growth hormone was extracted from human pituitary glands. Growth hormone is now produced by recombinant DNA technology and is prescribed for a variety of reasons. GH therapy has been a focus of social and ethical controversies for 50 years. This article describes the history of GH treatment and the current uses and risks arising from GH use. Other articles describe GH physiology, diseases of GH excess (acromegaly and pituitary gigantism), deficiency, the recent phenomenon of HGH controversies, growth hormone in sports, and growth hormone for cows. Medical uses HGH deficiency in children Growth hormone deficiency is treated by replacing growth hormone. Lonapegsomatropin was approved for medical use in the United States in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain data about the measurement loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Signaling
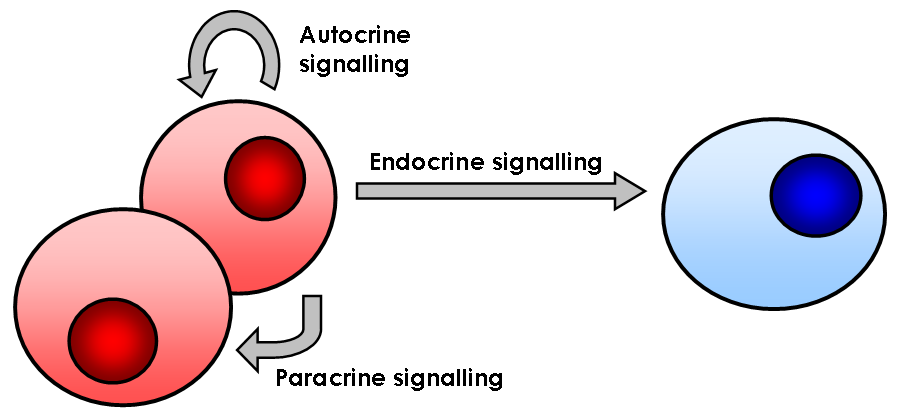
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the interio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPK/ERK Pathway
The MAPK/ERK pathway (also known as the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway) is a chain of proteins in the cell that communicates a signal from a receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. The signal starts when a signaling molecule binds to the receptor on the cell surface and ends when the DNA in the nucleus expresses a protein and produces some change in the cell, such as cell division. The pathway includes many proteins, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), originally called extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), which communicate by adding phosphate groups to a neighboring protein ( phosphorylating it), thereby acting as an "on" or "off" switch. When one of the proteins in the pathway is mutated, it can become stuck in the "on" or "off" position, a necessary step in the development of many cancers. In fact, components of the MAPK/ERK pathway were first discovered in cancer cells, and drugs that reverse the "on" or "off" switch are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RASopathy
The RASopathies are developmental syndromes caused by germline mutations (or in rare cases by somatic mosaicism) in genes that alter the Ras subfamily and mitogen-activated protein kinases that control signal transduction, including: * Capillary malformation-AV malformation syndrome * Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome * Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome * Hereditary gingival fibromatosis type 1 * Neurofibromatosis type 1 * Noonan syndrome * Costello syndrome, Noonan-like * Legius syndrome, Noonan-like * Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines, formerly called LEOPARD syndrome Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML) which is part of a group called Ras/MAPK pathway syndromes, is a rare autosomal dominant, multisystem disease caused by a mutation in the protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 11 gene (''PT ..., Noonan-like * SYNGAP1-related intellectual disability References {{Medicine, state=collapsed Autosomal dominant disorders Congenital vascular defects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia— acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which a person's spine has a sideways curve. The curve is usually "S"- or "C"-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to another condition such as muscle spasms, cerebral palsy, Marfan syndrome, and tumors such as neurofibromatosis. Diagnosis is confirmed with X-rays. Scoliosis is typically classified as either structural in which the curve is fixed, or functional in which the underlying spine is normal. Treatment depends on the degree of curve, location, and cause. Minor curves may simply be watched periodically. Treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectus Excavatum
Pectus excavatum is a structural deformity of the anterior thoracic wall in which the sternum and rib cage are shaped abnormally. This produces a caved-in or sunken appearance of the chest. It can either be present at birth or develop after puberty. Pectus excavatum can impair cardiac and respiratory function and cause pain in the chest and back. People with the condition may experience severe negative psychosocial effects and avoid activities that expose the chest. Signs and symptoms The hallmark of the condition is a sunken appearance of the sternum. The most common form is a cup-shaped concavity, involving the lower end of the sternum; a broader concavity involving the upper costal cartilages is possible. The lower-most ribs may protrude ("flared ribs"). Pectus excavatum defects may be symmetric or asymmetric. People may also experience chest and back pain, which is usually of musculoskeletal origin. In mild cases, cardiorespiratory function is normal, although the heart c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |