pectus excavatum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pectus excavatum is a structural deformity of the anterior
 Pectus excavatum is initially suspected from visual examination of the anterior chest. Auscultation of the chest can reveal displaced heart beat and valve prolapse. There can be a heart murmur occurring during
Pectus excavatum is initially suspected from visual examination of the anterior chest. Auscultation of the chest can reveal displaced heart beat and valve prolapse. There can be a heart murmur occurring during 
 An alternative to surgery, the vacuum bell, was described in 2006; the procedure is also referred to as treatment by ''cup suction''. It consists of a bowl shaped device which fits over the caved-in area; the air is then removed by the use of a hand pump. The vacuum created by this lifts the sternum upwards, lessening the severity of the deformity. It has been proposed as an alternative to surgery in less severe cases. Once the defect visually disappears, two additional years of use of the vacuum bell is required to make what may be a permanent correction. The treatment, in combination with physiotherapy exercises, has been judged by some as "a promising useful alternative" to surgery provided the thorax is flexible; the duration of treatment that is required has been found to be "directly linked to age, severity and the frequency of use". Long-term results are still lacking.
A single-center study reported in the
An alternative to surgery, the vacuum bell, was described in 2006; the procedure is also referred to as treatment by ''cup suction''. It consists of a bowl shaped device which fits over the caved-in area; the air is then removed by the use of a hand pump. The vacuum created by this lifts the sternum upwards, lessening the severity of the deformity. It has been proposed as an alternative to surgery in less severe cases. Once the defect visually disappears, two additional years of use of the vacuum bell is required to make what may be a permanent correction. The treatment, in combination with physiotherapy exercises, has been judged by some as "a promising useful alternative" to surgery provided the thorax is flexible; the duration of treatment that is required has been found to be "directly linked to age, severity and the frequency of use". Long-term results are still lacking.
A single-center study reported in the
 There has been controversy as to the best surgical approach for correction of pectus excavatum. It is important for the surgeon to select the appropriate operative approach based on each individual's characteristics.
Surgical correction has been shown to repair any functional symptoms that may occur in the condition, such as respiratory problems or heart murmurs, provided that permanent damage has not already arisen from an extremely severe case. Surgical correction of the pectus excavatum has been shown to significantly improve cardiovascular function; there is inconclusive evidence so far as to whether it might also improve pulmonary function. One of the most popular techniques for repair of pectus excavatum today is the minimally invasive operation, also known as MIRPE or Nuss technique.
There has been controversy as to the best surgical approach for correction of pectus excavatum. It is important for the surgeon to select the appropriate operative approach based on each individual's characteristics.
Surgical correction has been shown to repair any functional symptoms that may occur in the condition, such as respiratory problems or heart murmurs, provided that permanent damage has not already arisen from an extremely severe case. Surgical correction of the pectus excavatum has been shown to significantly improve cardiovascular function; there is inconclusive evidence so far as to whether it might also improve pulmonary function. One of the most popular techniques for repair of pectus excavatum today is the minimally invasive operation, also known as MIRPE or Nuss technique.
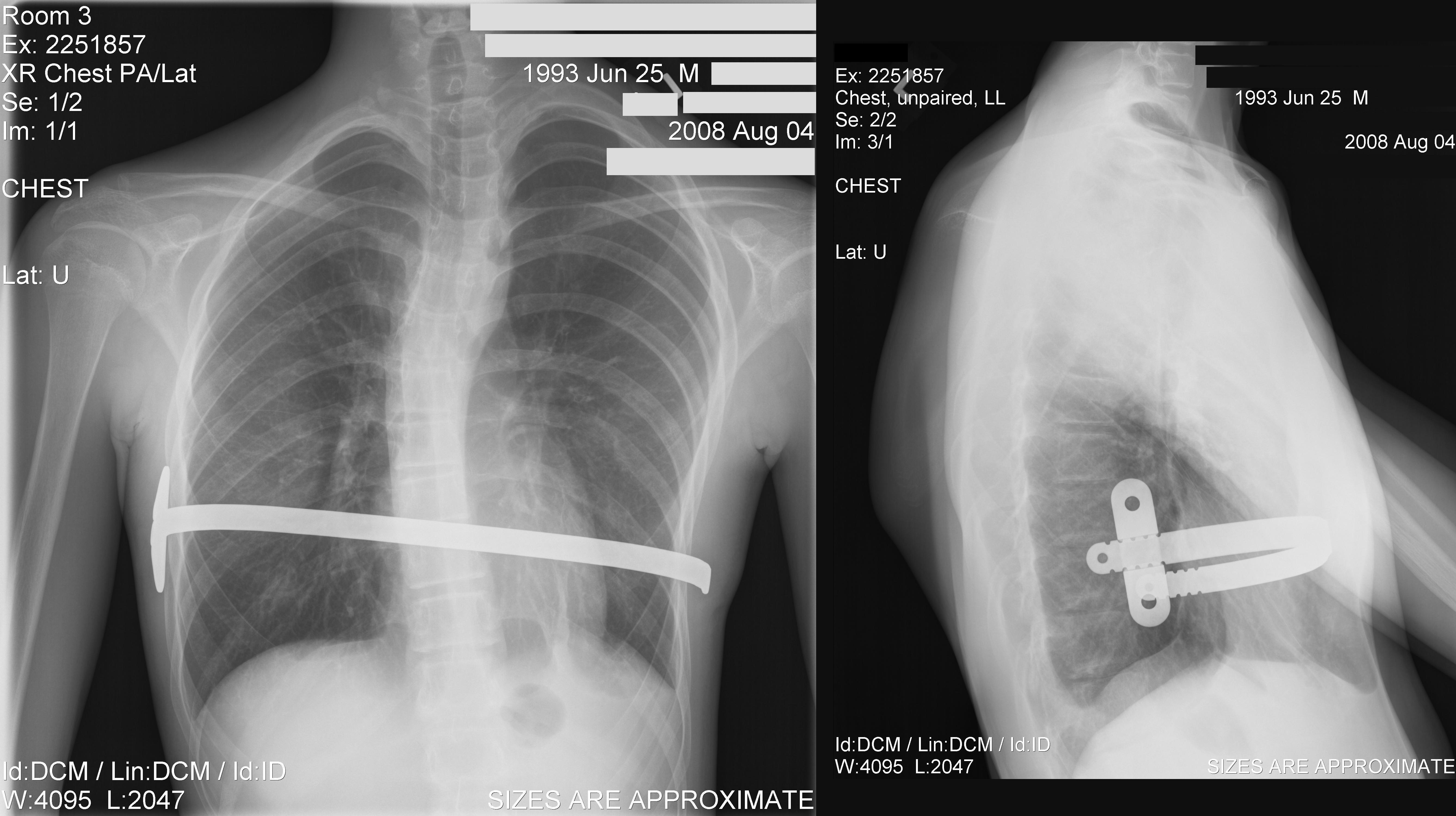 In 1987, Donald Nuss, based at
In 1987, Donald Nuss, based at
www.ctds.info
thoracic wall
The thoracic wall or chest wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity.
Structure
The bony skeletal part of the thoracic wall is the rib cage, and the rest is made up of muscle, skin, and fasciae.
The chest wall has 10 layers, namely (from ...
in which the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. ...
and rib cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi ...
are shaped abnormally. This produces a caved-in or sunken appearance of the chest
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
. It can either be present at birth or develop after puberty.
Pectus excavatum can impair cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon di ...
and respiratory function and cause pain in the chest and back.
People with the condition may experience severe negative psychosocial
The psychosocial approach looks at individuals in the context of the combined influence that psychological factors and the surrounding social environment have on their physical and mental wellness and their ability to function. This approach is ...
effects and avoid activities that expose the chest.
Signs and symptoms
The hallmark of the condition is a sunken appearance of the sternum. The most common form is a cup-shaped concavity, involving the lower end of the sternum; a broader concavity involving the upper costal cartilages is possible. The lower-most ribs may protrude ("flared ribs"). Pectus excavatum defects may be symmetric or asymmetric. People may also experience chest and back pain, which is usually of musculoskeletal origin. In mild cases, cardiorespiratory function is normal, although the heart can be displaced and/or rotated. In severe cases, the right atrium may be compressed,mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. It is the primary form of myxomatous degeneration of the valve. There ...
may be present, and physical capability may be limited due to base lung capacity being decreased.
Psychological symptoms manifest with feelings of embarrassment, social anxiety
Social anxiety is the anxiety and fear specifically linked to being in social settings (i.e., interacting with others). Some categories of disorders associated with social anxiety include anxiety disorders, mood disorders, autism spectrum diso ...
, shame, limited capacity for activities and communication, negativity, intolerance, frustration, and even depression.
Causes
Researchers are unsure of the cause of pectus excavatum. Some researchers take the stance that it is acongenital disorder
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities c ...
(birth defect), but not genetic. Others assume that there is some genetic component. A small sample size test found that in at least some cases, 37% of individuals have an affected first degree family member. , a number of genetic marker A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be ...
s for pectus excavatum had also been discovered.
It was believed for decades that pectus excavatum is caused by an overgrowth of costal cartilage, however people with pectus excavatum actually tend to have shorter, not longer, costal cartilage relative to rib length.
Pectus excavatum can be present in other conditions too, including Noonan syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored ...
, Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a ...
and Loeys–Dietz syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aort ...
as well as other connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Many children with spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genet ...
develop pectus excavatum due to their diaphragmatic breathing.
Pathophysiology
Physiologically, increased pressure ''in utero'', rickets and increased traction on thesternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. ...
due to abnormalities of the diaphragm
Diaphragm may refer to:
Anatomy
* Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen
* Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure
* Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure
Other
* Diap ...
have been postulated as specific mechanisms. Because the heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
is located behind the sternum, and because individuals with pectus excavatum have been shown to have visible deformities of the heart seen both on radiological imaging and after autopsies, it has been hypothesized that there is impairment of the function of the cardiovascular system in individuals with pectus excavatum. While some studies have demonstrated decreased cardiovascular function, no consensus has been reached based on newer physiological tests such as echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in ...
of the presence or degree of impairment in cardiovascular function. However, a 2016 meta-analysis found significant evidence that surgical correction of pectus excavatum improves patient cardiac performance.
Diagnosis
 Pectus excavatum is initially suspected from visual examination of the anterior chest. Auscultation of the chest can reveal displaced heart beat and valve prolapse. There can be a heart murmur occurring during
Pectus excavatum is initially suspected from visual examination of the anterior chest. Auscultation of the chest can reveal displaced heart beat and valve prolapse. There can be a heart murmur occurring during systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ' ...
caused by proximity between the sternum and the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
.
Lung sounds are usually clear yet diminished due to decreased base lung capacity.
Many scales have been developed to determine the degree of deformity in the chest wall. Most of these are variants on the distance between the sternum and the spine. One such index is the ''Backer ratio'' which grades severity of deformity based on the ratio between the diameter of the vertebral body nearest to xiphosternal junction
The xiphoid process , or xiphisternum or metasternum, is a small cartilaginous process (extension) of the inferior (lower) part of the sternum, which is usually ossified in the adult human. It may also be referred to as the ensiform process. B ...
and the distance between the xiphosternal junction and the nearest vertebral body. More recently the '' Haller index'' has been used based on CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
measurements. An index over 3.25 is often defined as severe. The Haller index is the ratio between the horizontal distance of the inside of the ribcage and the shortest distance between the vertebrae and sternum.

Chest x-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in me ...
s are also useful in the diagnosis. The chest x-ray in pectus excavatum can show an opacity in the right lung area that can be mistaken for an infiltrate (such as that seen with pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severi ...
). Some studies also suggest that the Haller index can be calculated based on chest x-ray as opposed to CT scanning in individuals who have no limitation in their function.
Pectus excavatum is differentiated from other disorders by a series of elimination of signs and symptoms. Pectus carinatum is excluded by the simple observation of a collapsing of the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. ...
rather than a protrusion. Kyphoscoliosis is excluded by diagnostic imaging of the spine, wherein pectus excavatum the spine usually appears normal in structure.
Treatment
Pectus excavatum requires no corrective procedures in mild cases. Treatment of severe cases can involve eitherinvasive
Invasive may refer to:
*Invasive (medical) procedure
*Invasive species
*Invasive observation, especially in reference to surveillance
*Invasively progressive spread of disease from one organ in the body to another, especially in reference to cancer ...
or non-invasive techniques or a combination of both. Before an operation proceeds several tests are usually performed. These include, but are not limited to, a CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
, pulmonary function test
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity ...
s, and cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular he ...
exams (such as auscultation and ECGs). After a CT scan is taken, the Haller index is measured. The patient's Haller is calculated by obtaining the ratio of the transverse diameter (the horizontal distance of the inside of the ribcage) and the anteroposterior diameter (the shortest distance between the vertebrae and sternum). A Haller Index of greater than 3.25 is generally considered severe, while normal chest has an index of 2.5. The cardiopulmonary tests are used to determine the lung capacity and to check for heart murmurs.
Conservative treatment
The chest wall is elastic, gradually stiffening with age. Non-surgical treatments have been developed that aim at gradually alleviating the pectus excavatum condition, making use of the elasticity of the chest wall, including thecostal cartilage
The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension. ...
s, in particular in young cases.
Exercise
Physical exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
has an important role in conservative pectus excavatum treatment though is not seen as a means to resolve the condition on its own. It is used in order to halt or slow the progression of mild or moderate excavatum conditions and as supplementary treatment to improve a poor posture, to prevent secondary complications, and to prevent relapse after treatment.
Exercises are aimed at improving posture, strengthening back and chest muscles, and enhancing exercise capacity, ideally also increasing chest expansion. Pectus exercises include deep breathing and breath holding exercises, as well as strength training
Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises that are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the lifting of weights. It can also incorporate a variety of training te ...
for the back and chest muscles. Additionally, aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise (also known as endurance activities, cardio or cardio-respiratory exercise) is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, inv ...
s to improve cardiopulmonary function are employed.
Vacuum bell
 An alternative to surgery, the vacuum bell, was described in 2006; the procedure is also referred to as treatment by ''cup suction''. It consists of a bowl shaped device which fits over the caved-in area; the air is then removed by the use of a hand pump. The vacuum created by this lifts the sternum upwards, lessening the severity of the deformity. It has been proposed as an alternative to surgery in less severe cases. Once the defect visually disappears, two additional years of use of the vacuum bell is required to make what may be a permanent correction. The treatment, in combination with physiotherapy exercises, has been judged by some as "a promising useful alternative" to surgery provided the thorax is flexible; the duration of treatment that is required has been found to be "directly linked to age, severity and the frequency of use". Long-term results are still lacking.
A single-center study reported in the
An alternative to surgery, the vacuum bell, was described in 2006; the procedure is also referred to as treatment by ''cup suction''. It consists of a bowl shaped device which fits over the caved-in area; the air is then removed by the use of a hand pump. The vacuum created by this lifts the sternum upwards, lessening the severity of the deformity. It has been proposed as an alternative to surgery in less severe cases. Once the defect visually disappears, two additional years of use of the vacuum bell is required to make what may be a permanent correction. The treatment, in combination with physiotherapy exercises, has been judged by some as "a promising useful alternative" to surgery provided the thorax is flexible; the duration of treatment that is required has been found to be "directly linked to age, severity and the frequency of use". Long-term results are still lacking.
A single-center study reported in the Journal of Pediatric Surgery
The ''Journal of Pediatric Surgery'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering pediatric surgery. It was established in 1966 and is published by Elsevier. It is the official journal of the Section on Surgery of the American Academy of Ped ...
found that use of vacuum bell therapy resulted in an excellent correction in twenty percent of patients, but "is not a substitute for the Nuss procedure which can achieve an excellent result in 90% of patients". Variables predictive of an excellent outcome include age ≤ 11 years, chest wall depth ≤ 1.5 cm, chest wall flexibility, and vacuum bell use over 12 consecutive months.
In an article by ''Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery'', the results found that vacuum bell treatment is safe for correcting the deformity non-surgically. The treatment has been shown to have higher success rates in patients who present earlier, have a mild and/or symmetrical deformity, a flexible chest wall and lack of costal flaring.
The vacuum bell can also be used in preparation to surgery.
Orthoses
Brazilian orthopedist Sydney Haje developed a non-surgical protocol for treating pectus carinatum as well as pectus excavatum. The method involves wearing a compressiveorthosis
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functi ...
and adhering to an exercise protocol.
Mild cases have also reportedly been treated with corset-like orthopedic support vests and exercise.
Thoracic surgery
 There has been controversy as to the best surgical approach for correction of pectus excavatum. It is important for the surgeon to select the appropriate operative approach based on each individual's characteristics.
Surgical correction has been shown to repair any functional symptoms that may occur in the condition, such as respiratory problems or heart murmurs, provided that permanent damage has not already arisen from an extremely severe case. Surgical correction of the pectus excavatum has been shown to significantly improve cardiovascular function; there is inconclusive evidence so far as to whether it might also improve pulmonary function. One of the most popular techniques for repair of pectus excavatum today is the minimally invasive operation, also known as MIRPE or Nuss technique.
There has been controversy as to the best surgical approach for correction of pectus excavatum. It is important for the surgeon to select the appropriate operative approach based on each individual's characteristics.
Surgical correction has been shown to repair any functional symptoms that may occur in the condition, such as respiratory problems or heart murmurs, provided that permanent damage has not already arisen from an extremely severe case. Surgical correction of the pectus excavatum has been shown to significantly improve cardiovascular function; there is inconclusive evidence so far as to whether it might also improve pulmonary function. One of the most popular techniques for repair of pectus excavatum today is the minimally invasive operation, also known as MIRPE or Nuss technique.
Magnetic mini-mover procedure
The magnetic mini-mover procedure (3MP) is a minimally invasive procedure used to correct pectus excavatum by using two magnets to realign the sternum with the rest of the chest and ribcage. One magnet is inserted 1 cm into the patient's body on the lower end of the sternum, the other is placed externally onto a custom fitted brace. These two magnets generate around 0.04 tesla (T) in order to slowly move the sternum outwards over a number of years. The maximummagnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and t ...
that can be applied to the body safely is around 4 T, making this technique safe from a magnetic viewpoint. The 3MP technique's main advantages are that it is more cost-effective than major surgical approaches such as the Nuss procedure and it is considerably less painful postoperatively.
Its effectiveness is limited to younger children in early- to mid-puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a b ...
because older individuals have less compliant (flexible) chest walls. One potential adverse interaction with other medical devices is possible inactivation of artificial pacemaker
An artificial cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural cardiac pacemaker) or pacemaker is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to the chambers of the heart ei ...
s if present.
Ravitch technique
The Ravitch technique is an invasive surgery that was introduced in 1949 and developed in the 1950s. It involves creating an incision along the chest through which the cartilage is removed and the sternum detached. A small bar is inserted underneath the sternum to hold it up in the desired position. The bar is left implanted until the cartilage grows back, typically about six months. The bar is subsequently removed in a simple outpatient procedure; this technique is thus a two-stage procedure. The Ravitch technique is not widely practiced because it is so invasive. It is more often used in older individuals, where the sternum has calcified when the deformity is asymmetrical, or when the less invasive Nuss procedure has proven unsuccessful.Nuss procedure
 In 1987, Donald Nuss, based at
In 1987, Donald Nuss, based at Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters
Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters (CHKD), located in Norfolk, Virginia, United States, is the only freestanding children's hospital in Virginia. The hospital treats infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 and even some ad ...
in Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 cen ...
, performed the first minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum (MIRPE) and presented it much later at a conference in 1997.
His two-stage procedure, widely known as the ''Nuss procedure'', involves slipping in one or more concave steel bars into the chest, underneath the sternum.
The bar is flipped to a convex position so as to push outward on the sternum, correcting the deformity. The bar usually stays in the body for about two years, although many surgeons are currently moving toward leaving them in for up to five years. When the bones have solidified into place, the bar is removed through outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory surgery, day surgery, day case surgery, or same-day surgery, is surgery that does not require an overnight hospital stay.The International Association for Ambulatory Surgery (IAAS) would not consider ...
.
Although initially designed to be performed in younger children of less than 10 years of age, whose sternum and cartilage is more flexible, there are successful series of Nuss treatment in patients well into their teens and twenties.
Robicsek technique
In 1965, Francis Robicsek, based at Charlotte Memorial Hospital, now namedCarolinas Medical Center
Carolinas Medical Center (CMC) is an 874-bed non-profit, tertiary, research and academic medical center located in Charlotte, North Carolina, servicing the southern North Carolina, northern South Carolina, and the Metrolina region. Carolinas Med ...
in Charlotte
Charlotte ( ) is the List of municipalities in North Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located in the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont region, it is the county seat of Mecklenburg County, North Carolina, Meckl ...
, North Carolina, developed the Robicsek procedure. Each time the procedure is performed, it is individually tailored based on the extent and location of the deformity in the patient. The operation begins with an incision, no more than 4–6 centimeters, to the sternum. The pectoralis major muscles are then detached from the sternum. Using the upper limit of the sternal depression as a guide, the deformed cartilages are removed one by one, using sharp and blunt dissection. The lower tip of the sternum is then grabbed with a towel-clip and, using blunt dissection, is freed of tissue connections with the pericardium and the pleura. The sternum is then forcefully bent forward into a corrected position. To keep the sternum elevated, a piece of mesh is placed under the mobilized sternum and sutured under moderate tension bilaterally to the stumps of the ribs. The pectoralis muscles are united in front of the sternum and the wound is closed. The Robicsek procedure is a single-stage procedure (one surgery only).
The purported advantage of this technique is that it is less invasive than the Ravitch technique, but critics have suggested that the relapse rate may be high due to cartilage and bone displaying memory phenomenon.
Taulinoplasty
In 2016, Carlos Bardají, a Barcelona-based pediatric surgeon, together with Lluís Cassou, a biomedical engineer, published a paper describing an extra-thoracic surgical procedure for the correction of pectus excavatum called taulinoplasty. A specially designed implant and traction hardware were developed specifically for the procedure. In taulinoplasty, a small hole is drilled into the sternum at the deepest point of defect, and a double screw is driven into the hole. Then, a stainless steel implant is placed underneath the skin on top of the sternum and ribs, centered over the double screw. Traction tools are then used to lift the sternum up by the double screw using the implant and ribs for traction. Additional screws are then used to secure the implant onto the sternum holding the sternum in the desired position. Optionally, stainless steel wire may be wrapped around the implant and ribs to further secure the implant in place. Like the Nuss procedure, taulinoplasty requires follow-up surgery several years later to remove the implanted hardware once the sternum has permanently assumed its new position. The implant and related hardware used in taulinoplasty is a proprietary product of Ventura Medical Technologies and is marketed as a surgical kit under the brand name Pectus UP. Taulinoplasty was developed to be an alternative to the Nuss procedure that eliminates the risks and drawbacks of entering the thorax. In particular, patients usually have shorter operating and recovery times, and less post-operative pain than with the Nuss procedure.Plastic surgery
Implants
The implant allows pectus excavatum to be treated from a purely morphological perspective. Today it is used as a benchmark procedure as it is simple, reliable, and minimally intrusive while offering aesthetically pleasing results. This procedure does not, however, claim to correct existing cardiac and respiratory problems which, in very rare cases, can be triggered by the pectus excavatum condition. For female patients, the potential resulting breast asymmetry can be partially or completely corrected by this procedure. The process of creating a plaster-cast model, directly on the skin of the patient's thorax, can be used in the design of the implants. The evolution of medical imaging and CAD (computer-aided design) now allows customised 3D implants to be designed directly from the ribcage, therefore being much more precise, easier to place sub-pectorally and perfectly adapted to the shape of each patient. The implants are made of medical silicon rubber which is age-resistant and unbreakable (different to the silicon gel used in breast implants). They will last for life (apart from the case of adverse reactions) and are not visible externally. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour. The surgeon makes an incision of approximately seven centimetres, prepares the customised space in the chest, inserts the implant deep beneath the muscle, then closes the incision. Post-operative hospitalization is typically around three days. The recovery after the surgery typically requires only mild pain relief. Post-operatively, a surgical dressing is required for several days and compression vest for a month following the procedure. A check-up appointment is carried out after a week for puncture of seroma. If the surgery has minimal complications, the patient can resume normal activities quickly, returning to work after 15 days and participating in any sporting activities after three months.Lipofilling
The "lipofilling" technique consists of sucking fat from the patient using a syringe with a large gauge needle (usually from the abdomen or the outer thighs), then after centrifugation, the fat cells are re-injected beneath the skin into whichever hollow it is needed to fill. This technique is primarily used to correct small defects which may persist after conventional surgical treatment.Epidemiology
Pectus excavatum occurs in an estimated 1 in 150 to 1 in 1000 births, with male predominance (male-to-female ratio of 3:1). In 35% to 45% of cases family members are affected.Etymology
Pectus excavatum is fromLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
meaning ''hollowed chest''. It is sometimes referred to as sunken chest syndrome, cobbler's chest or funnel chest.
Society
American Olympic swimmerCody Miller
Cody William Miller (born January 9, 1992) is an American competitive swimmer. He is a former world record holder in both the men's 4×50 meter freestyle relay and the mixed 4×50 meter freestyle relay as well as a former American record holde ...
(born 1992) opted not to have treatment for pectus excavatum, even though it limited his lung capacity. He earned a gold medal in 2016.
Actor Joel Kinnaman underwent surgery prior to the filming of '' Altered Carbon'', inserting two metal bars to push the sternum outward in order to correct the deformity. English comedian and presenter Josh Widdicombe and YouTuber
A YouTuber is an online personality and/or influencer who produces videos on the video-sharing platform YouTube, typically posting to their personal YouTube channel. The term was first used in the English language in 2006.
Influence
Influe ...
/streamer Ludwig Ahgren are known to have this condition. Zachary Woods is another popular American actor that has pectus excavatum, which is noticeable in his shirtless scene in an episode of The Office (Season 8, episode 12). Dutch bodybuilder, actor and Muscle Meats CEO Oliver Richters, "The Dutch Giant", suffered from the condition before undergoing surgical correction
In animals
Pectus excavatum is also known to occur in animals, e.g. theMunchkin
A Munchkin is a native of the fictional Munchkin Country in the Oz books by Americans, American author L. Frank Baum. They first appear in the classic children's novel ''The Wonderful Wizard of Oz'' (1900) where they welcome Dorothy Gale to thei ...
breed of cat. Some procedures used to treat the condition in animals have not been used in human treatments, such as the use of a cast with sutures wrapped around the sternum and the use of internal and external splints. These techniques are generally used in immature animals with flexible cartilage.
See also
* Pectus carinatumReferences
Further reading
* *www.ctds.info
External links
* {{Authority control Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system