Severe Sepsis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to
 Within the first three hours of suspected sepsis, diagnostic studies should include white blood cell counts, measuring serum lactate, and obtaining appropriate cultures before starting antibiotics, so long as this does not delay their use by more than 45 minutes. To identify the causative organism(s), at least two sets of
Within the first three hours of suspected sepsis, diagnostic studies should include white blood cell counts, measuring serum lactate, and obtaining appropriate cultures before starting antibiotics, so long as this does not delay their use by more than 45 minutes. To identify the causative organism(s), at least two sets of
 Previously, SIRS criteria had been used to define sepsis. If the SIRS criteria are negative, it is very unlikely the person has sepsis; if it is positive, there is just a moderate probability that the person has sepsis. According to SIRS, there were different levels of sepsis: sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The definition of SIRS is shown below:
* SIRS is the presence of two or more of the following: abnormal
Previously, SIRS criteria had been used to define sepsis. If the SIRS criteria are negative, it is very unlikely the person has sepsis; if it is positive, there is just a moderate probability that the person has sepsis. According to SIRS, there were different levels of sepsis: sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The definition of SIRS is shown below:
* SIRS is the presence of two or more of the following: abnormal
 Early recognition and focused management may improve the outcomes in sepsis. Current professional recommendations include a number of actions ("bundles") to be followed as soon as possible after diagnosis. Within the first three hours, someone with sepsis should have received antibiotics and, intravenous fluids if there is evidence of either low blood pressure or other evidence for inadequate blood supply to organs (as evidenced by a raised level of lactate); blood cultures also should be obtained within this time period. After six hours the blood pressure should be adequate, close monitoring of blood pressure and blood supply to organs should be in place, and the lactate should be measured again if initially it was raised. A related bundle, the "Sepsis Six", is in widespread use in the United Kingdom; this requires the administration of antibiotics within an hour of recognition, blood cultures, lactate, and hemoglobin determination, urine output monitoring, high-flow oxygen, and intravenous fluids.
Apart from the timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, the management of sepsis also involves surgical drainage of infected fluid collections and appropriate support for organ dysfunction. This may include Kidney dialysis, hemodialysis in kidney failure, mechanical ventilation in lung dysfunction, transfusion of blood plasma, blood products, and drug and fluid therapy for circulatory failure. Ensuring adequate nutrition—preferably by enteral feeding, but if necessary, by parenteral nutrition—is important during prolonged illness. Medication to prevent
Early recognition and focused management may improve the outcomes in sepsis. Current professional recommendations include a number of actions ("bundles") to be followed as soon as possible after diagnosis. Within the first three hours, someone with sepsis should have received antibiotics and, intravenous fluids if there is evidence of either low blood pressure or other evidence for inadequate blood supply to organs (as evidenced by a raised level of lactate); blood cultures also should be obtained within this time period. After six hours the blood pressure should be adequate, close monitoring of blood pressure and blood supply to organs should be in place, and the lactate should be measured again if initially it was raised. A related bundle, the "Sepsis Six", is in widespread use in the United Kingdom; this requires the administration of antibiotics within an hour of recognition, blood cultures, lactate, and hemoglobin determination, urine output monitoring, high-flow oxygen, and intravenous fluids.
Apart from the timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, the management of sepsis also involves surgical drainage of infected fluid collections and appropriate support for organ dysfunction. This may include Kidney dialysis, hemodialysis in kidney failure, mechanical ventilation in lung dysfunction, transfusion of blood plasma, blood products, and drug and fluid therapy for circulatory failure. Ensuring adequate nutrition—preferably by enteral feeding, but if necessary, by parenteral nutrition—is important during prolonged illness. Medication to prevent
 The term "σήψις" (sepsis) was introduced by Hippocrates in the fourth century BC, and it meant the process of decomposition, decay or decomposition of organic matter. In the eleventh century, Avicenna used the term "blood rot" for diseases linked to severe Pus, purulent process. Though severe systemic toxicity had already been observed, it was only in the 19th century that the specific term – sepsis – was used for this condition.
The terms "septicemia", also spelled "septicaemia", and "blood poisoning" referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) version 9, which was in use in the US until 2013, used the term septicemia with numerous modifiers for different diagnoses, such as "Streptococcal septicemia". All those diagnoses have been converted to sepsis, again with modifiers, in ICD-10, such as "Sepsis due to streptococcus".
The current terms are dependent on the microorganism that is present: bacteremia if bacteria are present in the blood at abnormal levels and are the causative issue, viremia for viruses, and fungemia for a fungus.
By the end of the 19th century, it was widely believed that microbes produced substances that could injure the mammalian host and that soluble toxins released during infection caused the fever and shock that were commonplace during severe infections. Richard Friedrich Johannes Pfeiffer, Pfeiffer coined the term
The term "σήψις" (sepsis) was introduced by Hippocrates in the fourth century BC, and it meant the process of decomposition, decay or decomposition of organic matter. In the eleventh century, Avicenna used the term "blood rot" for diseases linked to severe Pus, purulent process. Though severe systemic toxicity had already been observed, it was only in the 19th century that the specific term – sepsis – was used for this condition.
The terms "septicemia", also spelled "septicaemia", and "blood poisoning" referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) version 9, which was in use in the US until 2013, used the term septicemia with numerous modifiers for different diagnoses, such as "Streptococcal septicemia". All those diagnoses have been converted to sepsis, again with modifiers, in ICD-10, such as "Sepsis due to streptococcus".
The current terms are dependent on the microorganism that is present: bacteremia if bacteria are present in the blood at abnormal levels and are the causative issue, viremia for viruses, and fungemia for a fungus.
By the end of the 19th century, it was widely believed that microbes produced substances that could injure the mammalian host and that soluble toxins released during infection caused the fever and shock that were commonplace during severe infections. Richard Friedrich Johannes Pfeiffer, Pfeiffer coined the term
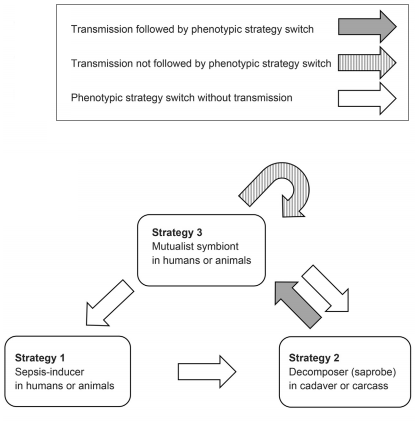 Some authors suggest that initiating sepsis by the normally Mutualism (biology), mutualistic (or neutral) members of the microbiome may not always be an accidental side effect of the deteriorating host immune system. Rather it is often an Adaptive behavior, adaptive microbial response to a sudden decline of host survival chances. Under this scenario, the microbe species provoking sepsis benefit from monopolizing the future cadaver, utilizing its biomass as decomposers, and then transmitted through soil or water to establish mutualistic relations with new individuals. The bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''
Some authors suggest that initiating sepsis by the normally Mutualism (biology), mutualistic (or neutral) members of the microbiome may not always be an accidental side effect of the deteriorating host immune system. Rather it is often an Adaptive behavior, adaptive microbial response to a sudden decline of host survival chances. Under this scenario, the microbe species provoking sepsis benefit from monopolizing the future cadaver, utilizing its biomass as decomposers, and then transmitted through soil or water to establish mutualistic relations with new individuals. The bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''
SIRS, Sepsis, and Septic Shock Criteria
* {{Authority control Sepsis, Articles containing video clips Infectious diseases Intensive care medicine Medical emergencies Neonatology Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is followed by suppression of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
. Common signs and symptoms include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, increased heart rate
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (su ...
, increased breathing rate, and confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
, or painful urination with a kidney infection
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications may ...
. The very young, old, and people with a weakened immune system
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
may have no symptoms of a specific infection, and the body temperature may be low or normal instead of having a fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
. Severe sepsis causes poor organ function or blood flow. The presence of low blood pressure
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, high blood lactate, or low urine output may suggest poor blood flow. Septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Con ...
is low blood pressure due to sepsis that does not improve after fluid replacement
Fluid replacement or fluid resuscitation is the medical practice of replenishing bodily fluid lost through sweating, bleeding, fluid shifts or other pathologic processes. Fluids can be replaced with oral rehydration therapy (drinking), intravenous ...
.
Sepsis is caused by many organisms including bacteria, viruses and fungi. Common locations for the primary infection include the lungs, brain, urinary tract
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, con ...
, skin, and abdominal organs
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso ...
. Risk factors include being very young or old, a weakened immune system from conditions such as cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
or diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, major trauma
Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Dependin ...
, and burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainl ...
s. Previously, a sepsis diagnosis required the presence of at least two systemic inflammatory response syndrome
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is the body's response to an infectious or noninfectious insult. Although the definition of SIRS refers to it as an "inflammatory" response, i ...
(SIRS) criteria in the setting of presumed infection. In 2016, a shortened sequential organ failure assessment score (SOFA score), known as the quick SOFA score (qSOFA), replaced the SIRS system of diagnosis. qSOFA criteria for sepsis include at least two of the following three: increased breathing rate, change in the level of consciousness, and low blood pressure. Sepsis guidelines recommend obtaining blood culture
A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or f ...
s before starting antibiotics; however, the diagnosis does not require the blood to be infected. Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
is helpful when looking for the possible location of the infection. Other potential causes of similar signs and symptoms include anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
, adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androge ...
, low blood volume
Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the los ...
, heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
, and pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain p ...
.
Sepsis requires immediate treatment with intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
and antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
s. Ongoing care often continues in an intensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensiv ...
. If an adequate trial of fluid replacement
Fluid replacement or fluid resuscitation is the medical practice of replenishing bodily fluid lost through sweating, bleeding, fluid shifts or other pathologic processes. Fluids can be replaced with oral rehydration therapy (drinking), intravenous ...
is not enough to maintain blood pressure, then the use of medications that raise blood pressure becomes necessary. Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air ...
and dialysis may be needed to support the function of the lungs and kidneys, respectively. A central venous catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more central ...
and an arterial catheter
An arterial line (also art-line or a-line) is a thin catheter inserted into an artery.
Use
Arterial lines are most commonly used in intensive care medicine and anesthesia to monitor blood pressure directly and in real-time (rather than by int ...
may be placed for access to the bloodstream and to guide treatment. Other helpful measurements include cardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: t ...
and superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein th ...
oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It ca ...
. People with sepsis need preventive measures for deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
, stress ulcer
A stress ulcer is a single or multiple mucosal defect usually caused by physiological (not psychological) stress which can become complicated by upper gastrointestinal bleeding. This ulcers can be caused by shock, sepsis, trauma or other conditions ...
s, and pressure ulcer
Pressure ulcers, also known as pressure sores, bed sores or pressure injuries, are localised damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combi ...
s unless other conditions prevent such interventions. Some people might benefit from tight control of blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
levels with insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
. The use of corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
is controversial, with some reviews finding benefit, and others not.
Disease severity partly determines the outcome. The risk of death from sepsis is as high as 30%, while for severe sepsis it is as high as 50%, and septic shock 80%. Sepsis affected about 49 million people in 2017, with 11 million deaths (1 in 5 deaths worldwide). In the developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
, approximately 0.2 to 3 people per 1000 are affected by sepsis yearly, resulting in about a million cases per year in the United States. Rates of disease have been increasing. Some data indicate that sepsis is more common among males than females, however, other data show a greater prevalence of the disease among women. Descriptions of sepsis date back to the time of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
.
Signs and symptoms
In addition to symptoms related to the actual cause, people with sepsis may have afever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, low body temperature, rapid breathing
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea b ...
, a fast heart rate, confusion
In medicine, confusion is the quality or state of being bewildered or unclear. The term "acute mental confusion"
, and edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
. Early signs include a rapid heart rate, decreased urination, and high blood sugar
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
. Signs of established sepsis include confusion, metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys ...
(which may be accompanied by a faster breathing rate that leads to respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis is a medical condition in which increased respiration elevates the blood pH beyond the normal range (7.35–7.45) with a concurrent reduction in arterial levels of carbon dioxide. This condition is one of the four primary di ...
), low blood pressure
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
due to decreased systemic vascular resistance
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome to push blood through the circulatory system and create flow. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) or may sometimes be ca ...
, higher cardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: t ...
, and disorders in blood-clotting that may lead to organ failure. Fever is the most common presenting symptom in sepsis, but fever may be absent in some people such as the elderly or those who are immunocompromised.
The drop in blood pressure
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dias ...
seen in sepsis can cause lightheadedness
Lightheadedness is a common and typically unpleasant sensation of dizziness or a feeling that one may faint. The sensation of lightheadedness can be short-lived, prolonged, or, rarely, recurring. In addition to dizziness, the individual may feel ...
and is part of the criteria for septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Con ...
.
Oxidative stress is observed in septic shock, with circulating levels of copper and vitamin C being decreased.
Cause
Infections leading to sepsis are usuallybacterial
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
but may be fungal
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
, parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has c ...
or viral. Gram-positive bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bact ...
were the primary cause of sepsis before the introduction of antibiotics in the 1950s. After the introduction of antibiotics, gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
became the predominant cause of sepsis from the 1960s to the 1980s. After the 1980s, gram-positive bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bact ...
, most commonly staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultative ...
, are thought to cause more than 50% of cases of sepsis. Other commonly implicated bacteria include ''Streptococcus pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus ''Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are ...
'', ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'', ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerugi ...
'', and ''Klebsiella
''Klebsiella'' is a genus of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule.
''Klebsiella'' species are found everywhere in nature. This is thought to be due to distinct sublineages developin ...
'' species. Fungal sepsis accounts for approximately 5% of severe sepsis and septic shock cases; the most common cause of fungal sepsis is an infection by '' Candida'' species of yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ...
, a frequent hospital-acquired infection
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is so ...
. The most common causes for parasitic sepsis are ''Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vert ...
'' (which leads to malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
), ''Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed '' schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World Health Organ ...
'' and ''Echinococcus
''Echinococcus'' is a genus within Cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum (colloquially known as flatworms). Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, or ...
''.
The most common sites of infection resulting in severe sepsis are the lungs, the abdomen, and the urinary tract. Typically, 50% of all sepsis cases start as an infection in the lungs. In one-third to one-half of cases, the source of infection is unclear.
Pathophysiology
Sepsis is caused by a combination of factors related to the particular invading pathogen(s) and to the status of the immune system of the host. The early phase of sepsis characterized by excessive inflammation (sometimes resulting in acytokine storm
A cytokine storm, also called hypercytokinemia, is a physiological reaction in humans and other animals in which the innate immune system causes an uncontrolled and excessive release of pro-inflammatory signaling molecules called cytokines. Norma ...
) may be followed by a prolonged period of decreased functioning of the immune system. Either of these phases may prove fatal. On the other hand, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) occurs in people without the presence of infection, for example, in those with burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainl ...
s, polytrauma Polytrauma and multiple trauma are medical terms describing the condition of a person who has been subjected to multiple traumatic injuries, such as a serious head injury in addition to a serious burn. The term is defined via an Injury Severity Sc ...
, or the initial state in pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancr ...
and chemical pneumonitis
Chemical pneumonitis is inflammation of the lung caused by aspirating or inhaling irritants. It is sometimes called a "chemical pneumonia", though it is not infectious. There are two general types of chemical pneumonitis: acute and chronic.
Irri ...
. However, sepsis also causes similar response to SIRS.
Microbial factors
Bacterialvirulence factor
Virulence factors (preferably known as pathogenicity factors or effectors in plant science) are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa) to achieve the following ...
s, such as glycocalyx
The glycocalyx, also known as the pericellular matrix, is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds the cell membranes of bacteria, epithelial cells, and other cells. In 1970, Martinez-Palomo discovered the cell coating in animal cells ...
and various adhesins Adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate adhesion or adherence to other cells or to surfaces, usually in the host they are infecting or living in. Adhesins are a type of virulence factor.
Adherence is an essent ...
, allow colonization, immune evasion, and establishment of disease in the host. Sepsis caused by gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
bacteria is thought to be largely due to a response by the host to the lipid A
Lipid A is a lipid component of an endotoxin held responsible for the toxicity of gram-negative bacteria. It is the innermost of the three regions of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS), also called endotoxin molecule, and its hydrophobic nature allows it ...
component of lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer m ...
, also called endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer ...
. Sepsis caused by gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bacte ...
bacteria may result from an immunological response to cell wall lipoteichoic acid Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a major constituent of the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. These organisms have an inner (or cytoplasmic) membrane and, external to it, a thick (up to 80 nanometer) peptidoglycan layer. The structure of LTA varies be ...
. Bacterial exotoxin
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, simi ...
s that act as superantigens
Superantigens (SAgs) are a class of antigens that result in excessive activation of the immune system. Specifically it causes non-specific activation of T-cells resulting in polyclonal T cell activation and massive cytokine release. SAgs are p ...
also may cause sepsis. Superantigens simultaneously bind major histocompatibility complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are calle ...
and T-cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
s in the absence of antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now ...
. This forced receptor interaction induces the production of pro-inflammatory chemical signals (cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
) by T-cells.
There are a number of microbial factors that may cause the typical septic inflammatory cascade. An invading pathogen is recognized by its pathogen-associated molecular pattern
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes. They are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in both plants and animals. A vast arra ...
s (PAMPs). Examples of PAMPs include lipopolysaccharides and flagellin
Flagellin is a globular protein that arranges itself in a hollow cylinder to form the filament in a bacterial flagellum. It has a mass of about 30,000 to 60,000 daltons. Flagellin is the principal component of bacterial flagella, and is present ...
in gram-negative bacteria, muramyl dipeptide
Muramyl dipeptide is constituent of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria composed of N-acetylmuramic acid linked by its lactic acid moiety to the N-terminus of an L-alanine D- isoglutamine dipeptide.
It can be recognized by the immune s ...
in the peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ...
of the gram-positive bacterial cell wall, and CpG bacterial DNA. These PAMPs are recognized by the pattern recognition receptors
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system. PRRs are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens. They are proteins expressed, mainly, by cells of ...
(PRRs) of the innate immune system, which may be membrane-bound or cytosolic. There are four families of PRRs: the toll-like receptors
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane-spanning receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize st ...
, the C-type lectin
A C-type lectin (CLEC) is a type of carbohydrate-binding protein known as a lectin. The C-type designation is from their requirement for calcium for binding. Proteins that contain C-type lectin domains have a diverse range of functions including ...
receptors, the NOD-like receptor
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the ...
s, and the RIG-I-like receptor
RIG-like receptors (retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptors, RLRs) are a type of intracellular pattern recognition receptor involved in the recognition of viruses by the innate immune system. RIG-I (retinoic-acid inducible gene or DDX58) is t ...
s. Invariably, the association of a PAMP and a PRR will cause a series of intracellular signalling cascades. Consequentially, transcription factors such as nuclear factor-kappa B
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
and activator protein-1, will up-regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Host factors
Upon detection of microbialantigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
s, the host systemic immune system is activated. Immune cells not only recognise pathogen-associated molecular patterns but also damage-associated molecular pattern
Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are molecules within cells that are a component of the innate immune response released from damaged or dying cells due to trauma or an infection by a pathogen. They are also known as danger-associated m ...
s from damaged tissues. An uncontrolled immune response is then activated because leukocyte
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
s are not recruited to the specific site of infection, but instead they are recruited all over the body. Then, an immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
state ensues when the proinflammatory T helper cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
1 (TH1) is shifted to TH2, mediated by interleukin 10
Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti- inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 ...
, which is known as "compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome". The apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
(cell death) of lymphocytes further worsens the immunosuppression. Neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
s, monocytes
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also infl ...
, macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, dendritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. ...
s, CD4+ T cells
In molecular biology, CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as T helper cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic ce ...
, and B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
s all undergo apoptosis, whereas regulatory T cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosup ...
s are more apoptosis resistant. Subsequently, multiple organ failure
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple organ failure" or "multisy ...
ensues because tissues are unable to use oxygen efficiently due to inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV, (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and mitochondria of eukaryotes.
It is the last enzyme in the respiratory electr ...
.
Inflammatory responses cause multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ (anatomy), organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medicine, medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple ...
through various mechanisms as described below. Increased permeability of the lung vessels causes leaking of fluids into alveoli, which results in pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
and acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
(ARDS). Impaired utilization of oxygen in the liver impairs bile salt
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
Prima ...
transport, causing jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
(yellowish discoloration of the skin). In kidneys, inadequate oxygenation results in tubular epithelial cell injury (of the cells lining the kidney tubules), and thus causes acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are cla ...
(AKI). Meanwhile, in the heart, impaired calcium transport, and low production of adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of ...
(ATP), can cause myocardial depression, reducing cardiac contractility and causing heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
. In the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
, increased permeability of the mucosa alters the microflora, causing mucosal bleeding and paralytic ileus
Ileus is a disruption of the normal propulsive ability of the intestine. It can be caused by lack of peristalsis or by mechanical obstruction.
The word 'ileus' is from Ancient Greek ''eileós'' (, "intestinal obstruction"). The term 'subileus' re ...
. In the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all par ...
, direct damage of the brain cells and disturbances of neurotransmissions causes altered mental status. Cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, interleukin 1
The Interleukin-1 family (IL-1 family) is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.
Discovery
Discovery of these cytokines began with studies on t ...
, and interleukin 6
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, it is encoded by the ''IL6'' gene.
In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth ...
may activate procoagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism ...
factors in the cells lining blood vessels, leading to endothelial damage. The damaged endothelial surface inhibits anticoagulant properties as well as increases antifibrinolysis, which may lead to intravascular clotting, the formation of blood clots
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cr ...
in small blood vessels, and multiple organ failure
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring medical intervention to achieve homeostasis.
Although Irwin and Rippe cautioned in 2005 that the use of "multiple organ failure" or "multisy ...
.
The low blood pressure seen in those with sepsis is the result of various processes, including excessive production of chemicals that dilate blood vessels such as nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its che ...
, a deficiency of chemicals that constrict blood vessels such as vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
, and activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channel
An ATP-sensitive potassium channel (or KATP channel) is a type of potassium channel that is gated by intracellular nucleotides, ATP and ADP. ATP-sensitive potassium channels are composed of Kir6.x-type subunits and sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) ...
s. In those with severe sepsis and septic shock, this sequence of events leads to a type of circulatory shock
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, fast heart rate, fast breathing, sweating, anxiety, and increased thi ...
known as distributive shock
Distributive shock is a medical condition in which abnormal distribution of blood flow in the smallest blood vessels results in inadequate supply of blood to the body's tissues and organs. It is one of four categories of shock, a condition where ...
.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is necessary to properly manage sepsis, as the initiation of rapid therapy is key to reducing deaths from severe sepsis. Some hospitals use alerts generated fromelectronic health record
An electronic health record (EHR) is the systematized collection of patient and population electronically stored health information in a digital format. These records can be shared across different health care settings. Records are shared throu ...
s to bring attention to potential cases as early as possible.
blood culture
A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or f ...
s using bottles with media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass el ...
for aerobic
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen.
Aerobic may also refer to
* Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity
* Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise
* Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of cellu ...
and anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenate ...
s are necessary. At least one should be drawn through the skin and one through each vascular access device (such as an IV catheter) that has been in place more than 48 hours. Bacteria are present in the blood in only about 30% of cases. Another possible method of detection is by polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
. If other sources of infection are suspected, cultures of these sources, such as urine, cerebrospinal fluid, wounds, or respiratory secretions, also should be obtained, as long as this does not delay the use of antibiotics.
Within six hours, if blood pressure remains low despite initial fluid resuscitation of 30 mL/kg, or if initial lactate is ≥ four mmol/L (36 mg/dL), central venous pressure Central venous pressure (CVP) is the blood pressure in the venae cavae, near the right atrium of the heart. CVP reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability of the heart to pump the blood back into the arterial system. CVP is ...
and central venous oxygen saturation should be measured. Lactate should be re-measured if the initial lactate was elevated. Evidence for point of care
Clinical point of care (POC) is the point in time when clinicians deliver healthcare products and services to patients at the time of care.
Clinical documentation
Clinical documentation is a record of the critical thinking and judgment of a health ...
lactate measurement over usual methods of measurement, however, is poor.
Within twelve hours, it is essential to diagnose or exclude any source of infection that would require emergent source control, such as a necrotizing soft tissue infection, an infection causing inflammation of the abdominal cavity lining, an infection of the bile duct, or an intestinal infarction. A pierced internal organ
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a f ...
(free air on an abdominal X-ray or CT scan), an abnormal chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
consistent with pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
(with focal opacification), or petechia
A petechia () is a small red or purple spot (≤4 mm in diameter) that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and Mucous membrane, mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian , 'freckle,' ...
e, purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
, or purpura fulminans
Purpura fulminans is an acute, often fatal, thrombotic disorder which manifests as blood spots, bruising and discolouration of the skin resulting from coagulation in small blood vessels within the skin and rapidly leads to skin necrosis and disse ...
may indicate the presence of an infection.
Definitions
 Previously, SIRS criteria had been used to define sepsis. If the SIRS criteria are negative, it is very unlikely the person has sepsis; if it is positive, there is just a moderate probability that the person has sepsis. According to SIRS, there were different levels of sepsis: sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The definition of SIRS is shown below:
* SIRS is the presence of two or more of the following: abnormal
Previously, SIRS criteria had been used to define sepsis. If the SIRS criteria are negative, it is very unlikely the person has sepsis; if it is positive, there is just a moderate probability that the person has sepsis. According to SIRS, there were different levels of sepsis: sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The definition of SIRS is shown below:
* SIRS is the presence of two or more of the following: abnormal body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
, respiratory rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is mea ...
, or blood gas, and white blood cell count.
* ''Sepsis'' is defined as SIRS in response to an infectious process.
* ''Severe sepsis'' is defined as sepsis with sepsis-induced organ dysfunction or tissue hypoperfusion (manifesting as hypotension, elevated lactate, or oliguria, decreased urine output). Severe sepsis is an infectious disease state associated with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
* ''Septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Con ...
'' is severe sepsis plus persistently low blood pressure
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dia ...
, despite the administration of intravenous fluids.
In 2016 a new consensus was reached to replace screening by systemic inflammatory response syndrome
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is the body's response to an infectious or noninfectious insult. Although the definition of SIRS refers to it as an "inflammatory" response, i ...
(SIRS) with the sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA score) and the abbreviated version (qSOFA). The three criteria for the qSOFA score include a respiratory rate greater than or equal to 22 breaths per minute, systolic blood pressure 100 mmHg or less and altered mental status. Sepsis is suspected when 2 of the qSOFA criteria are met. The SOFA score was intended to be used in the intensive care unit (ICU) where it is administered upon admission to the ICU and then repeated every 48 hours, whereas the qSOFA could be used outside the ICU. Some advantages of the qSOFA score are that it can be administered quickly and does not require labs. However, the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) raised concerns that qSOFA and SOFA criteria may lead to delayed diagnosis of serious infection, leading to delayed treatment. Although SIRS criteria can be too sensitive and not specific enough in identifying sepsis, SOFA also has its limitations and is not intended to replace the SIRS definition. qSOFA has also been found to be poorly sensitive though decently specific for the risk of death with SIRS possibly better for screening. NOTE - Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2021 Guidelines recommends "against using qSOFA compared with SIRS, NEWS, or MEWS as a single screening tool for sepsis or septic shock".
End-organ dysfunction
Examples of end organ damage, end-organ dysfunction include the following: * Lungs:acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
(ARDS) (PaO2/FiO2 ratio, PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300), different ratio in Acute respiratory distress syndrome#Terminology, pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome
* Brain: encephalopathy symptoms including agitation, confusion, coma; causes may include ischemia, bleeding, formation of blood clots in small blood vessels, microabscesses, multifocal necrotizing leukoencephalopathy
* Liver: disruption of protein synthetic function manifests acutely as progressive coagulopathy, disruption of blood clotting due to an inability to synthesize clotting factors and disruption of metabolic functions leads to impaired bilirubin metabolism, resulting in elevated unconjugated serum bilirubin levels
* Kidney: oliguria, low urine output or anuria, no urine output, electrolyte abnormalities, or volume overload
* Heart: systolic and diastolic heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
, likely due to cytokines, chemical signals that depress myocyte function, cellular damage, manifest as a troponin leak (although not necessarily ischemic in nature)
More specific definitions of end-organ dysfunction exist for SIRS in pediatrics.
* Cardiovascular dysfunction (after fluid resuscitation with at least 40 mL/kg of crystalloid)
** hypotension with blood pressure < 5th percentile for age or systolic blood pressure < 2 standard deviations below normal for age, or
** vasopressor requirement, or
** two of the following criteria:
*** unexplained metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys ...
with base deficit > 5 mEq/L
*** lactic acidosis: serum lactate 2 times the upper limit of normal
*** oliguria (urine output )
*** prolonged capillary refill > 5 seconds
*** core to peripheral temperature difference
* Respiratory dysfunction (in the absence of a cyanotic heart defect or a known chronic respiratory disease)
** the ratio of the arterial partial-pressure of oxygen to the fraction of oxygen in the gases inspired (PaO2/FiO2) < 300 (the definition of acute lung injury), or
** arterial partial-pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) > 65 torr (20 millimetre of mercury, mmHg) over baseline PaCO2 (evidence of hypercapnia, hypercapnic respiratory failure), or
** supplemental oxygen requirement of greater than FiO2 0.5 to maintain oxygen saturation ≥ 92%
* Neurologic dysfunction
** Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) ≤ 11, or
** altered level of consciousness, altered mental status with drop in GCS of 3 or more points in a person with developmental delay/intellectual disability
* Hematologic dysfunction
** platelet count or 50% drop from maximum in chronically thrombocytopenic, or
** international normalized ratio (INR) > 2
** Disseminated intravascular coagulation
* Kidney dysfunction
** serum creatinine ≥ 2 times the upper limit of normal for age or 2-fold increase in baseline creatinine in people with chronic kidney disease
* Liver dysfunction (only applicable to infants > 1 month)
** total serum bilirubin ≥ 4 mg/dL, or
** alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ≥ 2 times the upper limit of normal
Consensus definitions, however, continue to evolve, with the latest expanding the list of signs and symptoms of sepsis to reflect clinical bedside experience.
Biomarkers
Biomarkers can help diagnosis because they can point to the presence or severity of sepsis, although their exact role in the management of sepsis remains undefined. A 2013 review concluded moderate-quality evidence exists to support the use of the procalcitonin level as a method to distinguish sepsis from non-infectious causes of SIRS. The same review found the Sensitivity and specificity, sensitivity of the test to be 77% and the specificity to be 79%. The authors suggested that procalcitonin may serve as a helpful diagnostic marker for sepsis, but cautioned that its level alone does not definitively make the diagnosis. A 2012 systematic review found that SuPAR, soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (SuPAR) is a nonspecific marker of inflammation and does not accurately diagnose sepsis. This same review concluded, however, that SuPAR has prognostic value, as higher SuPAR levels are associated with an increased rate of death in those with sepsis. Serial measurement of lactate levels (approximately every 4 to 6 hours) may guide treatment and is associated with lower mortality in sepsis.Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for sepsis is broad and has to examine (to exclude) the non-infectious conditions that may cause the systemic signs of SIRS: alcohol withdrawal, acute pancreatitis,burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainl ...
s, pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain p ...
, thyrotoxicosis, anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
, adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androge ...
, and neurogenic shock. Hyperinflammatory syndromes such as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) may have similar symptoms and are on the differential diagnosis.
Neonatal sepsis
In common clinical usage, neonatal sepsis refers to a bacterial bacteremia, blood stream infection in the first month of life, such as meningitis,pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
, pyelonephritis, or gastroenteritis, but neonatal sepsis also may be due to infection with fungi, viruses, or parasites. Criteria with regard to hemodynamic compromise or respiratory failure are not useful because they present too late for intervention.
Management
 Early recognition and focused management may improve the outcomes in sepsis. Current professional recommendations include a number of actions ("bundles") to be followed as soon as possible after diagnosis. Within the first three hours, someone with sepsis should have received antibiotics and, intravenous fluids if there is evidence of either low blood pressure or other evidence for inadequate blood supply to organs (as evidenced by a raised level of lactate); blood cultures also should be obtained within this time period. After six hours the blood pressure should be adequate, close monitoring of blood pressure and blood supply to organs should be in place, and the lactate should be measured again if initially it was raised. A related bundle, the "Sepsis Six", is in widespread use in the United Kingdom; this requires the administration of antibiotics within an hour of recognition, blood cultures, lactate, and hemoglobin determination, urine output monitoring, high-flow oxygen, and intravenous fluids.
Apart from the timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, the management of sepsis also involves surgical drainage of infected fluid collections and appropriate support for organ dysfunction. This may include Kidney dialysis, hemodialysis in kidney failure, mechanical ventilation in lung dysfunction, transfusion of blood plasma, blood products, and drug and fluid therapy for circulatory failure. Ensuring adequate nutrition—preferably by enteral feeding, but if necessary, by parenteral nutrition—is important during prolonged illness. Medication to prevent
Early recognition and focused management may improve the outcomes in sepsis. Current professional recommendations include a number of actions ("bundles") to be followed as soon as possible after diagnosis. Within the first three hours, someone with sepsis should have received antibiotics and, intravenous fluids if there is evidence of either low blood pressure or other evidence for inadequate blood supply to organs (as evidenced by a raised level of lactate); blood cultures also should be obtained within this time period. After six hours the blood pressure should be adequate, close monitoring of blood pressure and blood supply to organs should be in place, and the lactate should be measured again if initially it was raised. A related bundle, the "Sepsis Six", is in widespread use in the United Kingdom; this requires the administration of antibiotics within an hour of recognition, blood cultures, lactate, and hemoglobin determination, urine output monitoring, high-flow oxygen, and intravenous fluids.
Apart from the timely administration of fluids and antibiotics, the management of sepsis also involves surgical drainage of infected fluid collections and appropriate support for organ dysfunction. This may include Kidney dialysis, hemodialysis in kidney failure, mechanical ventilation in lung dysfunction, transfusion of blood plasma, blood products, and drug and fluid therapy for circulatory failure. Ensuring adequate nutrition—preferably by enteral feeding, but if necessary, by parenteral nutrition—is important during prolonged illness. Medication to prevent deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
and gastric ulcers also may be used.
Antibiotics
Two sets of blood cultures (aerobic and anaerobic) are recommended without delaying the initiation of antibiotics. Cultures from other sites such as respiratory secretions, urine, wounds, cerebrospinal fluid, and catheter insertion sites (in-situ more than 48 hours) are recommended if infections from these sites are suspected. In severe sepsis and septic shock, broad-spectrum antibiotics (usually two, a β-lactam antibiotic with broad coverage, or broad-spectrum carbapenem combined with Quinolone antibiotic, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, or aminoglycosides) are recommended. The choice of antibiotics is important in determining the survival of the person. Some recommend they be given within one hour of making the diagnosis, stating that for every hour of delay in the administration of antibiotics, there is an associated 6% rise in mortality. Others did not find a benefit with early administration. Several factors determine the most appropriate choice for the initial antibiotic regimen. These factors include local patterns of bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics, whether the infection is thought to be a Hospital-acquired infection, hospital or community-acquired infection, and which organ systems are thought to be infected. Antibiotic regimens should be reassessed daily and narrowed if appropriate. Treatment duration is typically 7–10 days with the type of antibiotic used directed by the results of cultures. If the culture result is negative, antibiotics should be de-escalated according to the person's clinical response or stopped altogether if an infection is not present to decrease the chances that the person is infected with multiple drug resistance organisms. In case of people having a high risk of being infected with multiple drug resistance, multiple drug resistant organisms such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerugi ...
'', ''Acinetobacter baumannii'', the addition of an antibiotic specific to the gram-negative organism is recommended. For Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA), vancomycin or teicoplanin is recommended. For ''Legionella'' infection, addition of macrolide or fluoroquinolone is chosen. If fungal infection is suspected, an echinocandin, such as caspofungin or micafungin, is chosen for people with severe sepsis, followed by triazole (fluconazole and itraconazole) for less ill people. Prolonged antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended in people who has SIRS without any infectious origin such as acute pancreatitis and burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainl ...
s unless sepsis is suspected.
Once-daily dosing of aminoglycoside is sufficient to achieve peak plasma concentration for a clinical response without kidney toxicity. Meanwhile, for antibiotics with low volume distribution (vancomycin, teicoplanin, colistin), a loading dose is required to achieve an adequate therapeutic level to fight infections. Frequent infusions of beta-lactam antibiotics without exceeding total daily dose would help to keep the antibiotics level above minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), thus providing a better clinical response. Giving beta-lactam antibiotics continuously may be better than giving them intermittently. Access to therapeutic drug monitoring is important to ensure adequate drug therapeutic level while at the same time preventing the drug from reaching toxic level.
Intravenous fluids
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign has recommended 30 mL/kg of fluid to be given in adults in the first three hours followed by fluid titration according to blood pressure, urine output, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation with a target mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 65 mmHg. In children an initial amount of 20 mL/kg is reasonable in shock. In cases of severe sepsis and septic shock where acentral venous catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line(c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more central ...
is used to measure blood pressures dynamically, fluids should be administered until the central venous pressure Central venous pressure (CVP) is the blood pressure in the venae cavae, near the right atrium of the heart. CVP reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability of the heart to pump the blood back into the arterial system. CVP is ...
reaches 8–12 mmHg. Once these goals are met, the central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2), i.e., the oxygen saturation of venous blood as it returns to the heart as measured at the vena cava, is optimized. If the ScvO2 is less than 70%, blood may be given to reach a hemoglobin of 10 g/dL and then inotropes are added until the ScvO2 is optimized. In those with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
(ARDS) and sufficient tissue blood fluid, more fluids should be given carefully.
Crystalloid solution is recommended as the fluid of choice for resuscitation. Albumin can be used if a large amount of crystalloid is required for resuscitation. Crystalloid solutions shows little difference with hydroxyethyl starch in terms of risk of death. Starches also carry an increased risk of acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in kidney function that develops within 7 days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
Causes of AKI are cla ...
, and need for blood transfusion. Various colloid solutions (such as modified gelatin) carry no advantage over crystalloid. Albumin also appears to be of no benefit over crystalloids.
Blood products
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommended packed red blood cells transfusion for hemoglobin levels below 70 g/L if there is no myocardial ischemia, hypoxemia, or acute bleeding. In a 2014 trial, blood transfusions to keep target hemoglobin above 70 or 90 g/L did not make any difference to survival rates; meanwhile, those with a lower threshold of transfusion received fewer transfusions in total. Erythropoietin is not recommended in the treatment of anemia with septic shock because it may precipitate Thrombosis, blood clotting events. Fresh frozen plasma transfusion usually does not correct the underlying clotting abnormalities before a planned surgical procedure. However, platelet transfusion is suggested for platelet counts below (10 × 109/L) without any risk of bleeding, or (20 × 109/L) with high risk of bleeding, or (50 × 109/L) with active bleeding, before a planned surgery or an invasive procedure. IV immunoglobulin is not recommended because its beneficial effects are uncertain. Monoclonal and polyclonal preparations of intravenous immunoglobulin, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) do not lower the rate of death in newborns and adults with sepsis. Evidence for the use of immunoglobulin M, IgM-enriched polyclonal preparations of IVIG is inconsistent. On the other hand, the use of antithrombin#Medical uses, antithrombin to treat disseminated intravascular coagulation is also not useful. Meanwhile, the blood purification technique (such as hemoperfusion, plasma filtration, and coupled plasma filtration adsorption) to remove inflammatory mediators and bacterial toxins from the blood also does not demonstrate any survival benefit for septic shock.Vasopressors
If the person has been sufficiently fluid resuscitated but the mean arterial pressure is not greater than 65 mmHg, vasopressors are recommended. Norepinephrine (medication), Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) is recommended as the initial choice. Delaying initiation of vasopressor therapy during septic shock is associated with increased mortality. Norepinephrine is often used as a first-line treatment for hypotensive septic shock because evidence shows that there is a relative deficiency of vasopressin when shock continues for 24 to 48 hours. Norepinephrine raises blood pressure through a vasoconstriction effect, with little effect on stroke volume and heart rate. In some people, the required dose of vasopressor needed to increase the mean arterial pressure can become exceedingly high that it becomes toxic. In order to reduce the required dose of vasopressor, epinephrine may be added. Epinephrine is not often used as a first-line treatment for hypotensive shock because it reduces blood flow to the abdominal organs and increases lactate levels. Vasopressin can be used in septic shock because studies have shown that there is a relative deficiency of vasopressin when shock continues for 24 to 48 hours. However, vasopressin reduces blood flow to the heart, finger/toes, and abdominal organs, resulting in a lack of oxygen supply to these tissues. Dopamine is typically not recommended. Although dopamine is useful to increase the stroke volume of the heart, it causes more Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms than norepinephrine and also has an immunosuppressive effect. Dopamine is not proven to have protective properties on the kidneys. Dobutamine can also be used in hypotensive septic shock to increase cardiac output and correct blood flow to the tissues. Dobutamine is not used as often as epinephrine due to its associated side effects, which include reducing blood flow to the gut. Additionally, dobutamine increases the cardiac output by abnormally increasing the heart rate.Steroids
The use of steroids in sepsis is controversial. Studies do not give a clear picture as to whether and when glucocorticoids should be used. The 2016 Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommends low dose hydrocortisone only if both intravenous fluids and vasopressors are not able to adequately treat septic shock. The 2021 Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommends IV corticosteroids for adults with septic shock who have an ongoing requirement for vasopressor therapy. A 2019 Cochrane review found low-quality evidence of benefit, as did two 2019 reviews. During critical illness, a state ofadrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androge ...
and tissue resistance to corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
may occur. This has been termed critical illness–related corticosteroid insufficiency. Treatment with corticosteroids might be most beneficial in those with septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Con ...
and early severe ARDS, whereas its role in others such as those with pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types: acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancr ...
or severe pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
is unclear. However, the exact way of determining corticosteroid insufficiency remains problematic. It should be suspected in those poorly responding to resuscitation with fluids and vasopressors. Neither Cort-stim test, ACTH stimulation testing nor random cortisol levels are recommended to confirm the diagnosis. The method of stopping glucocorticoid drugs is variable, and it is unclear whether they should be slowly decreased or simply abruptly stopped. However, the 2016 Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommended to taper steroids when vasopressors are no longer needed.
Anesthesia
A target tidal volume of 6 mL/kg of predicted body weight (PBW) and a plateau pressure less than 30 cm H2O is recommended for those who require mechanical ventilation, ventilation due to sepsis-induced severe ARDS. High positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) is recommended for moderate to severe ARDS in sepsis as it opens more lung units for oxygen exchange. Predicted body weight is calculated based on sex and height, and tools for this are available. Recruitment maneuvers may be necessary for severe ARDS by briefly raising the transpulmonary pressure. It is recommended that the head of the bed be raised if possible to improve ventilation. However, beta2-adrenergic agonist, β2 adrenergic receptor agonists are not recommended to treat ARDS because it may reduce survival rates and precipitate Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms. A spontaneous breathing trial using continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), T piece, or inspiratory pressure augmentation can be helpful in reducing the duration of ventilation. Minimizing intermittent or continuous sedation is helpful in reducing the duration of mechanical ventilation. General anesthesia is recommended for people with sepsis who require surgical procedures to remove the infective source. Usually, inhalational and intravenous anesthetics are used. Requirements for anesthetics may be reduced in sepsis. Inhalational anaesthetic, Inhalational anesthetics can reduce the level of proinflammatory cytokines, altering leukocyte adhesion and proliferation, inducingapoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
(cell death) of the lymphocytes, possibly with a toxic effect on mitochondrial function. Although etomidate has a minimal effect on the cardiovascular system, it is often not recommended as a medication to help with intubation in this situation due to concerns it may lead to adrenal insufficiency, poor adrenal function and an increased risk of death. The small amount of evidence there is, however, has not found a change in the risk of death with etomidate.
Neuromuscular-blocking drug, Paralytic agents are not suggested for use in sepsis cases in the absence of Acute respiratory distress syndrome, ARDS, as a growing body of evidence points to reduced durations of mechanical ventilation, ICU and hospital stays. However, paralytic use in Acute respiratory distress syndrome, ARDS cases remains controversial. When appropriately used, paralytics may aid successful mechanical ventilation, however, evidence has also suggested that mechanical ventilation in severe sepsis does not improve oxygen consumption and delivery.
Source control
Source control refers to physical interventions to control a focus of infection and reduce conditions favorable to microorganism growth or host defense impairment, such as Incision and drainage, drainage of pus from an abscess. It is one of the oldest procedures for control of infections, giving rise to the Latin phrase ''Ubi pus, ibi evacua'', and remains important despite the emergence of more modern treatments.Early goal directed therapy
Early goal directed therapy (EGDT) is an approach to the management of severe sepsis during the initial 6 hours after diagnosis. It is a step-wise approach, with the physiologic goal of optimizing cardiac preload, afterload, and contractility. It includes giving early antibiotics. EGDT also involves monitoring of hemodynamic parameters and specific interventions to achieve key resuscitation targets which include maintaining a central venous pressure between 8–12 mmHg, a mean arterial pressure of between 65 and 90 mmHg, a central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) greater than 70% and a urine output of greater than 0.5 mL/kg/hour. The goal is to optimize oxygen delivery to tissues and achieve a balance between systemic oxygen delivery and demand. An appropriate decrease in serum lactate may be equivalent to ScvO2 and easier to obtain. In the original trial, early goal-directed therapy was found to reduce mortality from 46.5% to 30.5% in those with sepsis, and the Surviving Sepsis Campaign has been recommending its use. However, three more recent large randomized control trials (ProCESS, ARISE, and ProMISe), did not demonstrate a 90-day mortality benefit of early goal-directed therapy when compared to standard therapy in severe sepsis. It is likely that some parts of EGDT are more important than others. Following these trials the use of EGDT is still considered reasonable.Newborns
Neonatal sepsis can be difficult to diagnose as newborns may be asymptomatic. If a newborn shows signs and symptoms suggestive of sepsis, antibiotics are immediately started and are either changed to target a specific organism identified by diagnostic testing or discontinued after an infectious cause for the symptoms has been ruled out. Despite early intervention, death occurs in 13% of children who develop septic shock, with the risk partly based on other health problems. Those without multiple organ system failures or who require only one inotropic agent mortality is low.Other
Treating fever in sepsis, including people in septic shock, has not been associated with any improvement in mortality over a period of 28 days. Treatment of fever still occurs for other reasons. A 2012 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane review concluded that N-acetylcysteine does not reduce mortality in those with SIRS or sepsis and may even be harmful. Recombinant DNA, Recombinant activated protein C (drotrecogin alpha) was originally introduced for severe sepsis (as identified by a high APACHE II score), where it was thought to confer a survival benefit. However, subsequent studies showed that it increased adverse events—bleeding risk in particular—and did not decrease mortality. It was removed from sale in 2011. Another medication known as eritoran also has not shown benefit. In those withhigh blood sugar
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
levels, insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism o ...
to bring it down to 7.8–10 mmol/L (140–180 mg/dL) is recommended with lower levels potentially worsening outcomes. Glucose levels taken from capillary blood should be interpreted with care because such measurements may not be accurate. If a person has an arterial catheter, arterial blood is recommended for blood glucose testing.
Intermittent or continuous renal replacement therapy may be used if indicated. However, sodium bicarbonate is not recommended for a person with lactic acidosis secondary to hypoperfusion. Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), unfractionated heparin (UFH), and mechanical prophylaxis with intermittent pneumatic compression devices are recommended for any person with sepsis at moderate to high risk of venous thromboembolism. Stress ulcer prevention with proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) and H2 antagonist are useful in a person with risk factors of developing upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) such as on mechanical ventilation for more than 48 hours, coagulation disorders, liver disease, and renal replacement therapy. Achieving partial or full enteral feeding (delivery of nutrients through a feeding tube) is chosen as the best approach to provide nutrition for a person who is contraindicated for oral intake or unable to tolerate orally in the first seven days of sepsis when compared to parenteral nutrition, intravenous nutrition. However, omega-3 fatty acids are not recommended as immune supplements for a person with sepsis or septic shock. The usage of prokinetic agents such as metoclopramide, domperidone, and erythromycin are recommended for those who are septic and unable to tolerate enteral feeding. However, these agents may precipitate prolongation of the QT interval and consequently provoke a ventricular arrhythmia such as torsades de pointes. The usage of prokinetic agents should be reassessed daily and stopped if no longer indicated.
Prognosis
Sepsis will prove fatal in approximately 24.4% of people, and septic shock will prove fatal in 34.7% of people within 30 days (32.2% and 38.5% after 90 days). Lactate is a useful method of determining prognosis, with those who have a level greater than 4 mmol/L having a mortality of 40% and those with a level of less than 2 mmol/L having a mortality of less than 15%. There are a number of prognostic stratification systems, such as APACHE II and Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis. APACHE II factors in the person's age, underlying condition, and various physiologic variables to yield estimates of the risk of dying of severe sepsis. Of the individual covariates, the severity of the underlying disease most strongly influences the risk of death. Septic shock is also a strong predictor of short- and long-term mortality. Case-fatality rates are similar for culture-positive and culture-negative severe sepsis. The Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis (MEDS) score is simpler and useful in the emergency department environment. Some people may experience severe long-term cognitive decline following an episode of severe sepsis, but the absence of baseline neuropsychological data in most people with sepsis makes the incidence of this difficult to quantify or to study.Epidemiology
Sepsis causes millions of deaths globally each year and is the most common cause of death in people who have been hospitalized. The Incidence (epidemiology), number of new cases worldwide of sepsis is estimated to be 18 million cases per year. In the United States sepsis affects approximately 3 in 1,000 people, and severe sepsis contributes to more than 200,000 deaths per year. Sepsis occurs in 1–2% of all hospitalizations and accounts for as much as 25% of ICU bed utilization. Due to it rarely being reported as a primary diagnosis (often being a complication of cancer or other illness), the incidence, mortality, and morbidity rates of sepsis are likely underestimated. A study of U.S. states found approximately 651 hospital stays per 100,000 population with a sepsis diagnosis in 2010. It is the second-leading cause of death in non-coronaryintensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensiv ...
(ICU) and the tenth-most-common cause of death overall (the first being heart disease). Children under 12 months of age and elderly people have the highest incidence of severe sepsis. Among people from the U.S. who had multiple sepsis hospital admissions in 2010, those who were discharged to a skilled nursing facility or long-term care following the initial hospitalization were more likely to be readmitted than those discharged to another form of care. A study of 18 U.S. states found that, amongst people with Medicare (United States), Medicare in 2011, sepsis was the second most common principal reason for readmission within 30 days.
Several medical conditions increase a person's susceptibility to infection and developing sepsis. Common sepsis risk factors include age (especially the very young and old); conditions that weaken the immune system such as cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, or the asplenia, absence of a spleen; and major trauma
Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Dependin ...
and burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainl ...
s.
From 1979 to 2000, data from the United States National Hospital Discharge Survey showed that the incidence of sepsis increased fourfold, to 240 cases per 100,000 population, with a higher incidence in men when compared to women. However, the global prevalence of sepsis has been estimated to be higher in women. During the same time frame, the in-hospital case fatality rate was reduced from 28% to 18%. However, according to the nationwide inpatient sample from the United States, the incidence of severe sepsis increased from 200 per 10,000 population in 2003 to 300 cases in 2007 for population aged more than 18 years. The incidence rate is particularly high among infants, with an incidence of 500 cases per 100,000 population. Mortality related to sepsis increases with age, from less than 10% in the age group of 3 to 5 years to 60% by sixth decade of life. The increase in the average age of the population, alongside the presence of more people with chronic diseases or on immunosuppressive drug, immunosuppressive medications, and also the increase in the number of invasive procedures being performed, has led to an increased rate of sepsis.
History
 The term "σήψις" (sepsis) was introduced by Hippocrates in the fourth century BC, and it meant the process of decomposition, decay or decomposition of organic matter. In the eleventh century, Avicenna used the term "blood rot" for diseases linked to severe Pus, purulent process. Though severe systemic toxicity had already been observed, it was only in the 19th century that the specific term – sepsis – was used for this condition.
The terms "septicemia", also spelled "septicaemia", and "blood poisoning" referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) version 9, which was in use in the US until 2013, used the term septicemia with numerous modifiers for different diagnoses, such as "Streptococcal septicemia". All those diagnoses have been converted to sepsis, again with modifiers, in ICD-10, such as "Sepsis due to streptococcus".
The current terms are dependent on the microorganism that is present: bacteremia if bacteria are present in the blood at abnormal levels and are the causative issue, viremia for viruses, and fungemia for a fungus.
By the end of the 19th century, it was widely believed that microbes produced substances that could injure the mammalian host and that soluble toxins released during infection caused the fever and shock that were commonplace during severe infections. Richard Friedrich Johannes Pfeiffer, Pfeiffer coined the term
The term "σήψις" (sepsis) was introduced by Hippocrates in the fourth century BC, and it meant the process of decomposition, decay or decomposition of organic matter. In the eleventh century, Avicenna used the term "blood rot" for diseases linked to severe Pus, purulent process. Though severe systemic toxicity had already been observed, it was only in the 19th century that the specific term – sepsis – was used for this condition.
The terms "septicemia", also spelled "septicaemia", and "blood poisoning" referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) version 9, which was in use in the US until 2013, used the term septicemia with numerous modifiers for different diagnoses, such as "Streptococcal septicemia". All those diagnoses have been converted to sepsis, again with modifiers, in ICD-10, such as "Sepsis due to streptococcus".
The current terms are dependent on the microorganism that is present: bacteremia if bacteria are present in the blood at abnormal levels and are the causative issue, viremia for viruses, and fungemia for a fungus.
By the end of the 19th century, it was widely believed that microbes produced substances that could injure the mammalian host and that soluble toxins released during infection caused the fever and shock that were commonplace during severe infections. Richard Friedrich Johannes Pfeiffer, Pfeiffer coined the term endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer ...
at the beginning of the 20th century to denote the pyrogenic principle associated with ''Vibrio cholerae''. It was soon realized that endotoxins were expressed by most and perhaps all gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
. The lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer m ...
character of enteric endotoxins was elucidated in 1944 by Shear. The molecular character of this material was determined by Luderitz et al. in 1973.
It was discovered in 1965 that a strain of C3H/HeJ mouse was immune to the endotoxin-induced shock. The genetic locus for this effect was dubbed ''Lps''. These mice were also found to be hyper susceptible to infection by gram-negative bacteria. These observations were finally linked in 1998 by the discovery of the toll-like receptor gene 4 (TLR 4). Genetic mapping work, performed over a period of five years, showed that TLR4 was the sole candidate locus within the Lps critical region; this strongly implied that a mutation within TLR4 must account for the lipopolysaccharide resistance phenotype. The defect in the TLR4 gene that led to the endotoxin resistant phenotype was discovered to be due to a mutation in the cytoplasm.
Controversy occurred in the scientific community over the use of mouse models in research into sepsis in 2013 when scientists published a review of the mouse immune system compared to the human immune system and showed that on a systems level, the two worked very differently; the authors noted that as of the date of their article over 150 clinical trials of sepsis had been conducted in humans, almost all of them supported by promising data in mice and that all of them had failed. The authors called for abandoning the use of mouse models in sepsis research; others rejected that but called for more caution in interpreting the results of mouse studies, and more careful design of preclinical studies. One approach is to rely more on studying biopsies and clinical data from people who have had sepsis, to try to identify biomarkers and drug targets for intervention.
Society and culture
Economics
Sepsis was the most expensive condition treated in United States' hospital stays in 2013, at an aggregate cost of $23.6 billion for nearly 1.3 million hospitalizations. Costs for sepsis hospital stays more than quadrupled since 1997 with an 11.5 percent annual increase. By payer, it was the most costly condition billed to Medicare and the uninsured, the second-most costly billed to Medicaid, and the fourth-most costly billed to health insurance in the United States, private insurance.Education
A large international collaboration entitled the "Surviving Sepsis Campaign" was established in 2002 to educate people about sepsis and to improve outcomes with sepsis. The Campaign has published an evidence-based review of management strategies for severe sepsis, with the aim to publish a complete set of guidelines in subsequent years. The guidelines were updated in 2016 and again in 2021. Sepsis Alliance is a charitable organization that was created to raise sepsis awareness among both the general public and healthcare professionals.Research
 Some authors suggest that initiating sepsis by the normally Mutualism (biology), mutualistic (or neutral) members of the microbiome may not always be an accidental side effect of the deteriorating host immune system. Rather it is often an Adaptive behavior, adaptive microbial response to a sudden decline of host survival chances. Under this scenario, the microbe species provoking sepsis benefit from monopolizing the future cadaver, utilizing its biomass as decomposers, and then transmitted through soil or water to establish mutualistic relations with new individuals. The bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''
Some authors suggest that initiating sepsis by the normally Mutualism (biology), mutualistic (or neutral) members of the microbiome may not always be an accidental side effect of the deteriorating host immune system. Rather it is often an Adaptive behavior, adaptive microbial response to a sudden decline of host survival chances. Under this scenario, the microbe species provoking sepsis benefit from monopolizing the future cadaver, utilizing its biomass as decomposers, and then transmitted through soil or water to establish mutualistic relations with new individuals. The bacteria ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'', ''Proteus (bacterium), Proteus'' spp., ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerugi ...
'', ''Staphylococcus aureus'', ''Klebsiella
''Klebsiella'' is a genus of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule.
''Klebsiella'' species are found everywhere in nature. This is thought to be due to distinct sublineages developin ...
'' spp., ''Clostridium'' spp., ''Lactobacillus'' spp., ''Bacteroides'' spp. and the fungi '' Candida'' spp. are all capable of such a high level of phenotypic plasticity. Evidently, not all cases of sepsis arise through such adaptive microbial strategy switches.
Paul E. Marik's "Marik protocol", also known as the "HAT" protocol, proposed a combination of hydrocortisone, vitamin C, and thiamine as a treatment for preventing sepsis for people in intensive care. Marik's own initial research, published in 2017, showed a dramatic evidence of benefit, leading to the protocol becoming popular among intensive care physicians, especially after the protocol received attention on social media and National Public Radio, leading to criticism of science by press conference from the wider medical community. Subsequent independent research failed to replicate Marik's positive results, indicating the possibility that they had been compromised by bias. A systematic review of trials in 2021 found that the claimed benefits of the protocol could not be confirmed. Another more recent review found that "HAT therapy significantly reduced the duration of vasopressor use and improved the SOFA score but appeared not to have significant benefits in other outcomes for patients with sepsis."
Overall, the evidence for any role for vitamin C in the treatment of sepsis remains unclear .
References
External links
*SIRS, Sepsis, and Septic Shock Criteria
* {{Authority control Sepsis, Articles containing video clips Infectious diseases Intensive care medicine Medical emergencies Neonatology Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate