Selene Celotto on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Selene (; grc-gre, ╬ú╬Á╬╗╬«╬Ż╬Ě , meaning "Moon"'' A GreekÔÇôEnglish Lexicon'
s.v. ¤â╬Á╬╗╬«╬Ż╬Ě
) is the
 Surviving descriptions of Selene's physical appearance and character, apart from those which would apply to the moon itself, are scant. There is no mention of Selene as a goddess in either the '' Iliad'' or the '' Odyssey'' of Homer, while her only mention in
Surviving descriptions of Selene's physical appearance and character, apart from those which would apply to the moon itself, are scant. There is no mention of Selene as a goddess in either the '' Iliad'' or the '' Odyssey'' of Homer, while her only mention in
 The usual account of Selene's origin is given by
The usual account of Selene's origin is given by
221ÔÇô38

20
/ref> Selene gallops sidesaddle in advance, and wears a woolen undergarment and a mantle. Additionally, on a rein guide for a chariot a goddess thought to be Selene with a crescent and veil over her head is depicted, who stands with Helios on a gate tower and tries to repel the attacks of snake-legged Giants.
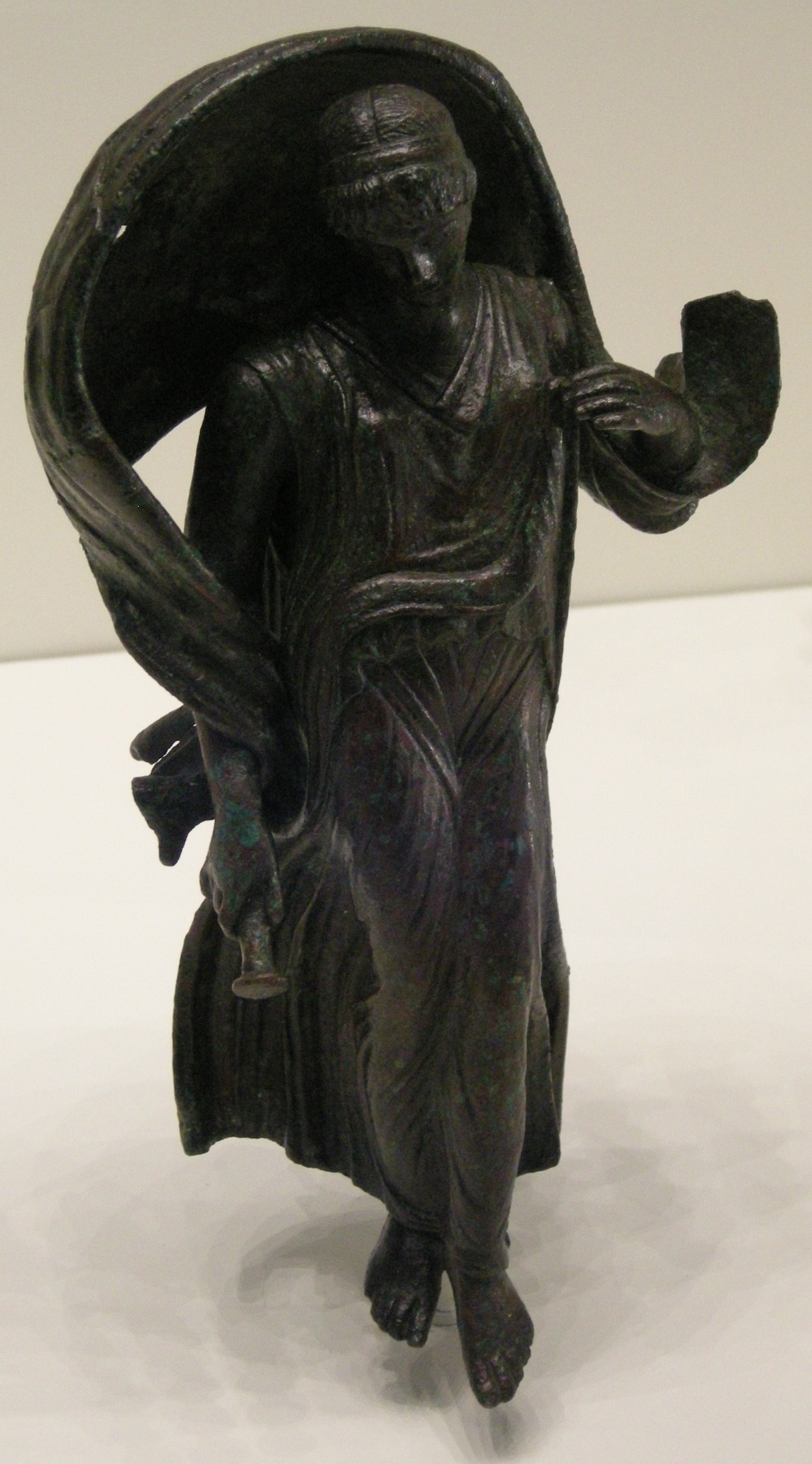 When Zeus desired to sleep with the mortal queen Alcmene and sire Heracles, he made the night last three days, and ordered Selene via Hermes to dawdle in the sky during that time.
Selene also played a small role in the first of Heracles' twelve labours; whereas for Hesiod, the Nemean Lion was born to Orthrus and the Chimera (or perhaps Echidna) and raised by
When Zeus desired to sleep with the mortal queen Alcmene and sire Heracles, he made the night last three days, and ordered Selene via Hermes to dawdle in the sky during that time.
Selene also played a small role in the first of Heracles' twelve labours; whereas for Hesiod, the Nemean Lion was born to Orthrus and the Chimera (or perhaps Echidna) and raised by

 In Lucian's ''Icaromenippus'', Selene complains to the titular Menippus of all the outrageous claims philosophers are making about her, such as wondering why she is ever waxing or gibbous, whether she is populated or not, and stating that she is getting her stolen light from the Sun, causing strife and ill feelings between her and her brother. She asks Menippus to report her grievances to Zeus, with the request that Zeus wipes all these natural philosophers from the face of the earth. Zeus agrees, urged by Selene's complaints and having long intended to deal with the philosophers himself.
In Lucian's ''Icaromenippus'', Selene complains to the titular Menippus of all the outrageous claims philosophers are making about her, such as wondering why she is ever waxing or gibbous, whether she is populated or not, and stating that she is getting her stolen light from the Sun, causing strife and ill feelings between her and her brother. She asks Menippus to report her grievances to Zeus, with the request that Zeus wipes all these natural philosophers from the face of the earth. Zeus agrees, urged by Selene's complaints and having long intended to deal with the philosophers himself.
 In antiquity, artistic representations of Selene/Luna included sculptural reliefs, vase paintings, coins, and gems. In
In antiquity, artistic representations of Selene/Luna included sculptural reliefs, vase paintings, coins, and gems. In
 Moon figures are found on Cretan rings and gems (perhaps indicating a Minoan moon cult), but apart from the role played by the moon itself in magic, folklore, and poetry, and despite the later worship of the Phrygian moon-god Men, there was relatively little worship of Selene. An oracular sanctuary existed near Thalamai in
Moon figures are found on Cretan rings and gems (perhaps indicating a Minoan moon cult), but apart from the role played by the moon itself in magic, folklore, and poetry, and despite the later worship of the Phrygian moon-god Men, there was relatively little worship of Selene. An oracular sanctuary existed near Thalamai in
pp. 157; 171
Online version at Harvard University Press
. * Aeschylus, ''Fragments'', edited and translated by Alan H. Sommerstein,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Allen, Thomas W., E. E. Sikes. ''The Homeric Hymns'', edited, with preface, apparatus criticus, notes, and appendices. London. Macmillan. 1904. *
Internet Archive
*
Online version at the Topos Text Project
* Aristotle, ''Aristotle in 23 Volumes, Vol. 19, translated by H. Rackham''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1934. * Astour, Michael C., ''Hellenosemitica: An Ethinic and Cultural Study in West Semitic Impact on Mycenaean Greece'', Brill Archive, 1965. * Athanassakis, Apostolos N., and Benjamin M. Wolkow, ''The Orphic Hymns'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 2013.
Google Books
* * Bekker, Immanuel, ''Anecdota Graeca: Lexica Segueriana'', Apud G.C. Nauckium, 1814. * Blum, Rudolf, ''Kallimachos: The Alexandrian Library and the Origins of Bibliography'', translated by Hans H. Wellisch, University of Wisconsin Press, 2011. . * ''BrillÔÇÖs New Pauly: Encyclopaedia of the Ancient World'', Volume 13, Sas-Syl, editors: Hubert Cancik, Helmuth Schneider,
Online version
* * * Caldwell, Richard, ''Hesiod's Theogony'', Focus Publishing/R. Pullins Company (June 1, 1987). . * Campbell, David A., ''Greek Lyric, Volume I: Sappho and Alcaeus'',
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cashford, Jules, (2003a), ''The Homeric Hymns'', Penguin Books, 2003.
Internet Archive
* Cashford, Jules, (2003b), ''The Moon: Myth and Image'', Four Walls Eight Windows, New York, 2003. . * Catullus, ''Catullus. Tibullus. Pervigilium Veneris.'', translated by F. W. Cornish, J. P. Postgate, J. W. Mackail, revised by G. P. Goold,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cicero, ''Cicero's Tusculan Disputations'', translated by C. D. Yonge; Harpers & Brothers, publishers, 1888. * de Clarac, Fr├ęd├ęric, ''Mus├ęe de Sculpture antique et moderne, ou description historique et graphique du Louvre'' (Paris: Imprimerie Royale, 1828, etc.), vol. 2. *
Internet Archive
* Cohen, Beth, "Outline as a Special Technique in Black- and Red-figure Vase-painting", in ''The Colors of Clay: Special Techniques in Athenian Vases'', Getty Publications, 2006, . * Collard and Cropp in Euripides, ''Fragments: Aegeus-Meleager'', edited and translated by Christopher Collard, Martin Cropp,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cook, Arthur Bernard, ''Zeus: A Study in Ancient Religion, Volume I: Zeus God of the Bright Sky'', Cambridge University Press 1914
Internet Archive
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cox, George W. ''The Mythology of the Aryan Nations Part, Vol. II'', London, C. Kegan Paul & Co., 1 Paternoster Square, 1878
Internet Archive
* Davidson, James, "Time and Greek Religion", in ''A Companion to Greek Religion'', edited by Daniel Ogden, John Wiley & Sons, 2010, . *
Online version by Bill Thayer
* Edmonds, John Maxwell, (1922), ''Lyra Graeca'', W. Heinemann, 1922. * Edmonds, Radcliffe (2013), ''Redefining Ancient Orphism: A Study in Greek Religion'', Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press. . * Empedocles in ''Early Greek Philosophy, Volume V: Western Greek Thinkers, Part 2. '', edited and translated by Andr├ę Laks, Glenn W. Most,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Euripides, ''The Complete Greek Drama', edited by Whitney J. Oates and Eugene O'Neill, Jr. in two volumes. 2''. ''The Phoenissae'', translated by E. P. Coleridge. New York. Random House. 1938. * Euripides, ''Fragments: Oedipus-Chrysippus: Other Fragments'', edited and translated by Christopher Collard, Martin Cropp,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Evelyn-White, Hugh, ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White''. Homeric Hymns. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914. * Fairbanks, Arthur, ''The Mythology of Greece and Rome''. D. AppletonÔÇôCentury Company, New York, 1907. * Faraone, Christopher A., ''Ancient Greek Love Magic'', Harvard University Press, 2009. . * Fowler, R. L. (2000), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 1: Text and Introduction'', Oxford University Press, 2000. . * Fowler, R. L. (2013), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 2: Commentary'', Oxford University Press, 2013. . * Freeman, Kathleen, ''Ancilla to the Pre-Socratic Philosophers: A Complete Translation of the Fragments in Diels, Fragmente Der Vorsokratiker'', Harvard University Press, 1983. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * ''The Greek Anthology, Volume I: Book 1: Christian Epigrams, Book 2: Description of the Statues in the Gymnasium of Zeuxippus, Book 3: Epigrams in the Temple of Apollonis at Cyzicus, Book 4: Prefaces to the Various Anthologies, Book 5: Erotic Epigrams'', translated by W. R. Paton. Revised by Michael A. Tueller,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Gury, Fran├žoise, "Selene, Luna" in '' Lexicon Iconographicum Mythologiae Classicae (LIMC)'' VII.1 Artemis Verlag, Z├╝rich and Munich, 1994. . * Grimal, Pierre, ''The Dictionary of Classical Mythology'', Wiley-Blackwell, 1996. . * Hansen, William F., ''Handbook of classical mythology'', ABC-CLIO, 2004. . * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
*
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Honan, Mary McMahon, ''Guide to the Pergamon Museum'', De Gruyter, 1904.
Online version at De Gruyter
* Hurwit, Jeffery M. (1999), ''"The" Athenian Acropolis: History, Mythology, and Archaeology from the Neolithic Era to the Present'', CUP Archive, 1999. . * Hurwit, Jeffery M. (2017), "Helios Rising: The Sun, the Moon, and the Sea in the Sculptures of the Parthenon", ''American Journal of Archaeology'', Vol. 121, No. 4 (October 2017), pp. 527ÔÇô558. . * Hyginus, Gaius Julius, '' Fabulae'', in ''The Myths of Hyginus'', edited and translated by Mary A. Grant, Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1960
Online version at ToposText
* Jebb, Richard Claverhouse, ''Bacchylides: The Poems and Fragments'', Georg Olms Verlag, 1905, 1994. . * Jones, Prudence H., "A Goddess Arrives: Nineteenth Century Sources of the New Age Triple Moon Goddess" in ''Culture and Cosmos'', 19(1): 45ÔÇô70. * Julius Pollux, ''Onomasticon: cum annotationibus interpretum''. VI - X, Volume 2, Kuehn, 1824
Google books
* Ker├ęnyi, Karl (1951), ''The Gods of the Greeks'', Thames and Hudson, London, 1951
Internet Archive
* Keightley, Thomas, ''The Mythology of Ancient Greece and Italy'', G. Bell and Sons, 1877. * Liddell, Henry George, Robert Scott, ''
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Lightfoot, J. L., ''Hellenistic Collection: Philitas, Alexander of Aetolia, Hermesianax, Euphorion, Parthenius,'' edited and translated by J. L. Lightfoot,
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Online version at Harvard University PressInternet Archive
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Mayerson, Philip, ''Classical Mythology in Literature, Art, and Music'', Focus publishing, R. Pullins Company, 2001. . * Meagher, Robert E., ''The Meaning of Helen: In Search of an Ancient Icon'', Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers, 2002. . * Mesomedes in ''Lyra Gr├Žca: Specimens of the Greek Lyric Poets, from Callinus to Soutsos.'' Edited, with critical Notes, and a biographical Introduction, by James Donaldson (Edinburgh & London, 1854) p. 96f. * Mitchell, Lucy M., "Sculptures of the Great Pergamon Altar" in The Century Magazine, 1883. * Morford, Mark P. O., Robert J. Lenardon, ''Classical Mythology'', Eighth Edition, Oxford University Press, 2007.
Internet Archive
* Most, G.W. (2018a), ''Hesiod, Theogony, Works and Days, Testimonia,'' Edited and translated by Glenn W. Most,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Most, G.W. (2018b), ''Hesiod: The Shield, Catalogue of Women, Other Fragments'',
Online version at Harvard University Press
* M├╝ller, Karl Wilhelm Ludwig, ''Fragmenta Historicorum Graecorum'', Volume I, 1841
Internet Archive
* Murray, Alexander Stuart (1892), ''Handbook of Greek Arch├Žology'', John Murray, 1892. * Murray, Alexander Stuart (1903), ''The Sculptures of the Parthenon'', John Murray, 1903. * n├ş Mheallaigh, Karen, ''The Moon in the Greek and Roman Imagination: Myth, Literature, Science and Philosophy'', Cambridge University Press, 2020. . * Nonnus, ''
Online version at Harvard University PressInternet Archive (1940)
* Nonnus, ''
Online version at Harvard University PressInternet Archive (1940, reprinted 1942)
* Obbink, Dirk (2002), "'All Gods are True' in Epicurus" in ''Traditions of Theology: Studies in Hellenistic Theology, Its Background and Aftermath,'' Dorothea, Frede, and Andr├ę Laks (eds.), Brill, Boston, 2002. * Obbink, Dirk (2011) "56. Orphism, Cosmogony, and Genealogy (Mus. fr. 14)" in ''Tracing Orpheus: Studies of Orphic Fragments'', edited by Miguel Herrero de J├íuregui, Walter de Gruyter, 2011. . * Osborne, Robin, "Looking on – Greek Style. Does the sculpted girl speak to women too?" in ''Classical Greece: Ancient Histories and Modern Archaeologies'', Morris, Ian (ed.), Cambridge University Press, 1994. . * Ovid, '' Amores'' in ''Heroides. Amores'', translated by Grant Showerman, revised by G. P. Goold,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid, '' Ars Amatoria'' in ''Art of Love. Cosmetics. Remedies for Love. Ibis. Walnut-tree. Sea Fishing. Consolation'', translated by J. H. Mozley, revised by G. P. Goold,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid, ''
Internet Archive
* Ovid, '' Heroides'' in ''Heroides. Amores'', translated by Grant Showerman, revised by G. P. Goold,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid. '' Metamorphoses, Volume I: Books 1-8''. Translated by Frank Justus Miller. Revised by G. P. Goold.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid. '' Metamorphoses, Volume II: Books 9-15''. Translated by Frank Justus Miller. Revised by G. P. Goold.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* '' Oxford Classical Dictionary'', second edition, Hammond, N.G.L. and Howard Hayes Scullard (editors), Oxford University Press, 1992. . * Page, Denys Lionel, Sir, ''Select Papyri, Volume III: Poetry'', translated by Denys L. Page,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Palagia, Olga (1998), ''The Pediments of the Parthenon'', BRILL, 1998. . * Palagia, Olga (2005), "Fire from Heaven: Pediments and Akroteria of the Parthenon" in ''The Parthenon: From Antiquity to the Present'', edited by Jenifer Neils, Cambridge University Press, 2005. . * Pannen, Imke, ''When the Bad Bleeds: Mantic Elements in English Renaissance Revenge Tragedy'', Volume 3 of Representations & Reflections; V&R unipress GmbH, 2010. . * Parisinou, Eva, "Brightness personified: light and devine image in ancient Greece" in ''Personification In The Greek World: From Antiquity To Byzantium'', editors Emma Stafford, Judith Herrin, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2005. . * Parker, Robert, ''Polytheism and Society at Athens'', Oxford University Press, 2005. . * Pausanias, ''Pausanias Description of Greece with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes.'' Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Picón, Carlos A.; Hemingway, Seán, ''Pergamon and the Hellenistic Kingdoms of the Ancient World'', Yale University Press, 2016, . * Pindar, ''Odes'', Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1990
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Plato, ''Plato in Twelve Volumes, Vol. 1 translated by Harold North Fowler''; Introduction by W.R.M. Lamb. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1966 * Plutarch, '' Moralia''. 16 vols. (vol. 13: 13.1 & 13.2, vol. 16: index), transl. by Frank Cole Babbitt (vol. 1ÔÇô5) et al., series: "
PDF
*
Internet Archive
* Ridgeway, Brunilde Sismondo, ''Hellenistic Sculpture II: The Styles of ca. 200–100 B.C.'', The University of Wisconsin Press, 2000. * Robertson, Martin (1981), ''A Shorter History of Greek Art'', Cambridge University Press. . * Robertson, Martin (1992), ''The Art of Vase-Painting in Classical Athens'', Cambridge University Press. . * Robertson, Noel (1996), "Athena's Shrines and Festivals" in ''Worshipping Athena: Panathenaia and Parthenon'', The University of Wisconsin Press. . * Roman, Luke, Monica Roman, ''Encyclopedia of Greek and Roman Mythology'', Facts on File, 2010. . * Roscher, Wilhelm Heinrich, ''├ťber Selene und Verwandtes'', B.G. Teubner, Leipzig 1890. * Savignoni L. 1899. "On Representations of Helios and of Selene", The Journal of Hellenic Studies 19
pp. 265ÔÇô272
* Seyffert, Oskar, ''A Dictionary of Classical Antiquities, Mythology, Religion, Literature and Art, from the German of Dr. Oskar Seyffert'', S. Sonnenschein, 1901
Internet Archive
* Seneca, ''Tragedies, Volume I: Hercules. Trojan Women. Phoenician Women. Medea. Phaedra.'' Edited and translated by John G. Fitch.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Shear, T.L., Jr., ''Trophies of Victory: Public Building in Periklean Athens'', Princeton University Press, 2016. * Servius, ''Commentary on the Georgics of Vergil'', Georgius Thilo, Ed. 1881
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library (Latin)
* Smith, William; '' Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', London (1873). * Sommerstein, Alan H., ''Aeschylus: Persians, Seven against Thebes, Suppliants, Prometheus Bound'', edited and translated by Alan H. Sommerstein,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Sorabella, Jean, "A Roman Sarcophagus and Its Patron." ''Metropolitan Museum Journal'', Vol. 36 (2001)
Downloadable PDF available at ''MetPublications''
* Sorrenti, Stefania, "Les repr├ęsentations figur├ęes de Jupiter Dolich├ęnien ├á Rome," in ''La terra sigillata tardo-italica decorata del Museo nazionale romano'', "L'Erma" di Bretschneider, 1999). * Statius, '' Thebaid, Volume I: Thebaid: Books 1-7'', edited and translated by D. R. Shackleton Bailey,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Statius, '' Thebaid, Volume II: Thebaid: Books 8-12. Achilleid'', edited and translated by D. R. Shackleton Bailey,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Stoll, Heinrich Wilhelm, ''Handbook of the religion and mythology of the Greeks, With a Short Account of The Religious System of the Romans'', tr. by R.B. Paul, and ed. by T.K. Arnold, London, Francis & John Rivington, 1852. *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* * Taylor, Thomas, ''The Hymns of Orpheus'', Philosophical Research Society; Limited edition (June 1987). . * Theocritus in ''Theocritus, Moschus, Bion,'' edited and translated by Neil Hopkinson,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Theocritus, Bion of Smyrna, Moschus, ''Theocritus, Bion et Moschus. Graece et Latine. Accedunt virorum doctorum animadversiones, scholia, indices; et M. ├ćmilii Porti Lexicon Doricum, Volume 2'', London Sumptibus Ricardi Priestley, 1826. * Thomas, Edmund. "From the panteon of the gods to the Pantheon of Rome" in ''Pantheons: Transformations of a Monumental Idea'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2004. . * Tryphiodorus, ''The Taking of Ilios'' in ''Oppian, Colluthus, and Tryphiodorus'', translated by A. W. Mair,
Online version at Harvard University PressInternet Archive
* Valerius Flaccus, ''Argonautica'', translated by J. H. Mozley,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Vergados, Athanassios, ''The "Homeric Hymn to Hermes": Introduction, Text and Commentary'', Walter de Gruyter, 2012. . * Verhelst, Berenice, ''Direct Speech in NonnusÔÇÖ ''Dionysiaca'': Narrative and rhetorical functions of the characters' "varied" and "many-faceted" words'', BRILL, 2016. (e-book). (hardback). * * Virgil, ''Georgics'' in ''Bucolics, Aeneid, and Georgics Of Vergil''. J. B. Greenough. Boston. Ginn & Co. 1900
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Walters, Henry Beauchamp, Samuel Birch, ''History of Ancient Pottery: Greek, Etruscan, and Roman, Volume 2'', John Murray, 1905. * West, M. L. (1983), ''The Orphic Poems'', Clarendon Press Oxford, 1983. . * West, M. L. (2003), ''Homeric Hymns. Homeric Apocrypha. Lives of Homer'', edited and translated by Martin L. West,
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Willetts, R. F., ''Cretan Cults and Festivals'', Greenwood Press, 1980. . * Xenis, Georgios A., ''Scholia vetera in Sophoclis "Oedipum Coloneum"'', De Gruyter, 2018.
Online version at De GruyterGoogle Books
* Zschietzschmann, W, ''Hellas and Rome: The Classical World in Pictures'', Kessinger Publishing, 2006. .
SELENE in Mythopedia
{{Authority control Divine women of Zeus Greek goddesses Lunar goddesses Personifications in Greek mythology Titans (mythology) Light goddesses Women of Helios Magic goddesses Metamorphoses characters Horned deities Childhood goddesses Characters in the Argonautica Women in Greek mythology Characters in Greek mythology Night goddesses Consorts of Pan (god) ur:ě│█î┘ä█î┘ć█ü
s.v. ¤â╬Á╬╗╬«╬Ż╬Ě
) is the
goddess
A goddess is a female deity. In many known cultures, goddesses are often linked with literal or metaphorical pregnancy or imagined feminine roles associated with how women and girls are perceived or expected to behave. This includes themes of s ...
and the personification
Personification occurs when a thing or abstraction is represented as a person, in literature or art, as a type of anthropomorphic metaphor. The type of personification discussed here excludes passing literary effects such as "Shadows hold their b ...
of the Moon. Also known as Mene, she is traditionally the daughter of the Titans Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
and Theia, and sister of the sun god
A solar deity or sun deity is a deity who represents the Sun, or an aspect of it. Such deities are usually associated with power and strength. Solar deities and Sun worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms. The ...
Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyper ...
and the dawn goddess Eos. She drives her moon chariot across the heavens. Several lovers are attributed to her in various myths, including Zeus, Pan, and the mortal Endymion Endymion primarily refers to:
* Endymion (mythology), an Ancient Greek shepherd
* ''Endymion'' (poem), by John Keats
Endymion may also refer to:
Fictional characters
* Prince Endymion, a character in the ''Sailor Moon'' anime franchise
* Raul ...
. In post-classical times, Selene was often identified with Artemis, much as her brother, Helios, was identified with Apollo. Selene and Artemis were also associated with Hecate and all three were regarded as moon and lunar goddesses, but only Selene was regarded as the personification
Personification occurs when a thing or abstraction is represented as a person, in literature or art, as a type of anthropomorphic metaphor. The type of personification discussed here excludes passing literary effects such as "Shadows hold their b ...
of the Moon itself. Her Roman equivalent is Luna.
Names and etymology
The name "Selene" is derived from the Greek noun ''selas'' ('), meaning "light, brightness, gleam". In theDoric Doric may refer to:
* Doric, of or relating to the Dorians of ancient Greece
** Doric Greek, the dialects of the Dorians
* Doric order, a style of ancient Greek architecture
* Doric mode, a synonym of Dorian mode
* Doric dialect (Scotland)
* Doric ...
and Aeolic dialects, her name was also spelled (''Selána'') and (''Selánna'') respectively.
Selene was also called Mene. The Greek word ''mene'', meant the moon, and the lunar month. The masculine form of ''mene'' (''men'') was also the name of the Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, ╬Ž¤ü¤ů╬│╬»╬▒, ''Phryg├şa'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires ...
n moon-god Men. Mene and Men both derive from Proto-Hellenic ''*m├ęns'' ("month"), itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*mߪŚhÔéün╠ąs'' (meaning moon, the lunar month), which probably comes from the root ''*mehÔéü-'' ("to measure"), and is cognate with the English words "Moon" and "month". The Greek Stoic philosopher Chrysippus
Chrysippus of Soli (; grc-gre, ╬ž¤ü¤Ź¤â╬╣¤Ç¤Ç╬┐¤é ߯ü ╬ú╬┐╬╗╬Á¤Ź¤é, ; ) was a Greek Stoic philosopher. He was a native of Soli, Cilicia, but moved to Athens as a young man, where he became a pupil of the Stoic philosopher Cleanthes. When Clean ...
interpreted Selene and Men as, respectively, the female and male aspects of the same god.
Just as Helios, from his identification with Apollo, is called Phoebus ("bright"), Selene, from her identification with Artemis, is also called Phoebe (feminine form). Also from Artemis, Selene was sometimes called "Cynthia", meaning "she of Mount Cynthus" (the birthplace of Artemis).
Descriptions
 Surviving descriptions of Selene's physical appearance and character, apart from those which would apply to the moon itself, are scant. There is no mention of Selene as a goddess in either the '' Iliad'' or the '' Odyssey'' of Homer, while her only mention in
Surviving descriptions of Selene's physical appearance and character, apart from those which would apply to the moon itself, are scant. There is no mention of Selene as a goddess in either the '' Iliad'' or the '' Odyssey'' of Homer, while her only mention in Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, ß╝ę¤â╬»╬┐╬┤╬┐¤é ''H─ôs├şodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
's '' Theogony'' is as the daughter of Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
and Theia, and sister of Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyper ...
and Eos. She was, however, the subject of one of the thirty-three '' Homeric Hymns'', which gives the following description:
Two other sources also mention her hair. The ''Homeric Hymn to Helios'' uses the same epithet ''╬Á߯ɤÇ╬╗¤î╬║╬▒╬╝╬┐¤é'' ("bright-tressed"), used in the above ''Hymn to Selene'' (elsewhere translated as "rich-", "lovely-", or "well-tressed"), while Epimenides uses the epithet ''ß╝á¤ů╬║¤î╬╝╬┐╬╣╬┐'' ("lovely-haired").
In late accounts, Selene (like the moon itself) is often described as having horns. The '' Orphic Hymn to Selene'' addresses her as "O bull-horned Moon", and further describes her as "torch-bearing, ... feminine and masculine, ... lover of horses," and grantor of "fulfillment and favor". Empedocles, Euripides and Nonnus all describe her as ╬│╬╗╬▒¤ů╬║ß┐¤Ç╬╣¤é (''glaukß╣ôpis'', "bright-eyed", a common epithet of the goddess Athena) while in a fragment from a poem, possibly written by Pamprepius, she is called ╬║¤ů╬▒╬Żß┐¤Ç╬╣¤é (''kyanß╣ôpis'', "dark-eyed"). Mesomedes of Crete calls her ╬│╬╗╬▒¤ů╬║߯░ (''glauk├á'', "silvery grey").
Family
Parents
 The usual account of Selene's origin is given by
The usual account of Selene's origin is given by Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, ß╝ę¤â╬»╬┐╬┤╬┐¤é ''H─ôs├şodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
in his '' Theogony'', where the sun-god
A solar deity or sun deity is a deity who represents the Sun, or an aspect of it. Such deities are usually associated with power and strength. Solar deities and Sun worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms. The ...
Hyperion
Hyperion may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Hyperion (Titan), one of the twelve Titans
* ''Hyperion'', a byname of the Sun, Helios
* Hyperion of Troy or Yperion, son of King Priam
Science
* Hyperion (moon), a moon of the planet Saturn
* ''Hyp ...
espoused his sister Theia, who gave birth to "great Helios and clear Selene and Eos who shines upon all that are on earth and upon the deathless Gods who live in the wide heaven". The '' Homeric Hymn to Helios'' follows this tradition: "Hyperion wedded glorious Eurypha├źssa, his own sister, who bare him lovely children, rosy-armed Eos and rich-tressed Selene and tireless Helios", with ''Eurypha├źssa'' ("widely shining") probably being an epithet of Theia. However, the '' Homeric Hymn to Hermes'' has Selene as the daughter of Pallas, the son of an otherwise unknown Megamedes. This Pallas is possibly identified with the Pallas, who, according to Hesiod's ''Theogony'', was the son of the Titan Crius, and thus Selene's cousin. Other accounts give still other parents for Selene: Euripides has Selene as the daughter of Helios (rather than sister), while an Aeschylus fragment possibly has Selene as the daughter of Leto, as does a scholium on Euripides's play '' The Phoenician Women'' which adds Zeus as the father. Furthermore, in Virgil's '' Aeneid'', when Nisus calls upon Selene/the Moon, he addresses her as "daughter of Latona."
Offspring
According to the '' Homeric Hymn to Selene'', the goddess bore Zeus a daughter, Pandia ("All-brightness"), "exceeding lovely amongst the deathless gods". The 7th century BC Greek poetAlcman
Alcman (; grc-gre, ß╝ł╬╗╬║╬╝╬Č╬Ż ''Alkm├ín''; fl. 7th century BC) was an Ancient Greek choral lyric poet from Sparta. He is the earliest representative of the Alexandrian canon of the Nine Lyric Poets.
Biography
Alcman's dates are u ...
makes Ersa ("Dew") the daughter of Selene and Zeus. Selene and Zeus were also said to be the parents of Nemea, the eponymous nymph of Nemea
Nemea (; grc, ╬Ł╬Á╬╝╬ş╬▒; grc-x-ionic, ╬Ł╬Á╬╝╬ş╬Ě) is an ancient site in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. Formerly part of the territory of Cleonae in ancient Argolis, it is today situated in the regional unit of Corinthia ...
, where Heracles slew the Nemean Lion, and where the Nemean Games were held.
From Pausanias we hear that Selene was supposed to have had fifty daughters, by her lover Endymion Endymion primarily refers to:
* Endymion (mythology), an Ancient Greek shepherd
* ''Endymion'' (poem), by John Keats
Endymion may also refer to:
Fictional characters
* Prince Endymion, a character in the ''Sailor Moon'' anime franchise
* Raul ...
, often assumed to represent the fifty lunar months of the Olympiad. Nonnus has Selene and Endymion as the parents of the beautiful Narcissus
Narcissus may refer to:
Biology
* ''Narcissus'' (plant), a genus containing daffodils and others
People
* Narcissus (mythology), Greek mythological character
* Narcissus (wrestler) (2nd century), assassin of the Roman emperor Commodus
* Tiberiu ...
, although in other accounts, including Ovid's '' Metamorphoses'', Narcissus was the son of Cephissus and Liriope.
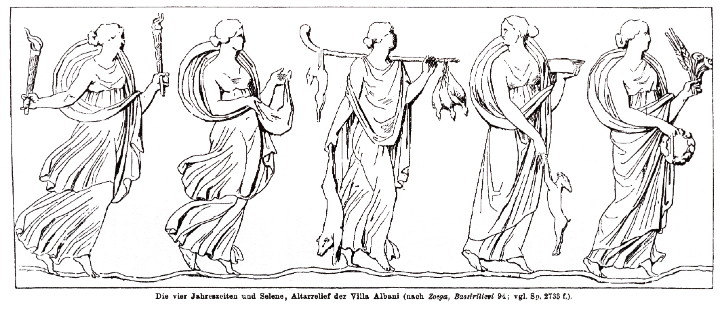
Quintus Smyrnaeus
Quintus Smyrnaeus (also Quintus of Smyrna; el, ╬ܤî¤Ő╬Ż¤ä╬┐¤é ╬ú╬╝¤ů¤ü╬Ż╬▒ß┐ľ╬┐¤é, ''Kointos Smyrnaios'') was a Greek epic poet whose ''Posthomerica'', following "after Homer", continues the narration of the Trojan War. The dates of Quintus Smy ...
makes Selene, by her brother Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyper ...
, the mother of the Horae, goddesses and personifications of the four seasons; Winter, Spring, Summer, and Autumn. Quintus describes them as the four handmaidens of Hera, but in most other accounts their number is three; Eirene ("peace"), Eunomia ("order"), and Dike ("justice"), and their parents are Zeus and Themis instead.
Lastly, Selene was said to be the mother of the legendary Greek poet Musaeus, with, according to Philochorus, the father being the legendary seer Eumolpus.
Mythology
Goddess of the Moon
Like her brother Helios, the Sun god, who drives his sun chariot across the sky each day, Selene is also said to drive a chariot across the heavens. There are no mentions of Selene's chariot in either Homer orHesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, ß╝ę¤â╬»╬┐╬┤╬┐¤é ''H─ôs├şodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
, but the '' Homeric Hymn to Selene'', gives the following description:
The earliest known depiction of Selene driving a chariot adorns the inside of an early 5th century BC red-figure cup attributed to the Brygos Painter, showing Selene plunging her chariot, drawn by two winged horses, into the sea (Berlin Antikensammlung F 2293). The geographer Pausanias, reports seeing a relief of Selene driving a single horse, as it seemed to him, or as some said, a mule, on the pedestal of the Statue of Zeus at Olympia
The Statue of Zeus at Olympia was a giant seated figure, about tall, made by the Greek sculptor Phidias around 435 BC at the sanctuary of Olympia, Greece, and erected in the Temple of Zeus there. Zeus is the sky and thunder god in ancient Gr ...
(c. 435 BC). While the sun chariot has four horses, Selene's usually has two, described as "snow-white" by Ovid. In some later accounts the chariot was drawn by oxen or bulls. Though the moon chariot is often described as being silver, for Pindar it was golden.
In antiquity, the lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth ...
phenomena were thought to be caused by witches, particularly the ones from Thessaly, who brought the Moon/Selene down with spells and invocations of magic. References to this magical trick, variously referred to as (''kathaire─ęn''), are scattered throughout ancient literature, whereas eclipses of both the Sun and the Moon were called ''kathaireseis'' ("casting-downs") by the Greek populace.Hill, D. E. "THE THESSALIAN TRICK." Rheinisches Museum F├╝r Philologie, vol. 116, no. 3/4, 1973, pp221ÔÇô38
JSTOR
JSTOR (; short for ''Journal Storage'') is a digital library founded in 1995 in New York City. Originally containing digitized back issues of academic journals, it now encompasses books and other primary sources as well as current issues of j ...
. Accessed 18 Jul. 2022. A famous example of that is Aglaonice of Thessaly, an ancient Greek astronomer, who was regarded as a sorceress for her (self-proclaimed) ability to make the Moon disappear from the sky (: ''kathaire─ęn t├ęn sel├ęnen''). This claim has been takenÔÇôby Plutarch at first, and subsequently by modern astronomersÔÇôto mean that she could predict the time and general area where an eclipse of the Moon would occur. Those who brought down the Moon were thought to bring ill fortune upon themselves, as evidenced by the proverb ' ("you are bringing down the Moon on yourself") said for those who caused self-inflicted evils; some witches supposedly avoided this fate by sacrificing their children or their eyeballs.
Endymion
Selene is best known for her affair with the beautiful mortalEndymion Endymion primarily refers to:
* Endymion (mythology), an Ancient Greek shepherd
* ''Endymion'' (poem), by John Keats
Endymion may also refer to:
Fictional characters
* Prince Endymion, a character in the ''Sailor Moon'' anime franchise
* Raul ...
. The late 7th-century ÔÇô early 6th-century BC poet Sappho
Sappho (; el, ╬ú╬▒¤Ç¤ć¤Ä ''Sapph┼Ź'' ; Aeolic Greek ''Ps├ípph┼Ź''; c. 630 ÔÇô c. 570 BC) was an Archaic Greek poet from Eresos or Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Sappho is known for her Greek lyric, lyric poetry, written to be sung while ...
apparently mentioned Selene and Endymion. However, the first account of the story comes from the third-century BC '' Argonautica'' of Apollonius of Rhodes, which tells of Selene's "mad passion" and her visiting the "fair Endymion" in a cave on Mount Latmus:
The eternally sleeping Endymion was proverbial, but exactly how this eternal sleep came about and what role, if any, Selene may have had in it is unclear. According to the '' Catalogue of Women'', Endymion was the son of Aethlius (a son of Zeus), and Zeus granted him the right to choose when he would die. A scholiast on Apollonius says that, according to Epimenides, Endymion fell in love with Hera, and Zeus punished him with eternal sleep. However, Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: ß╝ł¤Ç╬┐╬╗╬╗¤î╬┤¤ë¤ü╬┐¤é ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
says that because of Endymion's "surpassing beauty, the Moon fell in love with him, and Zeus allowed him to choose what he would, and he chose to sleep for ever, remaining deathless and ageless". Theocritus portrays Endymion's sleep as enviable because (presumably) of Selene's love for him. Cicero seems to make Selene responsible for Endymion's sleep, so that "she might kiss him while sleeping". The Roman playwright Seneca, has Selene abandoned the night sky for Endymion's sake having entrusted her "shining" moon chariot to her brother Helios to drive. The Greek satirist Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 ÔÇô after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
's dialogue between Selene and the love goddess Aphrodite has the two goddesses commiserate about their love affairs with Endymion and Adonis, and suggests that Selene has fallen in love with Endymion while watching him sleep each night. In his dialogue between Aphrodite and Eros, Lucian also has Aphrodite admonish her son Eros for bringing Selene "down from the sky". While Quintus Smyrnaeus
Quintus Smyrnaeus (also Quintus of Smyrna; el, ╬ܤî¤Ő╬Ż¤ä╬┐¤é ╬ú╬╝¤ů¤ü╬Ż╬▒ß┐ľ╬┐¤é, ''Kointos Smyrnaios'') was a Greek epic poet whose ''Posthomerica'', following "after Homer", continues the narration of the Trojan War. The dates of Quintus Smy ...
wrote that, while Endymion slept in his cave beside his cattle:
Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 ÔÇô after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
also records an otherwise unattested myth where a pretty young girl called Muia becomes Selene's rival for Endymion's affections; the chatty maiden would endlessly talk to him while he slept, causing him to wake up. This irritated Endymion, and enraged Selene, who transforms the girl into a fly ( grc, ╬╝¤ůß┐ľ╬▒, mu├şa). In memory of the beautiful Endymion, the fly still grudges all sleepers their rest and annoys them.
Philologist Max M├╝ller's interpretation of solar mythology as it related to Selene and Endymion concluded that the myth was a narrativized version of linguistic terminology. Because the Greek ''endyein'' meant "to dive," the name Endymion ("Diver") at first simply described the process of the setting sun "diving" into the sea. In this case, the story of Selene embracing Endymion, or Moon embraces Diver, refers to the sun setting and the moon rising.
Gigantomachy
Gaia
In Greek mythology, Gaia (; from Ancient Greek , a poetical form of , 'land' or 'earth'),, , . also spelled Gaea , is the personification of the Earth and one of the Greek primordial deities. Gaia is the ancestral motherÔÇösometimes parthenog ...
, angered about her children the Titans being thrown into Tartarus following their defeat, brought forth the Giants, to attack the gods, in a war that was called the Gigantomachy. When Gaia heard of a prophecy that a mortal would help the gods to defeat the giants, she sought to find a herb that would make them undefeatable. Zeus heard of that, and ordered Selene as well as her siblings Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyper ...
( Sun) and Eos ( Dawn) not to shine, and harvested all of that plant for himself. Selene's participation in the battle is evidenced by her inclusion in the Gigantomachy frieze of the Pergamon Altar
The Pergamon Altar () was a monumental construction built during the reign of the Ancient Greek King Eumenes II in the first half of the 2nd century BC on one of the terraces of the acropolis of Pergamon in Anatolia, Asia Minor.
The structure wa ...
, fighting against Giants next to her siblings Helios and Eos and her mother Theia in the southern frieze.Honan, p20
/ref> Selene gallops sidesaddle in advance, and wears a woolen undergarment and a mantle. Additionally, on a rein guide for a chariot a goddess thought to be Selene with a crescent and veil over her head is depicted, who stands with Helios on a gate tower and tries to repel the attacks of snake-legged Giants.
Fight with Typhon
According to the late account of Nonnus, when the gigantic monster Typhon laid siege against the heavens, he attacked Selene as well by hurling bulls at her, though she managed to stay in her course, and rushed at her hissing like a viper. Selene fought back the giant, locking horns with Typhon; afterwards, she carried many scars on her orb, reminiscent of their battle.Ampelus
Ampelus
Saint Ampelus (died 302) is a martyr venerated by the Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic churches on Nov. 20. He was killed by Romans with his companion, Gaius, during the reign of Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocl ...
was a very beautiful satyr youth, loved by the god Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, ╬ö╬╣¤î╬Ż¤ů¤â╬┐¤é ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
. One day, in Nonnus' account, Ampelus rode on a bull, and proceeded to compare himself to Selene, saying that he was her equal, having horns and riding bulls just like her. The goddess took offense, and sent a gadfly to sting Ampelus' bull. The bull panicked, threw Ampelus and gored him to death.
Heracles
Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; grc-gre, ß╝ş¤ü╬▒, HߪŚr─ü; grc, ß╝ş¤ü╬Ě, HߪŚr─ô, label=none in Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she ...
, other accounts have Selene involved in some way in its birth or rearing. Aelian Aelian or Aelianus may refer to:
* Aelianus Tacticus, Greek military writer of the 2nd century, who lived in Rome
* Casperius Aelianus, Praetorian Prefect, executed by Trajan
* Claudius Aelianus, Roman writer, teacher and historian of the 3rd centu ...
states: "They say that the Lion of Nemea fell from the moon", and quotes Epimenides as saying:
Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; grc-gre, ß╝ł╬Ż╬▒╬ż╬▒╬│¤î¤ü╬▒¤é, ''Anaxag├│ras'', "lord of the assembly"; 500 ÔÇô 428 BC) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, ...
also reports that the Nemean lion was said to have fallen from the moon. Pseudo-Plutarch's ''On Rivers'' has Hera collaborating with Selene, "employing magical incantations" to create the Nemean Lion from a chest filled with foam. Hyginus says that Selene had "nourished" the lion in a "two-mouthed cave".
Pan
According to Virgil, Selene also had a tryst with the god Pan, who seduced her with a "snowy bribe of wool". Scholia on Virgil add the story, ascribed toNicander
Nicander of Colophon ( grc-gre, ╬Ł╬»╬║╬▒╬Ż╬┤¤ü╬┐¤é ߯ü ╬Ü╬┐╬╗╬┐¤ć¤Ä╬Ż╬╣╬┐¤é, N├şkandros ho Kolophß╣ônios; fl. 2nd century BC), Greek poet, physician and grammarian, was born at Claros (Ahmetbeyli in modern Turkey), near Colophon, where his famil ...
, that as part of the seduction, Pan wrapped himself in a sheepskin.
Other accounts
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, ╬ö╬╣¤î╬┤¤ë¤ü╬┐¤é ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
recorded an unorthodox version of the myth, in which Basileia, who had succeeded her father Uranus to his royal throne, married her brother Hyperion, and had two children, a son Helios and a daughter Selene, "admired for both their beauty and their chastity". Because Basileia's other brothers envied these offspring, and feared that Hyperion would try to seize power for himself, they conspired against him. They put Hyperion to the sword, and drowned Helios in the river Eridanus. Selene herself, upon discovering this, took her own life. After these deaths, her brother appeared in a dream to their grieving mother and assured her that he and his sister would now transform into divine natures; and:
Plutarch recorded a fable-like story in which Selene asked her mother to weave her a garment to fit her measure, and her mother replied that she was unable to do so, as she kept changing shape and size, sometimes full, then crescent-shaped and others yet half her size.
 In Lucian's ''Icaromenippus'', Selene complains to the titular Menippus of all the outrageous claims philosophers are making about her, such as wondering why she is ever waxing or gibbous, whether she is populated or not, and stating that she is getting her stolen light from the Sun, causing strife and ill feelings between her and her brother. She asks Menippus to report her grievances to Zeus, with the request that Zeus wipes all these natural philosophers from the face of the earth. Zeus agrees, urged by Selene's complaints and having long intended to deal with the philosophers himself.
In Lucian's ''Icaromenippus'', Selene complains to the titular Menippus of all the outrageous claims philosophers are making about her, such as wondering why she is ever waxing or gibbous, whether she is populated or not, and stating that she is getting her stolen light from the Sun, causing strife and ill feelings between her and her brother. She asks Menippus to report her grievances to Zeus, with the request that Zeus wipes all these natural philosophers from the face of the earth. Zeus agrees, urged by Selene's complaints and having long intended to deal with the philosophers himself.
Claudian
Claudius Claudianus, known in English as Claudian (; c. 370 ÔÇô c. 404 AD), was a Latin poet associated with the court of the Roman emperor Honorius at Mediolanum (Milan), and particularly with the general Stilicho. His work, written almost ent ...
wrote that in her infancy, when her horns had not yet grown, Selene (along with Helios ÔÇô their sister Eos is not mentioned with them) was nursed by her aunt, the water goddess Tethys.
According to pseudo-Plutarch, Lilaeus was an Indian shepherd who only worshipped Selene among the gods and performed her rituals and mysteries at night. The other gods, angered, sent him two lions to tear him apart. Selene then turned Lilaeus into a mountain, Mt. Lilaeon.
Ovid mentions how in the myth of Phaethon, Helios' son who drove his father's chariot for a day, when Phaethon lost control of the chariot and burned the earth, Selene in the sky looked down to see in amazement her brother's horses running wild lower than normal.
Iconography
 In antiquity, artistic representations of Selene/Luna included sculptural reliefs, vase paintings, coins, and gems. In
In antiquity, artistic representations of Selene/Luna included sculptural reliefs, vase paintings, coins, and gems. In red-figure pottery
Red-figure vase painting is one of the most important styles of figural Greek vase painting.
It developed in Athens around 520 BCE and remained in use until the late 3rd century BCE. It replaced the previously dominant style of black-figure vas ...
before the early 5th century BC, she is depicted only as a bust, or in profile against a lunar disk. In later art, like other celestial divinities such as Helios, Eos, and Nyx
Nyx (; , , "Night") is the Greek goddess and personification of night. A shadowy figure, Nyx stood at or near the beginning of creation and mothered other personified deities, such as Hypnos (Sleep) and Thanatos (Death), with Erebus (Darknes ...
(Night), Selene rides across the heavens. She is usually portrayed either driving a chariot (see above) or riding sideways on horseback (sometimes riding an ox, a mule or a ram).
Selene was often paired with her brother Helios. Selene (probably) and Helios adorned the east pediment of the Parthenon, where the two, each driving a four-horsed chariot, framed a scene depicting the birth of Athena, with Helios and his chariot rising from the ocean on the left, and Selene and her chariot descending into the sea on the right. Selene and Helios also appear on the North Metopes of the Parthenon, with Selene this time entering the sea on horseback. From Pausanias, we learn that Selene and Helios also framed the birth of Aphrodite on the base of the Statue of Zeus at Olympia
The Statue of Zeus at Olympia was a giant seated figure, about tall, made by the Greek sculptor Phidias around 435 BC at the sanctuary of Olympia, Greece, and erected in the Temple of Zeus there. Zeus is the sky and thunder god in ancient Gr ...
. There are indications of a similar framing by Selene and Helios of the birth of Pandora
In Greek mythology, Pandora (Greek: , derived from , ''p─ün'', i.e. "all" and , ''d┼Źron'', i.e. "gift", thus "the all-endowed", "all-gifted" or "all-giving") was the first human woman created by Hephaestus on the instructions of Zeus. As Hes ...
on the base of the Athena Parthenos. Pausanias also reports seeing stone images of Helios, and Selene, in the market-place at Elea, with rays projecting from the head of Helios, and horns from the head of Selene. Selene also appears on horseback as part of the Gigantomachy frieze of the Pergamon Altar
The Pergamon Altar () was a monumental construction built during the reign of the Ancient Greek King Eumenes II in the first half of the 2nd century BC on one of the terraces of the acropolis of Pergamon in Anatolia, Asia Minor.
The structure wa ...
.
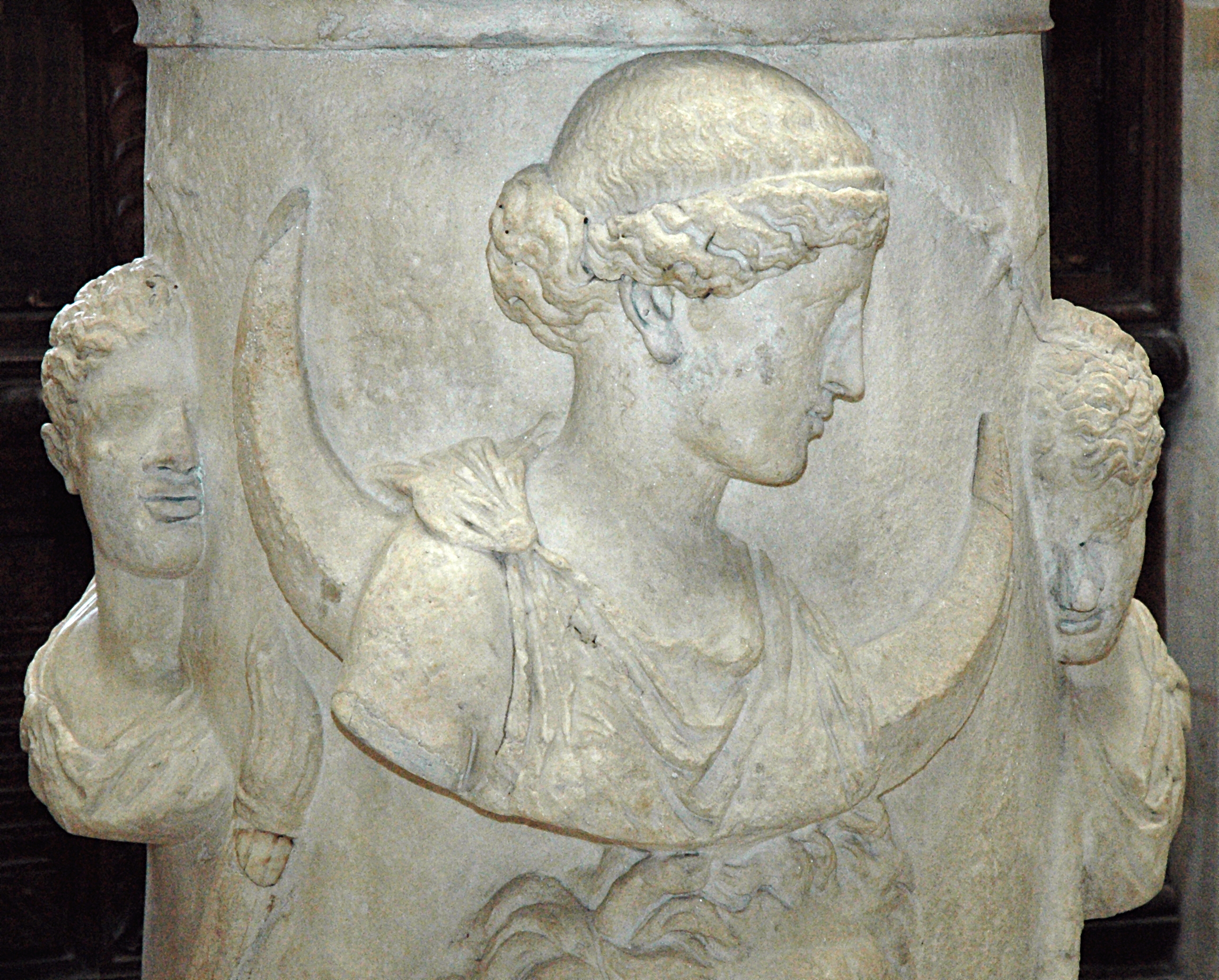
Selene is commonly depicted with a crescent moon, often accompanied by stars; sometimes, instead of a crescent, a lunar disc is used. Often a crescent moon rests on her brow, or the cusps of a crescent moon protrude, horn-like, from her head, or from behind her head or shoulders. Selene's head is sometimes surrounded by a nimbus, and from the Hellenistic period onwards, she is sometimes pictured with a torch.
In later second and third century AD Roman funerary art, the love of Selene for Endymion and his eternal sleep was a popular subject for artists. As frequently depicted on Roman sarcophagi, Selene, holding a billowing veil forming a crescent over her head, descends from her chariot to join her lover, who slumbers at her feet.
Cult
 Moon figures are found on Cretan rings and gems (perhaps indicating a Minoan moon cult), but apart from the role played by the moon itself in magic, folklore, and poetry, and despite the later worship of the Phrygian moon-god Men, there was relatively little worship of Selene. An oracular sanctuary existed near Thalamai in
Moon figures are found on Cretan rings and gems (perhaps indicating a Minoan moon cult), but apart from the role played by the moon itself in magic, folklore, and poetry, and despite the later worship of the Phrygian moon-god Men, there was relatively little worship of Selene. An oracular sanctuary existed near Thalamai in Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, ╬Ť╬▒╬║¤ë╬Ż╬»╬▒, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''ÔÇöto speak in a blunt, c ...
. Described by Pausanias, it contained statues of Pasipha├ź and Helios. Here ''Pasipha├ź'' is used as an epithet of Selene, instead of referring to the daughter of Helios and wife of Minos
In Greek mythology, Minos (; grc-gre, ╬ť╬»╬Ż¤ë¤é, ) was a King of Crete, son of Zeus and Europa. Every nine years, he made King Aegeus pick seven young boys and seven young girls to be sent to Daedalus's creation, the labyrinth, to be eaten ...
. Pausanias also described seeing two stone images in the market-place of Elis, one of the sun and the other of the moon, from the heads of which projected the rays of the sun and the horns of the crescent moon. Selene (along with Helios, Nyx and others) received an altar at the sanctuary of Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''D─ômߪŚt─ôr'' ; Doric: ''D─üm─ü╠üt─ôr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
at Pergamon, possibly in connection with the Orphic mysteries.
Originally, Pandia may have been an epithet of Selene, but by at least the time of the late ''Hymn to Selene'', Pandia had become a daughter of Zeus and Selene. Pandia (or Pandia Selene) may have personified the full moon, and an Athenian festival, called the Pandia, usually considered to be a festival for Zeus, was perhaps celebrated on the full moon and may have been associated with Selene. At Athens, wineless offerings (''nephalia'') were made to Selene, along with other celestial gods, Selene's siblings Helios and Eos, and Aphrodite Ourania; in Attica, it seems that Selene was identified with Aphrodite.
Selene was sometimes associated with childbirth, for it was believed that during the full moon women had the easiest labours; this helped in her identification with the goddess Artemis, as well as other goddesses connected to women's labours. The idea that Selene would also give easy labours to women paved way for identification with Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; grc-gre, ß╝ş¤ü╬▒, HߪŚr─ü; grc, ß╝ş¤ü╬Ě, HߪŚr─ô, label=none in Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she ...
and the Roman Juno and Lucina, three other childbirth goddesses; Plutarch calls Selene "Hera in material form." Roman philosopher Cicero connected Selene's Roman counterpart Luna's name to childbirth goddess Lucina's, both deriving from "light" (thus bringing the unborn child into the light). Nonnus also identified Selene with Eileithyia.
Selene played an important role in love magic. In Theocritus' second ''Idyll'', a young girl invokes Selene in a love-spell. The idyll opens with the girl ordering her maid to bring potions and magical utensils, followed by an invocation to Selene and Hecate, and finally the rather lengthy spell itself; once she finishes her spell, the girl recounts to Selene of how she met and was betrayed by her lover, and calls upon the goddess to witness and help her, hence the love tail is woven into the love spell. And, according to a scholium on Theocritus, Pindar wrote that lovesick women would pray to Selene for help, as Euripides apparently had Phaedra, Selene's great-niece, do in his lost play ''Hippolytus Veiled
''Hippolytus'' ( grc, ß╝╣¤Ç¤Ç¤î╬╗¤ů¤ä╬┐¤é, ''Hippolytos'') is an Theatre of ancient Greece, Ancient Greek tragedy by Euripides, based on the myth of Hippolytus of Athens, Hippolytus, son of Theseus. The play was first produced for the Dionysia#C ...
''. Plutarch wrote that Selene was called upon in love affairs because she, the Moon, constantly yearns for the Sun, and compared her in that regard to Isis.
Her and her brother's worship is also attested in Gytheum, a town in Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, ╬Ť╬▒╬║¤ë╬Ż╬»╬▒, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''ÔÇöto speak in a blunt, c ...
near Sparta, via an inscription (''C.I.G. 1392''). In the city of Epidaurus
Epidaurus ( gr, ß╝ś¤Ç╬»╬┤╬▒¤ů¤ü╬┐¤é) was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the ...
, in Argolis, Selene had an altar dedicated to her. Records show that a type of cake called (''bo├╗s'', "ox") decorated with horns to represent the full moon or an ox was offered to her and other divinities like Hecate, Artemis and Apollo.Allaire Brumfield, ''Cakes in the Liknon: Votives from the Sanctuary of Demeter and Kore on Acrocorinth'', Hesperia: The Journal of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens Vol. 66, No. 1 (Jan. - Mar., 1997)pp. 157; 171
The American School of Classical Studies at Athens
, native_name_lang = Greek
, image = American School of Classical Studies at Athens.jpg
, image_size =
, image_alt =
, caption = The ASCSA main building as seen from Mount Lykavittos
, latin_name =
, other_name =
, former_name =
, ...
. In addition, a type of flat, round moon-shaped cake was called 'selene' ("moon") and was offered "to the goddess."
The ancient Greeks called Monday "day of the Moon" (''ß╝í╬╝╬ş¤ü╬▒ ╬ú╬Á╬╗╬«╬Ż╬̤é'') after her.
Orphic literature
According to a certain Epigenes, the three Moirai, or Fates, were regarded in the Orphic tradition as representing the three divisions of Selene, "the thirtieth and the fifteenth and the first" (i.e. the crescent moon, full moon, and dark moon, as delinted by the divisions of the calendar month).Namesakes
In astronomy
Selene is the Greek proper name for the Moon, and580 Selene
Selene ( minor planet designation: 580 Selene) is a minor planet orbiting the Sun in the asteroid belt. The name Selene is that of an ancient Greek goddess of the Moon. The name may have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation ''19 ...
, a minor planet in the asteroid belt, is also named after this goddess.
In chemistry
The chemical element Selenium was named after Selene byJ├Âns Jacob Berzelius
Baron J├Âns Jacob Berzelius (; by himself and his contemporaries named only Jacob Berzelius, 20 August 1779 ÔÇô 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be on ...
, because of the element's similarity to the element tellurium, named for the Earth (Tellus
Tellus is a Latin word meaning "Earth" and may refer to:
* An alternative name for the planet Earth
* Tellus of Athens, a citizen of ancient Athens who was thought to be the happiest of men
* Tellus Mater or Terra Mater, the ancient Roman earth mo ...
).
Vehicles
The secondJapan
Japan ( ja, ŠŚąŠťČ, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese lunar orbiter spacecraft following was named SELENE (Selenological and Engineering Explorer) after Selene, and was also known as Kaguya in Japan. HMS Selene (P254)
HMS ''Selene'' was a S-class submarine of the third batch built for the Royal Navy during World War II. She survived the war and was sold for scrap in 1961.
Design and description
The last 17 boats of the third batch were significantly modifi ...
, a 1944 British submarine and Ghia Selene
The Ghia Selene was a series of concept cars created by Carrozzeria Ghia.
Selene I
The Selene I was designed by Tom Tjaarda. shown at the Turin Motor Show in 1959 and had a lot of similarities with the Renault Project 900 concept, in that it h ...
, a concept car from the Ghia design studio from 1959, also bore her name.
Genealogy
See also
* Horned deity *List of lunar deities
A lunar deity is a deity who represents the Moon, or an aspect of it. Lunar deities and Moon worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms. The following is a list of lunar deities:
African
American Aztec mythology
* ...
* Diana (mythology)
* Star and crescent
Notes
References
*Aelian Aelian or Aelianus may refer to:
* Aelianus Tacticus, Greek military writer of the 2nd century, who lived in Rome
* Casperius Aelianus, Praetorian Prefect, executed by Trajan
* Claudius Aelianus, Roman writer, teacher and historian of the 3rd centu ...
, ''On Animals, Volume III: Books 12-17'', translated by A. F. Scholfield, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 449, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1959Online version at Harvard University Press
. * Aeschylus, ''Fragments'', edited and translated by Alan H. Sommerstein,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 505. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2009. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Allen, Thomas W., E. E. Sikes. ''The Homeric Hymns'', edited, with preface, apparatus criticus, notes, and appendices. London. Macmillan. 1904. *
Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; grc-gre, ß╝ł╬Ż╬▒╬ż╬▒╬│¤î¤ü╬▒¤é, ''Anaxag├│ras'', "lord of the assembly"; 500 ÔÇô 428 BC) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, ...
, ''Anaxagoras of Clazomenae: Fragments and Testimonia: A Text and Translation with Notes and Essays'', edited and translated by Patricia Curd, University of Toronto Press, 2007. .
* Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: ß╝ł¤Ç╬┐╬╗╬╗¤î╬┤¤ë¤ü╬┐¤é ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, ''Apollodorus, The Library, with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes.'' Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921.
* Apollonius of Rhodes, ''Argonautica''; with an English translation by R. C. Seaton. William Heinemann, 1912Internet Archive
*
Aratus Solensis
Aratus (; grc-gre, ß╝î¤ü╬▒¤ä╬┐¤é ߯ü ╬ú╬┐╬╗╬Á¤Ź¤é; c. 315 BC/310 BC240) was a Greek didactic poet. His major extant work is his hexameter poem ''Phenomena'' ( grc-gre, ╬Ž╬▒╬╣╬Ż¤î╬╝╬Á╬Ż╬▒, ''Phain├│mena'', "Appearances"; la, Phaenomena), the ...
, ''Phaenomena'' translated by G. R. Mair. Loeb Classical Library Volume 129. London: William Heinemann, 1921Online version at the Topos Text Project
* Aristotle, ''Aristotle in 23 Volumes, Vol. 19, translated by H. Rackham''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1934. * Astour, Michael C., ''Hellenosemitica: An Ethinic and Cultural Study in West Semitic Impact on Mycenaean Greece'', Brill Archive, 1965. * Athanassakis, Apostolos N., and Benjamin M. Wolkow, ''The Orphic Hymns'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 2013.
Google Books
* * Bekker, Immanuel, ''Anecdota Graeca: Lexica Segueriana'', Apud G.C. Nauckium, 1814. * Blum, Rudolf, ''Kallimachos: The Alexandrian Library and the Origins of Bibliography'', translated by Hans H. Wellisch, University of Wisconsin Press, 2011. . * ''BrillÔÇÖs New Pauly: Encyclopaedia of the Ancient World'', Volume 13, Sas-Syl, editors: Hubert Cancik, Helmuth Schneider,
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 27 ...
, 2008. Online version
* * * Caldwell, Richard, ''Hesiod's Theogony'', Focus Publishing/R. Pullins Company (June 1, 1987). . * Campbell, David A., ''Greek Lyric, Volume I: Sappho and Alcaeus'',
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 142, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1990. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cashford, Jules, (2003a), ''The Homeric Hymns'', Penguin Books, 2003.
Internet Archive
* Cashford, Jules, (2003b), ''The Moon: Myth and Image'', Four Walls Eight Windows, New York, 2003. . * Catullus, ''Catullus. Tibullus. Pervigilium Veneris.'', translated by F. W. Cornish, J. P. Postgate, J. W. Mackail, revised by G. P. Goold,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 6, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1913. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cicero, ''Cicero's Tusculan Disputations'', translated by C. D. Yonge; Harpers & Brothers, publishers, 1888. * de Clarac, Fr├ęd├ęric, ''Mus├ęe de Sculpture antique et moderne, ou description historique et graphique du Louvre'' (Paris: Imprimerie Royale, 1828, etc.), vol. 2. *
Claudian
Claudius Claudianus, known in English as Claudian (; c. 370 ÔÇô c. 404 AD), was a Latin poet associated with the court of the Roman emperor Honorius at Mediolanum (Milan), and particularly with the general Stilicho. His work, written almost ent ...
, ''Rape of Persephone'' in ''Claudian with an English Translation by Maurice Platnauer'', Volume II, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 136. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press; London: William Heinemann, Ltd.. 1922. Internet Archive
* Cohen, Beth, "Outline as a Special Technique in Black- and Red-figure Vase-painting", in ''The Colors of Clay: Special Techniques in Athenian Vases'', Getty Publications, 2006, . * Collard and Cropp in Euripides, ''Fragments: Aegeus-Meleager'', edited and translated by Christopher Collard, Martin Cropp,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 504, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2008. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cook, Arthur Bernard, ''Zeus: A Study in Ancient Religion, Volume I: Zeus God of the Bright Sky'', Cambridge University Press 1914
Internet Archive
*
Propertius
Sextus Propertius was a Latin elegiac poet of the Augustan age. He was born around 50ÔÇô45 BC in Assisium and died shortly after 15 BC.
Propertius' surviving work comprises four books of ''Elegies'' ('). He was a friend of the poets Gallus a ...
, ''Elegies'' Edited and translated by G. P. Goold. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
18. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1990.Online version at Harvard University Press
* Cox, George W. ''The Mythology of the Aryan Nations Part, Vol. II'', London, C. Kegan Paul & Co., 1 Paternoster Square, 1878
Internet Archive
* Davidson, James, "Time and Greek Religion", in ''A Companion to Greek Religion'', edited by Daniel Ogden, John Wiley & Sons, 2010, . *
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, ╬ö╬╣¤î╬┤¤ë¤ü╬┐¤é ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
, ''Diodorus Siculus: The Library of History''. translated by C. H. Oldfather, twelve volumes, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press; London: William Heinemann, Ltd. 1989Online version by Bill Thayer
* Edmonds, John Maxwell, (1922), ''Lyra Graeca'', W. Heinemann, 1922. * Edmonds, Radcliffe (2013), ''Redefining Ancient Orphism: A Study in Greek Religion'', Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press. . * Empedocles in ''Early Greek Philosophy, Volume V: Western Greek Thinkers, Part 2. '', edited and translated by Andr├ę Laks, Glenn W. Most,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 528, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2016. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Euripides, ''The Complete Greek Drama', edited by Whitney J. Oates and Eugene O'Neill, Jr. in two volumes. 2''. ''The Phoenissae'', translated by E. P. Coleridge. New York. Random House. 1938. * Euripides, ''Fragments: Oedipus-Chrysippus: Other Fragments'', edited and translated by Christopher Collard, Martin Cropp,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 506. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2008. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Evelyn-White, Hugh, ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White''. Homeric Hymns. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914. * Fairbanks, Arthur, ''The Mythology of Greece and Rome''. D. AppletonÔÇôCentury Company, New York, 1907. * Faraone, Christopher A., ''Ancient Greek Love Magic'', Harvard University Press, 2009. . * Fowler, R. L. (2000), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 1: Text and Introduction'', Oxford University Press, 2000. . * Fowler, R. L. (2013), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 2: Commentary'', Oxford University Press, 2013. . * Freeman, Kathleen, ''Ancilla to the Pre-Socratic Philosophers: A Complete Translation of the Fragments in Diels, Fragmente Der Vorsokratiker'', Harvard University Press, 1983. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * ''The Greek Anthology, Volume I: Book 1: Christian Epigrams, Book 2: Description of the Statues in the Gymnasium of Zeuxippus, Book 3: Epigrams in the Temple of Apollonis at Cyzicus, Book 4: Prefaces to the Various Anthologies, Book 5: Erotic Epigrams'', translated by W. R. Paton. Revised by Michael A. Tueller,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 67, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2014. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Gury, Fran├žoise, "Selene, Luna" in '' Lexicon Iconographicum Mythologiae Classicae (LIMC)'' VII.1 Artemis Verlag, Z├╝rich and Munich, 1994. . * Grimal, Pierre, ''The Dictionary of Classical Mythology'', Wiley-Blackwell, 1996. . * Hansen, William F., ''Handbook of classical mythology'', ABC-CLIO, 2004. . * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
*
Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, ß╝ę¤â╬»╬┐╬┤╬┐¤é ''H─ôs├şodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
, '' Theogony'', in ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White'', Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Honan, Mary McMahon, ''Guide to the Pergamon Museum'', De Gruyter, 1904.
Online version at De Gruyter
* Hurwit, Jeffery M. (1999), ''"The" Athenian Acropolis: History, Mythology, and Archaeology from the Neolithic Era to the Present'', CUP Archive, 1999. . * Hurwit, Jeffery M. (2017), "Helios Rising: The Sun, the Moon, and the Sea in the Sculptures of the Parthenon", ''American Journal of Archaeology'', Vol. 121, No. 4 (October 2017), pp. 527ÔÇô558. . * Hyginus, Gaius Julius, '' Fabulae'', in ''The Myths of Hyginus'', edited and translated by Mary A. Grant, Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1960
Online version at ToposText
* Jebb, Richard Claverhouse, ''Bacchylides: The Poems and Fragments'', Georg Olms Verlag, 1905, 1994. . * Jones, Prudence H., "A Goddess Arrives: Nineteenth Century Sources of the New Age Triple Moon Goddess" in ''Culture and Cosmos'', 19(1): 45ÔÇô70. * Julius Pollux, ''Onomasticon: cum annotationibus interpretum''. VI - X, Volume 2, Kuehn, 1824
Google books
* Ker├ęnyi, Karl (1951), ''The Gods of the Greeks'', Thames and Hudson, London, 1951
Internet Archive
* Keightley, Thomas, ''The Mythology of Ancient Greece and Italy'', G. Bell and Sons, 1877. * Liddell, Henry George, Robert Scott, ''
A Greek-English Lexicon
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes'' ...
'', revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones with the assistance of Roderick McKenzie, Clarendon Press Oxford, 1940Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Lightfoot, J. L., ''Hellenistic Collection: Philitas, Alexander of Aetolia, Hermesianax, Euphorion, Parthenius,'' edited and translated by J. L. Lightfoot,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 508, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2010. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 ÔÇô after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
, ''Dialogues of the Dead. Dialogues of the Sea-Gods. Dialogues of the Gods. Dialogues of the Courtesans'', translated by M. D. MacLeod, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 431, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1961. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 ÔÇô after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
, ''Phalaris. Hippias or The Bath. Dionysus. Heracles. Amber or The Swans. The Fly. Nigrinus. Demonax. The Hall. My Native Land. Octogenarians. A True Story. Slander. The Consonants at Law. The Carousal (Symposium) or The Lapiths'' translated by A. M. Harmon. Loeb Classical Library No. 14. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1913. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Lucian
Lucian of Samosata, '; la, Lucianus Samosatensis ( 125 ÔÇô after 180) was a Hellenized Syrian satirist, rhetorician and pamphleteer
Pamphleteer is a historical term for someone who creates or distributes pamphlets, unbound (and therefore ...
, ''The Downward Journey or The Tyrant. Zeus Catechized. Zeus Rants. The Dream or The Cock. Prometheus. Icaromenippus or The Sky-man. Timon or The Misanthrope. Charon or The Inspectors. Philosophies for Sale'', translated by A. M. Harmon. Loeb Classical Library No. 54. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1915. Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Macrobius
Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius, usually referred to as Macrobius (fl. AD 400), was a Roman provincial who lived during the early fifth century, during late antiquity, the period of time corresponding to the Later Roman Empire, and when Latin was ...
, ''Saturnalia
Saturnalia is an ancient Roman festival and holiday in honour of the god Saturn, held on 17 December of the Julian calendar and later expanded with festivities through to 23 December. The holiday was celebrated with a sacrifice at the Temple ...
, Volume II: Books 3-5'', edited and translated by Robert A. Kaster, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 511, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2011. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Mayerson, Philip, ''Classical Mythology in Literature, Art, and Music'', Focus publishing, R. Pullins Company, 2001. . * Meagher, Robert E., ''The Meaning of Helen: In Search of an Ancient Icon'', Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers, 2002. . * Mesomedes in ''Lyra Gr├Žca: Specimens of the Greek Lyric Poets, from Callinus to Soutsos.'' Edited, with critical Notes, and a biographical Introduction, by James Donaldson (Edinburgh & London, 1854) p. 96f. * Mitchell, Lucy M., "Sculptures of the Great Pergamon Altar" in The Century Magazine, 1883. * Morford, Mark P. O., Robert J. Lenardon, ''Classical Mythology'', Eighth Edition, Oxford University Press, 2007.
Internet Archive
* Most, G.W. (2018a), ''Hesiod, Theogony, Works and Days, Testimonia,'' Edited and translated by Glenn W. Most,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 57, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2018. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Most, G.W. (2018b), ''Hesiod: The Shield, Catalogue of Women, Other Fragments'',
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
, No. 503, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2007, 2018. Online version at Harvard University Press
* M├╝ller, Karl Wilhelm Ludwig, ''Fragmenta Historicorum Graecorum'', Volume I, 1841
Internet Archive
* Murray, Alexander Stuart (1892), ''Handbook of Greek Arch├Žology'', John Murray, 1892. * Murray, Alexander Stuart (1903), ''The Sculptures of the Parthenon'', John Murray, 1903. * n├ş Mheallaigh, Karen, ''The Moon in the Greek and Roman Imagination: Myth, Literature, Science and Philosophy'', Cambridge University Press, 2020. . * Nonnus, ''
Dionysiaca
The ''Dionysiaca'' {{IPAc-en, ╦î, d, a╔¬, ., ╔Ö, ., n, ßÁ╗, ╦ł, z, a╔¬, ., ╔Ö, ., k, ╔Ö ( grc-gre, ╬ö╬╣╬┐╬Ż¤ů¤â╬╣╬▒╬║╬Č, ''Dionysiak├í'') is an ancient Greek epic poem and the principal work of Nonnus. It is an epic in 48 books, the longest survi ...
, Volume I: Books 1–15'', translated by W. H. D. Rouse
William Henry Denham Rouse (; 30 May 1863 ÔÇô 10 February 1950) was a pioneering British teacher who advocated the use of the "direct method" of teaching Latin and Greek.
Life
Rouse was born in Calcutta, British India on 30 May 1863. After his f ...
, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 344, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1940 (revised 1984). Online version at Harvard University Press
* Nonnus, ''
Dionysiaca
The ''Dionysiaca'' {{IPAc-en, ╦î, d, a╔¬, ., ╔Ö, ., n, ßÁ╗, ╦ł, z, a╔¬, ., ╔Ö, ., k, ╔Ö ( grc-gre, ╬ö╬╣╬┐╬Ż¤ů¤â╬╣╬▒╬║╬Č, ''Dionysiak├í'') is an ancient Greek epic poem and the principal work of Nonnus. It is an epic in 48 books, the longest survi ...
, Volume III: Books 36–48'', translated by W. H. D. Rouse
William Henry Denham Rouse (; 30 May 1863 ÔÇô 10 February 1950) was a pioneering British teacher who advocated the use of the "direct method" of teaching Latin and Greek.
Life
Rouse was born in Calcutta, British India on 30 May 1863. After his f ...
, Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 346, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1940. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Obbink, Dirk (2002), "'All Gods are True' in Epicurus" in ''Traditions of Theology: Studies in Hellenistic Theology, Its Background and Aftermath,'' Dorothea, Frede, and Andr├ę Laks (eds.), Brill, Boston, 2002. * Obbink, Dirk (2011) "56. Orphism, Cosmogony, and Genealogy (Mus. fr. 14)" in ''Tracing Orpheus: Studies of Orphic Fragments'', edited by Miguel Herrero de J├íuregui, Walter de Gruyter, 2011. . * Osborne, Robin, "Looking on – Greek Style. Does the sculpted girl speak to women too?" in ''Classical Greece: Ancient Histories and Modern Archaeologies'', Morris, Ian (ed.), Cambridge University Press, 1994. . * Ovid, '' Amores'' in ''Heroides. Amores'', translated by Grant Showerman, revised by G. P. Goold,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 41, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1977. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid, '' Ars Amatoria'' in ''Art of Love. Cosmetics. Remedies for Love. Ibis. Walnut-tree. Sea Fishing. Consolation'', translated by J. H. Mozley, revised by G. P. Goold,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 232, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1929Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid, ''
Ovid's Fasti
The ''Fasti'' ( la, F─üst─ź , "the Calendar"), sometimes translated as ''The Book of Days'' or ''On the Roman Calendar'', is a six-book Latin poem written by the Roman poet Ovid and published in AD 8. Ovid is believed to have left the ''Fasti'' ...
: With an English translation by Sir James George Frazer'', London: W. Heinemann LTD; Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1959Internet Archive
* Ovid, '' Heroides'' in ''Heroides. Amores'', translated by Grant Showerman, revised by G. P. Goold,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 41, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1977. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid. '' Metamorphoses, Volume I: Books 1-8''. Translated by Frank Justus Miller. Revised by G. P. Goold.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 42. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1977, first published 1916. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid. '' Metamorphoses, Volume II: Books 9-15''. Translated by Frank Justus Miller. Revised by G. P. Goold.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 43. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1984, first published 1916. Online version at Harvard University Press
* '' Oxford Classical Dictionary'', second edition, Hammond, N.G.L. and Howard Hayes Scullard (editors), Oxford University Press, 1992. . * Page, Denys Lionel, Sir, ''Select Papyri, Volume III: Poetry'', translated by Denys L. Page,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 360, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1941. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Palagia, Olga (1998), ''The Pediments of the Parthenon'', BRILL, 1998. . * Palagia, Olga (2005), "Fire from Heaven: Pediments and Akroteria of the Parthenon" in ''The Parthenon: From Antiquity to the Present'', edited by Jenifer Neils, Cambridge University Press, 2005. . * Pannen, Imke, ''When the Bad Bleeds: Mantic Elements in English Renaissance Revenge Tragedy'', Volume 3 of Representations & Reflections; V&R unipress GmbH, 2010. . * Parisinou, Eva, "Brightness personified: light and devine image in ancient Greece" in ''Personification In The Greek World: From Antiquity To Byzantium'', editors Emma Stafford, Judith Herrin, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2005. . * Parker, Robert, ''Polytheism and Society at Athens'', Oxford University Press, 2005. . * Pausanias, ''Pausanias Description of Greece with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes.'' Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Picón, Carlos A.; Hemingway, Seán, ''Pergamon and the Hellenistic Kingdoms of the Ancient World'', Yale University Press, 2016, . * Pindar, ''Odes'', Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1990
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Plato, ''Plato in Twelve Volumes, Vol. 1 translated by Harold North Fowler''; Introduction by W.R.M. Lamb. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1966 * Plutarch, '' Moralia''. 16 vols. (vol. 13: 13.1 & 13.2, vol. 16: index), transl. by Frank Cole Babbitt (vol. 1ÔÇô5) et al., series: "
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
" (LCL, vols. 197ÔÇô499). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press et al., 1927ÔÇô2004.
* Powell, Barry B. ''Classical Myth'', Ninth edition, Oxford University Press, 2020. .
* Psaroudakes, Stelios, "Mesomedes' ''Hymn to the Sun'': The Precipitation of ''Logos'' in the ''Melos''", in ''Music, Text, and Culture in Ancient Greece'', editors: Phillips, Tom, and Armand D'Angour, Oxford University Press, 2018. .
* Pseudo-Plutarch, ''About Rivers and Mountains and Things Found in Them'', translated by Thomas M. Banchich, with Sarah Brill, Emilyn Haremza, Dustin Hummel, and Ryan Post, Canisius College Translated Texts, Number 4, Canisius College
Canisius College is a private Jesuit college in Buffalo, New York. It was founded in 1870 by Jesuits from Germany and is named after St. Peter Canisius. Canisius offers more than 100 undergraduate majors and minors, and around 34 master's ...
, Buffalo, New York, 2010*
Quintus Smyrnaeus
Quintus Smyrnaeus (also Quintus of Smyrna; el, ╬ܤî¤Ő╬Ż¤ä╬┐¤é ╬ú╬╝¤ů¤ü╬Ż╬▒ß┐ľ╬┐¤é, ''Kointos Smyrnaios'') was a Greek epic poet whose ''Posthomerica'', following "after Homer", continues the narration of the Trojan War. The dates of Quintus Smy ...
, ''Quintus Smyrnaeus: The Fall of Troy'', translated by A.S. Way, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1913Internet Archive
* Ridgeway, Brunilde Sismondo, ''Hellenistic Sculpture II: The Styles of ca. 200–100 B.C.'', The University of Wisconsin Press, 2000. * Robertson, Martin (1981), ''A Shorter History of Greek Art'', Cambridge University Press. . * Robertson, Martin (1992), ''The Art of Vase-Painting in Classical Athens'', Cambridge University Press. . * Robertson, Noel (1996), "Athena's Shrines and Festivals" in ''Worshipping Athena: Panathenaia and Parthenon'', The University of Wisconsin Press. . * Roman, Luke, Monica Roman, ''Encyclopedia of Greek and Roman Mythology'', Facts on File, 2010. . * Roscher, Wilhelm Heinrich, ''├ťber Selene und Verwandtes'', B.G. Teubner, Leipzig 1890. * Savignoni L. 1899. "On Representations of Helios and of Selene", The Journal of Hellenic Studies 19
pp. 265ÔÇô272
* Seyffert, Oskar, ''A Dictionary of Classical Antiquities, Mythology, Religion, Literature and Art, from the German of Dr. Oskar Seyffert'', S. Sonnenschein, 1901
Internet Archive
* Seneca, ''Tragedies, Volume I: Hercules. Trojan Women. Phoenician Women. Medea. Phaedra.'' Edited and translated by John G. Fitch.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 62. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2018. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Shear, T.L., Jr., ''Trophies of Victory: Public Building in Periklean Athens'', Princeton University Press, 2016. * Servius, ''Commentary on the Georgics of Vergil'', Georgius Thilo, Ed. 1881
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library (Latin)
* Smith, William; '' Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', London (1873). * Sommerstein, Alan H., ''Aeschylus: Persians, Seven against Thebes, Suppliants, Prometheus Bound'', edited and translated by Alan H. Sommerstein,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 145. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2009. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Sorabella, Jean, "A Roman Sarcophagus and Its Patron." ''Metropolitan Museum Journal'', Vol. 36 (2001)
Downloadable PDF available at ''MetPublications''
* Sorrenti, Stefania, "Les repr├ęsentations figur├ęes de Jupiter Dolich├ęnien ├á Rome," in ''La terra sigillata tardo-italica decorata del Museo nazionale romano'', "L'Erma" di Bretschneider, 1999). * Statius, '' Thebaid, Volume I: Thebaid: Books 1-7'', edited and translated by D. R. Shackleton Bailey,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 207, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2004. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Statius, '' Thebaid, Volume II: Thebaid: Books 8-12. Achilleid'', edited and translated by D. R. Shackleton Bailey,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 498. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2004. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Stoll, Heinrich Wilhelm, ''Handbook of the religion and mythology of the Greeks, With a Short Account of The Religious System of the Romans'', tr. by R.B. Paul, and ed. by T.K. Arnold, London, Francis & John Rivington, 1852. *
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
, ''Geography'', Editors, H.C. Hamilton, Esq., W. Falconer, M.A., London. George Bell & Sons. 1903Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* * Taylor, Thomas, ''The Hymns of Orpheus'', Philosophical Research Society; Limited edition (June 1987). . * Theocritus in ''Theocritus, Moschus, Bion,'' edited and translated by Neil Hopkinson,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 28, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2015. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Theocritus, Bion of Smyrna, Moschus, ''Theocritus, Bion et Moschus. Graece et Latine. Accedunt virorum doctorum animadversiones, scholia, indices; et M. ├ćmilii Porti Lexicon Doricum, Volume 2'', London Sumptibus Ricardi Priestley, 1826. * Thomas, Edmund. "From the panteon of the gods to the Pantheon of Rome" in ''Pantheons: Transformations of a Monumental Idea'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2004. . * Tryphiodorus, ''The Taking of Ilios'' in ''Oppian, Colluthus, and Tryphiodorus'', translated by A. W. Mair,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 219, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 1928. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Valerius Flaccus, ''Argonautica'', translated by J. H. Mozley,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 286. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1928Online version at Harvard University Press
* Vergados, Athanassios, ''The "Homeric Hymn to Hermes": Introduction, Text and Commentary'', Walter de Gruyter, 2012. . * Verhelst, Berenice, ''Direct Speech in NonnusÔÇÖ ''Dionysiaca'': Narrative and rhetorical functions of the characters' "varied" and "many-faceted" words'', BRILL, 2016. (e-book). (hardback). * * Virgil, ''Georgics'' in ''Bucolics, Aeneid, and Georgics Of Vergil''. J. B. Greenough. Boston. Ginn & Co. 1900
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Walters, Henry Beauchamp, Samuel Birch, ''History of Ancient Pottery: Greek, Etruscan, and Roman, Volume 2'', John Murray, 1905. * West, M. L. (1983), ''The Orphic Poems'', Clarendon Press Oxford, 1983. . * West, M. L. (2003), ''Homeric Hymns. Homeric Apocrypha. Lives of Homer'', edited and translated by Martin L. West,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 496, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press, 2003. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Willetts, R. F., ''Cretan Cults and Festivals'', Greenwood Press, 1980. . * Xenis, Georgios A., ''Scholia vetera in Sophoclis "Oedipum Coloneum"'', De Gruyter, 2018.
Online version at De Gruyter
* Zschietzschmann, W, ''Hellas and Rome: The Classical World in Pictures'', Kessinger Publishing, 2006. .
External links
*SELENE in Mythopedia
{{Authority control Divine women of Zeus Greek goddesses Lunar goddesses Personifications in Greek mythology Titans (mythology) Light goddesses Women of Helios Magic goddesses Metamorphoses characters Horned deities Childhood goddesses Characters in the Argonautica Women in Greek mythology Characters in Greek mythology Night goddesses Consorts of Pan (god) ur:ě│█î┘ä█î┘ć█ü