Secessionist Towns And Cities on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a
"Secession"
Secession, Majority Rule and Equal Rights: a Few Questions
 Secession theorists have described a number of ways in which a political entity (city, county, canton, state) can secede from the larger or original state:
* Secession from
Secession theorists have described a number of ways in which a political entity (city, county, canton, state) can secede from the larger or original state:
* Secession from
The Constitutional Right of Secession in Political Theory and History
Creating New States: Theory and Practice of Secession
p. 222, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2007.
74 U.S. 700 (1868) at
In Pursuit of Sovereignty and Self-determination: Peoples, States and Secession in the International Order
 In 1974, Greek
In 1974, Greek
 The
The
 * Republic of Texas, Texas seceded from Mexico in 1836 (see Texas Revolution), after animosity between the Mexican government and the American settlers of the Coahuila y Tejas, Coahuila y Tejas State. It was later annexed by the United States in 1845.
* The Republic of the Rio Grande seceded from Mexico on January 17, 1840. It rejoined Mexico on November6 the same year.
* After the Federal government, federal system was abandoned by President of Mexico, President Antonio López de Santa Anna, Santa Anna, the Congress of Yucatán approved in 1840 a declaration of independence, establishing the Republic of Yucatán. The Republic rejoined Mexico in 1843.
* Republic of Texas, Texas seceded from Mexico in 1836 (see Texas Revolution), after animosity between the Mexican government and the American settlers of the Coahuila y Tejas, Coahuila y Tejas State. It was later annexed by the United States in 1845.
* The Republic of the Rio Grande seceded from Mexico on January 17, 1840. It rejoined Mexico on November6 the same year.
* After the Federal government, federal system was abandoned by President of Mexico, President Antonio López de Santa Anna, Santa Anna, the Congress of Yucatán approved in 1840 a declaration of independence, establishing the Republic of Yucatán. The Republic rejoined Mexico in 1843.
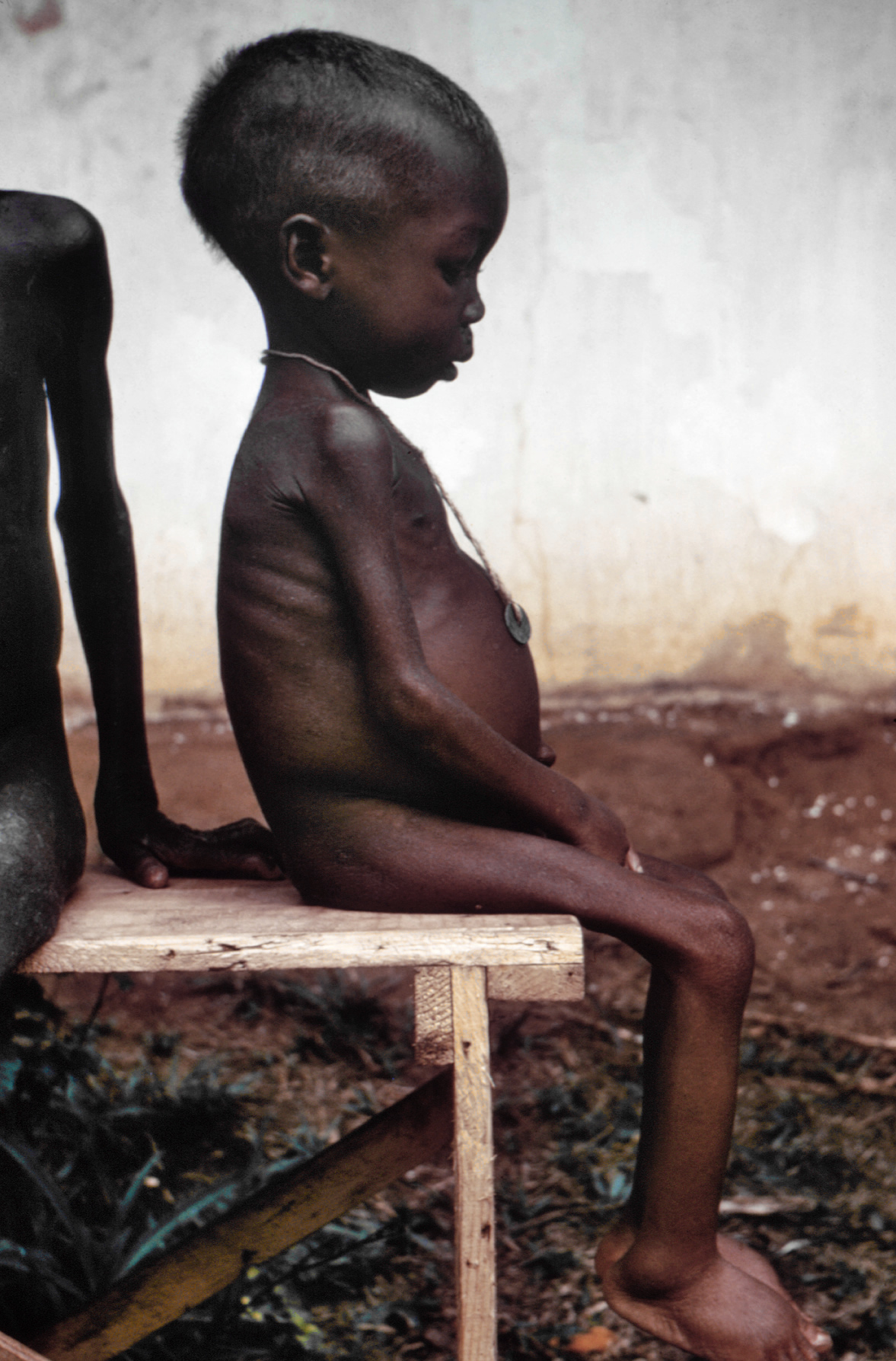 Between 1967 and 1970, the Eastern Region, Nigeria, Eastern Region seceded from Nigeria and established the Biafra, Republic of Biafra, which led to a Nigerian Civil War, war that ended with the state returning to Nigeria. In 1999, at the beginning of a Fourth Nigerian Republic, new democratic regime, other secessionist movements emerged, including the Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra, formed as a military wing of the Republic of Biafra.
Between 1967 and 1970, the Eastern Region, Nigeria, Eastern Region seceded from Nigeria and established the Biafra, Republic of Biafra, which led to a Nigerian Civil War, war that ended with the state returning to Nigeria. In 1999, at the beginning of a Fourth Nigerian Republic, new democratic regime, other secessionist movements emerged, including the Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra, formed as a military wing of the Republic of Biafra.
 The Constitution of the Soviet Union guaranteed all Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs the right to secede from the Union. In 1990, after free elections, the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, Lithuanian SSR Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania, declared independence and other Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs soon followed. Despite the Soviet central government's refusal to recognize the independence of the republics, the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Soviet Union dissolved in 1991.
The Constitution of the Soviet Union guaranteed all Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs the right to secede from the Union. In 1990, after free elections, the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, Lithuanian SSR Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania, declared independence and other Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs soon followed. Despite the Soviet central government's refusal to recognize the independence of the republics, the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Soviet Union dissolved in 1991.
 Present-day Spain (known officially as "the Spain, Kingdom of Spain") was assembled as a Nation state, central state in the French model between the Nueva Planta decrees, 18th and 1833 territorial division of Spain, 19th centuries from various component kingdoms with varying languages, cultures and legislations. Spain has several List of active separatist movements in Europe#Spain, secessionist movements, the most notable ones being in Catalan separatism, Catalonia, the Basque separatism, Basque Country and Galician independence, Galicia.
Present-day Spain (known officially as "the Spain, Kingdom of Spain") was assembled as a Nation state, central state in the French model between the Nueva Planta decrees, 18th and 1833 territorial division of Spain, 19th centuries from various component kingdoms with varying languages, cultures and legislations. Spain has several List of active separatist movements in Europe#Spain, secessionist movements, the most notable ones being in Catalan separatism, Catalonia, the Basque separatism, Basque Country and Galician independence, Galicia.
 The Republic of Ireland withdrew from the United Kingdom after Ireland Proclamation of the Irish Republic, proclaimed independence in 1916 and, as the Irish Free State, gained independence in 1922. The United Kingdom has a number of secession movements:
* In Northern Ireland, Irish republicanism, Irish republicans and Irish nationalism, nationalists have long called for the secession of Northern Ireland to join the Republic of Ireland. This is opposed by Unionism in Ireland, Unionists. A minority have supported the Ulster nationalism, independence of Northern Ireland from the United Kingdom without joining the Republic of Ireland.
* In Scotland, the Scottish National Party (SNP) campaigns for Scottish independence and direct Scottish membership in the European Union. It has representation at all levels of politics in Scotland, Scottish politics and forms the devolved Scottish government. Later pro-independence parties have had lesser electoral success. The Scottish Greens and the Scottish Socialist Party are most widely publicised. However all independence movements/parties are opposed by Unionism in Scotland, unionists. A 2014 Scottish independence referendum, referendum on independence in which voters were asked "Should Scotland be an independent country?" took place in September 2014. It saw "no" win, as 55.3% of voters voted against independence.
* In Wales, Plaid Cymru ''(Party of Wales)'' stands for Welsh independence within the European Union. It is also represented at all levels of Welsh politics and has often been the second largest party in the Senedd (Welsh Parliament).
* England:
** In Cornwall, supporters of Mebyon Kernow call for the creation of a Cornish Assembly and separation from England, giving the county significant Cornish self-government movement, self-government, whilst remaining within the United Kingdom as a fifth home nation.
** London has supporters of an independent or semi-autonomous city-state since the 2016 EU Referendum in which Londoners voted overwhelmingly to remain in the EU. A London independence party, known as Londependence, was established in June 2019. Their calls increased after the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 General Election in which most Londoners voted for the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, gaining a representative, bucking the national trend.
** The Northern Independence Party is a party formed in 2020 that seeks to make Northern England an independent state under the name Northumbria.
The Republic of Ireland withdrew from the United Kingdom after Ireland Proclamation of the Irish Republic, proclaimed independence in 1916 and, as the Irish Free State, gained independence in 1922. The United Kingdom has a number of secession movements:
* In Northern Ireland, Irish republicanism, Irish republicans and Irish nationalism, nationalists have long called for the secession of Northern Ireland to join the Republic of Ireland. This is opposed by Unionism in Ireland, Unionists. A minority have supported the Ulster nationalism, independence of Northern Ireland from the United Kingdom without joining the Republic of Ireland.
* In Scotland, the Scottish National Party (SNP) campaigns for Scottish independence and direct Scottish membership in the European Union. It has representation at all levels of politics in Scotland, Scottish politics and forms the devolved Scottish government. Later pro-independence parties have had lesser electoral success. The Scottish Greens and the Scottish Socialist Party are most widely publicised. However all independence movements/parties are opposed by Unionism in Scotland, unionists. A 2014 Scottish independence referendum, referendum on independence in which voters were asked "Should Scotland be an independent country?" took place in September 2014. It saw "no" win, as 55.3% of voters voted against independence.
* In Wales, Plaid Cymru ''(Party of Wales)'' stands for Welsh independence within the European Union. It is also represented at all levels of Welsh politics and has often been the second largest party in the Senedd (Welsh Parliament).
* England:
** In Cornwall, supporters of Mebyon Kernow call for the creation of a Cornish Assembly and separation from England, giving the county significant Cornish self-government movement, self-government, whilst remaining within the United Kingdom as a fifth home nation.
** London has supporters of an independent or semi-autonomous city-state since the 2016 EU Referendum in which Londoners voted overwhelmingly to remain in the EU. A London independence party, known as Londependence, was established in June 2019. Their calls increased after the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 General Election in which most Londoners voted for the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, gaining a representative, bucking the national trend.
** The Northern Independence Party is a party formed in 2020 that seeks to make Northern England an independent state under the name Northumbria.
 On June 25, 1991, Croatia and Slovenia seceded from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia also declared independence, after which the federation broke up, causing the separation of the remaining two countries Serbia and Montenegro. Several Yugoslav Wars, wars ensued between the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and seceding entities and among other ethnic groups in Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and later, Kosovo. Montenegro peacefully separated from its union with Serbia in 2006.
2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, Kosovo unilaterally declared de facto independence from Serbia on February 17, 2008, and was recognized by several dozen countries, but officially remains under United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo, United Nations administration.
On June 25, 1991, Croatia and Slovenia seceded from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia also declared independence, after which the federation broke up, causing the separation of the remaining two countries Serbia and Montenegro. Several Yugoslav Wars, wars ensued between the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and seceding entities and among other ethnic groups in Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and later, Kosovo. Montenegro peacefully separated from its union with Serbia in 2006.
2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, Kosovo unilaterally declared de facto independence from Serbia on February 17, 2008, and was recognized by several dozen countries, but officially remains under United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo, United Nations administration.
Reinventing Collapse
', New Society Books, 2008, * Pascalev, Mario, "Territory: An Account of the Territorial Authority of States"
Bowling Green State University, VDM, 2009. * Roeder, Philip G. 2018. National secession: persuasion and violence in independence campaigns. Cornell University Press. * Sorens, Jason, ''Secessionism: Identity, Interest, and Strategy'', McGill-Queen's University Press, 2012. * * Spencer, Metta, ''Separatism: Democracy and Disintegration'', Rowman & Littlefield, 1998. * Weller, Marc, ''Autonomy, Self Governance and Conflict Resolution (Kindle Edition)'', Taylor & Francis, 2007. * Wellman, Christopher Heath, ''A Theory of Secession'', Cambridge University Press, 2005. * ''Secession And International Law: Conflict Avoidanceregional Appraisals'',
Secession (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
* {{Authority control Secession, International law Separatism Sovereignty Changes in political power Partition (politics)
political entity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics
The Republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or the Union Republics ( rus, Сою́зные Респу́блики, r=Soyúznye Respúbliki) were national-based administrative units of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( ...
leaving the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
after its dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
leaving Mexico during the Texas Revolution, Biafra
Biafra, officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised secessionist state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the predominantly Igbo-populated form ...
leaving Nigeria and returning after losing the Nigerian Civil War
The Nigerian Civil War (6 July 1967 – 15 January 1970), also known as the Nigerian–Biafran War or the Biafran War, was a civil war fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state which had declared its independence f ...
, and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
leaving the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. Threats of secession can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.Allen Buchanan
Allen Edward Buchanan is a moral, political and legal philosopher. As of 2022, he held multiple academic positions: Laureate Professor of Philosophy at the University of Arizona, Distinguished Research Fellow at Oxford University, Visiting Profes ...
"Secession"
Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') combines an online encyclopedia of philosophy with peer-reviewed publication of original papers in philosophy, freely accessible to Internet users. It is maintained by Stanford University. Eac ...
, 2007. It is, therefore, a process, which commences once a group proclaims the act of secession (e.g. declaration of independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
). A secession attempt might be violent or peaceful, but the goal is the creation of a new state or entity independent from the group or territory it seceded from.
Secession theory
There is a great deal of theorizing about secession so that it is difficult to identify a consensus regarding its definition. There is also a claim that this subject has been neglected bypolitical philosophers
This is a list of notable political philosophers, including some who may be better known for their work in other areas of philosophy. The entries are in order by year of birth to show rough direction of influences and of development of political ...
and that by the 1980swhen it finally generated interestthe discourse concentrated on the moral justifications of the unilateral right to secession. It was only in the early 1990s when American philosopher Allen Buchanan
Allen Edward Buchanan is a moral, political and legal philosopher. As of 2022, he held multiple academic positions: Laureate Professor of Philosophy at the University of Arizona, Distinguished Research Fellow at Oxford University, Visiting Profes ...
offered the first systematic account of the subject and contributed to the normative
Normative generally means relating to an evaluative standard. Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good, desirable, or permissible, and others as bad, undesirable, or impermissible. A norm in ...
classification of the literature on secession. In his 1991 book ''Secession: The Morality of Political Divorce From Fort Sumter to Lithuania and Quebec'', Buchanan outlined limited rights to secession under certain circumstances, mostly related to oppression by people of other ethnic or racial groups, and especially those previously conquered by other people.Allen Buchanan, ''Secession: The Morality of Political Divorce From Fort Sumter to Lithuania and Quebec'', West View Press, 1991. In his collection of essays from secession scholars, ''Secession, State, and Liberty'', professor David Gordon challenges Buchanan, pointing out that the moral status of the seceding state is unrelated to the issue of secession itself.
According to the 2017 book ''Secession and Security'' by George Mason political scientist Ahsan Butt, states respond violently to secessionist movements if the potential state would pose a greater threat than a violent secessionist movement would. States perceive future war as likely with a potentially new state if the ethnic group driving the secessionist struggle has deep identity division with the central state, and if the regional neighbourhood is violent and unstable.
Justifications for secession
Some theories of secession emphasize a general right of secession for any reason ("Choice Theory") while others emphasize that secession should be considered only to rectify grave injustices ("Just Cause Theory"). Some theories do both. A list of justifications may be presented supporting the right to secede, as described by Allen Buchanan, Robert McGee,Anthony Birch
Anthony Harold Birch (17 February 1924 – 13 December 2014) was a British scholar and an expert in British politics and comparative politics. He was a leading figure in the development of Britain's distinctive school of political science. Politi ...
, Jane Jacobs
Jane Jacobs (''née'' Butzner; 4 May 1916 – 25 April 2006) was an American-Canadian journalist, author, theorist, and activist who influenced urban studies, sociology, and economics. Her book '' The Death and Life of Great American Cities ...
, Frances Kendall
Frances is a French and English given name of Latin origin. In Latin the meaning of the name Frances is 'from France' or 'free one.' The male version of the name in English is Francis. The original Franciscus, meaning "Frenchman", comes from the F ...
and Leon Louw
Leon Louw is a South African intellectual, author, speaker and policy advisor. He is the executive director and cofounder of the Free Market Foundation, a nonprofit organisation ranked at number 123 in a CEOWorld's 2017 list of the most influen ...
, Leopold Kohr
Leopold Kohr (1909–1994) was an economist, jurist and political scientist known both for his opposition to the "cult of bigness" in social organization and as one of those who inspired the ''Small Is Beautiful'' movement. For almost twenty years, ...
, Kirkpatrick Sale
Kirkpatrick Sale (born June 27, 1937) is an American author who has written prolifically about political decentralism, environmentalism, luddism and technology. He has been described as having a "philosophy unified by decentralism" and as being " ...
, Donald W. Livingston and various authors in David Gordon's "Secession, State and Liberty", includes:
* United States President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
James Buchanan
James Buchanan Jr. ( ; April 23, 1791June 1, 1868) was an American lawyer, diplomat and politician who served as the 15th president of the United States from 1857 to 1861. He previously served as secretary of state from 1845 to 1849 and repr ...
, Fourth Annual Message to Congress on the State of the Union December 3, 1860: "The fact is that our Union rests upon public opinion, and can never be cemented by the blood of its citizens shed in civil war. If it can not live in the affections of the people, it must one day perish. Congress possesses many means of preserving it by conciliation, but the sword was not placed in their hand to preserve it by force."
* Former President Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
, in a letter to William H. Crawford
William Harris Crawford (February 24, 1772 – September 15, 1834) was an American politician and judge during the early 19th century. He served as US Secretary of War and US Secretary of the Treasury before he ran for US president in the 1824 ...
, Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
under President James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
, on June 20, 1816: "In your letter to Fisk, you have fairly stated the alternatives between which we are to choose: 1, licentious commerce and gambling speculations for a few, with eternal war for the many; or, 2, restricted commerce, peace, and steady occupations for all. If any State in the Union will declare that it prefers separation with the first alternative, to a continuance in union without it, I have no hesitation in saying, 'let us separate.' I would rather the States should withdraw, which are for unlimited commerce and war, and confederate with those alone which are for peace and agriculture."
* Economic enfranchisement of an economically oppressed class that is regionally concentrated within the scope of a larger national territory.
* The right to liberty
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases, or a right or immunity enjoyed by prescription or by grant (i.e. privilege). It is a synonym for the word freedom.
In modern politics, liberty is understood as the state of being free within society fr ...
, freedom of association
Freedom of association encompasses both an individual's right to join or leave groups voluntarily, the right of the group to take collective action to pursue the interests of its members, and the right of an association to accept or decline membe ...
and private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
* Consent as important democratic principle; will of majority to secede should be recognized
* Making it easier for states to join with others in an experimental union
* Dissolving such union when goals for which it was constituted are not achieved
* Self-defense
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of force in ...
when larger group presents lethal threat to minority or the government cannot adequately defend an area
* Self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
of peoples
* Preserving culture, language, etc. from assimilation or destruction by a larger or more powerful group
* Furthering diversity by allowing diverse cultures to keep their identity
Identity may refer to:
* Identity document
* Identity (philosophy)
* Identity (social science)
* Identity (mathematics)
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Identity'' (1987 film), an Iranian film
* ''Identity'' (2003 film), ...
* Rectifying past injustices, especially past conquest by a larger power
* Escaping "discriminatory redistribution", i.e., tax schemes, regulatory policies, economic programs, etc. that distribute resources away to another area, especially in an undemocratic fashion
* Enhanced efficiency when the state or empire becomes too large to administer efficiently
* Preserving "liberal purity" (or " conservative purity ") by allowing less (or more) liberal regions to secede
* Providing superior constitutional systems which allow flexibility of secession
* Keeping political entities small and human scale
Human scale is the set of physical qualities, and quantities of information, characterizing the human body, its motor, sensory, or mental capabilities, and human social institutions.
Science vs. human scale
Many of the objects of scientific in ...
through right to secession
Aleksander Pavkovic, associate professor at the Department of Politics and International Studies at Macquarie University
Macquarie University ( ) is a public research university based in Sydney, Australia, in the suburb of Macquarie Park. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the metropolitan area of S ...
in Australia and the author of several books on secession describes five justifications for a general right of secession within liberal political theory:Aleksandar PavkovicSecession, Majority Rule and Equal Rights: a Few Questions
Macquarie University
Macquarie University ( ) is a public research university based in Sydney, Australia, in the suburb of Macquarie Park. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the metropolitan area of S ...
Law Journal, 2003.
* Anarcho-Capitalism
Anarcho-capitalism (or, colloquially, ancap) is an anti-statist, libertarian, and anti-political philosophy and economic theory that seeks to abolish centralized states in favor of stateless societies with systems of private property enforce ...
: individual liberty to form political associations and private property rights together justify right to secede and to create a "viable political order" with like-minded individuals.
* Democratic Secessionism: the right of secession, as a variant of the right of self-determination, is vested in a "territorial community" which wishes to secede from "their existing political community"; the group wishing to secede then proceeds to delimit "its" territory by the majority.
* Communitarian Secessionism: any group with a particular "participation-enhancing" identity, concentrated in a particular territory, which desires to improve its members' political participation has a ''prima facie
''Prima facie'' (; ) is a Latin expression meaning ''at first sight'' or ''based on first impression''. The literal translation would be 'at first face' or 'at first appearance', from the feminine forms of ''primus'' ('first') and ''facies'' (' ...
'' right to secede.
* Cultural Secessionism: any group which was previously in a minority has a right to protect and develop its own culture and distinct national identity through seceding into an independent state.
* The Secessionism of Threatened Cultures: if a minority culture is threatened within a state that has a majority culture, the minority needs a right to form a state of its own which would protect its culture.
Types of secession
federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
or confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
(political entities with substantial reserved powers which have agreed to join together) versus secession from a unitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only th ...
(a state governed as a single unit with few powers reserved to sub-units)
* Colonial wars of independence from an imperial state
An Imperial State or Imperial Estate ( la, Status Imperii; german: Reichsstand, plural: ') was a part of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise si ...
* Recursive secession, such as India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
seceding from the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, then Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
seceding from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, or Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
seceding from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, then South Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated populat ...
seceding from Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
.
* National (seceding entirely from the national state) versus local (seceding from one entity of the national state into another entity of the same state)
* Central or enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
(seceding entity is completely surrounded by the original state) versus peripheral (along a border of the original state)
* Secession by contiguous units versus secession by non-contiguous units (exclaves
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
)
* Separation or partition
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
(although an entity secedes, the rest of the state retains its structure) versus dissolution (all political entities dissolve their ties and create several new states)
* Irredentism
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
where secession is sought in order to annex the territory to another state because of common ethnicity or prior historical links
* Minority (a minority of the population or territory secedes) versus majority (a majority of the population or territory secedes)
* Secession of better off regions versus secession of worse off regions
* The threat of secession is sometimes used as a strategy to gain greater autonomy within the original state
Arguments against secession
Allen Buchanan, who supports secession under limited circumstances, lists arguments that might be used against secession: * "Protecting Legitimate Expectations" of those who now occupy territory claimed by secessionists, even in cases where that land was stolen * "Self Defense" if losing part of the state would make it difficult to defend the rest of it * "Protecting Majority Rule" and the principle that minorities must abide by them * "Minimization of Strategic Bargaining" by making it difficult to secede, such as by imposing an exit tax * "Soft Paternalism" because secession will be bad for secessionists or others * "Threat of Anarchy" because smaller and smaller entities may choose to secede until there is chaos, although this is not the true meaning of the political and philosophical concept * "Preventing Wrongful Taking" such as the state's previous investment in infrastructure * "Distributive Justice" arguments that wealthier areas cannot secede from poorer onesExplanations for the 20th century increase in secessionism
According to University of California, Santa Barbara, political scientist Bridget L. Coggins, there are four potential explanations in the academic literature for the drastic increase in state birth during the 20th century: * Ethnonational mobilization – Ethnic minorities have been increasingly mobilized to pursue states of their own. * Institutional empowerment – The growing inability of empires and ethnic federations to maintain colonies and member states. * Relative strength – Increasingly powerful secessionist movements are more likely to achieve statehood. * Negotiated consent – Home states and the international community increasingly consent to secessionist demands. Other scholars have linked secession to resource discoveries and extraction. David B. Carter, H. E. Goemans and Ryan Griffiths find that border changes among states tend to conform to borders for previous administrative units. Several scholars have argued that changes in the international system have made it easier to survive and prosper as a small state.Tanisha Fazal
Tanisha Fazal is an American political scientist. She is Professor of Political Science at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, where she joined the faculty in 2017. She was previously a professor at the University of Notre Dame and Columbia U ...
and Ryan Griffiths link increased numbers of secessions to an international system that is more favorable for new states. For example, new states can obtain assistance from international organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster globa ...
, World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
. Alberto Alesina
Alberto Francesco Alesina (29 April 1957 – 23 May 2020) was an Italian political economics, political economist. Described as one of the leading political economists of his generation, he published many influential works in both the economics a ...
and Enrico Spolaore argue that greater levels of free trade and peace have reduced the benefits of being part of a larger state, thus motivating nations within larger states to seek secession.
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
's proclamations on self-determination in 1918 created a surge in secessionist demands.
Rights to secession
Mostsovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
s do not recognize the right to self-determination through secession in their constitutions. Many expressly forbid it. However, there are several existing models of self-determination through greater autonomy and through secession.Andrei KreptulThe Constitutional Right of Secession in Political Theory and History
Journal of Libertarian Studies
Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a libertarian nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, United States. It is named after the Austrian School economist Ludwig von Mises (1881–1973).
It wa ...
, Ludwig von Mises Institute
Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a libertarian nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, United States. It is named after the Austrian School economist Ludwig von Mises (1881–1973).
It wa ...
, Volume 17, no.4 (Fall 2003), pp. 39–100.
In liberal constitutional democracies the principle of majority rule
Majority rule is a principle that means the decision-making power belongs to the group that has the most members. In politics, majority rule requires the deciding vote to have majority, that is, more than half the votes. It is the binary deci ...
has dictated whether a minority can secede. In the United States Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
acknowledged that secession might be possible through amending the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
. The Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
in ''Texas v. White
''Texas v. White'', 74 U.S. (7 Wall.) 700 (1869), was a case argued before the United States Supreme Court in 1869. The case involved a claim by the Reconstruction government of Texas that United States bonds owned by Texas since 1850 had been ill ...
'' held secession could occur "through revolution, or through consent of the States".Aleksandar Pavković, Peter RadanCreating New States: Theory and Practice of Secession
p. 222, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2007.
74 U.S. 700 (1868) at
Cornell University Law School
Cornell Law School is the law school of Cornell University, a private Ivy League university in Ithaca, New York. One of the five Ivy League law schools, it offers four law degree programs, JD, LLM, MSLS and JSD, along with several dual-degr ...
Supreme Court collection. The British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy ...
in 1933 held that Western Australia could secede from the Commonwealth of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
only upon vote of a majority of the country as a whole; the previous two-thirds majority vote for secession via referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
was insufficient.Aleksandar Pavkovic and Peter RadanIn Pursuit of Sovereignty and Self-determination: Peoples, States and Secession in the International Order
Macquarie University
Macquarie University ( ) is a public research university based in Sydney, Australia, in the suburb of Macquarie Park. Founded in 1964 by the New South Wales Government, it was the third university to be established in the metropolitan area of S ...
Law Journal, 1, 2003.Chinese Communist Party
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victoriou ...
followed the Soviet Union in including the right of secession in its 1931 constitution in order to entice ethnic nationalities and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
into joining. However, the Party eliminated the right to secession in later years, and had anti-secession clause written into the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
before and after the founding the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. The 1947 Constitution of the Union of Burma
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
contained an express state right to secede from the union under a number of procedural conditions. It was eliminated in the 1974 constitution of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma
, conventional_long_name = Union of Burma Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma
, common_name = Burma
, status =
, status_text =
, p1 = Post-independence Burma, 1948–1962Uni ...
(officially the "Union of Myanmar
The State Peace and Development Council ( my, နိုင်ငံတော် အေးချမ်းသာယာရေး နှင့် ဖွံ့ဖြိုးရေး ကောင်စီ ; abbreviated SPDC or , ) was the offi ...
"). Burma still allows "local autonomy under central leadership".
As of 1996, the constitutions of Austria, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain of ...
have express or implied rights to secession. Switzerland allows for the secession from current and the creation of new cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, t ...
. In the case of proposed Quebec separation from Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the Supreme Court of Canada
The Supreme Court of Canada (SCC; french: Cour suprême du Canada, CSC) is the Supreme court, highest court in the Court system of Canada, judicial system of Canada. It comprises List of Justices of the Supreme Court of Canada, nine justices, wh ...
in 1998 ruled that only both a clear majority of the province and a constitutional amendment confirmed by all participants in the Canadian federation could allow secession.
The 2003 draft of the European Union Constitution allowed for the voluntary withdrawal of member states from the union, although the representatives of the member-state which wanted to leave could not participate in the withdrawal discussions of the European Council or of the Council of Ministers. There was much discussion about such self-determination by minorities before the final document underwent the unsuccessful ratification process in 2005. Although in 2007 the Treaty on European Union
The Treaty on European Union (2007) is one of the primary Treaties of the European Union, alongside the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU). The TEU form the basis of EU law, by setting out general principles of the EU's pu ...
included Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union
Withdrawal from the European Union is the legal and political process whereby an EU member state ceases to be a member of the Union. Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union ( TEU) states that "Any Member State may decide to withdraw from t ...
, the right to withdraw from the EU, which has been the case with Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or ...
.
As a result of the successful constitutional referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
held in 2003, every municipality in the Principality of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
has the right to secede from the Principality by a vote of a majority of the citizens residing in this municipality.
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
have a range of different forms of indigenous sovereignty
Indigenous rights are those rights that exist in recognition of the specific condition of the Indigenous peoples. This includes not only the most basic human rights of physical survival and integrity, but also the rights over their land (includ ...
and have the right of self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
, but under current understanding of international law they have a mere "remedial" right to secession in extreme cases of abuse of their rights, because independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
and sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
hood is a territorial and diplomatic claim and not one of self-determination and self-government
__NOTOC__
Self-governance, self-government, or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of ...
respectively, generally leaving rights to secession to the internal legislation of sovereign states.
Secession movements
:' National secessionist movements advocate for the claim that a population within a state is a nation that has the right to form its own nation-state. Movements that work towards political secession may describe themselves as beingautonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
, separatist
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seeking greate ...
, independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
, self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
, partition
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of a ...
, devolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories h ...
, decentralization
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those regarding planning and decision making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group.
Conce ...
, sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
, self-governance
__NOTOC__
Self-governance, self-government, or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of ...
or decolonization
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
movements instead of, or in addition to, being secession movements.
Countries which separated from a colonial empire but which were never an integral part of the colonial state are not included in the list below; instead see Decolonization
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
and Unilateral declaration of independence
A unilateral declaration of independence (UDI) is a formal process leading to the establishment of a new state by a subnational entity which declares itself independent and sovereign without a formal agreement with the state which it is secedi ...
.
Australia
During the 19th century, the singleBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
colony
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the ''metropole, metropolit ...
in eastern mainland Australia, New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
(NSW) was progressively divided up by the British government as new settlements were formed and spread. Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
(Vic) in 1851 and Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
(Qld) in 1859.
However, settlers agitated to divide the colonies throughout the later part of the century; particularly in central Queensland
Central Queensland is an ambiguous geographical division of Queensland ( a state in Australia) that centres on the eastern coast, around the Tropic of Capricorn. Its major regional centre is Rockhampton. The region extends from the Capricorn Coas ...
(centred in Rockhampton
Rockhampton is a city in the Rockhampton Region of Central Queensland, Australia. The population of Rockhampton in June 2021 was 79,967, Estimated resident population, 30 June 2018. making it the fourth-largest city in the state outside of the ...
) in the 1860s and 1890s, and in North Queensland
North Queensland or the Northern Region is the northern part of the Australian state of Queensland that lies just south of Far North Queensland. Queensland is a massive state, larger than many countries, and its tropical northern part has been ...
(with Bowen Bowen may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Bowen, Queensland, a town
* Bowen Hills, Queensland, a suburb
** Bowen Hills railway station, a railway station in Bowen Hills
** Bowen Park, Brisbane, a park in Bowen Hills
* Bowen Bridge, crossing the Derw ...
as a potential colonial capital) in the 1870s. Other secession (or territorial separation) movements arose and these advocated the secession of New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
in northern central New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Deniliquin
Deniliquin () is a town in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia, close to the border with Victoria. It is the largest town in the Edward River Council local government area.
Deniliquin is located at the intersection of the Riverina ...
in the Riverina
The Riverina
is an agricultural region of south-western New South Wales, Australia. The Riverina is distinguished from other Australian regions by the combination of flat plains, warm to hot climate and an ample supply of water for irrigation ...
district also in NSW, and Mount Gambier
Mount Gambier is the second most populated city in South Australia, with an estimated urban population of 33,233 . The city is located on the slopes of Mount Gambier, a volcano in the south east of the state, about south-east of the capital Ad ...
in the eastern part of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
.
;Western Australia
Secession movements have surfaced several times in Western Australia (WA), where a 1933 referendum for secession from the Federation of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, South Australia (which also governed what is now the Northern Territory), and Western A ...
passed with a two-thirds majority. The referendum had to be ratified by the British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy ...
, which declined to act, on the grounds that it would contravene the Australian Constitution
The Constitution of Australia (or Australian Constitution) is a constitutional document that is supreme law in Australia. It establishes Australia as a federation under a constitutional monarchy and outlines the structure and powers of the ...
.
* The Principality of Hutt River
The Principality of Hutt River, often referred to by its former name, the Hutt River Province, was a micronation in Australia. The principality claimed to be an independent sovereign state, founded on 21 April 1970. It was dissolved on 3 Augus ...
claimed to have seceded from Australia in 1970, although its status was not recognised by Australia or any other country.
Austria
After being liberated by theRed Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
and the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
seceded from Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
on April 27, 1945. This took place after seven years under Nazi rule, which began with the annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in March 1938. The secession only took place once Nazi Germany had been defeated by the Allies.
Bangladesh
The Banga Sena (Bengal Army) is a separatistHindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
organisation, which supports the making of a Bangabhumi
Bangabhumi ( bn, বঙ্গভূমি, meaning the land of Vanga, also spelt Bongobhumi) also known as Bir Bongo ( bn, বীর বঙ্গ), is a separatist movement to create a Bengali Hindu country for Bangladeshi Hindus in southwestern ...
/separate homeland for Bengali Hindus
Bengali Hindus ( bn, বাঙ্গালী হিন্দু/বাঙালি হিন্দু, translit=Bāṅgālī Hindu/Bāṅāli Hindu) are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Benga ...
in the People's Republic of Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ...
. The group is led by Kalidas Baidya.
The Shanti Bahini ( bn, শান্তি বাহিনী, "Peace Force") is the name of the military wing of the Parbatya Chattagram Jana Sanghati Samiti
The Parbatya Chattagram Jana Samhati Samiti ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম জনসংহতি সমিতি; ''United People's Party of the Chittagong Hill Tracts''; abbreviated PCJSS) is a political party form ...
- the United People's Party of the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম, Parbotto Chottogram), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, are group of districts within the Chittagong Division in southeast ...
aims are to create an indigenous Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
orientated Chacomas state within SE Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
.
Belgium and the Netherlands
On August 25, 1830, during the reign ofWilliam I
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087 ...
, the nationalistic opera ''La muette de Portici
''La muette de Portici'' (''The Mute Girl of Portici'', or ''The Dumb Girl of Portici''), also called ''Masaniello'' () in some versions, is an opera in five acts by Daniel Auber, with a libretto by Germain Delavigne, revised by Eugène Scribe.
...
'' was performed in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
. Soon after, the Belgian Revolt occurred, which resulted in the Belgian secession from the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
.
Brazil
In 1825, soon after theEmpire of Brazil
The Empire of Brazil was a 19th-century state that broadly comprised the territories which form modern Brazil and (until 1828) Uruguay. Its government was a representative parliamentary constitutional monarchy under the rule of Emperors Dom Pe ...
managed to defeat the Cortes-Gerais and the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the l ...
in an Independence War, the Platinean nationalists in Cisplatina
Cisplatina () was a Brazilian province in existence from 1821 to 1828 created by the Luso-Brazilian invasion of the Banda Oriental. From 1815 until 1822 Brazil was a constituent kingdom of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarv ...
declared independence and joined the United Provinces, which led to a stagnated war between both, as they were both weakened, without manpower and fragile politically. The peace treaty accepted Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
's independence, reasserted the rule of both nations over their land and some important points like free navigation in the Silver River.
Three rather disorganized secessionist rebellions happened in Grão-Pará, Bahia and Maranhão, where the people were unhappy with the Empire (these provinces were Portuguese bastions in the Independence War). The Malê Revolt
Male, in biology, is the half of a sex system that produces sperm cells.
* Male plant, a plant that gives rise to male gametophytes
Male may also refer to:
Gender
* Male, the gender of men and boys
** Man, a male adult
** Boy, a young male person ...
, in Bahia, was an Islamic slave revolt. These three rebellions were bloodily crushed by the Empire of Brazil.
The Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the 19 ...
was one of the most nativist of all Brazilian regions, which in five revolts (1645–1654, 1710, 1817, 1824, 1848), the province ousted the Dutch West India Company, tried to secede from the Portuguese Empire and from the Brazilian Empire. In the attempts the rebels were crushed, the leaders shot and its territory divided, nevertheless they kept revolting until its territory was a little fraction of what it was before.
In the Ragamuffin War
The Ragamuffin War (Portuguese: ''Guerra dos Farrapos'' or ''Revolução Farroupilha'') was a Republican uprising that began in southern Brazil, in the province (current state) of Rio Grande do Sul in 1835. The rebels were led by generals Bento ...
, the Province of Rio Grande do Sul was undergoing a (at that time common) liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
vs conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization i ...
"cold" war. After Emperor Pedro II of Brazil
Don (honorific), Dom PedroII (2 December 1825 – 5 December 1891), nicknamed "the Magnanimity, Magnanimous" ( pt, O Magnânimo), was the List of monarchs of Brazil, second and last monarch of the Empire of Brazil, reigning for over 58 years. ...
favoured the conservatives, the liberals took the Capital and declared an independent Republic, fighting their way to the Province of Santa Catarina, declaring the Juliana Republic
The Juliana Republic (Portuguese: ''República Juliana'') or Catarinense Republic (''República Catarinense''), officially the Free and Independent Catharinense Republic (''República Catharinense Livre e Independente''), was a revolutionary st ...
. Eventually they were slowly forced back, and made a reunification peace with the Empire. The war was not a secessionist war, even if it could become if the Empire were defeated, after the Empire agreed to aid its economy by taxing Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
's products (like dry meat), the rebels reunited with the Empire and even filled its ranks, as the rebels were very good fighters.
In modern times, the South Region of Brazil
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
has been the centre of a secessionist movement led by an organization called The South is My Country since the 1990s. Reasons cited for South Region Brazil's secession are taxation due to it being one of the wealthiest regions in the country and political disputes with the northernmost states of Brazil as well as the recent scandal revolving around the Workers Party found to be making shady deals with state-owned oil company Petrobras
Petróleo Brasileiro S.A., better known by the portmanteau Petrobras (), is a state owned enterprise, state-owned Brazilian multinational corporation in the petroleum industry headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The company's name transla ...
and the impeachment of then-President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
Dilma Rousseff
Dilma Vana Rousseff (; born 14 December 1947) is a Brazilian economist and politician who served as the 36th president of Brazil, holding the position from 2011 until her impeachment and removal from office on 31 August 2016. She is the first w ...
additionally there is also an ethnic divide as the South Region is predominately European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
populated primarily by Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and other European countries in contrast to the rest of Brazil which is a multicultural melting pot "Racial Democracy
Racial democracy ( pt, Democracia racial) is a term used by some to describe race relations in Brazil. The term denotes some scholars' belief that Brazil has escaped racism and racial discrimination. Those researchers contend that Brazilians do ...
". The South Region in 2016 voted in an unofficial referendum called "Plebisul" in which 616,917 (or half a million) voters overwhelmingly supported secession and the creation of an independent South Region by 95%. Another Brazilian secession movement is based in the state of Sao Paulo
SAO or Sao may refer to:
Places
* Sao civilisation, in Middle Africa from 6th century BC to 16th century AD
* Sao, a town in Boussé Department, Burkina Faso
* Saco Transportation Center (station code SAO), a train station in Saco, Maine, U.S ...
which seeks to create to make the state an independent country from the rest of Brazil.
Cameroon
In October 2017,Ambazonia
Ambazonia, officially the Federal Republic of Ambazonia, also referred to as Amba Land, is an unrecognised breakaway state in West Africa which claims the Northwest Region and Southwest Region of Cameroon, though it currently controls almost ...
declared its independence from Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
. Less than a month beforehand, tensions had escalated into open warfare between separatists and the Cameroon Armed Forces
The Cameroon Armed Forces (french: Forces armées camerounaises (FAC)) are the military of the Republic of Cameroon. The armed forces number 40,000 personnel in ground, air, and naval forces. There are approximately 40,000 troops in the army acr ...
.
The conflict, known as the "Anglophone Crisis", is deeply rooted in the October 1, 1961 incomplete decolonization of the former British Southern Cameroons (UNGA Resolution 1608). On January 1, 1960, French Cameroon
French Cameroon or French Cameroons (french: link=no, Cameroun) was a French mandate territory in Central Africa. It now forms part of the independent country of Cameroon.
History Beginnings
The area of present-day Cameroon came under Germ ...
was granted independence from France as the Republic of Cameroon and was admitted into the United Nations. The more advanced democratic and self-ruling people of British Cameroon
British Cameroon or the British Cameroons was a British mandate territory in British West Africa, formed of the Northern Cameroons and Southern Cameroons. Today, the Northern Cameroons forms parts of the Borno, Adamawa and Taraba states of N ...
were instead limited to two choices. Through a UN plebiscite, they were directed to either join the federation of Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
or the independent Republic of Cameroon as a federation of two equal states. While the Northern Cameroons voted to join Nigeria, the Southern Cameroons voted to integrate into the Republic of Cameroon, but they did so without a formal UN Treaty of Union on record at the UN. In 1972, Cameroon used its majority population to abolish the federation and implement a system which resulted in the occupation of the former South Cameroons territory by French-speaking Cameroon administrators. To make matters worse in 1984, Cameroon returned to its name at independence "Republic of Cameroun" which did not include the territory of the former British Southern Cameroons or Ambazonia.
For more than fifty years the English-speaking people of the Former British Southern Cameroons made multiple attempts both nationally and internationally to get the Cameroon government to address these issue and possibly return to the previously agreed federation at independence. When all these attempts failed in 2016 and Cameroon engaged in a military crackdown including cutting the internet in the English-speaking regions, the people of Southern Cameroons declared on October 1, 2017, the restoration of their UN state of Southern Cameroons, which they called the "Federal Republic of Ambazonia".
Canada
Throughout Canada's history, there has been tension betweenEnglish-speaking
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language ...
and French-speaking Canadians. Under the Constitutional Act of 1791
The Clergy Endowments (Canada) Act 1791, commonly known as the Constitutional Act 1791 (), was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain which passed under George III. The current short title has been in use since 1896.
History
The act refor ...
, the Province of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen p ...
(including parts of what are today Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
and Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
) was divided in two: Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec an ...
(which retained French law
The Law of France refers to the legal system in the French Republic, which is a civil law legal system primarily based on legal codes and statutes, with case law also playing an important role. The most influential of the French legal codes is ...
and institutions and is now part of the provinces of Quebec and Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
) and Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the ...
(a new colony intended to accommodate the many new English-speaking settlers, including the United Empire Loyalists
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America duri ...
, and now part of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
). The intent was to provide each group with its own colony. In 1841, the two Canadas were merged into the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British North America, British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham ...
. The union proved contentious, however, resulting in a legislative deadlock between English and French legislators. The difficulties of the union led (amongst other factors) in 1867 to Confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
, the adoption of a federal system
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments ( provincial, state, cantonal, territorial, or other sub-unit governments) in a single po ...
that united the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British North America, British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
(later joined by other British colonies in North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
). The federal framework did not eliminate all tensions, however, leading to the Quebec sovereignty movement
The Quebec sovereignty movement (french: Mouvement souverainiste du Québec) is a political movement whose objective is to achieve the sovereignty of Quebec, a province of Canada since 1867, including in all matters related to any provision of ...
in the latter half of the 20th century.
Other occasional secessionist movements have included anti-Confederation movements in 19th century Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (french: provinces de l'Atlantique), is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec. The four provinces are New Brunswick, Newfoundlan ...
(see Anti-Confederation Party
''Anti-Confederation'' was the name used in what is now the Maritimes by several parties opposed to Canadian Confederation. The Anti-Confederation parties were accordingly opposed by the Confederation Party, that is, the Conservative and Liberal- ...
), the North-West Rebellion
The North-West Rebellion (french: Rébellion du Nord-Ouest), also known as the North-West Resistance, was a resistance by the Métis people under Louis Riel and an associated uprising by First Nations Cree and Assiniboine of the District of S ...
of 1885, and various small separatism movements in Alberta particularly (see Alberta separatism
Alberta separatism comprises a series of 20th- and 21st-century movements (both historic and current) advocating the secession of the province of Alberta from Canada, by joining the United States of America. The main issues driving separatist ...
) and Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada� ...
generally (see, for example, Western Canada Concept
The Western Canada Concept was a Western Canada, Western Canadian federal political party founded in 1980 to promote the separation of the provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, and the Yukon and Northwest Territories ...
).
Central America
After the 1823 collapse of theFirst Mexican Empire
The Mexican Empire ( es, Imperio Mexicano, ) was a constitutional monarchy, the first independent government of Mexico and the only former colony of the Spanish Empire to establish a monarchy after independence. It is one of the few modern-era, ...
, the former Captaincy-General of Guatemala was organized into a new Federal Republic of Central America
The Federal Republic of Central America ( es, República Federal de Centroamérica), originally named the United Provinces of Central America ( es, Provincias Unidas del Centro de América), and sometimes simply called Central America, in it ...
. In 1838 Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the cou ...
seceded. The Federal Republic was formally dissolved in 1840, all but one of the states having seceded amidst general disorder.
China
* The ''Anti-Secession Law
The Anti-Secession Law () is a law of the China, People's Republic of China, passed by the 3rd Session of the 10th National People's Congress. It was ratified on March 14, 2005, and went into effect immediately. President of the People's R ...
'' against the Taiwan independence movement
The Taiwan independence movement is a political movement which advocates the formal declaration of an independent and sovereign Taiwanese state, as opposed to Chinese unification or the status quo in Cross-Strait relations.
Currently, Tai ...
* Western regions of Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
(East Turkistan
East Turkestan ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان, Sherqiy Türkistan, bold=no; zh, s=东突厥斯坦; also spelled East Turkistan), is a loosely-defined geographical and historical region in the western provinces of the People's Republic of ...
) and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
are the focus of secessionist calls by the Tibetan independence movement
The Tibetan Independence Movement () is the political movement advocating for the separation and independence of Tibet from the People's Republic of China. It is principally led by the Tibetan diaspora in countries like India and the United Stat ...
and East Turkestan Independence Movement
The East Turkestan independence movement ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان مۇستەقىللىق ھەرىكىتى; zh, s=东突厥斯坦独立运动) is a political movement that seeks the independence of East Turkestan, a large and spa ...
.
* The Special Administrative Region of Hong Kong has a secessionist movement in the city that the Chinese Communist Party has placed on national security agenda in 2017 which is called the Hong Kong independence movement
Hong Kong independence is a political movement that advocates the establishment of Hong Kong as an independent sovereign state. Hong Kong is one of two Special administrative regions of China (SAR) which enjoys a certain degree of autonomy ...
.
Congo
In 1960 theState of Katanga
The State of Katanga; sw, Inchi Ya Katanga) also sometimes denoted as the Republic of Katanga, was a breakaway state that proclaimed its independence from Congo-Léopoldville on 11 July 1960 under Moise Tshombe, leader of the local ''Co ...
declared independence from the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
. United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
troops crushed it in Operation Grand Slam
Operation Grand Slam was a key military operation of the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965. It refers to a plan drawn up by the Pakistan Army in May 1965 that consisted of an attack on the vital Akhnoor Bridge in Indian-administered Jammu and Kash ...
.
Cyprus
 In 1974, Greek
In 1974, Greek irredentists
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
launched a ''coup d'état'' in Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
, in an attempt to annex the island with Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
. Almost immediately, the Turkish Army
The Turkish Land Forces ( tr, Türk Kara Kuvvetleri), or Turkish Army (Turkish: ), is the main branch of the Turkish Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. The army was formed on November 8, 1920, after the collapse of the ...
invaded northern Cyprus to protect the interests of the ethnic Turkish minority, who in the following year formed the ''Turkish Federated State of Cyprus'' and in 1983 declared independence as the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recog ...
, recognized only by Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
.
East Timor
 The
The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-weste ...
(also known as East Timor) has been described as having "seceded" from Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. After Portuguese sovereignty was terminated in 1975, East Timor was occupied by Indonesia. However the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
and the International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordanc ...
refused to recognize this incorporation. Therefore, the resulting civil war and eventual 2002 East Timorese vote for complete separation are better described as an independence movement.
Ethiopia
Following the May 1991 victory ofEritrean People's Liberation Front
The Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF), colloquially known as Shabia, was an armed Marxist–Leninist organization that fought for the independence of Eritrea from Ethiopia. It emerged in 1970 as a far-left to left-wing nationalist group ...
forces against the communist Derg
The Derg (also spelled Dergue; , ), officially the Provisional Military Administrative Council (PMAC), was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia, then including present-day Eritrea, from 1974 to 1987, when the military leadership formally " c ...
regime during the Eritrean War of Independence
The Eritrean War of Independence was a war for independence which Eritrean independence fighters waged against successive Ethiopian governments from 1 September 1961 to 24 May 1991.
Eritrea was an Italian colony from the 1880s until the d ...
, Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
(formerly known as "Medri Bahri
Medri Bahri ( ti, ምድሪ ባሕሪ, English: Land of the Sea Kingdom), also known as Mereb Melash, was an Eritrean kingdom emerged in 1137 until conquest by the Ethiopian Empire in 1879. It was situated in modern-day Eritrea, and was ruled by ...
") gained de facto independence from Ethiopia. Following the United Nations observed 1993 Eritrean independence referendum
An independence referendum was held in Eritrea, at the time part of Ethiopia, between 23 and 25 April 1993. The result was 99.83% in favour, with a 98.5% turnout. Independence from Ethiopia was declared on 27 April.
Conduct
The UN Observer Mis ...
, Eritrea gained de jure independence.
European Union
Before theTreaty of Lisbon
The Treaty of Lisbon (initially known as the Reform Treaty) is an international agreement that amends the two treaties which form the constitutional basis of the European Union (EU). The Treaty of Lisbon, which was signed by the EU member sta ...
entered into force on 1December 2009 no provision in the treaties
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal perso ...
or law of the European Union
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its valu ...
outlined the ability of a state to voluntarily withdraw from the EU. The European Constitution did propose such a provision and, after the failure to ratify the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe, that provision was then included in the Lisbon Treaty.
The treaty introduces an exit clause for members who wish to withdraw from the Union. This formalises the procedure by stating that a member state may notify the European Council that it wishes to withdraw, upon which withdrawal negotiations begin; if no other agreement is reached the treaty ceases to apply to the withdrawing state two years after such notification.
On January 31, 2020, the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union. This is informally known as Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 CET).The UK also left the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or ...
.
Finland
Finland successfully and peacefully seceded from the newly formed and unstable Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic in 1917, the latter led by Lenin who had goodwill towards the Finns due to their having helped in his revolutionary struggle. Unsuccessful attempts at greater autonomy or peaceful secession had already been made during the preceding Russian Empire but had been denied by the Russian emperor.France
France was one of the European Great Powers with populous foreign empires; like the othersthe United Kingdom, Spain, Portugal, Italy, Belgium and the Netherlands; and formerly Germany and the Ottoman Empirepopulous states abroad have all seceded, in most cases granted independence. These generally took place at similar stages by continent, see decolonization of the Ottoman Empire, Decolonization of the Americas, Americas, Decolonization of Asia, Asia and Decolonization of Africa, Africa. As to France's contiguous state, these have few present representatives at national level, see: * Alsace independence movement * Breton independence * Corsican nationalism * Occitan nationalismGran Colombia
After a decade of tumultuous federalism, Ecuador and Venezuela seceded from Gran Colombia in 1830, leaving the similarly tumultuous United States of Colombia, now the Republic of Colombia which also lost Panama in 1903.India
Pakistan seceded from the British Indian empire in what is known as Partition of India, the Partition. Today, the Constitution of India does not allow States and union territories of India, Indian states to secede from the Union. The Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Indian Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir hosts some paramilitary Kashmiri nationalism, Muslim-state-advocating nationalists, operating against the Indian establishment. They are mostly in the Kashmir Valley, Valley of Kashmir since 1989, where the Indian Army sometimes patrol, having bases along the Line of Control, nearby international border. They are supported via Pakistan which has allegedly funded many terrorist, separatist outfits for destabilising India according to the Research and Analysis Wing, Indian Research and Analysis Wing, though the country denies any direct involvement. The Insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir, Kashmir insurgency reached at its peak influence in the 1990s. Other secessionist movements in Nagaland, Assam, Manipur, Indian Punjab, Punjab (known as the Khalistan movement), Mizoram and Tripura, Tamil Nadu . The violent Naxalite–Maoist insurgency operates in East India, eastern rural India is rarely considered secessionist as its goal is to overthrow the government of India. The Communist Party of India (Maoist)'s commanders idealise a Communist state, Communist republic to be made up swathes of India.Iran
Active secession movements include: Iranian Azeri, Assyrian independence movement, Bakhtiary lurs movement in 1876, Iranian Kurdistan; Kurdistan Democratic Party of Iran, Kurdistan Democratic Party of Iran (KDPI), Khūzestān Province Balochistan and independence movement for free separated Balochistan, (''Arab nationalism, Arab nationalist''); Al-Ahwaz Arab People's Democratic Popular Front, Democratic Solidarity Party of Al-Ahwaz (See Politics of Khūzestān Province#Arab politics and separatism, Politics of Khūzestān Province: Arab politics and separatism), and Balochistan People's Party (BPP) supporting Baloch people, Baloch Baloch nationalism, Separatism.Italy
The Movement for the Independence of Sicily (Movimento Indipendentista Siciliano, MIS) has its roots in the Sicilian Independence Movement of the late 1940s; they have been around for 60 years. Today, the MIS no longer exists, though many other parties have been born. One is Nation Sicily (Sicilia Nazione), which still believes in the idea that Sicily, due to its deeply personal and ancient history, has to be a sovereign country. Moreover, a common ideology shared by all the Sicilian Independentist Movement, Sicilian independentist movements is to fight against Cosa Nostra and all the other Sicilian Mafia, Mafia organizations, that have a very deep influence over Sicily's public and private institutions. Also, the Sicilian branch of the Five Star Movement, which is according to the polls Sicily's most popular party, has publicly expressed the intention to start working for a possible secession from Italy in the case where the Government of Italy, central government would not collaborate in shifting the nation's administrative organization from a unitary country to a federal state. Lega Nord has been seeking the independence of the so-called region of Padania, which includes lands along the Po Valley in northern Italy. Some organizations separately work for the Venetian nationalism, independence of Venetia or Veneto and the South Tyrolean secessionist movement, secession or reunification of South Tyrol with Austria. Lega Nord governing Lombardy has expressed a will to turning the region into a sovereign country. Also the island of Sardinia is home to a notable Sardinian nationalism, nationalist movement. In Southern Italy several movements have expressed a will to secede from Italy. This newborn ideology is so-called neo-Bourbonic, because the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was under the control of the House of Bourbon. The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was created in 1816 after the Congress of Vienna, and it comprised both Sicily and continental Southern Italy. The Kingdom came to an end in 1861, being annexed to the newborn Kingdom of Italy. However, the patriotic feelings shared among the southern Italian population is more ancient, starting in 1130 with the Kingdom of Sicily, which was composed by both the island and south Italy. According to the neo-Bourbonic movements the Italian regions which should secede are Sicily, Calabria, Basilicata, Apulia, Molise, Campania, Abruzzo, and Latio's provinces of Province of Rieti, Rieti, Province of Latina, Latina and Province of Frosinone, Frosinone. The major movements and parties which believe in this ideology are Unione Mediterranea, Mo! and Brigandage in Southern Italy after 1861, Briganti.Japan
The ethnic Ryukyuan people, Ryukyuan (a branch of modern Okinawan) people had their own state historically (Ryukyu Kingdom). Although some Okinawan people have sought to become independent from Japan since they were annexed by Japan in 1879, and especially after 1972 when the islands were transferred from U.S. rule to Japan, their activism and movement have been consistently supported by single digit of Okinawan people.Malaysia
When racial and PAP-UMNO relations, partisan strife erupted, Singapore Singapore in Malaysia#Expulsion, was expelled from the Malaysian federation in 1965.Mexico
 * Republic of Texas, Texas seceded from Mexico in 1836 (see Texas Revolution), after animosity between the Mexican government and the American settlers of the Coahuila y Tejas, Coahuila y Tejas State. It was later annexed by the United States in 1845.
* The Republic of the Rio Grande seceded from Mexico on January 17, 1840. It rejoined Mexico on November6 the same year.
* After the Federal government, federal system was abandoned by President of Mexico, President Antonio López de Santa Anna, Santa Anna, the Congress of Yucatán approved in 1840 a declaration of independence, establishing the Republic of Yucatán. The Republic rejoined Mexico in 1843.
* Republic of Texas, Texas seceded from Mexico in 1836 (see Texas Revolution), after animosity between the Mexican government and the American settlers of the Coahuila y Tejas, Coahuila y Tejas State. It was later annexed by the United States in 1845.
* The Republic of the Rio Grande seceded from Mexico on January 17, 1840. It rejoined Mexico on November6 the same year.
* After the Federal government, federal system was abandoned by President of Mexico, President Antonio López de Santa Anna, Santa Anna, the Congress of Yucatán approved in 1840 a declaration of independence, establishing the Republic of Yucatán. The Republic rejoined Mexico in 1843.
Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to historiographically as the 'Dutch Republic', was a federal republic formally established from the formal creation of a federal state in 1581 by several Provinces of the Netherlands, Dutch provinces Dutch Revolt, seceded from Spanish Netherlands, Spain.New Zealand
Secession movements have surfaced several times in the South Island of New Zealand. A Prime Minister of New Zealand, Premier of New Zealand, Sir Julius Vogel, was amongst the first people to make this call, which was voted on by the Parliament of New Zealand as early as 1865. The desire for South Island independence was one of the main factors in moving the capital of New Zealand from Auckland to Wellington in the same year. The NZ South Island Party with a pro-South agenda, fielded only five candidates (4.20% of electoral seats) candidates in the 1999 New Zealand general election, 1999 General Election but achieved only 0.14% (2622 votes) of the general vote. The reality today is that although "South Islanders" are most proud of their geographic region, secession does not carry any real constituency; the party was not able to field any candidates in the 2008 election due to being unable to enlist 500 paying members, a requirement by the New Zealand Electoral commission. The party is treated more as a "joke" party than any real political force.Nigeria
 Between 1967 and 1970, the Eastern Region, Nigeria, Eastern Region seceded from Nigeria and established the Biafra, Republic of Biafra, which led to a Nigerian Civil War, war that ended with the state returning to Nigeria. In 1999, at the beginning of a Fourth Nigerian Republic, new democratic regime, other secessionist movements emerged, including the Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra, formed as a military wing of the Republic of Biafra.
Between 1967 and 1970, the Eastern Region, Nigeria, Eastern Region seceded from Nigeria and established the Biafra, Republic of Biafra, which led to a Nigerian Civil War, war that ended with the state returning to Nigeria. In 1999, at the beginning of a Fourth Nigerian Republic, new democratic regime, other secessionist movements emerged, including the Movement for the Actualization of the Sovereign State of Biafra, formed as a military wing of the Republic of Biafra.
Norway and Sweden
Swedish Empire, Sweden, having left the Kalmar Union with Denmark–Norway in the 16th century, entered into a loose Union between Sweden and Norway, personal union with Kingdom of Norway (1814), Norway in 1814. Following a constitutional crisis, on June 7, 1905 the Storting, Norwegian Storting declared that King Oscar II of Norway, OscarII had failed to fulfill his constitutional duties. He was therefore no longer Monarchy of Norway, King of Norway and because the union depended on the two countries sharing a king, it was thus dissolved. After negotiations Sweden agreed to this on October 26 and on April 14.Pakistan
After the Awami League won the 1970 Pakistani general election, 1970 national elections, negotiations to form a new government floundered, resulting in the Bangladesh Liberation War by which East Pakistan seceded, to becomeBangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
. The Balochistan Liberation Army (also Baloch Liberation Army or Boluchistan Liberation army) (BLA) is a Baloch nationalist militant secessionist organization. The stated goals of the organization include the establishment of an independent state of Balochistan (region), Balochistan free of Pakistani, Iranian and Afghan Federations. The name Baloch Liberation Army first became public in summer 2000, after the organization claimed credit for a series of bomb attacks in markets and removal of railways lines.
Papua New Guinea
The island of Bougainville Island, Bougainville has made several efforts to secede from Papua New Guinea.Somalia
Somaliland is an autonomous region, which is part of the Somalia, Federal Republic of Somalia. Those who call the area the ''Republic of Somaliland'' consider it to be the successor state of the former British Somaliland protectorate. Having established its own local government in Somalia in 1991, the region's self-declared independence remains Diplomatic recognition, unrecognized by any country or international organization.South Africa
In 1910, following the British Empire's defeat of the Afrikaners in the Boer Wars, four self-governing colonies in the south of Africa were merged into the Union of South Africa. The four regions were the Cape Colony, Orange Free State, Colony of Natal, Natal and Transvaal Colony, Transvaal. Three other territories, High Commissioner for Southern Africa, High Commission Territories of Bechuanaland (now Botswana), Basutoland (now Lesotho) and Swaziland (now Eswatini) later became independent states in the 1960s. Following the election of the National Party (South Africa), Nationalist government in 1948, some English language, English-speaking whites in Natal advocated either secession or a loose federation. There were also calls for secession, with Natal and the eastern part of the Cape Province breaking away. following the 1960 South African republic referendum, referendum in 1960 on establishing a republic, and in 1993, prior to South Africa's first elections under universal suffrage and the end of apartheid, some Zulu people, Zulu leaders in KwaZulu-Natal considered secession as did some politicians in the Cape Province. In 2008, a political movement calling for the return to independence of the Cape resurged in the shape of the political organisation, the Cape Party. The Cape Party contested their first elections on 22 April 2009. They finished the Western Cape provincial elections in 2019 with 9,331 votes, or 0,45% of votes, gaining no seats The idea has gained popularity in the early half of the 2020s, with polling suggesting that 58% of Western Cape Voters want a referendum on independence in July 2021.South Sudan
A 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum, referendum took place in Southern Sudan from 9to 15 January 2011, on whether the region should remain a part of Sudan or become independent. The referendum was one of the consequences of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement, 2005 Naivasha Agreement between the Government of Sudan, Khartoum central government and the South Sudan People's Defence Forces, Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement (SPLA/M). A simultaneous referendum was supposed to be held in Abyei on whether to become part of Southern Sudan but it has been postponed due to conflict over demarcation and residency rights. On 7 February 2011, the referendum commission published the final results, with 98.83% voting in favour of independence. While the ballots were suspended in 10 of the 79 counties for exceeding 100% of the voter turnout, the number of votes were still well over the requirement of 60% turnout, and the majority vote for secession is not in question. The predetermined date for the creation of an independent state was 9July 2011.Soviet Union
 The Constitution of the Soviet Union guaranteed all Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs the right to secede from the Union. In 1990, after free elections, the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, Lithuanian SSR Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania, declared independence and other Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs soon followed. Despite the Soviet central government's refusal to recognize the independence of the republics, the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Soviet Union dissolved in 1991.
The Constitution of the Soviet Union guaranteed all Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs the right to secede from the Union. In 1990, after free elections, the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, Lithuanian SSR Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania, declared independence and other Republics of the Soviet Union, SSRs soon followed. Despite the Soviet central government's refusal to recognize the independence of the republics, the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Soviet Union dissolved in 1991.
Spain
 Present-day Spain (known officially as "the Spain, Kingdom of Spain") was assembled as a Nation state, central state in the French model between the Nueva Planta decrees, 18th and 1833 territorial division of Spain, 19th centuries from various component kingdoms with varying languages, cultures and legislations. Spain has several List of active separatist movements in Europe#Spain, secessionist movements, the most notable ones being in Catalan separatism, Catalonia, the Basque separatism, Basque Country and Galician independence, Galicia.
Present-day Spain (known officially as "the Spain, Kingdom of Spain") was assembled as a Nation state, central state in the French model between the Nueva Planta decrees, 18th and 1833 territorial division of Spain, 19th centuries from various component kingdoms with varying languages, cultures and legislations. Spain has several List of active separatist movements in Europe#Spain, secessionist movements, the most notable ones being in Catalan separatism, Catalonia, the Basque separatism, Basque Country and Galician independence, Galicia.
Sri Lanka
The Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, operated a de facto independent state for Tamils called Tamil Eelam in eastern and northern Sri Lanka until 2009.Switzerland
In 1847, seven disaffected Catholic Church in Switzerland, Catholic cantons formed a separate alliance because of moves to change the cantons of Switzerland from aconfederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
to a more centralized government federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
. This effort was crushed in the Sonderbund War and a new Swiss Federal Constitution was created.
Ukraine
In 2014 after the start of Russian military intervention in Ukraine (2014–present), Russian intervention in Ukraine, several groups of people declared independence of several Ukrainian regions: * The Donetsk People's Republic was declared to be independent from Ukraine on 7April 2014, comprising the territory of the Donetsk Oblast. There have been War in Donbas (2014–2022), military confrontations between the Ukrainian Army and the forces of the Donetsk People's Republic when the Ukrainian Government attempted to reassert control over the oblast. * The Lugansk Parliamentary Republic was proclaimed on 27 April 2014. before being succeeded by the Lugansk People's Republic. The Lugansk forces have successfully occupied vital buildings in Lugansk since 8April, and controlled the City Council, prosecutor's office, and police station since 27 April. The Government of the Luhansk Oblast, Lugansk Oblast announced its support for a referendum, and granted the governorship to independence leader Valeriy Bolotov.United Kingdom
 The Republic of Ireland withdrew from the United Kingdom after Ireland Proclamation of the Irish Republic, proclaimed independence in 1916 and, as the Irish Free State, gained independence in 1922. The United Kingdom has a number of secession movements:
* In Northern Ireland, Irish republicanism, Irish republicans and Irish nationalism, nationalists have long called for the secession of Northern Ireland to join the Republic of Ireland. This is opposed by Unionism in Ireland, Unionists. A minority have supported the Ulster nationalism, independence of Northern Ireland from the United Kingdom without joining the Republic of Ireland.
* In Scotland, the Scottish National Party (SNP) campaigns for Scottish independence and direct Scottish membership in the European Union. It has representation at all levels of politics in Scotland, Scottish politics and forms the devolved Scottish government. Later pro-independence parties have had lesser electoral success. The Scottish Greens and the Scottish Socialist Party are most widely publicised. However all independence movements/parties are opposed by Unionism in Scotland, unionists. A 2014 Scottish independence referendum, referendum on independence in which voters were asked "Should Scotland be an independent country?" took place in September 2014. It saw "no" win, as 55.3% of voters voted against independence.
* In Wales, Plaid Cymru ''(Party of Wales)'' stands for Welsh independence within the European Union. It is also represented at all levels of Welsh politics and has often been the second largest party in the Senedd (Welsh Parliament).
* England:
** In Cornwall, supporters of Mebyon Kernow call for the creation of a Cornish Assembly and separation from England, giving the county significant Cornish self-government movement, self-government, whilst remaining within the United Kingdom as a fifth home nation.
** London has supporters of an independent or semi-autonomous city-state since the 2016 EU Referendum in which Londoners voted overwhelmingly to remain in the EU. A London independence party, known as Londependence, was established in June 2019. Their calls increased after the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 General Election in which most Londoners voted for the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, gaining a representative, bucking the national trend.
** The Northern Independence Party is a party formed in 2020 that seeks to make Northern England an independent state under the name Northumbria.
The Republic of Ireland withdrew from the United Kingdom after Ireland Proclamation of the Irish Republic, proclaimed independence in 1916 and, as the Irish Free State, gained independence in 1922. The United Kingdom has a number of secession movements:
* In Northern Ireland, Irish republicanism, Irish republicans and Irish nationalism, nationalists have long called for the secession of Northern Ireland to join the Republic of Ireland. This is opposed by Unionism in Ireland, Unionists. A minority have supported the Ulster nationalism, independence of Northern Ireland from the United Kingdom without joining the Republic of Ireland.
* In Scotland, the Scottish National Party (SNP) campaigns for Scottish independence and direct Scottish membership in the European Union. It has representation at all levels of politics in Scotland, Scottish politics and forms the devolved Scottish government. Later pro-independence parties have had lesser electoral success. The Scottish Greens and the Scottish Socialist Party are most widely publicised. However all independence movements/parties are opposed by Unionism in Scotland, unionists. A 2014 Scottish independence referendum, referendum on independence in which voters were asked "Should Scotland be an independent country?" took place in September 2014. It saw "no" win, as 55.3% of voters voted against independence.
* In Wales, Plaid Cymru ''(Party of Wales)'' stands for Welsh independence within the European Union. It is also represented at all levels of Welsh politics and has often been the second largest party in the Senedd (Welsh Parliament).
* England:
** In Cornwall, supporters of Mebyon Kernow call for the creation of a Cornish Assembly and separation from England, giving the county significant Cornish self-government movement, self-government, whilst remaining within the United Kingdom as a fifth home nation.
** London has supporters of an independent or semi-autonomous city-state since the 2016 EU Referendum in which Londoners voted overwhelmingly to remain in the EU. A London independence party, known as Londependence, was established in June 2019. Their calls increased after the 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 General Election in which most Londoners voted for the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, gaining a representative, bucking the national trend.
** The Northern Independence Party is a party formed in 2020 that seeks to make Northern England an independent state under the name Northumbria.
United States
Discussions and threats of secession often surfaced in Politics of the United States, American politics during the first half of the 19th century, and secession was declared by the Confederate States of America in the Southern United States, South during the American Civil War. However, in 1869, the Supreme Court of the United States, United States Supreme Court ruled in ''Texas v. White
''Texas v. White'', 74 U.S. (7 Wall.) 700 (1869), was a case argued before the United States Supreme Court in 1869. The case involved a claim by the Reconstruction government of Texas that United States bonds owned by Texas since 1850 had been ill ...
'' that unilateral secession was not permitted, saying that the union between a state (Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
in the case before the bar) "was as complete, as perpetual, and as indissoluble as the union between the original States. There was no place for reconsideration or revocation, except through revolution or through consent of the States."
Yemen
Yemen Arab Republic, North Yemen and South Yemen merged in 1990; tensions led to a 1994 southern secession which was crushed in a 1994 civil war in Yemen, civil war.Yugoslavia
 On June 25, 1991, Croatia and Slovenia seceded from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia also declared independence, after which the federation broke up, causing the separation of the remaining two countries Serbia and Montenegro. Several Yugoslav Wars, wars ensued between the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and seceding entities and among other ethnic groups in Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and later, Kosovo. Montenegro peacefully separated from its union with Serbia in 2006.
2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, Kosovo unilaterally declared de facto independence from Serbia on February 17, 2008, and was recognized by several dozen countries, but officially remains under United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo, United Nations administration.
On June 25, 1991, Croatia and Slovenia seceded from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia also declared independence, after which the federation broke up, causing the separation of the remaining two countries Serbia and Montenegro. Several Yugoslav Wars, wars ensued between the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and seceding entities and among other ethnic groups in Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and later, Kosovo. Montenegro peacefully separated from its union with Serbia in 2006.
2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, Kosovo unilaterally declared de facto independence from Serbia on February 17, 2008, and was recognized by several dozen countries, but officially remains under United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo, United Nations administration.
See also
Lists
* List of historical autonomist and secessionist movements * List of active autonomist and secessionist movements * List of unrecognized countries * List of U.S. state secession proposals * List of U.S. county secession proposalsTopics
* Intersectionality *Irredentism
Irredentism is usually understood as a desire that one state annexes a territory of a neighboring state. This desire is motivated by ethnic reasons (because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to the population of the parent sta ...
* Autonomy
* Bioregionalism
* City state
* Decentralization
* Economic secession
* Homeland
* Micronation
* Nullification (U.S. Constitution)
* Schism (religion)
* Separatism
* Urban secession
* Partition (politics), Partition
Movements
* Balochistan Liberation Army * Black Liberation Army * Cape Independence * Cascadia (independence movement), Cascadia *East Turkestan Independence Movement
The East Turkestan independence movement ( ug, شەرقىي تۈركىستان مۇستەقىللىق ھەرىكىتى; zh, s=东突厥斯坦独立运动) is a political movement that seeks the independence of East Turkestan, a large and spa ...
* Essex Junto
* European Free Alliance
* Free State Project
* Hartford Convention
* Kurdistan
* League of the South
* New York City secession
* Orania, Northern Cape
* Quebec sovereignty movement, Secession of Quebec
* Scottish Secession Church
* Second Vermont Republic
* South Carolina Exposition and Protest
* Texas Secession Movement
* Tibetan Independence Movement
* Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
Notes
References
Further reading
* Buchanan, Allen, ''Justice, Legitimacy, and Self-Determination: Moral Foundations for International Law (Oxford Political Theory)'', Oxford University Press, 2007. * Buchanan, Allen, ''Secession: The Morality Of Political Divorce From Fort Sumter To Lithuania And Quebec'', Westview Press, 1991. * Coppieters, Bruno; Richard Sakwa, Richard (eds.), ''Contextualizing Secession: Normative Studies in Comparative Perspective'', Oxford University Press, USA, 2003 * Dos Santos, Anne Noronha, ''Military Intervention and Secession in South Asia: The Cases of Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Kashmir, and Punjab (Psi Reports)'', Praeger Security International, 2007. * Gordon, David, ''Secession, State and Liberty'', Transactions Publishers, 1998. * Hannum, Hurst, ''Autonomy, Sovereignty, and Self-Determination: The Accommodation of Conflicting Rights'', University of Pennsylvania Press, 1996. * Hawes, Robert F., ''One Nation, Indivisible? A Study of Secession and the Constitution'', Fultus Corporation, 2006. * Jovanovic, Miodrag, ''Constitutionalizing Secession in Federalized States: A Procedural Approach'', Ashgate Publishing, 2006. * Kohen, Marcelo G. (ed.), ''Secession: International Law Perspectives'', Cambridge University Press, 2006. * Kohr, Leopold, ''The Breakdown of Nations'', Routledge & K. Paul, 1957. * Lehning, Percy, ''Theories of Secession'', Routledge, 1998. * López Martín, Ana Gemma and Perea Unceta, José Antonio, ''Statehood and Secession: Lessons from Spain and Catalonia'', Routledge, 2021 * Norman, Wayne, ''Negotiating Nationalism: Nation-Building, Federalism, and Secession in the Multinational State'', Oxford University Press, USA, 2006. * Dmitry Orlov (writer), Orlov, Dimitry,Reinventing Collapse
', New Society Books, 2008, * Pascalev, Mario, "Territory: An Account of the Territorial Authority of States"
Bowling Green State University, VDM, 2009. * Roeder, Philip G. 2018. National secession: persuasion and violence in independence campaigns. Cornell University Press. * Sorens, Jason, ''Secessionism: Identity, Interest, and Strategy'', McGill-Queen's University Press, 2012. * * Spencer, Metta, ''Separatism: Democracy and Disintegration'', Rowman & Littlefield, 1998. * Weller, Marc, ''Autonomy, Self Governance and Conflict Resolution (Kindle Edition)'', Taylor & Francis, 2007. * Wellman, Christopher Heath, ''A Theory of Secession'', Cambridge University Press, 2005. * ''Secession And International Law: Conflict Avoidanceregional Appraisals'',
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
Publications, 2006.
External links
Secession (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
* {{Authority control Secession, International law Separatism Sovereignty Changes in political power Partition (politics)