Scranton Aces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Scranton is a city in the

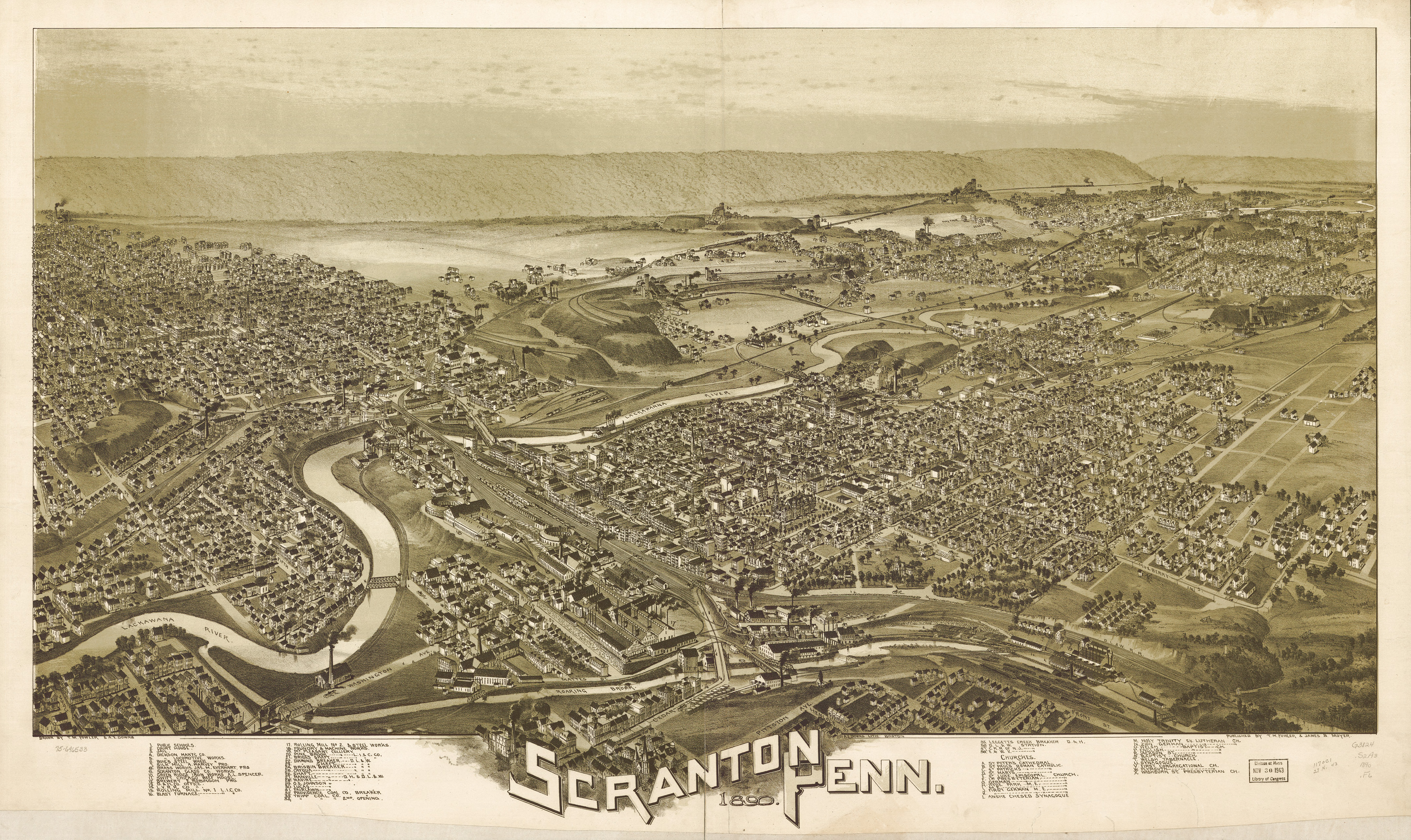
 Though
Though


 By the United States Census of 1900, the population of Scranton was about 102,026, making it the third largest city in Pennsylvania and 38th largest U.S. city.
At the turn of the 20th century, wealthy businessmen and industrialists built impressive Victorian mansions in the Hill and Green Ridge sections of the city. Most were descended from colonists and belonged to the Republican Party. The industrial workers, who tended to be later immigrants from Ireland and southern and eastern Europe, were predominately Catholic. With a flood of immigrants in the market, they suffered poor working conditions and wages.
In 1902, the dwindling local iron ore supply, labor issues, and an aging plant cost the city the industry on which it was founded. The Lackawanna Steel Company and many of its workers were moved to
By the United States Census of 1900, the population of Scranton was about 102,026, making it the third largest city in Pennsylvania and 38th largest U.S. city.
At the turn of the 20th century, wealthy businessmen and industrialists built impressive Victorian mansions in the Hill and Green Ridge sections of the city. Most were descended from colonists and belonged to the Republican Party. The industrial workers, who tended to be later immigrants from Ireland and southern and eastern Europe, were predominately Catholic. With a flood of immigrants in the market, they suffered poor working conditions and wages.
In 1902, the dwindling local iron ore supply, labor issues, and an aging plant cost the city the industry on which it was founded. The Lackawanna Steel Company and many of its workers were moved to
, ''The Times-Tribune,'' October 10, 2010, accessed May 23, 2016 The public transportation system began to expand beyond the trolley lines pioneered by predecessors of the Scranton Railways system. The
 After
After
Hilton Scranton Hotel & Conference Center
at the corner of Adams Avenue & Lackawanna Avenue in the heart of downtown Scranton. Due to the rage for paranormal-themed televisions shows, a popular downtown historic Scranton Ghost Walk has been expanded to operate 365 days a year. Other attractions include the
File:Scranton_-_Scranton_Electric_Building_(48472743896).jpg, Scranton Electric Building
File:Scranton_-_Scranton_City_Hall_(48472742281).jpg,
 Many of Scranton's attractions celebrate its heritage as an industrial center in iron and coal production and its ethnic diversity. The
Many of Scranton's attractions celebrate its heritage as an industrial center in iron and coal production and its ethnic diversity. The
Scranton Fringe Festival
(a performing arts festival held in the downtown section of the city in fall). Scranton's primary concert venue is the
 The Harry Chapin song "30,000 Pounds of Bananas" is about an actual fatal 1965 accident in Scranton, where a driver hauling bananas lost control of his truck as it barreled down Pennsylvania Route 307, Moosic Street.
Blue Valentine (film) was partially filmed in Scranton.
The film adaptation of the Pulitzer Prize for Drama and Tony Award winning play, That Championship Season, is set in and was filmed in Scranton.
The city is home to the Pennsylvania Paper and Supply Company, Pennsylvania Paper & Supply Company, which was the inspiration for a branch of the fictional paper company Dunder Mifflin on NBC's series ''The Office (U.S. TV series), The Office''. The Scranton branch is the setting for the majority of the show's episodes.
The city was the setting of the home of Roy Munson (portrayed by Woody Harrelson) in the 1996 American sports comedy Kingpin (1996 film), ''Kingpin''. The scenes were shot in Pittsburgh as a stand in for Scranton.
The city is imagined as a member of the class of interstellar Okies in James Blish's 1962 novel, ''A Life for the Stars'', in which 2273 AD Scranton, equipped with a space drive, flies away and leaves an impoverished Earth behind.
In 2017, Scranton got national recognition from late night television host John Oliver when he made jokes about how infatuated Scranton community members were with the little train that runs during the weather reports on Scranton's American Broadcasting Company, ABC-affiliated TV station WNEP-TV. The train had been featured in multiple of their Talkback16 segments. After a follow-up segment, Oliver donated a train set to WNEP. It was too big for their backyard, so they donated it to The
The Harry Chapin song "30,000 Pounds of Bananas" is about an actual fatal 1965 accident in Scranton, where a driver hauling bananas lost control of his truck as it barreled down Pennsylvania Route 307, Moosic Street.
Blue Valentine (film) was partially filmed in Scranton.
The film adaptation of the Pulitzer Prize for Drama and Tony Award winning play, That Championship Season, is set in and was filmed in Scranton.
The city is home to the Pennsylvania Paper and Supply Company, Pennsylvania Paper & Supply Company, which was the inspiration for a branch of the fictional paper company Dunder Mifflin on NBC's series ''The Office (U.S. TV series), The Office''. The Scranton branch is the setting for the majority of the show's episodes.
The city was the setting of the home of Roy Munson (portrayed by Woody Harrelson) in the 1996 American sports comedy Kingpin (1996 film), ''Kingpin''. The scenes were shot in Pittsburgh as a stand in for Scranton.
The city is imagined as a member of the class of interstellar Okies in James Blish's 1962 novel, ''A Life for the Stars'', in which 2273 AD Scranton, equipped with a space drive, flies away and leaves an impoverished Earth behind.
In 2017, Scranton got national recognition from late night television host John Oliver when he made jokes about how infatuated Scranton community members were with the little train that runs during the weather reports on Scranton's American Broadcasting Company, ABC-affiliated TV station WNEP-TV. The train had been featured in multiple of their Talkback16 segments. After a follow-up segment, Oliver donated a train set to WNEP. It was too big for their backyard, so they donated it to The
City of Scranton
{{authority control Scranton, Pennsylvania, 1778 establishments in Pennsylvania Cities in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania Cities in Pennsylvania County seats in Pennsylvania Lackawanna Heritage Valley Municipalities of the Anthracite Coal Region of Pennsylvania Populated places established in 1778
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, United States, and the county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US st ...
of Lackawanna County
Lackawanna County (; unm, Lèkaohane) is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in Northeastern Pennsylvania and had a population of 215,896 as of the 2020 census. Its county seat and largest city is Scranton.
The county ...
. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 U.S. census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
, Scranton is the largest city in Northeastern Pennsylvania
Northeastern Pennsylvania (NEPA) is a geographic region of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania that includes the Pocono Mountains, the Endless Mountains, and the industrial cities of Scranton, Wilkes-Barre, Pittston, Hazleton, Nanticoke, and Carbon ...
, the Wyoming Valley
The Wyoming Valley is a historic industrialized region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. The region is historically notable for its influence in helping fuel the American Industrial Revolution with its many anthracite coal-mines. As a metropolitan are ...
, and the Scranton–Wilkes-Barre–Hazleton Metropolitan Statistical Area, which has a population of 562,037 as of 2020. It is the sixth largest city in Pennsylvania. The contiguous network of five cities and more than 40 boroughs all built in a straight line in Northeastern Pennsylvania's urban area act culturally and logistically as one continuous city, so while the city of Scranton itself is a smaller town, the larger unofficial city of Scranton/Wilkes-Barre contains nearly half a million residents in roughly 200 square miles. Scranton/Wilkes-Barre is the cultural and economic center of a region called Northeastern Pennsylvania, which is home to over 1.3 million residents.
Scranton hosts a federal court building for the United States District Court for the Middle District of Pennsylvania
The United States District Court for the Middle District of Pennsylvania (in case citations, M.D. Pa.) is a district level federal court with jurisdiction over approximately one half of Pennsylvania. The court was created in 1901 by subdividing t ...
. The city is conventionally divided into nine districts: North Scranton, Southside, Westside, the Hill Section, Central City, Minooka, East Mountain, Providence and Green Ridge, though these areas do not have legal status. The city is the geographic and cultural center of the Lackawanna River
The Lackawanna River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the Susquehanna River in Northeastern Pennsylvania. It flows through a region of th ...
valley (a local name for a small part of the Wyoming Valley) and Northeastern Pennsylvania, as well as the largest of the former anthracite coal
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the high ...
mining communities in a contiguous quilt-work that also includes Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the secon ...
, Nanticoke Nanticoke may refer to:
* Nanticoke people in Delaware, United States
* Nanticoke language, an Algonquian language
* Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape, a state-recognized tribe in New Jersey
Place names Canada
* Nanticoke, Ontario
** Nanticoke Generating S ...
, Pittston
Pittston is a city in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is situated between Scranton and Wilkes-Barre in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The city gained prominence in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as an active anthracite coal ...
, and Carbondale. Scranton was incorporated on February 14, 1856, as a borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle Ag ...
in Luzerne County
Luzerne County is a county in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and is water. It is Northeastern Pennsylvania's second-largest county by total area. As of ...
and as a city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
on April 23, 1866. It became a major industrial city and a center of mining and railroads; it attracted thousands of new immigrants. It was the site of the Scranton General Strike in 1877.
People in northern Luzerne County sought a new county in 1839, but the Wilkes-Barre area resisted losing its assets. Lackawanna County did not gain independent status until 1878. Under legislation allowing the issue to be voted by residents of the proposed territory, voters favored the new county by a proportion of 6 to 1, with Scranton residents providing the major support. The city was designated as the county seat when Lackawanna County was established in 1878, and a judicial district was authorized in July 1879.
The city's nickname "Electric City" began when electric lights were introduced in 1880 at the Dickson Manufacturing Company
Dickson Manufacturing Company was an American manufacturer of boilers, blast furnaces and steam engines used in various industries but most known in railway steam locomotives. The company also designed and constructed steam powered mine cable ...
. Six years later, the United States' first streetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
s powered only by electricity began operating in the city. Rev. David Spencer, a local Baptist minister, later proclaimed Scranton as the "Electric City".
The city's industrial production and population peaked in the 1930s and 1940s, fueled by demand for coal and textiles, especially during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. But while the national economy boomed after the war, demand for the region's coal declined as other forms of energy became more popular, which also harmed the rail industry. Foreseeing the decline, city leaders formulated the Scranton Plan in 1945 to diversify the local economy beyond coal, but the city's economy continued to decline. The Knox Mine disaster
Knox may refer to:
Places United States
* Fort Knox, a United States Army post in Kentucky
** United States Bullion Depository, a high security storage facility commonly called Fort Knox
* Fort Knox (Maine), a fort located on the Penobscot River i ...
of 1959 essentially ended coal mining in the region. Scranton's population dropped from its peak of 143,433 in the 1930 census
The United States census of 1930, conducted by the Census Bureau one month from April 1, 1930, determined the resident population of the United States to be 122,775,046, an increase of 13.7 percent over the 106,021,537 persons enumerated during ...
to 76,089 in the 2010 census. The city now has large health care, academic, and manufacturing sectors.
Scranton is located north of Allentown Allentown may refer to several places in the United States and topics related to them:
* Allentown, California, now called Toadtown, California
* Allentown, Georgia, a town in Wilkinson County
* Allentown, Illinois, an unincorporated community in T ...
, north of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
, and northwest of New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
.
History
Pre-industrial (1776–1845)
Present-day Scranton and its surrounding area had been long inhabited by the native Lenape tribe, from whose language "Lackawanna" (or ''lac-a-wa-na,'' meaning "stream that forks") is derived. In 1778, Isaac Tripp, the area's first known white settler, built his home here; it still stands in North Scranton, formerly a separate town known as Providence. More settlers fromConnecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
came to the area in the late 18th and early 19th centuries after the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, as their state claimed this area as part of their colonial charter.
They gradually established mills and other small businesses in a village that became known as Slocum Hollow. People in the village during this time carried the traits and accent of their New England settlers, which were somewhat different from most of Pennsylvania. Some area settlers from Connecticut participated in what was known as the Pennamite Wars, where settlers competed for control of the territory which had been included in royal colonial land grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
s to both states. (This claim between Connecticut and Pennsylvania was settled by negotiation with the federal government after independence.)
Arrival of industry (1846–1899)


 Though
Though anthracite coal
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the high ...
was being mined in Carbondale to the north and Wilkes-Barre to the south, the industries that precipitated the city's early rapid growth were iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
and steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
. In the 1840s, brothers Selden T. and George W. Scranton
George Whitfield Scranton (May 11, 1811 – March 24, 1861) was an American industrialist and politician, a Republican member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Pennsylvania from March 4, 1859, until his death in 1861. Moving to Penns ...
, who had worked at Oxford Furnace
Oxford Furnace is a historic blast furnace on Washington Avenue, near the intersection with Belvidere Avenue, in Oxford, Oxford Township, Warren County, New Jersey. The furnace was built by Jonathan Robeson (c. 1695–1766) in 1741 and produced ...
in Oxford, New Jersey, founded what became Lackawanna Iron & Coal, later developing as the Lackawanna Steel Company
The Lackawanna Steel Company was an American steel manufacturing company that existed as an independent company from 1840 to 1922, and as a subsidiary of the Bethlehem Steel company from 1922 to 1983. Founded by the Scranton family, it was once t ...
. It initially started producing iron nails, but that venture failed due to low-quality iron. The Erie Railroad
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the northeastern United States, originally connecting New York City — more specifically Jersey City, New Jersey, where Erie's Pavonia Terminal, long demolished, used to stand — with Lake Erie ...
's construction in New York State was delayed by its having to acquire iron rails as imports from England. The Scrantons' firm decided to switch its focus to producing T-rails for the Erie; the company soon became a major producer of rails for the rapidly expanding railroads.
In 1851, the Scrantons built the Lackawanna and Western Railroad
__NOTOC__
Lackawanna (; from a Lenni Lenape word meaning "stream that forks") is the name of various places and later businesses in the mid-Atlantic United States, generally tracing their name in some manner from the Lackawanna River in Pennsylvani ...
(L&W) northward, with recent Irish immigrants supplying most of the labor, to meet the Erie Railroad in Great Bend, Pennsylvania
Great Bend is a borough in Susquehanna County, Pennsylvania, United States, north of Scranton. According to 2020 Census data, Great Bend's population was 634, down 13.6% from 2010. Great Bend sits along the Susquehanna River, less than two miles ...
. Thus they could transport manufactured rails from the Lackawanna Valley to New York and the Midwest. They also invested in coal mining operations in the city to fuel their steel operations, and to market it to businesses. In 1856, they expanded the railroad eastward as the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad) was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey (and by ferry with New York City), a distance of . Incorporated in ...
(DL&W), in order to tap into the New York City metropolitan market. This railroad, with its hub in Scranton, was Scranton's largest employer for almost one hundred years.
The Pennsylvania Coal Company built a gravity railroad
A gravity railroad (American English) or gravity railway (British English) is a railroad on a slope that allows cars carrying minerals or passengers to coast down the slope by the force of gravity alone. The speed of the cars is controlled by a bra ...
in the 1850s through the city for the purpose of transporting coal. The gravity railroad was replaced by a steam railroad built in 1886 by the Erie and Wyoming Valley Railroad (later absorbed by the Erie Railroad). The Delaware and Hudson
The Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H) is a railroad that operates in the Northeastern United States. In 1991, after more than 150 years as an independent railroad, the D&H was purchased by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). CP operates D&H ...
(D&H) Canal Company, which had its own gravity railroad from Carbondale to Honesdale
Honesdale is a borough in and the county seat of Wayne County, Pennsylvania, United States. The borough's population was 4,458 at the time of the 2020 census.
Honesdale is located northeast of Scranton in a rural area that provides many recrea ...
, built a steam railroad
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas:
Rapid transit
A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid acceleratio ...
that entered Scranton in 1863.
During this short period of time, the city rapidly transformed from a small, agrarian-based village of people with New England roots to a multicultural, industrial-based city. From 1860 to 1900, the city's population increased more than tenfold. Most new immigrants, such as the Irish, Italians, Jewish, and south Germans and Polish, were Catholic, a contrast to the majority-Protestant early settlers of colonial descent. National, ethnic, religious and class differences were wrapped into political affiliations, with many new immigrants joining the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
(and, for a time in the late 1870s, the Greenbacker-Labor Party.)
In 1856, the Borough of Scranton was officially incorporated. It was incorporated as a city of 35,000 in 1866 in Luzerne County, when the surrounding boroughs of Hyde Park (now part of the city's West Side) and Providence (now part of North Scranton) were merged with Scranton. Twelve years later in 1878, the state passed a law enabling creation of new counties where a county's population surpassed 150,000, as did Luzerne's. The law appeared to enable the creation of Lackawanna County
Lackawanna County (; unm, Lèkaohane) is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in Northeastern Pennsylvania and had a population of 215,896 as of the 2020 census. Its county seat and largest city is Scranton.
The county ...
, and there was considerable political agitation around the authorizing process. Scranton was designated by the state legislature as the county seat of the newly formed county, which was also established as a separate judicial district, with state judges moving over from Luzerne County after courts were organized in October 1878. This was the last county in the state to be organized.
Creation of the new county, which enabled both more local control and political patronage, helped begin the Scranton General Strike of 1877. This was in part due to the larger Great Railroad Strike
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended 52 day ...
, in which railroad workers began to organize and participate in walkouts after wage cuts in Martinsburg, West Virginia
Martinsburg is a city in and the seat of Berkeley County, West Virginia, in the tip of the state's Eastern Panhandle region in the lower Shenandoah Valley. Its population was 18,835 in the 2021 census estimate, making it the largest city in the E ...
. The national economy had lagged since the Panic of 1873, and workers in many industries struggled with low wages and intermittent work. In Scranton, mineworkers followed the railroad men off the job, as did others. A protest of 5,000 strikers ended in violence, with a total of four men killed, and 20 to 50 injured, including the mayor. He had established a militia, but called for help from the governor and state militia. Governor John Hartranft
John Frederick Hartranft (December 16, 1830 – October 17, 1889) was the United States military officer who read the death warrant to the individuals who were executed on July 7, 1865 for conspiring to assassinate American President Abraham Lin ...
eventually brought in federal troops to quell the strike. The workers gained nothing in wages, but began to organize more purposefully into labor unions that could wield more power.
The nation's first successful, continuously operating electrified streetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
(trolley) system was established in the city in 1886, inspiring the nickname "The Electric City". In 1896, the city's various streetcar companies were consolidated into the Scranton Railway Company, which ran trolleys until 1954. By 1890, three other railroads had built lines to tap into the rich supply of coal in and around the city, including the Erie Railroad, the Central Railroad of New Jersey
The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines , was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of ...
and finally the New York, Ontario and Western Railway
The New York, Ontario and Western Railway, more commonly known as the O&W or NYO&W, was a regional railroad with origins in 1868, lasting until March 29, 1957 (the last train ran from Norwich to Middletown, NY on this date), after which it was or ...
(NYO&W).
As the vast rail network spread above ground, an even larger network of railways served the rapidly expanding system of coal veins underground. Miners, who in the early years were typically Welsh and Irish, were hired as cheaply as possible by the coal barons. The workers endured low pay, long hours and unsafe working conditions. Children as young as eight or nine worked 14-hour days separating slate from coal in the breakers. Often, the workers were forced to use company-provided housing and purchase food and other goods from stores owned by the coal companies. With hundreds of thousands of immigrants arriving in the industrial cities, mine owners did not have to search for labor and workers struggled to keep their positions. Later miners came from Italy and eastern Europe, which people fled because of poverty and lack of jobs.
Business was booming at the end of the 19th century. The tonnage of coal mined increased virtually every year, as did the steel manufactured by the Lackawanna Steel Company. At one point the company had the largest steel plant in the United States, and it was still the second largest producer at the turn of the 20th century. By 1900, the city had a population of more than 100,000.
In the late 1890s, Scranton was home to a series of early International League
The International League (IL) is a Minor League Baseball league that operates in the United States. Along with the Pacific Coast League, it is one of two leagues playing at the Triple-A level, which is one grade below Major League Baseball ...
baseball teams.
Labor history
Given its industrial basis, Scranton has had a notable labor history; various coal worker unions struggled throughout the coal-mining era to improve working conditions, raise wages, and guarantee fair treatment for workers. The Panic of 1873 and other economic difficulties caused a national recession and loss of business. As the economy contracted, the railroad companies reduced wages of workers in most classes (while sometimes reserving raises for their top management). A major strike of railroad workers in August 1877, part of theGreat Railroad Strike
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended 52 day ...
, attracted workers from the steel industry and mining as well, and developed as the Scranton General Strike. Four rioters were killed during unrest during the strike, after the mayor mustered a militia. With violence suppressed by militia and federal troops, workers finally returned to their jobs, not able to gain any economic relief. William Walker Scranton
William Walker Scranton (April 4, 1844 – December 3, 1916) was an American businessman based in Scranton, Pennsylvania. He became president and manager of the Lackawanna Iron and Coal Company after his father's death in 1872. The company ...
, from the prominent family, was then general manager of Lackawanna Iron and Coal. He later founded Scranton Steel Company.
The labor issues and growth of industry in Scranton contributed to Lackawanna County being established by the state legislature in 1878, with territory taken from Luzerne County. Scranton was designated as the county seat. This strengthened its local government.
The unions failed to gain higher wages that year, but in 1878 they elected labor leader Terence V. Powderly
Terence Vincent Powderly (January 22, 1849 – June 24, 1924) was an American labor union leader, politician and attorney, best known as head of the Knights of Labor in the late 1880s. Born in Carbondale, Pennsylvania, he was later elected mayor ...
of the Knights of Labor
Knights of Labor (K of L), officially Noble and Holy Order of the Knights of Labor, was an American labor federation active in the late 19th century, especially the 1880s. It operated in the United States as well in Canada, and had chapters also ...
as mayor of Scranton. After that, he became national leader of the KoL, a predominately Catholic organization that had a peak membership of 700,000 circa 1880. While the Catholic Church had prohibited membership in secret organizations since the mid-18th century, by the late 1880s with the influence of Archbishop James Gibbons
James Cardinal Gibbons (July 23, 1834 – March 24, 1921) was a senior-ranking American prelate of the Catholic Church who served as Apostolic Vicar of North Carolina from 1868 to 1872, Bishop of Richmond from 1872 to 1877, and as ninth ...
of Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
, it supported the Knights of Labor as representing workingmen and union organizing.
The landmark Coal strike of 1902
The Coal strike of 1902 (also known as the anthracite coal strike) was a strike by the United Mine Workers of America in the anthracite coalfields of eastern Pennsylvania. Miners struck for higher wages, shorter workdays, and the recognition of ...
was called by anthracite miners across the region and led by the United Mine Workers
The United Mine Workers of America (UMW or UMWA) is a North American labor union best known for representing coal miners. Today, the Union also represents health care workers, truck drivers, manufacturing workers and public employees in the Unit ...
under John Mitchell. The strike was settled by a compromise brokered by President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
. A statue of John Mitchell was installed in his honor on the grounds of the Lackawanna County Courthouse in Scranton, "the site of the Coal Strike of 1902 negotiations in which President Roosevelt participated. Because of the significance of these negotiations, the statue and the Courthouse were added to the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic v ...
in 1997. John Mitchell is buried in Cathedral Cemetery in Scranton."
Growth, prosperity and consequences (1900–1945)


 By the United States Census of 1900, the population of Scranton was about 102,026, making it the third largest city in Pennsylvania and 38th largest U.S. city.
At the turn of the 20th century, wealthy businessmen and industrialists built impressive Victorian mansions in the Hill and Green Ridge sections of the city. Most were descended from colonists and belonged to the Republican Party. The industrial workers, who tended to be later immigrants from Ireland and southern and eastern Europe, were predominately Catholic. With a flood of immigrants in the market, they suffered poor working conditions and wages.
In 1902, the dwindling local iron ore supply, labor issues, and an aging plant cost the city the industry on which it was founded. The Lackawanna Steel Company and many of its workers were moved to
By the United States Census of 1900, the population of Scranton was about 102,026, making it the third largest city in Pennsylvania and 38th largest U.S. city.
At the turn of the 20th century, wealthy businessmen and industrialists built impressive Victorian mansions in the Hill and Green Ridge sections of the city. Most were descended from colonists and belonged to the Republican Party. The industrial workers, who tended to be later immigrants from Ireland and southern and eastern Europe, were predominately Catholic. With a flood of immigrants in the market, they suffered poor working conditions and wages.
In 1902, the dwindling local iron ore supply, labor issues, and an aging plant cost the city the industry on which it was founded. The Lackawanna Steel Company and many of its workers were moved to Lackawanna, New York
Lackawanna is a Administrative divisions of New York#City, city in Erie County, New York, Erie County, New York (state), New York, United States, just south of the city of Buffalo, New York, Buffalo in western New York (state), New York State. T ...
, developed on Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
just south of Buffalo. With a port on the lake, the company could receive iron ore shipped from the Mesabi Range
The Mesabi Iron Range is a mining district in northeastern Minnesota following an elongate trend containing large deposits of iron ore. It is the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iron Range of Minnesota. ...
in Minnesota, which was being newly mined.
Scranton forged ahead as the capital of the anthracite coal industry. Attracting the thousands of workers needed to mine coal, the city developed new neighborhoods dominated by Italian and Eastern European immigrants, who brought their foods, cultures and religions. Many of the immigrants joined the Democratic Party. Their national churches and neighborhoods were part of the history of the city. Several Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
churches were founded and built during this period. A substantial Jewish community was also established, with most members coming from the Russian Empire and eastern Europe. Working conditions for miners were improved by the efforts of labor leaders such as John Mitchell, who led the United Mine Workers
The United Mine Workers of America (UMW or UMWA) is a North American labor union best known for representing coal miners. Today, the Union also represents health care workers, truck drivers, manufacturing workers and public employees in the Unit ...
.
The sub-surface mining weakened whole neighborhoods, however, damaging homes, schools, and businesses when the land collapsed. In 1913 the state passed the Davis Act to establish the Bureau of Surface Support in Scranton. Because of the difficulty in dealing with the coal companies, citizens organized the Scranton Surface Protection Association, chartered by the Court of Common Pleas on November 24, 1913 "to protect the lives and property of the citizens of the City of Scranton and the streets of said city from injury, loss and damage caused by mining and mine caves."
In 1915 and 1917, the city and Commonwealth sought injunctions to prevent coal companies from undermining city streets but lost their cases. North Main Avenue and Boulevard Avenue, "both entitled to surface support, caved in as a result" of court decisions that went against civil authorities and allowed the coal companies to continue their operations.
"The case of ''Penman v. Jones'' came out differently. The Lackawanna Iron & Coal Co. had leased coal lands to the Lackawanna Iron & Steel Co., an allied interest, which passed the leases on to the Scranton Coal Co. Areas of central Scranton, the Hill Section, South Side, Pine Brook, Green Ridge and Hyde Park were affected by their mining activities. Mr. Penman was the private property owner in the case. The coal operators were defeated in this case."Cheryl A. Kashuba, "Scranton takes on mining, cave-ins", ''The Times-Tribune,'' October 10, 2010, accessed May 23, 2016 The public transportation system began to expand beyond the trolley lines pioneered by predecessors of the Scranton Railways system. The
Lackawanna and Wyoming Valley Railroad
The Lackawanna & Wyoming Valley Railroad, more commonly known as the Laurel Line, was a Pennsylvania third rail electric interurban streetcar line which operated commuter train service from 1903 to 1952, and freight service until 1976. Its main li ...
, commonly referred to as the Laurel Line, was built as an interurban passenger and freight carrier to Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the secon ...
. Its Scranton station, offices, powerhouse and maintenance facility were built on the former grounds of the Lackawanna Steel Company, and operations started in 1903. Beginning in 1907, Scrantonians could also ride trolley cars to the northern suburbs of Clarks Summit and Dalton
Dalton may refer to:
Science
* Dalton (crater), a lunar crater
* Dalton (program), chemistry software
* Dalton (unit) (Da), the atomic mass unit
* John Dalton, chemist, physicist and meteorologist
Entertainment
* Dalton (Buffyverse), minor cha ...
. They could travel to Lake Winola and Montrose using the Northern Electric
Northern Electric was an electricity supply and distribution company serving north east England.
History
It had its origins as the North Eastern Electricity Board, formed as part of the nationalisation of the electricity industry by the Elect ...
Railroad. After the 1920s, no new trolley lines were built, but bus operations were started and expanded to meet service needs. In 1934, Scranton Railways was re-incorporated as the Scranton Transit Company, reflecting that shift in transportation modes.
Starting in the early 1920s, the Scranton Button Company
The Scranton Button Company was a United States, U.S. corporation, founded in Scranton, Pennsylvania, in 1885.
For much of its early history it was controlled by Canadians, Canadian immigrant William Connell (Pennsylvania), William Connell (Septem ...
(founded in 1885 and a major maker of shellac buttons) became one of the primary makers of phonograph records. They pressed records for Emerson (whom they bought in 1924), as well as Regal, Cameo, Romeo
Romeo Montague () is the male protagonist of William Shakespeare's tragedy ''Romeo and Juliet''. The son of Lord Montague and his wife, Lady Montague, he secretly loves and marries Juliet, a member of the rival House of Capulet, through a priest ...
, Banner
A banner can be a flag or another piece of cloth bearing a symbol, logo, slogan or another message. A flag whose design is the same as the shield in a coat of arms (but usually in a square or rectangular shape) is called a banner of arms. Also, ...
, Domino
Dominoes is a family of tile-based games played with gaming pieces, commonly known as dominoes. Each domino is a rectangular tile, usually with a line dividing its face into two square ''ends''. Each end is marked with a number of spots (also ca ...
, Conqueror. In July 1929, the company merged with Regal, Cameo, Banner, and the U.S. branch of Pathé
Pathé or Pathé Frères (, styled as PATHÉ!) is the name of various French people, French businesses that were founded and originally run by the Pathé Brothers of France starting in 1896. In the early 1900s, Pathé became the world's largest ...
(makers of Pathé and Perfect) to become the American Record Corporation
American Record Corporation (ARC), also referred to as American Record Company, American Recording Corporation, or ARC Records, was an American record company.
Overview
ARC was created in January 1929 by Louis G. Sylvester, president of Scran ...
. By 1938, the Scranton company was also pressing records for Brunswick, Melotone, and Vocalion
Vocalion Records is an American record company and label.
History
The label was founded in 1916 by the Aeolian Company, a maker of pianos and organs, as Aeolian-Vocalion; the company also sold phonographs under the Vocalion name. "Aeolian" was ...
. In 1946, the company was acquired by Capitol Records
Capitol Records, LLC (known legally as Capitol Records, Inc. until 2007) is an American record label distributed by Universal Music Group through its Capitol Music Group imprint. It was founded as the first West Coast-based record label of note ...
, which continued to produce phonograph records
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog signal, analog sound Recording medium, storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove ...
through the end of the vinyl era.
By the mid-1930s, the city population had swelled beyond 140,000 due to growth in the mining and silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
textile industries. World War II created a great demand for energy, which led to the highest production from mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
in the area since World War I.
Post–World War II (1946–1984)
 After
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, coal lost favor to oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
as a heating fuel, largely because the latter types were more convenient to use. While some U.S. cities prospered in the post-war boom, the fortunes and population of Scranton (and the rest of Lackawanna and Luzerne counties) began to diminish. Coal production and rail traffic declined rapidly throughout the 1950s, causing a loss of jobs.
In 1954, Worthington Scranton
Worthington Scranton (August 29, 1876 – February 13, 1955) was a 20th-century American lawyer, businessman, and philanthropist who became president of the Scranton Gas and Water Company in Scranton, Pennsylvania, a city which was named after his ...
and his wife, Marion Margery Scranton
Marion Margery Warren Scranton (April 12, 1884 – June 23, 1960) was a 20th century women’s suffrage activist and leading member of the Republican Party in the United States. Known as “the Duchess and the Grand Old Dame of the Grand Old Pa ...
, contributed one million dollars to establish the Scranton Foundation (now the Scranton Area Community Foundation
The Scranton Area Community Foundation is a public 501(c)(3) community foundation headquartered in Scranton, Pennsylvania, which was established in 1954 as a community trust by Worthington Scranton and Marion Margery Scranton to support charitab ...
), which was launched to support charitable and educational organizations in the city of Scranton.
The Knox Mine Disaster
Knox may refer to:
Places United States
* Fort Knox, a United States Army post in Kentucky
** United States Bullion Depository, a high security storage facility commonly called Fort Knox
* Fort Knox (Maine), a fort located on the Penobscot River i ...
of January 1959 virtually ended the mining industry in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The waters of the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
flooded the mines. The DL&W Railroad, nearly bankrupted by the drop in coal traffic and the effects of Hurricane Diane, merged in 1960 with the Erie Railroad.
Demand for public transportation also declined as new highways were built by federal subsidies and people purchased automobiles. In 1952, the Laurel Line ceased passenger service. The Scranton Transit Company, whose trolleys had given the city its nickname, transferred all operations to buses as the 1954 holiday season approached; by the end of 1971, it ceased all operations. The city was left without any public transportation system for almost a year until the Lackawanna County government formed COLTS, which began operations in late 1972 with 1950s-era GM busses from New Jersey.
Scranton had been the hub of its operations until the Erie Lackawanna
The Erie Lackawanna Railway , known as the Erie Lackawanna Railroad until 1968, was formed from the 1960 merger of the Erie Railroad and the Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad. The official motto of the line was "The Friendly Service Route" ...
merger, after which it no longer served in this capacity. This was another severe blow to the local labor market. The NYO&W Railroad, which depended heavily on its Scranton branch for freight traffic, was abandoned in 1957. Mine subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
was a spreading problem in the city as pillar supports in abandoned mines began to fail; cave-ins sometimes consumed entire blocks of homes. The area was left scarred by abandoned coal mining structures, strip mines, and massive culm dump
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overli ...
s, some of which caught fire and burned for many years until they were extinguished through government efforts. In 1970, the Secretary of Mines for Pennsylvania suggested that so many underground voids had been left by mining underneath Scranton that it would be "more economical" to abandon the city than make them safe. In 1973, the last mine operations in Lackawanna County (which were in what is now McDade Park
McDade Park is a community park located in Scranton in Lackawanna County, in northeastern Pennsylvania. It is named after former U.S. Representative Joseph M. McDade. The park is located on of land, containing an outdoor pool, a fishing pond a ...
, and another on the Scranton/Dickson City
Dickson City is a borough in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, north of Scranton. Coal mining was an important industry in the past. The borough's population peaked at 12,395 in 1930 and was 6,051 at the 2020 census.
History
Dickson City was o ...
line) were closed. During the 1960s and 1970s, the silk and other textile industries shrank as jobs were moved to the South or overseas.
In 1962, businessman Alex Grass
Alexander Grass (August 3, 1927 – August 27, 2009) was an American businessman and lawyer who founded Rite Aid, one of the United States' largest drugstore chains.
Early life
Grass was born in Scranton, Pennsylvania, to Jewish parents, Louis ...
opened his first "Thrif D Discount Center" drugstore on Lackawanna Avenue in downtown Scranton. The store, an immediate success, was the progenitor of the Rite Aid
Rite Aid Corporation is an American drugstore chain based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1962 in Scranton, Pennsylvania, by Alex Grass under the name Thrift D Discount Center. The company ranked No. 148 in the Fortune 500 lis ...
national drugstore chain.
During the 1970s and 1980s, many downtown storefronts and theaters became vacant. Suburban development followed the highways and suburban shopping malls became the dominant venues for shopping and entertainment.
Stabilization and restoration (1985–present)
Since the mid-1980s, the city has emphasized revitalization. Local government and much of the community at large have adopted a renewed interest in the city's buildings and history. Some historic properties have been renovated and marketed as tourist attractions. TheSteamtown National Historic Site
Steamtown National Historic Site (NHS) is a railroad museum and heritage railroad located on in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, at the site of the former Scranton yards of the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W). The museum is buil ...
captures the area's once-prominent position in the railroad industry. The former DL&W train station was restored as the Radisson Lackawanna Station Hotel
The Radisson Lackawanna Station Hotel, built as the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad Station, is a French Renaissance style building in Scranton, Pennsylvania. It was built as a train station and office building in 1908; closed in 1970; li ...
. The Electric City Trolley Museum
The Electric City Trolley Museum is a transport museum located in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, next to the Steamtown National Historic Site. The museum displays and operates restored trolleys and interurbans on former lines of the Lackawanna ...
was created next to the DL&W yards that the Steamtown NHS occupies.
Since the mid-1980s the Scranton Cultural Center
The Scranton Cultural Center at the Masonic Temple (formerly the Masonic Temple and Scottish Rite Cathedral) is a theatre and cultural center in Scranton, Pennsylvania. The Cultural Center's mission statement is "to rejuvenate a national architect ...
has operated the architecturally significant Masonic Temple and Scottish Rite Cathedral, designed by Raymond Hood
Raymond Mathewson Hood (March 29, 1881 – August 14, 1934) was an American architect who worked in the Neo-Gothic and Art Deco styles. He is best known for his designs of the Tribune Tower, American Radiator Building, and Rockefeller Center. Thr ...
, as the region's performing arts center. The Houdini Museum
The Houdini Museum is located at Scranton, Pennsylvania. Harry Houdini appeared in Scranton and did several special challenges there. His brother, Hardeen, also appeared in Scranton and in its sister city, Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Wilkes-Barr ...
was opened in Scranton in 1990 by nationally known magician Dorothy Dietrich
Dorothy Dietrich (born October 31, 1969) is an American stage magician and escapology, escapologist, best known for performing the bullet catch in her mouth (although Adelaide Herrmann reputedly did this earlier) and the first woman to perform a s ...
.
In 2003, Hilton Hotels & Resorts
Hilton Hotels & Resorts (formerly known as Hilton Hotels) is a global brand of full-service hotels and resorts and the flagship brand of American multinational hospitality company Hilton Worldwide, Hilton.
The original company was founded by C ...
opened thHilton Scranton Hotel & Conference Center
at the corner of Adams Avenue & Lackawanna Avenue in the heart of downtown Scranton. Due to the rage for paranormal-themed televisions shows, a popular downtown historic Scranton Ghost Walk has been expanded to operate 365 days a year. Other attractions include the
Montage Mountain ski resort
Montage Mountain is a ski area in Pennsylvania, located from downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania. It is located about northwest of Philadelphia and New York City. There are 26 trails, two terrain parks, and one of Pennsylvania's longest snow tubin ...
(formerly Snö Mountain), the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins, AHL affiliate of the Pittsburgh Penguins
The Pittsburgh Penguins (colloquially known as the Pens) are a professional ice hockey team based in Pittsburgh. They compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division of the Eastern Conference, and have playe ...
; the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders (formerly the Scranton/Wilkes Barre Yankees and, before that, the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre Red Barons), AAA affiliate of the New York Yankees
The New York Yankees are an American professional baseball team based in the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of the Bronx. The Yankees compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Amer ...
; and their PNC Field
PNC Field is a 10,000-seat minor league baseball stadium that is located in Moosic, Pennsylvania in the Wyoming Valley, Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area that was built in 1989 and rebuilt in 2013. The stadium is home to the Scranton/Wilke ...
, and the Toyota Pavilion at Montage Mountain
The Pavilion (originally known as the Montage Mountain Performing Arts Center) is an outdoor amphitheater located in Scranton, Pennsylvania, within the Montage Mountain Ski Resort. A temporary fixture was originally built in 1992, known as the Mo ...
concert venue.
According to ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'', the city was close to bankruptcy in July 2012, with the wages of all municipal officials, including the mayor and fire chief, being cut to $7.25/hour. Financial consultant Gary Lewis, who lives in Scranton, was quoted as estimating that "on 5 July the city had just $5,000 cash in hand."
Since the revitalization began, many coffee shops, restaurants, and bars have opened in the downtown, creating a vibrant night-life. The low cost of living
Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living. Changes in the cost of living over time can be operationalized in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare the cost of maintaining a c ...
, pedestrian-friendly
Walkability is a term for planning concepts best understood by the mixed-use of amenities in high-density neighborhoods where people can access said amenities by foot. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport ...
downtown, and the construction of loft-style apartments in older, architecturally significant buildings have attracted young professionals and artists. Many are individuals who grew up in Scranton, moved to big cities after high school and college, and decided to return to the area to take advantage of its amenities. Many buildings around the city that were once empty are currently being restored. Many of the restored buildings will be used to entice new business into the city. Some of the newly renovated buildings are already being used.
Scranton City Hall
Scranton City Hall is located at Washington and Mulberry (US 11/ PA 307) streets in the downtown section of that city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. It is a three-story limestone ashlar Victorian Gothic Revival building with sandstone trim, de ...
Image:St._Peter%27s_Cathedral.JPG, St. Peter's Cathedral
Image:Electric_City_Mural.JPG, Electric City Mural
Image:First_Liberty_Building.JPG, First Liberty Building
Image:Scranton_Post_Office.JPG, US Post Office and Federal Building
File:Scranton_-_Scranton_Cultural_Center_(48472741161).jpg, Scranton Cultural Center
Image:Brooks_Building.JPG, Brooks Building
Image:Downtown_Scranton_at_night.JPG, Downtown Scranton at night
File:Scranton_-_Scranton_Times_Building_(48472734656).jpg, ''Scranton Times'' Building
File:Scranton_-_Radisson_Lackawanna_Station_Hotel_(48472745076).jpg, Lackawanna Station Hotel
Geography
Scranton's total area of includes of land and of water, according to theUnited States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
. Scranton is drained by the Lackawanna River
The Lackawanna River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the Susquehanna River in Northeastern Pennsylvania. It flows through a region of th ...
.
Center City is about 750 feet (229 m) above sea level, although the hilly city's inhabited portions range about from . The city is flanked by mountains to the east and west whose elevations range from .
Climate
Scranton has ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Dfa''), with four distinct seasons. Summers have occasional heat wave
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
s bringing temperatures well above , while winters can have cold snaps bringing temperatures below . The monthly daily average temperature in January, the coldest month, is , while the same figure in July, the warmest month, is . Extremes in temperatures have ranged from down to on January 21, 1994; there is an average of 15 days of + highs, 39 days where the high fails to rise above freezing, and 3 days where the minimum is at or below . Precipitation is generally ''slightly'' greater during late spring and summer, while winter is generally the driest. On average, each month sees 10 to 13 days of precipitation, and the mean annual total is . Snowfall is variable, with some winters bringing light snow and others bringing numerous snowstorms. For the 1991–2020 period, snowfall has averaged per year, with January accounting for the most of the seasonal total; on average, the first and last dates of measurable (≥) snowfall are November 14 and March 31, respectively, with snow in October and April a rare occurrence.
Demographics
As of the 2020census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses incl ...
, there were 76,328 people and 31,039 households residing in the city. The racial makeup of the city was 83.1% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, 5.9% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.1% Native American, 4.7% Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 0.1% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific Islands. As an ethnic group, ethnic/race (human categorization), racial term, it is used to describe the original p ...
, 4.4% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to Vic ...
or Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
of any race make up 14.8% of the population.
As of the 2010 census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses incl ...
, there were 76,089 people, 30,069 households, and 18,124 families residing in the city. The population density was 3,006/mi2 (1,161/km2). There were 33,853 housing units at an average density of 1,342/mi2 (518/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 84.11% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
, 5.45% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.23% Native American, 2.98% Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 0.04% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific Islands. As an ethnic group, ethnic/race (human categorization), racial term, it is used to describe the original p ...
, 4.69% from other races
Other often refers to:
* Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy
Other or The Other may also refer to:
Film and television
* ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack
* ''The Other'' (1930 film), a ...
, and 2.49% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to Vic ...
or Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
of any race make up 9.90% of the population. The largest ancestry in the city is Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, making up 26.5% of the population.
There were 30,069 households, out of which 24.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 39.8% were married couples living together, 13.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 42.1% were non-families. The city had 36.7% of its households with single occupancy and 18.1% whose individuals was aged at least 65. The average household size was 2.29 and the average family size was 3.01.
The age distribution of the population included 20.8% under 18, 12.3% from 18 to 24, 25.5% from 25 to 44, 21.2% from 45 to 64, and 20.1% at least 65. The median age was 39. For every 100 females, there were 87.0 males. For every 100 females aged at least 18, there were 83.0 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $28,805, and the median income for a family was $41,642. Males had a median income of $30,829 versus $21,858 for females. The per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
for the city was $16,174. Found below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for t ...
are 15.0% of the population, 10.7% of families, 18.9% of those under age 18 and 12.0% of those at least age 65.
As of the 2006 American Community Survey, the average family size is 2.95. Of the population that's 25 years old and over, 83.3% of them have graduated from high school. 18.7% of them have a Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six ...
or higher. In labor force (population 16 years and over), 57.6% of them work. The per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
(in 2006 inflation-adjusted dollars) is $17,187.
Arts and culture
Landmarks and attractions
 Many of Scranton's attractions celebrate its heritage as an industrial center in iron and coal production and its ethnic diversity. The
Many of Scranton's attractions celebrate its heritage as an industrial center in iron and coal production and its ethnic diversity. The Scranton Iron Furnaces
The Scranton Iron Furnaces is a historic site that preserves the heritage of iron making in the U.S. State of Pennsylvania and is located in Scranton, near the Steamtown National Historic Site. It protects the remains of four stone blast furnac ...
are remnants of the city's founding industry and of the Scranton family's Lackawanna Steel Company. The Steamtown National Historic Site
Steamtown National Historic Site (NHS) is a railroad museum and heritage railroad located on in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, at the site of the former Scranton yards of the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W). The museum is buil ...
seeks to preserve the history of railroads in the Northeast. The Electric City Trolley Museum
The Electric City Trolley Museum is a transport museum located in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, next to the Steamtown National Historic Site. The museum displays and operates restored trolleys and interurbans on former lines of the Lackawanna ...
preserves and operates pieces of Pennsylvania streetcar history. Tourists may go for trolley rides from Downtown Scranton to PNC Field on Montage Mountain. The Lackawanna Coal Mine
The Lackawanna Coal Mine is a museum and retired coal mine located in McDade Park in Scranton, Pennsylvania.
History
The Lackawanna Coal Mine was opened by Continental Coal Company in 1903. Lackawanna County, including Scranton, is part of the ...
tour at McDade Park
McDade Park is a community park located in Scranton in Lackawanna County, in northeastern Pennsylvania. It is named after former U.S. Representative Joseph M. McDade. The park is located on of land, containing an outdoor pool, a fishing pond a ...
, conducted inside a former mine, describes the history of mining and railroads in the Scranton area. The former DL&W Passenger Station is now the Radisson Lackawanna Station Hotel
The Radisson Lackawanna Station Hotel, built as the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad Station, is a French Renaissance style building in Scranton, Pennsylvania. It was built as a train station and office building in 1908; closed in 1970; li ...
.
Museums in Scranton include the Everhart Museum
The Everhart Museum of Natural History, Science & Art is a non-profit art and natural history museum located in Nay Aug Park in Scranton, Pennsylvania, United States. It was founded in 1908 by Dr. Isaiah Fawkes Everhart, a local medical doctor ...
in Nay Aug Park, which houses a collection of natural history, science and art exhibits; and the Houdini Museum
The Houdini Museum is located at Scranton, Pennsylvania. Harry Houdini appeared in Scranton and did several special challenges there. His brother, Hardeen, also appeared in Scranton and in its sister city, Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Wilkes-Barr ...
, which features films, exhibits, and a stage show in a unique, century-old building. Terence Powderly's house
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
, still a private dwelling, is one of the city's many historic buildings and, with Steamtown, the city's other National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
. In addition, The Lackawanna Historical Society, founded in 1886 and located at the George H. Catlin House in Scranton's Hill Section, focuses on the history of Lackawanna County. Tripp House, built by the Tripp family in 1771, is the oldest building in the city.
The city's religious history is evident in the Basilica of the National Shrine of St. Ann
The Basilica of the National Shrine of St. Ann is a Minor Basilica and National Shrine of the Catholic Church located in Scranton, Pennsylvania within the Diocese of Scranton.
Description
The first temporary chapel on this site, founded by the Pa ...
, which draws thousands of pilgrims to its annual novena
A novena (from Latin: ''novem'', "nine") is an ancient tradition of devotional praying in Christianity, consisting of private or public prayers repeated for nine successive days or weeks. The nine days between the Feast of the Ascension and Pen ...
, and St. Stanislaus Cathedral, the seat of the Polish National Catholic Church
The Polish National Catholic Church (PNCC) is an independent Old Catholic church based in the United States and founded by Polish-Americans.
The PNCC is not in communion with the Roman Catholic Church.http://www.saplv.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/ ...
in North America. The history of the founding of this denomination is tied to Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
immigration to Scranton in the late 19th century.
Since the 1970s, Scranton has hosted ''La Festa Italiana'', a three-day Italian festival that takes place on Labor Day
Labor Day is a federal holiday in the United States celebrated on the first Monday in September to honor and recognize the American labor movement and the works and contributions of laborers to the development and achievements of the United St ...
weekend on the courthouse square. The festival originally took place around Columbus Day
Columbus Day is a national holiday in many countries of the Americas and elsewhere, and a federal holiday in the United States, which officially celebrates the anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the Americas on October 12, 1492.
...
, but was moved because Scranton generally receives cold weather in October.
Scranton's large Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
population is represented in the annual Saint Patrick's Day Parade, first held in 1862. Organized by the St. Patrick's Day Parade Association of Lackawanna County, it is the nation's fourth largest in attendance and second largest in per capita attendance. Held on the Saturday before Saint Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick ( ga, Lá Fhéile Pádraig, lit=the Day of the Festival of Patrick), is a cultural and religious celebration held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick (), the foremost patr ...
, the parade includes more than 8,000 people, including floats, bagpipe players, high school bands and Irish groups. In 2008, attendance estimates were as high as 150,000 people.
For recreation, there is Montage Mountain Ski Resort
Montage Mountain is a ski area in Pennsylvania, located from downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania. It is located about northwest of Philadelphia and New York City. There are 26 trails, two terrain parks, and one of Pennsylvania's longest snow tubin ...
, known as Sno Mountain for a short period, which rivals the numerous resorts of the Poconos in popularity and offers a relatively comprehensive range of difficulty levels. The Steamtown Marathon has been held each October since 1996 and finishes in downtown Scranton. Nay Aug
Nay Aug Park is the largest park in Scranton, Pennsylvania, Scranton, Pennsylvania, United States. An amusement park on the site closed in the 1990s, but a small amusement area still operates near the swimming pool complex. The park also houses t ...
park is the largest of several parks in Scranton and was designed by Frederick Law Olmsted
Frederick Law Olmsted (April 26, 1822August 28, 1903) was an American landscape architect, journalist, social critic, and public administrator. He is considered to be the father of landscape architecture in the USA. Olmsted was famous for co- ...
, who also laid out Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West Side, Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the List of New York City parks, fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban par ...
in Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, New York City. The city is the home to numerous artistic organizations, including thScranton Fringe Festival
(a performing arts festival held in the downtown section of the city in fall). Scranton's primary concert venue is the
Toyota Pavilion at Montage Mountain
The Pavilion (originally known as the Montage Mountain Performing Arts Center) is an outdoor amphitheater located in Scranton, Pennsylvania, within the Montage Mountain Ski Resort. A temporary fixture was originally built in 1992, known as the Mo ...
, a partially covered amphitheater that seats 17,500. Its summer concerts have included James Taylor
James Vernon Taylor (born March 12, 1948) is an American singer-songwriter and guitarist. A six-time Grammy Award winner, he was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 2000. He is one of the best-selling music artists of all time, havi ...
, Dave Matthews Band
Dave Matthews Band (also known by the initials DMB) is an American rock band formed in Charlottesville, Virginia, in 1991. The band's founding members were singer-songwriter and guitarist Dave Matthews, bassist Stefan Lessard, drummer and bac ...
, and many other musical acts.
Scranton Cultural Center
The Scranton Cultural Center at the Masonic Temple (formerly the Masonic Temple and Scottish Rite Cathedral) is a theatre and cultural center in Scranton, Pennsylvania. The Cultural Center's mission statement is "to rejuvenate a national architect ...
at the Masonic
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to Fraternity, fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of Stonemasonry, stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their inte ...
Temple is an impressive piece of architecture which houses several auditoriums and a large ballroom. It hosts the Northeast Philharmonic, Broadway Theater and other touring performances.
The tallest building in Scranton is the Scranton Times Tower, a lattice radio tower on the Times building, which is illuminated during Christmas season.
Libraries
The Lackawanna County Library System administers the libraries in Scranton, including the Albright Memorial Library, the Lackawanna County Children's Library and the Nancy Kay Holmes Library. As of 2008, Scranton libraries serve more than 96,000 people and have a circulation of over 547,000.Sports
Scranton's professional sports date to 1887, when the minor-league Scranton Indians became the city's first professional baseball team. Many more followed, including teams in thePennsylvania State League
The Pennsylvania State League was an American minor league baseball sports league that operated from 1892 to 1895, then became the first Atlantic League (1896–1900), Atlantic League. The league member teams were exclusively based in Pennsylvania ...
, Eastern League, Atlantic League, New York State League
The New York State League was an independent baseball league that played six seasons between 2007 and 2012 in New York State and the New York City metro area. Over 500 NYSL players have been signed by professional teams. Players from forty-eight ...
, New York–Penn League
The New York–Penn League (NYPL) was a Minor League Baseball league that operated in the northeastern United States from 1939 to 2020. Classified as a Class A Short Season league, its season started in June, after major-league teams signed th ...
and the New York–Pennsylvania League. The Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders
The Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders (often abbreviated to SWB RailRiders) are a Minor League Baseball team of the International League (IL) and the Triple-A (baseball), Triple-A affiliate of the New York Yankees. They are located in Moosic, Pen ...
of the International League
The International League (IL) is a Minor League Baseball league that operates in the United States. Along with the Pacific Coast League, it is one of two leagues playing at the Triple-A level, which is one grade below Major League Baseball ...
play their home games at PNC Field
PNC Field is a 10,000-seat minor league baseball stadium that is located in Moosic, Pennsylvania in the Wyoming Valley, Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area that was built in 1989 and rebuilt in 2013. The stadium is home to the Scranton/Wilke ...
in Moosic
Moosic ( ) is a borough in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, south of downtown Scranton and northeast of downtown Wilkes-Barre, on the Lackawanna River.
Moosic is in a former coal-mining region. A few older industries existed at one time, includ ...
, south of Scranton.
In football, the Scranton Eagles, a discontinued semi-pro/minor league team, dominated their Empire Football League, winning 11 championships. The former arena football
Indoor American football, or arena football, is a variation of gridiron football played at ice hockey-sized indoor arenas. While varying in details from league to league, the rules of indoor football are designed to allow for play in a smaller ...
Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Pioneers
The Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Pioneers were a minor league arena football team that played in the AF2. The team was part of the East Division in the American conference. The Pioneers were an expansion team for the league's 2002 season, and were the ...
, who played eight seasons at the Mohegan Sun Arena
The Mohegan Sun Arena is a 10,000 seat multi-purpose arena in Uncasville, Connecticut, located inside the Mohegan Sun casino resort. The arena facility features of configurable exhibition space and a clear span. It was built by the Perini Buil ...
, formerly Wachovia Arena, in Wilkes-Barre Township made the playoffs in their last six years of existence and contended for the ArenaCup VIII
The 2007 AF2 season was the eighth season of the AF2. It was preceded by 2006 and succeeded by 2008. The regular season began on Friday, March 30 and ended on July 28. The league champions were the Tulsa Talons, who defeated the Wilkes-Barre/Scr ...
in 2007 and the ArenaCup X
The 2009 AF2 season was the AF2's 10th and final season. It was preceded by 2008. The regular season began on Friday, March 20 and finished on Saturday, July 25. The league champion was the Spokane Shock, who defeated the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Pi ...
in 2009, their final year, but lost both times. Another semi-pro/minor league team the North East Pennsylvania Miners of the [Big North East Football Federation started play in the area in 2007.
The NEPA Shock are a Semi-Pro/Minor League team that currently operate out of the Dickson City borough. The Shock were established in 2012 and participate in arena style football as a member of the Great Eastern Football Association.
Scranton previously had pro basketball teams, including the Scranton Apollos, Scranton Miners and Scranton Zappers. Syracuse Orange, Syracuse University men's basketball coach Jim Boeheim played for the Miners before turning to coaching. In 2012, the city played host to the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre Steamers of the Premier Basketball League. The team went inactive after that season, and no professional teams played in the city. In 2018, the Scranton Shamrocks joined the American Basketball Association (2000–present), once again bringing professional basketball to the region.
Professional ice hockey arrived in 1999 when the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins of the American Hockey League began play at Mohegan Sun Arena at Casey Plaza in Wilkes-Barre Township. The team won conference championships in 2001, 2004, and 2008.
The Electric City Shock SC semi-professional soccer team was founded in 2013 as part of the National Premier Soccer League. The team is on the fourth tier of the American Soccer Pyramid and plays at the University of Scranton's Fitzpatrick Field.
Watres Armory in Scranton hosted a World Heavyweight Championship fight between titlist Larry Holmes and challenger Lucien Rodrigues of France on March 27, 1983. Holmes retained his title via a unanimous 12-round decision without losing a single round in any official scorecard.
Starting in 2014, Scranton also became home to the Skyliners Drum and Bugle Corps, a professional marching drum corps in the Drum Corps Associates circuit. They compete with other corps throughout the nation, as well as play multiple community parades, events and performances. The Skyliners have won numerous awards for their performances, including national and world open titles.
Education
Primary and secondary education
The city's public schools are operated by the Scranton School District (Pennsylvania), Scranton School District (SSD), which serves almost 10,000 students. The city has two public high schools for grades 9–12: Scranton High School (Pennsylvania), Scranton High School just northwest of the downtown and West Scranton High School located on the West Side of the city. The district also has three public middle schools for grades 6–8: Northeast Intermediate, South Scranton Intermediate, and West Scranton Intermediate. In addition, SSD maintains 12 public elementary schools for grades K–5. Scranton has two private high schools: Scranton Preparatory School, a private Jesuit school, and Bais Moshe, Yeshiva Bais Moshe, an Haredi Judaism, Ultra Orthodox school. Holy Cross High School (Pennsylvania), Holy Cross High School in Dunmore, Pennsylvania, Dunmore is a Catholic high school operated by the Diocese of Scranton that serves students in Scranton and the surrounding area. The diocese also operates several private elementary schools in the city. Protestant schools that serve the Scranton area include Abington Christian Academy, Canaan Christian Academy, The Geneva School, Summit Academy, and Triboro Christian Academy. The Pennsylvania Department of Education provides oversight for the Scranton School for Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Children. The Scranton State School for the Deaf, a state-run school was replaced by the Scranton School for Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Children. Penn Foster High School, a distance education high school, is headquartered in Scranton. Merakey Education Center is a small private school located in North Scranton. Scranton, West Scranton, Scranton Prep and Holy Cross all compete athletically in Pennsylvania's Lackawanna League which is a part of District 2 of the Pennsylvania Interscholastic Athletic Association.Colleges and universities
The city hosts five colleges and universities: The University of Scranton, Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Johnson College, Lackawanna College, Marywood University, and two technical schools, Fortis Institute and The Career Technology Center of Lackawanna County. The Pennsylvania State University operates a Penn State Worthington Scranton, Commonwealth Campus, Penn State Worthington Scranton, Penn State Scranton, north of the city, in the borough of Dunmore, Pennsylvania, Dunmore. Luzerne County Community College, LCCC, a community college operating out ofNanticoke Nanticoke may refer to:
* Nanticoke people in Delaware, United States
* Nanticoke language, an Algonquian language
* Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape, a state-recognized tribe in New Jersey
Place names Canada
* Nanticoke, Ontario
** Nanticoke Generating S ...
in Luzerne County
Luzerne County is a county in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and is water. It is Northeastern Pennsylvania's second-largest county by total area. As of ...
, operates a satellite campus at The Marketplace at Steamtown. Penn Foster Career School, a distance education vocational school, is headquartered in Scranton.
Media
The Wyoming Valley, Scranton/Wilkes-Barre area is the 55th largest U.S. television market. Local television stations include: * WNEP-TV ABC affiliate * WBRE-TV NBC affiliate * WYOU-TV CBS affiliate * WVIA-TV PBS affiliate * WOLF-TV FOX affiliate * WQMY MyNetworkTV affiliate * WSWB CW affiliate * WQPX Ion Television affiliate Local public-access television and government-access television (ECTV) programming is aired on Comcast cable TV channels 19 and 21. Scranton hosts the headquarters of Times-Shamrock Communications, which publishes the city's major newspaper, ''The Times-Tribune (Scranton), The Times-Tribune'', a Pulitzer Prize-winning broadsheet daily founded in 1870. ''Times-Shamrock'' also publishes the'' Electric City'', a weekly entertainment tabloid, and ''The Citizens' Voice'', a daily tabloid based inWilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the secon ...
. ''Times Leader'' is a daily paper that primarily covers nearby Wilkes-Barre. The ''Times Leader'' also publishes ''Go Lackawanna'', a Sunday newspaper serving Scranton and surrounding municipalities, and the ''Weekender'' is a Wilkes-Barre-based entertainment tabloid with distribution in Scranton.
''The Aquinas'' is the weekly student newspaper of the University of Scranton. ''The Scranton Post'' is a weekly general interest broadsheet which bills itself as the city's first online newspaper. There are several other print publications with a more narrow focus, including the ''Union News,'' ''La Voz Latina,'' and ''Melanian News.''
The Scranton/Wilkes-Barre radio market is ranked #71 in the country by Arbitron.
Infrastructure
Transportation
The main highways that serve Scranton are Interstate 81 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 81, which runs North to Binghamton, New York and Ontario and south to Wilkes-Barre, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg and Tennessee; Interstate 84 (Pennsylvania–Massachusetts), Interstate 84, which runs east to Milford, Pennsylvania, Milford and New England States; Interstate 380 (Pennsylvania), Interstate 380, which runs southeast to Pocono Pines, Pennsylvania, Pocono Pines and Interstate 80 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 80 east to New York City and west to San Francisco; Interstate 476/Pennsylvania Turnpike Northeast Extension, which runs south to Allentown and Philadelphia; U.S. Route 6 in Pennsylvania, U.S. Route 6, which runs east to Carbondale/Honesdale and parallel to I-84 to New England States and west to Erie, Pennsylvania, Erie; and U.S. Route 11 in Pennsylvania, U.S. Route 11, which runs parallel to I-81. Scranton's provider of public transportation is the County of Lackawanna Transit System (COLTS). COLTS buses provide extensive service within the city and more limited service that reaches in all directions to Carbondale, Covington Township, Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Daleville, Pittston, and Benton Township, Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, Fleetville. The other bussing company is the Luzerne County Transportation Authority (LCTA), which mainly runs through The Minooka section (closest to Luzerne County) and Downtown Scranton by The Mall at Steamtown. LCTA takes passengers from Scranton to the Mohegan Sun Pocono racino in Plains, Pennsylvania, Plains The Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International Airport is located in nearby Avoca, Pennsylvania, Avoca. The airport is serviced by American Airlines, Regional Sky and United Airlines, United. Martz Trailways and Greyhound Lines provide coach bus transportation from its downtown station to New York City, Philadelphia and other places in the Northeast. Private operators such as Posten Taxi and McCarthy Flowered Cabs service the Scranton area. They are hired by telephone through central dispatch and cannot be hailed on the street as in larger cities.Railroads
Rail transportation, in both freight and passenger, were vital to the city's historic growth. The city was a hub, serving theCentral Railroad of New Jersey
The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines , was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of ...
(CNJ), the Delaware and Hudson Railway, the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad) was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey (and by ferry with New York City), a distance of . Incorporated in ...
(DLW), the Erie Railroad
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the northeastern United States, originally connecting New York City — more specifically Jersey City, New Jersey, where Erie's Pavonia Terminal, long demolished, used to stand — with Lake Erie ...
, and the Lackawanna and Wyoming Valley Railroad
The Lackawanna & Wyoming Valley Railroad, more commonly known as the Laurel Line, was a Pennsylvania third rail electric interurban streetcar line which operated commuter train service from 1903 to 1952, and freight service until 1976. Its main li ...
(LWV), with routes radiating in all directions, to New York State's Southern Tier, to several points in Pennsylvania, and to parts in northern New Jersey. The Scranton station (Central Railroad of New Jersey), CNJ station and the Radisson Lackawanna Station Hotel, DLW station were the last to lose passenger service, in the early 1950s and in 1970, respectively.
Freight rail remains important and vital even today in Scranton.
The Norfolk Southern Railway runs freight trains on the former Delaware, Lackawanna & Western (DL&W) line between Scranton and Binghamton, having taken over operations from the Canadian Pacific Railway (Delaware and Hudson Railway division) in 2015. The Reading Blue Mountain & Northern Railroad serves the former DL&W Keyser Valley branch in the city.
The Delaware-Lackawanna Railroad, as designated operator of county-owned rail lines, oversees the former Delaware and Hudson line from Scranton north to Carbondale, the former DL&W line east to the Delaware Water Gap and the former Lackawanna and Wyoming Valley Railroad third-rail interurban streetcar line south to Montage Mountain, Moosic and the Minooka Industrial Track. These lines host the seasonal passenger trains of both the Steamtown National Historic Site
Steamtown National Historic Site (NHS) is a railroad museum and heritage railroad located on in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, at the site of the former Scranton yards of the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W). The museum is buil ...
and the Electric City Trolley Museum
The Electric City Trolley Museum is a transport museum located in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, next to the Steamtown National Historic Site. The museum displays and operates restored trolleys and interurbans on former lines of the Lackawanna ...
and are under the jurisdiction of the Pennsylvania Northeast Regional Railroad Authority.
The PNRRA was created by Lackawanna County
Lackawanna County (; unm, Lèkaohane) is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in Northeastern Pennsylvania and had a population of 215,896 as of the 2020 census. Its county seat and largest city is Scranton.
The county ...
and Monroe County, Pennsylvania, Monroe County to oversee the use of common rail freight lines in Northeastern Pennsylvania
Northeastern Pennsylvania (NEPA) is a geographic region of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania that includes the Pocono Mountains, the Endless Mountains, and the industrial cities of Scranton, Wilkes-Barre, Pittston, Hazleton, Nanticoke, and Carbon ...
, including one formerly owned by Conrail running from Scranton, through the the Poconos, Pocono Mountains towards New Jersey and the New York City market.
One of its primary objectives is to re-establish rail passenger service to Hoboken, New Jersey and thence by connection to New York.
Indeed, regular passenger train service to Scranton is slated to be restored under a plan to extend NJ Transit service from Hoboken via the Lackawanna Cut-Off. That project is ongoing as rail is being laid down in New Jersey. The trains would pass the Lackawanna Station building and pull in at Scranton (NJT station), a new Scranton station on Lackawanna Avenue along the northernmost track east of Bridge 60 (the railroad bridge over the Lackawanna River
The Lackawanna River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the Susquehanna River in Northeastern Pennsylvania. It flows through a region of th ...
) and the Cliff Street underpass.
Fire department
The Scranton Fire Department, Bureau of Fire was incorporated as a paid service in 1901. It is a full-time service consisting of about 139 firefighters. Its headquarters is on Mulberry Street in Central City. The fire department has seven operating fire stations. It has nine firefighting vehicles, including five Fire engine, engines, two trucks (ladders), one Heavy rescue vehicle, rescue, and an assistant chief's vehicle.Police
Police headquarters is located on North Washington Avenue in downtown Scranton. Special Units include Arson Investigations, Auto Theft Task Force, Child Abuse Investigation, Crime Scene Investigation, Criminal Investigation, Juvenile Unit, Special Investigations Unit, Special Operations Group (SWAT/SOG), Canine Unit, Community Development and Highway Unit. The Police department has recently opened two new satellite stations. The Highway Unit was relocated to one new station at N. Keyser Ave & Morgan Highway. The second was opened at the Valley View Housing complex. There are plans for at least one more, and possibly two.Notable people
Arts
* J. Grubb Alexander, silent film screenwriter * Pete Barbutti, actor * Walter Bobbie, theatre director and choreographer * Alan Brown (filmmaker), Alan Brown, filmmaker * Sonny Burke, big band leader * Mark Cohen (photographer), Mark Cohen, photographer * Karl R. Coolidge, screenwriter * Ann Crowley (singer), Ann Crowley, singer and actress * Emile de Antonio, documentary film director and producer * Carrie De Mar, actress, singer, and vaudevillian *Dorothy Dietrich
Dorothy Dietrich (born October 31, 1969) is an American stage magician and escapology, escapologist, best known for performing the bullet catch in her mouth (although Adelaide Herrmann reputedly did this earlier) and the first woman to perform a s ...
, stage magician, escapologist, co-owner of Houdini Museum
The Houdini Museum is located at Scranton, Pennsylvania. Harry Houdini appeared in Scranton and did several special challenges there. His brother, Hardeen, also appeared in Scranton and in its sister city, Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Wilkes-Barr ...
* Margot Douaihy, writer and author
* Cy Endfield, screenwriter, film and theater director, author, magician, and inventor
* Ann Evers, film actress
* Wanda Hawley, silent film actress
* Allan Jones (actor), Allan Jones, singer and actor
* Jane Jacobs, writer and activist
* Gloria Jean, singer and actress
* Stephen Karam, playwright and screenwriter
* JP Karliak, actor, voice actor, and comedian
* Jean Kerr, author and playwright
* Michael Patrick King, television and film writer, director and producer, co-creator of ''2 Broke Girls'' and ''The Comeback (TV series), The Comeback''
* William Kotzwinkle, novelist and screenwriter
* Michael Kuchwara, theater critic, columnist, and journalist
* Gershon Legman, cultural critic and folklorist
* Bradford Louryk, theater artist and actor
* Charles Emmett Mack, actor
* Jeanne Madden, singer, star of musical theater and 1930s films
* Carl Marzani, political activist, volunteer soldier in Spanish Civil War, organizer for the Communist Party USA, U.S. intelligence official, documentary filmmaker, author, and publisher
* Judy McGrath, MTV Networks CEO
* Charles MacArthur, playwright and screenwriter
* The Menzingers, punk band
* W. S. Merwin, 17th United States Poet Laureate, U.S. Poet Laureate
* Jason Miller (playwright), Jason Miller, actor, director, and Pulitzer Prize for Drama, Pulitzer Prize–winning playwright of ''That Championship Season''
* Russ Morgan, big band-era bandleader
* Motionless in White, gothic metalcore band
* Bruce Mozert, photographer
* Jay Parini, writer and academic
* Jerry Penacoli, actor and director
* Byrne Piven, stage actor
* Cynthia Rothrock, martial artist and star of martial arts films
* Lizabeth Scott, actress and singer
* Katy Selverstone, actress, Lisa Robbins on ''The Drew Carey Show''
* Melanie Smith (actress), Melanie Smith, television actress
* Thomas L. Thomas, concert singer
* Tigers Jaw, indie rock, emo band
* Beverly Tyler, actress and singer
* Sally Victor, milliner
* Ned Washington, Academy Award-winning lyricist
* Lauren Weisberger, author, ''The Devil Wears Prada (novel), The Devil Wears Prada''
Government
* Joe Biden, 46th President of the United States (2021–), 47th Vice President of the United States, U.S. senator from Delaware (1973–2009) * John Blake (Pennsylvania politician), John Blake, former Pennsylvania State Senator * Marion Cowan Burrows, former Massachusetts state legislator * Frank Carlucci, former U.S. Secretary of Defense and ambassador to Portugal * Bob Casey Sr., Robert P. Casey, former governor of Pennsylvania * Bob Casey Jr., Robert P. Casey Jr., U.S. senator * Gaynor Cawley, former Pennsylvania State Representative * David J. Davis, former Pennsylvania lieutenant governor * Mike Dunleavy (politician), Mike Dunleavy, governor of Alaska * Hugh Rodham (born 1911), Hugh E. Rodham, father of Hillary Clinton * Hermann Eilts, former U.S. ambassador to Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Bangladesh * John R. Farr, U.S. Congresman * Kathleen Kane, former Pennsylvania attorney general and felon *Terence V. Powderly
Terence Vincent Powderly (January 22, 1849 – June 24, 1924) was an American labor union leader, politician and attorney, best known as head of the Knights of Labor in the late 1880s. Born in Carbondale, Pennsylvania, he was later elected mayor ...
, former head of Knights of Labor
* Robert Reich, professor and political commentator, former U.S. Secretary of Labor
* Mary Scranton, former First Lady of Pennsylvania
* William Scranton, former governor of Pennsylvania and U.S. ambassador to the United Nations
* William Scranton III, former Pennsylvania lieutenant governor
* Joel Wachs, Los Angeles city council member
* John Anthony Walker, former United States Navy, U.S. Navy Warrant officer (United States), chief warrant officer convicted of Espionage, spying for the Soviet Union
* Louis A. Watres, former Pennsylvania lieutenant governor
Sports
* Hank Bullough, NFL player and coach * P. J. Carlesimo, college, Olympic, and professional basketball coach and television broadcaster * Jimmy Caras , professional pool player * Nick Chickillo, former NFL player * Nestor Chylak, Baseball Hall of Famer and former American League Umpire (baseball), umpire * Joe Collins, Major League Baseball player, six-time World Series champion * Patty Costello, professional bowler, International Bowling Congress Hall of Fame, and Pro Bowlers Tour Hall of Fame member * Jim Crowley, football player and coach, one-fourth of University of Notre Dame's legendary "Four Horsemen (American football), Four Horsemen" backfield * Paul Foytack, Major League Baseball pitcher * Charlie Gelbert, Major League Baseball player * Joe Grzenda, Major League Baseball player * Cosmo Iacavazzi, college and American Football League, AFL player * Edgar Jones (running back), Edgar Jones, college and professional football player * Gary Lavelle, Major League Baseball player * Bill Lazor, NFL offensive coordinator * Dave Lettieri, Olympic cyclist * Ralph Lomma, popularized miniature golf * Mike Lynn, general manager and executive Minnesota Vikings * Joe McCarthy (outfielder), Joe McCarthy, Major League Baseball player * Matt McGloin, former NFL quarterback * Gerry McNamara, assistant coach, Syracuse Orange men's basketball, Syracuse Orange * Mike McNally, former Major League Baseball player, member ofNew York Yankees
The New York Yankees are an American professional baseball team based in the Boroughs of New York City, New York City borough of the Bronx. The Yankees compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) Amer ...
first World Series championship team
* Mike Munchak, former head coach of NFL's Tennessee Titans, college and National Football League, NFL player, member of Pro Football Hall of Fame
* Joe O'Malley, football player
* Jim O'Neill (baseball), Jim O'Neill, Major League Baseball player
* Steve O'Neill, former Major League Baseball player and manager
* Jackie Paterson, Scottish boxer
* Jim Rempe, pocket billiards champion and member of the Billiard Congress of America Hall of Fame
* Adam Rippon, figure skater
* Tim Ruddy, college and National Football League player
* Dutch Savage, professional wrestler
* Greg Sherman, general manager of NHL's Colorado Avalanche
* Chick Shorten, Major League Baseball player
* Marc Spindler, college and National Football League, NFL player
* Brian Stann, mixed martial artist, Ultimate Fighting Championship, UFC analyst for Fox Sports, former World Extreme Cagefighting, WEC Light Heavyweight (MMA), Light Heavyweight champion
Others
* Joseph Bambera, Roman Catholic Diocese of Scranton, Bishop of Scranton * Mamie Cadden, Irish midwife and murderer * Lisa Caputo, Citigroup group * Howard Gardner, developmental psychologist and professor * Frank Gibney, journalist and scholar * Hugh Glass, American frontiersman *Alex Grass
Alexander Grass (August 3, 1927 – August 27, 2009) was an American businessman and lawyer who founded Rite Aid, one of the United States' largest drugstore chains.
Early life
Grass was born in Scranton, Pennsylvania, to Jewish parents, Louis ...
, founder of Rite Aid
Rite Aid Corporation is an American drugstore chain based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1962 in Scranton, Pennsylvania, by Alex Grass under the name Thrift D Discount Center. The company ranked No. 148 in the Fortune 500 lis ...
* Lansing C. Holden, architect
* Jeffrey Bruce Klein, investigative journalist, co-founded ''Mother Jones (magazine), Mother Jones'' magazine
* Gino J. Merli, Medal of Honor recipient during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
* John Mitchell, labor organizer, founding member and president, United Mine Workers of America
* Robert C. Morlino, Roman Catholic Diocese of Madison, Bishop of Madison, Wisconsin
* John O'Connor (cardinal), John Joseph O'Connor, former bishop of Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York and Roman Catholic Diocese of Scranton, Bishop of Scranton
* Karen Ann Quinlan, key figure in right to die controversy
* William Henry Richmond, coal mine operator
* Martin F. Scanlon, U.S. Air Force general
* B. F. Skinner, behaviorist and author
* Mabel Cox Surdam, photographer
* Charles Sumner Woolworth, Charles Sumner "Sum" Woolworth, retailer, philanthropist, co-founder of F. W. Woolworth Company, Woolworth
* Mel Ziegler, co-founder, The Republic of Tea and Banana Republic (clothing retailer), Banana Republic
In popular culture
 The Harry Chapin song "30,000 Pounds of Bananas" is about an actual fatal 1965 accident in Scranton, where a driver hauling bananas lost control of his truck as it barreled down Pennsylvania Route 307, Moosic Street.
Blue Valentine (film) was partially filmed in Scranton.
The film adaptation of the Pulitzer Prize for Drama and Tony Award winning play, That Championship Season, is set in and was filmed in Scranton.
The city is home to the Pennsylvania Paper and Supply Company, Pennsylvania Paper & Supply Company, which was the inspiration for a branch of the fictional paper company Dunder Mifflin on NBC's series ''The Office (U.S. TV series), The Office''. The Scranton branch is the setting for the majority of the show's episodes.
The city was the setting of the home of Roy Munson (portrayed by Woody Harrelson) in the 1996 American sports comedy Kingpin (1996 film), ''Kingpin''. The scenes were shot in Pittsburgh as a stand in for Scranton.
The city is imagined as a member of the class of interstellar Okies in James Blish's 1962 novel, ''A Life for the Stars'', in which 2273 AD Scranton, equipped with a space drive, flies away and leaves an impoverished Earth behind.
In 2017, Scranton got national recognition from late night television host John Oliver when he made jokes about how infatuated Scranton community members were with the little train that runs during the weather reports on Scranton's American Broadcasting Company, ABC-affiliated TV station WNEP-TV. The train had been featured in multiple of their Talkback16 segments. After a follow-up segment, Oliver donated a train set to WNEP. It was too big for their backyard, so they donated it to The
The Harry Chapin song "30,000 Pounds of Bananas" is about an actual fatal 1965 accident in Scranton, where a driver hauling bananas lost control of his truck as it barreled down Pennsylvania Route 307, Moosic Street.
Blue Valentine (film) was partially filmed in Scranton.
The film adaptation of the Pulitzer Prize for Drama and Tony Award winning play, That Championship Season, is set in and was filmed in Scranton.
The city is home to the Pennsylvania Paper and Supply Company, Pennsylvania Paper & Supply Company, which was the inspiration for a branch of the fictional paper company Dunder Mifflin on NBC's series ''The Office (U.S. TV series), The Office''. The Scranton branch is the setting for the majority of the show's episodes.
The city was the setting of the home of Roy Munson (portrayed by Woody Harrelson) in the 1996 American sports comedy Kingpin (1996 film), ''Kingpin''. The scenes were shot in Pittsburgh as a stand in for Scranton.
The city is imagined as a member of the class of interstellar Okies in James Blish's 1962 novel, ''A Life for the Stars'', in which 2273 AD Scranton, equipped with a space drive, flies away and leaves an impoverished Earth behind.
In 2017, Scranton got national recognition from late night television host John Oliver when he made jokes about how infatuated Scranton community members were with the little train that runs during the weather reports on Scranton's American Broadcasting Company, ABC-affiliated TV station WNEP-TV. The train had been featured in multiple of their Talkback16 segments. After a follow-up segment, Oliver donated a train set to WNEP. It was too big for their backyard, so they donated it to The Electric City Trolley Museum
The Electric City Trolley Museum is a transport museum located in downtown Scranton, Pennsylvania, next to the Steamtown National Historic Site. The museum displays and operates restored trolleys and interurbans on former lines of the Lackawanna ...
.
Musician John Legend was the head of the music department and choir director of Scranton's Bethel AME Church from 1995-2004.
Lyricist Richard Bernhard Smith wrote the song, Winter Wonderland, while being treated at the West Mountain Sanitarium in Scranton, Pennsylvania, Scranton for tuberculosis.
American singer, actress and television personality Cher lived in Scranton as a baby and spent time at a Catholic orphanage in the city run by the Sisters of Mercy. Cher wrote about the experience in the song, Sisters of Mercy.
Sister cities
Scranton has the following official sister cities: * Naga, Camarines Sur, Naga, Camarines Sur, Philippines * Ballina, County Mayo, Ballina, County Mayo, Connacht, Ireland * Guardia Lombardi, Campania, Italy * Balakovo, Saratov Oblast, Russia * Trnava, Trnava Region, Slovakia * Perugia, Umbria, Italy * City of San Marino, San Marino, San Marino * Caronia, Sicily, Italy * Little Rock, Arkansas, Little Rock, Arkansas, United States * Chicago, Illinois, United StatesSee also
* Farley's Eatery and Pub * The Office (American TV series), The Office * Polish Cathedral style * Scranton Army Ammunition Plant * Weston Field (Scranton), Weston FieldNotes
References
External links
City of Scranton
{{authority control Scranton, Pennsylvania, 1778 establishments in Pennsylvania Cities in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania Cities in Pennsylvania County seats in Pennsylvania Lackawanna Heritage Valley Municipalities of the Anthracite Coal Region of Pennsylvania Populated places established in 1778