Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile, is the
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city of
Chile as well as one of the
largest cities in the Americas. It is the center of Chile's most densely populated
region, the
Santiago Metropolitan Region, whose total population is 8 million which is nearly 40% of the country's population, of which more than 6 million live in the city's continuous urban area. The city is entirely in the country's
central valley. Most of the city lies between
above mean sea level.
Founded in 1541 by the Spanish
conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, O ...
Pedro de Valdivia, Santiago has been the capital city of Chile since colonial times. The city has a downtown core of 19th-century neoclassical architecture and winding side-streets, dotted by art deco, neo-gothic, and other styles. Santiago's cityscape is shaped by several stand-alone hills and the fast-flowing
Mapocho River, lined by parks such as
Parque Forestal and
Balmaceda Park. The
Andes Mountains
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the List of mountain ranges#Mountain ranges by length, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range i ...
can be seen from most points in the city. These mountains contribute to a considerable
smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and '' fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then inte ...
problem, particularly during winter, due to the lack of rain. The city outskirts are surrounded by vineyards and Santiago is within an hour of both the mountains and the Pacific Ocean.
Santiago is the political and financial center of Chile and is home to the regional headquarters of many multinational corporations. The Chilean executive and judiciary are located in Santiago, but Congress meets mostly in nearby
Valparaíso. Santiago is named after the biblical figure
Saint James Saint James or St. James may refer to:
People Saints
*James, brother of Jesus (died 62 or 69), also known as James the Just
*James the Great (died 44), Apostle, also known as James, son of Zebedee, or Saint James the Greater
**Saint James Matamoro ...
. The city will host the
2023 Pan American Games
The 2023 Pan American Games ( es, Juegos Panamericanos de 2023, links=no), officially the XIX Pan American Games and commonly known as Santiago 2023, is a forthcoming international multi-sport event governed by the Panam Sports Organization, s ...
.
Nomenclature

In Chile, there are several entities which have the name of "Santiago" that are often confused. The
commune of Santiago
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
, sometimes referred to as "Downtown/Central Santiago" (''Santiago Centro''), is an
administrative division that comprises roughly the area occupied by the city during its colonial period. The commune, administered by the Municipality of Santiago and headed by a mayor, is part of the
Santiago Province headed by a provincial delegate, which is in itself a subdivision of the
Santiago Metropolitan Region headed by a
governor. While the mayor and governor are elected by popular vote, the provincial delegate is designated by the
President of the Republic as its local representative.
Despite these classifications, when the term "Santiago" is used without another descriptor, it usually refers to what is also known as Greater Santiago (''Gran Santiago''), the
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
defined by its urban continuity that includes the
commune of Santiago
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
and more than 40 other communes, which together comprise the majority of the
Santiago Province and some areas of neighboring provinces (see
Political divisions). The definition of this metropolitan area has evolved due to the continuing expansion of the city and the absorption of smaller cities and rural areas.
The name of "Santiago" originates in the name chosen by the Spanish conqueror, Pedro de Valdivia, when he founded the city in 1541. Valdivia honored
James the Great, the
patron saint of
Spain. In the
Spanish language, the name of this saint is rendered in different ways, as
Diego,
Jaime,
Jacobo
Jacobo is both a surname and a given name of Spanish origin. Based on the name Jacob. Notable people with the name include:
Surname:
* Alfredo Jacobo (born 1982), Olympic breaststroke swimmer from Mexico
* Cesar Chavez Jacobo, Dominican profession ...
or
Santiago; the latter is derived from the
Galician evolution of
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
''Sanctu Iacobu''. There is no indigenous name for the area occupied by Santiago;
Mapuche language uses the name "Santiaw" as an adaptation of the Spanish name of the city.
When founded, Valdivia used the name "Santiago del Nuevo Extremo" or "
Nueva Extremadura", based on the territory he expected to colonize and that he named honoring his native
Extremadura. The name didn't persist for long and was eventually replaced by the local name of Chile. To differentiate with
other cities called Santiago, the South American city is sometimes called "Santiago de Chile" in Spanish and other languages.
The city and region's
demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
is ''santiaguinos'' (male) and ''santiaguinas'' (female).
History
Prehistory
According to certain archeological investigations, it is believed that the first human groups reached the Santiago basin in the
10th millennium BC
The 10th millennium BC spanned the years 10,000 BC to 9001 BC (c. 12 ka to c. 11 ka). It marks the beginning of the transition from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic via the interim Mesolithic ( Northern Europe and Western Europe) and Epip ...
. The groups were mainly
nomadic hunter-gatherers, who traveled from the coast to the interior in search of
guanacos
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco g ...
during the time of the Andean snowmelt. About the year 800, the first
sedentary inhabitants began to settle due to the formation of agricultural communities along the
Mapocho River, mainly
maize,
potatoes
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern United ...
and
beans, and the domestication of
camelids in the area.
The villages established in the areas belonging to the
Picunches (the name given by Chileans) or
Promaucae people Promaucae, also spelled as ''Promaucas'' or ''Purumaucas'' (from Quechua ''purum awqa'': wild enemy), were an indigenous pre-Columbian Mapuche tribal group that lived in the present territory of Chile, south of the Maipo River basin of Santiago, C ...
(name given by the Incas), were subject to the
Inca Empire throughout the late fifteenth century and into the early sixteenth century. The Incas settled in the valley of
mitimas, the main installation settled in the center of the present city, with strongholds such as
Huaca de Chena and the sanctuary of
El Plomo hill. The area would have served as a basis for the failed Inca expeditions southward road junction as the
Inca Trail
The Inca Trail to Machu Picchu (also known as ''Camino Inca'' or ''Camino Inka'') is a hiking trail in Peru that terminates at Machu Picchu. It consists of three overlapping trails: ''Mollepata'', ''Classic'', and ''One Day''. ''Mollepata'' is ...
.
Founding of the city

Having been sent by
Francisco Pizarro from
Peru and having made the long journey from
Cuzco,
Extremadura conquistador
Pedro de Valdivia reached the valley of the Mapocho on 13 December 1540. The hosts of Valdivia camped by the river in the slopes of the
Tupahue hill and slowly began to interact with the
Picunche people
The Picunche (a Mapudungun word meaning "North People"), also referred to as ''picones'' by the Spanish, were a Mapudungun-speaking people living to the north of the Mapuches or Araucanians (a name given to those Mapuche living between the Itata an ...
who inhabited the area. Valdivia later summoned the chiefs of the area to a parliament, where he explained his intention to found a city on behalf of the king
Carlos I of Spain, which would be the capital of his governorship of
Nueva Extremadura. The natives accepted and even recommended the foundation of the town on a small island between two branches of the river next to a small hill called
Huelén.
On 12 February 1541 Valdivia officially founded the city of ''Santiago del Nuevo Extremo'' (''Santiago of New Extremadura'') near the Huelén, renamed by the conqueror as
Santa Lucia
Santa Lucia and similar terms may refer to:
Architecture
* Abbey of Santa Lucia, a medieval abbey in the comune of Rocca di Cambio, Abruzzo, central Italy
* Monastero di Santa Lucia, Adrano, a former Benedictine monastery in Catania, Italy
* S ...
. Following colonial rule, Valdivia entrusted the layout of the new town to master builder
Pedro de Gamboa, who would design the city
grid layout. In the center of the city, Gamboa designed a
Plaza Mayor
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true geometric square, used for community gatherings. ...
, around which various plots for the
Cathedral and the
governor's house were selected. In total, eight blocks from north to south, and ten from east to west, were built. Each solar (quarter block) was given to the settlers, who built houses of mud and straw.
Valdivia left months later to the south with his troops, beginning the
War of Arauco
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía (historic region), Araucanía. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to estab ...
. Santiago was left unprotected. The indigenous hosts of
Michimalonco
Michima Lonco (fl. mid-16th century) (''michima'' means "foreigner" and ''lonco'' means "head" or "chief" in Mapudungun language) was a Picunche chief said to be a great warrior, born in the Aconcagua Valley and educated in Cusco by the Inca E ...
used this to their advantage, and attacked the fledgling city. On 11 September 1541, the city was destroyed by the natives, but the 55-strong Spanish Garrison managed to defend the fort. The resistance was led by
Inés de Suárez, a mistress to Valdivia. When she realized they were being overrun, she ordered the execution of all native prisoners, and proceeded to put their heads on pikes and also threw a few heads to the natives. In face of this barbaric act, the natives dispersed in terror. The city would be slowly rebuilt, giving prominence to the newly founded
Concepción, where the
Royal Audiencia of Chile was then founded in 1565. However, the constant danger faced by Concepción, due partly to its proximity to the War of Arauco and also to a succession of devastating earthquakes, would not allow the definitive establishment of the Royal Court in Santiago until 1607. This establishment reaffirmed the city's role as capital.
During the early years of the city the Spanish suffered from severe shortages of food and other supplies. The cause of this was a strategy by the local indigenous
Picunche to stop cultivation and retreat to more distant places.
[ Isolated from reinforcements the Spanish had to resort to eat whatever they found, lack of clothes meant some Spanish came to dress with hides from dogs, cats, sea lions and foxes.]
Colonial Santiago
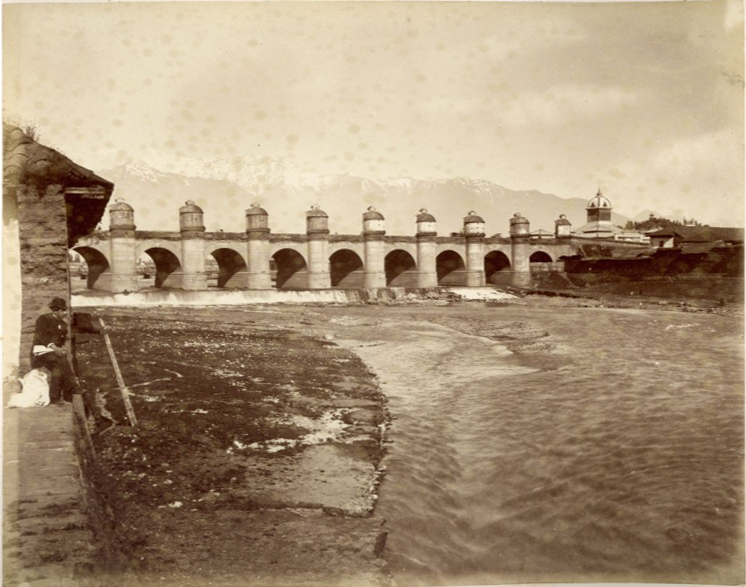
 Although early Santiago appeared to be in imminent danger of permanent destruction, threatened by Indigenous attacks, earthquakes, and a series of
Although early Santiago appeared to be in imminent danger of permanent destruction, threatened by Indigenous attacks, earthquakes, and a series of floods
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrolog ...
, the city began to grow rapidly. Of the 126 blocks designed by Gamboa in 1558, 40 were occupied, and in 1580, the first major buildings in the city began to rise, the start of construction highlighted with the placing of the foundation stone of the first Cathedral in 1561 and the building of the church of San Francisco in 1572. Both of these constructions consisted of mainly adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of e ...
and stone. In addition to construction of important buildings, the city began to develop as nearby lands welcomed tens of thousands of livestock.
A series of disasters impeded the development of the city during the 16th and 17th centuries: an earthquake, a 1575 smallpox epidemic, in 1590, 1608, and 1618, the Mapocho River floods, and, finally, the earthquake of 13 May 1647, which killed over 600 people and affected more than 5,000 others. However, these disasters would not stop the growth of the capital of the Captaincy General of Chile at a time when all the power of the country was centered on the Plaza de Armas santiaguina.
In 1767, the corregidor Luis Manuel de Zañartu
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archai ...
, launched one of the most important architectural works of the entire colonial period, Calicanto Bridge, effectively connecting the city to La Chimba
LA most frequently refers to Los Angeles, the second largest city in the United States.
La, LA, or L.A. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* La (musical note), or A, the sixth note
* "L.A.", a song by Elliott Smith on ''Figur ...
on the north side of the river, and began the construction of embankments to prevent overflows of the Mapocho River. Although its builders were able to complete the bridge, the piers were constantly being damaged by the river. In 1780, Governor Agustín de Jáuregui
Agustín de Jáuregui y Aldecoa (May 17, 1708/1711 – April 29, 1784) was a Spanish politician and soldier who served as governor of Chile (1772–80) and viceroy of Peru (1780–84).
Early life
Jáuregui was born in Lecároz, the son of Matías ...
hired the Italian architect Joaquín Toesca
Gioacchino Toesca e Ricci (1745–1799; known as Joaquín Toesca in the Spanish Empire) was an Italian architect who worked at the service of the Spanish Empire, mainly in Chile. He was mainly a Neoclassical architect although he also built Baro ...
, who would design, among other important works, the façade of the cathedral, the Palacio de La Moneda, the canal San Carlos
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow unde ...
, and the final construction of the embankments during the government of Ambrosio O'Higgins. These important works were opened permanently in 1798. The O'Higgins government also oversaw the opening of the road to Valparaíso in 1791, which connected the capital with the country's main port.
Capital of the Republic
 18 September 1810 was proclaimed the First Government Junta in Santiago, beginning the process of establishing the independence of Chile. The city, which became the capital of the new nation, was threatened by various events, especially the nearby military actions.
Although some institutions, such as the
18 September 1810 was proclaimed the First Government Junta in Santiago, beginning the process of establishing the independence of Chile. The city, which became the capital of the new nation, was threatened by various events, especially the nearby military actions.
Although some institutions, such as the National Institute National Institute may refer to:
* National Institute on Aging, United States (U.S.)
* National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S.
* National Institute of Mental Health, U.S.
* Belgranian National Institute, Argentina
* San Martín National Ins ...
and the National Library, were installed in the Patria Vieja
Patria Vieja (, ) refers to a time period in the History of Chile occurring between the First Junta of the Government (September 18, 1810) and the Disaster of Rancagua (October 1, 1814). In this period, Chilean measures were taken for the impri ...
, they were closed after the patriot defeat at the Battle of Rancagua in 1814. The royal government lasted until 1817, when the Army of the Andes secured victory in battle of Chacabuco, reinstating the patriot government in Santiago. Independence, however, was not assured. The Spanish army gained new victories in 1818 and headed for Santiago, but their march was definitively halted on the plains of the Maipo River, during the Battle of Maipú
The Battle of Maipú ( es, Batalla de Maipú) was a battle fought near Santiago, Chile on April 5, 1818, between South American rebels and Spanish royalists, during the Chilean War of Independence. The Patriot rebels led by Argentine general Jo ...
on 5 April 1818.
 With the end of the war, Bernardo O'Higgins was accepted as Supreme Director and, like his father, began a number of important works for the city. During the call Patria Nueva, closed institutions reopened. The
With the end of the war, Bernardo O'Higgins was accepted as Supreme Director and, like his father, began a number of important works for the city. During the call Patria Nueva, closed institutions reopened. The General Cemetery
''General Cemetery'' (Spanish: ''Cementerio general'') is a 2013 Peruvian supernatural horror film directed by Dorian Fernandez Moris. Written by Javier Velasquez, the plot is based on urban legends in the city's main cemetery. The film stars Air ...
opened, work on the canal San Carlos
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow unde ...
was completed, and, in the south arm of the Mapocho River, known as La Cañada, the drying riverbed, used for sometime as a landfill, was turned into an avenue, now known as the Alameda de las Delicias.
Two new earthquakes hit the city, one on 19 November 1822, and another on 20 February 1835. These two events, however, did not prevent the city's rapid, continued growth. In 1820 the city reported 46,000 inhabitants, while in 1854, the population reached 69,018. In 1865, the census reported 115,337 inhabitants. This significant increase was the result of suburban growth to the south and west of the capital, and in part to La Chimba, a vibrant district growing from the division of old properties that existed in the area. This new peripheral development led to the end of the traditional checkerboard structure that previously governed the city center.
19th century
 During the years of the Republican era, institutions such as the University of Chile (Universidad de Chile), the Normal School of Preceptors, the School of Arts and Crafts, and the Quinta Normal, which included the Museum of Fine Arts (now Museum of Science and Technology) and the National Museum of Natural History, were founded. Created primarily for educational use, they also became examples of public planning during that period. In 1851 the first telegraph system connecting the capital with the Port of Valparaíso was inaugurated.
During the years of the Republican era, institutions such as the University of Chile (Universidad de Chile), the Normal School of Preceptors, the School of Arts and Crafts, and the Quinta Normal, which included the Museum of Fine Arts (now Museum of Science and Technology) and the National Museum of Natural History, were founded. Created primarily for educational use, they also became examples of public planning during that period. In 1851 the first telegraph system connecting the capital with the Port of Valparaíso was inaugurated.Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna
Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna (August 25, 1831 – January 25, 1886) was a Chilean writer, journalist, historian and politician. Vicuña Mackenna was of Irish and Basque descent.
Biography
Benjamín Vicuña Mackenna was born in Santiago, the ...
. Among the main works during this period are the remodeling of the Cerro Santa Lucía which, despite its central location, had been in a state of poor repair.[ In an effort to transform Santiago, Vicuña Mackenna began construction of the ''Camino de Cintura'', a road surrounding the entire city. A new redevelopment of the ]Alameda Avenue
Avenida Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins ( en, General Liberator Bernardo O'Higgins Avenue), popularly known as La Alameda (meaning, a street bordered by poplar trees), is the main avenue of Santiago, Chile. It runs east-west in the center o ...
turned it into the main road of the city.
 Also during this time and with the work of European landscapers in 1873, O'Higgins Park came into existence. The park, open to the public, became a landmark in Santiago due to its large gardens, lakes, and carriage trails. Other important buildings were opened during this era, such as the Teatro Municipal opera house, and the
Also during this time and with the work of European landscapers in 1873, O'Higgins Park came into existence. The park, open to the public, became a landmark in Santiago due to its large gardens, lakes, and carriage trails. Other important buildings were opened during this era, such as the Teatro Municipal opera house, and the Club Hípico de Santiago
Club Hípico de Santiago is a thoroughbred horse race track in Santiago, Chile.
History
The Club Hípico de Santiago, opened in 1870, is Chile's oldest racetrack and home to South America's oldest stakes race, the Clásico El Ensayo. It is one ...
. At the same time, the 1875 International Exposition was held in the grounds of the Quinta Normal.Santiago Estación Central railway station
Alameda (unofficially Estación Central) is a major railway station in Santiago, Chile, serving the south of the country, and is the city's primary and railway station, and is the only major railway station in Santiago after the closure of Mapoc ...
. Under construction at the time, the station would be opened permanently in 1884. During those years, railways connected the city to Valparaíso as well as regions in the north and south of Chile. The streets of Santiago were paved and by 1875 there were 1,107 railway cars in the city, while 45,000 people used tram services on a daily basis.
The centennial Santiago
 With the arrival of the new century, the city began to experience various changes related to the strong development of industry. Valparaíso, which had hitherto been the economic center of the country slowly lost prominence at the expense of the capital. By 1895, 75% of the national manufacturing industry was in the capital and only 28% in the harbor city, and by 1910, major banks and shops were set up in the streets of the city center, leaving Valparaíso.
The enactment of the Autonomous Municipalities' act allowed municipalities to create various administrative divisions around the then Santiago ''departamento'', with the aim of improving local ruling. Maipú, Ñuñoa, Renca, Lampa and Colina were to be created in 1891, Providencia and Barrancas in 1897, and
With the arrival of the new century, the city began to experience various changes related to the strong development of industry. Valparaíso, which had hitherto been the economic center of the country slowly lost prominence at the expense of the capital. By 1895, 75% of the national manufacturing industry was in the capital and only 28% in the harbor city, and by 1910, major banks and shops were set up in the streets of the city center, leaving Valparaíso.
The enactment of the Autonomous Municipalities' act allowed municipalities to create various administrative divisions around the then Santiago ''departamento'', with the aim of improving local ruling. Maipú, Ñuñoa, Renca, Lampa and Colina were to be created in 1891, Providencia and Barrancas in 1897, and Las Condes
Las Condes is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. The area is inhabited primarily by upper-mid- to high income families, and known in the Chilean collective consciousness as home to the country's economi ...
in 1901. The La Victoria ''departamento'' was split with the creation of Lo Cañas
Lo may refer to any of the following:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lo!'', the third published nonfiction work of the author Charles Fort
* L.O., a fictional character in the Playhouse Disney show Happy Monster Band
* ''Lo'' (film), a 2009 indep ...
in 1891, which would be split into La Granja and Puente Alto Puente, a word meaning ''bridge'' in Spanish language, may refer to:
People
* Puente (surname)
Places
*La Puente, California, USA
* Puente Alto, city and commune of Chile
*Puente de Ixtla, city in Mexico
*Puente Genil, village in the Spanish provi ...
in 1892, La Florida in 1899, and La Cisterna
La Cisterna (, Spanish for "the cistern") is a commune of Chile and census-designated city located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It was founded on 30 May 1925. It is part of Greater Santiago.
Demographics
According to the ...
in 1925.
The San Cristobal Hill in this period began a long process of development. In 1903 an astronomical observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. His ...
was installed and the following year the first stone was placed for its 14-meter Virgin Mary statue, nowadays visible from various points of city. However, the shrine would not be completed until some decades later.
With the 1910 Chile Centennial celebrations, many urban projects were undertaken. The railway network was extended allowing connection of the city with its nascent suburbs by a new rail ring and route to the Cajón del Maipo
Cajón del Maipo is a canyon located in the Andean southeastern portion of the Santiago Metropolitan Region, Chile. It encompasses the upper Maipo River basin, where the river has entrenched itself in a narrow valley. The zone features a series ...
, while a new railway station was built in the north of the city: the Mapocho Station. At the Mapocho river's southern side, the Parque Forestal was created and new buildings such as the Museum of Fine Arts, the Barros Arana public boarding school and the National Library were opened. In addition, the work would include a sewer system, covering about 85% of the urban population.
Population explosion
 The 1920 census estimated the population of Santiago to be 507,296 inhabitants, equivalent to 13.6% of the population of Chile. This represented an increase of 52.5% from the census of 1907, i.e. an annual growth of 3.3%, almost three times the national figure. This growth was mainly due to the arrival of farmers from the south who came to work in factories and railroads which were under construction. However, this growth was experienced on the outskirts and not in the town itself.
The 1920 census estimated the population of Santiago to be 507,296 inhabitants, equivalent to 13.6% of the population of Chile. This represented an increase of 52.5% from the census of 1907, i.e. an annual growth of 3.3%, almost three times the national figure. This growth was mainly due to the arrival of farmers from the south who came to work in factories and railroads which were under construction. However, this growth was experienced on the outskirts and not in the town itself.
 During this time the downtown district was consolidated into a commercial, financial and administrative center, with the establishment of various portals and locales around Ahumada Street and a Civic District in the immediate surroundings of the
During this time the downtown district was consolidated into a commercial, financial and administrative center, with the establishment of various portals and locales around Ahumada Street and a Civic District in the immediate surroundings of the Palace of La Moneda
Palacio de La Moneda (, ''Palace of the Mint''), or simply La Moneda, is the seat of the President of the Republic of Chile. It also houses the offices of three cabinet ministers: Interior, General Secretariat of the Presidency and General Secre ...
. The latter project involved the construction of various modernist buildings for the establishment of the offices of ministries
Ministry may refer to:
Government
* Ministry (collective executive), the complete body of government ministers under the leadership of a prime minister
* Ministry (government department), a department of a government
Religion
* Christian mi ...
and other public services, as well as commencing the construction of medium-rise buildings. On the other hand, the traditional inhabitants of the center began to migrate out of the city to more rural areas like Providencia and Ñuñoa, which hosted the oligarchy and the European immigrant professionals, and San Miguel for middle-class families. Furthermore, in the periphery villas were built various partners from various organizations of the time. Modernity expanded in the city, with the appearance of the first theaters, the extension of the telephone network and the opening of the Airport Los Cerrillos in 1928, among other advances.
 The feeling that the early 20th century was an era of economic growth due to technological advances contrasted dramatically with the standard of living of lower social classes. The growth of the previous decades led to an unprecedented population explosion starting in 1929. The
The feeling that the early 20th century was an era of economic growth due to technological advances contrasted dramatically with the standard of living of lower social classes. The growth of the previous decades led to an unprecedented population explosion starting in 1929. The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
caused the collapse of the nitrate industry in the north, leaving 60,000 unemployed, which added to the decline in agricultural exports, resulting in a total number for the unemployed to be about 300,000 nationwide. These unemployed workers saw Santiago and its booming industry as the only chance to survive. Many migrants arrived in Santiago with nothing and thousands had to survive on the streets due to the great difficulty in finding a place they could rent. Widespread disease, including tuberculosis, claimed the lives of hundreds of the homeless. Unemployment and living costs increased dramatically whilst the salaries of the population of Santiago fell.
The situation would change only several years later with a new industrial boom fostered by CORFO and the expansion of the state apparatus from the late 1930s. At this time, the aristocracy lost much of its power and the middle class, composed of merchants, bureaucrats and professionals, acquired the role of setting national policy. In this context, Santiago began to develop a substantial middle- and lower-class population, while the upper classes sought refuge in the districts of the capital. Thus, the old moneyed class trips to Cousino and Alameda Park, lost hegemony over popular entertainment venues such as the National Stadium emerged in 1938.
Greater Santiago
In the following decades, Santiago continued to grow unabated. In 1940, the city accumulated 952,075 inhabitants, in 1952 this figure rose to 1,350,409 residents and the census of 1960 totaled 1,907,378 santiaguinos. This growth was reflected in the urbanization of rural areas on the periphery, where families of middle and lower class with stable housing were established: in 1930 the urban area had an area of 6500 hectares, which in 1960 reached 20,900 and in 1980 to 38,296. Although most of the communities continued to grow, it is mainly concentrated in outlying communities such as Barrancas to the west, Conchalí northern and La Cisterna
La Cisterna (, Spanish for "the cistern") is a commune of Chile and census-designated city located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It was founded on 30 May 1925. It is part of Greater Santiago.
Demographics
According to the ...
and La Granja to the south. For the upper class, it began to approach the foothills of Las Condes
Las Condes is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. The area is inhabited primarily by upper-mid- to high income families, and known in the Chilean collective consciousness as home to the country's economi ...
and La Reina sector. The center, however, lost people leaving more space for the development of trade, banking and government.
 Regulation of the growth only began to be implemented during the 1960s with the creation of various development plans for Greater Santiago, a concept that reflected the new reality of a much larger city. In 1958 the Intercommunal Plan of Santiago was released. The proposed scheme set a limit of 38 600 urban and semi hectares for a maximum population of 3,260,000 inhabitants, included plans for the construction of new avenues, like the Américo Vespucio Avenue and Panamericana route 5, and the expansion of 'industrial belts'. The celebration of the World Cup in 1962 gave new impetus to implement plans for city improvement. In 1966 the
Regulation of the growth only began to be implemented during the 1960s with the creation of various development plans for Greater Santiago, a concept that reflected the new reality of a much larger city. In 1958 the Intercommunal Plan of Santiago was released. The proposed scheme set a limit of 38 600 urban and semi hectares for a maximum population of 3,260,000 inhabitants, included plans for the construction of new avenues, like the Américo Vespucio Avenue and Panamericana route 5, and the expansion of 'industrial belts'. The celebration of the World Cup in 1962 gave new impetus to implement plans for city improvement. In 1966 the Santiago Metropolitan Park
The Santiago Metropolitan Park is an urban park located within the city of Santiago, capital of Chile. Consisting of the San Cristóbal, Chacarillas and Los Gemelos hills, and the areas of Tupahue, Lo Saldés, Pirámide and Bosque Santiago, the ...
was established in the Cerro San Cristóbal, MINVU began eradicating shanty towns and building new homes. Finally, the Edificio Diego Portales was constructed in 1972.
In 1967 the new International Airport Pudahuel was opened, and, after years of discussion, in 1969 construction began on the Santiago Metro. The first phase ran beneath the western section of the Alameda and was opened in 1975. The Metro would become one of the most prestigious buildings in the city. In the following years it continued to expand, with two perpendicular lines in place by the end of 1978. Building telecommunications infrastructure was also an important development of this period, as reflected in the construction of the Torre Entel, which since its construction in 1975 has become one of the symbols of the capital and the tallest structure in the country for two decades.
After the coup of 1973 and the establishment of the military regime, major changes in urban planning did not take place until the 1980s, when the government adopted a neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent fa ...
economic model. In 1979, the master plan was amended. The urban area was extended to more than 62 000 ha for real estate development. This created urban sprawl, especially in La Florida, with the city reaching 40 619 ha in size in the early 1990s. The 1992 census showed that Santiago had become the country's most populous municipality with 328,881 inhabitants. Meanwhile, a strong earthquake struck the city on 3 March 1985. Although it caused few casualties, it left many people homeless and destroyed many old buildings.
The metropolis in the early twenty-first century

 With the start of the transition to democracy in 1990, the city of Santiago had surpassed three million inhabitants, with the majority living in the south: La Florida was the most populous area, followed by
With the start of the transition to democracy in 1990, the city of Santiago had surpassed three million inhabitants, with the majority living in the south: La Florida was the most populous area, followed by Puente Alto Puente, a word meaning ''bridge'' in Spanish language, may refer to:
People
* Puente (surname)
Places
*La Puente, California, USA
* Puente Alto, city and commune of Chile
*Puente de Ixtla, city in Mexico
*Puente Genil, village in the Spanish provi ...
and Maipú. The real estate development in these municipalities and others like Quilicura and Peñalolén largely came from the construction of housing projects for middle-class families. Meanwhile, high-income families moved into the foothills, now called Barrio Alto, increasing the population of Las Condes
Las Condes is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. The area is inhabited primarily by upper-mid- to high income families, and known in the Chilean collective consciousness as home to the country's economi ...
and giving rise to new communes like Vitacura
Vitacura is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It is one of the most expensive and fashionable areas of Santiago. Inhabitants are primarily high income families. It belongs to the Northeastern zone of ...
and Lo Barnechea
Lo Barnechea is a commune located in the northeastern zone of Santiago de Chile, northeastern sector of the province of Santiago and its area corresponds to 48% of this province. Its urban boundaries are: to the north with Los Andes, Chile, Los An ...
.
The Providencia Avenue
Avenida Providencia is a major thoroughfare in Santiago, Chile. It runs along the commune of Providencia.
Description
Providencia begins at the northern terminus of Vicuña Mackenna Avenue as a continuation of Alameda Avenue. Immediately, the op ...
area became an important commercial hub in the eastern sector. This development was extended to Barrio Alto, which became an attractive location for the construction of high-rise buildings. Major companies and financial corporations were established in the area, which gave rise to a thriving modern business center known as ''Sanhattan
Sanhattan, a portmanteau of ''Santiago'' and ''Manhattan'', is the popular ironic sobriquet given to Chile's capital Santiago's high-end financial district. It is located to the northeast of the capital, in the western end of the Las Condes commun ...
''. The departure of these companies to Barrio Alto and the construction of shopping centers all around the city created a crisis in the city center. To reinvent the area, the main shopping streets were turned into pedestrian walkways, such as the Paseo Ahumada, and the government instituted tax benefits for the construction of residential buildings, which attracted young adults.
The city began to face a series of problems generated by disorganized growth. Air pollution reached critical levels during the winter months and a layer of smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and '' fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then inte ...
settled over the city. The authorities adopted legislative measures to reduce industrial pollution and placed restrictions on vehicle use. The Metro was expanded considerably, lines were extended and three new lines were built between 1997 and 2006 in the southeastern sector. A new extension to Maipú was inaugurated in 2011, at which point the metropolitan railway had a total length of 105 km. In the case of bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
es, the system underwent a major reform in the early 1990s. In 2007 the master plan known as Transantiago
Red Metropolitana de Movilidad (English: ''Metropolitan Mobility Network''; named Transantiago until March 2019) is a public transport system that serves Santiago, the capital of Chile. It is considered the most ambitious transport reform undertak ...
was established. It has faced a number of problems since its launch.
Entering the twenty-first century, rapid development continued in Santiago. The Civic District was renewed with the creation of the Plaza de la Ciudadanía and construction of the Ciudad Parque Bicentenario
Ciudad () is the Spanish word for City
Ciudad may also refer to:
*La Ciudad (archaeological site), Hohokam ruins in Phoenix, Arizona
*La Ciudad, district of Durango City, Mexico
*''La ciudad'', novel by Mario Levrero 1970
*La Ciudad ''The City'' ...
to commemorate the bicentenary __NOTOC__
A bicentennial or bicentenary is the two-hundredth anniversary of a part, or the celebrations thereof. It may refer to:
Europe
*French Revolution bicentennial, commemorating the 200th anniversary of 14 July 1789 uprising, celebrated i ...
of the Republic. The development of tall buildings continues in the eastern sector, which culminated in the opening of the skyscrapers Titanium La Portada and Gran Torre Santiago
The Costanera Center Torre 2, better known as Gran Torre Santiago (Great Santiago Tower), and previously known as Torre Gran Costanera, is a 62-story skyscraper in Santiago, Chile, the second tallest in Latin America (behind Mexico's T.Op Torre ...
in the Costanera Center complex. However, socioeconomic inequality and geosocial fragmentation remain two of the most important problems in both the city and the country.
On 27 February 2010, a strong earthquake struck the capital, causing some damage to older buildings. However, some modern buildings were also rendered uninhabitable, generating much debate about the actual implementation of mandatory earthquake standards in the modern architecture of Santiago.
Geography
 The city lies in the center of the ''Santiago Basin'', a large bowl-shaped valley consisting of broad and fertile lands surrounded by mountains. The city has a varying elevation, gradually increasing from in the western areas to more than in the eastern areas. Santiago's
The city lies in the center of the ''Santiago Basin'', a large bowl-shaped valley consisting of broad and fertile lands surrounded by mountains. The city has a varying elevation, gradually increasing from in the western areas to more than in the eastern areas. Santiago's international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
, in the west, lies at an altitude of . Plaza Baquedano, near the center, lies at . Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo, at the eastern edge of the city, has an elevation of .
The Santiago Basin is part of the Intermediate Depression and is remarkably flat, interrupted only by a few "island hills;" among them are Cerro Renca, Cerro Blanco
Cerro Blanco is a hill and historical landmark in the city of Santiago, Chile. This geographic feature
rises above the surrounding terrain and covers a surface area of . It is bordered by Recoleta Avenue on the east, Santos Dumont Avenue on ...
, and Cerro Santa Lucía. The basin is approximately in a north–south direction and from east to west. The Mapocho River flows through the city.
The city is flanked by the main chain of the Andes to the east and the Chilean Coastal Range to the west. On the north, it is bordered by the ''Cordón de Chacabuco'', a mountain range of the Andes. At the southern border lies the ''Angostura de Paine'', an elongated spur of the Andes that almost reaches the coast.
The mountain range immediately bordering the city on the east is known as the Sierra de Ramón
Sierra (Spanish for "mountain range" and "saw", from Latin '' serra'') may refer to the following:
Places Mountains and mountain ranges
* Sierra de Juárez, a mountain range in Baja California, Mexico
* Sierra de las Nieves, a mountain range i ...
, which was formed due to tectonic activity of the San Ramón Fault The San Ramón ( es, Falla de San Ramón) is a Chilean geological fault, located in eastern Santiago Metropolitan Region, passing through the eastern part of Santiago marking the boundary between the Chilean Central Valley and the Andes. As an acti ...
. This range reaches 3296 meters at Cerro de Ramón
Cerro is Spanish for "hill" or "mountain".
Toponyms
;Bolivia:
* Cerro Rico, the "Rich Mountain" containing silver ore near Potosi, Bolivia
;Brazil:
*Cerro Branco, a municipality of Rio Grande do Sul
*Cerro Grande, Rio Grande do Sul, a municipa ...
. The Sierra de Ramón represents the "Precordillera
Precordillera is a Spanish geographical term for hills and mountains lying before a greater range, foothills. The term is derived from ''cordillera'' (mountain range)—literally "pre-mountain range"—and applied usually to the Andes.
Some places ...
" of the Andes. further east is the even larger Cordillera of the Andes, which has mountains and volcanoes that exceed and on which some glaciers are present. The tallest is the Tupungato mountain at . Other mountains include Tupungatito, San José
San José or San Jose (Spanish for Saint Joseph) most often refers to:
*San Jose, California, United States
*San José, Costa Rica, the nation's capital
San José or San Jose may also refer to:
Places Argentina
* San José, Buenos Aires
** San ...
, and Maipo. Cerro El Plomo
Cerro El Plomo is a mountain in the Andes near Santiago, Chile. With an elevation of 5,434 m (17,783 ft), it is the largest peak visible from Santiago on clear days. The adequate season to climb this mountain is between November and March. I ...
is the highest mountain visible from Santiago's urban area.
During recent decades, urban growth has outgrown the boundaries of the city, expanding to the east up the slopes of the Andean Precordillera
Precordillera is a Spanish geographical term for hills and mountains lying before a greater range, foothills. The term is derived from ''cordillera'' (mountain range)—literally "pre-mountain range"—and applied usually to the Andes.
Some places ...
. In areas such as La Dehesa, Lo Curro, and El Arrayan, urban development is present at over 1,000 meters of altitude.Vachellia caven
''Vachellia caven'' (Roman cassie, , aromo criollo, caven, , , espinillo, espinillo de baado, espino, espino maulino) is an ornamental tree in the family Fabaceae. ''Vachellia caven'' is native to Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay, and Urugua ...
'' (also known as ''Acacia caven'' and espinillo) and ''Prosopis chilensis
''Prosopis chilensis'' is a species of tree in the genus ''Prosopis'', belonging to the family Fabaceae. It is found in parts of central Chile, southern Peru, Bolivia, and Andean (northwestern) Argentina. Its common names include Chilean mesqui ...
'' in the west and an association of ''Vachellia caven'' and Baccharis paniculata
''Baccharis'' is a genus of perennials and shrubs in the aster family (Asteraceae). They are commonly known as baccharises but sometimes referred to as "brooms", because many members have small thin leaves resembling the true brooms. They are n ...
in the east around the Andean foothills.
File:La Parva, centro de esquí (2011D2021A).jpg, Ski Center La Parva
File:2019-04-06-12h10m43.jpg, Santiago Metropolitan Park
File:Santiago en invierno.jpg, Santiago in the winter
File:Santiago de Chile.jpg, Santiago in the summer
Climate
Santiago has a cool semi-arid climate (''BSk'' according to the Köppen climate classification), with Mediterranean (''Csb'') patterns: warm dry summers (October to March) with temperatures reaching up to on the hottest days; winters (April to September) are cool and humid, with cool to cold mornings; typical daily maximum temperatures of , and low temperatures near . In climate station of Quinta Normal (near downtown) the precipitation average is 341.8 mm, and in climate station of Tobalaba (in higher grounds near the Andes mountains) the precipitation average is 367.8 mm.
In the airport area of Pudahuel, mean rainfall is per year, about 80% of which occurs during the winter months (May to September), varying between of rainfall during these months. That amount contrasts with a very sunny season during the summer months between December and March, when rainfall does not exceed on average, caused by an anticyclonic dominance continued for about seven or eight months. There is significant variation within the city, with rainfall at the lower-elevation Pudahuel site near the airport being about 20 percent lower than at the older Quinta Normal site near the city center.
Santiago's rainfall is highly variable and heavily influenced by the El Niño Southern Oscillation
EL, El or el may refer to:
Religion
* El (deity), a Semitic word for "God"
People
* EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer
* El DeBarge, music artist
* El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American po ...
cycle, with rainy years coinciding with El Niño events and dry years with La Niña events.[Rutllant, Josè and Fuenzalida, Humberto; "Synoptic Aspects of the Central Chile Rainfall Variability Associated with the Southern Oscillation," ''International Journal of Climatology'', vol. 11 (1991), pp. 63–76] The wettest year since records began in 1866 was 1900 with [ Paskoff, Roland P.; "Geomorphological Processes and Characteristic Landforms in the Mediterranean Regions of the World," ''Mediterranean Type Ecosystems''; in ''Ecological Studies'', Volume 7, 1973, pp. 53–60] – part of a "pluvial" from 1898 to 1905 that saw an average of over eight years incorporating the second wettest year in 1899 with – and the driest 1924 with .Precordillera
Precordillera is a Spanish geographical term for hills and mountains lying before a greater range, foothills. The term is derived from ''cordillera'' (mountain range)—literally "pre-mountain range"—and applied usually to the Andes.
Some places ...
, being rare in eastern districts, and extremely rare in most of the city.[ In winter, the ]snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
is about , and it ranges from .[''René Garreaud-Salazar']
"Impacto en la variabilidad de la línea de nieve en crecidas invernales en cuencas pluvio-nivales de Chile central"
. Sociedad Chilena de Ingeniería Hidráulica, XI Congreso Chileno. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
The city is affected only occasionally by snowfall. The period between 2000 and 2017 has been registered 9 snowfalls and only two have been measured in the central sector (2007 and 2017). The amount of snow registered in Santiago on 15 July 2017 ranged between 3.0 cm in Quinta Normal and 10.0 cm in La Reina (Tobalaba).
Temperatures vary throughout the year from an average of in January to in June and July. In the summer days are very warm to hot, often reaching over and a record high close to , while nights are very pleasant and cool, at . During autumn and winter the temperature drops, and is slightly lower than . The temperature may even drop to , especially during the morning. The historic low of was in July 1976.[
Santiago's location within a watershed is one of the most important factors determining the climate of the city. The coastal mountain range serves as a screen that stops the spread of maritime influence, contributing to the increase in annual and daily thermal oscillation (the difference between the maximum and minimum daily temperatures can reach 14 °C) and maintaining low relative humidity, close to an annual average of 70%. It also prevents the entry of air masses, with the exception of some coastal low clouds that penetrate to the basin through the river valleys.
Prevailing winds are from the southwest, with an average of , especially during the summer; the winter is less windy.
]
Natural disasters
Due to Santiago's location on the Pacific Ring of Fire at the boundary of the Nazca
Nazca (; sometimes spelled Nasca; qu, Naska) is a city and system of valleys on the southern coast of Peru. It is also the name of the largest existing town in the Nazca Province. The name is derived from the Nazca culture, which flourished in ...
and South American plate
The South American Plate is a major tectonic plate which includes the continent of South America as well as a sizable region of the Atlantic Ocean seabed extending eastward to the African Plate, with which it forms the southern part of the Mid-A ...
s, it experiences a significant amount of tectonic activity.[Buchenau, Jürgen, and Lyman L. Johnson. ''Aftershocks: Earthquakes and Popular Politics in Latin America''. Albuquerque: U of New Mexico, 2009. Print.] The first earthquake on record to strike Santiago occurred in 1575
__NOTOC__
Year 1575 ( MDLXXV) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–June
* January 21 – Queen Elizabeth I of England grants a monopoly on producin ...
, 34 years after the official founding of Santiago. The 1647 Santiago earthquake
The 1647 Santiago earthquake struck Santiago, Chile on the night of 13 May (22:30 local time, 02:30 UTC on 14 May) and is said to have brought virtually every building in the city to the ground. The earthquake was felt throughout the so-called Cap ...
devastated the city, and inspired Heinrich von Kleist's novel, ''The Earthquake In Chile
''The Earthquake in Chile'' (german: Das Erdbeben in Chili) is a short story written by Heinrich von Kleist (1777–1811) and published in 1807. The story's central characters are two lovers caught up in the chaos of the 1647 Santiago earthquake in ...
''.1960 Valdivia earthquake
The 1960 Valdivia earthquake and tsunami ( es, link=no, Terremoto de Valdivia) or the Great Chilean earthquake (''Gran terremoto de Chile'') on 22 May 1960 was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded. Various studies have placed it at 9.4– ...
and the 1985 Algarrobo earthquake
An earthquake measuring 8.0 struck Santiago Chile on 3 March 1985, and ended up killing 177 people and injuring about 2,575 others. This earthquake was being felt between the northern Antofagasta Region and the southern Los Lagos Region. It wa ...
both caused damage in Santiago, and led to the development of strict building codes with a view to minimizing future earthquake damage. In 2010 Chile was struck by the sixth largest earthquake ever recorded, reaching 8.8 on the moment magnitude scale. 525 people died, of whom 13 were in Santiago, and the damage was estimated at 15–30 billion US dollars. 370,000 homes were damaged, but the building codes implemented after the earlier earthquakes meant that despite the size of the earthquake, damage was far less than that caused a few weeks earlier by the 2010 Haiti earthquake
A disaster, catastrophic Moment magnitude scale, magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake struck Haiti at 16:53 local time (21:53 UTC) on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. The epicenter was near the town of Léogâne, Ouest (department), Ouest department, a ...
, in which at least 100,000 people died. Large megathrust earthquakes aside, smaller local faults in an around Santiago pose significant earthquake risks.[
The easternmost neighborhoods of the city lies in a zone prone to ]landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
s. Landslides of the debris flow type in particular are a significant hazard.
Environmental issues
Santiago's air is the most polluted air in Chile. In the 1990s air pollution fell by about one-third, but there has been little progress since 2000. A study by a Chilean university found in 2010 that pollution in Santiago had doubled since 2002. Particulate matter air pollution is a serious public health concern in Santiago, with atmospheric concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 regularly exceeding standards established by the US Environmental Protection Agency and World Health Organization.
A final major source of Santiago air pollution, one that continues year-round, is the smelter of the El Teniente copper mine. The government does not usually report it as being a local pollution source, as it is just outside the reporting area of the Santiago Metropolitan Region, being from downtown.
During winter months, thermal inversion (a meteorological phenomenon whereby a stable layer of warm air holds down colder air close to the ground) causes high levels of smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and '' fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then inte ...
and air pollution to be trapped and concentrated within the Central Valley.
As of March 2007, only 61% of the wastewater in Santiago was treated, which increased up to 71% by the end of the same year. However, in March 2012, the Mapocho Wastewater Treatment Plant began operations, increasing the wastewater treatment capacity of the city to 100%, making Santiago the first capital city in Latin America to treat all of its municipal sewage.
Stray dogs
A free-ranging dog is a dog that is not confined to a yard or house. Free-ranging dogs include street dogs, village dogs, stray dogs, feral dogs, etc., and may be owned or unowned. The global dog population is estimated to be 900 million, of w ...
are common in Santiago. However, rabies is practically non-existent in Chile.
Demographics
According to data collected in the 2002 census by the National Institute of Statistics, the Santiago metropolitan area population reached 5,428,590 inhabitants, equivalent to 35.9% of the national total and 89.6% of total regional inhabitants. This figure reflects broad growth in the population of the city during the 20th century: it had 383,587 inhabitants in 1907; 1,010,102 in 1940; 2,009,118 in 1960; 3,899,619 in 1982; and 4,729,118 in 1992.[Se consideran en total las comunas de la Provincia de Santiago, más ]Padre Hurtado
Padre Hurtado () is a Chilean commune in the Talagante Province, in the Metropolitan Region. Part of the Greater Santiago conurbation and one of the outermost communes of it, the commune is named after Saint Alberto Hurtado, who was popularly k ...
, Pirque, Puente Alto Puente, a word meaning ''bridge'' in Spanish language, may refer to:
People
* Puente (surname)
Places
*La Puente, California, USA
* Puente Alto, city and commune of Chile
*Puente de Ixtla, city in Mexico
*Puente Genil, village in the Spanish provi ...
y San Bernardo. Estas cifras no son equivalentes a la de la ciudad de Santiago pues excluyen ciertas áreas fuera de dichas comunas e incluyen algunas zonas rurales; sin embargo, representa a un 95,4% de la población total del área metropolitana. (percentage of total population, 2007) The growth of Santiago has undergone several changes over the course of its history. In its early years, the city had a rate of growth 2.9% annually until the 17th century, then down to less than 2% per year until the early 20th century figures. During the 20th century, Santiago experienced a demographic explosion as it absorbed migration from mining camps in northern Chile during the economic crisis of the 1930s. The population surged again via migration from rural sectors between 1940 and 1960. This migration was coupled with high fertility rates, and annual growth reached 4.9% between 1952 and 1960. Growth has declined, reaching 1.4% in the early 2000s. The size of the city expanded constantly; The 20,000 hectares Santiago covered in 1960 doubled by 1980, reaching 64,140 hectares in 2002. The population density in Santiago is 8,464 inhabitants/km2.
The population of Santiago
The growth of Santiago has undergone several changes over the course of its history. In its early years, the city had a rate of growth 2.9% annually until the 17th century, then down to less than 2% per year until the early 20th century figures. During the 20th century, Santiago experienced a demographic explosion as it absorbed migration from mining camps in northern Chile during the economic crisis of the 1930s. The population surged again via migration from rural sectors between 1940 and 1960. This migration was coupled with high fertility rates, and annual growth reached 4.9% between 1952 and 1960. Growth has declined, reaching 1.4% in the early 2000s. The size of the city expanded constantly; The 20,000 hectares Santiago covered in 1960 doubled by 1980, reaching 64,140 hectares in 2002. The population density in Santiago is 8,464 inhabitants/km2.
The population of Santiago[ has seen a steady increase in recent years. In 1990 the total population under 20 years was 38.0% and 8.9% were over 60. Estimates in 2007 show that 32.9% of men and 30.7% of women were less than 20 years old, while 10.2% of men and 13.4% of women were over 60 years. For the year 2020, it is estimated that the figures will be 26.7% and 16.8%.
4,313,719 people in Chile say they were born in one of the communes of the Santiago Metropolitan Region,][ which, according to the 2002 census, amounts to 28.5% of the national total. 67.6% of the inhabitants of Santiago claim to have been born in one of the communes of the metropolitan area. In communes such as ]Santiago Centro
The Commune of Santiago is the central commune of the Santiago Province, located at the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Region in Chile's Central Zone. Locally, Santiago is usually abbreviated ''Stgo.'' It is also called as "Santiago Centro" ...
and Independencia, according to 2017 census, 1/3 of residents is a Latin American immigrant (28% and 31% of the population of these communes, respectively).[ Canal 13]
Censo 2017: 28% de habitantes en la comuna de Santiago son inmigrantes
. Published: 2018-5-5. Other communes of Greater Santiago with high numbers of immigrants are Estación Central (17%) and Recoleta (16%).[Estas son las comunas de Chile con mayor porcentaje de población extranjera](_blank)
. ''24 Horas Chile''. Published 2018-5-5.
Economy
Santiago is the industrial and financial center of Chile, and generates 45% of the country's GDP. Some international institutions, such as ECLAC (Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean), have their offices in Santiago. The strong economy and low government debt is attracting migrants from Europe and the United States.
Santiago's steady economic growth over the past few decades has transformed it into a modern metropolis. The city is now home to a growing theater and restaurant scene, extensive suburban development, dozens of shopping centers, and a rising skyline, including the second tallest building in Latin America, the Gran Torre Santiago
The Costanera Center Torre 2, better known as Gran Torre Santiago (Great Santiago Tower), and previously known as Torre Gran Costanera, is a 62-story skyscraper in Santiago, Chile, the second tallest in Latin America (behind Mexico's T.Op Torre ...
. It includes several major universities, and has developed a modern transportation infrastructure, including a free flow
Open road tolling (ORT), also called all-electronic tolling, cashless tolling, or free-flow tolling, is the collection of tolls on toll roads without the use of toll booths. An electronic toll collection system is usually used instead. The m ...
toll-based, partly underground urban freeway system and the Metro de Santiago
The Santiago Metro ( es, Metro de Santiago) is a rapid transit system serving the city of Santiago, the capital of Chile. It currently consists of seven lines (numbered 1-6 and 4A), 136 stations, and of revenue route. The system is managed by th ...
, South America's most extensive subway system.
Santiago is an economically divided city ( Gini coefficient of 0.47). The western half (''zona poniente'') of the city is, on average, much poorer than the eastern communes, where the high-standard public and private facilities are concentrated.
Commercial development
 The Costanera Center, a mega project in Santiago's Financial District, includes a mall, a tower, two office towers of each, and a hotel tall. In January 2009 the retailer in charge,
The Costanera Center, a mega project in Santiago's Financial District, includes a mall, a tower, two office towers of each, and a hotel tall. In January 2009 the retailer in charge, Cencosud
Cencosud S.A. is a publicly traded multinational retail company. It's the largest retail company in Chile and the third largest listed retail company in Latin America, competing with the Brazilian Companhia Brasileira de Distribuição and the Mex ...
, said in a statement that the construction of the mega-mall would gradually be reduced until financial uncertainty is cleared. In January 2010, Cencosud announced the restart of the project, and this was taken generally as a symbol of the country's success over the global financial crisis. Close to Costanera Center another skyscraper is already in use, Titanium La Portada, tall. Although these are the two biggest projects, there are many other office buildings under construction in Santiago, as well as hundreds of high rise residential buildings. In February 2011, Gran Torre Santiago
The Costanera Center Torre 2, better known as Gran Torre Santiago (Great Santiago Tower), and previously known as Torre Gran Costanera, is a 62-story skyscraper in Santiago, Chile, the second tallest in Latin America (behind Mexico's T.Op Torre ...
, part of the Costanera Center project, located in the called Sanhattan
Sanhattan, a portmanteau of ''Santiago'' and ''Manhattan'', is the popular ironic sobriquet given to Chile's capital Santiago's high-end financial district. It is located to the northeast of the capital, in the western end of the Las Condes commun ...
district, reached the 300-meter mark, officially becoming the tallest structure in Latin America.
Commerce
Santiago is Chile's retail capital. Falabella
The Falabella is an Argentine list of horse breeds, breed of small horse. It is among the smallest of horse breeds, with a height at the withers in the range ..
History
The ancestral stock of the horse of South America descended from horses bro ...
, Paris, Johnson, Ripley
Ripley may refer to:
People and characters
* Ripley (name)
* ''Ripley'', the test mannequin aboard the first International Space Station space station Dragon 2 space test flight Crew Dragon Demo-1
* Ellen Ripley, a fictional character from the Ali ...
, La Polar
La Polar is the fourth largest retail company in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a lo ...
, and several other department stores dot the mall landscape of Chile. The east side neighborhoods like Vitacura
Vitacura is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. It is one of the most expensive and fashionable areas of Santiago. Inhabitants are primarily high income families. It belongs to the Northeastern zone of ...
, La Dehesa
La Dehesa is a suburban neighborhood in Lo Barnechea Commune of Santiago, Chile. It borders Las Condes to the south and Vitacura to the west. It is located in a valley near the Andes, in the northeast of the city, north of the Mapocho River. ...
, and Las Condes
Las Condes is a commune of Chile located in Santiago Province, Santiago Metropolitan Region. The area is inhabited primarily by upper-mid- to high income families, and known in the Chilean collective consciousness as home to the country's economi ...
are home to Santiago's Alonso de Cordova street, and malls like Parque Arauco, Alto Las Condes
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: ''altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In 4-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in choruses by ...
, Mall Plaza (a chain of malls present in Chile and other Latin American countries) and Costanera Center are known for their luxurious shopping. Alonso de Cordova, Santiago's equivalent to Rodeo Drive or Rua Oscar Freire in São Paulo, has exclusive stores like Louis Vuitton, Hermès, Emporio Armani, Salvatore Ferragamo, Ermenegildo Zegna, Swarovski
Swarovski (, ) is an Austrian producer of glass based in Wattens, Austria, and has existed as a family-owned business since its founding in 1895 by Daniel Swarovski.
The company is split into three major industry areas: the Swarovski Crystal ...
, MaxMara, Longchamp, and others. Alonso de Cordova also houses some of Santiago's most famous restaurants, art galleries, wine showrooms and furniture stores. The Costanera Center has stores like Armani Exchange, Banana Republic, Façonnable, Hugo Boss, Swarovski
Swarovski (, ) is an Austrian producer of glass based in Wattens, Austria, and has existed as a family-owned business since its founding in 1895 by Daniel Swarovski.
The company is split into three major industry areas: the Swarovski Crystal ...
, and Zara (retailer), Zara. There are plans for a Saks Fifth Avenue in Santiago. Several mercados in the city such as the Mercado Central de Santiago sell local goods. Barrio Bellavista and Barrio Lastarria have some of the most exclusive night clubs, chic cafés and restaurants.
Transport
Air
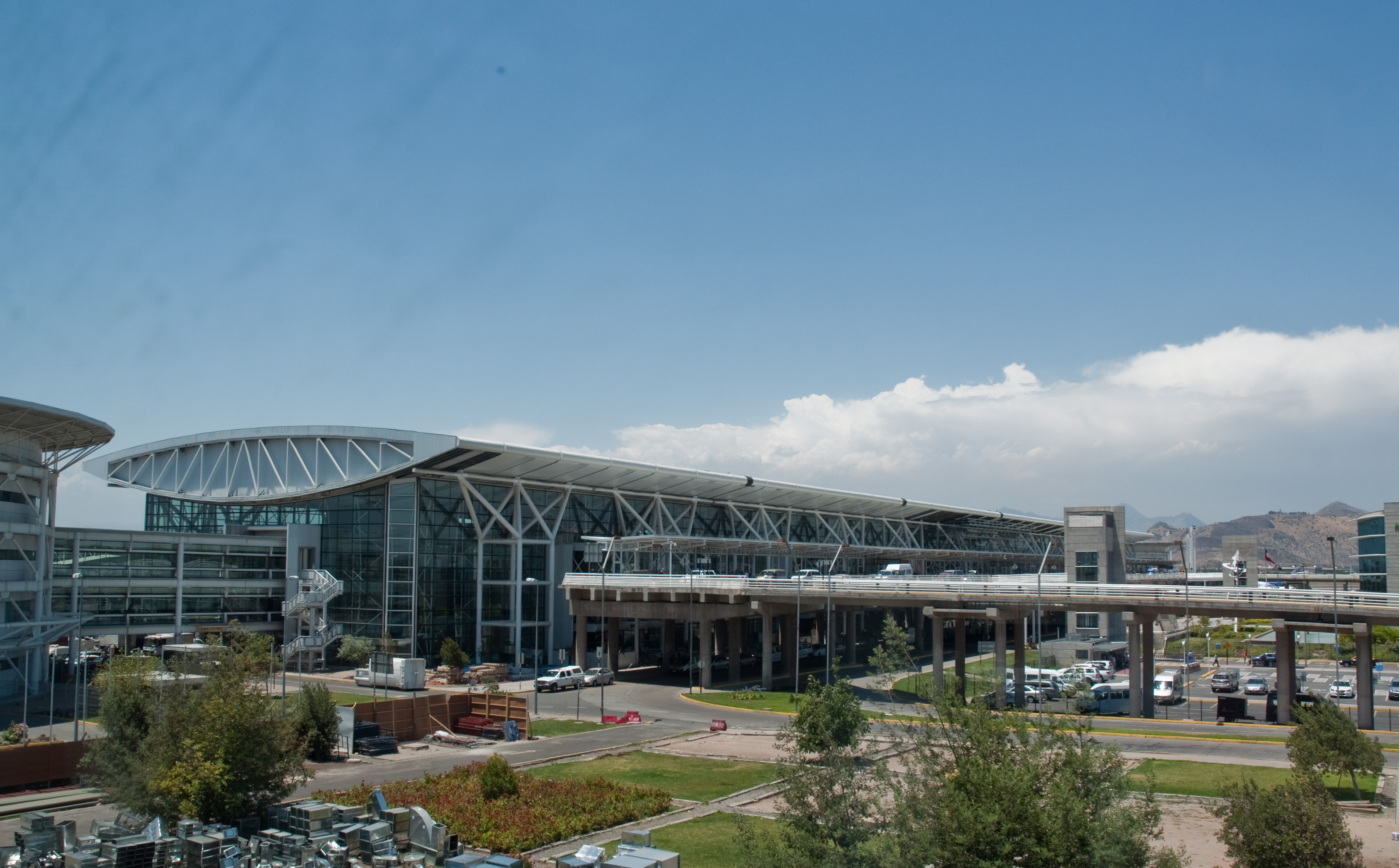 Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport (IATA: SCL) is Santiago's national and international airport and the principal airline hub, hub of LATAM Chile, LATAM Airlines, Sky Airline, Aerocardal and JetSmart. The airport is located in the western commune of Pudahuel. The largest airport in Chile, it is ranked sixth in passenger traffic among Latin American airports, with 14,168,282 passengers served in 2012 – a 17% increase over 2011. It is located 15 km from the city center.
Peldehue airport in Colina began operations on December 13, 2021. It will be able to service up to 25 flights per hour.
Santiago is also served by Eulogio Sánchez Airport (ICAO: SCTB), a small, privately owned general aviation airport in the commune of La Reina.
Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport (IATA: SCL) is Santiago's national and international airport and the principal airline hub, hub of LATAM Chile, LATAM Airlines, Sky Airline, Aerocardal and JetSmart. The airport is located in the western commune of Pudahuel. The largest airport in Chile, it is ranked sixth in passenger traffic among Latin American airports, with 14,168,282 passengers served in 2012 – a 17% increase over 2011. It is located 15 km from the city center.
Peldehue airport in Colina began operations on December 13, 2021. It will be able to service up to 25 flights per hour.
Santiago is also served by Eulogio Sánchez Airport (ICAO: SCTB), a small, privately owned general aviation airport in the commune of La Reina.
Rail

 Trains operated by Chile's national railway company, Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE), connect Santiago to several cities in the south-central part of the country: Rancagua, San Fernando, Chile, San Fernando, Talca (connected to the coastal city of Constitución, Chile, Constitución by a different train service), Linares, Chile, Linares and Chillán. All such trains arrive and depart from the Estación Central railway station (Central Station), which can be accessed by bus or subway. The proposed Santiago–Valparaíso railway line would connect Santiago with Valparaíso in 45 minutes, and expansions of the commuter rail network to Melitrén, Melipilla and Santiago-Batuco commuter rail, Batuco are under discussion.
Trains operated by Chile's national railway company, Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE), connect Santiago to several cities in the south-central part of the country: Rancagua, San Fernando, Chile, San Fernando, Talca (connected to the coastal city of Constitución, Chile, Constitución by a different train service), Linares, Chile, Linares and Chillán. All such trains arrive and depart from the Estación Central railway station (Central Station), which can be accessed by bus or subway. The proposed Santiago–Valparaíso railway line would connect Santiago with Valparaíso in 45 minutes, and expansions of the commuter rail network to Melitrén, Melipilla and Santiago-Batuco commuter rail, Batuco are under discussion.
Inter-urban buses
Bus companies provide passenger transportation from Santiago to most areas of the country as well as to foreign destinations, while some also provide parcel shipping and delivery services.
There are several bus terminals in Santiago:
* Terminal San Borja: located in Metro station "Estación Central metro station, Estación Central." Provides buses to all destinations in Chile and to some towns around Santiago.
* Terminal Alameda: located in Metro station "Universidad de Santiago." Provides buses to all destinations in Chile.
* Terminal Santiago: located one block west of Terminal Alameda. Provides buses to all destinations in Chile as well as to destinations in most countries in South America, except Bolivia.
* Terrapuerto Los Héroes: located two blocks east of Metro station "Los Héroes." Provides buses to south of Chile and some northern cities, as well as Argentina (Mendoza and Buenos Aires) and Paraguay (Asunción).
* Terminal Pajaritos: located in Metro station "Pajaritos." Provides buses to the international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
, inter-regional services to Valparaíso, Viña del Mar and several other coastal cities and towns.
* Terminal La Cisterna: located in Metro station "La Cisterna." Provides buses to towns around southern Santiago, Viña del Mar, Temuco and Puerto Montt.
* Terminal La Paz: located about two blocks away from the fresh fruit and vegetables market "Vega Central;" the closest Metro station is "Puente Cal y Canto." It connects the rural areas north of Santiago.
Highways
 A network of
A network of free flow
Open road tolling (ORT), also called all-electronic tolling, cashless tolling, or free-flow tolling, is the collection of tolls on toll roads without the use of toll booths. An electronic toll collection system is usually used instead. The m ...
toll highways connects the various areas of the city. They include the Vespucio Norte and Vespucio Sur highways, which surround the city completing a nearly full circle; Autopista Central, the section of the Pan American highway crossing the city from north to south, divided in two highways apart; and the Costanera Norte, running next to the Mapocho River and connecting the international airport with the downtown and with the wealthier areas of the city to the east, where it divides into two highways.
Other non-free flow toll roads connecting Santiago to other cities, include: Rutas del Pacífico (Chile Route 68, Ruta 68), the continuation of the Avenida Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins, ''Alameda'' Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins Avenue to the west, provides direct access to Valparaíso and Viña del Mar; Autopista del Sol (Ruta 78), connects Melipilla and the port of San Antonio, Chile, San Antonio with the capital; Autopista Ruta del Maipo (a.k.a. "Acceso Sur") is an alternative to the Pan American highway to access the various localities south of Santiago; Autopista Los Libertadores provides access to the main border crossing to Argentina, via Colina and Los Andes, Chile, Los Andes; and Autopista Nororiente, which provides access to the suburban development known as Chicureo, north of the capital.
Public transport
 Santiago has 37% of Chile's vehicles, with a total of 991,838 vehicles, 979,346 of which are motorized. An extensive network of streets and avenues stretching across Santiago facilitate travel between the different communities that make up the metropolitan area.
In the 1990s the government attempted to reorganize the public transport system. New routes were introduced in 1994 and the buses were painted yellow. The system, however, had serious issues with routes overlapping, high levels of air and noise pollution, and safety problems for both riders and drivers. To tackle these issues a new transport system, called
Santiago has 37% of Chile's vehicles, with a total of 991,838 vehicles, 979,346 of which are motorized. An extensive network of streets and avenues stretching across Santiago facilitate travel between the different communities that make up the metropolitan area.
In the 1990s the government attempted to reorganize the public transport system. New routes were introduced in 1994 and the buses were painted yellow. The system, however, had serious issues with routes overlapping, high levels of air and noise pollution, and safety problems for both riders and drivers. To tackle these issues a new transport system, called Transantiago
Red Metropolitana de Movilidad (English: ''Metropolitan Mobility Network''; named Transantiago until March 2019) is a public transport system that serves Santiago, the capital of Chile. It is considered the most ambitious transport reform undertak ...
, was devised. The system was launched in earnest on 10 February 2007, combining core services across the city with the subway and with local feeder routes, under a unified system of payment through a Contactless smart card, contactless smartcard called "Tarjeta bip!" The change was not well received by users, who complained of lack of buses, too many bus-to-bus transfers, and diminished coverage. Some of these problems were resolved, but the system earned a bad reputation which it has not been able to shake off. , the fare evasion rate is stubbornly high.
In 2019, the government introduced the new public transport system named Red Metropolitana de Movilidad, RED.
In recent years many cycle paths have been constructed, but so far the number is limited and with little connections between the routes. Most cyclists ride on the street, and the use of helmets and lights is not widespread, even though it is mandatory.

Metro
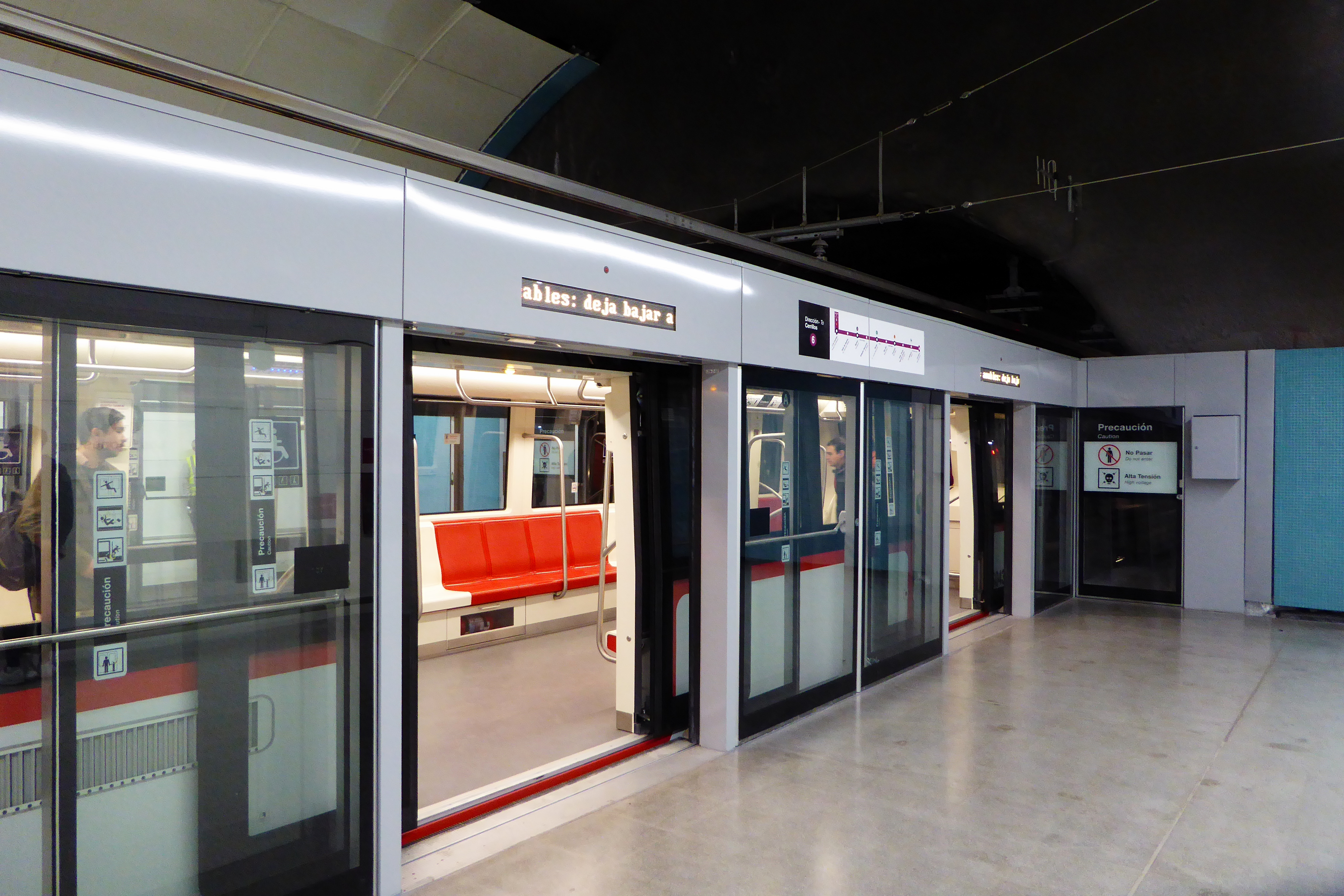 Santiago Metro has six operating lines (1, 2, 3, 4, 4A, 5 and 6), extending over and connecting 118 stations. The system carries around 2,400,000 passengers per day. Two underground lines (Line 4 and 4A) and an extension of Line 2 were inaugurated in 2005 and 2006, while an extension of Line 5 was inaugurated in 2011.
Santiago Metro has six operating lines (1, 2, 3, 4, 4A, 5 and 6), extending over and connecting 118 stations. The system carries around 2,400,000 passengers per day. Two underground lines (Line 4 and 4A) and an extension of Line 2 were inaugurated in 2005 and 2006, while an extension of Line 5 was inaugurated in 2011.
Commuter rail
EFE provides suburban rail service under the brandname of Metrotren. There are 2 southbound routes. The most popular is the Metrotren Nos service, between the Central Station of Santiago and Nos station, in San Bernardo. This line, inaugurated in 2017, serves 8 million people per year, with 12 trains serving 10 stations with a frequency of 6 minutes during rush hours, and 12 during the rest of the time. The other route is the Metrotren Rancagua service, between the Central Station of Santiago and the Rancagua station, connecting Santiago with the regional capital of O'Higgins.
Bus

Transantiago
Red Metropolitana de Movilidad (English: ''Metropolitan Mobility Network''; named Transantiago until March 2019) is a public transport system that serves Santiago, the capital of Chile. It is considered the most ambitious transport reform undertak ...
is the name for the city's public transport system. It works by combining local (feeder) bus lines and main bus lines, as well for the EFE commuter trains and the Metro network. It includes an integrated fare system, which allows passengers to make bus-to-bus, bus-to-metro or bus-to-train transfers for the price of one ticket, using a contactless smartcard (bip!). This system also offers reduced fares for the elderly, as well as high school and university students.
Vehicles for hire
Taxicabs are common in Santiago and are painted black with yellow roofs and have orange license plates. So-called ''radiotaxis'' may be called up by telephone and can be any make, model, or color but should always have the orange plates. ''Colectivos'' are shared taxicabs that carry passengers along a specific route for a fixed fee.
Cabify, Uber and DiDi also operate in Santiago.
Public transportation statistics
The average amount of time people spend commuting with public transit in Santiago - to and from work, for example - on a weekday is 84 min. 23% of public transit riders ride for more than 2 hours every day. The average amount of time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is 15 min, while 21% of riders wait for over 20 minutes on average every day. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is 7.4 km, while 15% travel for over 12 km in a single direction.
Internal transport
 As of 2006, Santiago was home to 992,000 vehicles, 979,000 of which were motorized. This made up 37.3% of Chile's total vehicle count. 805,000 cars passed through the city, which is 37.6% of the national total or one car for every seven people.
The main road is the Avenida Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins, better known as Alameda Avenue, which runs northeast and southwest. From north to south, it is crossed by Autopista Central and the Independencia Avenue (Santiago de Chile), Independencia, Gran Avenida José Miguel Carrera, Gran Avenida, Avenida Recoleta, Recoleta, Avenida Santa Rosa, Santa Rosa, Vicuña Mackenna Avenue, Vicuña Mackenna and Tobalaba Avenida, Tobalaba avenues. Other major roads include the Avenida Los Pajaritos to the west and
As of 2006, Santiago was home to 992,000 vehicles, 979,000 of which were motorized. This made up 37.3% of Chile's total vehicle count. 805,000 cars passed through the city, which is 37.6% of the national total or one car for every seven people.
The main road is the Avenida Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins, better known as Alameda Avenue, which runs northeast and southwest. From north to south, it is crossed by Autopista Central and the Independencia Avenue (Santiago de Chile), Independencia, Gran Avenida José Miguel Carrera, Gran Avenida, Avenida Recoleta, Recoleta, Avenida Santa Rosa, Santa Rosa, Vicuña Mackenna Avenue, Vicuña Mackenna and Tobalaba Avenida, Tobalaba avenues. Other major roads include the Avenida Los Pajaritos to the west and Providencia Avenue
Avenida Providencia is a major thoroughfare in Santiago, Chile. It runs along the commune of Providencia.
Description
Providencia begins at the northern terminus of Vicuña Mackenna Avenue as a continuation of Alameda Avenue. Immediately, the op ...
and Apoquindo Avenue to the east. Finally, the Américo Vespucio Avenue acts as a ring road.
During the 2000s, several urban highways were built through Santiago in order to improve the situation for vehicles. The road General Velásquez and sections of the Pan-American Highway in Santiago were converted into the Autopista Central, while Américo Vespucio became variously the highways Vespucio Norte Express and Vespucio Sur, as well as Vespucio Oriente in the future. Following the edge of the Mapocho River, Costanera Norte was built to link the northeast of the capital to the airport and the downtown area. All these highways, totaling 210 km in length, have a free flow toll system.
Administrative divisions
Greater Santiago lacks a metropolitan government for its administration, which is distributed between authorities, complicating the operation of the city as a single entity. The highest authorities in Santiago are considered to be the governor of the Santiago Metropolitan Region, who is popularly elected to the office, now held by Claudio Orrego, and the regional presidential delegate of Santiago Metropolitan Region, an official appointed by the president of Chile, post currently occupied by Constanza Martínez.
The conurbation of Greater Santiago does not fit perfectly into any administrative division, as it extends into four different Provinces of Chile, provinces and 35 Communes of Chile, communes plus 11 Satellite city, satellite communes which together make the Santiago Metropolitan Area. The majority of its (as of 2002)Note: Communes in the peripheries are not shown to their full extent.
Culture
Only a few historical buildings from the Spanish colonial period remain in the city, because – like the rest of the country – Santiago is regularly hit by earthquakes. Extant buildings include the Casa Colorada (1769), the San Francisco Church, Santiago de Chile, San Francisco Church (1586), and Posada del Corregidor (1750).
The cathedral on the central square ( Plaza de Armas) is a sight that ranks as high as the Palacio de La Moneda, the Presidential Palace. The original building was built between 1784 and 1805, and architect Joaquín Toesca was in charge of its construction. Other buildings surrounding the Plaza de Armas are the Central Post Office Building (Santiago), Central Post Office Building, which was finished in 1882, and the Palacio de la Real Audiencia de Santiago, built between 1804 and 1807. It houses the Chilean National History Museum, with 12,000 objects that can be exhibited. On the southeast corner of the square stands the green cast-iron Commercial Edwards building, which was built in 1893. East of that is the colonial building of the Casa Colorada (1769), which houses the Museum of Santiago. Close by is the Municipal Theatre of Santiago, which was built in 1857 by the French architect Brunet of Edward Baines. It was badly damaged by an earthquake in 1906. Not far from the theater is the Subercaseaux Mansion and the National Library, one of the largest libraries of South America.
The Former National Congress Building, the Palacio de los Tribunales de Justicia de Santiago, Justice Palace, and the Royal Customs Palace (''Palacio de la Real Aduana de Santiago'') are located close to each other. The latter houses the Museo Chileno de Arte Precolombino, Museum of pre-Columbian art. A fire destroyed the building of the Congress in 1895, which was then rebuilt in a neoclassical style and reopened in 1901. The Congress was deposed under the military dictatorship (1973–89) of Augusto Pinochet, and after the dictatorship was newly constituted on 11 March 1990, in Valparaíso.
The building of the Justice Palace (Palacio de Tribunales) is located on the south side of the Montt Square. It was designed by the architect Emilio Doyére and built between 1907 and 1926. The building is home to the Supreme Court of Chile. The panel of 21 judges is the highest judicial power in Chile. The building is also the headquarters of the Court of Appeals of Santiago.
Bandera street leads toward the building of the Santiago Stock Exchange (the ''Bolsa de Comercio''), completed in 1917, the Club de la Unión (Chile), Club de la Unión (opened in 1925), the Universidad de Chile (1872), and toward the oldest churchhouse in the city, the San Francisco Church (constructed between 1586 and 1628), with its Marian statue of the ''Virgen del Socorro'' ("Our Lady of Help"), which was brought to Chile by Pedro de Valdivia. North of the ''Plaza de Armas'' ("Square of Arms," where the colonial militia was mustered) are the Paseo Puente, the Santo Domingo Church, Santiago de Chile, Santo Domingo Church (1771), and the Mercado Central de Santiago, Central Market (Mercado Central), an ornamental iron building. Also in downtown Santiago is the Torre Entel, a 127.4-meter-high television tower with observation deck completed in 1974; the tower serves as a communication center for the communications company, ENTEL Chile.
The Costanera Center was completed in 2009, and includes housing, shopping, and entertainment venues. The project, with a total area of 600,000 square meters, includes the 300-meter high Gran Torre Santiago
The Costanera Center Torre 2, better known as Gran Torre Santiago (Great Santiago Tower), and previously known as Torre Gran Costanera, is a 62-story skyscraper in Santiago, Chile, the second tallest in Latin America (behind Mexico's T.Op Torre ...
(South America's tallest building) and other commercial buildings. The four office towers are served by highway and subway connections.
File:Teatro Municipal de Santiago de Chile.JPG, Municipal Theatre of Santiago
File:Palacio de La Moneda.png, Palacio de La Moneda
File:Museo de Arte Contemporáneo Santiago2.jpg, Museo de Arte Contemporáneo (Santiago, Chile), Contemporary Art Museum of Santiago
File:Bellasartes.jpg, Chilean National Museum of Fine Arts, Fine Arts Museum
File:BibliotecaNacionaldeChile.JPG, Biblioteca Nacional de Chile
File:Excongreso.jpg, Former Congress Building
Heritage and monuments

 Within the metropolitan area of Santiago, there are 174 National Monuments of Chile, heritage sites in the custody of the National Monuments Council, among which are archeological, architectural and historical monuments, neighborhoods and typical areas. Of these, 93 are located within the
Within the metropolitan area of Santiago, there are 174 National Monuments of Chile, heritage sites in the custody of the National Monuments Council, among which are archeological, architectural and historical monuments, neighborhoods and typical areas. Of these, 93 are located within the commune of Santiago
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
, considered the historic center of the city. Although no santiaguino monument has been declared a World Heritage Site by Unesco three have already been proposed by the Chilean government: the Incan sanctuary of Cerro El Plomo, El Plomo, San Francisco Church, Santiago de Chile, the church and convent of San Francisco and the palace of La Moneda.
In the center of Santiago are several buildings built during the Spanish domination and that mostly correspond to, as the Santiago Metropolitan Cathedral, Metropolitan Cathedral and the aforementioned church of San Francisco Catholic churches. Buildings of the period are those located on the sides of Plaza de Armas, as the seat of Palacio de la Real Audiencia de Santiago, Real Audiencia, the Central Post Office Building (Santiago), Post Office or the Casa Colorada.
During the nineteenth century and the advent of independence, new architectural works began to be erected in the capital of the young republic. The aristocracy built small palaces for residential use, mainly around the neighborhood Republica and preserved until today. To this other structures adopted artistic trends from Europe, as the Club Hípico de Santiago, Equestrian Club of Santiago, the head offices of the University of Chile and the Pontifical Catholic University of Chile, Catholic University, Estación Central (railway station), Central Station and the Mapocho Station, Mercado Central de Santiago, Mercado Central, join the National Library, Museum of Fine Arts and the Barrio París-Londres, among others.
Various green areas in the city contain within and around various sites of heritage character. Among the most important are the fortifications of Santa Lucía Hill, Santa Lucia hill, the Sanctuary on San Cristóbal Hill, shrine of the Virgin Mary on the summit of San Cristóbal Hill, San Cristobal hill, the lavish crypt of the General Cemetery
''General Cemetery'' (Spanish: ''Cementerio general'') is a 2013 Peruvian supernatural horror film directed by Dorian Fernandez Moris. Written by Javier Velasquez, the plot is based on urban legends in the city's main cemetery. The film stars Air ...
, Parque Forestal, the O'Higgins Park and the Quinta Normal Park.
Cultural activities and entertainment

 In Santiago's major theater companies are located, hosting several national and international projects, with the highest expression during the International Theatre Festival known as Santiago a Mil International Theater Festival, Santiago a Mil, which takes place every January since 1994 and has gathered more than one million spectators. Also is the Planetarium at the University of Santiago de Chile.
To carry out various cultural, artistic and musical events, there are several precincts within which highlight the Estación Mapocho, Mapocho Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Matucana 100, 100 Matucana Cultural Center, the Centro Cultural Gabriela Mistral, Gabriela Mistral Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Palacio de La Moneda, the Movistar Arena and the Teatro Caupolicán, Caupolican Theater. On the other hand, the opera and ballet performances are permanently accepted by the Municipal Theatre of Santiago, located in the heart of the city and which has a capacity of 1500 spectators.
There are 18 cinemas in the capital with a total of 144 rooms and over 32,000 seats, the projection centers than 5 arthouse add.
For children and teenagers, there are several entertainment venues, such as amusement park Fantasilandia, the Chilean National Zoo, National Zoo or the Buin Zoo on the outskirts of the city. The Barrio Bellavista, Bellavista, Barrio Brasil, Brasil, Barrio Manuel Montt, Manuel Montt, Plaza Ñuñoa and Barrio Suecia, Suecia account for most of the nightclubs, restaurants and bars in the city, the main evening entertainment centers in the capital. In order to promote the economic development of other regions, the law prohibits the construction of a casino in the metropolitan region, but nearby are the casino from the coastal city of Vina del Mar, 120 km from distance from Santiago, and Monticello Grand Casino in Mostazal, 56 kilometers south of Santiago, which opened in 2008.
In Santiago's major theater companies are located, hosting several national and international projects, with the highest expression during the International Theatre Festival known as Santiago a Mil International Theater Festival, Santiago a Mil, which takes place every January since 1994 and has gathered more than one million spectators. Also is the Planetarium at the University of Santiago de Chile.
To carry out various cultural, artistic and musical events, there are several precincts within which highlight the Estación Mapocho, Mapocho Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Matucana 100, 100 Matucana Cultural Center, the Centro Cultural Gabriela Mistral, Gabriela Mistral Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Palacio de La Moneda, the Movistar Arena and the Teatro Caupolicán, Caupolican Theater. On the other hand, the opera and ballet performances are permanently accepted by the Municipal Theatre of Santiago, located in the heart of the city and which has a capacity of 1500 spectators.
There are 18 cinemas in the capital with a total of 144 rooms and over 32,000 seats, the projection centers than 5 arthouse add.
For children and teenagers, there are several entertainment venues, such as amusement park Fantasilandia, the Chilean National Zoo, National Zoo or the Buin Zoo on the outskirts of the city. The Barrio Bellavista, Bellavista, Barrio Brasil, Brasil, Barrio Manuel Montt, Manuel Montt, Plaza Ñuñoa and Barrio Suecia, Suecia account for most of the nightclubs, restaurants and bars in the city, the main evening entertainment centers in the capital. In order to promote the economic development of other regions, the law prohibits the construction of a casino in the metropolitan region, but nearby are the casino from the coastal city of Vina del Mar, 120 km from distance from Santiago, and Monticello Grand Casino in Mostazal, 56 kilometers south of Santiago, which opened in 2008.
Museums and libraries
Santiago has a wealth of museums of different kinds, among which are three of 'National' class administered by the Directorate of Libraries, Archives and Museums (DIBAM): the National History Museum (Santiago, Chile), National History Museum, Chilean National Museum of Fine Arts, National Museum of Fine Arts and the National Museum of Natural History.
Most of the museums are located in the historic city center, occupying the old buildings of colonial origin, such as with the National History Museum, which is located in the Palacio de la Real Audiencia de Santiago, Palacio de la Real Audiencia. La Casa Colorada houses the Museum of Santiago, while the Colonial Museum is housed in a wing of the San Francisco Church, Santiago de Chile, Church of San Francisco and the Museo Chileno de Arte Precolombino, Museum of Pre-Columbian Art occupies part of the old Palacio de la Real Aduana de Santiago, Palacio de la Aduana. The Museum of Fine Arts, though it is located in the city center, was built in the early twentieth century, especially for housing the museum and in the back of the building was laid in 1947, the Santiago Museum of Contemporary Art, Museum of Contemporary Art, under the Faculty of Arts of the University of Chile.
The Quinta Normal Park also has several museums, among which are the already mentioned of Natural History, Artequin Museum, the Museum of Science and Technology, Santiago, Museum of Science and Technology and the Museo Ferroviario. In other parts of the city there are some museums such as the Museo Nacional Aeronáutico y del Espacio, Aeronautical Museum in Cerrillos, Tajamares del Mapocho, Museum of Tajamares in Providence and the Museo Interactivo Mirador in La Granja. The latter opened in 2000 and designed mainly for children and youth has been visited by more than 2.8 million visitors, making it the busiest museum in the country.
The most important public library is the National Library located in downtown Santiago. Its origins date back to 1813, when it was created by the nascent Republic and was moved to its current premises a century later, also home to the headquarters of the National Archives of Chile, National Archives. In order to provide more closeness to the population, incorporating new technologies and complement the services provided by public libraries and the National Library was opened in 2005 the Library of Santiago at Barrio Matucana.
Music
Santiago has two symphony orchestras:
* ''Orquesta Filarmónica de Santiago'' ("Santiago Philharmonic Orchestra"), which performs in the ''Teatro Municipal'' (Municipal Theatre of Santiago)
* ''Orquesta Sinfónica de Chile'' ("Chile Symphony Orchestra"), part of the Universidad de Chile, performs in its theater.
There are a number of jazz establishments, some of them, including "El Perseguidor," "Thelonious," and "Le Fournil Jazz Club," are located in Bellavista, one of Santiago's "hippest" neighborhoods, though "Club de Jazz de Santiago," the oldest and most traditional one, is in Ñuñoa. Annual festivals featured in Santiago include Lollapalooza and the Maquinaria festival.
Newspapers
The most widely circulated newspapers in Chile are published by ''El Mercurio'' and ''Copesa'' and have earned more than the 91% of revenues generated in printed advertizing in Chile.
Some newspapers available in Santiago are:
* ''El Mercurio''
* ''La Tercera''
* ''La Cuarta''
* ''Las Últimas Noticias''
* ''La Segunda''
* ''The Clinic (newspaper), The Clinic''
* ''The Santiago Times''
Media
Santiago is home to the major Chilean television networks including the public broadcaster Televisión Nacional de Chile, TVN and the privately held Canal 13 (Chilean TV channel), Canal 13, Chilevisión, La Red (Chilean TV channel), La Red and Mega (Chilean TV channel), Mega. In addition, the radio stations ADN Radio Chile, Radio Agricultura, Radio Concierto, Radio Cooperativa (Chile), Radio Cooperativa, Radio Pudahuel and Rock & Pop (Chilean radio), Radio Rock & Pop are located in the city.
Sports
Santiago is home to some of Chile's most successful football clubs. Colo-Colo, founded on 19 April 1925, has a long tradition, and has played continuously in the highest league since the establishment of the first Chilean league in 1933. The club's wins include 30 Primera División de Chile, national titles, 10 Copa Chile successes, and champions of the Copa Libertadores tournament in 1991, the only Chilean team to have won this tournament. The club hosts its home games in the Estadio Monumental David Arellano, Estadio Monumental in the commune of Macul.
 Club Universidad de Chile, Universidad de Chile has 18 national titles and 5 Copa Chile wins. In 2011 they were champions of Copa Sudamericana, the only Chilean team to have won this tournament. The club was founded on 24 May 1927, under the name Club Deportivo Universitario as a union of Club Náutico and Federación Universitaria. The founders were students of the University of Chile. In 1980, the organization separated from the University of Chile and the club is now completely independent. The team plays its home games in the Estadio Nacional de Chile in the commune of Ñuñoa.
Club Deportivo Universidad Católica (UC) was founded on 21 April 1937. It consists of fourteen different departments. This team plays its home games in Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo. Universidad Católica has 13 national titles, making it the third most successful football club in the country. It has played the Copa Libertadores more than 20 times, reaching the final in 1993, losing to São Paulo FC.
Several other football clubs are based in Santiago, including Unión Española, Audax Italiano, Club Deportivo Palestino, Palestino, Santiago Morning, Deportes Magallanes, Magallanes and A.C. Barnechea, Barnechea. In addition to football, several sports are played in the city, tennis and basketball being the main ones. The
Club Universidad de Chile, Universidad de Chile has 18 national titles and 5 Copa Chile wins. In 2011 they were champions of Copa Sudamericana, the only Chilean team to have won this tournament. The club was founded on 24 May 1927, under the name Club Deportivo Universitario as a union of Club Náutico and Federación Universitaria. The founders were students of the University of Chile. In 1980, the organization separated from the University of Chile and the club is now completely independent. The team plays its home games in the Estadio Nacional de Chile in the commune of Ñuñoa.
Club Deportivo Universidad Católica (UC) was founded on 21 April 1937. It consists of fourteen different departments. This team plays its home games in Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo. Universidad Católica has 13 national titles, making it the third most successful football club in the country. It has played the Copa Libertadores more than 20 times, reaching the final in 1993, losing to São Paulo FC.
Several other football clubs are based in Santiago, including Unión Española, Audax Italiano, Club Deportivo Palestino, Palestino, Santiago Morning, Deportes Magallanes, Magallanes and A.C. Barnechea, Barnechea. In addition to football, several sports are played in the city, tennis and basketball being the main ones. The Club Hípico de Santiago
Club Hípico de Santiago is a thoroughbred horse race track in Santiago, Chile.
History
The Club Hípico de Santiago, opened in 1870, is Chile's oldest racetrack and home to South America's oldest stakes race, the Clásico El Ensayo. It is one ...
and the Hipódromo Chile are the two Race track, horseracing tracks in the city.
Santiago hosted the final stages of the official 1959 Basketball World Cup, where Chile national basketball team, Chile won the bronze medal.
The city held a round of the all-electric FIA Formula E, FIA Formula E Championship on 3 February 2018, on a temporary street circuit incorporating the Plaza Baquedano and Parque Forestal. It was the first Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile, FIA sanctioned race in the country.
The 2023 Pan American Games
The 2023 Pan American Games ( es, Juegos Panamericanos de 2023, links=no), officially the XIX Pan American Games and commonly known as Santiago 2023, is a forthcoming international multi-sport event governed by the Panam Sports Organization, s ...
will be held in Santiago.
Recreation
There is an extensive network of bicycle trails in the city, especially in the Providencia commune. The longest section is the Americo Vespuccio road, which contains a very wide dirt path with many trees through the center of a street used by motorists on both sides. The next longest path is along the Mapocho River along Andrés Bello Avenue. Many people use folding bicycles to commute to work.
The city's main parks are:
* Cerro San Cristóbal – Cerro San Cristóbal, San Cristóbal Hill, which includes the Chilean National Zoo
* ''Parque O'Higgins'' – Parque O'Higgins, Chile, O'Higgins Park
* ''Parque Forestal'' – Parque Forestal, Chile, Forestal Park, park located at the city center alongside Mapocho river
* Cerro Santa Lucía – Santa Lucía Hill
* Parque Araucano in Las Condes adjacent to the Parque Arauco shopping mall contains 30 hectares of gardens. It is closed for maintenance on Mondays.
* Parque Inés de Suarez, Providencia
* Parque Padre Hurtado (a.k.a. Parque Intercomunal)
There are ski resorts to the east of the city (Valle Nevado, La Parva, El Colorado) and wineries in the plains west of the city.
Cultural venues include:
* Museo de Bellas Artes (Santiago), Museo de Bellas Artes – Fine Arts Museum
*Museo Violeta Parra, an art museum dedicated to Chilean folk artist Violeta Parra [opened in 2015]
* Barrio Bellavista, cultural and bohemian neighborhood
* Estación Central railway station, Central Station, railway station designed by Gustave Eiffel
* Estadio Víctor Jara, Chile, Víctor Jara Stadium
* Ex Congreso Nacional, Ex National Congress
* Plaza de Armas, central square
* Palacio de La Moneda, government palace * Teatro Municipal (Municipal Theatre of Santiago), the principal opera house of the country. The main sport venues are Estadio Nacional de Chile, Estadio Nacional (site of the 1962 FIFA World Cup, 1962 World Cup final), Estadio Monumental David Arellano, Estadio Santa Laura, and Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo.
* Teatro Municipal (Municipal Theatre of Santiago), the principal opera house of the country. The main sport venues are Estadio Nacional de Chile, Estadio Nacional (site of the 1962 FIFA World Cup, 1962 World Cup final), Estadio Monumental David Arellano, Estadio Santa Laura, and Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo.
Religion
As in most of Chile, the majority of the population of Santiago is Catholic Church, Catholic. According to the National Census, carried out in 2002 by the National Statistics Bureau (National Statistics Institute (Chile), INE), in the Santiago Metropolitan Region, 3,129,249 people 15 and older identified themselves as Catholics, equivalent to 68.7% of the total population, while 595,173 (13.1%) described themselves as Evangelicals, Evangelical Protestants. Around 1.2% of the population declared themselves as being Jehovah's Witnesses, while 2.0% identified themselves as Latter-day Saints (Mormons), 0.3% as Judaism, Jewish, 0.1% as Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox and 0.1% as Muslim. Approximately 10.4% of the population of the Metropolitan Region stated that they were Atheism, atheist or Agnosticism, agnostic, while 5.4% declared that they followed other religions.
In 2010 construction was initiated on the Santiago Bahá'í Temple, serving as the Baháʼí House of Worship for South America, in the commune of Peñalolen. Construction at the site was completed and the temple was dedicated in October 2016.
Education
The city is home to numerous universities, colleges, research institutions, and libraries.
The largest university and one of the oldest in the Americas is Universidad de Chile. The roots of the university date back to the year 1622, as on 19 August the first university in Chile under the name of Santo Tomás de Aquino was founded. On 28 July 1738, it was named the Real Universidad de Philip the Apostle, San Felipe in honor of King Philip V of Spain. In the vernacular, it is also known as Casa de Bello (Spanish: House of Bello – after their first Rector, Andrés Bello). On 17 April 1839, after Chile's independence from the Kingdom of Spain, it was renamed the Universidad de Chile, and reopened on 17 September 1843.
The Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile (PUC) was founded in June 1888 and was ranked as the best school in Latin America in 2014. On 11 February 1930 it was declared a university by a decree of Pope Pius XI. It received recognition by the Chilean government as an appointed Pontifical University in 1931. Joaquín Larraín Gandarillas (1822–1897), Archbishop of Anazarba, was the founder and first rector of the PUC. The PUC is a modern university; the campus of San Joaquin has a number of contemporary buildings and offers many parks and sports facilities. Several courses are conducted in English. Ex-president, Sebastián Piñera, minister Ricardo Raineri, and minister Hernán de Solminihac all attended PUC as students and worked in PUC as professors. In the 2010 admission process, approximately 48% of the students who achieved the best score in the Prueba de Selección Universitaria matriculated in the UC.
Higher education
Traditional

 * Universidad de Chile (university), Universidad de Chile (U or UCH)
* Pontifical Catholic University of Chile, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile (PUC)
* Universidad de Santiago de Chile (USACH)
* Universidad Metropolitana de Ciencias de la Educación (UMCE)
* Universidad Tecnológica Metropolitana (UTEM)
* Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María (UTFSM)
* Universidad de Chile (university), Universidad de Chile (U or UCH)
* Pontifical Catholic University of Chile, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile (PUC)
* Universidad de Santiago de Chile (USACH)
* Universidad Metropolitana de Ciencias de la Educación (UMCE)
* Universidad Tecnológica Metropolitana (UTEM)
* Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María (UTFSM)
Non-traditional
* Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez (UAI)
* Universidad del Desarrollo (UDD)
* Universidad Diego Portales (UDP)
* Universidad Alberto Hurtado (UAH)
* Universidad Central de Chile (Ucen)
* Universidad Nacional Andrés Bello (Unab)
* Academy of Christian Humanism University, Universidad Academia de Humanismo Cristiano (UAHC)
* Universidad Mayor (UM)
* Universidad Finis Terrae
* University of the Andes, Chile, Universidad de Los Andes
* Universidad Gabriela Mistral (UGM)
* University of the Pacific (Chile), Universidad del Pacífico
* Universidad de las Américas (Chile), Universidad de las Américas
* Universidad de Artes, Ciencias y Comunicación (UNIACC)
* Universidad San Sebastián (USS)
* Universidad Bolivariana
Other
* Ruprecht Karls University of Heidelberg's ''Postgraduierten- und Weiterbildungszentrum der Universität Heidelberg'' i
Santiago
* David Rockefeller Center for Latin American Studies (DRCLAS) Regional Office i
Santiago
* Stanford Faculty i
Santiago
* Diplomatic Academy of Chile
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Santiago is Sister city, twinned with:
* Beijing, China
* Buenos Aires, Argentina
* Guangzhou, China
* Kyiv, Ukraine
* London, England, United Kingdom
* Madrid, Spain
* Miami, United States
* Minneapolis, United States
* Riga, Latvia
* São Paulo, Brasil
* Tangier, Morocco
Cooperation and friendship
* Paris, France
* Tunis, Tunisia
Union of Ibero-American Capital Cities
Santiago is part of the Union of Ibero-American Capital Cities from 12 October 1982.
Gallery
File:Sculptures at the Pre-Columbian Art Museum in Santiago, Chile.jpg, Chemamull statues at Precolumbian Art Museum of Santiago
File:Club de la Unión.jpg, Club de La Unión
File:Bolsa de Comercio de Santiago.jpg, Façade of the Santiago Stock Exchange
File:Fachada Basilica del Salvador.jpg, Basílica del Salvador
File:PaseoBulnes.jpg, Paseo Bulnes, downtown Santiago
File:Paseo Ahumada 2009.jpg, Paseo Ahumada, downtown Santiago
File:Alameda - Santiago de Chile.jpg, Entel Tower
File:Santiago (15130325641).jpg, A street in Santiago
See also
*
References
Bibliography
External links
*
*
*
{{Authority control
Santiago, Chile,
Capitals in South America
Populated places established in 1541
1541 establishments in the Captaincy General of Chile
Capitals of Chilean regions
 Having been sent by Francisco Pizarro from Peru and having made the long journey from Cuzco, Extremadura conquistador Pedro de Valdivia reached the valley of the Mapocho on 13 December 1540. The hosts of Valdivia camped by the river in the slopes of the Tupahue hill and slowly began to interact with the
Having been sent by Francisco Pizarro from Peru and having made the long journey from Cuzco, Extremadura conquistador Pedro de Valdivia reached the valley of the Mapocho on 13 December 1540. The hosts of Valdivia camped by the river in the slopes of the Tupahue hill and slowly began to interact with the 
 Although early Santiago appeared to be in imminent danger of permanent destruction, threatened by Indigenous attacks, earthquakes, and a series of
Although early Santiago appeared to be in imminent danger of permanent destruction, threatened by Indigenous attacks, earthquakes, and a series of  18 September 1810 was proclaimed the First Government Junta in Santiago, beginning the process of establishing the independence of Chile. The city, which became the capital of the new nation, was threatened by various events, especially the nearby military actions.
Although some institutions, such as the
18 September 1810 was proclaimed the First Government Junta in Santiago, beginning the process of establishing the independence of Chile. The city, which became the capital of the new nation, was threatened by various events, especially the nearby military actions.
Although some institutions, such as the  With the end of the war, Bernardo O'Higgins was accepted as Supreme Director and, like his father, began a number of important works for the city. During the call Patria Nueva, closed institutions reopened. The
With the end of the war, Bernardo O'Higgins was accepted as Supreme Director and, like his father, began a number of important works for the city. During the call Patria Nueva, closed institutions reopened. The  During the years of the Republican era, institutions such as the University of Chile (Universidad de Chile), the Normal School of Preceptors, the School of Arts and Crafts, and the Quinta Normal, which included the Museum of Fine Arts (now Museum of Science and Technology) and the National Museum of Natural History, were founded. Created primarily for educational use, they also became examples of public planning during that period. In 1851 the first telegraph system connecting the capital with the Port of Valparaíso was inaugurated.
A new momentum in the urban development of the capital took place during the so-called "Liberal Republic" and the administration of Mayor
During the years of the Republican era, institutions such as the University of Chile (Universidad de Chile), the Normal School of Preceptors, the School of Arts and Crafts, and the Quinta Normal, which included the Museum of Fine Arts (now Museum of Science and Technology) and the National Museum of Natural History, were founded. Created primarily for educational use, they also became examples of public planning during that period. In 1851 the first telegraph system connecting the capital with the Port of Valparaíso was inaugurated.
A new momentum in the urban development of the capital took place during the so-called "Liberal Republic" and the administration of Mayor  Also during this time and with the work of European landscapers in 1873, O'Higgins Park came into existence. The park, open to the public, became a landmark in Santiago due to its large gardens, lakes, and carriage trails. Other important buildings were opened during this era, such as the Teatro Municipal opera house, and the
Also during this time and with the work of European landscapers in 1873, O'Higgins Park came into existence. The park, open to the public, became a landmark in Santiago due to its large gardens, lakes, and carriage trails. Other important buildings were opened during this era, such as the Teatro Municipal opera house, and the  With the arrival of the new century, the city began to experience various changes related to the strong development of industry. Valparaíso, which had hitherto been the economic center of the country slowly lost prominence at the expense of the capital. By 1895, 75% of the national manufacturing industry was in the capital and only 28% in the harbor city, and by 1910, major banks and shops were set up in the streets of the city center, leaving Valparaíso.
The enactment of the Autonomous Municipalities' act allowed municipalities to create various administrative divisions around the then Santiago ''departamento'', with the aim of improving local ruling. Maipú, Ñuñoa, Renca, Lampa and Colina were to be created in 1891, Providencia and Barrancas in 1897, and
With the arrival of the new century, the city began to experience various changes related to the strong development of industry. Valparaíso, which had hitherto been the economic center of the country slowly lost prominence at the expense of the capital. By 1895, 75% of the national manufacturing industry was in the capital and only 28% in the harbor city, and by 1910, major banks and shops were set up in the streets of the city center, leaving Valparaíso.
The enactment of the Autonomous Municipalities' act allowed municipalities to create various administrative divisions around the then Santiago ''departamento'', with the aim of improving local ruling. Maipú, Ñuñoa, Renca, Lampa and Colina were to be created in 1891, Providencia and Barrancas in 1897, and  The 1920 census estimated the population of Santiago to be 507,296 inhabitants, equivalent to 13.6% of the population of Chile. This represented an increase of 52.5% from the census of 1907, i.e. an annual growth of 3.3%, almost three times the national figure. This growth was mainly due to the arrival of farmers from the south who came to work in factories and railroads which were under construction. However, this growth was experienced on the outskirts and not in the town itself.
The 1920 census estimated the population of Santiago to be 507,296 inhabitants, equivalent to 13.6% of the population of Chile. This represented an increase of 52.5% from the census of 1907, i.e. an annual growth of 3.3%, almost three times the national figure. This growth was mainly due to the arrival of farmers from the south who came to work in factories and railroads which were under construction. However, this growth was experienced on the outskirts and not in the town itself.
 During this time the downtown district was consolidated into a commercial, financial and administrative center, with the establishment of various portals and locales around Ahumada Street and a Civic District in the immediate surroundings of the
During this time the downtown district was consolidated into a commercial, financial and administrative center, with the establishment of various portals and locales around Ahumada Street and a Civic District in the immediate surroundings of the  The feeling that the early 20th century was an era of economic growth due to technological advances contrasted dramatically with the standard of living of lower social classes. The growth of the previous decades led to an unprecedented population explosion starting in 1929. The
The feeling that the early 20th century was an era of economic growth due to technological advances contrasted dramatically with the standard of living of lower social classes. The growth of the previous decades led to an unprecedented population explosion starting in 1929. The  Regulation of the growth only began to be implemented during the 1960s with the creation of various development plans for Greater Santiago, a concept that reflected the new reality of a much larger city. In 1958 the Intercommunal Plan of Santiago was released. The proposed scheme set a limit of 38 600 urban and semi hectares for a maximum population of 3,260,000 inhabitants, included plans for the construction of new avenues, like the Américo Vespucio Avenue and Panamericana route 5, and the expansion of 'industrial belts'. The celebration of the World Cup in 1962 gave new impetus to implement plans for city improvement. In 1966 the
Regulation of the growth only began to be implemented during the 1960s with the creation of various development plans for Greater Santiago, a concept that reflected the new reality of a much larger city. In 1958 the Intercommunal Plan of Santiago was released. The proposed scheme set a limit of 38 600 urban and semi hectares for a maximum population of 3,260,000 inhabitants, included plans for the construction of new avenues, like the Américo Vespucio Avenue and Panamericana route 5, and the expansion of 'industrial belts'. The celebration of the World Cup in 1962 gave new impetus to implement plans for city improvement. In 1966 the 
 With the start of the transition to democracy in 1990, the city of Santiago had surpassed three million inhabitants, with the majority living in the south: La Florida was the most populous area, followed by
With the start of the transition to democracy in 1990, the city of Santiago had surpassed three million inhabitants, with the majority living in the south: La Florida was the most populous area, followed by  The city lies in the center of the ''Santiago Basin'', a large bowl-shaped valley consisting of broad and fertile lands surrounded by mountains. The city has a varying elevation, gradually increasing from in the western areas to more than in the eastern areas. Santiago's
The city lies in the center of the ''Santiago Basin'', a large bowl-shaped valley consisting of broad and fertile lands surrounded by mountains. The city has a varying elevation, gradually increasing from in the western areas to more than in the eastern areas. Santiago's  The Costanera Center, a mega project in Santiago's Financial District, includes a mall, a tower, two office towers of each, and a hotel tall. In January 2009 the retailer in charge,
The Costanera Center, a mega project in Santiago's Financial District, includes a mall, a tower, two office towers of each, and a hotel tall. In January 2009 the retailer in charge,  Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport (IATA: SCL) is Santiago's national and international airport and the principal airline hub, hub of LATAM Chile, LATAM Airlines, Sky Airline, Aerocardal and JetSmart. The airport is located in the western commune of Pudahuel. The largest airport in Chile, it is ranked sixth in passenger traffic among Latin American airports, with 14,168,282 passengers served in 2012 – a 17% increase over 2011. It is located 15 km from the city center.
Peldehue airport in Colina began operations on December 13, 2021. It will be able to service up to 25 flights per hour.
Santiago is also served by Eulogio Sánchez Airport (ICAO: SCTB), a small, privately owned general aviation airport in the commune of La Reina.
Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport (IATA: SCL) is Santiago's national and international airport and the principal airline hub, hub of LATAM Chile, LATAM Airlines, Sky Airline, Aerocardal and JetSmart. The airport is located in the western commune of Pudahuel. The largest airport in Chile, it is ranked sixth in passenger traffic among Latin American airports, with 14,168,282 passengers served in 2012 – a 17% increase over 2011. It is located 15 km from the city center.
Peldehue airport in Colina began operations on December 13, 2021. It will be able to service up to 25 flights per hour.
Santiago is also served by Eulogio Sánchez Airport (ICAO: SCTB), a small, privately owned general aviation airport in the commune of La Reina.

 Trains operated by Chile's national railway company, Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE), connect Santiago to several cities in the south-central part of the country: Rancagua, San Fernando, Chile, San Fernando, Talca (connected to the coastal city of Constitución, Chile, Constitución by a different train service), Linares, Chile, Linares and Chillán. All such trains arrive and depart from the Estación Central railway station (Central Station), which can be accessed by bus or subway. The proposed Santiago–Valparaíso railway line would connect Santiago with Valparaíso in 45 minutes, and expansions of the commuter rail network to Melitrén, Melipilla and Santiago-Batuco commuter rail, Batuco are under discussion.
Trains operated by Chile's national railway company, Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE), connect Santiago to several cities in the south-central part of the country: Rancagua, San Fernando, Chile, San Fernando, Talca (connected to the coastal city of Constitución, Chile, Constitución by a different train service), Linares, Chile, Linares and Chillán. All such trains arrive and depart from the Estación Central railway station (Central Station), which can be accessed by bus or subway. The proposed Santiago–Valparaíso railway line would connect Santiago with Valparaíso in 45 minutes, and expansions of the commuter rail network to Melitrén, Melipilla and Santiago-Batuco commuter rail, Batuco are under discussion.
 Santiago has 37% of Chile's vehicles, with a total of 991,838 vehicles, 979,346 of which are motorized. An extensive network of streets and avenues stretching across Santiago facilitate travel between the different communities that make up the metropolitan area.
In the 1990s the government attempted to reorganize the public transport system. New routes were introduced in 1994 and the buses were painted yellow. The system, however, had serious issues with routes overlapping, high levels of air and noise pollution, and safety problems for both riders and drivers. To tackle these issues a new transport system, called
Santiago has 37% of Chile's vehicles, with a total of 991,838 vehicles, 979,346 of which are motorized. An extensive network of streets and avenues stretching across Santiago facilitate travel between the different communities that make up the metropolitan area.
In the 1990s the government attempted to reorganize the public transport system. New routes were introduced in 1994 and the buses were painted yellow. The system, however, had serious issues with routes overlapping, high levels of air and noise pollution, and safety problems for both riders and drivers. To tackle these issues a new transport system, called  Santiago Metro has six operating lines (1, 2, 3, 4, 4A, 5 and 6), extending over and connecting 118 stations. The system carries around 2,400,000 passengers per day. Two underground lines (Line 4 and 4A) and an extension of Line 2 were inaugurated in 2005 and 2006, while an extension of Line 5 was inaugurated in 2011. Line 6 was inaugurated in 2017, adding 10 stations to the network and approximately of track. Line 3 opened on January 22, 2019, with 18 new stations
Santiago Metro has six operating lines (1, 2, 3, 4, 4A, 5 and 6), extending over and connecting 118 stations. The system carries around 2,400,000 passengers per day. Two underground lines (Line 4 and 4A) and an extension of Line 2 were inaugurated in 2005 and 2006, while an extension of Line 5 was inaugurated in 2011. Line 6 was inaugurated in 2017, adding 10 stations to the network and approximately of track. Line 3 opened on January 22, 2019, with 18 new stations


 In Santiago's major theater companies are located, hosting several national and international projects, with the highest expression during the International Theatre Festival known as Santiago a Mil International Theater Festival, Santiago a Mil, which takes place every January since 1994 and has gathered more than one million spectators. Also is the Planetarium at the University of Santiago de Chile.
To carry out various cultural, artistic and musical events, there are several precincts within which highlight the Estación Mapocho, Mapocho Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Matucana 100, 100 Matucana Cultural Center, the Centro Cultural Gabriela Mistral, Gabriela Mistral Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Palacio de La Moneda, the Movistar Arena and the Teatro Caupolicán, Caupolican Theater. On the other hand, the opera and ballet performances are permanently accepted by the Municipal Theatre of Santiago, located in the heart of the city and which has a capacity of 1500 spectators.
There are 18 cinemas in the capital with a total of 144 rooms and over 32,000 seats, the projection centers than 5 arthouse add.
For children and teenagers, there are several entertainment venues, such as amusement park Fantasilandia, the Chilean National Zoo, National Zoo or the Buin Zoo on the outskirts of the city. The Barrio Bellavista, Bellavista, Barrio Brasil, Brasil, Barrio Manuel Montt, Manuel Montt, Plaza Ñuñoa and Barrio Suecia, Suecia account for most of the nightclubs, restaurants and bars in the city, the main evening entertainment centers in the capital. In order to promote the economic development of other regions, the law prohibits the construction of a casino in the metropolitan region, but nearby are the casino from the coastal city of Vina del Mar, 120 km from distance from Santiago, and Monticello Grand Casino in Mostazal, 56 kilometers south of Santiago, which opened in 2008.
In Santiago's major theater companies are located, hosting several national and international projects, with the highest expression during the International Theatre Festival known as Santiago a Mil International Theater Festival, Santiago a Mil, which takes place every January since 1994 and has gathered more than one million spectators. Also is the Planetarium at the University of Santiago de Chile.
To carry out various cultural, artistic and musical events, there are several precincts within which highlight the Estación Mapocho, Mapocho Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Matucana 100, 100 Matucana Cultural Center, the Centro Cultural Gabriela Mistral, Gabriela Mistral Cultural Center, Centro Cultural Palacio de La Moneda, the Movistar Arena and the Teatro Caupolicán, Caupolican Theater. On the other hand, the opera and ballet performances are permanently accepted by the Municipal Theatre of Santiago, located in the heart of the city and which has a capacity of 1500 spectators.
There are 18 cinemas in the capital with a total of 144 rooms and over 32,000 seats, the projection centers than 5 arthouse add.
For children and teenagers, there are several entertainment venues, such as amusement park Fantasilandia, the Chilean National Zoo, National Zoo or the Buin Zoo on the outskirts of the city. The Barrio Bellavista, Bellavista, Barrio Brasil, Brasil, Barrio Manuel Montt, Manuel Montt, Plaza Ñuñoa and Barrio Suecia, Suecia account for most of the nightclubs, restaurants and bars in the city, the main evening entertainment centers in the capital. In order to promote the economic development of other regions, the law prohibits the construction of a casino in the metropolitan region, but nearby are the casino from the coastal city of Vina del Mar, 120 km from distance from Santiago, and Monticello Grand Casino in Mostazal, 56 kilometers south of Santiago, which opened in 2008.
 Club Universidad de Chile, Universidad de Chile has 18 national titles and 5 Copa Chile wins. In 2011 they were champions of Copa Sudamericana, the only Chilean team to have won this tournament. The club was founded on 24 May 1927, under the name Club Deportivo Universitario as a union of Club Náutico and Federación Universitaria. The founders were students of the University of Chile. In 1980, the organization separated from the University of Chile and the club is now completely independent. The team plays its home games in the Estadio Nacional de Chile in the commune of Ñuñoa.
Club Deportivo Universidad Católica (UC) was founded on 21 April 1937. It consists of fourteen different departments. This team plays its home games in Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo. Universidad Católica has 13 national titles, making it the third most successful football club in the country. It has played the Copa Libertadores more than 20 times, reaching the final in 1993, losing to São Paulo FC.
Several other football clubs are based in Santiago, including Unión Española, Audax Italiano, Club Deportivo Palestino, Palestino, Santiago Morning, Deportes Magallanes, Magallanes and A.C. Barnechea, Barnechea. In addition to football, several sports are played in the city, tennis and basketball being the main ones. The
Club Universidad de Chile, Universidad de Chile has 18 national titles and 5 Copa Chile wins. In 2011 they were champions of Copa Sudamericana, the only Chilean team to have won this tournament. The club was founded on 24 May 1927, under the name Club Deportivo Universitario as a union of Club Náutico and Federación Universitaria. The founders were students of the University of Chile. In 1980, the organization separated from the University of Chile and the club is now completely independent. The team plays its home games in the Estadio Nacional de Chile in the commune of Ñuñoa.
Club Deportivo Universidad Católica (UC) was founded on 21 April 1937. It consists of fourteen different departments. This team plays its home games in Estadio San Carlos de Apoquindo. Universidad Católica has 13 national titles, making it the third most successful football club in the country. It has played the Copa Libertadores more than 20 times, reaching the final in 1993, losing to São Paulo FC.
Several other football clubs are based in Santiago, including Unión Española, Audax Italiano, Club Deportivo Palestino, Palestino, Santiago Morning, Deportes Magallanes, Magallanes and A.C. Barnechea, Barnechea. In addition to football, several sports are played in the city, tennis and basketball being the main ones. The 