Santa Ana River (Venezuela) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Santa Ana River is the largest river entirely within
The Santa Ana River is the largest river entirely within
The National Map
accessed March 16, 2011 and its
 The Santa Ana River rises in the southern
The Santa Ana River rises in the southern
 The Santa Ana River watershed shares boundaries with many adjacent river basins. In the northwest is the San Gabriel River, which empties into the Pacific at
The Santa Ana River watershed shares boundaries with many adjacent river basins. In the northwest is the San Gabriel River, which empties into the Pacific at
 Historically, the Santa Ana was named "the best stream in Southern California or steelhead trout habitat. The steelhead is an anadromous fish, similar to
Historically, the Santa Ana was named "the best stream in Southern California or steelhead trout habitat. The steelhead is an anadromous fish, similar to
 When Spanish explorer
When Spanish explorer
 When the
When the
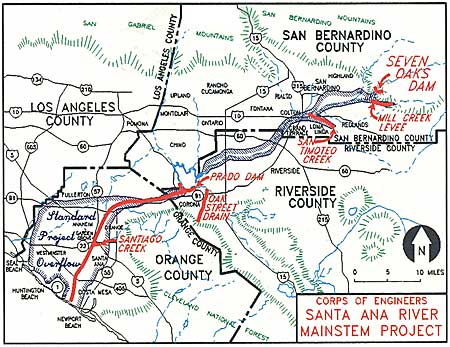 With the increased flood protection afforded by the Prado Dam, major industrial development migrating south from the Los Angeles Basin, and the Southern California housing boom in the 1950s and 1960s, the Santa Ana River watershed began its third and final transitionâfrom agricultural to urban. The population of the Santa Ana River basin increased dramatically, but brought with it the threat of greater damage from floods, somewhat compromising the protection afforded by Prado Dam. Because housing and urban areas encroached on the river's historic
With the increased flood protection afforded by the Prado Dam, major industrial development migrating south from the Los Angeles Basin, and the Southern California housing boom in the 1950s and 1960s, the Santa Ana River watershed began its third and final transitionâfrom agricultural to urban. The population of the Santa Ana River basin increased dramatically, but brought with it the threat of greater damage from floods, somewhat compromising the protection afforded by Prado Dam. Because housing and urban areas encroached on the river's historic
 As with many Southern California rivers, the Santa Ana is heavily polluted and used. The main stem above
As with many Southern California rivers, the Santa Ana is heavily polluted and used. The main stem above
 There are many recreational opportunities along the Santa Ana River. The Santa Ana River watershed includes parts of the
There are many recreational opportunities along the Santa Ana River. The Santa Ana River watershed includes parts of the
"How California is turning drainage canals back to rivers"
''
 State Route 1 (Pacific Coast Highway) (Newport Beach/Huntington Beach)
* Victoria Street/Hamilton Avenue (Costa Mesa/Huntington Beach)
*
State Route 1 (Pacific Coast Highway) (Newport Beach/Huntington Beach)
* Victoria Street/Hamilton Avenue (Costa Mesa/Huntington Beach)
*  Interstate 405 ( San Diego Freeway) (Costa Mesa/Fountain Valley)
* Talbert Avenue/MacArthur Boulevard (Santa Ana/Fountain Valley)
* Slater Avenue/West Segerstrom Avenue (Santa Ana/Fountain Valley)
* Warner Avenue (Santa Ana/Fountain Valley)
* Harbor Boulevard (Santa Ana)
* Edinger Avenue (Santa Ana)
* McFadden Avenue (Santa Ana)
* Bolsa Avenue/1st Street (Santa Ana)
* 5th Street (Santa Ana)
* Former
Interstate 405 ( San Diego Freeway) (Costa Mesa/Fountain Valley)
* Talbert Avenue/MacArthur Boulevard (Santa Ana/Fountain Valley)
* Slater Avenue/West Segerstrom Avenue (Santa Ana/Fountain Valley)
* Warner Avenue (Santa Ana/Fountain Valley)
* Harbor Boulevard (Santa Ana)
* Edinger Avenue (Santa Ana)
* McFadden Avenue (Santa Ana)
* Bolsa Avenue/1st Street (Santa Ana)
* 5th Street (Santa Ana)
* Former  State Route 22 ( Garden Grove Freeway) (Orange)
*
State Route 22 ( Garden Grove Freeway) (Orange)
*  Interstate 5 ( Santa Ana Freeway) (Orange)
* Chapman Avenue (Orange/Anaheim)
* Orangewood Avenue (Orange/Anaheim)
*
Interstate 5 ( Santa Ana Freeway) (Orange)
* Chapman Avenue (Orange/Anaheim)
* Orangewood Avenue (Orange/Anaheim)
*  State Route 57 ( Orange Freeway) (Orange/Anaheim)
* Metrolink
State Route 57 ( Orange Freeway) (Orange/Anaheim)
* Metrolink  State Route 91 (
State Route 91 ( State Route 90 ( Imperial Highway) (Anaheim)
*
State Route 90 ( Imperial Highway) (Anaheim)
* 
* Green River Road (Corona)
* Metrolink 91 & Inland Empire-Orange County Lines (Corona)
*  State Route 71 ( Corona Freeway)
* Prado Dam
* River Road (Norco/Eastvale)
* Hamner Avenue (Norco)
*
State Route 71 ( Corona Freeway)
* Prado Dam
* River Road (Norco/Eastvale)
* Hamner Avenue (Norco)
*  Interstate 15 (
Interstate 15 ( State Route 60 ( Pomona Freeway) (Jurupa Valley/Riverside)
* Market Street (Jurupa Valley/Riverside)
State Route 60 ( Pomona Freeway) (Jurupa Valley/Riverside)
* Market Street (Jurupa Valley/Riverside)
* Riverside Avenue (Colton)
* La Cadena Drive (Colton)
* Metrolink Inland Empire-Orange County Line (Colton)
* Railroad Bridge (Colton)
* Mount Vernon Avenue (Colton)
* Amtrak 
 Interstate 215 ( San Bernardino/
Interstate 215 ( San Bernardino/ State Route 210 ( Foothill Freeway) (Redlands)
* Orange Street (Redlands)
* Greenspot Road (Highland)
* Santa Ana Canyon Road
*
State Route 210 ( Foothill Freeway) (Redlands)
* Orange Street (Redlands)
* Greenspot Road (Highland)
* Santa Ana Canyon Road
*  State Route 38
State Route 38
Guide to the Santa Ana River Report.
Special Collections and Archives, The UC Irvine Libraries, Irvine, California.
Santa Ana Watershed Association
{{Authority control Rivers of Orange County, California Rivers of Riverside County, California Rivers of San Bernardino County, California San Bernardino Mountains Santa Ana Mountains Geography of Santa Ana, California Rivers of Southern California Watersheds of California
 The Santa Ana River is the largest river entirely within
The Santa Ana River is the largest river entirely within Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most po ...
in the United States. It rises in the San Bernardino Mountains
The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at at San Gorgonio Mountain â ...
and flows for most of its length through San Bernardino and Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
counties, before cutting through the northern Santa Ana Mountains
The Santa Ana Mountains are a short peninsular mountain range along the coast of Southern California in the United States. They extend for approximately southeast of the Los Angeles Basin largely along the border between Orange and Riverside co ...
via Santa Ana Canyon
Santa Ana Canyon ( es, Cañón de Santa Ana), or the Santa Ana Narrows, is the water gap where the Santa Ana River passes between the Santa Ana Mountains and the Chino Hills, near the intersection of Orange, Riverside, and San Bernardino counties, ...
and flowing southwest through urban Orange County
Orange County most commonly refers to:
*Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area
Orange County may also refer to:
U.S. counties
*Orange County, Florida, containing Orlando
*Orange County, Indiana
*Orange County, New ...
to drain into the Pacific Ocean. The Santa Ana River is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map
accessed March 16, 2011 and its
drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, t ...
is in size.
The Santa Ana drainage basin has a diversity of terrain, ranging from high peaks of inland mountains in the north and east, to the hot, dry interior and semidesert basins of the Inland Empire
The Inland Empire (IE) is a metropolitan area and region inland of and adjacent to coastal Southern California, centering around the cities of San Bernardino and Riverside, and bordering Los Angeles County to the west. It includes the cities o ...
, to the flat coastal plain of Orange County. Although it includes areas of alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
and highland forest, the majority of the watershed consists of arid desert and chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant community and geographical feature found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is shaped by a Mediterranean c ...
environments. Due to low regional rainfall, the river carries only a small flow except during the brief winter season, when it is prone to massive flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
s. The San Jacinto River, which drains the southern half of the watershed, rarely reaches the Santa Ana except in extremely wet years. A wide variety of animal and plant communities depend on the riparian zones and remnant wetlands along the Santa Ana River.
Humans have lived on the Santa Ana River for at least 9,000 years. The villages of Lupukngna, Genga, Pajbenga
Pajbenga, alternative spelling Pagbigna and Pasbengna, was a Tongva village located at Santa Ana, California, near the El Refugio Adobe, which was the home of José Sepulveda (now located near the intersection of Raitt Street and Myrtle Street). I ...
, Totpavit
Totpavit, alternative spellings Totabit and possibly Totavet, was a Tongva village located in what is now Olive, California. The village was located between the Santa Ana River and Santiago Creek. It was part of a series of villages along the San ...
, and Hutuknga
Hutuknga (alternative spellings: Hotuuknga or Hutuukuga) was a large Tongva village located in the foothills along the present channel of the Santa Ana River in what is now Yorba Linda, California. People from the village were recorded in mission ...
were located along the river. The river was first seen by Europeans in 1769, when it received its name from members of the Spanish Portola expedition. Because it was one of the only reliable sources of water in a wide region, many large ranchos developed along the river and one of its major tributaries, Santiago Creek
Santiago Creek is a major watercourse in Orange County in the U.S. state of California. About long, it drains most of the northern Santa Ana Mountains and is a tributary to the Santa Ana River. It is one of the longest watercourses entirely within ...
. After the area became part of the United States, the economy transitioned to agriculture, before urbanizing in the 20th century. Many cities established during this time including Santa Ana, Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
and Anaheim
Anaheim ( ) is a city in northern Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area. As of the 2020 United States Census, the city had a population of 346,824, making it the most populous city in Orange County, the 10th-most p ...
derived their names from the river. In order to protect urban areas from the river's flood threat, major channelization and dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, a ...
ming projects were undertaken, resulting in the loss of much of the natural river channel.
Course
 The Santa Ana River rises in the southern
The Santa Ana River rises in the southern San Bernardino Mountains
The San Bernardino Mountains are a high and rugged mountain range in Southern California in the United States. Situated north and northeast of San Bernardino and spanning two California counties, the range tops out at at San Gorgonio Mountain â ...
, at the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of two tiny streams, Heart Bar Creek and Coon Creek, at an elevation of . Its highest sources are Dollar Lake, at , and Dry Lake, at , both on the northern flank of San Gorgonio Mountain
San Gorgonio Mountain, also known locally as Mount San Gorgonio, or Old Greyback, is the highest peak in Southern California and the Transverse Ranges at .
It is in the San Bernardino Mountains, east of the city of San Bernardino and north-nort ...
, at the headwaters of the South Fork Santa Ana River. The river flows west through a wide, deep and heavily forested mountain valley. About from its headwaters, it receives its first major tributary, Bear Creek, which enters from the north. Bear Creek receives its water from Big Bear Lake
Big Bear Lake is a reservoir in the San Bernardino Mountains, in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is a snow and rain fed lake, having no other means of tributaries or mechanical replenishment. At a surface elevation of , it ...
, a popular recreational mountain lake. The river turns south, passing through the Seven Oaks Dam
Seven Oaks Dam is a high earth and rock fill embankment dam across the Santa Ana River in the San Bernardino Mountains, about northeast of Redlands in San Bernardino County, southern California. It impounds Seven Oaks Reservoir in the San Berna ...
, and reaches the arid Inland Empire lowland covering large parts of San Bernardino County and Riverside County. It receives Mill Creek from the south and passes to the south of San Bernardino, then receives City Creek from the north and San Timoteo Creek
San Timoteo Creek (also called San Timoteo Wash, colloquially known as San Tim) is a stream in Riverside and San Bernardino counties in southern California, United States. A tributary of the Santa Ana River, it flows through San Timoteo Canyon ...
from the south. Due to water diversions for groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in ...
, the river bed is usually dry in this stretch between Mill Creek and the outlet of the Veolia water treatment plant north of Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
, which restores a year-round flow. From there to Prado Dam the river supports a riparian zone with considerable greenery.
Not far below the confluence with San Timoteo Creek, Lytle Creek enters from the north. Lytle Creek is one of the largest tributaries of the Santa Ana river, rising from three forks in the San Gabriel Mountains and flowing southeast, before emptying into the Santa Ana River as Lytle Creek Wash. From there, the river turns southwest, and after passing through western Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
, it discharges into the normally dry flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
reservoir formed by Prado Dam. Two major tributaries of the river join in the reservoir area: Chino Creek from the north, and Temescal Creek from the south. Temescal Creek drains the largest area of all the tributaries, because it provides the outflow from Lake Elsinore, into which the San Jacinto River flows. It is also one of the longest, at in length. Except during the wettest years when Lake Elsinore fills high enough to overflow, Temescal Creek contributes little to no water into the Santa Ana River.
Below Prado Dam, the Santa Ana River crosses into Orange County
Orange County most commonly refers to:
*Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area
Orange County may also refer to:
U.S. counties
*Orange County, Florida, containing Orlando
*Orange County, Indiana
*Orange County, New ...
, and cuts between the Santa Ana Mountains and Chino Hills
The Chino Hills are a mountain range on the border of Orange, Los Angeles, and San Bernardino counties, California, with a small portion in Riverside County. The Chino Hills State Park preserves open space and habitat in them.
Geography
The C ...
via the narrow Santa Ana Canyon
Santa Ana Canyon ( es, Cañón de Santa Ana), or the Santa Ana Narrows, is the water gap where the Santa Ana River passes between the Santa Ana Mountains and the Chino Hills, near the intersection of Orange, Riverside, and San Bernardino counties, ...
. The river roughly bisects the county as it flows southwest towards the ocean. In Anaheim
Anaheim ( ) is a city in northern Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area. As of the 2020 United States Census, the city had a population of 346,824, making it the most populous city in Orange County, the 10th-most p ...
, the entire flow of the river (except during wet seasons) is diverted into spreading ground
A spreading ground is a water conservation facility that retains surface water long enough for it to percolate into the soil. Spreading grounds must be located where underlying soils are permeable and connected to a target aquifer.
Locating them ...
s for groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in ...
of the north Orange County aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
, providing about half of the county's municipal water supply. Downstream of there, the river is mostly confined to a concrete channel, serving only for flood control and urban runoff
Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces (roads, parking lots and sidewalks) are constructed during land development. During rain , storms and other precipit ...
drainage, and is usually dry or a small trickle. At Orange it receives Santiago Creek
Santiago Creek is a major watercourse in Orange County in the U.S. state of California. About long, it drains most of the northern Santa Ana Mountains and is a tributary to the Santa Ana River. It is one of the longest watercourses entirely within ...
from the east before entering Santa Ana. After crossing under Interstate 5 it passes through the River View Golf Course, one of its few non-concreted sections within Orange County, and then becomes a concrete channel again through most of Santa Ana and Fountain Valley to a point below the 405 Freeway, where the river bed becomes natural (though the banks remain concrete). The mouth of the river is located in a small tidal lagoon between Huntington State Beach
Huntington State Beach is a protected beach in Southern California, located in the Huntington Beach, California, City of Huntington Beach in Orange County, California, Orange County. It extends from Newport Beach (Santa Ana River) north to Ca ...
in Huntington Beach
Huntington Beach is a seaside city in Orange County in Southern California, located southeast of Downtown Los Angeles. The city is named after American businessman Henry E. Huntington. The population was 198,711 during the 2020 census, maki ...
and Newport Beach
Newport Beach is a coastal city in South Orange County, California. Newport Beach is known for swimming and sandy beaches. Newport Harbor once supported maritime industries however today, it is used mostly for recreation. Balboa Island, Newport ...
.
Watershed
The Santa Ana River drains the largest watershed of California's South Coast region, covering in parts of San Bernardino, Riverside, Orange and Los Angeles Counties. Although the river does not pass through Los Angeles County, some of its tributaries, including San Antonio Creek extend into it. The watershed consists mainly of high mountain ranges that surround and divide large, dry alluvial valleys. The San Gabriel, San Bernardino and San Jacinto Mountains encircle the aridInland Empire
The Inland Empire (IE) is a metropolitan area and region inland of and adjacent to coastal Southern California, centering around the cities of San Bernardino and Riverside, and bordering Los Angeles County to the west. It includes the cities o ...
lowland on the north and east. The Santa Ana Mountains and Chino Hills divide the Inland Empire from the Orange County coastal plain; the Santa Ana Canyon is the only natural break in the range between the two lowlands. The southern part of the watershed, drained by the San Jacinto River into Lake Elsinore and via Temescal Creek into the Santa Ana River, constitutes some 45% of the total area and extend its boundaries as far south as the Colorado Desert
California's Colorado Desert is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert. It encompasses approximately , including the heavily irrigated Coachella and Imperial valleys. It is home to many unique flora and fauna.
Geography and geology
The Colorado De ...
at Anza-Borrego Desert State Park. The river has over 50 named tributaries, most of which are intermittent streams.
As of 2000, about 4.8 million people lived in the Santa Ana River watershed. Most of the population is concentrated close to the river in urban centers such as San Bernardino, Riverside, Anaheim and Santa Ana. The Inland Empire still has large areas dedicated to agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
and ranching
A ranch (from es, rancho/Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of a farm. These terms are most often ...
, although it is rapidly urbanizing. In Orange County, nearly all the valley lands are urbanized. Some major bodies of water in the watershed include Irvine Lake
Irvine Lake is a reservoir in Orange County, California, United States. It is on Santiago Creek, located in Silverado, California, east of the city of Irvine and close to Irvine Regional Park. The reservoir is currently operated by the Serrano ...
, Lake Mathews
Lake Mathews is a large reservoir in Riverside County, California, located in the Cajalco Canyon in the foothills of the Temescal Mountains. It is the western terminus for the Colorado River Aqueduct that provides much of the water used by the ...
, Lake Perris, Diamond Valley Lake, Lake Skinner
Skinner Reservoir, also known as Lake Skinner, is a reservoir in western Riverside County, California, located at the foot of Bachelor Mountain in the Auld Valley, approximately northeast of Temecula. It was created in 1973 by the construction o ...
, and Big Bear Lake
Big Bear Lake is a reservoir in the San Bernardino Mountains, in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is a snow and rain fed lake, having no other means of tributaries or mechanical replenishment. At a surface elevation of , it ...
. All of these are water supply reservoirs constructed by county or state water agencies, and with the exception of Big Bear, much of the water is imported from other parts of California due to the arid local climate. Diamond Valley Lake, with a storage capacity of , is the largest and most recently constructed. Lake Elsinore is the only major natural lake in the watershed.
 The Santa Ana River watershed shares boundaries with many adjacent river basins. In the northwest is the San Gabriel River, which empties into the Pacific at
The Santa Ana River watershed shares boundaries with many adjacent river basins. In the northwest is the San Gabriel River, which empties into the Pacific at Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporate ...
. In Orange County, the San Diego Creek
San Diego Creek is a urban waterway flowing into Upper Newport Bay in Orange County, California in the United States. Its watershed covers in parts of eight cities, including Irvine, Tustin, and Costa Mesa. From its headwaters in Laguna Woods ...
, Aliso Creek, and San Juan Creek
San Juan Creek, also called the San Juan River, is a long stream in Orange and Riverside Counties, draining a watershed of .7.5 Minute Quadrangle Map, U.S. Geological Survey, San Juan Capistrano, 1968, photorevised 1981 Its mainstem begins in ...
watersheds border the Santa Ana watershed on the south. Further south, in San Diego County, the watershed is bordered by those of San Mateo Creek, the Santa Margarita River
The Santa Margarita River which with the addition of what is now Temecula Creek, was formerly known as the Temecula River, is a short intermittent river on the Pacific coast of southern California in the United States, approximately U.S. Geologic ...
, and the San Luis Rey River. On the east the watershed shares borders with those of the Whitewater River and the Coachella Valley
, map_image = Wpdms shdrlfi020l coachella valley.jpg
, map_caption = Coachella Valley
, location = California, United States
, coordinates =
, width =
, boundaries = Salton Sea (southeast), Santa Rosa Mountains (southwest), San Jacint ...
, flowing into the Salton Sea
The Salton Sea is a shallow, landlocked, highly saline body of water in Riverside and Imperial counties at the southern end of the U.S. state of California. It lies on the San Andreas Fault within the Salton Trough that stretches to the Gulf o ...
, and on the north with the Mojave River, which flows into the endorheic basin of the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in ...
.
In Orange County, the river flows across a vast, gently sloping alluvial fan created from its own sediments therefor its drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, t ...
is extremely narrow because the surrounding land slopes away from the river bed. In its natural state the river would frequently change course into one of many intermittent channels that fan out across the plain. Today, these auxiliary river-beds have been artificially disconnected from the Santa Ana River and converted into flood control channels, including the Talbert and Huntington Beach channels, which empty into the Pacific very near the mouth of the Santa Ana River. The combined Talbert-Huntington Beach watershed drains of mostly suburbanized land. The river originally had many different outlets to the Pacific, one of which even extended as far north as the San Gabriel River. The original mouth of the river was located at Newport Bay, which drained into the Pacific Ocean, at what is today the entrance to Newport Harbor. Based on a U.S. Coastal Survey from 1878, Newport Bay was predominantly a river estuary with few open channels. The river flowed into the bay bringing with it heavy silt and making boating difficult. To eventually create Newport Harbor, sand deposited by the Santa Ana River had to be constantly dredged away. In 1920, the Bitter Point Dam was built to divert the river away from the bay and on its current course to the ocean at Huntington Beach. Stone jetties were built to form the new river mouth. All of the Islands in Newport Harbor are the product of dredging and man made forming from the sands and silt deposited over time by the Santa Ana River.
Geology
Ancientigneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
, metamorphic and sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
underlie and form the geologic base of the Santa Ana River watershed. Most of the strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum ( : strata) is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as ei ...
in the flat valleys and basins of the watershed are underlain by thousands of feet of sediment deposited by shallow seas that covered parts of Southern California in ancient times.. Most of the mountains in and around the basin consist of granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such ...
s about 75 million years old. However, above elevations of ancient metamorphic rock up to 1.7 billion years old is exposed.. This rock originally formed at the bottom of the ancestral Pacific Ocean and was uplifted to the highest peaks of the mountains by tectonic action. Even during the ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
s, Southern California mountains were not subjected to extensive glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
, so the rock has remained for tens of millions of years without significant erosion.
Diverse and complex faulting and geologic instability have shaped the Santa Ana River watershed. The San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is Fault (geology)#Strike-slip fau ...
runs across the northern section of the watershed and is responsible for the formation of the San Bernardino and San Gabriel Mountains, part of the Transverse Ranges
The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa B ...
of Southern California. The ElsinoreâWhittier Fault
The Whittier Fault is a geologic fault located in eastern Los Angeles County in Southern California, that is one of the two upper branches of the Elsinore Fault Zone, with the Chino Fault the second.
Geology
The Whittier Fault is a right-l ...
Zone crosses the Santa Ana River further downstream, near the Orange/Riverside County line. Tectonic action along this fault created the Santa Ana Mountains, Puente Hills, East Orange Hills, Chino Hills, Loma Ridge, and the other mountain ranges and ridges that run northwestâsoutheast across the lower section of the watershed â the coastal Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges (also called the Lower California province) are a group of mountain ranges that stretch from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Coast Ranges, which ...
. While the Transverse Ranges rise above in many places, the highest peaks of the Peninsular Ranges reach less than half that elevation.
The cutting of Santa Ana Canyon across the Peninsular Ranges is attributed to the wetter Southern California climate during the Wisconsinian Glaciation and earlier ice ages, during which rivers in Southern California were substantially bigger in volume. The Santa Ana River, which existed prior to the creation of the Peninsular Ranges, maintained its course as an antecedent stream due to its increased erosive power. The canyon was eroded through bedrock that today divides the groundwater basins of the Inland Empire and the coastal plain. Because groundwater in the watershed generally flows from east to west, it is forced to the surface at the bedrock "sill" of Santa Ana Canyon, resulting in a perennial stream that prior to development flowed freely across the coastal plain to the Pacific. During this period, the Santa Ana changed course multiple times, eroding now-dry wind gaps
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
in the Peninsular Range and the coastal mesas around Huntington Beach and Newport Beach.
Ecology
Hundreds of species of animals and plants characterize the Santa Ana River's diversity of climates and vegetation zones. There are over ten of these vegetation zones in the watershedâincluding the sparsely vegetatedalpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
and subalpine zone
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial f ...
s in the mountains, mid-elevation forests of pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accep ...
, lodgepole and oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
, chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant community and geographical feature found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is shaped by a Mediterranean c ...
, coastal sage scrub
Coastal sage scrub, also known as coastal scrub, CSS, or soft chaparral, is a low scrubland plant community of the California coastal sage and chaparral subecoregion, found in coastal California and northwestern coastal Baja California. It is w ...
, the increasingly rare riparian forest and marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
es along the river bed, lined with trees and rushes, and the thinly vegetated coastal areas virtually flush with sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
. The watershed supports up to 200 bird species, 50 mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
species, 13 reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
species, 7 amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
species, and 15 fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
species, including steelhead trout.
The largest portion of the watershed, the Inland Empire portion, is dominated by a hot, dry desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
climate that supports sparse wildlife, while the climate and vegetation of the San Jacinto River and Temescal Creek watershed is similar to that of the southern Central Valley. Downstream of the desert was once the coastal sage scrub
Coastal sage scrub, also known as coastal scrub, CSS, or soft chaparral, is a low scrubland plant community of the California coastal sage and chaparral subecoregion, found in coastal California and northwestern coastal Baja California. It is w ...
and dry grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
community of the Orange County coastal plain, but that region has been almost entirely lost to urbanization. Rimming the arid portions of the watershed are the chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant community and geographical feature found primarily in the U.S. state of California, in southern Oregon, and in the northern portion of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is shaped by a Mediterranean c ...
zones, consisting of sclerophyll
Sclerophyll is a type of vegetation that is adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. The plants feature hard leaf, leaves, short Internode (botany), internodes (the distance between leaves along the stem) and leaf orientation which is paral ...
ous, thick, low bushes and small trees. The chaparral generally is found between elevations of , and occurs mainly closer to the coast on the windward side of the Peninsular Ranges. The scrub oak Scrub oak is a common name for several species of small, shrubby oaks. It may refer to:
*the Chaparral plant community in California, or to one of the following species.
In California
*California scrub oak (''Quercus berberidifolia''), a widespr ...
is one of the most common plants in chaparral regions, forming a dense groundcover that makes it difficult for humans and large animals such as mountain lions, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecologica ...
s, and bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the red lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada through most of the contiguous United States to Oaxaca in Mexico. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUC ...
s to traverse. Chaparral growth is determined by wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
s and droughts, and depends on the semi-arid climate of the region.
Perennial and seasonal streams often are lined with live oak and sycamore, which transition into the riparian zones of the main stem Santa Ana River. The largest unbroken riparian corridor is the stretch between Riverside and Prado Dam, where the river has been largely left in its natural state despite pollution from urban runoff. In addition, the flood control basin behind Prado Dam contains of seasonal wetlands. The Santa Ana sucker
The Santa Ana sucker (''Catostomus santaanae'') is a freshwater ray-finned fish, endemic to California. It is closely related to the mountain sucker and has dark grey upper parts and silvery underparts. It grows to a maximum length of , but most ...
, a small bottom-dwelling fish, was once found along most of the Santa Ana River, but is now rarely seen. Near the mouth, the river was once abundant in salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated ...
es, which stretched for miles on either side of the river, even near Upper Newport Bay
The Upper Newport Bay (known locally as "The Back Bay") is a large coastal wetland (an estuary) in Newport Beach, Southern California and a major stopover for birds on the Pacific Flyway. Dozens of species, including endangered ones, can be ob ...
, which has also served as an alternate mouth of the river.
The alpine and subalpine zones, despite their high elevation (above ) and significant rainfall (at least per year, except in drought years), are sparsely vegetated. The windswept terrain of the alpine zone is primarily small brush and weeds, while treesâmostly small gnarled pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accep ...
s and juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arcti ...
sâoccur in canyons and shielded depressions in the subalpine zone. Inland elevations above support much denser forest. Jeffrey pine
''Pinus jeffreyi'', also known as Jeffrey pine, Jeffrey's pine, yellow pine and black pine, is a North American pine tree. It is mainly found in California, but also in the westernmost part of Nevada, southwestern Oregon, and northern Baja Califo ...
, ponderosa pine, black oak
Black Oak may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Black Oak, Arkansas
* Black Oak, Daviess County, Indiana
* Black Oak, Lake County, Indiana, a neighborhood of Gary, Indiana
* Black Oak, Missouri
Other
* Black Oak Arkansas, American band
** ...
, lodgepole pine, and willow constitute most of the forested lands. The mountain habitats of the watershed support many animals typical of Californian mountain regions, including squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squ ...
s, chipmunks, black bears, mule deer, and many species of migratory birds. In the canyons of the San Bernardinos, the river is abundant in rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coasta ...
and is lined with alders, willow and cottonwoods. Where the river and its large upper tributaries empty out of the mountain canyons into the Inland Empire basin, they are surrounded by the alluvial scrub zone, a mix of desert and upper riparian vegetation. Along the main stem, this zone begins at the base of Seven Oaks Dam
Seven Oaks Dam is a high earth and rock fill embankment dam across the Santa Ana River in the San Bernardino Mountains, about northeast of Redlands in San Bernardino County, southern California. It impounds Seven Oaks Reservoir in the San Berna ...
and ends at the Lytle Creek confluence.
 Historically, the Santa Ana was named "the best stream in Southern California or steelhead trout habitat. The steelhead is an anadromous fish, similar to
Historically, the Santa Ana was named "the best stream in Southern California or steelhead trout habitat. The steelhead is an anadromous fish, similar to salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
, that migrates up rivers and streams to spawn. Unlike salmon, which usually only reproduce once, steelhead may reproduce multiple times and have a much longer life span. Steelhead was once found along the entire main stem of the Santa Ana River, as well as on some of its main tributariesâSantiago Creek
Santiago Creek is a major watercourse in Orange County in the U.S. state of California. About long, it drains most of the northern Santa Ana Mountains and is a tributary to the Santa Ana River. It is one of the longest watercourses entirely within ...
, San Antonio and Chino Creeks, Cucamonga Creek, Lytle Creek, City Creek, and Mill Creek. Few, if any, steelhead were present in Temescal Creek (although one of its tributaries was stocked in the 1930s) and none inhabited the San Jacinto River, because it is disconnected from most of the Santa Ana River system. Up to the 1950s, significant numbers of steelhead trout still migrated in from the ocean. Because of pollution and modifications to the river, very few steelhead still use the river. There is a population of wild stream resident coastal rainbow trout upstream of Seven Oaks Dam and in the upper reaches of a few tributaries. Despite the rarity of steelhead, in recent years fin samples from 13 trout were collected from Harding Canyon in the Santiago Creek
Santiago Creek is a major watercourse in Orange County in the U.S. state of California. About long, it drains most of the northern Santa Ana Mountains and is a tributary to the Santa Ana River. It is one of the longest watercourses entirely within ...
tributary of the Santa Ana River and genetic analysis has shown them to be of native and not hatchery stocks.
Invasive speciesâthose that are not native to the regionâhave caused problems in the watershed for many years. One of the most troublesome invasive species is the giant reed
''Arundo donax'' is a tall perennial cane. It is one of several so-called reed species. It has several common names including giant cane, elephant grass, carrizo, arundo, Spanish cane, Colorado river reed, wild cane, and giant reed. ''Arundo'' an ...
, which plagues many coastal Southern California waterways. The giant reed is similar to a tall grass or thin bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, bu ...
, but grows quickly and can take over native stands of vegetation, block the streambed, hurts the habitat of native animals, and increases the hazard of wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
s. Perhaps the largest effect that giant reed has is its usage of water. To support its fast growth rate, the giant reed population in the Santa Ana River watershed can consume of water per year.
Other invasive species also have affected the Santa Ana River. One of the most prominent is the brown-headed cowbird, which feeds off parasites and insects identified with cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
, which were brought to Southern California during the Spanish Rancho period. The brown-headed cowbird is a "brood parasite", or a bird that lays its eggs in another bird's nest. One of the most afflicted birds is the least Bell's vireo
Bell's vireo (''Vireo bellii'') is a songbird that migrates between a breeding range in Western North America and a winter range in Central America. It is dull olive-gray above and whitish below. It has a faint white eye ring and faint wing bar ...
, whose population also suffers from the loss of riparian habitat. The least Bell's vireo is considered an endangered species, as is the southwestern willow flycatcher, whose habitat is often shared with the other bird. The saltcedar
The genus ''Tamarix'' (tamarisk, salt cedar, taray) is composed of about 50â60 species of flowering plants in the family Tamaricaceae, native to drier areas of Eurasia and Africa. The generic name originated in Latin and may refer to the Tam ...
is another invasive large weed that also, like the giant reed, uses large amounts of water. Unlike giant reed, the saltcedar has deeper roots, not only making it more difficult to remove but allowing it to access and use up deep groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
. However, the saltcedar is similar in that it also provides little usable habitat for native animals.
History
First peoples
Human habitation on the Santa Ana River dates back 9,000 to 12,000 years ago, close to the early stages of theHolocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
period. The first Native Americans to live in the area were nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
ic tribes that traveled from place to place, grazing animals on fertile grasslands and gathering fruits and seeds for food. The ancestors of these early people originated from the Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, easter ...
and Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
people of the northwestern United States. Eventually, the human population of the watershed reached a peak of about 15,000. About 8,000 years ago, the climate experienced a change becoming more arid and the originally nomadic tribes began to stay in individual places longer, becoming semi-nomadic. However, they did not establish agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, nor did they raise animals or live in villages. Like many Native American tribes in California, acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and borne ...
s were a staple food of many of the inland valley people. People closer to the ocean often fished and hunted small animals, often from tide pool
A tide pool or rock pool is a shallow pool of seawater that forms on the rocky intertidal shore. Many of these pools exist as separate bodies of water only at low tide.
Many tide pool habitats are home to especially adaptable animals that ...
s and coastal stream areas, for food.
Several major premodern Native American groups eventually gained control of lands along the river: the Yuhaviatam
The Yuhaaviatam of San Manuel Nation is a federally recognized tribe of Serrano people in San Bernardino County, California.
or Yuharetum people in the upper basin, the Payomkowishum in the southeastern basin, the Cahuilla
The Cahuilla , also known as ÊĂvilÌuqaletem or Ivilyuqaletem, are a Native American people of the various tribes of the Cahuilla Nation, living in the inland areas of southern California.Tongva people
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous peoples of California, Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Channel Islands of California, Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . Some descendants of the people p ...
in the lower basin.. The Yuhaviatam generally lived in the mountain headwaters of the Santa Ana River and its tributaries rimming the present-day Inland Empire basin, in present-day San Bernardino County, as well as in the foothills
Foothills or piedmont are geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range, higher hill range or an upland area. They are a transition zone between plains and low relief hills and the adjacent topograp ...
of the San Bernardino Mountains. The Tongva lived on the flat coastal plains of present-day Orange County south of the Santa Ana Mountains. They were also the larger of the two groups, controlling all the coastal lands from the San Gabriel Mountains
The San Gabriel Mountains ( es, Sierra de San Gabriel) are a mountain range located in northern Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County and western San Bernardino County, California, United States. The mountain range is part of the Tr ...
in the north to Aliso Creek in the south, including all of the Los Angeles Basin
The Los Angeles Basin is a sedimentary basin located in Southern California, in a region known as the Peninsular Ranges. The basin is also connected to an anomalous group of east-west trending chains of mountains collectively known as the Tr ...
. These peoples established villages, some of which were multiethnic and multilingual, including Lupukngna, Genga, Pajbenga
Pajbenga, alternative spelling Pagbigna and Pasbengna, was a Tongva village located at Santa Ana, California, near the El Refugio Adobe, which was the home of José Sepulveda (now located near the intersection of Raitt Street and Myrtle Street). I ...
, Totpavit
Totpavit, alternative spellings Totabit and possibly Totavet, was a Tongva village located in what is now Olive, California. The village was located between the Santa Ana River and Santiago Creek. It was part of a series of villages along the San ...
, and Hutuknga
Hutuknga (alternative spellings: Hotuuknga or Hutuukuga) was a large Tongva village located in the foothills along the present channel of the Santa Ana River in what is now Yorba Linda, California. People from the village were recorded in mission ...
.
Spanish period
 When Spanish explorer
When Spanish explorer Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of ''John''. It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking communities around the world and in the Philippines, and also (pronounced differently) in the Isle of Man. In Spanish, t ...
sailed along the Southern California coast on his voyage of 1542, he passed the mouth of the Santa Ana River without noting it. Neither did any of the subsequent Spanish sea-borne explorers leave any written notice of the river mouth.
It was not until 1769 that Gaspar de PortolĂ led the first overland expedition northwards through coastal Southern Californiaâstill a largely unexplored part of the Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
province of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
âand gave the river its name. On July 28, the party camped "about three leagues" from where the Santa Ana River exits the canyon through the northern Santa Ana Mountains, near present-day Olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
. Fray Juan CrespĂ, one of the members of the expedition, wrote in his diary that he called the spot "Jesus de los Temblores", referring to an earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
that struck while they were camped alongside there. Crespi also noted that the soldiers were calling the river "Rio de Santa Ana", probably because they had recently celebrated Saint Anne's Day. That name remains today (the second oldest place name in Orange County, after Santiago Creek
Santiago Creek is a major watercourse in Orange County in the U.S. state of California. About long, it drains most of the northern Santa Ana Mountains and is a tributary to the Santa Ana River. It is one of the longest watercourses entirely within ...
), and the name of the mountain range and city were derived from the river.
Although no missions were actually located along the Santa Ana River or within the watershed, the river basin was nearly depleted of native people because the Spanish forced them to work at nearby missions, including Mission San Gabriel Arcangel
Mission (from Latin ''missio'' "the act of sending out") may refer to:
Organised activities Religion
*Christian mission, an organized effort to spread Christianity
*Mission (LDS Church), an administrative area of The Church of Jesus Christ of ...
and Mission San Luis Rey
Mission San Luis Rey de Francia ( es, Misión San Luis Rey de Francia) is a former Spanish mission in San Luis Rey, a neighborhood of Oceanside, California. This Mission lent its name to the Luiseño tribe of Mission Indians.
At its prime, ...
. The affected tribes were usually renamed after the missions, resulting in tribal names such as Gabrieliño and Luiseño. Difficult working and living conditions and European diseases such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
killed much of the native population during the roughly 50-year-long Mission Period. The Secularization Act of 1833, passed by the newly independent country of Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: MĂ©xico), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, eventually brought an end to the Mission Period. The post-Mission Period native population was almost entirely devastated. The population was very little, their native religions were nearly lost, and most of their land had been taken by Spanish settlers. Although the Mexican government's original intention with the Secularization Act was to provide the Native Americans with their own land and property, most of the provisions made by the act never actually happened. Spanish settlers continued to press into the remaining tribal lands, and eventually, the tribes were forced into the surrounding desert lands or into the high mountains.
Following the Mission Period came the Rancho Period. This occurred when the enormous land holdings of the missions were subdivided into ranchos owned by individuals. Some of the new private ranchos were merely converted mission ranchos. The first private rancho along the Santa Ana River was Rancho Santiago de Santa Ana Rancho Santiago de Santa Ana was a Spanish land concession in present-day Orange County, California, given by Spanish Alta California Governor JosĂ© JoaquĂn de Arrillaga in 1810 to Jose Antonio Yorba and his nephew Pablo Peralta. The grant exten ...
, a rancho on the left bank of the lower Santa Ana River. This rancho was acquired by Don Juan Pablo Grijalva as early as 1801. Other ranchos on the river followed, including ones in inland areas that had not been exploited in the Mission Period. The ranchos (beginning with the missions) established the tradition of raising cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
in coastal Southern California, a custom upheld until the late 19th century. Agriculture, however, although established, was not yet a major industry. A flood that raged down the Santa Ana in 1825 caused the river's course to change temporarily to an outlet at Newport Bay, depositing sediment that partially created Balboa Island
Balboa Island is a harborside community in Newport Beach, California, accessible to the public via bridge, ferry and several public docks. The community is surrounded by a paved concrete boardwalk open to pedestrian traffic, designated as a pu ...
. Spread throughout the ranchos on the Santa Ana River were a few towns, military outposts and trading posts. The Santa Ana River valley was one of the most prosperous regions in Southern California for many decades.
American settlement
In the late 1840s, California fought for its independence from Mexico in theMexicanâAmerican War
The MexicanâAmerican War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
. The Santa Ana river played an important part in the victory of the Americans over the Mexican army. In 1847, one year after the Bear Flag Revolt
The California Republic ( es, La RepĂșblica de California), or Bear Flag Republic, was an unrecognized breakaway state from Mexico, that for 25 days in 1846 militarily controlled an area north of San Francisco, in and around what is now Son ...
, a Mexican military force set out northwards to attack a smaller American force in the Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ăngeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world' ...
area. However, the Santa Ana River flooded, preventing the Mexicans from crossing the river to attack the Americans. When the river's flow finally subsided, the American forces had been reinforced enough to drive the Mexicans out of the region..
 When the
When the California Republic
The California Republic ( es, La RepĂșblica de California), or Bear Flag Republic, was an unrecognized breakaway state from Mexico, that for 25 days in 1846 militarily controlled an area north of San Francisco, in and around what is now Son ...
was assimilated into the United States in 1848, American settlers began to move into the Santa Ana River region in great numbers. The Mexican ranchos were divided into smaller individual properties, and irrigated agriculture began on a large scale. The city of Santa Ana Viejo, the original location of Santa Ana, was founded in this period. In 1854, Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into several ...
s settled in the upper Inland Empire area and started the city of San Bernardino, gaining prosperity by using water from the river, as well as Lytle Creek and Mill Creek, to irrigate crops. The cattle industry began to decline as farms began to replace ranches. Soon, white settlers in the region were more numerous than Hispanics as well. The California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848â1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California fro ...
around this time was responsible for attracting many of these people to the state, but many remained in Southern California afterwards.
In 1860, a much closer gold rush occurred in the San Bernardino Mountains when prospector William Holcomb discovered significant deposits, just over the northern drainage divide of the Santa Ana River. This discovery exploded into a full-scale gold mining operation in days. The Santa Ana River served as a conduit for miners traveling to the region and many of the forests in the upper basin experienced clearcutting
Clearcutting, clearfelling or clearcut logging is a forestry/ logging practice in which most or all trees in an area are uniformly cut down. Along with shelterwood and seed tree harvests, it is used by foresters to create certain types of fore ...
as a result of the high resource demands of the boom. Gold was also discovered in Lytle Creek in that same year. Following the gold rush, the cultivation of citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering plant, flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as Orange (fruit), oranges, Lemon, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and lim ...
became the mainstay of the economy of the lower Santa Ana River area. Through the late 19th century, citrus fields covered much of the coastal plain and led to the naming of Orange County.
Floods, droughts and legacy
Notwithstanding the increased prosperity in the 1860s, this decade was also the scene of a series of natural disasters. In theGreat Flood of 1862
The Great Flood of 1862 was the largest flood in the recorded history of Oregon, Nevada, and California, occurring from December 1861 to January 1862. It was preceded by weeks of continuous rains and snows in the very high elevations that began in ...
, heavy rains dropped by a series of winter storms caused the Santa Ana to burst its banks, flooding thousands of acres of land and killing 20 to 40 people in the greatest flood it had experienced in recorded history. The levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually soil, earthen and that often runs parallel (geometry), parallel to ...
s along the river burst in many places, flooding part of the Inland Empire into a continuous body of water several miles wide stretching from the mouth of Santa Ana Canyon to where the river cuts through the Santa Ana Mountains. Downstream in Orange County, the river overwhelmed nearly all the existing floodworks and transformed the coastal plain into a transient inland sea. The flow, now calculated as a 1,000-year flood, peaked at roughly , over half the average flow of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
.. Even after the flood, detrimental conditions continued in the region. For the two years following the flood, an intense drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
caused the deaths of tens of thousands of head of livestock. Despite all of the hardships experienced in the three years, after conditions finally returned to normal, the Santa Ana River watershed again became a prospering agricultural region. The cities of Santa Ana and Riverside
Riverside may refer to:
Places Australia
* Riverside, Tasmania, a suburb of Launceston, Tasmania
Canada
* Riverside (electoral district), in the Yukon
* Riverside, Calgary, a neighbourhood in Alberta
* Riverside, Manitoba, a former rural m ...
were established in 1869 and 1870, respectively.
1934 and 1938 saw a further pair of devastating floods that in part brought an end to the area's citrus industry. In the Los Angeles flood of 1938, the Santa Ana again burst its banks and flooded Anaheim
Anaheim ( ) is a city in northern Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area. As of the 2020 United States Census, the city had a population of 346,824, making it the most populous city in Orange County, the 10th-most p ...
and Orange in up to of water, stripping away thousands of acres of rich topsoil and destroying many of the citrus groves. Almost 60 people were killed in the disaster and about of land were flooded, despite the fact that the flow in the river was only one-third of that of the 1862 flood. With the extreme damage from the floods, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
made the decision to dam and concrete the river beginning in the 1940s, and declared it as the greatest flood hazard in the U.S. west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. Prado Dam, built in 1941, was designed to capture floodwaters from the Inland Empire about upstream from the river's mouth. The dam's impoundment, Prado Flood Control Basin, was designed to handle a 70-year flood.
 With the increased flood protection afforded by the Prado Dam, major industrial development migrating south from the Los Angeles Basin, and the Southern California housing boom in the 1950s and 1960s, the Santa Ana River watershed began its third and final transitionâfrom agricultural to urban. The population of the Santa Ana River basin increased dramatically, but brought with it the threat of greater damage from floods, somewhat compromising the protection afforded by Prado Dam. Because housing and urban areas encroached on the river's historic
With the increased flood protection afforded by the Prado Dam, major industrial development migrating south from the Los Angeles Basin, and the Southern California housing boom in the 1950s and 1960s, the Santa Ana River watershed began its third and final transitionâfrom agricultural to urban. The population of the Santa Ana River basin increased dramatically, but brought with it the threat of greater damage from floods, somewhat compromising the protection afforded by Prado Dam. Because housing and urban areas encroached on the river's historic floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
âan area once occupied by farmsâand the river became confined to a narrow channelâa flood similar to the ones surrounding the turn of the 20th century would cause much more damage. The construction of roads and buildings also heightened the runoff that would flow into the river during rainfall, a process known as urban runoff
Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces (roads, parking lots and sidewalks) are constructed during land development. During rain , storms and other precipit ...
. In fact, the river flooded again in 1969, and while much of the runoff from the Inland Empire was captured behind Prado Damâprobably saving Orange County from an even greater floodâSantiago Creek, a large tributary flowing from the Santa Ana Mountains, eroded its banks until it swept away portions of residential communities in the cities of Tustin
Tustin is a city located in Orange County, California, in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. In 2020, Tustin had a population of 80,276. The city is located next to the county seat, Santa Ana, California, Santa Ana, and does not include the un ...
and Orange.
In 1964, the Santa Ana River Mainstem Project, which involved concreting the lower of the river, was first proposed. Construction work began in 1989, and today, through much of Orange County, the river's channel is essentially an enormous box culvert
A culvert is a structure that channels water past an obstacle or to a subterranean waterway. Typically embedded so as to be surrounded by soil, a culvert may be made from a pipe, reinforced concrete or other material. In the United Kingdom ...
. The second dam, Seven Oaks Dam, was completed in 1999. This dam captures flood runoff from Santa Ana Canyon before it can enter the Inland Empire. The dam was designed to withstand a 350-year flood. Today, the river lies mainly between levees and concrete channels, and especially in its lower course, functions only as a flood drainage channel.
Pollution and restoration
 As with many Southern California rivers, the Santa Ana is heavily polluted and used. The main stem above
As with many Southern California rivers, the Santa Ana is heavily polluted and used. The main stem above Seven Oaks Dam
Seven Oaks Dam is a high earth and rock fill embankment dam across the Santa Ana River in the San Bernardino Mountains, about northeast of Redlands in San Bernardino County, southern California. It impounds Seven Oaks Reservoir in the San Berna ...
is free-flowing, as are many of its upper tributaries. Once the river enters the Inland Empire basin, however, much of its flow is diverted for municipal
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
and agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
water use. Most of the flow in the river below the city of San Bernardino consists of effluent from 45 wastewater treatment plants
Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environmen ...
and dry season urban runoff
Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces (roads, parking lots and sidewalks) are constructed during land development. During rain , storms and other precipit ...
, which is collected behind Prado Dam.''New strategies for America's watersheds'', p. 102. Any flow that makes it downstream to Orange County is diverted by another pair of dams into approximately of groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
recharge basins, providing approximately of municipal water for the county every year, or one-third of its water supply. Downstream of that dam, the river gathers further urban runoff before finally making it into the Pacific. The Santa Ana River is included on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) list of "304 (l) 'toxic hot spots' list of impaired waterways".
In Orange County, the Orange County Water District, formed in 1932 to manage the county's groundwater, uses the treated water from upstream to recharge a massive reservoir, or aquifer, that runs roughly nine miles from Lakeview Avenue to Ball Road. The water percolates through layers of sand and gravel, which work to scrub, or purify it. There, it joins treated wastewater pumped from the Orange County Sanitation Department's state-of-the-art plant in Fountain Valley. Those two types of water account for 60 to 70 percent of the aquifer, which can hold 500,000 acre feet. Combined with water imported from Northern California and the Colorado River, the OCWD maintains that the aquifer could serve the water needs of all its clients for a year.
A number of organizations have been formed to try to gain public interest in restoring the river. One of the most prominent is the Santa Ana Watershed Project Authority (SAWPA), formed by five municipal water districts in the Santa Ana River area. A second one is the Santa Ana River Dischargers Association. Both have conducted studies as to what beneficial uses the Santa Ana River would have aside from water supply and flood control, as well as the removal of some of the concreted sections of the lower river. This set of studies is known as the "Use-Attainability Analysis", which was submitted to the state Congress, which approved it. However, upon submission to the EPA, it was rejected. As a result, little work has been done to repair the ecological damage that has been caused by urbanization along the river.''New strategies for America's watersheds'', p. 103. Other projects include the Santa Ana Watershed Planning Advisory Committee, and the Santa Ana River Watershed Alliance (SARWA).
Recreation
 There are many recreational opportunities along the Santa Ana River. The Santa Ana River watershed includes parts of the
There are many recreational opportunities along the Santa Ana River. The Santa Ana River watershed includes parts of the Cleveland National Forest
Cleveland National Forest encompasses 460,000 acres (), mostly of chaparral, with a few riparian areas. A warm dry mediterranean climate prevails over the forest. It is the southernmost U.S. National Forest of California. It is administered by th ...
, San Bernardino National Forest, Angeles National Forest
The Angeles National Forest (ANF) of the United States Forest Service, U.S. Forest Service is located in the San Gabriel Mountains and Sierra Pelona Mountains, primarily within Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County in southern Calif ...
, Mount San Jacinto State Wilderness Area, Chino Hills State Park
Chino Hills State Park is a state park of California, in the United States. It is located in the Chino Hills, foothills of the Santa Ana Mountains. It is a critical link in the ChinoâPuente Hills wildlife corridor, and a major botanical habit ...
, and Lake Perris State Recreation Area. Big Bear Lake
Big Bear Lake is a reservoir in the San Bernardino Mountains, in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is a snow and rain fed lake, having no other means of tributaries or mechanical replenishment. At a surface elevation of , it ...
, Lake Elsinore, and Lake Irvine
Irvine Lake is a reservoir in Orange County, California, United States. It is on Santiago Creek, located in Silverado, California, east of the city of Irvine and close to Irvine Regional Park. The reservoir is currently operated by the Serrano ...
are popular recreational lakes in the watershed. The river never actually flows through any of these lakes, but they each have drainage to the river via tributaries.
The Santa Ana River bicycle path
The Santa Ana River Trail is a multi-use trail complex that runs alongside the Santa Ana River in southern California. The trail stretches from the Pacific Ocean at Huntington Beach along the Santa Ana River to the OrangeâRiverside county line. ...
which, when complete, will run from the river's mouth at Huntington Beach to near the San Bernardino Mountains, currently extends about along the river to Prado Dam. The proposed distance along the trail is over . In Riverside County, the Hidden Valley Wildlife Area also has of recreational paths. Some entities have been opting for a Santa Ana River Park, which would encompass a strip of land on either side of the river for its entire course. The city of Redlands would like to develop riverside green space near the historic downtown district. The Santa Ana River Lakes, located near Anaheim, are a popular recreational fish farm
upright=1.3, Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture) at Loch Ainort, Isle of Skye">mariculture.html" ;"title="Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture">Salmon farming in the sea (mariculture) at Loch Ainort, Isle of Skye, Scotland
Fish farming or ...
fed with water from the river. Ultimately, the trail could link a network of river-bottom parks. In 2014, naturalists navigated the stretch of river flanked by Chino Hills State Park on the north and the Cleveland National Forest on the south. The rafts made it before the vegetation was impenetrable but they were convinced there were possibilities of improving public access and recreational opportunities.Sahagun, Louis (October 27, 2014"How California is turning drainage canals back to rivers"
''
Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' (abbreviated as ''LA Times'') is a daily newspaper that started publishing in Los Angeles in 1881. Based in the LA-adjacent suburb of El Segundo since 2018, it is the sixth-largest newspaper by circulation in the Un ...
''
Crossings
The Santa Ana River has 70 significant crossings, bridges and dams. This list places them from mouth to source.
Orange County
Orange County most commonly refers to:
*Orange County, California, part of the Los Angeles metropolitan area
Orange County may also refer to:
U.S. counties
*Orange County, Florida, containing Orlando
*Orange County, Indiana
*Orange County, New ...
* Santa Ana River bicycle path
The Santa Ana River Trail is a multi-use trail complex that runs alongside the Santa Ana River in southern California. The trail stretches from the Pacific Ocean at Huntington Beach along the Santa Ana River to the OrangeâRiverside county line. ...
(Costa Mesa/Huntington Beach)
* Adams Avenue (Costa Mesa/Huntington Beach)
* Pacific Electric Railway
The Pacific Electric Railway Company, nicknamed the Red Cars, was a privately owned mass transit system in Southern California consisting of electrically powered streetcars, interurban cars, and buses and was the largest electric railway system ...
Railway Bridge (future Orange County Streetcar)
* Fairview Street (Santa Ana)
* Westminster Avenue/17th Street (Santa Ana)
* Santa Ana River bicycle path
The Santa Ana River Trail is a multi-use trail complex that runs alongside the Santa Ana River in southern California. The trail stretches from the Pacific Ocean at Huntington Beach along the Santa Ana River to the OrangeâRiverside county line. ...
(Santa Ana)
* Garden Grove Boulevard/Memory Lane (Orange/Santa Ana)
* Orange County Line
The Orange County Line is a commuter rail line run by Metrolink from Los Angeles through Orange County to Oceanside in San Diego County, connecting with the Coaster commuter rail service to San Diego. The Orange County Line carries passengers ...
& Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, Trade name, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national Passenger train, passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous United Stat ...
'' Pacific Surfliner'' (Orange/Anaheim)
* Katella Avenue (Orange/Anaheim)
* Railroad Bridge (Orange/Anaheim)
* Taft Avenue/Ball Road (Orange/Anaheim)
* Lincoln Avenue (Orange/Anaheim)
* Glassell Street/Kraemer Boulevard (Orange/Anaheim)
* Metrolink Inland EmpireâOrange County Line (Anaheim)
* Tustin Avenue (Anaheim)
* Riverside Freeway
The Riverside Freeway is one of the named principal Southern California freeways
The Southern California freeways are a vast network of interconnected freeways in the megaregion of Southern California, serving a population of 23 million peop ...
) (Anaheim)
* Lakeview Avenue (Anaheim)
* Santa Ana River bicycle path
The Santa Ana River Trail is a multi-use trail complex that runs alongside the Santa Ana River in southern California. The trail stretches from the Pacific Ocean at Huntington Beach along the Santa Ana River to the OrangeâRiverside county line. ...
(Anaheim)
* Weir Canyon Road (Anaheim/Yorba Linda)
* Gypsum Canyon Road (Yorba Linda)
Ontario Freeway
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
) (Norco)
* Van Buren Boulevard (Jurupa Valley)
* Metrolink Riverside Line
Metrolink's Riverside Line is a commuter rail line running from Los Angeles Union Station in Downtown Los Angeles to Riverside along the Union Pacific Railroad. It runs weekday peak commuter hours only, with very little midday and reverse co ...
(Jurupa Valley/Riverside)
* Mission Boulevard/Buena Vista Avenue (Jurupa Valley/Riverside)
* Sunset Limited
The ''Sunset Limited'' is an Amtrak passenger train that for most of its history has operated between New Orleans and Los Angeles, over the nation's second transcontinental route. However, up until Hurricane Katrina in 2005, it operated betwe ...
& Texas Eagle (Colton)
* Interstate 10
Interstate 10 (I-10) is the southernmost cross-country highway in the American Interstate Highway System. I-10 is the fourth-longest Interstate in the United States at , following I-90, I-80, and I-40. This freeway is part of the originally pl ...
( San Bernardino/ Redlands Freeway) (Colton)
* Riverside Freeway
The Riverside Freeway is one of the named principal Southern California freeways
The Southern California freeways are a vast network of interconnected freeways in the megaregion of Southern California, serving a population of 23 million peop ...
) (San Bernardino)
* E Street (San Bernardino)
* Waterman Avenue (San Bernardino)
* Arrow rail line (San Bernardino)
* Orange Show Road (San Bernardino)
* Tippecanoe Avenue (San Bernardino)
* Alabama Street (Redlands)
* Seven Oaks Dam
Seven Oaks Dam is a high earth and rock fill embankment dam across the Santa Ana River in the San Bernardino Mountains, about northeast of Redlands in San Bernardino County, southern California. It impounds Seven Oaks Reservoir in the San Berna ...
* See also
*List of rivers of Orange County, California
This is a list of rivers of Orange County, California, part of the Greater Los Angeles Area in Southern California.The Santa Ana River and San Gabriel River are the largest in Orange County; their extensive watersheds extend into neighboring ...
* List of tributaries of the Santa Ana River
* Populated places on the Santa Ana River
* List of rivers of California
* List of watershed topics
References
External links
Archival collections
Guide to the Santa Ana River Report.
Special Collections and Archives, The UC Irvine Libraries, Irvine, California.
Other
Santa Ana Watershed Association
{{Authority control Rivers of Orange County, California Rivers of Riverside County, California Rivers of San Bernardino County, California San Bernardino Mountains Santa Ana Mountains Geography of Santa Ana, California Rivers of Southern California Watersheds of California