Sanhedrin 1994-1997 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
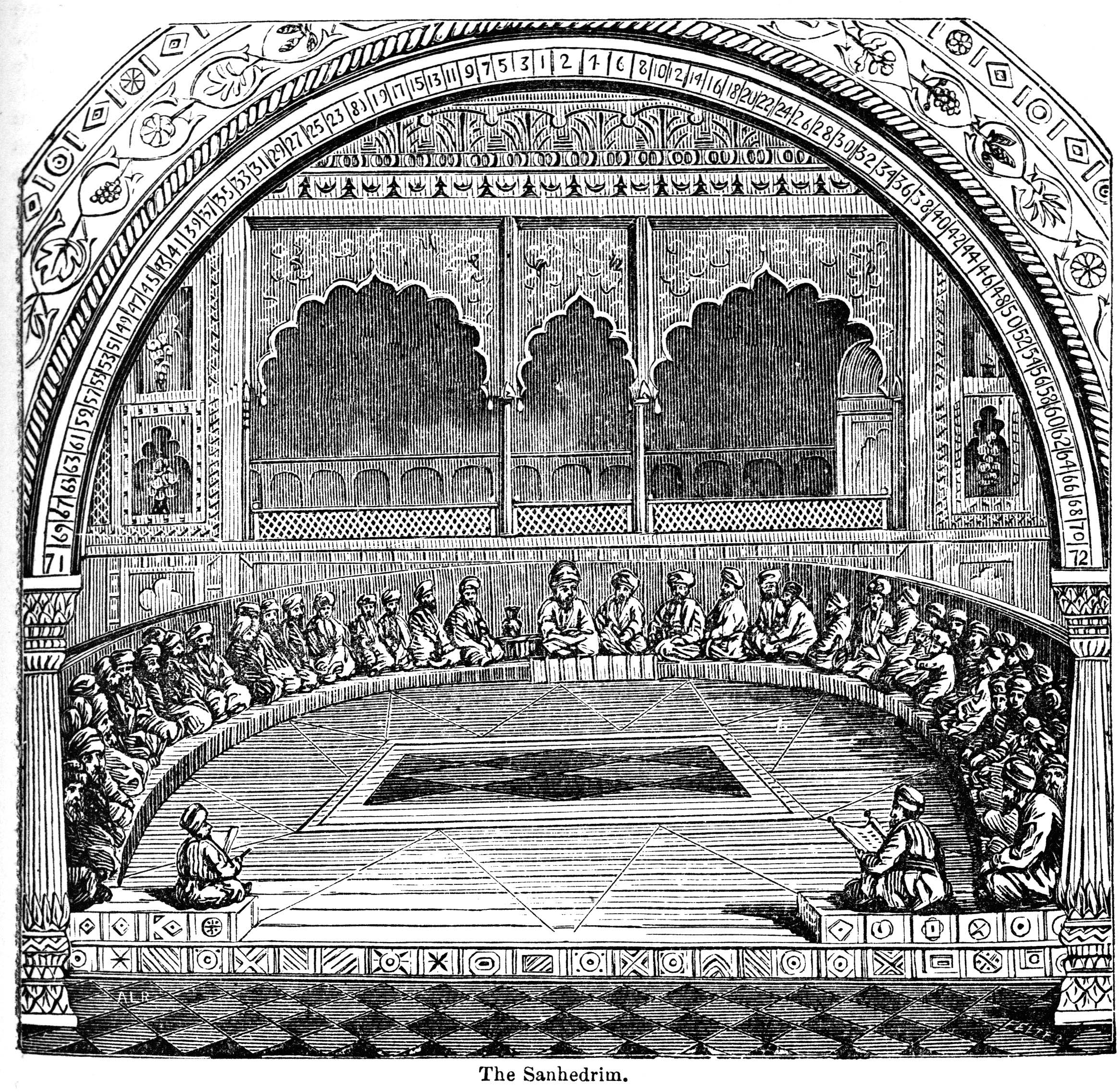 The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence '
The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence '
 Rabbinic texts indicate that following the
Rabbinic texts indicate that following the
"Julian and the Jews 361–363 CE"
an
. As a reaction against Julian's pro-Jewish stance, the later emperor Theodosius I (r. 379–395 CE) forbade the Sanhedrin to assemble and declared ordination illegal. Capital punishment was prescribed for any Rabbi who received ordination, as well as complete destruction of the town where the ordination occurred. However, since the Hebrew calendar was based on witnesses' testimony, which had become far too dangerous to collect, rabbi Hillel II recommended change to a mathematically based calendar that was adopted at a clandestine, and maybe final, meeting in 358 CE. This marked the last universal decision made by the Great Sanhedrin. Gamaliel VI (400–425) was the Sanhedrin's last president. With his death in 425, Theodosius II outlawed the title of
/ref> in Jerusalem under the Caliph 'Umar, and in Babylon (Iraq), but none of these attempts were given any attention by Rabbinic authorities and little information is available about them.
 The "Grand Sanhedrin" was a Jewish high court convened by
The "Grand Sanhedrin" was a Jewish high court convened by
Sanhedrin Launched in Tiberias Israel National News January 20, 2005
/ref> where the original Sanhedrin was disbanded, in which it claimed to re-establish the body according to the proposal of Maimonides and the Jewish legal rulings of Rabbi Yosef Karo. The controversial attempt has been subject to debate within different Jewish communities.
Secular and religious history of the Jewish Sanhedrin
English web site of the re-established Jewish Sanhedrin in Israel
by Rabbi Aryeh Kaplan
''Jewish Encyclopedia'': "Sanhedrin"
* {{Jewish history 1st-century BC establishments in the Hasmonean Kingdom 420s disestablishments in the Roman Empire Governing assemblies of religious organizations Historical legislatures Jewish courts and civil law Jews and Judaism in the Roman Empire Jews and Judaism in the Byzantine Empire Judaism-related controversies Rabbinical organizations Hasmonean Kingdom
 The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence '
The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly
Assembly may refer to:
Organisations and meetings
* Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions
* General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representa ...
' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as '' semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form o ...
s" after the destruction of the Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
.
There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi
Nasi may refer to:
Food Dishes
Nasi Goreng is an Indonesian and Malay word for ''cooked rice'', featured in many Southeast Asian dishes
*Nasi goreng, a popular rice dish often simply called ''nasi''
*Other Southeast Asian ''nasi'' dishes:
**Nasi ...
'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din
The ''av beit din'' ( ''ʾabh bêth dîn'', "chief of the court" or "chief justice"), also spelled ''av beis din'' or ''abh beth din'' and abbreviated ABD (), was the second-highest-ranking member of the Sanhedrin during the Second Temple period, ...
'' or the chief of the court, who was second to the ; and 69 general members.
In the Second Temple period
The Second Temple period in Jewish history lasted approximately 600 years (516 BCE - 70 CE), during which the Second Temple existed. It started with the return to Zion and the construction of the Second Temple, while it ended with the First Jewis ...
, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a building called the Hall of Hewn Stones. The Great Sanhedrin convened every day except festivals and the sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as G ...
day (Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; he, שַׁבָּת, Šabbāṯ, , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical storie ...
).
After the destruction of the Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
and the failure of the Bar Kokhba revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt ( he, , links=yes, ''Mereḏ Bar Kōḵḇāʾ''), or the 'Jewish Expedition' as the Romans named it ( la, Expeditio Judaica), was a rebellion by the Jews of the Judea (Roman province), Roman province of Judea, led b ...
, the Great Sanhedrin moved to Galilee, which became part of the Roman province of Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina (literally, "Palestinian Syria";Trevor Bryce, 2009, ''The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia''Roland de Vaux, 1978, ''The Early History of Israel'', Page 2: "After the revolt of Bar Cochba in 135 ...
. In this period the Sanhedrin was sometimes referred as the ''Galilean Patriarchate'' or ''Patriarchate of Palaestina'', being the governing legal body of Galilean Jewry. In the late 200s CE, to avoid persecution, the name ''Sanhedrin'' was dropped and its decisions were issued under the name of (house of learning). The last universally binding decision of the Great Sanhedrin appeared in 358 CE, when the Hebrew calendar was established. The Great Sanhedrin was finally disbanded in 425 CE after continued persecution by the Eastern Roman Empire.
Over the centuries, there have been attempts to revive the institution, such as the Grand Sanhedrin convened by Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, and modern attempts in Israel.
Hebrew Bible
In the Hebrew Bible (, ; , )Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
and the Israelites were commanded by God to establish courts of judges who were given full authority over the people of Israel, who were commanded by God through Moses to obey the judgments made by the courts and every Torah-abiding law they established. Judges in ancient Israel were the religious leaders and teachers of the nation of Israel. The Mishnah (Sanhedrin 1:6) arrives at the number twenty-three based on an exegetical
Exegesis ( ; from the Greek , from , "to lead out") is a critical explanation or interpretation of a text. The term is traditionally applied to the interpretation of Biblical works. In modern usage, exegesis can involve critical interpretation ...
derivation: it must be possible for a " community" to vote for both conviction and exoneration (). The minimum size of a "community" is 10 men, thus 10 vs 10. One more is required to achieve a majority (11 vs. 10), but a simple majority cannot convict (), and so an additional judge is required (12 vs. 10). Finally, a court should not have an even number of judges to prevent deadlocks; thus 23 (12 vs. 10 and 1). This court dealt with only religious matters. In regard to the Sanhedrin of 70 Elders to help Moses, years before in Egypt these men had been Hebrew officials under Egyptian taskmasters; they were beaten by the Egyptians when they refused to beat fellow Jews in order to finish building projects. As a reward they became the Sanhedrin of 70 Elders.
History
Early Sanhedrin
The Hasmonean court in Judea, presided over by Alexander Jannaeus, until 76 BCE, followed by his wife, Queen Salome Alexandra, was called or ''Sanhedrin.'' The exact nature of this early Sanhedrin is not clear. It may have been a body of sages or priests, or a political, legislative and judicial institution. The first historical record of the body was during the administration of Aulus Gabinius, who, according to Josephus, organized five in 57 BCE as Roman administration was not concerned with religious affairs unless sedition was suspected. Only after the destruction of the Second Temple was the Sanhedrin made up only of sages.Herodian and early Roman rule
The first historic mention of a '' Synhedrion'' ( Greek: ) occurs in the Psalms of Solomon (XVII:49), a Jewish religious book written in Greek. The Mishnah tractate Sanhedrin (IV:2) states that the Sanhedrin was to be recruited from the following sources: Priests (Kohanim), Levites (Levi'im), and ordinary Jews who were members of those families having a pure lineage such that their daughters were allowed to marry priests. In theSecond Temple period
The Second Temple period in Jewish history lasted approximately 600 years (516 BCE - 70 CE), during which the Second Temple existed. It started with the return to Zion and the construction of the Second Temple, while it ended with the First Jewis ...
, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Hall of Hewn Stones in the Temple in Jerusalem. The court convened every day except festivals and the sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as G ...
day (Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; he, שַׁבָּת, Šabbāṯ, , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the week—i.e., Saturday. On this day, religious Jews remember the biblical storie ...
).
The trial of Jesus, and early Christianity
A is mentioned 22 times in the Greek New Testament, including in the Gospels in relation to the trial of Jesus, and in the ''Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its messag ...
'', which mentions a "Great " in chapter 5 where rabbi Gamaliel appeared, and also in chapter 7 in relation to the stoning death of Saint Stephen.
During Jewish–Roman Wars
After the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE, the Sanhedrin was re-established in Yavneh with reduced authority. The seat of the Patriarchate moved to Usha under the presidency of Gamaliel II in 80 CE. In 116 it moved back to Yavneh, and then again back to Usha.After Bar Kokhba Revolt
 Rabbinic texts indicate that following the
Rabbinic texts indicate that following the Bar Kokhba revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt ( he, , links=yes, ''Mereḏ Bar Kōḵḇāʾ''), or the 'Jewish Expedition' as the Romans named it ( la, Expeditio Judaica), was a rebellion by the Jews of the Judea (Roman province), Roman province of Judea, led b ...
, southern Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Galil ...
became the seat of rabbinic learning in the Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
. This region was the location of the court of the Patriarch which was situated first at Usha, then at Bet Shearim, later at Sepphoris
Sepphoris (; grc, Σέπφωρις, Séphōris), called Tzipori in Hebrew ( he, צִפּוֹרִי, Tzipori),Palmer (1881), p115/ref> and known in Arabic as Saffuriya ( ar, صفورية, Ṣaffūriya) since the 7th century, is an archaeolog ...
and finally at Tiberias.
The Great Sanhedrin moved in 140 to Shefaram
Shefa-Amr, also Shfar'am ( ar, شفاعمرو, Šafāʻamr, he, שְׁפַרְעָם, Šəfarʻam) is an Arab citizens of Israel, Arab city in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. In it had a population of , with a Sunni I ...
under the presidency of Shimon ben Gamliel II, and subsequently to Beit She'arim (Roman-era Jewish village)
Beit She'arim ( / / Bet Sharei) or Besara ( gr, Βήσαρα) was a Roman-era Jewish village from the 1st century BCE until the 3rd century CE which, at one time, was the seat of the Sanhedrin.
In the mid-2nd century, the village briefly beca ...
and later to Sepphoris
Sepphoris (; grc, Σέπφωρις, Séphōris), called Tzipori in Hebrew ( he, צִפּוֹרִי, Tzipori),Palmer (1881), p115/ref> and known in Arabic as Saffuriya ( ar, صفورية, Ṣaffūriya) since the 7th century, is an archaeolog ...
, under the presidency of Judah ha-Nasi. Finally, it moved to Tiberias in 220, under the presidency of Gamaliel III
Gamaliel III ( he, רבן גמליאל ברבי, read as ''Rabban Gamaliel beRabbi'', that is: ''son of Rebbi'', after his father Judah haNasi) was a 3rd-century rabbi (first generation of amoraim).
His father appointed him his successor as '' n ...
(220–230), a son of Judah ha-Nasi, where it became more of a consistory, but still retained, under the presidency of Judah II (230–270), the power of excommunication.
During the presidency of Gamaliel IV
Gamaliel IV (flourished probably late 3rd century CE; also known as Gamaliel IV ben Judah II) was the son of the nasi Judah II and father of Judah III.
Gamaliel was the president of the Sanhedrin between 270 and 290 CE. However, due to Roman pe ...
(270–290), due to Roman persecution, it dropped the name Sanhedrin; and its authoritative decisions were subsequently issued under the name of '' Beth HaMidrash''.
In the year 363, the emperor Julian
Julian may refer to:
People
* Julian (emperor) (331–363), Roman emperor from 361 to 363
* Julian (Rome), referring to the Roman gens Julia, with imperial dynasty offshoots
* Saint Julian (disambiguation), several Christian saints
* Julian (give ...
(r. 355–363 CE), an apostate from Christianity, ordered the Temple rebuilt. The project's failure has been ascribed to the Galilee earthquake of 363
The Galilee earthquake of 363 was a pair of severe earthquakes that shook the Galilee and nearby regions on May 18 and 19. The maximum perceived intensity for the events was estimated to be VII (''Very strong'') on the Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karn ...
, and to the Jews' ambivalence about the project. Sabotage is a possibility, as is an accidental fire. Divine intervention was the common view among Christian historians of the time.Se"Julian and the Jews 361–363 CE"
an
. As a reaction against Julian's pro-Jewish stance, the later emperor Theodosius I (r. 379–395 CE) forbade the Sanhedrin to assemble and declared ordination illegal. Capital punishment was prescribed for any Rabbi who received ordination, as well as complete destruction of the town where the ordination occurred. However, since the Hebrew calendar was based on witnesses' testimony, which had become far too dangerous to collect, rabbi Hillel II recommended change to a mathematically based calendar that was adopted at a clandestine, and maybe final, meeting in 358 CE. This marked the last universal decision made by the Great Sanhedrin. Gamaliel VI (400–425) was the Sanhedrin's last president. With his death in 425, Theodosius II outlawed the title of
Nasi
Nasi may refer to:
Food Dishes
Nasi Goreng is an Indonesian and Malay word for ''cooked rice'', featured in many Southeast Asian dishes
*Nasi goreng, a popular rice dish often simply called ''nasi''
*Other Southeast Asian ''nasi'' dishes:
**Nasi ...
, the last remains of the ancient Sanhedrin. An imperial decree of 426 diverted the patriarchs' tax () into the imperial treasury. The exact reason for the abrogation of the patriarchate is not clear, though Gamaliel VI, the last holder of the office who had been for a time elevated by the emperor to the rank of prefect, may have fallen out with the imperial authorities. Thereafter, Jews were gradually excluded from holding public office.
Powers
The Talmud tractate Sanhedrin identifies two classes of rabbinical courts called Sanhedrin, a Great Sanhedrin () and a Lesser Sanhedrin (). Each city could have its own lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges, but there could be only one Great Sanhedrin of 71, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases decided by lesser courts. The uneven numbers of judges were predicated on eliminating the possibility of a tie, and the last to cast his vote was the head of the court.Function and procedures
The Sanhedrin as a body claimed powers that lesser Jewish courts did not have. As such, they were the only ones who could try the king, extend the boundaries of the Temple and Jerusalem, and were the ones to whom all questions of law were finally put. Before 191 BCE theHigh Priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rever ...
acted as the ''ex officio'' head of the Sanhedrin,Goldwurm, Hersh and Holder, Meir, ''History of the Jewish People'', I "The Second Temple Era" ( Mesorah Publications: 1982) . but in 191 BCE, when the Sanhedrin lost confidence in the High Priest, the office of ''Nasi'' was created. After the time of Hillel the Elder
Hillel ( he, הִלֵּל ''Hīllēl''; variously called ''Hillel HaGadol'', ''Hillel HaZaken'', ''Hillel HaBavli'' or ''HaBavli'', was born according to tradition in Babylon c. 110 BCE, died 10 CE in Jerusalem) was a Jewish religious leader, sag ...
(late 1st century BCE and early 1st century CE), the Nasi was almost invariably a descendant of Hillel. The second highest-ranking member of the Sanhedrin was called the ''Av Beit Din
The ''av beit din'' ( ''ʾabh bêth dîn'', "chief of the court" or "chief justice"), also spelled ''av beis din'' or ''abh beth din'' and abbreviated ABD (), was the second-highest-ranking member of the Sanhedrin during the Second Temple period, ...
'', or 'Head of the Court' (literally, means 'father of the house of judgment'), who presided over the Sanhedrin when it sat as a criminal court.
During the Second Temple period, the Sanhedrin met in a building known as the Hall of Hewn Stones (), which has been placed by the Talmud and many scholars as built into the northern wall of the Temple Mount, half inside the sanctuary and half outside, with doors providing access variously to the Temple and to the outside. The name presumably arises to distinguish it from the buildings in the Temple complex used for ritual purposes, which could not be constructed of stones hewn by any iron implement.
In some cases, it was necessary only for a 23-member panel (functioning as a Lesser Sanhedrin) to convene. In general, the full panel of 71 judges was convened only on matters of national significance (''e.g.'', a declaration of war) or when the 23-member panel failed to reach a conclusive verdict.
By the end of the Second Temple period, the Sanhedrin reached its pinnacle of importance, legislating all aspects of Jewish religious and political life within parameters laid down by Biblical and Rabbinic tradition.
Summary of Patriarchal powers
The following is a summary of the powers and responsibilities of the Patriarchate from the onset of the third century, based on rabbinic sources as understood by L.I. Levine: #Representative to Imperial authorities; #Focus of leadership in the Jewish community: ##Receiving daily visits from prominent families; ##Declaration of public fast days; ##Initiating or abrogating the ban ('' herem''); #Appointment of judges to Jewish courts in the Land of Israel; #Regulation of the calendar; #Issuing enactments and decrees with respect to the applicability or release from legal requirements, e.g.: ##Use of sabbatical year produce and applicability of sabbatical year injunctions; ##Repurchase or redemption of formerly Jewish land from gentile owners; ##Status of Hellenistic cities of the Land of Israel re: purity, tithing, sabbatical year; ##Exemptions from tithing; ##Conditions in divorce documents; ##Use of oil produced by gentiles; #Dispatching emissaries to diaspora communities; #Taxation: both the power to tax and the authority to rule/intervene on the disposition of taxes raised for local purposes by local councils. Up to the middle of the fourth century, the Patriarchate retained the prerogative of determining the Hebrew calendar and guarded the intricacies of the needed calculations, in an effort to constrain interference by the Babylonian community. Christian persecution obliged Hillel II to fix the calendar in permanent form in 359 CE. This institution symbolized the passing of authority from the Patriarchate to the Babylonian Talmudic academies.Archaeological findings
In 2004, excavations in Tiberias conducted by the Israel Antiquities Authority uncovered a structure dating to the 3rd century CE that may have been the seat of the Sanhedrin when it convened in that city. At the time it was called .Nasi (president)
Before 191 BCE theHigh Priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rever ...
acted as the ''ex officio'' head of the Sanhedrin, but in 191 BCE, when the Sanhedrin lost confidence in the High Priest, the office of Nasi
Nasi may refer to:
Food Dishes
Nasi Goreng is an Indonesian and Malay word for ''cooked rice'', featured in many Southeast Asian dishes
*Nasi goreng, a popular rice dish often simply called ''nasi''
*Other Southeast Asian ''nasi'' dishes:
**Nasi ...
was created. The Sanhedrin was headed by the chief scholars of the great Talmudic Academies in the Land of Israel
The Talmudic Academies in Syria Palaestina were ''yeshivot'' that served as centers for Jewish scholarship and the development of Jewish law in Syria Palaestina (and later Palaestina Prima and Palaestina Secunda) between the destruction of the Se ...
, and with the decline of the Sanhedrin, their spiritual and legal authority was generally accepted, the institution itself being supported by voluntary contributions by Jews throughout the ancient world. Being a member of the house of Hillel and thus a descendant of King David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
, the Patriarch, known in Hebrew as the ''Nasi
Nasi may refer to:
Food Dishes
Nasi Goreng is an Indonesian and Malay word for ''cooked rice'', featured in many Southeast Asian dishes
*Nasi goreng, a popular rice dish often simply called ''nasi''
*Other Southeast Asian ''nasi'' dishes:
**Nasi ...
'' (prince), enjoyed almost royal authority. Their functions were political rather than religious, though their influence was not limited to the secular realm. The Patriarchate attained its zenith under Judah ha-Nasi who compiled the Mishnah, a compendium of views from Judean thought leaders of Judaism other than the Torah.
Revival attempts
The Sanhedrin is traditionally viewed as the last institution that commanded universal authority among the Jewish people in the long chain of tradition fromMoses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
until the present day. Since its dissolution in 358 CE by imperial decree, there have been several attempts to re-establish this body either as a self-governing body, or as a puppet of a sovereign government.
There are records of what may have been attempts to reform the Sanhedrin in Arabia,The Persian conquest of Jerusalem in 614 compared with Islamic conquest of 638/ref> in Jerusalem under the Caliph 'Umar, and in Babylon (Iraq), but none of these attempts were given any attention by Rabbinic authorities and little information is available about them.
Napoleon Bonaparte's "Grand Sanhedrin"
 The "Grand Sanhedrin" was a Jewish high court convened by
The "Grand Sanhedrin" was a Jewish high court convened by Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
to give legal sanction to the principles expressed by the Assembly of Notables
An Assembly of Notables (French: ''Assemblée des notables'') was a group of high-ranking nobles, ecclesiastics, and state functionaries convened by the King of France on extraordinary occasions to consult on matters of state. Assemblymen were p ...
in answer to the twelve questions submitted to it by the government (see ''Jew. Encyc. v. 468, s.v. France'').
On October 6, 1806, the Assembly of Notables issued a proclamation to all the Jewish communities of Europe, inviting them to send delegates to the Sanhedrin, to convene on October 20. This proclamation, written in Hebrew, French, German, and Italian, speaks in extravagant terms of the importance of this revived institution and of the greatness of its imperial protector. While the action of Napoleon aroused in many Jews of Germany the hope that, influenced by it, their governments also would grant them the rights of citizenship, others looked upon it as a political contrivance. When in the war against Prussia (1806–07) the emperor invaded Poland and the Jews rendered great services to his army, he remarked, laughing, "The sanhedrin is at least useful to me." David Friedländer and his friends in Berlin described it as a spectacle that Napoleon offered to the Parisians.
State of Israel
Since the dissolution of the Sanhedrin in 358 CE, there has been no universally recognized authority within Halakha. Maimonides (1135–1204) was one of the greatest scholars of the Middle Ages, and is arguably one of the most widely accepted scholars among the Jewish people since the closing of the Talmud in 500. Influenced by the rationalist school of thought and generally showing a preference for a natural (as opposed to miraculous) redemption for the Jewish people, Maimonides proposed a rationalist solution for achieving the goal of re-establishing the highest court in Jewish tradition and reinvesting it with the same authority it had in former years. There have been several attempts to implement Maimonides' recommendations, the latest being in modern times. There have been rabbinical attempts to renew Semicha and re-establish a Sanhedrin by Rabbi Jacob Berab in 1538, RabbiYisroel Shklover
Yisroel ben Shmuel Ashkenazi of Shklov (c. 1770 – May 22, 1839) was a Lithuanian Jewish Talmudist, one of a group of Talmudical scholars of Shklov who were attracted to Vilna by Rabbi Elijah ben Solomon Zalman, known as the Vilna Gaon (1720–97 ...
in 1830, Rabbi Aharon Mendel haCohen in 1901, Rabbi Zvi Kovsker in 1940 and Rabbi Yehuda Leib Maimon in 1949.
In October 2004 (Tishrei 5765), a group of rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as '' semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form o ...
s representing varied Orthodox communities in Israel undertook a ceremony in Tiberias,/ref> where the original Sanhedrin was disbanded, in which it claimed to re-establish the body according to the proposal of Maimonides and the Jewish legal rulings of Rabbi Yosef Karo. The controversial attempt has been subject to debate within different Jewish communities.
See also
* Council of Jamnia *Beth din shel Kohanim
The Beth Din of the priests or Court of the Priests ("house of judgement of the priests" Hebrew: בית דין של כהנים) was the court of Jewish law, composed of twenty-three senior priests that would oversee the day-to-day operation of the ...
* Great Assembly – or ('Men of the Great Assembly')
* Magnum Concilium, a similar body in medieval England
* Synedrion, a general term for judiciary organs of Greek and Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
city states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
and treaty organisations.
* Tombs of the Sanhedrin
Tombs of the Sanhedrin ( he, קברי הסנהדרין, ''Kivrei HaSanhedrin''), also Tombs of the Judges, is an underground complex of 63 rock-cut tombs located in a public park in the northern Jerusalem neighborhood of Sanhedria. Built in the ...
References
Bibliography
*Chen, S.J.D., ''"Patriarchs and Scholarchs,"'' PAAJR 48 (1981), 57–85. *Goodman, M., ''"The Roman State and the Jewish Patriarch in the Third Century,"'' in L.I. Levnie (ed.), ''The Galilee in late Antiquity'' (New York, 1992), 127.39. *Habas (Rubin), E., ''"Rabban Gamaliel of Yavneh and his Sons: The Patriarchate before and after the Bar Kokhva Revolt,"'' JJS 50 (1999), 21–37. *Levine, L.I., ''"The Patriarch (Nasi) in Third-Century Palestine,"'' ANRW 2.19.2 (1979), 649–88.External links
Secular and religious history of the Jewish Sanhedrin
English web site of the re-established Jewish Sanhedrin in Israel
by Rabbi Aryeh Kaplan
''Jewish Encyclopedia'': "Sanhedrin"
* {{Jewish history 1st-century BC establishments in the Hasmonean Kingdom 420s disestablishments in the Roman Empire Governing assemblies of religious organizations Historical legislatures Jewish courts and civil law Jews and Judaism in the Roman Empire Jews and Judaism in the Byzantine Empire Judaism-related controversies Rabbinical organizations Hasmonean Kingdom