Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix;


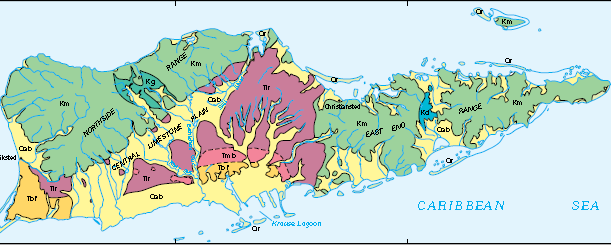 Saint Croix lies at . The easternmost point in the United States of America in the western hemisphere is Saint Croix's Point Udall. The island has an area of . The terrain is rugged, though not extremely so. The highest point on the island, Mount Eagle, is high. Most of the east end is quite hilly and steep, as is the north side from Christiansted west. From the north-side hills, a fairly even plain slopes down to the south coast; this was cultivated as the prime sugar land on the island.
Saint Croix lies at . The easternmost point in the United States of America in the western hemisphere is Saint Croix's Point Udall. The island has an area of . The terrain is rugged, though not extremely so. The highest point on the island, Mount Eagle, is high. Most of the east end is quite hilly and steep, as is the north side from Christiansted west. From the north-side hills, a fairly even plain slopes down to the south coast; this was cultivated as the prime sugar land on the island.
 Christianity is the predominant religion; the island has been called the "Land of Churches" for the approximately 150 churches that serve its 50,000 residents.
Christianity is the predominant religion; the island has been called the "Land of Churches" for the approximately 150 churches that serve its 50,000 residents.
 Saint Croix was once an agricultural powerhouse in the Caribbean, but this period ended with the rapid industrialization of the island's economy in the 1960s. Like many other Caribbean islands today, Saint Croix has tourism as one of its main sources of revenue. A number of other industries on the island contribute to the economy.
Saint Croix was home to
Saint Croix was once an agricultural powerhouse in the Caribbean, but this period ended with the rapid industrialization of the island's economy in the 1960s. Like many other Caribbean islands today, Saint Croix has tourism as one of its main sources of revenue. A number of other industries on the island contribute to the economy.
Saint Croix was home to  Saint Croix is also home to the
Saint Croix is also home to the
File:Saint Croix carnival dancer.jpg , A costumed carnival dancer
File:Saint Croix carnival dancer2.jpg , Parade of costumed carnival dancers
File:Saint Croix carnival dancer3.jpg , A costumed carnival dancer
File:Saint Croix carnival dancer4.jpg , A costumed carnival dancer
File:Mochajombies.jpg , A

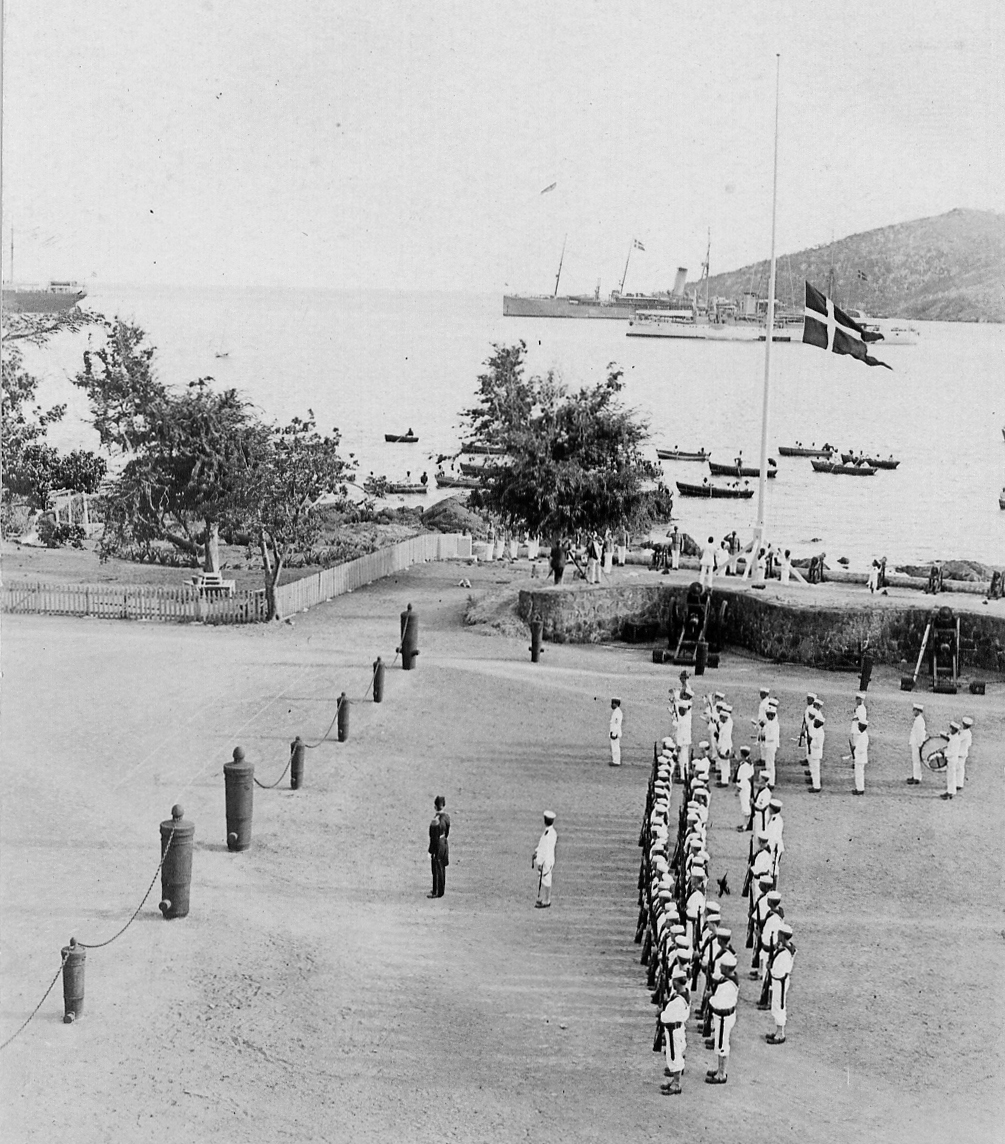
 Fort Christiansværn built in 1749 and other buildings are maintained by the
Fort Christiansværn built in 1749 and other buildings are maintained by the
 The waters surrounding St. Croix are warm year-round, with temperatures ranging from – , making it a popular destination for watersports including scuba diving, snorkeling, kayaking, paddleboarding, surfing, kite surfing, parasailing, jet skiing, fishing, and sailing. Two of the island's most popular underwater sites for scuba divers are the
The waters surrounding St. Croix are warm year-round, with temperatures ranging from – , making it a popular destination for watersports including scuba diving, snorkeling, kayaking, paddleboarding, surfing, kite surfing, parasailing, jet skiing, fishing, and sailing. Two of the island's most popular underwater sites for scuba divers are the
Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
, and a county and constituent district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
of the United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
(USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sover ...
.
St. Croix is the largest of the islands in the territory, while the capital Charlotte Amalie is located on St. Thomas. As of the 2020 United States Census, St. Croix’s population was 41,004. The island's highest point is Mount Eagle, at . St. Croix's nickname is "Twin City", for its two towns, Frederiksted
Frederiksted is both the town and one of the two administrative districts of St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is a grid-planned city, designed by surveyor Jens Beckfor, originally to 14x14 blocks but built 7x7 to enhance the island commerce in ...
on the western end and Christiansted on the northeast part of the island.
Name
The island's indigenous Taino name is ''Ay Ay'' ("the river"). Its indigenous Carib name is ''Cibuquiera'' ("the stony land"). Its modern name, ''Saint Croix'', is derived from the French ''Sainte-Croix'', itself a translation of theSpanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
name ''Isla de la Santa Cruz'' (meaning "island of the Holy Cross"), given by Columbus in 1493. The French name was partially retained under Danish rule as ''Sankt Croix'', and the island was finally given its current spelling following the US takeover in 1917. The associated demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
for the island is Crucian or Cruzan, derived from the original Spanish name.History


Igneri
The Igneri were an indigenous Arawak people of the southern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. Historically, it was believed that the Igneri were conquered and displaced by the Island Caribs in an invasion some time before European contact. Howev ...
pottery indicates that people's presence on the island from 1 to 700, followed by the Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
from 700 to 1425, before the encroachment by the Caribs in 1425. However, the island was devoid of habitation by 1590.
The island was inhabited by various indigenous groups during its prehistory. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
landed on Santa Cruz (Holy Cross), as he called it, on 14 November 1493, and immediately was attacked by the Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language ...
, who lived at Salt River on the north shore. This is the first recorded fight between the Spanish and a New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
native population, and Columbus gave the battle site the name ''Cabo de la Flecha'' (Cape of the Arrow). The Spanish never colonized the Islands, but most or all of the native population was eventually dispersed or killed. By the end of the 16th century, the islands were said to be uninhabited.
Dutch and English settlers landed at Saint Croix in 1625, joined by some French refugees from Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially the Saint Christopher Island, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis cons ...
. However, the English expelled the Dutch and French settlers, before they themselves were evicted by a Spanish invasion from Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
in August 1650. The Spanish occupation was short-lived, since a French force of 166 men attacked, and in the following year 1651 had established a colony of 300 on the island. From 1651 until 1664, the Knights of Malta (at the time a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
), ruled the island in the name of Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
. The island then passed to the French West India Company
The French West India Company (french: Compagnie française des Indes occidentales) was a French trading company founded on 28 May 1664, some three months before the foundation of the corresponding eastern company, by Jean-Baptiste Colbert and diss ...
. The colony was evacuated to San Domingo
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and t ...
in 1695, when France battled the English and Dutch in the War of the Grand Alliance
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
. The island then lay uninhabited and abandoned for another 38 years.
In 1725, St. Thomas Governor Frederik Moth encouraged the Danish West Indies Company's directors to consider purchasing Santa Cruz (Saint Croix). On 15 June 1733, France and Denmark-Norway concluded a treaty by which the Danish West India Company
The Danish West India Company () or Danish West IndiaGuinea Company (') was a Denmark–Norway, Dano-Norwegian chartered company that operated out of the colonies in the Danish West Indies. It is estimated that 120,000 Atlantic slave trade, enslav ...
bought Saint Croix for 750,000 livres
The (; ; abbreviation: ₶.) was one of numerous currencies used in medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in Early Modern France.
The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 gr ...
. Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
ratified the treaty on 28 June, and received half the payment in French coins, with the remaining half paid in 18 months. On 16 November 1733, Moth was named the first Danish governor of Saint Croix. The 1742 census lists 120 sugar plantations, 122 cotton plantations, and 1906 slaves, compared to 360 whites on the island. By 1754, the number of slaves had grown to 7,566. That year, King Frederick Frederick may refer to:
People
* Frederick (given name), the name
Nobility
Anhalt-Harzgerode
*Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670)
Austria
* Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198
* Frederick ...
took direct control of Saint Croix from the company.
For nearly 200 years, Saint Croix, St. Thomas and St. John were known as the Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies ( da, Dansk Vestindien) or Danish Antilles or Danish Virgin Islands were a Danish colonization of the Americas, Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, Saint Thomas ...
. By the mid to late 18th century, "at the peak of the plantation economy, the enslaved population of Saint Croix numbered between 18,000 and 20,000, the white population ranging between 1,500 and 2,000".
Future Founding Father
The following list of national founding figures is a record, by country, of people who were credited with establishing a state. National founders are typically those who played an influential role in setting up the systems of governance, (i.e. ...
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
and his brother lived with their mother Rachel Faucette on Saint Croix, after she returned to the island in 1765. Their residence was in the upper floor of a house at 34 Company Street, while Rachel used the lower floor as a shop selling food items. Within two years, however, Hamilton lost his father, James Hamilton, by abandonment, and his mother to death. Official documents from the island, a 1768 probate court testimony from his uncle, established Alexander's age at 13. By 1769, Hamilton's cousin, aunt, uncle, and grandmother had also died. His brother James became an apprentice carpenter, and Alexander Hamilton became the ward of Thomas Stevens, a merchant on King Street. Hamilton was soon clerking in the export-import business of Beekman and Cruger, at the intersection of King and King's Cross Streets. In 1772, local businessmen funded Hamilton's further education in New York.
The slave trade was abolished in the Danish colonies in 1792, although the prohibition did not go into effect until the end of 1802. Existing enslaved people were freed in 1848, after the 1848 St. Croix Slave Revolt led by General " Buddhoe" Gottlieb.
The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
occupation of the Danish West Indies took place at the end of March 1801, with the arrival of a British fleet at St Thomas. Denmark-Norway accepted the Articles of Capitulation and the British occupied the islands without a shot being fired. Their occupation lasted only until April 1802, when Britain returned the islands to Denmark-Norway.
A second British invasion of the Danish West Indies took place in December 1807, when a British fleet captured St Thomas on 22 December, and Saint Croix on 25 December. Denmark-Norway did not resist and the invasion again was bloodless. This occupation lasted until 20 November 1815. Both invasions were due to Denmark's alliance with France during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
. On the conclusion of a peace with France, the islands were returned to Denmark.
The island was shaken by the 1878 St. Croix labor riot.
In 1916, Denmark sold Saint Croix, St. Thomas, and St. John to the United States, formalizing the transfer in the Treaty of the Danish West Indies
The Treaty of the Danish West Indies, officially the Convention between the United States and Denmark for cession of the Danish West Indies, was a 1916 treaty transferring sovereignty of the Virgin Islands in the Danish West Indies from Den ...
, in exchange for a sum of US$25 million in gold. In a national referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
on the issue, 64.2% of Danish voters approved the sale. An unofficial referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
held in the islands resulted in 99.83% vote in favor of the purchase. Formal transfer of the islands to the U.S. took place on 1 April 1917.
The island's inhabitants were granted United States citizenship in 1927. Industrialization of the island and its move away from an agrarian society took place in the 1960s. The 1972 Fountain Valley massacre
The Fountain Valley massacre was a mass shooting that occurred on the afternoon of 6 September 1972 at the Fountain Valley Golf Course in St. Croix, United States Virgin Islands. The incident left eight resort employees and tourists dead. Another ...
, a mass shooting
There is a lack of consensus on how to define a mass shooting. Most terms define a minimum of three or four victims of gun violence (not including the shooter or in an inner city) in a short period of time, although an Australian study from 20 ...
during a robbery at a golf club, led to a devastating reduction in tourism that lasted many years. The 2012 shutdown of the Hovensa refinery resulted in the loss of many jobs. Agriculture has seen a slow resurgence, due to an increase in demand for local produce and agricultural products.
In 1989, Hurricane Hugo
Hurricane Hugo was a powerful Cape Verde tropical cyclone that inflicted widespread damage across the northeastern Caribbean and the Southeastern United States in September 1989. Across its track, Hugo affected approximately 2 million peop ...
struck the island with Category 4 winds. The United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
, the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, ...
, and the United States Marshals Service
The United States Marshals Service (USMS) is a federal law enforcement agency in the United States. The USMS is a bureau within the U.S. Department of Justice, operating under the direction of the Attorney General, but serves as the enforceme ...
were ordered in to restore order.
Category 5 Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria was a deadly Saffir–Simpson scale#Category 5, Category 5 Tropical cyclone, hurricane that devastated the northeastern Caribbean in September 2017, particularly Dominica, Saint Croix, and Puerto Rico. It is regarded as the wo ...
's weaker outer eyewall crossed St. Croix in September 2017; sustained winds reached over 150 mph and gusted up to 250 mph in some places on the western end of the island. Maria damaged or destroyed 70% of the buildings on St. Croix, including schools and the island's only hospital.
Geography
 Saint Croix lies at . The easternmost point in the United States of America in the western hemisphere is Saint Croix's Point Udall. The island has an area of . The terrain is rugged, though not extremely so. The highest point on the island, Mount Eagle, is high. Most of the east end is quite hilly and steep, as is the north side from Christiansted west. From the north-side hills, a fairly even plain slopes down to the south coast; this was cultivated as the prime sugar land on the island.
Saint Croix lies at . The easternmost point in the United States of America in the western hemisphere is Saint Croix's Point Udall. The island has an area of . The terrain is rugged, though not extremely so. The highest point on the island, Mount Eagle, is high. Most of the east end is quite hilly and steep, as is the north side from Christiansted west. From the north-side hills, a fairly even plain slopes down to the south coast; this was cultivated as the prime sugar land on the island.
Climate
The trade wind blows more or less along the length of the island. The hills of the western part of the island receive a good deal more rain than the east end; annual rainfall is on the whole extremely variable, averaging perhaps a year. The east end of the island is a dry desert range with a substantial amount of cactus, while the west end has lush vegetation and palm trees. The island has multiple ecosystems in a small geographic area. Fairly severe and extended drought has always been a problem, particularly considering the lack of fresh ground water and lack of freshwater streams or rivers on the island. The island has adesalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
plant, but most residential homes and businesses have built-in cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by t ...
s used to collect rainwater.
Demographics
Inhabitants are called Crucians (frequently written as "Cruzans"). Due to Saint Croix's history of immigration, there is much debate as to what constitutes a native Crucian. The consensus in Crucian society is that if one is ''bahn ya'' ("born here" in Crucian dialect) on Saint Croix, they can claim to be Crucian, but not necessarily a ''native Crucian''. Those considered to be the ''native Crucians'' (or by the more politically correct term: ''ancestral native Crucian'') of Saint Croix are persons who can trace their ancestry to the era prior to U.S. Virgin Islands acquisition of American citizenship in 1927. Ancestral native Crucians (approximately one-fourth to one-third of Saint Croix's population) largely consist of the descendants of enslaved Africans brought to the island by Europeans during the 18th and 19th centuries, as well as the descendants of paid laborers recruited by the Danes from the British and Dutch West Indies after the Danish emancipation law in 1848. As on other Caribbean islands, many ancestral natives are also descended from European settlers and planters that migrated to the West Indies during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. Due to a low number of European females in the colonial West Indies, many European males in colonial Saint Croix produced offspring with the majority African population, whose mixed-heritage descendants bear the surnames of their European ancestors. In addition, there are also a handful of ancestral families on the island (traditionally known as ''bukra'') of full European ancestry. Due to historical economic and political differences, as well as the remnants of a 19th-century caste system based on skin complexion, socioeconomic class differences among ancestral native Crucians can vary widely, even within the same family. Most ancestral native Crucians today are employed by the Government of the Virgin Islands, although there are others who are involved in the tourism industry, as well as the legal and medical professions. Puerto Rican migration was prevalent in the 1930s, '40s and '50s, when many Puerto Ricans relocated to Saint Croix for work after the collapse of the sugar industry. However, the total population actually declined by 50% in the century preceding 1945. TheUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
purchase of two-thirds of the nearby Puerto Rican island of Vieques during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
resulted in the displacement of thousands of ''Viequenses'', many of whom relocated to Saint Croix because of its similar size and geography. The local holiday, Puerto Rico/U.S. Virgin Islands Friendship Day, has been celebrated since the 1960s on the second Monday of October, which is also the same date as Columbus Day
Columbus Day is a national holiday in many countries of the Americas and elsewhere, and a federal holiday in the United States, which officially celebrates the anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the Americas on October 12, 1492.
...
. Puerto Ricans in Saint Croix, most of whom have lived on the island for more than a generation, have kept their culture alive while integrating it into the native Crucian culture and society. For example, in informal situations, many Puerto Ricans in Saint Croix speak a unique Spanglish
Spanglish (a portmanteau of the words "Spanish" and "English") is any language variety (such as a contact dialect, hybrid language, pidgin, or creole language) that results from conversationally combining Spanish and English. The term is mos ...
-like combination of Puerto Rican Spanish
Puerto Rican Spanish (''español puertorriqueño'' ) is the variety (linguistics), variety of the Spanish language as characteristically spoken in Puerto Rico and by millions of people of Puerto Rican people, Puerto Rican descent living in the ...
and the local Crucian Creole English.
Migration from "down-island" (a local colloquial term for islands in the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
located to the east and southeast), occurred mainly throughout the 1960s and 70s. In that period, agriculture declined as the major industry in Saint Croix and was replaced by tourism, alumina production, and oil refining. Jobs were plentiful in these industries and down-islanders came to Saint Croix by the thousands. The demand for imported labor in Saint Croix was exacerbated by the fact that many ancestral native Crucians, having acquired American citizenship several decades earlier, migrated to the mainland United States to pursue educational and career opportunities. Many down-islanders made Saint Croix their permanent home, while others eventually relocated to the mainland United States or returned to their native countries. Most down-islanders came from St. Kitts and Nevis, Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
, St. Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerin ...
and Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
, although people from every Anglophone Caribbean
The languages of the Caribbean reflect the region's diverse history and culture. There are six official languages spoken in the Caribbean:
:*Spanish (official language of Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, Bay Islands (Honduras), Corn Isl ...
nation can be easily found on St. Croix. Down islanders and their Saint Croix-born offspring form the majority of Saint Croix's middle class, which has dwindled in size since the 2008 global recession.
Although down-island migration to Saint Croix is most commonly thought of as a mid-20th century phenomenon brought upon by American immigration policy, it is important to note that persons of both European and African descent from the nearby islands of Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The territo ...
, St. Martin, Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
, Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), ...
, St. Kitts, Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and Ne ...
, Antigua
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the Lesser Antilles. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Bar ...
, and Montserrat
Montserrat ( ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about long and wide, with r ...
have been migrating to Saint Croix since the 1600s. In addition, many ancestral native Crucians also share family ties with Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
, as Bajans were heavily recruited to Saint Croix to work on sugar plantations throughout the late 19th century.
Continental Americans, although small in number in comparison with Caribbean immigrants, have also been part of the Saint Croix community. Most reside on the East End of Saint Croix and tend to work in the tourism industry, real estate, and legal professions. Many are temporary residents or retirees, as well.
Arab Palestinians have been an influential part of the local economy since the 1960s, when they first started to migrate to St. Croix to set up shops, supermarkets and gas stations.
In the 21st century, recent waves of migration to Saint Croix have included people from the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
, Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and various South American nations.
Saint Croix's history of migration has sometimes caused tensions between immigrants and Crucians whose ancestry on the island dates back for generations. Tensions have subsided to some extent in recent years, mainly due to intermarriage among Crucians and other Caribbean peoples. In the late 1990s, many people supported legislation to define as a "native U.S. Virgin Islander" anyone who could trace their ancestry on the island to 1927, the year in which U.S. Virgin Islanders were granted United States citizenship. This effort by a select group of nationalist senators eventually failed after much public outcry and controversy. It was learned that most native-born U.S. Virgin Islanders would not qualify as "native" under the proposed legislation, as their immigrant ancestors had arrived later than 1927, but thousands of Danish citizens would have qualified.
In 2009, the proposed U.S. Virgin Islands Constitution voted by the Fifth Constitutional Convention established three definitions of U.S. Virgin Islanders: "Ancestral Native Virgin Islander" – those with ancestral ties (and their descendants); "Native Virgin Islander" – those born on the island (and their descendants); and "Virgin Islander" – any United States citizen who has resided in the territory for five years. The proposed constitution was rejected by the United States Congress in 2010 for violating the principle of equal rights for all citizens of the territory, "native" or not, and was sent back to the convention for further consideration.
The total population of the island as per the 2010 U.S. Census is 50,601.
Subdivisions
Saint Croix is divided into the followingsubdistricts A subdistrict or sub-district is an administrative division that is generally smaller than a district.
Equivalents
* Administrative posts of East Timor, formerly Portuguese-language
* Kelurahan, in Indonesia
* Mukim, a township in Brunei, Indon ...
(with population as per the 2010 U.S. Census):
# Anna's Hope Village (pop. 4,041)
# Christiansted (pop. 2,626)
# East End (pop. 2,453)
# Frederiksted
Frederiksted is both the town and one of the two administrative districts of St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is a grid-planned city, designed by surveyor Jens Beckfor, originally to 14x14 blocks but built 7x7 to enhance the island commerce in ...
(pop. 3,091)
# Northcentral (pop. 4,977)
# Northwest (pop. 4,863)
# Sion Farm (pop. 13,003)
# Southcentral (pop. 8,049)
# Southwest (pop. 7,498)
Language
English has been the dominant language on St. Croix since the 1700s and has been the official language since 1917, when theDanish West Indies
The Danish West Indies ( da, Dansk Vestindien) or Danish Antilles or Danish Virgin Islands were a Danish colonization of the Americas, Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, Saint Thomas ...
were purchased by the United States. Previously, the official language was Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
, although it was not widely spoken. Other languages spoken throughout St. Croix's colonial history have included Irish, Scots, Spanish, and French, as well as a now-extinct Dutch Creole spoken by St. Thomas and St. John-born people living in St. Croix, as well as the local creole English, which still exists today.
Known on the island as '' Crucian'', Virgin Islands Creole English is spoken by the majority of the population in informal situations. Spanish is spoken by migrants from Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
and the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
and their St. Croix-born offspring, and various French creoles
The French Louisianians (french: Louisianais), also known as Louisiana Frenchmen, are Latin French people native to the states that were established out of French Louisiana. They are commonly referred to as French Creoles (french: Créoles). T ...
are spoken by St. Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerin ...
n, Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically ...
n (Dominica), and Haitian immigrants. Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
is common among the large Palestinian
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
community on St. Croix. Immigrants from the Anglophone Caribbean that migrated to St. Croix after their formative years tend to speak the English creoles of their respective islands in informal situations, which are, for the most part, mutually intelligible with Virgin Islands Creole English
Virgin Islands Creole, or Virgin Islands Creole English, is an English-based creole consisting of several varieties spoken in the Virgin Islands and the nearby SSS islands of Saba, Saint Martin and Sint Eustatius, where it is known as Saban E ...
.
Religion
 Christianity is the predominant religion; the island has been called the "Land of Churches" for the approximately 150 churches that serve its 50,000 residents.
Christianity is the predominant religion; the island has been called the "Land of Churches" for the approximately 150 churches that serve its 50,000 residents.
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
denominations are the most prevalent, but there is also a significant Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
presence due to Saint Croix's large Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to Vic ...
population, as well as Irish influence during the Danish colonial period. Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
, Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
, Moravian, Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
, Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement
and Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventism, Adventist Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the Names of the days of the week#Numbered days of the week, seventh day of the ...
are among the Protestant denominations prevalent on the island. There are also followers of the Jehovah's Witness
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ev ...
faith, as well as the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
(also known as LDS or Mormon).
As in most of the Caribbean, various forms of Rastafari
Rastafari, sometimes called Rastafarianism, is a religion that developed in Jamaica during the 1930s. It is classified as both a new religious movement and a social movement by scholars of religion. There is no central authority in control of ...
are practiced on the island. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is prevalent among the small local Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
population, and there is a small Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
presence as well. Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Islam is also practiced by the Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
population.
Economy
 Saint Croix was once an agricultural powerhouse in the Caribbean, but this period ended with the rapid industrialization of the island's economy in the 1960s. Like many other Caribbean islands today, Saint Croix has tourism as one of its main sources of revenue. A number of other industries on the island contribute to the economy.
Saint Croix was home to
Saint Croix was once an agricultural powerhouse in the Caribbean, but this period ended with the rapid industrialization of the island's economy in the 1960s. Like many other Caribbean islands today, Saint Croix has tourism as one of its main sources of revenue. A number of other industries on the island contribute to the economy.
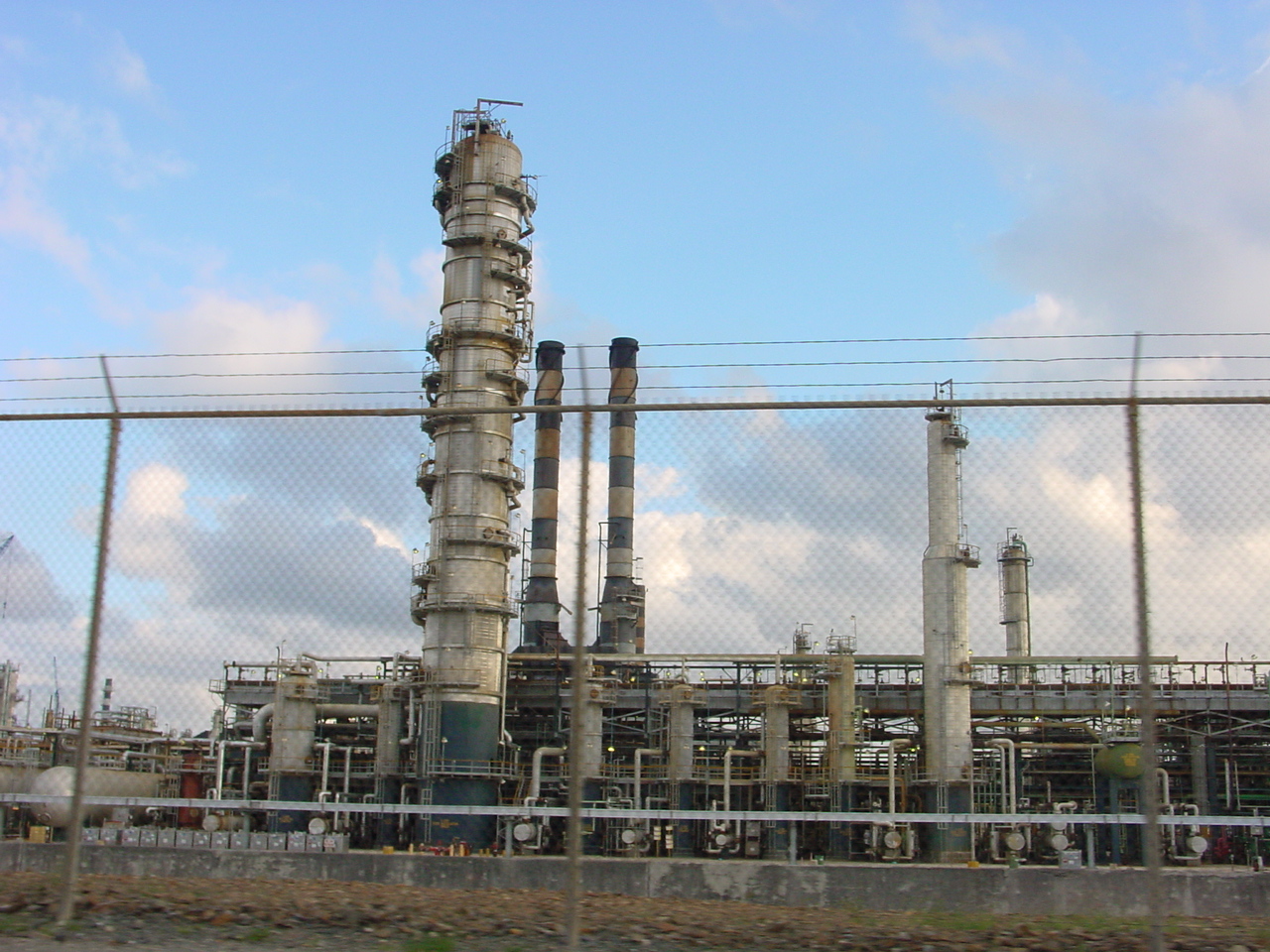
Saint Croix was home to HOVENSA
Limetree Bay Refinery (known also as Hovensa) is an oil refinery located on the island of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. The refinery was a joint venture between Hess Corporation and PDVSA. For most of its operating life as HOV ...
, one of the world's largest oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefie ...
. HOVENSA is a limited liability company
A limited liability company (LLC for short) is the US-specific form of a private limited company. It is a business structure that can combine the pass-through taxation of a partnership or sole proprietorship with the limited liability of a ...
owned and operated by Hess Oil Virgin Islands Corp. (HOVIC), a division of U.S.-based Hess Corporation
Hess Corporation (formerly Amerada Hess Corporation) is an American global independent energy company involved in the exploration and production of crude oil and natural gas. It was formed by the merger of Hess Oil and Chemical and Amerada Petrol ...
, and Petroleos de Venezuela, SA (PDVSA), the national oil company of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
. Gas prices on the island were slightly higher than average when compared to gas prices in the continental United States.
On January 18, 2012, the company announced that the HOVENSA refinery would be permanently shut down. This had a major adverse effect on the economy of Saint Croix and the entire U.S. Virgin Islands, as the refinery employed 1,200 residents and 950 contractors. The refinery has since reopened under new ownership.
 Saint Croix is also home to the
Saint Croix is also home to the Cruzan Rum Distillery
Cruzan Rum ( ) is a rum producer in Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands owned by Beam Suntory. Founded in 1760, it claims the distinction of being "the most honored rum distillery in the world." For eight generations, and through various changes in ...
, makers of Cruzan Rum
Cruzan Rum ( ) is a rum producer in Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands owned by Beam Suntory. Founded in 1760, it claims the distinction of being "the most honored rum distillery in the world." For eight generations, and through various changes in ...
, a brand of Beam Suntory, Inc. The Cruzan Rum Distillery was founded in 1760 as Estate Diamond
Cruzan Rum ( ) is a rum producer in Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands owned by Beam Suntory. Founded in 1760, it claims the distinction of being "the most honored rum distillery in the world." For eight generations, and through various changes in ...
, and for many years used locally grown sugar cane to produce a single "dark"-style rum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is usually aged in oak barrels. Rum is produced in nearly every sugar-producing region of the world, such as the Ph ...
. The distillery now imports sugar cane molasses from other countries in the region, primarily from the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
and South America. In recent years, Cruzan Rum, along with Bacardi
Bacardi Limited (; ) is one of the largest privately held, family-owned spirits companies in the world. Originally known for its Bacardi brand of white rum, it now has a portfolio of more than 200 brands and labels. Founded in Cuba in 1862 an ...
from Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
and Gosling's from Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = " Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, e ...
, has contributed to the resurgence of "single barrel," super-premium rum. The quality and smoothness of the Cruzan Estate Rums has won more than 30 Spirit Awards. Cruzan Estate Diamond Rum (aged five years in American oak barrels) and Cruzan Single Barrel Estate Rum (aged 12 years in American oak barrels) are two examples.
Diageo
Diageo plc () is a Multinational corporation, multinational alcoholic beverage company, with its headquarters in London, England. It operates from 132 sites around the world. It was the world's largest distiller before being overtaken by Kweich ...
has completed construction of a new distillery on a 26-acre industrial site next to the Hovensa Refinery. The new distillery produces Captain Morgan
Captain Morgan is a brand of flavored rums (including, in Europe, some rum-flavored "premium spirit drinks") produced by British alcohol conglomerate Diageo. It is named after the 17th-century Welsh privateer of the Caribbean, Sir Henry Morgan. ...
Rum. Diageo's entrance into the U.S. Virgin Islands rum industry has been controversial. The cash-strapped U.S. Virgin Islands government secured $250 million in bonds for the plant, about which the Puerto Rican government has bitterly complained.
Transportation
Cars drive on the left hand side of the road, but nearly all the automobiles on the island have left side steering columns. This has proven difficult for new residents and visitors from right-hand traffic locales such as the mainland United States, the French andDutch West Indies
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-wes ...
, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico. Roads are with numerous potholes.
There is a public bus service called Virgin Islands Transit, also known as VITRAN, operated by the Virgin Islands Department of Public Works.
In addition to taxis and buses, St. Croix has shared taxi
Shared may refer to:
* Sharing
* Shared ancestry or Common descent
* Shared care
* Shared-cost service
* Shared decision-making in medicine
* Shared delusion, various meanings
* Shared government
* Shared intelligence or collective intellige ...
s, locally known as "taxi buses" (also found on the other U.S. Virgin Islands). Taxi buses are full-sized vans running a route from Frederiksted to Christiansted. Taxi buses are privately owned and operated; they do not follow a regular schedule, and there are no pre-specified stops. People simply wait by the side of the road until a taxi bus approaches, then flag the driver down by waving. Passengers can get out anywhere along the taxi route. Taxi buses are not metered and are required by law to charge a flat rate of $2.50, regardless of where a rider gets on and off. Taxis to specific locations are much more expensive and are typically used by tourists.
Ferry service to St. Thomas was restarted in April 2017. The QE IV Ferry makes one trip per day departing from Gallows Bay, Christiansted to Charlotte Amalie, St. Thomas. The journey takes 2.5 hours and costs $50. The QE IV Ferry does not operate during hazardous weather conditions. Some Ferry companies based in St. Thomas and St. John sometimes operate St. Croix-to-St. Thomas service for special occasions, such as the St. Croix Agricultural Fair in February, Virgin Islands Carnival, Crucian Christmas Carnival, as well as horse races.
The Henry E. Rohlsen International Airport
Henry E. Rohlsen Airport is a public airport located six miles (10 km) southwest of Christiansted on the island of St. Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. The airport is named after Henry E. Rohlsen, a St. Croix native who was one ...
serves St. Croix with regular flights from the U.S. mainland, Puerto Rico, and the Eastern Caribbean
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ri ...
. Seaplanes, operated by Seaborne Airlines
Seaborne Virgin Island Inc, operating as Seaborne Airlines, is a FAR Part 121 airline headquartered in Carolina, Puerto Rico, near the territory's capital of San Juan. It operates a seaplane shuttle service between St. Croix and St. Thomas. O ...
, make the trip from St. Croix to St. Thomas, departing and arriving in Christiansted Harbor.
Although St. Croix is a U.S. territory, the U.S. Virgin Islands are maintained as a free port
Free economic zones (FEZ), free economic territories (FETs) or free zones (FZ) are a class of special economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate areas in which com ...
in a separate customs zone. Therefore, travelers to and from the contiguous United States and Puerto Rico must clear U.S. customs but do not need to present a passport, and only need proof of U.S. citizenship or nationality. The immigration status of non-U.S. citizens may be verified during this process.
Education
The St. Croix School District operates a number of public schools in St. Croix. There also exist multiple private schools, including St. Croix Montessori, Star Apple Montessori School, TheGood Hope Country Day School
Good Hope Country Day School, formerly St. Croix Country Day School prior to a merger in 2013 with the Good Hope School, is an independent, non-sectarian, non-profit, college preparatory school serving all grades from PreK-12 located in Kingshill, ...
, AZ Academy, St. Mary's Catholic School, Free Will Baptist, St. Croix SDA School, and The Manor School. The only colleges on the island are the University of the Virgin Islands
The University of the Virgin Islands (or UVI) is a public historically black land-grant university in the United States Virgin Islands.
History
UVI was founded as the College of the Virgin Islands on March 16, 1962. In 1986, it officially be ...
, St. Croix campus and Barry University
Barry University is a private Catholic university in Miami Shores, Florida. Founded in 1940 by the Adrian Dominican Sisters, it is one of the largest Catholic universities in the Southeast and is within the territory of the Archdiocese of Miami ...
, which operates a physician assistant training program.
Culture
Festivals
The island's largest festival, termed "Crucian Christmas Carnival," is celebrated on St. Croix throughout late December and early January. Another significant festival is the Agricultural and Food Fair held in mid-February. Several times a year, there is a nighttime festival in Christiansted called "Jump-Up" and a monthly event called "Sunset Jazz" inFrederiksted
Frederiksted is both the town and one of the two administrative districts of St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is a grid-planned city, designed by surveyor Jens Beckfor, originally to 14x14 blocks but built 7x7 to enhance the island commerce in ...
, where local jazz musicians play on Frederiksted Beach. Every year on the Saturday before Mardi Gras, there is a local Mardi Croix parade and a dog parade through the North Shore.
The St. Croix Half Ironman Triathlon is held in the first week of May. The Triathlon includes a swim, a bike ride, and a run. Because the bicycle route includes a ride up an extremely steep hill known as "The Beast", this triathlon is often nicknamed "Beauty and the Beast".
Moko jumbie
In the mythology of Mangaia in the Cook Islands, Moko is a wily character and grandfather of the heroic Ngaru.
Moko is a ruler or king of the lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging acro ...
Points of interest
Frederiksted
Frederiksted is both the town and one of the two administrative districts of St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is a grid-planned city, designed by surveyor Jens Beckfor, originally to 14x14 blocks but built 7x7 to enhance the island commerce in ...
maintains its Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardia ...
architecture and original seven street by seven street city design and is host to several historic structures. Among them are St. Patrick's Catholic Church built in the 1840s and its primary school, the Customs House, the 19th Century Apothecary, and many other buildings; some of which due to hurricanes past have fallen into very scenic ruins. Frederiksted operates at a more relaxed pace than most of the island, and is more lively during Carnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival typi ...
in January and whenever visiting cruise ships are in port.
Salt River Bay National Historical Park and Ecological Preserve
Salt River Bay National Historic Park and Ecological Preserve is a unit of the National Park Service on the island of St. Croix in the U.S. Virgin Islands. It preserves upland watersheds, mangrove forests, and estuarine and marine environments ...
contains the only known site where members of a Columbus expedition set foot on what is now United States territory. It also preserves upland watersheds, mangrove forests, and estuarine and marine environments that support threatened and endangered species. The site is marked by Fort Salé, a remaining earthworks fortification from the French period of occupation, about 1617. The park also preserves prehistoric and colonial-era archeological sites including the only existent example of a ball court in the Caribbean. This is one of two sites on the island for bioluminescent bays (the other being Altona Lagoon).
 Fort Christiansværn built in 1749 and other buildings are maintained by the
Fort Christiansværn built in 1749 and other buildings are maintained by the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
as the Christiansted National Historic Site
Christiansted National Historic Site commemorates urban colonial development of the Virgin Islands. It features 18th and 19th century structures in the heart of Christiansted, the capital of the former Danish West Indies on St. Croix Island.
Th ...
.
Buck Island Reef National Monument
Buck Island Reef National Monument protects Buck Island, a small, uninhabited 176-acre (712,000 m²) island about north of the northeast coast of Saint Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands, and 18,839 acres of submerged lands, totaling 19,015 acres. It ...
preserves a island just north of St. Croix and the surrounding reefs. This is a popular destination for snorkelers. Buck Island maintains a U.S. Coast Guard weather station and is also home to a student monitored lemon shark breeding ground. Green Cay (pronounced green key) is a small island located southwest of Buck Island; it is managed by the US Fish and Wildlife Service. It hosts a nearby reef popular among scuba divers and snorkelists—Tamarind Reef.
The farmer's market (1 Estate, Kingshill, 00850, St. Croix) offers local fruit and vegetables, as well as plants, local food, and delicious juices. The outdoor vendors open every Saturday from 6 a.m. to 12 p.m., sometimes longer. You can visit the farmer's market all-year round to taste the fresh fruit and vegetables and enjoy a typical Cruzan breakfast.
Scuba diving, snorkeling, and watersports

 The waters surrounding St. Croix are warm year-round, with temperatures ranging from – , making it a popular destination for watersports including scuba diving, snorkeling, kayaking, paddleboarding, surfing, kite surfing, parasailing, jet skiing, fishing, and sailing. Two of the island's most popular underwater sites for scuba divers are the
The waters surrounding St. Croix are warm year-round, with temperatures ranging from – , making it a popular destination for watersports including scuba diving, snorkeling, kayaking, paddleboarding, surfing, kite surfing, parasailing, jet skiing, fishing, and sailing. Two of the island's most popular underwater sites for scuba divers are the Frederiksted Pier
The Frederiksted Pier (officially named: Ann E. Abramson Marine Facility) is the 1,526-foot (0.465 km or 0.29 mile), deep water, cruise ship pier located in Frederiksted, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is located at the west end of Saint Croix, U ...
and the drop-off into deep water at Salt River Bay National Historical Park and Ecological Preserve
Salt River Bay National Historic Park and Ecological Preserve is a unit of the National Park Service on the island of St. Croix in the U.S. Virgin Islands. It preserves upland watersheds, mangrove forests, and estuarine and marine environments ...
.
Frederiksted
Frederiksted is both the town and one of the two administrative districts of St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. It is a grid-planned city, designed by surveyor Jens Beckfor, originally to 14x14 blocks but built 7x7 to enhance the island commerce in ...
is known for reef diving and access to wreck diving. The western side of the island has calm waters that allow snorkeling with access from the beach. Paddleboarding is popular near Frederiksted for the same reason. The Frederiksted Pier attracts scuba divers and snorkelers, as well as those who simply jump off it. The shallow water and sandy bottom around the pier are ideal for recreational diving
Recreational diving or sport diving is diving for the purpose of leisure and enjoyment, usually when using scuba equipment. The term "recreational diving" may also be used in contradistinction to "technical diving", a more demanding aspect of r ...
by novice scuba divers in PADI Discover Scuba Diving programs (also called resort diving), for extended shore diving, night diving
Night diving is underwater diving done during the hours of darkness. It frequently refers specifically to recreational diving which takes place in darkness. The diver can experience a different underwater environment at night, because many marine ...
, and for underwater photography
Underwater photography is the process of taking photographs while under water. It is usually done while scuba diving, but can be done while diving on surface supply, snorkeling, swimming, from a submersible or remotely operated underwater v ...
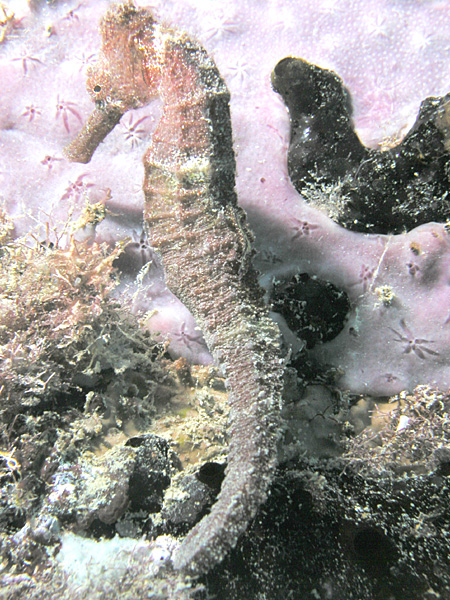
, especially of its abundant seahorse
A seahorse (also written ''sea-horse'' and ''sea horse'') is any of 46 species of small marine fish in the genus ''Hippocampus''. "Hippocampus" comes from the Ancient Greek (), itself from () meaning "horse" and () meaning "sea monster" or " ...
population.
A few hundred meters off the northern coast of the island, from Salt River to Cane Bay, the bottom drops suddenly into a deep trench, where coral reefs, abundant tropical fish, and migrant sea turtles may be observed. Kayaking is popular in the Salt River area as well.
The town of Christiansted, a short distance from Buck Island and Green Cay, is a former capital of the Danish West Indies. It lies just east of the northern underwater drop-off and is protected by a reef.
Bioluminescent bays
There are two bioluminescent bays or bio bays on St. Croix. The most widely known and visited is located atSalt River Bay National Historical Park and Ecological Preserve
Salt River Bay National Historic Park and Ecological Preserve is a unit of the National Park Service on the island of St. Croix in the U.S. Virgin Islands. It preserves upland watersheds, mangrove forests, and estuarine and marine environments ...
. A second bio bay can be found at Altona Lagoon. Bio bays are extremely rare with "only seven-year-round lagoons known to exist in the Caribbean".
A combination of factors creates the necessary conditions for bioluminescence: red mangrove Red mangrove may refer to at least three plant species:
* ''Rhizophora mangle''
* ''Rhizophora mucronata''
* ''Rhizophora stylosa''
{{Short pages monitor