Republic Of The Marshall Islands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent
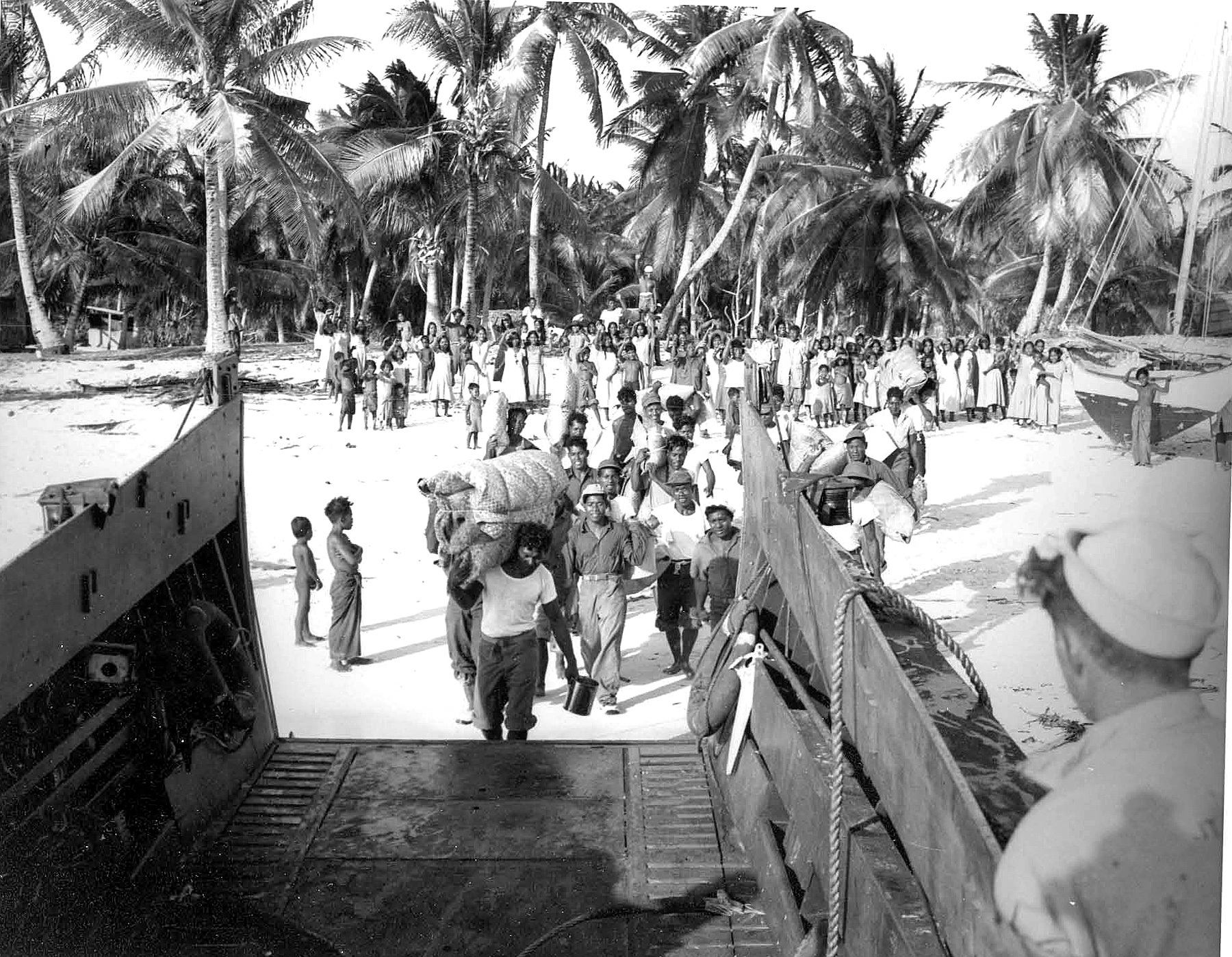

 Evidence suggests that around 3,000 years ago successive waves of human migrants from
Evidence suggests that around 3,000 years ago successive waves of human migrants from  Nuclear testing began in 1946 on
Nuclear testing began in 1946 on
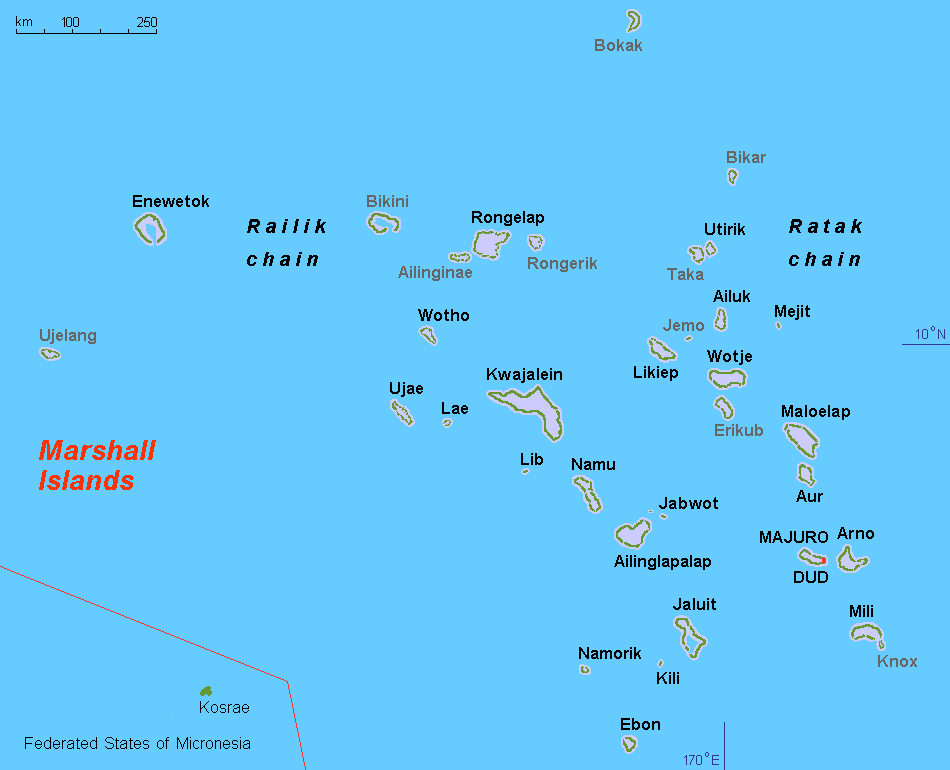



 The Marshall Islands sit atop ancient submerged volcanoes rising from the ocean floor, about halfway between
The Marshall Islands sit atop ancient submerged volcanoes rising from the ocean floor, about halfway between
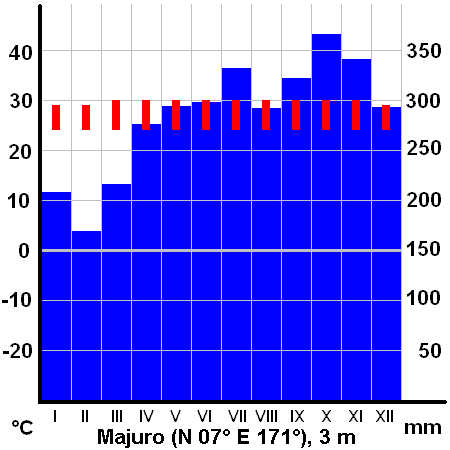 The climate has a relatively dry season from December to April and a
The climate has a relatively dry season from December to April and a
 Historical population figures for the Marshall Islands are unknown. In 1862, the population of the Islands was estimated at 10,000. In 1960, the population of the Islands was approximately 15,000. The 2011
Historical population figures for the Marshall Islands are unknown. In 1862, the population of the Islands was estimated at 10,000. In 1960, the population of the Islands was approximately 15,000. The 2011
 Major religious groups in the Republic of the Marshall Islands include the United Church of Christ – Congregational in the Marshall Islands, with 51.5% of the population; the
Major religious groups in the Republic of the Marshall Islands include the United Church of Christ – Congregational in the Marshall Islands, with 51.5% of the population; the
. United States
 The government of the Marshall Islands operates under a mixed parliamentary-presidential system as set forth in its 1979 Constitution. Elections are held every four years in
The government of the Marshall Islands operates under a mixed parliamentary-presidential system as set forth in its 1979 Constitution. Elections are held every four years in
 The
The
 Although the ancient skills are now in decline, the Marshallese were once able navigation, navigators, using the celestial navigation, stars and Marshall Islands stick chart, stick-and-shell charts.
Although the ancient skills are now in decline, the Marshallese were once able navigation, navigators, using the celestial navigation, stars and Marshall Islands stick chart, stick-and-shell charts.
 The islands have few natural resources, and their imports far exceed exports. According to the CIA, the value of exports in 2013 was approximately $53.7 million while estimated imports were $133.7 million. Agricultural products include coconuts, tomatoes, melons, taro, breadfruit, fruits, pigs and chickens. Industry is made of the production of copra and craft items, tuna processing and tourism. The GDP in 2016 was an estimated $180 million, with a real growth rate of 1.7%. The GDP per capita was $3,300.
The International Monetary Fund reported in mid-2016 that the economy of the Republic had expanded by about 0.5 percent in the Fiscal Year 2015 thanks to an improved fisheries sector. A surplus of 3% of GDP was recorded "owing to record-high fishing license fees. Growth is expected to rise to about 1.5 percent and inflation to about 0.5 percent in FY2016, as the effects of the drought in earlier 2016 are offset by the resumption of infrastructure projects."
In 2018, the Republic of Marshall Islands passed the Sovereign Currency Act of 2018, Sovereign Currency Act, which made it the first country to issue their own
The islands have few natural resources, and their imports far exceed exports. According to the CIA, the value of exports in 2013 was approximately $53.7 million while estimated imports were $133.7 million. Agricultural products include coconuts, tomatoes, melons, taro, breadfruit, fruits, pigs and chickens. Industry is made of the production of copra and craft items, tuna processing and tourism. The GDP in 2016 was an estimated $180 million, with a real growth rate of 1.7%. The GDP per capita was $3,300.
The International Monetary Fund reported in mid-2016 that the economy of the Republic had expanded by about 0.5 percent in the Fiscal Year 2015 thanks to an improved fisheries sector. A surplus of 3% of GDP was recorded "owing to record-high fishing license fees. Growth is expected to rise to about 1.5 percent and inflation to about 0.5 percent in FY2016, as the effects of the drought in earlier 2016 are offset by the resumption of infrastructure projects."
In 2018, the Republic of Marshall Islands passed the Sovereign Currency Act of 2018, Sovereign Currency Act, which made it the first country to issue their own
 Agricultural production is concentrated on small farms. The most important commercial crop is
Agricultural production is concentrated on small farms. The most important commercial crop is
''Ocean's End: Travels Through Endangered Seas''
New York: Basic Books. (Contains extended account of sea-level rise threat and the legacy of U.S. Atomic testing.)
Embassy of the Republic of the Marshall Islands Washington, DC
official government site
Marshall Islands
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Country Profile
from New Internationalist
Marshall Islands
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Marshall Islands
from the BBC News *
Marshall Islands Journal
Weekly independent national newspaper
Digital Micronesia – ''Marshalls''
by Dirk HR Spennemann, Associate Professor in Cultural Heritage Management
Plants & Environments of the Marshall Islands
Book turned website by Dr. Mark Merlin of the University of Hawaii
Atomic Testing Information
* [http://www.nola.com/news/gulf-oil-spill/index.ssf/2010/05/kenner_hearing_marshall_island.html "Kenner hearing: Marshall Islands-flagged rig in Gulf oil spill was reviewed in February"]
NOAA's National Weather Service – Marshall Islands
Canoes of the Marshall Islands
Alele Museum – Museum of the Marshall Islands
WUTMI – Women United Together Marshall Islands
{{Coord, 9.82, N, 169.29, E, type:country_region:MH_dim:500000, display=title Marshall Islands, Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Associated states of the United States Countries in Micronesia Island countries Member states of the United Nations Republics Small Island Developing States Former colonies in Oceania Former German colonies Former Japanese colonies Former Spanish colonies German New Guinea South Seas Mandate Spanish East Indies Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands World War II sites States and territories established in 1986 1986 establishments in Oceania English-speaking countries and territories Countries in Oceania Eastern Indo-Pacific
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
and microstate
A microstate or ministate is a sovereign state having a very small population or very small land area, usually both. However, the meanings of "state" and "very small" are not well-defined in international law.Warrington, E. (1994). "Lilliputs ...
near the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, slightly west of the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific O ...
. Geographically, the country is part of the larger island group of Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
. The country's population of 58,413 people (at the 2018 World Bank Census) is spread out over five islands and 29 coral atoll
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class (biology), class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important C ...
s, comprising 1,156 individual island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
s and islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanent ...
s. The capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city is Majuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
. It has the largest portion of its territory composed of water of any sovereign state, at 97.87%. The islands share maritime boundaries
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Bound ...
with Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of To ...
to the north, Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
to the southeast, ''The Wor ...
Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
to the south, and Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
to the west. About 52.3% of Marshall Islanders (27,797 at the 2011 Census) live on Majuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
. In 2016, 73.3% of the population were defined as being "urban". The UN also indicates a population density of , and its projected 2020 population is 59,190.
Micronesian settlers reached the Marshall Islands using canoes circa 2nd millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC.
In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.
The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era:
The first half of the mil ...
, with interisland navigation made possible using traditional stick charts. They eventually settled there. Islands in the archipelago were first explored by Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
in the 1520s, starting with Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East ...
, a Portuguese explorer in the service of Spain, Juan Sebastián Elcano
Juan Sebastián Elcano (Elkano in modern Basque; sometimes given as ''del Cano''; 1486/1487Some sources state that he was born in 1476. Most of this sources try to make a point about him participating on a military campaign at the Mediterranean w ...
and Miguel de Saavedra. Spanish explorer Alonso de Salazar
Toribio Alonso de Salazar, (died 5 September 1526) born in Biscay, was a Spanish navigator of Basque origin, who was the first Westerner to arrive on the Marshall Islands on August 21, 1526.
De Salazar was part of the Fray García Jofre de Loa ...
reported sighting an atoll in August 1526. Other expeditions by Spanish and English ships followed. The islands derive their name from John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remains the longest-serving chief justice and fourth-longes ...
, who visited in 1788. The islands were historically known by the inhabitants as "" (Gifts from God). Spain claimed the islands in 1592, and the European powers recognized its sovereignty over the islands in 1874. They had been part of the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales españolas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia-Pacific, Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico C ...
formally since 1528. Later, Spain sold some of the islands to the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1885, and they became part of German New Guinea
German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ...
that year, run by the trading companies doing business in the islands, particularly the Jaluit Company. In World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent fo ...
occupied the Marshall Islands, which, in 1920, the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
combined with other former German territories to form the South Seas Mandate
The South Seas Mandate, officially the Mandate for the German Possessions in the Pacific Ocean Lying North of the Equator, was a League of Nations mandate in the "South Seas" given to the Empire of Japan by the League of Nations following Wo ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
took control of the islands in the Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign
The Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign were a series of battles fought from August 1942 through February 1944, in the Pacific theatre of World War II between the United States and Japan. They were the first steps of the drive across the cent ...
in 1944. Nuclear testing began on Bikini Atoll
Bikini Atoll ( or ; Marshallese: , , meaning "coconut place"), sometimes known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 1800s and 1946 is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a central lagoon. After the Second ...
in 1946 and concluded in 1958.
The U.S. government formed the Congress of Micronesia in 1965, a plan for increased self-governance of Pacific islands. The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
History
Spain initially claimed the islands that later composed the territory of the Trus ...
in May 1979 provided independence to the Marshall Islands, whose constitution and president (Amata Kabua
Amata Kabua (November 17, 1928 – December 19, 1996) was the first President of the Marshall Islands from 1979 until his death in 1996 (five consecutive terms).
Background
Amata Kabua was a scion of Marshallese Royalty. Amata Kabua is the son o ...
) were formally recognized by the US. Full sovereignty or self-government
__NOTOC__
Self-governance, self-government, or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of ...
was achieved in a Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
with the United States. Marshall Islands has been a member of the Pacific Community
The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories. The organisation's headquarters are in Nouméa ...
(SPC) since 1983 and a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
member state since 1991. Politically, the Marshall Islands is a parliamentary republic with an executive presidency
This is a list of sovereign states by system of government. There is also a political mapping of the world that shows what form of government each country has, as well as a brief description of what each form of government entails. The list ...
in free association with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, with the U.S. providing defense, subsidies, and access to U.S.-based agencies such as the Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdiction ...
and the United States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U ...
. With few natural resources, the islands' wealth is based on a service economy
Service economy can refer to one or both of two recent economic developments:
* The increased importance of the service sector in industrialized economies. The current list of Fortune 500 companies contains more service companies and fewer ma ...
, as well as fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
; aid from the United States represents a large percentage of the islands' gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
, but most financial aid from the Compact of Free Association expires in 2023. , negotiations regarding an extension of the aid period were ongoing. The country uses the United States dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the officia ...
as its currency. In 2018, it also announced plans for a new cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It i ...
to be used as legal tender.
The majority of the citizens of the Republic of Marshall Islands are of Marshallese descent, though there are small numbers of immigrants from the United States, China, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and other Pacific islands. The two official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
s are Marshallese, which is one of the Oceanic languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages ...
, and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
. Almost the entire population of the islands practices some religion: three-quarters of the country follows either the United Church of Christ – Congregational in the Marshall Islands (UCCCMI) or the Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
.
History


 Evidence suggests that around 3,000 years ago successive waves of human migrants from
Evidence suggests that around 3,000 years ago successive waves of human migrants from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
spread across the Western Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, populating its many small islands. The Marshall Islands were settled by Micronesians
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Ethno ...
in the 2nd millennium BC. Little is known of the islands' early history. Marshall Islanders, among the many great Oceanic voyagers, designed stick chart
Stick charts were made and used by the Marshallese people, Marshallese to navigate the Pacific Ocean by canoe off the coast of the Marshall Islands. The charts represented major swell (ocean), ocean swell patterns and the ways the islands disru ...
s to map ocean swells and navigate between the islands. Present-day seafaring
Seamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The'' Oxford Dictionary'' states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."
It involves topics a ...
, however, has remained an extension of maritime culture across the archipelago.
The Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
explorer Alonso de Salazar
Toribio Alonso de Salazar, (died 5 September 1526) born in Biscay, was a Spanish navigator of Basque origin, who was the first Westerner to arrive on the Marshall Islands on August 21, 1526.
De Salazar was part of the Fray García Jofre de Loa ...
landed there in 1526, and the archipelago came to be known as "''Los Pintados''" ("The Painted (Ones)", possibly referring to the indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
people first found there), "''Las Hermanas''" ("The Sisters") and "''Los Jardines''" ("The Gardens") within the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
. It first fell within the jurisdiction of the Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Amer ...
, and was then administered by Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
, through the Captaincy General of the Philippines
The Captaincy General of the Philippines ( es, Capitanía General de Filipinas ; tl, Kapitaniya Heneral ng Pilipinas) was an administrative district of the Spanish Empire in Southeast Asia governed by a Governor-General of the Philippines, gove ...
, upon the independence of Latin America and the dissolution of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
starting in 1821.
American whaling ships visited the islands in the 19th century. The first on record was the ''Awashonks
Awashonks (also spelled Awashunckes, Awashunkes or Awasoncks) was a saunkskwa, a female sachem ( chief) of the Sakonnet (also spelled Saconet) tribe in Rhode Island. She lived near the southern edge of the Plymouth Colony on Patuxet homelands, not ...
'' in 1835 and last was the ''Andrews Hicks'' in 1905.
The islands were only formally possessed by Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
for much of their colonial history, and on European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
maps were grouped with the Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the centra ...
which today make up Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caro ...
and the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, or alternatively the "Nuevas Filipinas" ("New Philippines"). The islands were mostly left to their own affairs except for short-lived religious missions (documented in 1668 and 1731) during the 16th and 17th centuries. They were largely ignored by European powers except for cartographic demarcation treaties between the Iberian Empires (Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and Castilian Spain) in 1529, 1750 and 1777. The archipelago corresponding to the present-day country was independently named by Krusenstern, after British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
explorer
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remains the longest-serving chief justice and fourth-longes ...
, who visited them together with Thomas Gilbert in 1788, en route from Botany Bay
Botany Bay (Dharawal: ''Kamay''), an open oceanic embayment, is located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, south of the Sydney central business district. Its source is the confluence of the Georges River at Taren Point and the Cook ...
to Canton with two ships of the First Fleet
The First Fleet was a fleet of 11 ships that brought the first European and African settlers to Australia. It was made up of two Royal Navy vessels, three store ships and six convict transports. On 13 May 1787 the fleet under the command ...
, and started to establish German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
trading posts, which were not formally contested by Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
.
The Marshall Islands were formally claimed by Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
in 1874 through its capital in the East Indies, Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
. This marked the start of several strategic moves by the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
during the 1870s and 80s to annex them (claiming them to be "by chance unoccupied"). This policy culminated in a tense naval episode in 1885, which did not degenerate into a conflict due to the poor readiness of Spain's naval forces and the unwillingness for open military action from the German side.
Following papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
mediation and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
compensation of $4.5 million, Spain reached an agreement with Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 1885: the 1885 Hispano-German Protocol of Rome. This accord established a protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over m ...
and set up trading stations on the islands of Jaluit
Jaluit Atoll ( Marshallese: , , or , ) is a large coral atoll of 91 islands in the Pacific Ocean and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is , and it encloses a lagoon with an area of . Most ...
(Joló) and Ebon to carry out the flourishing copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from copr ...
(dried coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
meat) trade. Marshallese Iroij
Iroijlaplap ( Marshallese: ; feminine: Leroijlaplap, ) are the traditional paramount chiefs in the Marshall Islands. Ordinary chiefs bear the title of Iroij (feminine: Leroij); -' is a superlative suffix.
Legal basis
Article III of the Const ...
(high chiefs) continued to rule under indirect colonial German administration, rendered tacitly effective by the wording in the 1885 Protocol, which demarcated an area subject to Spanish sovereignty (0-11ºN, 133-164ºE) omitting the Eastern Carolines, that is, the Marshall and Gilbert archipelagos, where most of the German trading posts were located. The disputes were rendered moot after the selling of the whole Caroline archipelago to Germany 13 years later.
At the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
assumed control of the Marshall Islands. The Japanese headquarters was established at the German center of administration, Jaluit
Jaluit Atoll ( Marshallese: , , or , ) is a large coral atoll of 91 islands in the Pacific Ocean and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is , and it encloses a lagoon with an area of . Most ...
. On January 31, 1944, American forces landed on Kwajalein
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
and U.S. Marines and Army troops later took control of the islands from the Japanese on February 3, following intense fighting on Kwajalein and Enewetak
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with it ...
atolls. In 1947, the United States, as the occupying power, entered into an agreement with the UN Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and ...
to administer much of Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
, including the Marshall Islands, as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
History
Spain initially claimed the islands that later composed the territory of the Trus ...
.
From 1946 to 1958, it served as the Pacific Proving Grounds
The Pacific Proving Grounds was the name given by the United States government to a number of sites in the Marshall Islands and a few other sites in the Pacific Ocean at which it conducted nuclear testing between 1946 and 1962. The U.S. tested a ...
for the United States and was the site of 67 nuclear test
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by ...
s on various atolls. The world's first hydrogen bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lowe ...
, codenamed "Mike
Mike may refer to:
Animals
* Mike (cat), cat and guardian of the British Museum
* Mike the Headless Chicken, chicken that lived for 18 months after his head had been cut off
* Mike (chimpanzee), a chimpanzee featured in several books and docume ...
", was tested at the Enewetak atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with it ...
in the Marshall Islands on November 1 (local date) in 1952, by the United States.
 Nuclear testing began in 1946 on
Nuclear testing began in 1946 on Bikini Atoll
Bikini Atoll ( or ; Marshallese: , , meaning "coconut place"), sometimes known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 1800s and 1946 is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a central lagoon. After the Second ...
after residents were evacuated. Over the years, 67 weapon tests were conducted, including the 15-megaton Castle Bravo hydrogen bomb test, which produced significant fallout in the region. The testing concluded in 1958. Over the years, just one of over 60 islands was cleaned by the U.S. government, and the inhabitants are still waiting for the 2 billion dollars in compensation assessed by the Nuclear Claims Tribunal. Many of the islanders and their descendants still live in exile, as the islands remain contaminated with high levels of radiation.
A significant radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
installation was constructed on Kwajalein
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
atoll.
On May 1, 1979, in recognition of the evolving political status of the Marshall Islands, the United States recognized the constitution of the Marshall Islands
The Constitution of the Marshall Islands is the supreme law of the Republic of the Marshall Islands, in force from 1 May 1979.
Its text is both English and Marshallese.
The Constitution was approved on 1 March 1979 by constitutional referendum, ...
and the establishment of the Government of the Republic of the Marshall Islands. The constitution incorporates both American and British constitutional concepts.
There have been a number of local and national elections since the Republic of the Marshall Islands was founded. The United Democratic Party, running on a reform platform, won the 1999 parliamentary election, taking control of the presidency and cabinet.
The islands signed a Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
with the United States in 1986. Trusteeship was ended under United Nations Security Council Resolution 683
United Nations Security Council resolution 683, adopted on 22 December 1990, after recalling Resolution 21 (1947) which approved the Trusteeship Territory of the Japanese Mandated Islands (since known as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Island ...
of December 22, 1990. Until 1999 the islanders received US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
180M for continued American use of Kwajalein atoll, US$250M in compensation for nuclear test
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by ...
ing, and US$600M in other payments under the compact.
Despite the constitution, the government was largely controlled by Iroij. It was not until 1999, following political corruption
Political corruption is the use of powers by government officials or their network contacts for illegitimate private gain.
Forms of corruption vary, but can include bribery, lobbying, extortion, cronyism, nepotism, parochialism, patronage, in ...
allegations, that the aristocratic
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word's ...
government was overthrown, with Imata Kabua
Imata Jabro Kabua (20 May 1943 – 18 September 2019) was a Marshallese politician, who served as the President of the Marshall Islands from 14 January 1997 to 10 January 2000. He became the Iroijlaplap of Kwajalein
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marsh ...
replaced by the commoner
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither ...
Kessai Note
Kessai Hesa Note (born August 7, 1950 in Ailinglaplap) was President of the Marshall Islands from 2000 to 2008.
Elected in 1979 alongside Litokwa Tomeing, Note is one of the two longest-serving members of Nitijeļā. He was the Minister of Inter ...
.
The Runit Dome was built on Runit Island
Runit Island () is one of 40 islands of the Enewetak Atoll of the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean. The island is the site of a radioactive waste repository left by the United States after it conducted a series of nuclear tests on Enewetak A ...
to deposit U.S.-produced radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
soil and debris, including lethal amounts of plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
. There are ongoing concerns about deterioration of the waste site and a potential radioactive spill.
On 3 February 2018, the Marshall Islands became the first country in the world to the recognise its cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It i ...
as its own legal tender for digital currency
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital cu ...
.
In January 2020, David Kabua
David Kabua (born May 26, 1951) is a Marshall Islands, Marshallese politician who has served as President of the Marshall Islands since 13 January 2020. He has represented Wotho Atoll in the Legislature of the Marshall Islands since 2008 and serve ...
, son of founding president Amata Kabua
Amata Kabua (November 17, 1928 – December 19, 1996) was the first President of the Marshall Islands from 1979 until his death in 1996 (five consecutive terms).
Background
Amata Kabua was a scion of Marshallese Royalty. Amata Kabua is the son o ...
, was elected as the new President of the Marshall Islands
The following is a list of presidents of the Marshall Islands, since the establishment of that office in 1979. The president of the Republic of the Marshall Islands is the head of state and government of the Marshall Islands. The President is el ...
. His predecessor Hilda Heine
Hilda Cathy Heine (born April 6, 1951) is a Marshallese educator and politician, who served as the eighth President of the Marshall Islands. Prior to assuming office, she served as the Minister of Education. She was the first individual from the ...
lost the position after a vote.
Since the late 1980s, Marshallese have migrated to the US, with over 4,000 in Arkansas and over 7,000 in Hawaii in the 2010 US Census.
Geography



 The Marshall Islands sit atop ancient submerged volcanoes rising from the ocean floor, about halfway between
The Marshall Islands sit atop ancient submerged volcanoes rising from the ocean floor, about halfway between Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, north of Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
and Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
, east of the ''The Wor ...
Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
, and south of the disputed U.S. territory of Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of To ...
, to which it also lays claim. The atolls and islands form two groups: the Ratak (sunrise) and the Ralik (sunset). The two island chains lie approximately parallel to one another, running northwest to southeast, comprising about of ocean but only about of land mass. Each includes 15 to 18 islands and atolls. The country consists of a total of 29 atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
s and five individual islands situated in about of the Pacific. The largest atoll with a land area of is Kwajalein. It surrounds a lagoon.
Twenty-four of the atolls and islands are inhabited. The remaining atolls are uninhabited due to poor living conditions, lack of rain, or nuclear contamination. The uninhabited atolls are:
* Ailinginae Atoll
Ailinginae Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is an uninhabited (due to Castle Bravo nuclear testing) coral atoll of 25 islands in the Pacific Ocean, on the northern end of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is only , but it enclos ...
* Bikar (Bikaar) Atoll
* Bikini Atoll
Bikini Atoll ( or ; Marshallese: , , meaning "coconut place"), sometimes known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 1800s and 1946 is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a central lagoon. After the Second ...
* Bokak Atoll
Bokak Atoll ( Marshallese: or , ) or Taongi Atoll is an uninhabited coral atoll in the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands, in the North Pacific Ocean. Due to its relative isolation from the main islands in the group, Bokak's flora and fauna has ...
* Erikub Atoll
* Jemo Island
Jemo Island Atoll ( Marshallese: or , ) is an uninhabited coral island in the Pacific Ocean, in the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands north-east of Likiep Atoll. The island is oval-shaped and occupies the southwestern end of a narrow submarine r ...
* Nadikdik Atoll
Knox Atoll (Marshallese language, Marshallese: , ) is an uninhabited coral atoll of 18 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and is the southernmost atoll of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. The total land area is only , but it encloses a largely ...
* Rongerik Atoll
Rongerik Atoll or Rongdrik Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 17 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and is located in the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands, approximately east of Bikini Atoll. Its total land area is only , but it encloses ...
* Toke Atoll
Toke Atoll or Taka Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a small, uninhabited coral atoll in the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. It is one of the smaller atolls in the Marshalls and located at . It is visited regularly by the residents of nearby Utiri ...
* Ujelang Atoll
Ujelang Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 30 islands in the Pacific Ocean, in the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is , and it encloses a lagoon of . It is the westernmost island in the Marshall Islands, approxim ...
The average altitude above sea level for the entire country is .
Shark sanctuary
In October 2011, the government declared that an area covering nearly of ocean shall be reserved as ashark sanctuary
A shark sanctuary is an area that forbids commercial fishing operations from targeting and retaining caught sharks, including their fins. The first shark sanctuary was created by Palau in 2009. It was followed by Maldives, Honduras, The Bahamas and ...
. This is the world's largest shark sanctuary, extending the worldwide ocean area in which sharks are protected from . In protected waters, all shark fishing is banned and all by-catch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
must be released. However, some have questioned the ability of the Marshall Islands to enforce this zone.
Territorial claim on Wake Island
The Marshall Islands also lays claim toWake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of To ...
. While Wake island has been administered by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
since 1899, the Marshallese government refers to it by the name ''Ānen Kio'' (new orthography) or ''Enen-kio'' (old orthography).
Climate
wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the sea ...
from May to November. Many Pacific typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
s begin as tropical storms in the Marshall Islands region, and grow stronger as they move west toward the Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
.
Population has outstripped the supply of fresh water, usually from rainfall. The northern atolls get of rainfall annually; the southern atolls about twice that. The threat of drought is commonplace throughout the island chains.
Climate change
Climate change is a serious threat to the Marshall Islands, with typhoons becoming stronger and sea levels rising. The sea around the Pacific islands has risen a year since 1993, which is more than twice the rate of the worldwide average. InKwajalein
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
, there is a high risk of permanent flooding; when sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cry ...
s to , 37% of buildings will be permanently flooded in that scenario. In Ebeye
Ebeye ( ; Marshallese: , or in older orthography, ; locally, , , after the English pronunciation) is the most populous island of Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands, as well as the center for Marshallese culture in the Ralik Chain of the arc ...
, the risk of sea level rise is even higher, with 50% of buildings being permanently flooded in the same scenario. With of sea level rise, parts of the Majuro atoll
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The atol ...
will be permanently flooded and other parts are having a high risk of flooding especially the eastern part of the atoll would be significantly at risk. With sea level rise all the buildings of Majuro will be permanently flooded or would be at a high risk to be flooded.
The per capita emissions were 2.56t in 2020. The government of Marshall Islands pledged to be net zero in 2050, with a decrease of 32% decrease of GHGs in 2025, 45% decrease in 2030 and a 58% decrease in 2035 all compared to 2010 levels.
Fauna
Birds
Most birds found in the Marshall Islands, with the exception of those few introduced by man, are either sea birds or a migratory species. There are about 70 species of birds, including 31 seabirds. 15 of these species actually nest locally. Sea birds include theblack noddy
The black noddy or white-capped noddy (''Anous minutus'') is a seabird from the family Laridae. It is a medium-sized species of tern with black plumage and a white cap. It closely resembles the lesser noddy (''Anous tenuirostris'') with which it w ...
and the white tern
The white tern or common white tern (''Gygis alba'') is a small seabird found across the tropical oceans of the world. It is sometimes known as the fairy tern, although this name is potentially confusing as it is also the common name of '' Sternu ...
. The only land bird is the house sparrow
The house sparrow (''Passer domesticus'') is a bird of the sparrow family Passeridae, found in most parts of the world. It is a small bird that has a typical length of and a mass of . Females and young birds are coloured pale brown and grey, a ...
, introduced by humans.
Marine
There are about 300 species of fish, 250 of which arereef fish
Coral reef fish are fish which live amongst or in close relation to coral reefs. Coral reefs form complex ecosystems with tremendous biodiversity. Among the myriad inhabitants, the fish stand out as colourful and interesting to watch. Hundreds ...
.
* Turtles: green turtles
The green sea turtle (''Chelonia mydas''), also known as the green turtle, black (sea) turtle or Pacific green turtle, is a species of large sea turtle of the family Cheloniidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Chelonia''. Its range exten ...
, hawksbill
The hawksbill sea turtle (''Eretmochelys imbricata'') is a critically endangered sea turtle belonging to the family Cheloniidae. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Eretmochelys''. The species has a global distribution, that is large ...
, Leatherback sea turtle
The leatherback sea turtle (''Dermochelys coriacea''), sometimes called the lute turtle or leathery turtle or simply the luth, is the largest of all living turtles and the heaviest non-crocodilian reptile, reaching lengths of up to and weights ...
s, and Olive ridley sea turtle
The olive ridley sea turtle (''Lepidochelys olivacea''), also known commonly as the Pacific ridley sea turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is the second-smallest and most abundant of all sea turtles found in th ...
s.
* Sharks: There are at least 22 shark species including: Blue shark
The blue shark (''Prionace glauca''), also known as the great blue shark, is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, which inhabits deep waters in the world's temperate and tropical oceans. Averaging around and preferring co ...
, Silky shark
The silky shark (''Carcharhinus falciformis''), also known by numerous names such as blackspot shark, gray whaler shark, olive shark, ridgeback shark, sickle shark, sickle-shaped shark and sickle silk shark, is a species of requiem shark, in the f ...
, Bigeye thresher
The bigeye thresher (''Alopias superciliosus'') is a species of thresher shark, family Alopiidae, found in temperate and tropical oceans worldwide. Like the other thresher sharks, nearly half its total length consists of the elongated upper lobe ...
shark, Pelagic thresher
The pelagic thresher (''Alopias pelagicus'') is a species of thresher shark, family Alopiidae; this group of sharks is characterized by the greatly elongated upper lobes of their caudal fins. The pelagic thresher occurs in the tropical and subtro ...
shark, Oceanic whitetip shark
The oceanic whitetip shark (''Carcharhinus longimanus''), also known as shipwreck shark, Brown Milbert's sand bar shark, brown shark, lesser white shark, nigano shark, oceanic white-tipped whaler, and silvertip shark, is a large pelagic requiem ...
, and Tawny nurse shark
The tawny nurse shark (''Nebrius ferrugineus'') is a species of carpet shark in the family Ginglymostomatidae, and the only extant member of the genus '' Nebrius''.
It is found widely along coastlines in the Indo-Pacific, preferring reefs, s ...
.
Arthropods
* Scorpions: dwarf wood scorpion, and Common house scorpion.Pseudoscorpion
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.
Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans sin ...
s are occasionally found.
*Spiders: Two: a scytodes
''Scytodes'' is a genus of Scytodidae, spitting spiders that occur all around the world. The most widely distributed species is ''Scytodes thoracica'', which originally had a Palearctic realm, palearctic distribution, but has been introduced to ...
, ''Dictis striatipes''; and ''Jaluiticola
''Jaluiticola'' is a genus of jumping spiders endemic to the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country an ...
'' a genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of jumping spiders
Jumping spiders are a group of spiders that constitute the family Salticidae. As of 2019, this family contained over 600 described genera and over 6,000 described species, making it the largest family of spiders at 13% of all species. Jumping spi ...
endemic to the Marshall Islands. Its only species is ''Jaluiticola hesslei''.
* Amphipod
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far descr ...
: One – ''Talorchestia spinipalma
''Talorchestia'' is a genus of amphipod of the family (biology), family Talitridae, containing the following species:
*''Talorchestia affinis'' Maccagno, 1936
*''Talorchestia africana'' Bate, 1862
*''Talorchestia antennulata'' Chevreux, 1915
*'' ...
''.
* Orthoptera
Orthoptera () is an order of insects that comprises the grasshoppers, locusts, and crickets, including closely related insects, such as the bush crickets or katydids and wētā. The order is subdivided into two suborders: Caelifera – grassho ...
: cockroaches
Cockroaches (or roaches) are a paraphyletic group of insects belonging to Blattodea, containing all members of the group except termites. About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. Some species are well-known a ...
, American cockroach
The american cockroach (''Periplaneta americana'') is the largest species of common cockroach, and often considered a pest. In certain regions of the U.S. it is colloquially known as the waterbug, though it is not a true waterbug since it is not ...
es, short-horned grasshopper
The AcrididaeMacLeay WS (1821) ''Horae Entomologicae or Essays on the Annulose Animals'' 2 are the predominant family of grasshoppers, comprising some 10,000 of the 11,000 species of the entire suborder Caelifera. The Acrididae are best known be ...
, cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
s.
* Crabs include hermit crab
Hermit crabs are anomuran decapod crustaceans of the superfamily Paguroidea that have adapted to occupy empty scavenged mollusc shells to protect their fragile exoskeletons. There are over 800 species of hermit crab, most of which possess an a ...
s, and coconut crab
The coconut crab (''Birgus latro'') is a species of terrestrial hermit crab, also known as the robber crab or palm thief. It is the largest terrestrial arthropod in the world, with a weight of up to . It can grow to up to in width from the tip ...
s.
Demographics
 Historical population figures for the Marshall Islands are unknown. In 1862, the population of the Islands was estimated at 10,000. In 1960, the population of the Islands was approximately 15,000. The 2011
Historical population figures for the Marshall Islands are unknown. In 1862, the population of the Islands was estimated at 10,000. In 1960, the population of the Islands was approximately 15,000. The 2011 Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses incl ...
counted 53,158 island residents. Over two-thirds of the residents of the Marshall Islands live in the capital city, Majuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
, and the secondary urban center, Ebeye
Ebeye ( ; Marshallese: , or in older orthography, ; locally, , , after the English pronunciation) is the most populous island of Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands, as well as the center for Marshallese culture in the Ralik Chain of the arc ...
(located in Kwajalein Atoll
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
). This figures excludes Marshall Islands natives who have relocated elsewhere; the Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
allows them to freely relocate to the United States and obtain work there. Approximately 4,300 Marshall Islands natives relocated to Springdale, Arkansas
Springdale is the List of cities and towns in Arkansas, fourth-largest city in Arkansas, United States. It is located in both Washington County, Arkansas, Washington and Benton County, Arkansas, Benton counties in Northwest Arkansas. Located on th ...
in the United States; this figure represents the largest population concentration of Marshall Islands natives outside their island home.
Most residents of the Marshall Islands are Marshallese. Marshallese people
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Ethno ...
are of Micronesian origin and are believed to have migrated from Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
to the Marshall Islands several thousand years ago. A minority of Marshallese have some recent Asian ancestry (mainly Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
). About one-half of the nation's population lives in Majuro and Ebeye.
The official languages of the Marshall Islands are English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and Marshallese. Both languages are widely spoken.
Religion
 Major religious groups in the Republic of the Marshall Islands include the United Church of Christ – Congregational in the Marshall Islands, with 51.5% of the population; the
Major religious groups in the Republic of the Marshall Islands include the United Church of Christ – Congregational in the Marshall Islands, with 51.5% of the population; the Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
, 24.2%; the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, 8.4%;International Religious Freedom Report 2009: Marshall Islands. United States
Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor
The Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor Affairs (DRL) is a bureau within the United States Department of State. The bureau is under the purview of the Under Secretary of State for Civilian Security, Democracy, and Human Rights.
DRL's resp ...
(September 14, 2007). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work
A creative work is a manifestation of creative effort including fine artwork (sculpture, paintings, drawing, sketching, performance art), dance, writing (literature), filmmaking, ...
.'' and The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
(Mormons), 8.3%. Also represented are Bukot Nan Jesus (also known as Assembly of God Part Two), 2.2%; Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compete ...
, 1.0%; Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventism, Adventist Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the Names of the days of the week#Numbered days of the week, seventh day of the ...
, 0.9%; Full Gospel The term Full Gospel or Fourfold Gospel is a theological doctrine used by some evangelical denominations that summarizes the Gospel in four aspects, namely salvation, sanctification, divine healing and second coming of Christ.
Doctrine
This term ...
, 0.7%; and the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
, 0.6%. Persons without any religious affiliation account for a very small percentage of the population. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is also present through Ahmadiyya Muslim Community
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
which is based in Majuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
, with the first mosque opening in the capital in September 2012.
Father A. Erdland, a Catholic priest of the Missionaries of the Sacred Heart
The Missionaries of the Sacred Heart of Jesus (MSC; la, Missionarii Sacratissimi Cordis; french: Missionnaires du Sacré-Coeur) are a missionary congregation in the Catholic Church. It was founded in 1854 by Servant of God Jules Chevalier (182 ...
of Hiltrup (German Empire, called in German ''Herz-Jesu-Missionare'' and in Latin ''Missionarii Sacratissimi Cordis''), lived in Jaluit
Jaluit Atoll ( Marshallese: , , or , ) is a large coral atoll of 91 islands in the Pacific Ocean and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is , and it encloses a lagoon with an area of . Most ...
between 1904 and 1914. After doing considerable research on Marshallese culture and language, he published a 376-page monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject.
In library cataloging, ''monograph ...
on the islands in 1914. Father H. Linckens, another Sacred Heart missionary, visited the Marshall Islands in 1904 and 1911 for several weeks. In 1912 he published a small work on Catholic missionary activities and the people of the Marshall Islands. The Catholics are under the responsibility of the Apostolic Prefecture of the Marshall Islands
The Roman Catholic Apostolic Prefecture of the Marshall Islands ( la, Praefectura Apostolica Insularum Marshallensium) is a Latin rite apostolic prefecture (pre-diocesan missionary ecclesiastical jurisdiction of the Catholic Church, below apostol ...
(''Praefectura Apostolica Insularum Marshallensium'') with headquarters at the Cathedral of the Assumption in Majuro, which was created by Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
in 1993 through the papal bull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e., cows), bulls have long been an important symbol in many religions,
includin ...
''Quo expeditius''.
Health
During theCastle Bravo
Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of ''Operation Castle''. Detonated on March 1, 1954, the device was the most powerful ...
test of the first deployable thermonuclear bomb, a miscalculation resulted in the explosion being over twice as large as predicted. The nuclear fallout
Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed. It commonly refers to the radioac ...
spread eastward onto the inhabited Rongelap
Rongelap Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 61 islands (or motus) in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is . It encloses a lagoon with an area of . ...
and Rongerik Atoll
Rongerik Atoll or Rongdrik Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 17 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and is located in the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands, approximately east of Bikini Atoll. Its total land area is only , but it encloses ...
s. These islands were not evacuated before the explosion. Many of the Marshall Islands natives have since suffered from radiation burns and radioactive dusting, suffering the similar fates as the Japanese fishermen aboard the ''Daigo Fukuryū Maru
was a Japanese tuna fishing boat with a crew of 23 men which was contaminated by nuclear fallout from the United States Castle Bravo thermonuclear weapon test at Bikini Atoll on March 1, 1954.
The crew suffered acute radiation syndrome (ARS) ...
'', but have received little, if any, compensation from the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
.
Government
 The government of the Marshall Islands operates under a mixed parliamentary-presidential system as set forth in its 1979 Constitution. Elections are held every four years in
The government of the Marshall Islands operates under a mixed parliamentary-presidential system as set forth in its 1979 Constitution. Elections are held every four years in universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stanc ...
(for all citizens above 18), with each of the twenty-four constituencies (see below) electing one or more representatives (senators) to the lower house of RMI's unicameral legislature, the Nitijela
The Legislature of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Nitijeļā ) has 33 members, elected for a four-year term in single-seat and five multi-seat constituencies. The last election was November 18, 2019. Elections in the Marshall Islands are officially ...
. (Majuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
, the capital atoll, elects five senators.) The President, who is head of state as well as head of government, is elected by the 33 senators of the Nitijela. Four of the five Marshallese presidents who have been elected since the Constitution was adopted in 1979 have been traditional paramount chief
A paramount chief is the English-language designation for the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a chief-based system. This term is used occasionally in anthropological and arch ...
s.
In January 2016, senator Hilda Heine was elected by Parliament as the first female president of the Marshall Islands; previous president Casten Nemra lost office after serving two weeks in a vote of no confidence
A motion of no confidence, also variously called a vote of no confidence, no-confidence motion, motion of confidence, or vote of confidence, is a statement or vote about whether a person in a position of responsibility like in government or mana ...
.
Legislative power lies with the Nitijela. The upper house of Parliament, called the Council of Iroij, is an advisory body comprising twelve paramount chiefs. The executive branch consists of the President and the Presidential Cabinet, which consists of ten ministers appointed by the President with the approval of the Nitijela. The twenty-four electoral districts into which the country is divided correspond to the inhabited islands and atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
s. There are currently four political parties in the Marshall Islands: Aelon̄ Kein Ad
(, in Marshallese pronounced ), also called the Kabua Party, is a political party in the Marshall Islands, headed by David Kabua. It is a coalition of other parties, including the United People's Party led by former president Litokwa Tomeing. T ...
(AKA), United People's Party (UPP), Kien Eo Am Kien or Kiens may refer to:
* Kien, Bern, a village in Bern, Switzerland
* Kien, Burkina Faso, a village
* ''Kien'' (album), a 2008 album by the Japanese group Bleach
* Pine Ridge Airport (ICAO: KIEN), Pine Ridge, South Dakota , US
* Kiens, a com ...
(KEA) and United Democratic Party (UDP). Rule is shared by the AKA and the UDP. The following senators are in the legislative body:
* Ailinglaplap Atoll
Ailinglaplap or Ailinglapalap ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 56 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain in the Marshall Islands. It is located northwest of Jaluit Atoll. Its total land area is on ...
– Christopher Loeak
Christopher Jorebon Loeak (born 11 November 1952) is a Marshallese politician who was the President of the Marshall Islands from 2012 to 2016. He was elected by parliament as President in January 2012, following the 2011 general election.
Per ...
(AKA), Alfred Alfred, Jr. (IND)
* Ailuk Atoll
Ailuk Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 57 islets in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. It is located approximately north from Wotje. Its total land area is only , but it en ...
– Maynard Alfred (UDP)
* Arno Atoll
Arno Atoll ( mh, Arņo, ) is a coral atoll of 133 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is only . Unlike most other atolls, Arno encloses three different la ...
– Mike Halferty (KEA), Jejwadrik H. Anton (IND)
* Aur Atoll
Aur Atoll ( Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 42 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is only , but it encloses a lagoon with an area of . It is located ...
– Hilda C. Heine (AKA)
* Ebon Atoll
Ebon Atoll (Marshallese language, Marshallese: , ) is a coral atoll of 22 islands in the Pacific Ocean, forming a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its land area is , and it encloses a deep lagoon with an area of . ...
– John M. Silk (UDP)
* Enewetak Atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with it ...
– Jack J. Ading
Jack J. Ading (born 1 September 1960 is a Marshallese people, Marshallese politician who served as a Cabinet of the Marshall Islands, member of the cabinet, and as a member of Nitijela.
He has a degree in accounting from Hawaii Pacific Universi ...
(UPP)
* Jabat Island
Jabat Island (or Jabot Island or Jabwot Island; Marshallese: , ) is an island in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is only , and has a length of . It is located ...
– Kessai H. Note (UDP)
* Jaluit Atoll
Jaluit Atoll ( Marshallese: , , or , ) is a large coral atoll of 91 islands in the Pacific Ocean and forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. Its total land area is , and it encloses a lagoon with an area of . Most ...
– Casten Nemra (IND), Daisy Alik Momotaro (IND)
* Kili Island – Eldon H. Note (UDP)
* Kwajalein Atoll
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
– Michael Kabua (AKA), David R. Paul (KEA), Alvin T. Jacklick (KEA)
* Lae Atoll – Thomas Heine (AKA)
* Lib Island – Jerakoj Jerry Bejang (AKA)
* Likiep Atoll – Leander Leander, Jr. (IND)
* Majuro Atoll – Sherwood M. Tibon (KEA), Anthony Muller (KEA), Brenson Wase (UDP), David Kramer (KEA), Kalani Kaneko (KEA)
* Maloelap Atoll – Bruce Bilimon (IND)
* Mejit, Mejit Island – Dennis Momotaro (AKA)
* Mili Atoll – Wilbur Heine (AKA)
* Namdrik Atoll – Wise Zackhras (IND)
* Namu Atoll – Tony Aiseia (AKA)
* Rongelap Atoll – Kenneth A. Kedi (IND)
* Ujae Atoll – Atbi Riklon (IND)
* Utirik Atoll – Amenta Mathew (KEA)
* Wotho Atoll – David Kabua
David Kabua (born May 26, 1951) is a Marshall Islands, Marshallese politician who has served as President of the Marshall Islands since 13 January 2020. He has represented Wotho Atoll in the Legislature of the Marshall Islands since 2008 and serve ...
(AKA)
* Wotje Atoll – Litokwa Tomeing (UPP)
Foreign affairs and defense
 The
The Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
with the United States gives the U.S. sole responsibility for international defense of the Marshall Islands. It gives the islanders (the Demographics of the Marshall Islands, Marshallese) the right to emigrate to the United States without any visa. But as Alien (United States), aliens they can be placed in removal proceedings if convicted of certain criminal offenses.
The Marshall Islands was admitted to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
based on the United Nations Security Council, Security Council's recommendation on August 9, 1991, in United Nations Security Council Resolution 704, Resolution 704 and the United Nations General Assembly, General Assembly's approval on September 17, 1991, in Resolution 46/3. In international politics within the United Nations, the Marshall Islands has often voted consistently with the United States with respect to General Assembly resolutions.
On April 28, 2015, the Iranian navy seized the Marshall Island-flagged MV Maersk Tigris, MV ''Maersk Tigris'' near the Strait of Hormuz. The ship had been chartered by Germany's Rickmers Ship Management, which stated that the ship contained no special cargo and no military weapons. The ship was reported to be under the control of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard according to the Pentagon. Tensions escalated in the region due to the intensifying of Saudi–Yemeni War, Saudi-led coalition attacks in Yemen. The Pentagon reported that the destroyer USS Farragut (DDG-99), USS ''Farragut'' and a maritime reconnaissance aircraft were dispatched upon receiving a distress call from the ship ''Tigris'' and it was also reported that all 34 crew members were detained. US Defense Department, US defense officials have said that they would review U.S. defense obligations to the Government of the Marshall Islands in the wake of recent events and also condemned the shots fired at the bridge as "inappropriate". It was reported in May 2015 that Tehran would release the ship after it paid a penalty.
In March 2017, at the 34th regular session of the UN Human Rights Council, Vanuatu made a joint statement on behalf of the Marshall Islands and some other Pacific nations raising human rights violations in the Western New Guinea, which has been occupied by Indonesia since 1963, and requested that the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights produce a report. Indonesia rejected allegations.
Since 1991 the Republic of Marshall Islands Sea Patrol, a division of Marshall Islands Police, has operated the 160 ton patrol vessel RMIS Lomor (03), RMIS ''Lomor''. ''Lomor'' is one of 22 Pacific Forum patrol vessels Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
provided to smaller nations in the Pacific Islands Forum, Pacific Forum. While some other nations' missions for their vessels include sovereignty, protection, the terms of the Compact of Free Association restrict ''Lomor'' to civilian missions, like fishery protection and search and rescue.
In 2021, the governments of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
decided to fund two major law enforcement developments of the Marshall Islands.
In February 2021, the Marshall Islands announced it would be formally withdrawing from the Pacific Islands Forum in a joint statement with Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
, ''The Wor ...
Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
, and the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise a ...
after a dispute regarding Henry Puna's election as the Forum's secretary-general.
Culture
 Although the ancient skills are now in decline, the Marshallese were once able navigation, navigators, using the celestial navigation, stars and Marshall Islands stick chart, stick-and-shell charts.
Although the ancient skills are now in decline, the Marshallese were once able navigation, navigators, using the celestial navigation, stars and Marshall Islands stick chart, stick-and-shell charts.
Sports
Major sports played in the Marshall Islands include volleyball, basketball (primarily by men), baseball, soccer and a number of water sports. The Marshall Islands has been represented at the Olympics at all games since the 2008 Beijing Olympics. In the 2020 Tokyo Olympics the Marshall Islands were represented by two swimmers.Association football
The Marshall Islands have a small club league, including Kobeer as the most successful club. One tournament was held by ''Play Soccer Make Peace''. There is a small Football Association on the island ofMajuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
. The sport of association football in its growth is new to the Marshall Islands. The Marshall Islands does not yet have a Marshall Islands Soccer Federation, national football team presently. The Marshall Islands is the only sovereign country in the world that does not have a record of a national football match.
Marshall Islands Baseball / Softball Federation
Softball and baseball are held under one sports federation in the Marshall Islands. The President is Jeimata Nokko Kabua. Both sports are growing at a fast pace with hundreds of Marshallese people behind the Marshall Islands Baseball / Softball Federation. The Marshall Islands achieved a silver medal in the Micronesian Games in 2012, as well as medals in the SPG Games.Economy
cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It i ...
and certify it as legal tender; the currency is called the "Sovereign".
Shipping
The Marshall Islands plays a vital role in the international shipping industry as a flag of convenience for commercial vessels. The Marshallese registry began operations in 1990, and is managed through a joint venture with International Registries, Inc., a US-based corporation that has offices in major shipping centers worldwide. As of 2017, the Marshallese ship registry was the second largest in the world, after that of Panama. Unlike some flag countries, there is no requirement that a Marshallese flag vessel be owned by a Marshallese individual or corporation. Following the 2015 seizure of the ''MV Maersk Tigris'', the United States announced that its treaty obligation to defend the Marshall Islands did not extend to foreign-owned Marshallese flag vessels at sea. As a result of ship-to-ship transfers by Marshallese flag tanker vessels, the Marshall Islands have statistically been one of the largest importers of crude oil from the United States, despite the fact that the islands have no oil refining capacity.Labor
In 2007, the Marshall Islands joined the International Labour Organization, which means its labor laws will comply with international benchmarks. This may affect business conditions in the islands.Taxation
The income tax has two brackets, with rates of 8% and 12%. The corporate tax is 3% of revenue.Foreign assistance
United States government assistance is the mainstay of the economy. Under terms of the AmendedCompact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
, the U.S. is committed to provide US$57.7 million per year in assistance to the Marshall Islands (RMI) through 2013, and then US$62.7 million through 2023, at which time a trust fund, made up of U.S. and RMI contributions, will begin perpetual annual payouts.
The United States Army maintains the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site on Kwajalein
Kwajalein Atoll (; Marshallese: ) is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents (about 1,000 mostly U.S. civilia ...
Atoll. Marshallese land owners receive rent for the base.
Agriculture
 Agricultural production is concentrated on small farms. The most important commercial crop is
Agricultural production is concentrated on small farms. The most important commercial crop is copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from copr ...
, followed by coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
, breadfruit, Pandanus tectorius, pandanus, banana, Cyrtosperma merkusii, taro and Tacca leontopetaloides, arrowroot. The livestock consists primarily of pigs and chickens.
Industry
Small-scale industry is limited to handicrafts, fish processing, andcopra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from copr ...
.
Fishing
Majuro is the world's busiest tuna transshipment port, with 704 transshipments totaling 444,393 tons in 2015. Majuro is also a tuna processing center; the Pan Pacific Foods plant exports processed tuna to a number of countries, primarily the United States under the Bumble Bee Foods, Bumble Bee brand. Fishing license fees, primarily for tuna, provide noteworthy income for the government. In 1999, a private company built a tuna loining plant with more than 400 employees, mostly women. But the plant closed in 2005 after a failed attempt to convert it to produce tuna steaks, a process that requires half as many employees. Operating costs exceeded revenue, and the plant's owners tried to partner with the government to prevent closure. But government officials personally interested in an economic stake in the plant refused to help. After the plant closed, it was taken over by the government, which had been the guarantor of a $2 million loan to the business.Energy
On September 15, 2007, Witon Barry (of the Tobolar Copra processing plant in the Marshall Islands capital ofMajuro
Majuro (; Marshallese: ' ) is the capital and largest city of the Marshall Islands. It is also a large coral atoll of 64 islands in the Pacific Ocean. It forms a legislative district of the Ratak (Sunrise) Chain of the Marshall Islands. The ato ...
) said power authorities, private companies, and entrepreneurs had been experimenting with coconut oil as alternative to diesel fuel for vehicles, electricity generation, power generators, and ships. Coconut trees abound in the Pacific's tropical islands. Copra, the meat of the coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
, yields coconut oil (1 liter for every 6 to 10 coconuts). In 2009, a 57 kW solar power plant was installed, the largest in the Pacific at the time, including New Zealand. It is estimated that 330 kW of solar and 450 kW of wind power would be required to make the College of the Marshall Islands energy self-sufficient. Marshalls Energy Company (MEC), a government entity, provides the islands with electricity. In 2008, 420 solar home systems of 200 Wp each were installed on Ailinglaplap Atoll, sufficient for limited electricity use.
Education
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative (HRMI) finds that the Marshall Islands are fulfilling only 66.1% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to education based on the country's level of income. HRMI breaks down the right to education by looking at the rights to both primary education and secondary education. While taking into consideration the Marshall Islands' income level, the nation is achieving 65.5% of what should be possible based on its resources (income) for primary education and 66.6% for secondary education. The Ministry of Education (Marshall Islands), Ministry of Education is the education agency of the islands. Marshall Islands Public School System operates the state schools in the Marshall Islands. In the 1994–1995 school year the country had 103 elementary schools and 13 secondary schools. There were 27 private elementary schools and one private high school. Christian groups operated most of the private schools. Historically the Marshallese population was taught in English first with Marshallese instruction coming later, but this was reversed in the 1990s to keep the islands' cultural heritage and so children could write in Marshallese. Now English language instruction begins in grade 3. Christine McMurray and Roy Smith wrote in ''Diseases of Globalization: Socioeconomic Transition and Health'' that this could potentially weaken the children's English skills. There are two tertiary education, tertiary institutions operating in the Marshall Islands, the College of the Marshall Islands and the University of the South Pacific.Transportation
The Marshall Islands are served by the Marshall Islands International Airport in Majuro, the Bucholz Army Airfield in Kwajalein, and List of airports in the Marshall Islands, other small airports and airstrips. Airlines include United Airlines, Nauru Airlines, Air Marshall Islands, and Asia Pacific Airlines (United States), Asia Pacific Airlines.Media and communications
The Marshall Islands have several AM and FM radio stations. AM stations are 1098 5 kW V7AB Majuro (Radio Marshalls, national coverage) and 1224 AFN Kwajalein (both public radio) as well as 1557 Micronesia Heatwave. The FM stations are 97.9 V7AD Majuro, V7AA 96.3 FM Uliga and 104.1 V7AA Majuro (Baptist religious). BBC World is broadcast on 98.5 FM Majuro. The most recent station is Power 103.5 which started broadcasting in 2016. American Forces Network, AFRTS stations include 99.9 AFN Kwajalein (country), 101.1 AFN (adult rock) and 102.1 AFN (hot AC). There is one broadcast television station, MBC-TV operated by the state. Cable TV is available. On cable TV, most programs are shown two weeks later than in North America but news in real time can be viewed on CNN, CNBC and BBC. American Forces Radio and Television also provides TV service to Kwajalein Atoll. The Marshall Islands National Telecommunications Authority (NTA) provides telephone, cable TV (MHTV), FAX, cellular and Internet services. The Authority is a private corporation with significant ownership by the national government.Newspapers
''Loan Ran Kein'', a Marshallese language paper, was published from 1953 to 1954. The current national newspaper is a bilingual (Marshallese and English) weekly, ''The Marshall Islands Journal''. It has been published since 1980.See also
* Outline of the Marshall Islands * Index of Marshall Islands–related articles * List of islands of the Marshall Islands *Pacific Proving Grounds
The Pacific Proving Grounds was the name given by the United States government to a number of sites in the Marshall Islands and a few other sites in the Pacific Ocean at which it conducted nuclear testing between 1946 and 1962. The U.S. tested a ...
* List of island countries
* ''The Plutonium Files''
* Visa policy of the Marshall Islands
* Naval Base Marshall Islands
Notes
References
Bibliography
*Further reading
* * * Hein, J. R., F. L. Wong, and D. L. Mosier (2007). ''Bathymetry of the Republic of the Marshall Islands and Vicinity''. Miscellaneous Field Studies; Map-MF-2324. Reston, VA: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey. * * * Woodard, Colin (2000)''Ocean's End: Travels Through Endangered Seas''
New York: Basic Books. (Contains extended account of sea-level rise threat and the legacy of U.S. Atomic testing.)
External links
Government
Embassy of the Republic of the Marshall Islands Washington, DC
official government site
General information
Marshall Islands
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Country Profile
from New Internationalist
Marshall Islands
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Marshall Islands
from the BBC News *
News media
Marshall Islands Journal
Weekly independent national newspaper
Other
Digital Micronesia – ''Marshalls''
by Dirk HR Spennemann, Associate Professor in Cultural Heritage Management
Plants & Environments of the Marshall Islands
Book turned website by Dr. Mark Merlin of the University of Hawaii
Atomic Testing Information
* [http://www.nola.com/news/gulf-oil-spill/index.ssf/2010/05/kenner_hearing_marshall_island.html "Kenner hearing: Marshall Islands-flagged rig in Gulf oil spill was reviewed in February"]
NOAA's National Weather Service – Marshall Islands
Canoes of the Marshall Islands
Alele Museum – Museum of the Marshall Islands
WUTMI – Women United Together Marshall Islands
{{Coord, 9.82, N, 169.29, E, type:country_region:MH_dim:500000, display=title Marshall Islands, Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Associated states of the United States Countries in Micronesia Island countries Member states of the United Nations Republics Small Island Developing States Former colonies in Oceania Former German colonies Former Japanese colonies Former Spanish colonies German New Guinea South Seas Mandate Spanish East Indies Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands World War II sites States and territories established in 1986 1986 establishments in Oceania English-speaking countries and territories Countries in Oceania Eastern Indo-Pacific