Religion in Sub-Saharan Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

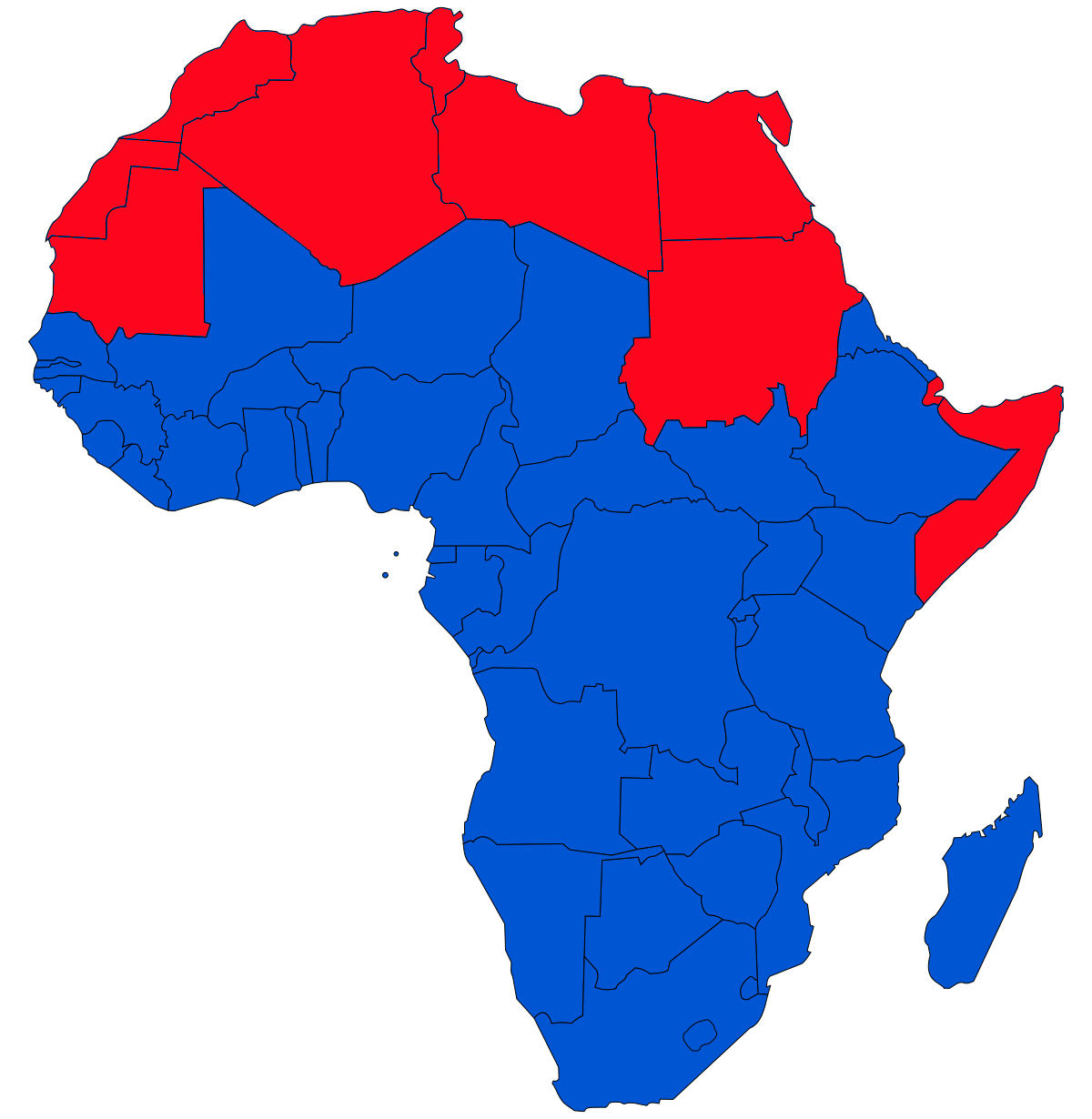
 Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of
 The ancient Greeks sometimes referred to sub-Saharan Africa as ''
The ancient Greeks sometimes referred to sub-Saharan Africa as ''
 Sub-Saharan Africa has a wide variety of
Sub-Saharan Africa has a wide variety of


 Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
, East Africa, Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo ...
, and Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
. Geopolitically, in addition to the African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
(UN). This is considered a non-standardized geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organization describing the region (e.g. UN, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The African Union uses a different regional breakdown, recognizing all 55 member states on the continent - grouping them into 5 distinct and standard regions.
The term serves as a grouping counterpart to North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, which is instead grouped with the definition of MENA
MENA, an acronym in the English language, refers to a grouping of countries situated in and around the Middle East and North Africa. It is also known as WANA, SWANA, or NAWA, which alternatively refers to the Middle East as Western Asia (or a ...
(i.e. Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
–North Africa) as it is part of the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
, and most North African states are likewise members of the Arab League. However, while they are also member states of the Arab League, the Comoros, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, and Mauritania (and sometimes Sudan) are all geographically considered to be part of sub-Saharan Africa. Overall, the UN Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)french: Programme des Nations unies pour le développement, PNUD is a United Nations agency tasked with helping countries Poverty reduction, eliminate poverty and achieve Sustainable development, ...
applies the "sub-Saharan" classification to 46 of Africa's 55 countries, excluding Djibouti, SADR, Somalia, and Sudan.
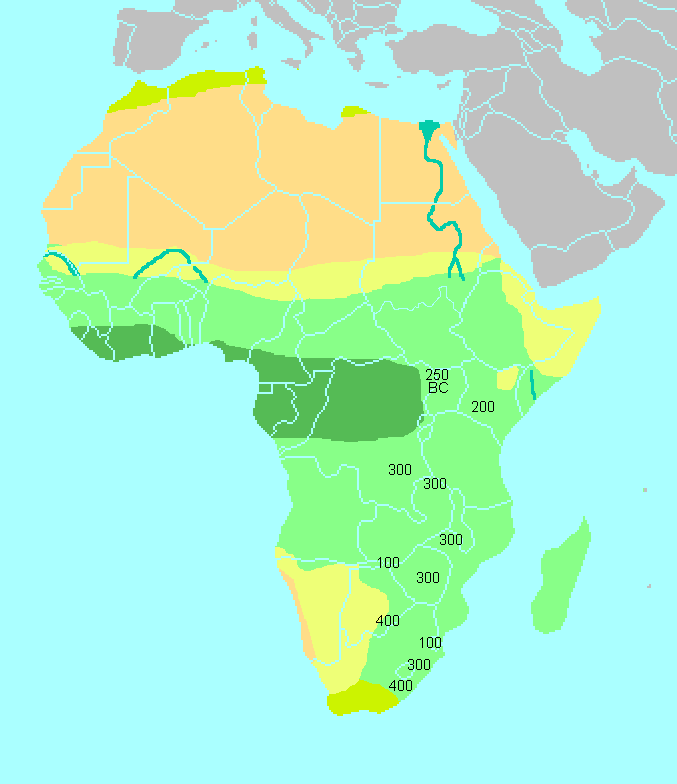
Since probably 3900 BCE, the Saharan and sub-Saharan regions of Africa have been separated by the extremely harsh climate of the sparsely populated Sahara, forming an effective barrier that is interrupted only by the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
in Sudan, though navigation on the Nile was blocked by the Sudd and the river's cataracts. There is also an evident genetic divide between North Africa and sub-Saharan Africa that dates back to the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
. The Sahara pump theory
The Sahara pump theory is a hypothesis that explains how flora and fauna migrated between Eurasia and Africa via a land bridge in the Levant region. It posits that extended periods of abundant rainfall lasting many thousands of years (pluvial p ...
explains how flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' ...
and fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''Biota (ecology ...
(including ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'') left Africa to penetrate Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
and beyond. African pluvial
In geology and climatology, a pluvial is either a modern climate characterized by relatively high precipitation or an interval of time of variable length, decades to thousands of years, during which a climate is characterized by relatively high ...
periods are associated with a " Wet Sahara" phase, during which larger lakes and more rivers existed.
Nomenclature
 The ancient Greeks sometimes referred to sub-Saharan Africa as ''
The ancient Greeks sometimes referred to sub-Saharan Africa as ''Aethiopia
Ancient Aethiopia, ( gr, Αἰθιοπία, Aithiopía; also known as Ethiopia) first appears as a geographical term in classical documents in reference to the upper Nile region of Sudan, as well as certain areas south of the Sahara desert. Its ...
'', but sometimes also applied this name more specifically to a state, originally applied to the Kingdom of Kush
The Kingdom of Kush (; Egyptian: 𓎡𓄿𓈙𓈉 ''kꜣš'', Assyrian: ''Kûsi'', in LXX grc, Κυς and Κυσι ; cop, ''Ecōš''; he, כּוּשׁ ''Kūš'') was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, centered along the Nile Valley in wh ...
and the Sudan area, but then usurped by Axum in the 4th century which led to the name being designated to the nation of Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
.
Geographers historically divided the region into several distinct ethnographic
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject ...
sections based on each area's respective inhabitants.
Commentators in Arabic in the medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
used the general term ''bilâd as-sûdân'' ('Land of the Blacks') for the vast Sudan region (an expression denoting West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
and Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo ...
), or sometimes extending from the coast of West Africa to Western Sudan
Sudan is the geographical region to the south of the Sahara, stretching from Western Africa to Central and Eastern Africa. The name derives from the Arabic ' (), or "the lands of the Black people, Blacks", referring to West Africa and northern ...
.Nehemia Levtzion
Nehemia Levtzion ( he, נחמיה לבציון; November 24, 1935 — August 15, 2003) was an Israeli scholar of African history, Near East, Islamic, and African studies, and the President of the Open University of Israel from 1987 to 1992 and the ...
, Randall Lee Pouwels, The History of Islam in Africa, (Ohio University Press, 2000), p. 255. Its equivalent in Southeast Africa
Southeast Africa or Southeastern Africa is an African region that is intermediate between East Africa and Southern Africa. It comprises the countries Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, Tanzania ...
was ''Zanj
Zanj ( ar, زَنْج, adj. , ''Zanjī''; fa, زنگی, Zangi) was a name used by medieval Muslim geographers to refer to both a certain portion of Southeast Africa (primarily the Swahili Coast) and to its Bantu inhabitants. This word is al ...
'' ('Country of the Blacks'), which was situated in the vicinity of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
region.
The geographers drew an explicit ethnographic distinction between the Sudan region and its analogue Zanj, from the area to their extreme east on the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
coast in the Horn of Africa. In modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea was ''Al-Habash
Al-Habash ( ar, الحبشة, al-habāsha) was an ancient region in the Horn of Africa situated in the northern highlands of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea.Sven Rubenson, The survival of Ethiopian independence, (Tsehai, 2003), p.30.
Origin
The ...
'' or Abyssinia,Sven Rubenson, The survival of Ethiopian independence, (Tsehai, 2003), p. 30. which was inhabited by the ''Habash'' or Abyssinians, who were the forebears of the Habesha.Jonah Blank, Mullahs on the mainframe: Islam and modernity among the Daudi Bohras, (University of Chicago Press, 2001), p. 163. In northern Somalia was '' Barbara'' or the ''Bilad al-Barbar'' ("Land of the Berbers"), which was inhabited by the Eastern ''Baribah'' or ''Barbaroi'', as the ancestors of the Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared ...
were referred to by medieval Arab and ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
geographers, respectively.F.R.C. Bagley et al., ''The Last Great Muslim Empires'', (Brill: 1997), p. 174Bethwell A. Ogot
Bethwell Allan Ogot (born 1929) is a historian from Kenya. He specialises in African history, research methods and theory. One of his works starts by saying that "to tell the story of a past so as to portray an inevitable destiny is, for human ...
, ''Zamani: A Survey of East African History'', (East African Publishing House: 1974), p. 104James Hastings, ''Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics Part 12: V. 12'', (Kessinger Publishing, LLC: 2003), p. 490
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the populations south of the Sahara were divided into three broad ancestral groups: Hamites
Hamites is the name formerly used for some Northern and Horn of Africa peoples in the context of a now-outdated model of dividing humanity into different races which was developed originally by Europeans in support of colonialism and slavery ...
and Semites
Semites, Semitic peoples or Semitic cultures is an obsolete term for an ethnic, cultural or racial group.Afroasiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
family; Negro
In the English language, ''negro'' is a term historically used to denote persons considered to be of Black African heritage. The word ''negro'' means the color black in both Spanish and in Portuguese, where English took it from. The term can be ...
es in most of the rest of the subcontinent (hence, the toponym ''Black Africa'' for Africa south of the Sahara), who spoke languages belonging to the Niger-Congo and Nilo-Saharan families; and Khoisan in Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
, who spoke languages belonging to the Khoisan family.
The term "sub-Saharan" has been criticized by Herbert Ekwe-Ekwe as racist because it refers to the area south of the Sahara by geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
conventions (as opposed to North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, which refers to a cardinal direction). Ekwe-Ekwe considers the term to imply a linguistic connotation of inferiority through its use of the prefix '' sub-'' (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for 'under' or 'below'; cf. sub-arctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, ...
), which he sees as a linguistic vestige of European colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
.
Climate zones and ecoregions
climate zone
Climate classifications are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. One of the most used is the Köppen climate ...
s or biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
s. South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
in particular are considered megadiverse countries. It has a dry winter season and a wet summer season.
* The Sahel extends across all of Africa at a latitude of about 10° to 15° N. Countries that include parts of the Sahara Desert proper in their northern territories and parts of the Sahel in their southern region include Mauritania, Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mal ...
, Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesChad and Sudan. The Sahel has a hot semi-arid climate.
* South of the Sahel, a belt of
 According to
According to
, SWI swissinfo.ch – the international service of the Swiss Broadcasting Corporation (SBC), 18 January 2007 It spread throughout the Sahel and southern Sahara. After the Sahara became a desert, it did not present a totally impenetrable barrier for travelers between north and south because of the application of animal husbandry towards carrying water, food, and supplies across the desert. Prior to the introduction of the camel, the use of oxen, mule, and horses for desert crossing was common, and trade routes followed chains of oases that were strung across the desert. The
 The Bantu expansion is a major migration movement that originated in West Central Africa (possibly around Cameroon) around 2500 BCE, reaching East and Central Africa by 1000 BCE and Southern Africa by the early centuries CE.
The
The Bantu expansion is a major migration movement that originated in West Central Africa (possibly around Cameroon) around 2500 BCE, reaching East and Central Africa by 1000 BCE and Southern Africa by the early centuries CE.
The
 Archeological finds in Central Africa provide evidence of human settlement that may date back over 10,000 years. According to Zangato and Holl, there is evidence of iron-smelting in the Central African Republic and Cameroon that may date back to 3,000 to 2,500 BCE. Extensive walled sites and settlements have recently been found in Zilum, Chad. The area is located approximately southwest of Lake Chad, and has been
Archeological finds in Central Africa provide evidence of human settlement that may date back over 10,000 years. According to Zangato and Holl, there is evidence of iron-smelting in the Central African Republic and Cameroon that may date back to 3,000 to 2,500 BCE. Extensive walled sites and settlements have recently been found in Zilum, Chad. The area is located approximately southwest of Lake Chad, and has been

 The
The  In
In
 On the coastal section of Southeast Africa, a mixed Bantu community developed through contact with Muslim
On the coastal section of Southeast Africa, a mixed Bantu community developed through contact with Muslim
 Settlements of
Settlements of

 According to , the population of sub-Saharan Africa was 1.1 billion in 2019. The current growth rate is 2.3%. The UN predicts for the region a population between 2 and 2.5 billion by 2050 with a population density of 80 per km2 compared to 170 for Western Europe, 140 for Asia and 30 for the Americas.
Sub-Saharan African countries top the list of countries and territories by fertility rate with 40 of the highest 50, all with Total fertility rate, TFR greater than 4 in 2008. All are above the world average except
According to , the population of sub-Saharan Africa was 1.1 billion in 2019. The current growth rate is 2.3%. The UN predicts for the region a population between 2 and 2.5 billion by 2050 with a population density of 80 per km2 compared to 170 for Western Europe, 140 for Asia and 30 for the Americas.
Sub-Saharan African countries top the list of countries and territories by fertility rate with 40 of the highest 50, all with Total fertility rate, TFR greater than 4 in 2008. All are above the world average except
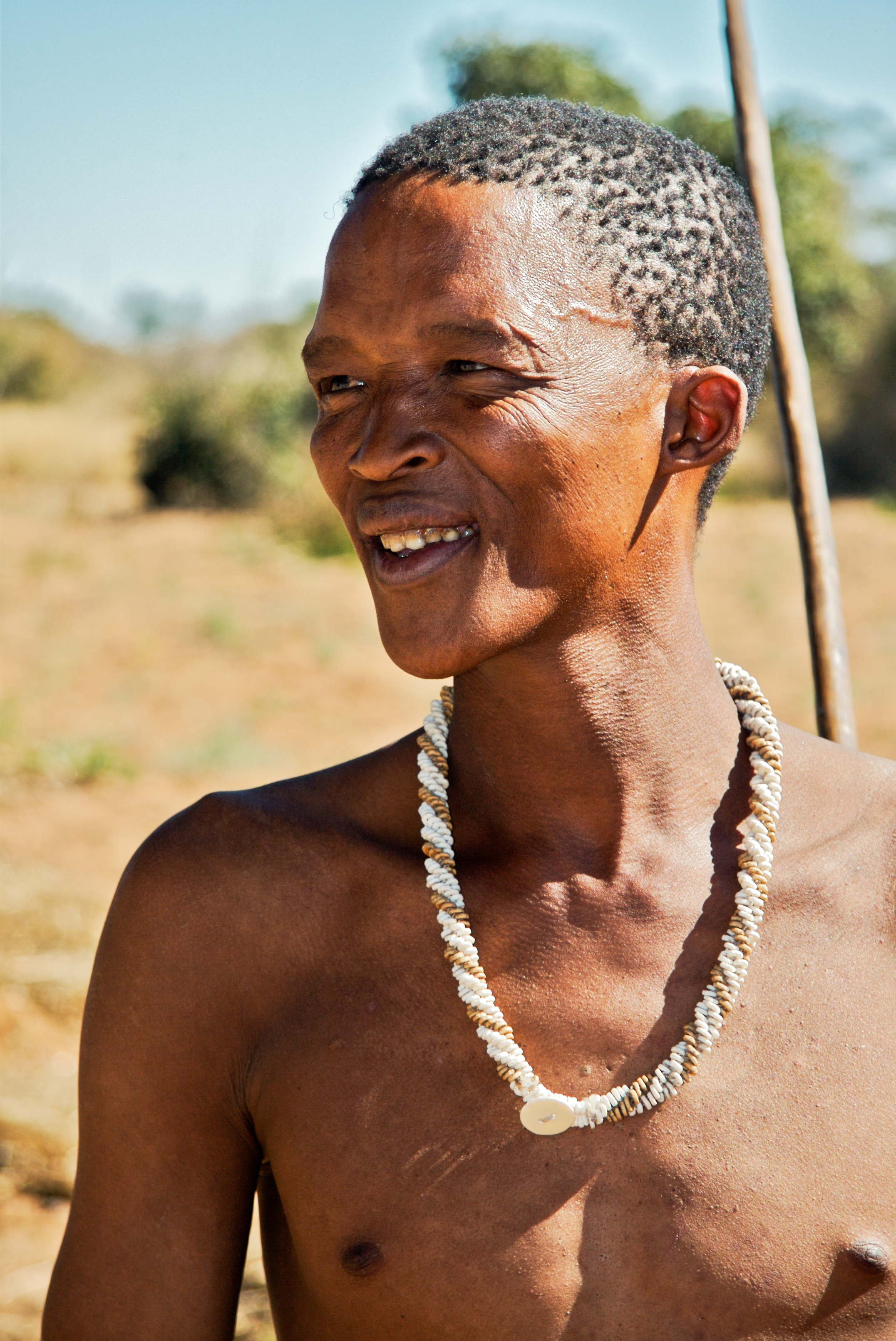





 Sub-Saharan Africa contains over 1,500 languages.
Sub-Saharan Africa contains over 1,500 languages.
"On external genealogical relationships of the Khoe family".
In Brenzinger, Matthias and Christa König (eds.), ''Khoisan languages and linguistics: the Riezlern symposium 2003.'' Quellen zur Khoisan-Forschung 17. Köln: Rüdiger Köppe. In Southern Africa, their speakers are the Khoikhoi and San people, San (Bushmen), in Southeast Africa, the Sandawe people, Sandawe and Hadza people, Hadza.


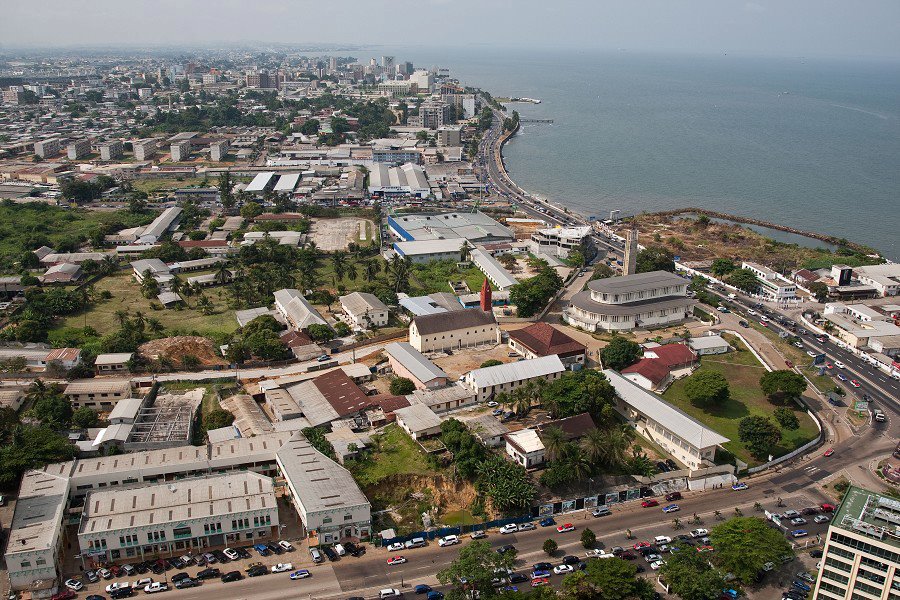
 Sub-Saharan Africa has several large cities.
Sub-Saharan Africa has several large cities.
 In the mid-2010s, private capital flows to sub-Saharan Africa primarily from the BRICs, private-sector investment portfolios, and remittances began to exceed official development assistance.
As of 2011, Africa is one of the fastest developing regions in the world. Six of the world's ten fastest-growing economies over the previous decade were situated below the Sahara, with the remaining four in East and Central Asia. Between 2011 and 2015, the Economic growth, economic growth rate of the average nation in Africa is expected to surpass that of the average nation in Asia. Sub-Saharan Africa is by then projected to contribute seven out of the ten fastest growing economies in the world. According to the World Bank, the economic growth rate in the region had risen to 4.7% in 2013, with a rate of 5.2% forecasted for 2014. This continued rise was attributed to increasing investment in infrastructure and resources as well as steady expenditure per household.
424 million people in sub-Saharan Africa were reportedly living in severe poverty in 2019. In 2022, 460 million people—an increase of 36 million in only three years—were anticipated to be living in extreme poverty as a result of the pandemic and the war. Sub-Saharan Africa's government debt rose from 28% of gross domestic product in 2012 to 50% of gross domestic product in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic caused it to rise to 57% of gross domestic product in 2021.
Sub-Saharan Africa was severely harmed when government revenue declined from 22% of GDP in 2011 to 17% in 2021. 15 African nations are at significant risk of debt, and 7 are currently in financial crisis according to the IMF. The region went on to receive IMF Special Drawing Rights of $23 billion in 2021 to assist critical public spending.
In the mid-2010s, private capital flows to sub-Saharan Africa primarily from the BRICs, private-sector investment portfolios, and remittances began to exceed official development assistance.
As of 2011, Africa is one of the fastest developing regions in the world. Six of the world's ten fastest-growing economies over the previous decade were situated below the Sahara, with the remaining four in East and Central Asia. Between 2011 and 2015, the Economic growth, economic growth rate of the average nation in Africa is expected to surpass that of the average nation in Asia. Sub-Saharan Africa is by then projected to contribute seven out of the ten fastest growing economies in the world. According to the World Bank, the economic growth rate in the region had risen to 4.7% in 2013, with a rate of 5.2% forecasted for 2014. This continued rise was attributed to increasing investment in infrastructure and resources as well as steady expenditure per household.
424 million people in sub-Saharan Africa were reportedly living in severe poverty in 2019. In 2022, 460 million people—an increase of 36 million in only three years—were anticipated to be living in extreme poverty as a result of the pandemic and the war. Sub-Saharan Africa's government debt rose from 28% of gross domestic product in 2012 to 50% of gross domestic product in 2019. The COVID-19 pandemic caused it to rise to 57% of gross domestic product in 2021.
Sub-Saharan Africa was severely harmed when government revenue declined from 22% of GDP in 2011 to 17% in 2021. 15 African nations are at significant risk of debt, and 7 are currently in financial crisis according to the IMF. The region went on to receive IMF Special Drawing Rights of $23 billion in 2021 to assist critical public spending.
 , 50% of Africa was rural with no access to electricity. Africa generates 47 GW of electricity, less than 0.6% of the global market share. Many countries are affected by power shortages.
The percentage of residences with access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa is the lowest in the world. In some remote regions, fewer than one in every 20 households has electricity.
Because of rising prices in commodities such as coal and oil, thermal sources of energy are proving to be too expensive for power generation. Sub-Saharan Africa is expected to build additional hydropower generation capacity of at least 20,165 MW by 2014. The region has the potential to generate 1,750 TWh of energy, of which only 7% has been explored. The failure to exploit its full energy potential is largely due to significant underinvestment, as at least four times as much (approximately $23 billion a year) and what is currently spent is invested in operating high cost power systems and not on expanding the infrastructure.
African governments are taking advantage of the readily available water resources to broaden their energy mix. Hydro Turbine Markets in sub-Saharan Africa generated revenues of $120.0 million in 2007 and is estimated to reach $425.0 million. Asian countries, notably China, India, and Japan, are playing an active role in power projects across the African continent. The majority of these power projects are hydro-based because of China's vast experience in the construction of hydro-power projects and part of the Energy & Power Growth Partnership Services programme.
With electrification numbers, sub-Saharan Africa with access to the Sahara and being in the tropical zones has massive potential for solar photovoltaic electrical potential. Six hundred million people could be served with electricity based on its photovoltaic potential. China is promising to train 10,000 technicians from Africa and other developing countries in the use of solar energy technologies over the next five years. Training African technicians to use solar power is part of the China-Africa science and technology cooperation agreement signed by Chinese science minister Xu Guanhua and African counterparts during premier Wen Jiabao's visit to Ethiopia in December 2003.
The New Partnership for Africa's Development (NEPAD) is developing an integrated, continent-wide energy strategy. This has been funded by, amongst others, the African Development Bank (AfDB) and the EU-Africa Infrastructure Trust Fund. These projects must be sustainable, involve a cross-border dimension and/or have a regional impact, involve public and private capital, contribute to poverty alleviation and economic development, and involve at least one country in sub-Saharan Africa.
Renewable Energy Performance Platform was established by the European Investment Bank the United Nations Environment Programme with a five-year goal of improving energy access for at least two million people in sub-Saharan Africa. It has so far invested around $45 million to renewable energy projects in 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Solar power and hydropower are among the energy methods used in the projects.
, 50% of Africa was rural with no access to electricity. Africa generates 47 GW of electricity, less than 0.6% of the global market share. Many countries are affected by power shortages.
The percentage of residences with access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa is the lowest in the world. In some remote regions, fewer than one in every 20 households has electricity.
Because of rising prices in commodities such as coal and oil, thermal sources of energy are proving to be too expensive for power generation. Sub-Saharan Africa is expected to build additional hydropower generation capacity of at least 20,165 MW by 2014. The region has the potential to generate 1,750 TWh of energy, of which only 7% has been explored. The failure to exploit its full energy potential is largely due to significant underinvestment, as at least four times as much (approximately $23 billion a year) and what is currently spent is invested in operating high cost power systems and not on expanding the infrastructure.
African governments are taking advantage of the readily available water resources to broaden their energy mix. Hydro Turbine Markets in sub-Saharan Africa generated revenues of $120.0 million in 2007 and is estimated to reach $425.0 million. Asian countries, notably China, India, and Japan, are playing an active role in power projects across the African continent. The majority of these power projects are hydro-based because of China's vast experience in the construction of hydro-power projects and part of the Energy & Power Growth Partnership Services programme.
With electrification numbers, sub-Saharan Africa with access to the Sahara and being in the tropical zones has massive potential for solar photovoltaic electrical potential. Six hundred million people could be served with electricity based on its photovoltaic potential. China is promising to train 10,000 technicians from Africa and other developing countries in the use of solar energy technologies over the next five years. Training African technicians to use solar power is part of the China-Africa science and technology cooperation agreement signed by Chinese science minister Xu Guanhua and African counterparts during premier Wen Jiabao's visit to Ethiopia in December 2003.
The New Partnership for Africa's Development (NEPAD) is developing an integrated, continent-wide energy strategy. This has been funded by, amongst others, the African Development Bank (AfDB) and the EU-Africa Infrastructure Trust Fund. These projects must be sustainable, involve a cross-border dimension and/or have a regional impact, involve public and private capital, contribute to poverty alleviation and economic development, and involve at least one country in sub-Saharan Africa.
Renewable Energy Performance Platform was established by the European Investment Bank the United Nations Environment Programme with a five-year goal of improving energy access for at least two million people in sub-Saharan Africa. It has so far invested around $45 million to renewable energy projects in 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Solar power and hydropower are among the energy methods used in the projects.
''Radio the Chief Medium for News in Sub-Saharan Africa''
. Gallup 23 June 2008. Average coverage stands at more than a third of the population. Countries such as Gabon, Seychelles, and
 According to researchers at the Overseas Development Institute, the lack of infrastructure in many developing countries represents one of the most significant limitations to economic growth and achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).Christian K.M. Kingombe 2011
According to researchers at the Overseas Development Institute, the lack of infrastructure in many developing countries represents one of the most significant limitations to economic growth and achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).Christian K.M. Kingombe 2011
Mapping the new infrastructure financing landscape
. London: Overseas Development InstituteJohn J. Saul and Colin Leys
Sub-Saharan Africa in Global Capitalism
, ''Monthly Review'', 1999, Volume 51, Issue 03 (July–August)Fred Magdoff
Twenty-First-Century Land Grabs: Accumulation by Agricultural Dispossession
, ''Monthly Review'', 2013, Volume 65, Issue 06 (November) Less than 40% of rural Africans live within two kilometers of an all-season road, the lowest level of rural accessibility in the developing world. Spending on roads averages just below 2% of GDP with varying degree among countries. This compares with 1% of GDP that is typical in industrialised countries, and 2–3% of GDP found in fast-growing emerging economies. Although the level of expenditure is high relative to the size of Africa's economies, it remains small in absolute terms, with low-income countries spending an average of about US$7 per capita per year. Infrastructure investments and maintenance can be very expensive, especially in such as areas as landlocked, rural and sparsely populated countries in Africa. Infrastructure investments contributed to Africa's growth, and increased investment is necessary to maintain growth and tackle poverty. The returns to investment in infrastructure are very significant, with on average 30–40% returns for telecommunications (ICT) investments, over 40% for electricity generation and 80% for roads.
In Africa, it is argued that in order to meet the MDGs by 2015 infrastructure investments would need to reach about 15% of GDP (around $93 billion a year). Currently, the source of financing varies significantly across sectors. Some sectors are dominated by state spending, others by overseas development aid (ODA) and yet others by private investors. In sub-Saharan Africa, the state spends around $9.4 billion out of a total of $24.9 billion. In irrigation, SSA states represent almost all spending; in transport and energy a majority of investment is state spending; in Information and communication technologies, ICT and water supply and sanitation, the private sector represents the majority of capital expenditure. Overall, aid, the private sector and non-OECD financiers between them exceed state spending. The private sector spending alone equals state capital expenditure, though the majority is focused on ICT infrastructure investments. External financing increased from $7 billion (2002) to $27 billion (2009). China, in particular, has emerged as an important investor.
Infrastructure investments contributed to Africa's growth, and increased investment is necessary to maintain growth and tackle poverty. The returns to investment in infrastructure are very significant, with on average 30–40% returns for telecommunications (ICT) investments, over 40% for electricity generation and 80% for roads.
In Africa, it is argued that in order to meet the MDGs by 2015 infrastructure investments would need to reach about 15% of GDP (around $93 billion a year). Currently, the source of financing varies significantly across sectors. Some sectors are dominated by state spending, others by overseas development aid (ODA) and yet others by private investors. In sub-Saharan Africa, the state spends around $9.4 billion out of a total of $24.9 billion. In irrigation, SSA states represent almost all spending; in transport and energy a majority of investment is state spending; in Information and communication technologies, ICT and water supply and sanitation, the private sector represents the majority of capital expenditure. Overall, aid, the private sector and non-OECD financiers between them exceed state spending. The private sector spending alone equals state capital expenditure, though the majority is focused on ICT infrastructure investments. External financing increased from $7 billion (2002) to $27 billion (2009). China, in particular, has emerged as an important investor.
 The region is a major exporter to the world of gold, uranium, chromium, vanadium, antimony, coltan, bauxite, iron ore, copper, and manganese. South Africa is a major exporter of manganese as well as chromium. A 2001 estimate is that 42% of the world's reserves of chromium may be found in South Africa. South Africa is the largest producer of platinum, with 80% of the total world's annual mine production and 88% of the world's platinum reserve. Sub-Saharan Africa produces 33% of the world's bauxite, with Guinea as the major supplier. Zambia is a major producer of copper. The Democratic Republic of Congo is a major source of coltan. Production from DR Congo is very small, but the country has 80% of the proven reserves in Africa, which are 80% of those worldwide. Sub-Saharan Africa is a major producer of gold, producing up to 30% of global production. Major suppliers are South Africa, Ghana, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Guinea, and Mali. South Africa had been first in the world in terms of gold production since 1905, but in 2007 it moved to second place, according to GFMS, the precious metals consultancy. Uranium is major commodity from the region. Significant suppliers are Niger, Namibia, and South Africa. Namibia was the number one supplier from sub-Saharan Africa in 2008. The region produces 49% of the world's diamonds.
By 2015, it is estimated that 25% of North American oil will be from sub-Saharan Africa, ahead of the Middle East. Sub-Saharan Africa has been the focus of an intense race for oil by the West, China, India, and other emerging economies, even though it holds only 10% of proven oil reserves, less than the Middle East. This race has been referred to as the second Scramble for Africa. All reasons for this global scramble come from the reserves' economic benefits. Transportation cost is low and no pipelines have to be laid as in Central Asia. Almost all reserves are offshore, so political turmoil within the host country will not directly interfere with operations. Sub-Saharan oil is viscous, with a very low sulfur content. This quickens the refining process and effectively reduces costs. New sources of oil are being located in sub-Saharan Africa more frequently than anywhere else. Of all new sources of oil, are in sub-Saharan Africa.
The region is a major exporter to the world of gold, uranium, chromium, vanadium, antimony, coltan, bauxite, iron ore, copper, and manganese. South Africa is a major exporter of manganese as well as chromium. A 2001 estimate is that 42% of the world's reserves of chromium may be found in South Africa. South Africa is the largest producer of platinum, with 80% of the total world's annual mine production and 88% of the world's platinum reserve. Sub-Saharan Africa produces 33% of the world's bauxite, with Guinea as the major supplier. Zambia is a major producer of copper. The Democratic Republic of Congo is a major source of coltan. Production from DR Congo is very small, but the country has 80% of the proven reserves in Africa, which are 80% of those worldwide. Sub-Saharan Africa is a major producer of gold, producing up to 30% of global production. Major suppliers are South Africa, Ghana, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Guinea, and Mali. South Africa had been first in the world in terms of gold production since 1905, but in 2007 it moved to second place, according to GFMS, the precious metals consultancy. Uranium is major commodity from the region. Significant suppliers are Niger, Namibia, and South Africa. Namibia was the number one supplier from sub-Saharan Africa in 2008. The region produces 49% of the world's diamonds.
By 2015, it is estimated that 25% of North American oil will be from sub-Saharan Africa, ahead of the Middle East. Sub-Saharan Africa has been the focus of an intense race for oil by the West, China, India, and other emerging economies, even though it holds only 10% of proven oil reserves, less than the Middle East. This race has been referred to as the second Scramble for Africa. All reasons for this global scramble come from the reserves' economic benefits. Transportation cost is low and no pipelines have to be laid as in Central Asia. Almost all reserves are offshore, so political turmoil within the host country will not directly interfere with operations. Sub-Saharan oil is viscous, with a very low sulfur content. This quickens the refining process and effectively reduces costs. New sources of oil are being located in sub-Saharan Africa more frequently than anywhere else. Of all new sources of oil, are in sub-Saharan Africa.
 Sub-Saharan Africa has more variety of grains than anywhere in the world. Between 13,000 and 11,000 BCE wild grains began to be collected as a source of food in the cataract region of the Nile, south of Egypt. The collecting of wild grains as source of food spread to Syria, parts of Turkey, and Iran by the eleventh millennium BCE. By the tenth and ninth millennia southwest Asians domesticated their wild grains, wheat, and barley after the notion of collecting wild grains spread from the Nile.Christopher Ehret, (2002). The Civilization of Africa. University of Virginia Press: Charlottesville, p. 98, .
Numerous crops have been domesticated in the region and spread to other parts of the world. These crops included sorghum, castor beans, coffee, cottonVandaveer, Chelsie(2006)
Sub-Saharan Africa has more variety of grains than anywhere in the world. Between 13,000 and 11,000 BCE wild grains began to be collected as a source of food in the cataract region of the Nile, south of Egypt. The collecting of wild grains as source of food spread to Syria, parts of Turkey, and Iran by the eleventh millennium BCE. By the tenth and ninth millennia southwest Asians domesticated their wild grains, wheat, and barley after the notion of collecting wild grains spread from the Nile.Christopher Ehret, (2002). The Civilization of Africa. University of Virginia Press: Charlottesville, p. 98, .
Numerous crops have been domesticated in the region and spread to other parts of the world. These crops included sorghum, castor beans, coffee, cottonVandaveer, Chelsie(2006)
What was the cotton of Kush?
KillerPlants.com, Plants That Change History Archive. okra, black-eyed peas, watermelon, gourd, and pearl millet. Other domesticated crops included teff, enset, African rice, Yam (vegetable), yams, kola nuts, Elaeis guineensis, oil palm, and raffia palm. Domesticated animals include the guinea fowl and the donkey. Agriculture represents 20% to 30% of GDP and 50% of exports. In some cases, 60% to 90% of the labor force are employed in agriculture. Most agricultural activity is subsistence farming. This has made agricultural activity Climate change vulnerability, vulnerable to climate change and global warming. Biotechnology has been advocated to create high yield, pest and environmentally resistant crops in the hands of small farmers. The Bill and Melinda Gates foundation is a strong advocate and donor to this cause. Biotechnology and GM crops have met resistance both by natives and environmental groups.
Cash crops include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar, and tobacco.Bowden, Rob (2007). Africa South of the Sahara. Coughlan Publishing: p. 37, .
The OECD says Africa has the potential to become an agricultural superbloc if it can unlock the wealth of the savannahs by allowing farmers to use their land as collateral for credit. There is such international interest in sub-Saharan agriculture, that the World Bank increased its financing of African agricultural programs to $1.3 billion in the 2011 fiscal year. Recently, there has been a trend to purchase large tracts of land in sub-Sahara for agricultural use by developing countries.
Early in 2009, George Soros highlighted a new farmland buying frenzy caused by growing population, scarce water supplies and climate change. Chinese interests bought up large swathes of Senegal to supply it with sesame. Aggressive moves by China, South Korea, and Gulf states to buy vast tracts of agricultural land in sub-Saharan Africa could soon be limited by a new global international protocol.
Agriculture represents 20% to 30% of GDP and 50% of exports. In some cases, 60% to 90% of the labor force are employed in agriculture. Most agricultural activity is subsistence farming. This has made agricultural activity Climate change vulnerability, vulnerable to climate change and global warming. Biotechnology has been advocated to create high yield, pest and environmentally resistant crops in the hands of small farmers. The Bill and Melinda Gates foundation is a strong advocate and donor to this cause. Biotechnology and GM crops have met resistance both by natives and environmental groups.
Cash crops include cotton, coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar, and tobacco.Bowden, Rob (2007). Africa South of the Sahara. Coughlan Publishing: p. 37, .
The OECD says Africa has the potential to become an agricultural superbloc if it can unlock the wealth of the savannahs by allowing farmers to use their land as collateral for credit. There is such international interest in sub-Saharan agriculture, that the World Bank increased its financing of African agricultural programs to $1.3 billion in the 2011 fiscal year. Recently, there has been a trend to purchase large tracts of land in sub-Sahara for agricultural use by developing countries.
Early in 2009, George Soros highlighted a new farmland buying frenzy caused by growing population, scarce water supplies and climate change. Chinese interests bought up large swathes of Senegal to supply it with sesame. Aggressive moves by China, South Korea, and Gulf states to buy vast tracts of agricultural land in sub-Saharan Africa could soon be limited by a new global international protocol.
 Forty percent of African scientists live in OECD countries, predominantly in Europe, the United States and Canada. This has been described as an African brain drain. According to Naledi Pandor, the South African Minister of Science and Technology, even with the drain enrollments in sub-Saharan African universities tripled between 1991 and 2005, expanding at an annual rate of 8.7%, which is one of the highest regional growth rates in the world. In the last 10 to 15 years interest in pursuing university-level degrees abroad has increased.
According to the CIA, low global literacy rates are concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia and South Asia. However, literacy rates in sub-Saharan Africa vary significantly between countries. The highest registered literacy rate in the region is in Zimbabwe (90.7%; 2003 est.), while the lowest literacy rate is in South Sudan (27%).
Research on human capital formation was able to determine, that the numeracy levels of sub-Saharan Africa and Africa, in general, were higher than numeracy levels in South Asia. In the 1940s more than 75% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa was numerate. The numeracy of the West African countries, Benin and Ghana, was even higher with more than 80% of the population being numerate. In contrast, numeracy in South Asia was only around 50%.
Sub-Saharan African countries that have higher diversity has been found to lead to a poorer economy. Researchers have argued that this is because of ethnic favoritism in their politics. Sub-Saharan leaders are more likely to provide better resources to their coethnic groups when in power. A study found that children are more likely to attend school by 2.25% increase on average. While they complete school on 1.80% increase on average. Similarly a 1% increase in GDP is associated with a 1.5-percentage-point increase in the effect primary school attendance.
Sub-Saharan African countries spent an average of 0.3% of their GDP on science and technology on in 2007. This represents an increase from US$1.8 billion in 2002 to US$2.8 billion in 2007, a 50% increase in spending.
Forty percent of African scientists live in OECD countries, predominantly in Europe, the United States and Canada. This has been described as an African brain drain. According to Naledi Pandor, the South African Minister of Science and Technology, even with the drain enrollments in sub-Saharan African universities tripled between 1991 and 2005, expanding at an annual rate of 8.7%, which is one of the highest regional growth rates in the world. In the last 10 to 15 years interest in pursuing university-level degrees abroad has increased.
According to the CIA, low global literacy rates are concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia and South Asia. However, literacy rates in sub-Saharan Africa vary significantly between countries. The highest registered literacy rate in the region is in Zimbabwe (90.7%; 2003 est.), while the lowest literacy rate is in South Sudan (27%).
Research on human capital formation was able to determine, that the numeracy levels of sub-Saharan Africa and Africa, in general, were higher than numeracy levels in South Asia. In the 1940s more than 75% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa was numerate. The numeracy of the West African countries, Benin and Ghana, was even higher with more than 80% of the population being numerate. In contrast, numeracy in South Asia was only around 50%.
Sub-Saharan African countries that have higher diversity has been found to lead to a poorer economy. Researchers have argued that this is because of ethnic favoritism in their politics. Sub-Saharan leaders are more likely to provide better resources to their coethnic groups when in power. A study found that children are more likely to attend school by 2.25% increase on average. While they complete school on 1.80% increase on average. Similarly a 1% increase in GDP is associated with a 1.5-percentage-point increase in the effect primary school attendance.
Sub-Saharan African countries spent an average of 0.3% of their GDP on science and technology on in 2007. This represents an increase from US$1.8 billion in 2002 to US$2.8 billion in 2007, a 50% increase in spending.
 At the World Conference held in Jomtien Beach, Jomtien, Thailand in 1990, delegates from 155 countries and representatives of some 150 organizations gathered with the goal to promote Universal Primary Education, universal primary education and the radical reduction of illiteracy before the end of the decade. The World Education Forum, held ten years later in Dakar, Senegal, provided the opportunity to reiterate and reinforce these goals. This initiative contributed to having education made a priority of the Millennium Development Goals in 2000, with the aim of achieving universal schooling (MDG2) and eliminating gender disparities, especially in primary and secondary education (MDG3).Agence Française de Développement, Agence universitaire de la Francophonie, Orange, & UNESCO. (2015). Digital Services for Education in Africa. ''Savoirs communs, 17.''
At the World Conference held in Jomtien Beach, Jomtien, Thailand in 1990, delegates from 155 countries and representatives of some 150 organizations gathered with the goal to promote Universal Primary Education, universal primary education and the radical reduction of illiteracy before the end of the decade. The World Education Forum, held ten years later in Dakar, Senegal, provided the opportunity to reiterate and reinforce these goals. This initiative contributed to having education made a priority of the Millennium Development Goals in 2000, with the aim of achieving universal schooling (MDG2) and eliminating gender disparities, especially in primary and secondary education (MDG3).Agence Française de Développement, Agence universitaire de la Francophonie, Orange, & UNESCO. (2015). Digital Services for Education in Africa. ''Savoirs communs, 17.''
Since the World Education Forum in Dakar, considerable efforts have been made to respond to these demographic challenges in terms of education. The amount of funds raised has been decisive. Between 1999 and 2010, public spending on education as a percentage of Gross national product, gross national product (GNP) increased by 5% per year in sub-Saharan Africa, with major variations between countries, with percentages varying from 1.8% in Cameroon to over 6% in Burundi.UNESCO. (2012). ''Education for All Global Monitoring Report 2012 – Youth and Skills: Putting Education to Work.'' Luxembourg: UNESCO Publications.
As of 2015, governments in sub-Saharan Africa spend on average 18% of their total budget on education, against 15% in the rest of the world. In the years immediately after the Dakar Forum, the efforts made by the African States towards achieving Education For All, EFA produced multiple results in sub-Saharan Africa. The greatest advance was in access to primary education, which governments had made their absolute priority. The number of children in a primary school in sub-Saharan Africa thus rose from 82 million in 1999 to 136.4 million in 2011. In Niger, for example, the number of children entering school increased by more than three-and-a-half times between 1999 and 2011. In Ethiopia, over the same period, over 8.5 million more children were admitted to primary school. The net rate of first-year access in sub-Saharan Africa has thus risen by 19 points in 12 years, from 58% in 1999 to 77% in 2011. Despite the considerable efforts, the latest available data from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics estimates that, for 2012, there were still 57.8 million children who were not in school. Of these, 29.6 million were in sub-Saharan Africa alone, a figure which has not changed for several years. Many sub-Saharan countries have notably included the first year of secondary school in basic education. In Rwanda, the first year of secondary school was attached to primary education in 2009, which significantly increased the number of pupils enrolled at this level of education. In 2012, the primary completion rate (PCR) – which measures the proportion of children reaching the final year of primary school – was 70%, meaning that more than three out of ten children entering primary school do not reach the final primary year. Literacy rates have gone up in sub-Saharan Africa, and internet access has improved considerably. Nonetheless, a lot must yet happen for this world to catch up. The statistics show that the literacy rate for sub-Saharan Africa was 65% in 2017. In other words, one-third of the people aged 15 and above were unable to read and write. The comparative figure for 1984 was an illiteracy rate of 49%. In 2017, only about 22% of Africans were internet users at all, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
 In 1987, the Bamako Initiative conference organized by the World Health Organization was held in Bamako, the capital of
In 1987, the Bamako Initiative conference organized by the World Health Organization was held in Bamako, the capital of  Malaria is an endemic illness in sub-Saharan Africa, where the majority of malaria cases and deaths worldwide occur. Routine immunization has been introduced in order to prevent measles. Onchocerciasis ("river blindness"), a common cause of blindness, is also endemic to parts of the region. More than 99% of people affected by the illness worldwide live in 31 countries therein. In response, the African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control (APOC) was launched in 1995 with the aim of controlling the disease. Maternal mortality is another challenge, with more than half of maternal deaths in the world occurring in sub-Saharan Africa. However, there has generally been progress here as well, as a number of countries in the region have halved their levels of maternal mortality since 1990. Additionally, the African Union in July 2003 ratified the Maputo Protocol, which pledges to prohibit female genital mutilation (FGM).
National health systems vary between countries. In
Malaria is an endemic illness in sub-Saharan Africa, where the majority of malaria cases and deaths worldwide occur. Routine immunization has been introduced in order to prevent measles. Onchocerciasis ("river blindness"), a common cause of blindness, is also endemic to parts of the region. More than 99% of people affected by the illness worldwide live in 31 countries therein. In response, the African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control (APOC) was launched in 1995 with the aim of controlling the disease. Maternal mortality is another challenge, with more than half of maternal deaths in the world occurring in sub-Saharan Africa. However, there has generally been progress here as well, as a number of countries in the region have halved their levels of maternal mortality since 1990. Additionally, the African Union in July 2003 ratified the Maputo Protocol, which pledges to prohibit female genital mutilation (FGM).
National health systems vary between countries. In
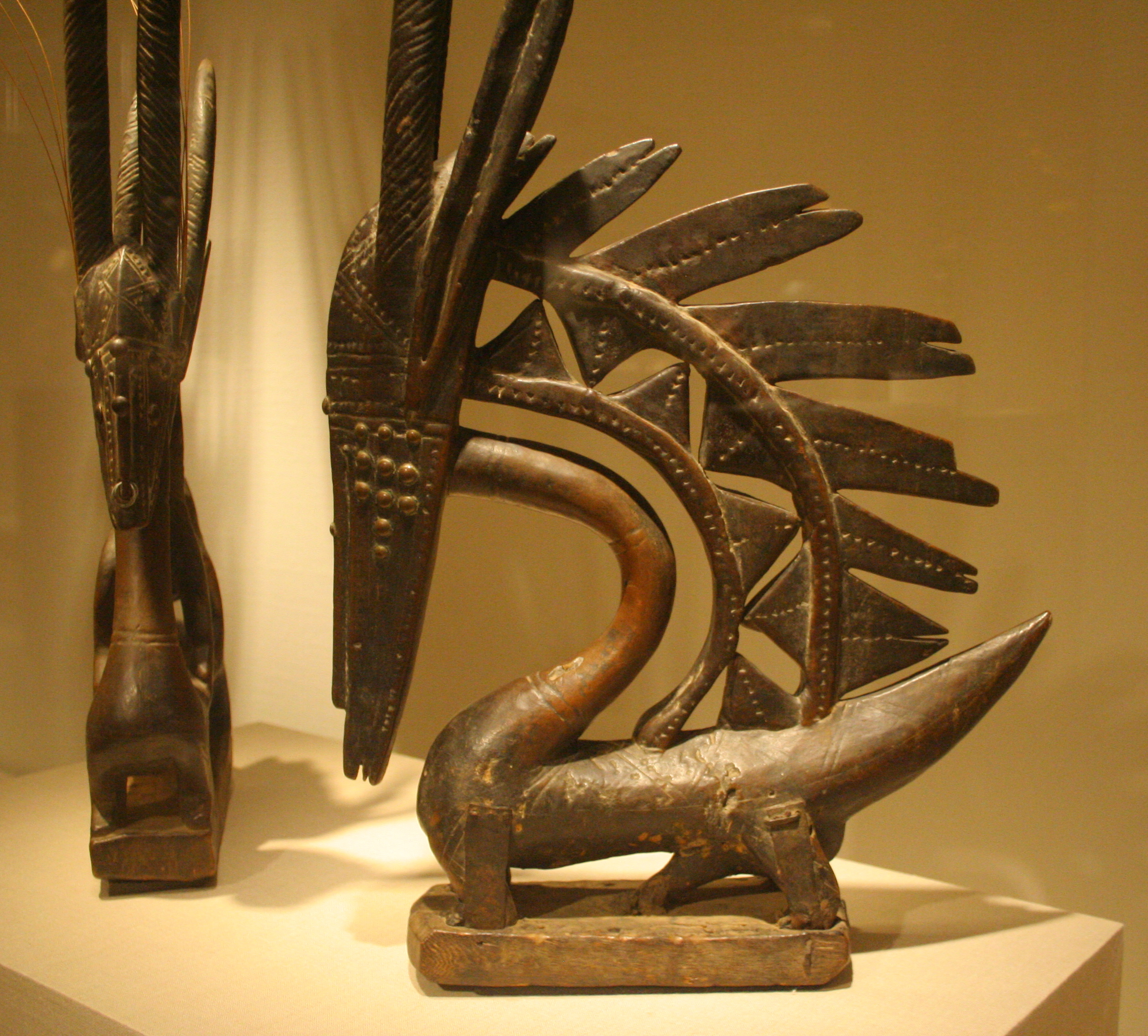 The oldest abstract art in the world is a shell necklace, dated to 82,000 years, in the Cave of Pigeons in Taforalt, eastern Morocco. The second-oldest abstract form of art, and the oldest rock art, is found in the Blombos Cave at the Cape in South Africa, dated 77,000 years. Sub-Saharan Africa has some of the oldest and most varied style of rock art in the world.
Although sub-Saharan African art is very diverse, there are some common themes. One is the use of the human figure. Second, there is a preference for sculpture. Sub-Saharan African art is meant to be experienced in three dimensions, not two. A house is meant to be experienced from all angles. Third, art is meant to be performed. Sub-Saharan Africans have a specific name for masks. The name incorporates the sculpture, the dance, and the spirit that incorporates the mask. The name denotes all three elements. Fourth, art that serves a practical function. The artist and craftsman are not separate. A sculpture shaped like a hand can be used as a stool. Fifth, the use of fractals or non-linear scaling. The shape of the whole is the shape of the parts at different scales. Before the discovery of fractal geometry], Leopold Sedar Senghor, Senegal's first president, referred to this as "dynamic symmetry". William Buller Fagg, William Fagg, a British art historian, has compared it to the logarithmic mapping of natural growth by biologist D'Arcy Thompson. Lastly, sub-Saharan African art is visually abstract, instead of naturalistic. Sub-Saharan African art represents spiritual notions, social norms, ideas, values, etc. An artist might exaggerate the head of a sculpture in relation to the body not because he does not know anatomy but because he wants to illustrate that the head is the seat of knowledge and wisdom. The visual abstraction of African art was very influential in the works o
The oldest abstract art in the world is a shell necklace, dated to 82,000 years, in the Cave of Pigeons in Taforalt, eastern Morocco. The second-oldest abstract form of art, and the oldest rock art, is found in the Blombos Cave at the Cape in South Africa, dated 77,000 years. Sub-Saharan Africa has some of the oldest and most varied style of rock art in the world.
Although sub-Saharan African art is very diverse, there are some common themes. One is the use of the human figure. Second, there is a preference for sculpture. Sub-Saharan African art is meant to be experienced in three dimensions, not two. A house is meant to be experienced from all angles. Third, art is meant to be performed. Sub-Saharan Africans have a specific name for masks. The name incorporates the sculpture, the dance, and the spirit that incorporates the mask. The name denotes all three elements. Fourth, art that serves a practical function. The artist and craftsman are not separate. A sculpture shaped like a hand can be used as a stool. Fifth, the use of fractals or non-linear scaling. The shape of the whole is the shape of the parts at different scales. Before the discovery of fractal geometry], Leopold Sedar Senghor, Senegal's first president, referred to this as "dynamic symmetry". William Buller Fagg, William Fagg, a British art historian, has compared it to the logarithmic mapping of natural growth by biologist D'Arcy Thompson. Lastly, sub-Saharan African art is visually abstract, instead of naturalistic. Sub-Saharan African art represents spiritual notions, social norms, ideas, values, etc. An artist might exaggerate the head of a sculpture in relation to the body not because he does not know anatomy but because he wants to illustrate that the head is the seat of knowledge and wisdom. The visual abstraction of African art was very influential in the works o
modernist
artist like Pablo Picasso, Henri Matisse, and Jacques Lipchitz.
 Traditional sub-Saharan African music is as diverse as the region's various populations. The common perception of sub-Saharan African music is that it is rhythmic music centered around the drums. This is partially true. A large part of sub-Saharan music, mainly among speakers of Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan languages, is rhythmic and centered around the drum. Sub-Saharan music is polyrhythmic, usually consisting of multiple rhythms in one composition. Dance involves moving multiple body parts. These aspects of sub-Saharan music has been transferred to the new world by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans and can be seen in its influence on music forms as samba, jazz, rhythm and blues, rock and roll, salsa music, salsa, reggae and rap music.Bowden, Rob(2007). Africa South of the Sahara. Coughlan Publishing: p. 40, .
But sub-Saharan music involves a lot of music with strings, horns, and very little poly-rhythms. Music from the eastern sahel and along the nile, among the Nilo-Saharan, made extensive use of strings and horns in ancient times. Among the Afro-Asiatics of Horn of Africa, Northeast Africa, we see extensive use of Music of Ethiopia, string instruments and the pentatonic scale. Dancing involve swaying body movements and footwork. Among the San people, San is extensive use of string instruments with emphasis on footwork.
Modern sub-Saharan African music has been influence by music from the New World (Jazz, Salsa, Rhythm and Blues etc.) vice versa being influenced by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans. Popular styles are Mbalax in Senegal and Gambia, Highlife in
Traditional sub-Saharan African music is as diverse as the region's various populations. The common perception of sub-Saharan African music is that it is rhythmic music centered around the drums. This is partially true. A large part of sub-Saharan music, mainly among speakers of Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan languages, is rhythmic and centered around the drum. Sub-Saharan music is polyrhythmic, usually consisting of multiple rhythms in one composition. Dance involves moving multiple body parts. These aspects of sub-Saharan music has been transferred to the new world by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans and can be seen in its influence on music forms as samba, jazz, rhythm and blues, rock and roll, salsa music, salsa, reggae and rap music.Bowden, Rob(2007). Africa South of the Sahara. Coughlan Publishing: p. 40, .
But sub-Saharan music involves a lot of music with strings, horns, and very little poly-rhythms. Music from the eastern sahel and along the nile, among the Nilo-Saharan, made extensive use of strings and horns in ancient times. Among the Afro-Asiatics of Horn of Africa, Northeast Africa, we see extensive use of Music of Ethiopia, string instruments and the pentatonic scale. Dancing involve swaying body movements and footwork. Among the San people, San is extensive use of string instruments with emphasis on footwork.
Modern sub-Saharan African music has been influence by music from the New World (Jazz, Salsa, Rhythm and Blues etc.) vice versa being influenced by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans. Popular styles are Mbalax in Senegal and Gambia, Highlife in
 African cuisine, Sub-Saharan African cuisine is very diverse. A lot of regional overlapping occurs, but there are dominant elements region by region.
West African cuisine can be described as starchy, flavorfully spicey. Dishes include fufu, kenkey, couscous, garri, foutou, and banku. Ingredients are of native starchy tubers, Yam (vegetable), yams, Eddoe, cocoyams, and cassava. Grains include millet, sorghum, and rice, usually in the Sahel, are incorporated. Oils include palm oil and shea butter (Sahel). One finds recipes that mix fish and meat. Beverages are palm wine(sweet or sour) and millet beer. Roasting, baking, boiling, frying, mashing, and spicing are all cooking techniques.
African cuisine, Sub-Saharan African cuisine is very diverse. A lot of regional overlapping occurs, but there are dominant elements region by region.
West African cuisine can be described as starchy, flavorfully spicey. Dishes include fufu, kenkey, couscous, garri, foutou, and banku. Ingredients are of native starchy tubers, Yam (vegetable), yams, Eddoe, cocoyams, and cassava. Grains include millet, sorghum, and rice, usually in the Sahel, are incorporated. Oils include palm oil and shea butter (Sahel). One finds recipes that mix fish and meat. Beverages are palm wine(sweet or sour) and millet beer. Roasting, baking, boiling, frying, mashing, and spicing are all cooking techniques.
 Southeast African cuisine especially those of the Swahili people, Swahilis reflects its Islamic, geographical Indian Ocean cultural links. Dishes include ugali, sukuma wiki, and halva. Spices such as curry, saffron, cloves, cinnamon, pomegranate juice, cardamon, ghee, and sage are used, especially among Muslims. Meat includes cattle, sheep, and goats, but is rarely eaten since its viewed as currency and wealth.
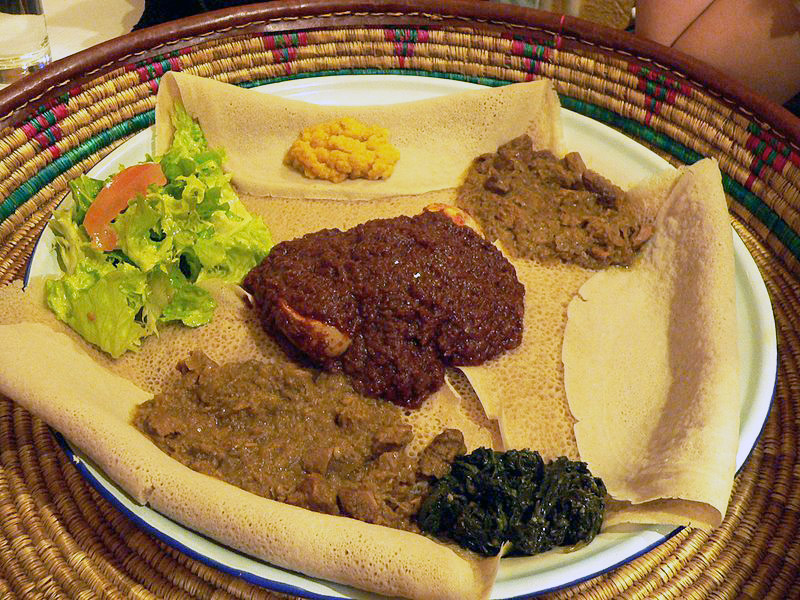
In the Horn of Africa, pork and non-fish seafood are avoided by Christians and Muslims. Dairy products and all meats are avoided during lent by Ethiopians. Maize (corn) is a major staple. Cornmeal is used to make ugali, a popular dish with different names. Teff is used to make injera or canjeero (Somali) bread. Other important foods include enset, noog, lentils, rice, banana, leafy greens, chiles, peppers, coconut milk, and tomatoes. Beverages are coffee (domesticated in Ethiopia), chai tea, fermented beer from banana or millet. Cooking techniques include roasting and marinating.
Southeast African cuisine especially those of the Swahili people, Swahilis reflects its Islamic, geographical Indian Ocean cultural links. Dishes include ugali, sukuma wiki, and halva. Spices such as curry, saffron, cloves, cinnamon, pomegranate juice, cardamon, ghee, and sage are used, especially among Muslims. Meat includes cattle, sheep, and goats, but is rarely eaten since its viewed as currency and wealth.
In the Horn of Africa, pork and non-fish seafood are avoided by Christians and Muslims. Dairy products and all meats are avoided during lent by Ethiopians. Maize (corn) is a major staple. Cornmeal is used to make ugali, a popular dish with different names. Teff is used to make injera or canjeero (Somali) bread. Other important foods include enset, noog, lentils, rice, banana, leafy greens, chiles, peppers, coconut milk, and tomatoes. Beverages are coffee (domesticated in Ethiopia), chai tea, fermented beer from banana or millet. Cooking techniques include roasting and marinating.
 Central African cuisine connects with all major regions of sub-Saharan Africa: Its cuisine reflects that. Ugali and fufu are eaten in the region. Central African cuisine is very starchy and spicy hot. Dominant crops include plantains, cassava, peanuts, chillis, and okra. Meats include beef, chicken, and sometimes exotic meats called bush meat (antelope, warthog, crocodile). Widespread spicy hot fish cuisine is one of the differentiating aspects. Mushroom is sometimes used as a meat substitute.
Traditional Southern African cuisine surrounds meat. Traditional society typically focused on raising, sheep, goats, and especially cattle. Dishes include braai (barbecue meat), sadza, bogobe, pap (food), pap (fermented cornmeal), milk products (buttermilk, yoghurt). Crops utilised are sorghum, maize (corn), pumpkin beans, leafy greens, and cabbage. Beverages include ting (fermented sorghum or maize), milk, chibuku (milky beer). Influences from the Indian and Malay communities can be seen in its use of curries, sambals, pickled fish, fish stews, chutney, and samosa. European influences can be seen in cuisines like biltong (dried beef strips), potjies (stews of maize, onions, tomatoes), French wines, and crueler or koeksister (sugar syrup cookie).
Central African cuisine connects with all major regions of sub-Saharan Africa: Its cuisine reflects that. Ugali and fufu are eaten in the region. Central African cuisine is very starchy and spicy hot. Dominant crops include plantains, cassava, peanuts, chillis, and okra. Meats include beef, chicken, and sometimes exotic meats called bush meat (antelope, warthog, crocodile). Widespread spicy hot fish cuisine is one of the differentiating aspects. Mushroom is sometimes used as a meat substitute.
Traditional Southern African cuisine surrounds meat. Traditional society typically focused on raising, sheep, goats, and especially cattle. Dishes include braai (barbecue meat), sadza, bogobe, pap (food), pap (fermented cornmeal), milk products (buttermilk, yoghurt). Crops utilised are sorghum, maize (corn), pumpkin beans, leafy greens, and cabbage. Beverages include ting (fermented sorghum or maize), milk, chibuku (milky beer). Influences from the Indian and Malay communities can be seen in its use of curries, sambals, pickled fish, fish stews, chutney, and samosa. European influences can be seen in cuisines like biltong (dried beef strips), potjies (stews of maize, onions, tomatoes), French wines, and crueler or koeksister (sugar syrup cookie).
 Like most of the world, sub-Saharan Africans have adopted Western-style clothing. In some country like Zambia, used Western clothing has flooded markets, causing great angst in the retail community. Sub-Saharan Africa boasts its own traditiona
Like most of the world, sub-Saharan Africans have adopted Western-style clothing. In some country like Zambia, used Western clothing has flooded markets, causing great angst in the retail community. Sub-Saharan Africa boasts its own traditiona
clothing style
Cotton seems to be the dominant material. In East Africa, one finds extensive use of cotton clothing. Shemma, shama, and kuta are types of Ethiopian clothing. Kanga (African garment), Kanga are Swahili culture, Swahili cloth that comes in rectangular shapes, made of pure cotton, and put together to make clothing. Kitenges are similar to kangas and kikoy, but are of a thicker cloth, and have an edging only on a long side. In West Africa, again cotton is the material of choice. In the Sahel and other parts of West Africa the boubou (clothing), boubou and kaftan style of clothing are featured. Kente cloth is created by the Akan people of Ghana and Ivory Coast, from silk of the various moth species in West Africa. Kente comes from the Akan language, Akan twi word ''kenten'' which means basket. It is sometimes used to make dashiki and kufi. Adire is a type of Yoruba cloth that is starch resistant. Raffia cloth and barkcloth are also utilised in the region.
In Central Africa, the Kuba people developed raffia cloth from the raffia plant fibers. It was widely used in the region. Barkcloth was also extensively used.
In Southern Africa one finds numerous uses of animal hide and skins for clothing. The Ndau in central Mozambique and the Shona mix hide with barkcloth and cotton cloth. Cotton cloth is referred to as machira. Xhosa, Tswana, Sotho, and Swazi also made extensive use of hides. Hides come from cattle, sheep, goat, and elephant. Leopard skins were coveted and were a symbol of kingship in Zulu society. Skins were tanned to form leather, dyed, and embedded with beads.
In West Africa, again cotton is the material of choice. In the Sahel and other parts of West Africa the boubou (clothing), boubou and kaftan style of clothing are featured. Kente cloth is created by the Akan people of Ghana and Ivory Coast, from silk of the various moth species in West Africa. Kente comes from the Akan language, Akan twi word ''kenten'' which means basket. It is sometimes used to make dashiki and kufi. Adire is a type of Yoruba cloth that is starch resistant. Raffia cloth and barkcloth are also utilised in the region.
In Central Africa, the Kuba people developed raffia cloth from the raffia plant fibers. It was widely used in the region. Barkcloth was also extensively used.
In Southern Africa one finds numerous uses of animal hide and skins for clothing. The Ndau in central Mozambique and the Shona mix hide with barkcloth and cotton cloth. Cotton cloth is referred to as machira. Xhosa, Tswana, Sotho, and Swazi also made extensive use of hides. Hides come from cattle, sheep, goat, and elephant. Leopard skins were coveted and were a symbol of kingship in Zulu society. Skins were tanned to form leather, dyed, and embedded with beads.
 Football (soccer) is the most popular sport in sub-Saharan Africa. Sub-Saharan men are its main patrons. Major competitions include the CAF Champions League, African Champions League, a competition for the best clubs on the continent and the CAF Confederation Cup, Confederation Cup, a competition primarily for the national cup winner of each African country. The Africa Cup of Nations is a competition of 16 national teams from various African countries held every two years. South Africa hosted the 2010 FIFA World Cup, a first for a sub-Saharan country. In 2010, Cameroon played in the FIFA World Cup, World Cup for the sixth time, which is the current record for a sub-Saharan team. In Nigeria at the 1996 Summer Olympics, 1996 Nigeria won the Olympic gold for football. In 2000 Cameroon maintained the continent's supremacy by winning the title too. Momentous achievements for sub-Saharan African football. Famous sub-Saharan football stars include Abedi Pele, Emmanuel Adebayor, George Weah, Michael Essien, Didier Drogba, Roger Milla, Nwankwo Kanu, Jay-Jay Okocha, Bruce Grobbelaar, Samuel Eto'o, Kolo Touré, Yaya Touré, Sadio Mané and Pierre-Emerick Aubameyang. The most talented sub-Saharan African football players find themselves courted and sought after by European leagues. There are currently more than 1000 Africans playing for European clubs. Sub-Saharan Africans have found themselves the target of racism by European fans. FIFA has been trying hard to crack down on racist outburst during games.
Football (soccer) is the most popular sport in sub-Saharan Africa. Sub-Saharan men are its main patrons. Major competitions include the CAF Champions League, African Champions League, a competition for the best clubs on the continent and the CAF Confederation Cup, Confederation Cup, a competition primarily for the national cup winner of each African country. The Africa Cup of Nations is a competition of 16 national teams from various African countries held every two years. South Africa hosted the 2010 FIFA World Cup, a first for a sub-Saharan country. In 2010, Cameroon played in the FIFA World Cup, World Cup for the sixth time, which is the current record for a sub-Saharan team. In Nigeria at the 1996 Summer Olympics, 1996 Nigeria won the Olympic gold for football. In 2000 Cameroon maintained the continent's supremacy by winning the title too. Momentous achievements for sub-Saharan African football. Famous sub-Saharan football stars include Abedi Pele, Emmanuel Adebayor, George Weah, Michael Essien, Didier Drogba, Roger Milla, Nwankwo Kanu, Jay-Jay Okocha, Bruce Grobbelaar, Samuel Eto'o, Kolo Touré, Yaya Touré, Sadio Mané and Pierre-Emerick Aubameyang. The most talented sub-Saharan African football players find themselves courted and sought after by European leagues. There are currently more than 1000 Africans playing for European clubs. Sub-Saharan Africans have found themselves the target of racism by European fans. FIFA has been trying hard to crack down on racist outburst during games.
 Rugby union, Rugby is also popular in sub-Saharan Africa. The Confederation of African Rugby governs rugby games in the region. South Africa is a major force in the game and won the Rugby World Cup in 1995 Rugby World Cup, 1995, 2007 Rugby World Cup, 2007 and 2019 Rugby World Cup, 2019. Africa is also allotted one guaranteed qualifying place in the Rugby World Cup.
Boxing is also a popular sport. Battling Siki the first world champion to come out of sub-Saharan Africa. Countries such as Nigeria, Ghana and South Africa have produced numerous professional world champions such as Dick Tiger, Hogan Bassey, Gerrie Coetzee, Samuel Peter, Azumah Nelson and Jake Matlala.
Cricket has a following. The African Cricket Association is an international body which oversees cricket in African countries. South Africa and Zimbabwe have their own governing bodies. In 2003 the Cricket World Cup was held in South Africa, first time it was held in sub-Saharan Africa.
Over the years,
Rugby union, Rugby is also popular in sub-Saharan Africa. The Confederation of African Rugby governs rugby games in the region. South Africa is a major force in the game and won the Rugby World Cup in 1995 Rugby World Cup, 1995, 2007 Rugby World Cup, 2007 and 2019 Rugby World Cup, 2019. Africa is also allotted one guaranteed qualifying place in the Rugby World Cup.
Boxing is also a popular sport. Battling Siki the first world champion to come out of sub-Saharan Africa. Countries such as Nigeria, Ghana and South Africa have produced numerous professional world champions such as Dick Tiger, Hogan Bassey, Gerrie Coetzee, Samuel Peter, Azumah Nelson and Jake Matlala.
Cricket has a following. The African Cricket Association is an international body which oversees cricket in African countries. South Africa and Zimbabwe have their own governing bodies. In 2003 the Cricket World Cup was held in South Africa, first time it was held in sub-Saharan Africa.
Over the years,
 Only seven African countries are not geopolitically a part of sub-Saharan Africa: Algeria,
Only seven African countries are not geopolitically a part of sub-Saharan Africa: Algeria,
savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
(the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
and East Sudanian savanna
The East Sudanian savanna is a hot, dry, tropical savanna ecoregion of Central and East Africa.
Geography
The East Sudanian savanna is the eastern half of the Sudanian savanna belt which runs east and west across Africa. The eastern lies eas ...
s) stretch from the Atlantic Ocean to the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
. The more humid Guinean
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
and Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic
The Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is a forest and savanna ecoregion of central Africa. It extends east and west across central Africa, covering parts of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Suda ...
lie between the savannas and the equatorial forests.
* The Horn of Africa includes hot desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
along the coast but a hot semi-arid climate can be found much more in the interior, contrasting with savanna and moist broadleaf forests in the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
.
* Tropical Africa
Although tropical Africa is mostly familiar to the West for its rainforests, this biogeographic realm of Africa is far more diverse. While the tropics are thought of as regions with hot moist climates, which are caused by latitude and the trop ...
encompasses tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
stretching along the southern coast of West Africa and across most of Central Africa (the Congo) west of the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
.
* In East Africa, woodlands, savannas, and grasslands are found in the equatorial zone, including the Serengeti
The Serengeti ( ) ecosystem is a Geography of Africa, geographical region in Africa, spanning northern Tanzania. The protected area within the region includes approximately of land, including the Serengeti National Park and several game res ...
ecosystem in Tanzania and Kenya.
* Distinctive Afromontane forests, grasslands, and shrublands are found in the high mountains and mountain ranges of eastern Africa, from the Ethiopian Highlands to South Africa.
* South of the equatorial forests, the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Southern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic are transition zones between the tropical forests and the miombo woodland
The Miombo woodland is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome (in the World Wide Fund for Nature scheme) located primarily in Central Africa. It includes four woodland savanna ecoregions (listed below) characterized b ...
belt that spans the continent from Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
to Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
and Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
.
* The Namib
The Namib ( ; pt, Namibe) is a coastal desert in Southern Africa. The name is of Khoekhoegowab origin and means "vast place". According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Nami ...
and Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
s lie in Southern Africa, and are surrounded by semi-deserts including the Karoo region of South Africa. The Bushveld
The Bushveld (from af, bosveld, af, bos 'bush' and af, veld) is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands, sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa. It encompasses most of Limpopo Province and a small part of ...
grasslands lie to the east of the deserts.
* The Cape Floristic Region is at Africa's southern tip, and is home to diverse subtropical and temperate forests, woodlands, grasslands, and shrublands.
History
Prehistory
 According to
According to paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
, early hominid skull anatomy was similar to that of their close cousins, the great African forest apes, gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
and chimpanzee. However, they had adopted a biped
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
al locomotion and freed hands, giving them a crucial advantage enabling them to live in both forested areas and on the open savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
at a time when Africa was drying up, with savanna encroaching on forested areas. This occurred 10 million to 5 million years ago.Shillington, Kevin(2005). History of Africa, Rev. 2nd Ed. New York: Palgrave Macmillan
Palgrave Macmillan is a British academic and trade publishing company headquartered in the London Borough of Camden. Its programme includes textbooks, journals, monographs, professional and reference works in print and online. It maintains off ...
, p. 2, .
By 3 million years ago several australopithecine
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' (cladistically including the genera ''Homo'', '' Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically includ ...
hominid species had developed throughout southern, eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
and central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo ...
. They were tool users rather than tool manufacturers. The next major evolutionary step occurred around 2.3 million BCE, when primitive stone tools
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone Ag ...
were used to scavenge the carcasses of animals killed by other predators, both for their meat and their marrow. In hunting, ''H. habilis'' was most likely not capable of competing with large predators and was more prey than hunter, although ''H. habilis'' probably did steal eggs from nests and may have been able to catch small game and weakened larger prey such as cubs and older animals. The tools were classed as Oldowan
The Oldowan (or Mode I) was a widespread stone tool archaeological industry (style) in prehistory. These early tools were simple, usually made with one or a few flakes chipped off with another stone. Oldowan tools were used during the Lower ...
.Shillington, Kevin(2005). History of Africa, Rev. 2nd Ed. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 2–3, .
Roughly 1.8 million years ago, ''Homo ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into '' H. erectus'' is an ongoing and unresol ...
'' first appeared in the fossil record in Africa. From ''Homo ergaster'', '' Homo erectus'' (upright man) evolved 1.5 million years ago. Some of the earlier representatives of this species were small-brained and used primitive stone tools
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone Ag ...
, much like ''H. habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly c ...
''. The brain later grew in size, and ''H. erectus'' eventually developed a more complex stone tool technology called the Acheulean
Acheulean (; also Acheulian and Mode II), from the French ''acheuléen'' after the type site of Saint-Acheul, is an archaeological industry of stone tool manufacture characterized by the distinctive oval and pear-shaped "hand axes" associated ...
. Potentially the first hominid to engage in hunting, ''H. erectus'' mastered the art of making fire. They were the first hominids to leave Africa, going on to colonize the entire Old World, and perhaps later on giving rise to ''Homo floresiensis
''Homo floresiensis'' also known as "Flores Man"; nicknamed "Hobbit") is an extinct species of small archaic human that inhabited the island of Flores, Indonesia, until the arrival of modern humans about 50,000 years ago.
The remains of an in ...
''. Although some recent writers suggest that '' H. georgicus'', a ''H. habilis'' descendant, was the first and most primitive hominid to ever live outside Africa, many scientists consider ''H. georgicus'' to be an early and primitive member of the ''H. erectus'' species.
The fossil and genetic evidence shows ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' developed in southern and eastern Africa by around 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. and gradually migrated across the continent in waves.
Between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago, their expansion out of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called British East Africa. The book is a lyrical meditation on ...
launched the colonization of the planet by modern humans. By 10,000 BCE, ''Homo sapiens'' had spread to all corners of the world. This dispersal of the human species is suggested by linguistic, cultural and genetic evidence.
During the 11th millennium BP, pottery was independently invented in West Africa, with the earliest pottery there dating to about 9,400 BC from central Mali. Simon Bradley, ''A Swiss-led team of archaeologists has discovered pieces of the oldest African pottery in central Mali, dating back to at least 9,400BC'', SWI swissinfo.ch – the international service of the Swiss Broadcasting Corporation (SBC), 18 January 2007 It spread throughout the Sahel and southern Sahara. After the Sahara became a desert, it did not present a totally impenetrable barrier for travelers between north and south because of the application of animal husbandry towards carrying water, food, and supplies across the desert. Prior to the introduction of the camel, the use of oxen, mule, and horses for desert crossing was common, and trade routes followed chains of oases that were strung across the desert. The
trans-saharan trade
Trans-Saharan trade requires travel across the Sahara between sub-Saharan Africa and North Africa. While existing from prehistoric times, the peak of trade extended from the 8th century until the early 17th century.
The Sahara once had a very d ...
was in full motion by 500 BCE with Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the cla ...
being a major economic force for its establishment. It is thought that the camel was first brought to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
after the Persian Empire conquered Egypt in 525 BCE, although large herds did not become common enough in North Africa for camels to be the pack animal of choice for the trans-saharan trade.
West Africa
 The Bantu expansion is a major migration movement that originated in West Central Africa (possibly around Cameroon) around 2500 BCE, reaching East and Central Africa by 1000 BCE and Southern Africa by the early centuries CE.
The
The Bantu expansion is a major migration movement that originated in West Central Africa (possibly around Cameroon) around 2500 BCE, reaching East and Central Africa by 1000 BCE and Southern Africa by the early centuries CE.
The Djenné-Djenno
Djenné-Djenno (also Jenne-Jeno; ) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the Niger River Valley in the country of Mali. Literally translated to "ancient Djenné", it is the original site of both Djenné and Mali and is considered to be among ...
city-state flourished from 250 BCE to 900 CE and was influential to the development of the Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, an ...
.
The Nok culture
The Nok culture (or Nok civilization) is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham village of Nok in Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok culture appeared in Nige ...
of Nigeria (lasting from 1,500 BCE to 200 CE) is known from a type of terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terracotta ...
figure.Breunig, Peter. 2014. Nok: African Sculpture in Archaeological Context: p. 21.
There were a number of medieval empires of the southern Sahara and the Sahel, based on trans-Saharan trade
Trans-Saharan trade requires travel across the Sahara between sub-Saharan Africa and North Africa. While existing from prehistoric times, the peak of trade extended from the 8th century until the early 17th century.
The Sahara once had a very d ...
, including the Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, an ...
and the Mali Empire, Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire (also transliterated as Songhay) was a state that dominated the western Sahel/Sudan in the 15th and 16th century. At its peak, it was one of the largest states in African history. The state is known by its historiographical ...
, the Kanem Empire Kanem may refer to:
* Kanem–Bornu Empire, existed in modern Chad and Nigeria known to Arabian geographers from the 9th century AD onward and lasted as the independent kingdom of Bornu until 1900
* Kanem Prefecture, of former prefectures of Chad
* ...
and the subsequent Bornu Empire Bornu may refer to:
* Bornu Empire, a historical state of West Africa
* Borno State
Borno State is a state in the North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria, bordered by Yobe to the west, Gombe to the southwest, and Adamawa to the south while it ...
. They built stone structures like in Tichit
Tichit or Tichitt ( ber, Ticit, ar, تيشيت) is a partly abandoned village at the foot of the Tagant Plateau in central southern Mauritania that is known for its vernacular architecture. The main agriculture in Tichit is date farming, and the ...
, but mainly constructed in adobe. The Great Mosque of Djenne
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
is most reflective of Sahelian architecture and is the largest adobe building in the world.
In the forest zone, several states and empires such as Bono State
Bono State (or Bonoman) was a trading state created by the Bono people, located in what is now southern Ghana. Bonoman was a medieval Akan kingdom in what is now Bono, Bono East and Ahafo region respectively named after the (Bono and Ahafo) an ...
, Akwamu
Akwamu was a state set up by the Akwamu people in present-day Ghana. After migrating from Bono state, the Akan founders of Akwamu settled in Twifo-Heman. The Akwamu led an expansionist empire in the 17th and 18th centuries. At the peak of their ...
and others emerged. The Ashanti Empire
The Asante Empire (Asante Twi: ), today commonly called the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted between 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana as well as parts of Iv ...
arose in the 18th century in modern-day Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
. The Kingdom of Nri
The Kingdom of Nri () was a medieval polity located in what is now Nigeria. The kingdom existed as a sphere of religious and political influence over a third of Igboland, and was administered by a priest-king called an '' Eze Nri''. The ''Eze Nri ...
, was established by the Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a ...
in the 11th century. Nri was famous for having a priest-king who wielded no military power. Nri was a rare African state which was a haven for freed slaves and outcasts who sought refuge in their territory. Other major states included the kingdoms of Ifẹ
Ifẹ̀ ( yo, Ifẹ̀, also ''Ilé-Ifẹ̀'') is an ancient Yoruba city in south-western Nigeria. The city is located in present-day Osun State. Ife is about 218 kilometers northeast of Lagos with a population of over 500,000 people, which is ...
and Oyo in the western block of Nigeria which became prominent about 700–900 and 1400 respectively, and center of Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
culture. The Yoruba's built massive mud walls around their cities, the most famous being Sungbo's Eredo
Sungbo's Eredo is a system of defensive walls and ditches that is located to the southwest of the Yoruba town of Ijebu Ode in Ogun State, southwest Nigeria (). It was built in 800–1000 AD in honour of the Ijebu noblewoman Oloye Bilikisu Sungbo. ...
. Another prominent kingdom in southwestern Nigeria was the Kingdom of Benin
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as the Edo Kingdom, or the Benin Empire ( Bini: ') was a kingdom within what is now southern Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was known as Dahomey from the 17th ce ...
9th–11th century whose power lasted between the 15th and 19th century and was one of the greatest Empires of African history documented all over the world. Their dominance reached as far as the well-known city of Eko which was named Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national capital of Nigeria until December 1991 fo ...
by the Portuguese traders and other early European settlers. The Edo-speaking people of Benin are known for their famous bronze casting and rich coral, wealth, ancient science and technology and the Walls of Benin
The Walls of Benin are a series of earthworks made up of banks and ditches, called ''ya'' in the Edo language, in the area around present-day Benin City, the capital of present-day Edo, Nigeria. They consist of of city iya and an estimated o ...
, which is the largest man-made structure in the world.
In the 18th century, the Oyo and the Aro confederacy
The Aro Confederacy (1690–1902) was a political union orchestrated by the Aro people, Igbo subgroup, centered in Arochukwu in present-day southeastern Nigeria. Their influence and presence was all over Eastern Nigeria, lower Middle Belt, an ...
were responsible for most of the slaves exported from modern-day Nigeria, selling them to European slave traders. Following the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, the British expanded their influence into the Nigerian interior. In 1885, British claims to a West African sphere of influence received international recognition, and in the following year the Royal Niger Company
The Royal Niger Company was a mercantile company chartered by the British government in the nineteenth century. It was formed in 1879 as the ''United African Company '' and renamed to ''National African Company'' in 1881 and to ''Royal Niger C ...
was chartered under the leadership of Sir George Goldie. In 1900, the company's territory came under the control of the British government, which moved to consolidate its hold over the area of modern Nigeria. On 1 January 1901, Nigeria became a British protectorate as part of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, the foremost world power at the time. Nigeria was granted its independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
in 1960 during the period of decolonization
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
.
Central Africa
 Archeological finds in Central Africa provide evidence of human settlement that may date back over 10,000 years. According to Zangato and Holl, there is evidence of iron-smelting in the Central African Republic and Cameroon that may date back to 3,000 to 2,500 BCE. Extensive walled sites and settlements have recently been found in Zilum, Chad. The area is located approximately southwest of Lake Chad, and has been
Archeological finds in Central Africa provide evidence of human settlement that may date back over 10,000 years. According to Zangato and Holl, there is evidence of iron-smelting in the Central African Republic and Cameroon that may date back to 3,000 to 2,500 BCE. Extensive walled sites and settlements have recently been found in Zilum, Chad. The area is located approximately southwest of Lake Chad, and has been radiocarbon dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
to the first millennium BCE.
Trade and improved agricultural techniques supported more sophisticated societies, leading to the early civilizations of Sao
SAO or Sao may refer to:
Places
* Sao civilisation, in Middle Africa from 6th century BC to 16th century AD
* Sao, a town in Boussé Department, Burkina Faso
* Saco Transportation Center (station code SAO), a train station in Saco, Maine, U.S. ...
, Kanem, Bornu, Shilluk, Baguirmi, and Wadai.
Following the Bantu Migration
The Bantu expansion is a hypothesis about the history of the major series of migrations of the original Proto-Bantu-speaking group, which spread from an original nucleus around Central Africa across much of sub-Saharan Africa. In the process, ...
into Central Africa, during the 14th century, the Luba Kingdom
The Kingdom of Luba or Luba Empire (1585–1889) was a pre-colonial Central African state that arose in the marshy grasslands of the Upemba Depression in what is now southern Democratic Republic of Congo.
Origins and foundation
Archaeologic ...
in southeast Congo came about under a king whose political authority derived from religious, spiritual legitimacy. The kingdom controlled agriculture and regional trade of salt and iron from the north and copper from the Zambian/Congo copper belt.Shillington, Kevin(2005). History of Africa, Rev. 2nd Ed. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 138–39, 142, .
Rival kingship factions which split from the Luba Kingdom later moved among the Lunda people, marrying into its elite and laying the foundation of the Lunda Empire
The Nation of Lunda (c. 1665 – c. 1887) was a confederation of states in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo, north-eastern Angola, and north-western Zambia, its central state was in Katanga.
Origin
Initially, the core of what would ...
in the 16th century. The ruling dynasty centralised authority among the Lunda under the Mwata Yamyo or Mwaant Yaav. The Mwata Yamyo's legitimacy, like that of the Luba king, came from being viewed as a spiritual religious guardian. This imperial cult
An imperial cult is a form of state religion in which an emperor or a dynasty of emperors (or rulers of another title) are worshipped as demigods or deities. "Cult" here is used to mean "worship", not in the modern pejorative sense. The cult may ...
or system of divine kings was spread to most of central Africa by rivals in kingship migrating and forming new states. Many new states received legitimacy by claiming descent from the Lunda dynasties.
The Kingdom of Kongo existed from the Atlantic west to the Kwango river to the east. During the 15th century, the Bakongo farming community was united with its capital at M'banza-Kongo, under the king title, Manikongo
The Manikongo, or Mwene Kongo, was the title of the ruler of the Kingdom of Kongo, a kingdom that existed from the 14th to the 19th centuries and consisted of land in present-day Angola, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republ ...
. Other significant states and peoples included the Kuba Kingdom
The Kuba Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Bakuba or Bushongo, is a traditional kingdom in Central Africa. The Kuba Kingdom flourished between the 17th and 19th centuries in the region bordered by the Sankuru, Lulua, and Kasai rivers ...
, producers of the famous raffia cloth, the Eastern Lunda, Bemba, Burundi, Rwanda, and the Kingdom of Ndongo
The Kingdom of Ndongo, formerly known as Angola or Dongo, was an early-modern African state located in what is now Angola.
The monarchy, Kingdom of Ndongo is first recorded in the sixteenth century. It was one of multiple vassal states to King ...
.
East Africa
Sudan

Nubia
Nubia () (Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), or ...
, covered by present-day northern Sudan and southern Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, was referred to as "Aethiopia
Ancient Aethiopia, ( gr, Αἰθιοπία, Aithiopía; also known as Ethiopia) first appears as a geographical term in classical documents in reference to the upper Nile region of Sudan, as well as certain areas south of the Sahara desert. Its ...
" ("land of the burnt face") by the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
.
Nubia in her greatest phase is considered sub-Saharan Africa's oldest urban civilisation. Nubia was a major source of gold for the ancient world. Nubians built famous structures and numerous pyramids. Sudan, the site of ancient Nubia, has more pyramids than anywhere else in the world.
Horn of Africa
 The
The Axumite Empire
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wha ...
spanned the southern Sahara, south Arabia and the Sahel along the western shore of the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
. Located in northern Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and Eritrea, Aksum was deeply involved in the trade network between India and the Mediterranean. Growing from the proto-Aksumite Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
period ( 4th century BCE), it rose to prominence by the 1st century CE. The Aksumites constructed monolithic stelae
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
to cover the graves of their kings, such as King Ezana's Stele
King Ezana's Stele is a 4th century obelisk in the ancient city of Axum, in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. The monument stands in the middle of the Northern Stelae Park, which contains hundreds of smaller and less decorated stelae. This stele is ...
. The later Zagwe dynasty
The Zagwe dynasty ( Ge'ez: ዛጔ ሥርወ መንግሥት) was an Agaw medieval dynasty that ruled the northern parts of Ethiopia and Eritrea, after the historical name of the Lasta province. Centered at Lalibela, it ruled large parts of the t ...
, established in the 12th century, built churches out of solid rock. These rock-hewn structures include the Church of St. George at Lalibela.
 In
In ancient Somalia
Somalia ( so, Soomaaliya; ), officially the Federal Republic of Somalia ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Federaalka Soomaaliya, ) and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. The country was an important c ...
, city-states flourished such as Opone
Opone ( grc, Οπώνη) was an ancient proto-Somali city situated in the Horn of Africa. It is primarily known for its trade with the Ancient Egyptians, Romans, Greeks, Persians, and the states of ancient India. Through archaeological remains, t ...
, Mosyllon and Malao
Malao ( grc, Μαλαὼ) was an ancient proto-Somali port in present-day Somaliland. The town was situated on the site of what later became the city of Berbera. It was a key trading member involved in the Red Sea-Indian Ocean commerce in the ea ...
that competed with the Sabaeans
The Sabaeans or Sabeans ( Sabaean:, ; ar, ٱلسَّبَئِيُّوْن, ''as-Sabaʾiyyūn''; he, סְבָאִים, Səḇāʾīm) were an ancient group of South Arabians. They spoke the Sabaean language, one of the Old South Arabian langu ...
, Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
ns and Axumites for the wealthy Indo
Indo may refer to:
* Indo-, a prefix indicating India or the Indian Subcontinent
* Indonesia, a country in Asia
** INDO LINES, callsign of Indonesian Airlines
** Indo people, people of mixed European and Indonesian ancestry
** Indo cuisine, fusion ...
–Greco
Greco may refer to:
People
* Greco (surname), a list of people with this surname
* a masculine variant of Greca (given name), an Italian feminine given name
* Greco Mafia clan, one of the most influential Mafia clans in Sicily and Calabria
Wine ...
–Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
trade.
In the Middle Ages several powerful Somali empires dominated the region's trade, including the Ajuran Sultanate
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in th ...
, which excelled in hydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
and fortress building, the Sultanate of Adal
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din II ...
, whose General Ahmed Gurey
Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi ( so, Axmed Ibraahim al-Qaasi or Axmed Gurey, Harari: አሕመድ ኢብራሂም አል-ጋዚ, ar, أحمد بن إبراهيم الغازي ; 1506 – 21 February 1543) was an imam and general of the Adal Sultan ...
was the first African commander in history to use cannon warfare on the continent during Adal's conquest of the Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that histori ...
, and the Geledi Sultanate
The Sultanate of the Geledi ( so, Saldanadda Geledi, ar, سلطنة غلدي) also known as the Gobroon Dynasty Somali Sultanate: The Geledi City-state Over 150 Years - Virginia Luling (2002) Page 229 was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of th ...
, whose military dominance forced governors of the Omani empire
The Omani Empire ( ar, الإمبراطورية العُمانية) was a maritime empire, vying with Portugal and Britain for trade and influence in the Persian Gulf and Indian Ocean. At its peak in the 19th century, Omani influence or control ...
north of the city of Lamu to pay tribute to the Somali Sultan Ahmed Yusuf.
Southeast Africa
According to the theory ofrecent African origin of modern humans
In paleoanthropology, the recent African origin of modern humans, also called the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA), recent single-origin hypothesis (RSOH), replacement hypothesis, or recent African origin model (RAO), is the dominant model of the ...
, the mainstream position held within the scientific community, all humans originate from either Southeast Africa or the Horn of Africa. During the first millennium CE, Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-sp ...
and Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
-speaking peoples moved into the region, and the latter now account for three-quarters of Kenya's population.
 On the coastal section of Southeast Africa, a mixed Bantu community developed through contact with Muslim
On the coastal section of Southeast Africa, a mixed Bantu community developed through contact with Muslim Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
traders, leading to the development of the mixed Arab, Persian and African Swahili City States. The Swahili culture
Swahili culture is the culture of the Swahili people inhabiting the Swahili coast. This littoral area encompasses Tanzania, Kenya, and Mozambique, as well as the adjacent islands of Zanzibar and Comoros and some parts of Malawi. They speak Swah ...
that emerged from these exchanges evinces many Arab and Islamic influences not seen in traditional Bantu culture, as do the many Afro-Arab
Afro-Arabs are Arabs of full or partial Black African descent. These include populations within mainly the Sudanese, Emiratis, Yemenis, Saudis, Omanis, Sahrawis, Mauritanians, Algerians, Egyptians and Moroccans, with considerably long est ...
members of the Bantu Swahili people. With its original speech community centered on the coastal parts of Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
(particularly Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
) and Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
a seaboard referred to as the Swahili Coast the Bantu Swahili language contains many Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
loan-words
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because the ...
as a consequence of these interactions.
The earliest Bantu inhabitants of the Southeast coast of Kenya and Tanzania encountered by these later Arab and Persian settlers have been variously identified with the trading settlements of Rhapta
Rhapta ( grc, Ῥάπτα and Ῥαπτά) was an emporion said to be on the coast of Southeast Africa, first described in the 1st century CE. Its location has not been firmly identified, although there are a number of plausible candidate sites. ...
, Azania
Azania ( grc, Ἀζανία) is a name that has been applied to various parts of southeastern tropical Africa. In the Roman period and perhaps earlier, the toponym referred to a portion of the Southeast Africa coast extending from northern Keny ...
and Menouthias referenced in early Greek and Chinese writings from 50 CE to 500 CE. These early writings perhaps document the first wave of Bantu settlers to reach Southeast Africa during their migration.
Between the 14th and 15th centuries, large medieval Southeast African kingdoms and states emerged, such as the Buganda,Roland Oliver, et al. "Africa South of the Equator," in Africa Since 1800. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2005, pp. 24–25. Bunyoro and Karagwe kingdoms of Uganda and Tanzania.
During the early 1960s, the Southeast African nations achieved independence from colonial rule.
Southern Africa
 Settlements of
Settlements of Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
-speaking peoples, who were iron-using agriculturists and herdsmen, were already present south of the Limpopo River by the 4th or 5th century displacing and absorbing the original Khoisan speakers. They slowly moved south, and the earliest ironworks in modern-day KwaZulu-Natal, KwaZulu-Natal Province are believed to date from around 1050. The southernmost group was the Xhosa people, whose language incorporates certain linguistic traits from the earlier Khoisan inhabitants. They reached the Great Fish River, Fish River in today's Eastern Cape, Eastern Cape Province.
Monomotapa was a medieval kingdom (c. 1250–1629), which existed between the Zambezi and Limpopo River, Limpopo rivers of Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
in the territory of modern-day Zimbabwe and Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
. Its old capital was located at Great Zimbabwe.
In 1487, Bartolomeu Dias became the first European to reach the southernmost tip of Africa. In 1652, a Victualler, victualling station was established at the Cape of Good Hope by Jan van Riebeeck on behalf of the Dutch East India Company. For most of the 17th and 18th centuries, the slowly expanding settlement was a Dutch Empire, Dutch possession.
In 1795, the Dutch colony was captured by the Kingdom of Great Britain, British during the French Revolutionary Wars. The British intended to use Cape Town as a major port on the route to Australia and Indian subcontinent, India. It was later returned to the Dutch in 1803, but soon afterward the Dutch East India Company declared bankruptcy, and the Dutch (now under French control) and the British found themselves at war again. The British captured the Dutch possession yet again at the Battle of Blaauwberg, commanded by Sir David Baird, 1st Baronet, Sir David Blair. The Zulu Kingdom was a Southern African tribal state in what is now KwaZulu-Natal in southeastern South Africa. The small kingdom gained world fame during and after their defeat in the Anglo-Zulu War. During the 1950s and early 1960s, most sub-Saharan African nations achieved independence from colonial rule.
Demographics
Population
 According to , the population of sub-Saharan Africa was 1.1 billion in 2019. The current growth rate is 2.3%. The UN predicts for the region a population between 2 and 2.5 billion by 2050 with a population density of 80 per km2 compared to 170 for Western Europe, 140 for Asia and 30 for the Americas.
Sub-Saharan African countries top the list of countries and territories by fertility rate with 40 of the highest 50, all with Total fertility rate, TFR greater than 4 in 2008. All are above the world average except
According to , the population of sub-Saharan Africa was 1.1 billion in 2019. The current growth rate is 2.3%. The UN predicts for the region a population between 2 and 2.5 billion by 2050 with a population density of 80 per km2 compared to 170 for Western Europe, 140 for Asia and 30 for the Americas.
Sub-Saharan African countries top the list of countries and territories by fertility rate with 40 of the highest 50, all with Total fertility rate, TFR greater than 4 in 2008. All are above the world average except South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
and Seychelles. More than 40% of the population in sub-Saharan countries is Demographics of Nigeria, younger than 15 years old, as well as in Sudan, with the exception of South Africa.
GDP per Capita (PPP) ''(2016, 2017 (PPP, US$))'', Life (Exp.) ''(Life Expectancy 2006)'', Literacy (Male/Female 2006), Trans ''(Transparency 2009)'', HDI ''(Human Development Index)'', EODBR ''(Ease of Doing Business Rank June 2008 through May 2009)'', SAB (''Starting a Business June 2008 through May 2009)'', PFI ''(Press Freedom Index 2009)''
Languages and ethnic groups




 Sub-Saharan Africa contains over 1,500 languages.
Sub-Saharan Africa contains over 1,500 languages.
Afroasiatic
With the exception of the extinct Sumerian language, Sumerian (a language isolate) of Mesopotamia, Afroasiatic has the oldest documented history of any language family in the world. Egyptian was recorded as early as 3200 BCE. The Semitic languages, Semitic branch was recorded as early as 2900 BCE in the form of the Akkadian language of Mesopotamia (Assyria and Babylonia) and circa 2500 BCE in the form of the Eblaite language of north eastern Syria. The distribution of the Afroasiatic languages within Africa is principally concentrated in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. Languages belonging to the family's Berber languages, Berber branch are mainly spoken in the north, with its speech area extending into the Sahel (northern Mauritania, northern Mali, northern Niger). The Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch of Afroasiatic is centered in the Horn, and is also spoken in the Nile Valley and parts of the African Great Lakes region. Additionally, the Semitic branch of the family, in the form of Arabic, is widely spoken in the parts of Africa that are within the Arab world. South Semitic languages are also spoken in parts of the Horn of Africa (Ethiopia, Eritrea). The Chadic languages, Chadic branch is distributed in Central and West Africa. Hausa language, Hausa, its most widely spoken language, serves as a lingua franca in West Africa (Niger, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Cameroon, and Chad).Khoisan
The several families lumped under the term Khoi-San include languages indigenous toSouthern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
and Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, though some, such as the Khoi languages, appear to have moved to their current locations not long before the Bantu expansion.Güldemann, Tom and Edward D. Elderkin (forthcoming"On external genealogical relationships of the Khoe family".
In Brenzinger, Matthias and Christa König (eds.), ''Khoisan languages and linguistics: the Riezlern symposium 2003.'' Quellen zur Khoisan-Forschung 17. Köln: Rüdiger Köppe. In Southern Africa, their speakers are the Khoikhoi and San people, San (Bushmen), in Southeast Africa, the Sandawe people, Sandawe and Hadza people, Hadza.
Niger–Congo
The Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family is the largest in the world in terms of the number of languages (1,436) it contains. The vast majority of languages of this family are tonal language, tonal such as Yoruba language, Yoruba, and Igbo language, Igbo, However, others such as Fulani language, Fulani, Wolof language, Wolof and Kiswahili are not. A major branch of the Niger–Congo languages isBantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
, which covers a greater geographic area than the rest of the family. Bantu speakers represent the majority of inhabitants in southern, central and southeastern Africa, though San people, San, Pygmy, and Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-sp ...
groups, respectively, can also be found in those regions. Bantu-speakers can also be found in parts of Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo ...
such as the Gabon, Equatorial Guinea and southern Cameroon. Swahili language, Swahili, a Bantu language with many Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, Farsi, Persian and other Middle Eastern and South Asian loan words, developed as a ''lingua franca'' for trade between the different peoples in southeastern Africa. In the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
of Southern Africa, the distinct people known as Bushmen (also "San", closely related to, but distinct from "Khoikhoi, Hottentots") have long been present. The San evince unique physical traits, and are the indigenous people of southern Africa. Pygmies are the pre-Bantu indigenous peoples of Central Africa.
Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are concentrated in the upper parts of the Chari River, Chari andNile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
rivers of Central Africa and Southeast Africa. They are principally spoken by Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-sp ...
peoples and are also spoken in Sudan among the Fur people, Fur, Masalit people, Masalit, Nubian people, Nubian and Zaghawa people, Zaghawa peoples and in West and Central Africa among the Songhai people, Songhai, Zarma people, Zarma and Kanuri people, Kanuri. The Old Nubian language is also a member of this family.
Major languages of Africa by region, family and number of primary language speakers in millions:
Genetic history
Major cities

 Sub-Saharan Africa has several large cities.
Sub-Saharan Africa has several large cities. Lagos
Lagos (Nigerian English: ; ) is the largest city in Nigeria and the second most populous city in Africa, with a population of 15.4 million as of 2015 within the city proper. Lagos was the national capital of Nigeria until December 1991 fo ...
is a city in the Nigerian States of Nigeria, state of Lagos State, Lagos. The city, with its adjoining conurbation, is List of Nigerian cities by population, the most populous in Nigeria, and the second-most populous in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
after Cairo, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. It is one of the fastest-growing cities in the world, and also one of the most populous urban agglomerations. Lagos is a major financial centre in Africa; this megacity has the highest GDP, and also houses Apapa, one of the largest and busiest ports on the continent.
Dar es Salaam is the former capital of, as well as the most populous city in, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
; it is a regionally important economic centre. It is located on the Swahili coast.
Johannesburg is the largest city in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
. It is the province, provincial capital and largest city in Gauteng, which is the wealthiest province in South Africa. While Johannesburg is not one of South Africa#Politics and government, South Africa's three capital cities, it is the seat of the Constitutional Court of South Africa, Constitutional Court. The city is located in the mineral-rich Witwatersrand range of hills, and is the centre of a large-scale gold and diamond trade.
Nairobi is the capital and the largest city of Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
. The name comes from the Maasai language, Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nyrobi'', which translates to "cool water", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city is popularly referred to as the Green City in the Sun.
Other major cities in sub-Saharan Africa include Abidjan, Cape Town, Kinshasa, Luanda, Mogadishu and Addis Ababa.
Economy
Energy and power
 , 50% of Africa was rural with no access to electricity. Africa generates 47 GW of electricity, less than 0.6% of the global market share. Many countries are affected by power shortages.
The percentage of residences with access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa is the lowest in the world. In some remote regions, fewer than one in every 20 households has electricity.
Because of rising prices in commodities such as coal and oil, thermal sources of energy are proving to be too expensive for power generation. Sub-Saharan Africa is expected to build additional hydropower generation capacity of at least 20,165 MW by 2014. The region has the potential to generate 1,750 TWh of energy, of which only 7% has been explored. The failure to exploit its full energy potential is largely due to significant underinvestment, as at least four times as much (approximately $23 billion a year) and what is currently spent is invested in operating high cost power systems and not on expanding the infrastructure.
African governments are taking advantage of the readily available water resources to broaden their energy mix. Hydro Turbine Markets in sub-Saharan Africa generated revenues of $120.0 million in 2007 and is estimated to reach $425.0 million. Asian countries, notably China, India, and Japan, are playing an active role in power projects across the African continent. The majority of these power projects are hydro-based because of China's vast experience in the construction of hydro-power projects and part of the Energy & Power Growth Partnership Services programme.
With electrification numbers, sub-Saharan Africa with access to the Sahara and being in the tropical zones has massive potential for solar photovoltaic electrical potential. Six hundred million people could be served with electricity based on its photovoltaic potential. China is promising to train 10,000 technicians from Africa and other developing countries in the use of solar energy technologies over the next five years. Training African technicians to use solar power is part of the China-Africa science and technology cooperation agreement signed by Chinese science minister Xu Guanhua and African counterparts during premier Wen Jiabao's visit to Ethiopia in December 2003.
The New Partnership for Africa's Development (NEPAD) is developing an integrated, continent-wide energy strategy. This has been funded by, amongst others, the African Development Bank (AfDB) and the EU-Africa Infrastructure Trust Fund. These projects must be sustainable, involve a cross-border dimension and/or have a regional impact, involve public and private capital, contribute to poverty alleviation and economic development, and involve at least one country in sub-Saharan Africa.
Renewable Energy Performance Platform was established by the European Investment Bank the United Nations Environment Programme with a five-year goal of improving energy access for at least two million people in sub-Saharan Africa. It has so far invested around $45 million to renewable energy projects in 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Solar power and hydropower are among the energy methods used in the projects.
, 50% of Africa was rural with no access to electricity. Africa generates 47 GW of electricity, less than 0.6% of the global market share. Many countries are affected by power shortages.
The percentage of residences with access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa is the lowest in the world. In some remote regions, fewer than one in every 20 households has electricity.
Because of rising prices in commodities such as coal and oil, thermal sources of energy are proving to be too expensive for power generation. Sub-Saharan Africa is expected to build additional hydropower generation capacity of at least 20,165 MW by 2014. The region has the potential to generate 1,750 TWh of energy, of which only 7% has been explored. The failure to exploit its full energy potential is largely due to significant underinvestment, as at least four times as much (approximately $23 billion a year) and what is currently spent is invested in operating high cost power systems and not on expanding the infrastructure.
African governments are taking advantage of the readily available water resources to broaden their energy mix. Hydro Turbine Markets in sub-Saharan Africa generated revenues of $120.0 million in 2007 and is estimated to reach $425.0 million. Asian countries, notably China, India, and Japan, are playing an active role in power projects across the African continent. The majority of these power projects are hydro-based because of China's vast experience in the construction of hydro-power projects and part of the Energy & Power Growth Partnership Services programme.
With electrification numbers, sub-Saharan Africa with access to the Sahara and being in the tropical zones has massive potential for solar photovoltaic electrical potential. Six hundred million people could be served with electricity based on its photovoltaic potential. China is promising to train 10,000 technicians from Africa and other developing countries in the use of solar energy technologies over the next five years. Training African technicians to use solar power is part of the China-Africa science and technology cooperation agreement signed by Chinese science minister Xu Guanhua and African counterparts during premier Wen Jiabao's visit to Ethiopia in December 2003.
The New Partnership for Africa's Development (NEPAD) is developing an integrated, continent-wide energy strategy. This has been funded by, amongst others, the African Development Bank (AfDB) and the EU-Africa Infrastructure Trust Fund. These projects must be sustainable, involve a cross-border dimension and/or have a regional impact, involve public and private capital, contribute to poverty alleviation and economic development, and involve at least one country in sub-Saharan Africa.
Renewable Energy Performance Platform was established by the European Investment Bank the United Nations Environment Programme with a five-year goal of improving energy access for at least two million people in sub-Saharan Africa. It has so far invested around $45 million to renewable energy projects in 13 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Solar power and hydropower are among the energy methods used in the projects.
Media
Radio is the major source of information in sub-Saharan Africa.English, Cynthia''Radio the Chief Medium for News in Sub-Saharan Africa''
. Gallup 23 June 2008. Average coverage stands at more than a third of the population. Countries such as Gabon, Seychelles, and
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
boast almost 100% penetration. Only five countries Burundi, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, Eritrea, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, and Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
still have a penetration of less than 10%. Broadband, Broadband penetration outside of South Africa has been limited where it is exorbitantly expensive. Access to the internet via cell phones is on the rise.
Television is the second major source of information. Because of power shortages, the spread of television viewing has been limited. Eight percent have television, a total of 62 million. But those in the television industry view the region as an untapped green market. Digital television and pay for service are on the rise.
Infrastructure
 According to researchers at the Overseas Development Institute, the lack of infrastructure in many developing countries represents one of the most significant limitations to economic growth and achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).Christian K.M. Kingombe 2011
According to researchers at the Overseas Development Institute, the lack of infrastructure in many developing countries represents one of the most significant limitations to economic growth and achievement of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).Christian K.M. Kingombe 2011Mapping the new infrastructure financing landscape
. London: Overseas Development InstituteJohn J. Saul and Colin Leys
Sub-Saharan Africa in Global Capitalism
, ''Monthly Review'', 1999, Volume 51, Issue 03 (July–August)Fred Magdoff
Twenty-First-Century Land Grabs: Accumulation by Agricultural Dispossession
, ''Monthly Review'', 2013, Volume 65, Issue 06 (November) Less than 40% of rural Africans live within two kilometers of an all-season road, the lowest level of rural accessibility in the developing world. Spending on roads averages just below 2% of GDP with varying degree among countries. This compares with 1% of GDP that is typical in industrialised countries, and 2–3% of GDP found in fast-growing emerging economies. Although the level of expenditure is high relative to the size of Africa's economies, it remains small in absolute terms, with low-income countries spending an average of about US$7 per capita per year. Infrastructure investments and maintenance can be very expensive, especially in such as areas as landlocked, rural and sparsely populated countries in Africa.
 Infrastructure investments contributed to Africa's growth, and increased investment is necessary to maintain growth and tackle poverty. The returns to investment in infrastructure are very significant, with on average 30–40% returns for telecommunications (ICT) investments, over 40% for electricity generation and 80% for roads.
In Africa, it is argued that in order to meet the MDGs by 2015 infrastructure investments would need to reach about 15% of GDP (around $93 billion a year). Currently, the source of financing varies significantly across sectors. Some sectors are dominated by state spending, others by overseas development aid (ODA) and yet others by private investors. In sub-Saharan Africa, the state spends around $9.4 billion out of a total of $24.9 billion. In irrigation, SSA states represent almost all spending; in transport and energy a majority of investment is state spending; in Information and communication technologies, ICT and water supply and sanitation, the private sector represents the majority of capital expenditure. Overall, aid, the private sector and non-OECD financiers between them exceed state spending. The private sector spending alone equals state capital expenditure, though the majority is focused on ICT infrastructure investments. External financing increased from $7 billion (2002) to $27 billion (2009). China, in particular, has emerged as an important investor.
Infrastructure investments contributed to Africa's growth, and increased investment is necessary to maintain growth and tackle poverty. The returns to investment in infrastructure are very significant, with on average 30–40% returns for telecommunications (ICT) investments, over 40% for electricity generation and 80% for roads.
In Africa, it is argued that in order to meet the MDGs by 2015 infrastructure investments would need to reach about 15% of GDP (around $93 billion a year). Currently, the source of financing varies significantly across sectors. Some sectors are dominated by state spending, others by overseas development aid (ODA) and yet others by private investors. In sub-Saharan Africa, the state spends around $9.4 billion out of a total of $24.9 billion. In irrigation, SSA states represent almost all spending; in transport and energy a majority of investment is state spending; in Information and communication technologies, ICT and water supply and sanitation, the private sector represents the majority of capital expenditure. Overall, aid, the private sector and non-OECD financiers between them exceed state spending. The private sector spending alone equals state capital expenditure, though the majority is focused on ICT infrastructure investments. External financing increased from $7 billion (2002) to $27 billion (2009). China, in particular, has emerged as an important investor.
Oil and minerals
 The region is a major exporter to the world of gold, uranium, chromium, vanadium, antimony, coltan, bauxite, iron ore, copper, and manganese. South Africa is a major exporter of manganese as well as chromium. A 2001 estimate is that 42% of the world's reserves of chromium may be found in South Africa. South Africa is the largest producer of platinum, with 80% of the total world's annual mine production and 88% of the world's platinum reserve. Sub-Saharan Africa produces 33% of the world's bauxite, with Guinea as the major supplier. Zambia is a major producer of copper. The Democratic Republic of Congo is a major source of coltan. Production from DR Congo is very small, but the country has 80% of the proven reserves in Africa, which are 80% of those worldwide. Sub-Saharan Africa is a major producer of gold, producing up to 30% of global production. Major suppliers are South Africa, Ghana, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Guinea, and Mali. South Africa had been first in the world in terms of gold production since 1905, but in 2007 it moved to second place, according to GFMS, the precious metals consultancy. Uranium is major commodity from the region. Significant suppliers are Niger, Namibia, and South Africa. Namibia was the number one supplier from sub-Saharan Africa in 2008. The region produces 49% of the world's diamonds.
By 2015, it is estimated that 25% of North American oil will be from sub-Saharan Africa, ahead of the Middle East. Sub-Saharan Africa has been the focus of an intense race for oil by the West, China, India, and other emerging economies, even though it holds only 10% of proven oil reserves, less than the Middle East. This race has been referred to as the second Scramble for Africa. All reasons for this global scramble come from the reserves' economic benefits. Transportation cost is low and no pipelines have to be laid as in Central Asia. Almost all reserves are offshore, so political turmoil within the host country will not directly interfere with operations. Sub-Saharan oil is viscous, with a very low sulfur content. This quickens the refining process and effectively reduces costs. New sources of oil are being located in sub-Saharan Africa more frequently than anywhere else. Of all new sources of oil, are in sub-Saharan Africa.
The region is a major exporter to the world of gold, uranium, chromium, vanadium, antimony, coltan, bauxite, iron ore, copper, and manganese. South Africa is a major exporter of manganese as well as chromium. A 2001 estimate is that 42% of the world's reserves of chromium may be found in South Africa. South Africa is the largest producer of platinum, with 80% of the total world's annual mine production and 88% of the world's platinum reserve. Sub-Saharan Africa produces 33% of the world's bauxite, with Guinea as the major supplier. Zambia is a major producer of copper. The Democratic Republic of Congo is a major source of coltan. Production from DR Congo is very small, but the country has 80% of the proven reserves in Africa, which are 80% of those worldwide. Sub-Saharan Africa is a major producer of gold, producing up to 30% of global production. Major suppliers are South Africa, Ghana, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Guinea, and Mali. South Africa had been first in the world in terms of gold production since 1905, but in 2007 it moved to second place, according to GFMS, the precious metals consultancy. Uranium is major commodity from the region. Significant suppliers are Niger, Namibia, and South Africa. Namibia was the number one supplier from sub-Saharan Africa in 2008. The region produces 49% of the world's diamonds.
By 2015, it is estimated that 25% of North American oil will be from sub-Saharan Africa, ahead of the Middle East. Sub-Saharan Africa has been the focus of an intense race for oil by the West, China, India, and other emerging economies, even though it holds only 10% of proven oil reserves, less than the Middle East. This race has been referred to as the second Scramble for Africa. All reasons for this global scramble come from the reserves' economic benefits. Transportation cost is low and no pipelines have to be laid as in Central Asia. Almost all reserves are offshore, so political turmoil within the host country will not directly interfere with operations. Sub-Saharan oil is viscous, with a very low sulfur content. This quickens the refining process and effectively reduces costs. New sources of oil are being located in sub-Saharan Africa more frequently than anywhere else. Of all new sources of oil, are in sub-Saharan Africa.
Agriculture
 Sub-Saharan Africa has more variety of grains than anywhere in the world. Between 13,000 and 11,000 BCE wild grains began to be collected as a source of food in the cataract region of the Nile, south of Egypt. The collecting of wild grains as source of food spread to Syria, parts of Turkey, and Iran by the eleventh millennium BCE. By the tenth and ninth millennia southwest Asians domesticated their wild grains, wheat, and barley after the notion of collecting wild grains spread from the Nile.Christopher Ehret, (2002). The Civilization of Africa. University of Virginia Press: Charlottesville, p. 98, .
Numerous crops have been domesticated in the region and spread to other parts of the world. These crops included sorghum, castor beans, coffee, cottonVandaveer, Chelsie(2006)
Sub-Saharan Africa has more variety of grains than anywhere in the world. Between 13,000 and 11,000 BCE wild grains began to be collected as a source of food in the cataract region of the Nile, south of Egypt. The collecting of wild grains as source of food spread to Syria, parts of Turkey, and Iran by the eleventh millennium BCE. By the tenth and ninth millennia southwest Asians domesticated their wild grains, wheat, and barley after the notion of collecting wild grains spread from the Nile.Christopher Ehret, (2002). The Civilization of Africa. University of Virginia Press: Charlottesville, p. 98, .
Numerous crops have been domesticated in the region and spread to other parts of the world. These crops included sorghum, castor beans, coffee, cottonVandaveer, Chelsie(2006)What was the cotton of Kush?
KillerPlants.com, Plants That Change History Archive. okra, black-eyed peas, watermelon, gourd, and pearl millet. Other domesticated crops included teff, enset, African rice, Yam (vegetable), yams, kola nuts, Elaeis guineensis, oil palm, and raffia palm. Domesticated animals include the guinea fowl and the donkey.
Education
Major progress in access to education
Since the World Education Forum in Dakar, considerable efforts have been made to respond to these demographic challenges in terms of education. The amount of funds raised has been decisive. Between 1999 and 2010, public spending on education as a percentage of Gross national product, gross national product (GNP) increased by 5% per year in sub-Saharan Africa, with major variations between countries, with percentages varying from 1.8% in Cameroon to over 6% in Burundi.UNESCO. (2012). ''Education for All Global Monitoring Report 2012 – Youth and Skills: Putting Education to Work.'' Luxembourg: UNESCO Publications.
As of 2015, governments in sub-Saharan Africa spend on average 18% of their total budget on education, against 15% in the rest of the world. In the years immediately after the Dakar Forum, the efforts made by the African States towards achieving Education For All, EFA produced multiple results in sub-Saharan Africa. The greatest advance was in access to primary education, which governments had made their absolute priority. The number of children in a primary school in sub-Saharan Africa thus rose from 82 million in 1999 to 136.4 million in 2011. In Niger, for example, the number of children entering school increased by more than three-and-a-half times between 1999 and 2011. In Ethiopia, over the same period, over 8.5 million more children were admitted to primary school. The net rate of first-year access in sub-Saharan Africa has thus risen by 19 points in 12 years, from 58% in 1999 to 77% in 2011. Despite the considerable efforts, the latest available data from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics estimates that, for 2012, there were still 57.8 million children who were not in school. Of these, 29.6 million were in sub-Saharan Africa alone, a figure which has not changed for several years. Many sub-Saharan countries have notably included the first year of secondary school in basic education. In Rwanda, the first year of secondary school was attached to primary education in 2009, which significantly increased the number of pupils enrolled at this level of education. In 2012, the primary completion rate (PCR) – which measures the proportion of children reaching the final year of primary school – was 70%, meaning that more than three out of ten children entering primary school do not reach the final primary year. Literacy rates have gone up in sub-Saharan Africa, and internet access has improved considerably. Nonetheless, a lot must yet happen for this world to catch up. The statistics show that the literacy rate for sub-Saharan Africa was 65% in 2017. In other words, one-third of the people aged 15 and above were unable to read and write. The comparative figure for 1984 was an illiteracy rate of 49%. In 2017, only about 22% of Africans were internet users at all, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Science and technology
Health
 In 1987, the Bamako Initiative conference organized by the World Health Organization was held in Bamako, the capital of
In 1987, the Bamako Initiative conference organized by the World Health Organization was held in Bamako, the capital of Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mal ...
, and helped reshape the health policy of sub-Saharan Africa. The new strategy dramatically increased accessibility through community-based healthcare reform, resulting in more efficient and equitable provision of services. A comprehensive approach strategy was extended to all areas of health care, with subsequent improvement in the health care indicators and improvement in health care efficiency and cost.
In 2011, sub-Saharan Africa was home to 69% of all people living with HIV/AIDS worldwide. In response, a number of initiatives have been launched to educate the public on HIV/AIDS. Among these are combination prevention programmes, considered to be the most effective initiative, the abstinence, be faithful, use a condom campaign, and the Desmond Tutu HIV Foundation's outreach programs. According to a 2013 special report issued by the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), the number of HIV positive people in Africa receiving anti-retro viral treatment in 2012 was over seven times the number receiving treatment in 2005, with an almost 1 million added in the last year alone. The number of AIDS-related deaths in sub-Saharan Africa in 2011 was 33 percent less than the number in 2005. The number of new HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa in 2011 was 25 percent less than the number in 2001.
Life expectancy at birth in sub-Saharan Africa increased from 40 years in 1960 to 61 years in 2017.
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
, most health care is provided by the government and largely administered by the Ministry of Health, Ghana, Ministry of Health and Ghana Health Services. The healthcare system has five levels of providers: health posts which are first-level primary care for rural areas, health centers and clinics, district hospitals, regional hospitals, and tertiary hospitals. These programs are funded by the government of Ghana, financial credits, Internally Generated Fund (IGF), and Donors-pooled Health Fund.
Religion
African countries below the Sahara are largely Christianity, Christian, while those above the Sahara, inNorth Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, are predominantly Islamic. There are also Muslim majorities in parts of the Horn of Africa (Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
and Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
) and in the Sahel and Sudan regions (the Gambia, Sierra Leone, Guinea, Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mal ...
, Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesEthiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and Eritrea, and on the Swahili Coast (Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
and Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
). Mauritius is the only country in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
to have a Hindu majority. In 2012, sub-Saharan Africa constituted in absolute terms the third Christianity by country, world's largest Christian population, after Europe and Latin America respectively. In 2012, sub-Saharan Africa also constitute in absolute terms the third Islam by country, world's largest Muslim population, after Asia and the Middle East and North Africa respectively.
Traditional African religions can be broken down into linguistic cultural groups, with common themes. Among Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo-speakers is a belief in a creator god or higher deity, along with ancestor spirits, territorial spirits, evil caused by human ill will and neglecting ancestor spirits, and priests of territorial spirits. New world religions such as Santería, West African Vodun, Vodun, and Candomblé, would be derived from this world. Among Nilo-Saharan speakers is the belief in Divinity; evil is caused by divine judgement and retribution; prophets as middlemen between Divinity and man. Among Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic-speakers is henotheism, the belief in one's own gods but accepting the existence of other gods; evil here is caused by malevolent spirits. The Semitic Abrahamic religion of Judaism is comparable to the latter world view. San religion is non-theistic but a belief in a Spirit or Power of existence which can be tapped in a trance-dance; trance-healers.
Generally, traditional African religions are united by an ancient complex animism and ancestor worship.
Traditional religions in sub-Saharan Africa often display complex ontology, cosmology and metaphysics. Mythologies, for example, demonstrated the difficulty fathers of creation had in bringing about order from chaos. Order is what is right and natural and any deviation is chaos. Cosmology and ontology is also neither simple or linear. It defines duality, the material and immaterial, male and female, heaven and earth. Common principles of being and becoming are widespread: Among the Dogon, the principle of ''Amma'' (being) and ''Nummo'' (becoming), and among the Bambara, ''Pemba'' (being) and ''Faro'' (becoming).
;West Africa
* Akan mythology
* Ashanti mythology (Ghana)
* Dahomey mythology, Dahomey (Fon) mythology
* Efik mythology (Nigeria, Cameroon)
* Igbo mythology (Nigeria)
* Serer religion and Serer creation myth (Senegal, Gambia and Mauritania)
* Yoruba mythology (Nigeria, Benin)
;Central Africa
* Dinka mythology (South Sudan)
* Lotuko mythology (South Sudan)
* Bushongo mythology (Congo)
* Bambuti mythology, Bambuti (Pygmy) mythology (Congo)
* Lugbara mythology (Congo)
;Southeast Africa
* Akamba mythology (eastern Kenya)
* Masai mythology (Kenya, Tanzania)
;Southern Africa
* Khoisan religion
* Lozi mythology (Zambia)
* Tumbuka mythology (Malawi)
* Zulu mythology (South Africa)
Sub-Saharan traditional divination systems display great sophistication. For example, the bamana sand divination uses well established symbolic codes that can be reproduced using four bits or marks. A binary system of one or two marks are combined. Random outcomes are generated using a fractal recursive process. It is analogous to a digital circuit but can be reproduced on any surface with one or two marks. This system is widespread in sub-Saharan Africa.
Culture
Sub-Saharan Africa is diverse, with many communities, villages, and cities, each with their own beliefs and traditions. Traditional African Societies are communal, they believe that the needs of the many far outweigh an individual needs and achievements. Basically, an individual's keep must be shared with other extended family members. Extended families are made up of various individuals and families who have shared responsibilities within the community. This extended family is one of the core aspects of every African community. "An African will refer to an older person as auntie or uncle. Siblings of parents will be called father or mother rather than uncle and aunt. Cousins will be called brother or sister". This system can be very difficult for outsiders to understand; however, it is no less important. "Also reflecting their communal ethic, Africans are reluctant to stand out in a crowd or to appear different from their neighbors or colleagues, a result of social pressure to avoid offense to group standards and traditions." Women also have a very important role in African culture because they take care of the house and children. Traditionally, in many cultures "men do the heavy work of clearing and plowing the land, women sow the seeds, tend the fields, harvest the crops, haul the water, and bear the major burden for growing the family's food". Despite their work in the fields, women are expected to be subservient to men in some African cultures. "When young women migrate to cities, this imbalance between the sexes, as well as financial need, often causes young women of lower economic status, who lack education and job training, to have sexual relationships with older men who are established in their work or profession and can afford to support a girlfriend or two".Art
 The oldest abstract art in the world is a shell necklace, dated to 82,000 years, in the Cave of Pigeons in Taforalt, eastern Morocco. The second-oldest abstract form of art, and the oldest rock art, is found in the Blombos Cave at the Cape in South Africa, dated 77,000 years. Sub-Saharan Africa has some of the oldest and most varied style of rock art in the world.
Although sub-Saharan African art is very diverse, there are some common themes. One is the use of the human figure. Second, there is a preference for sculpture. Sub-Saharan African art is meant to be experienced in three dimensions, not two. A house is meant to be experienced from all angles. Third, art is meant to be performed. Sub-Saharan Africans have a specific name for masks. The name incorporates the sculpture, the dance, and the spirit that incorporates the mask. The name denotes all three elements. Fourth, art that serves a practical function. The artist and craftsman are not separate. A sculpture shaped like a hand can be used as a stool. Fifth, the use of fractals or non-linear scaling. The shape of the whole is the shape of the parts at different scales. Before the discovery of fractal geometry], Leopold Sedar Senghor, Senegal's first president, referred to this as "dynamic symmetry". William Buller Fagg, William Fagg, a British art historian, has compared it to the logarithmic mapping of natural growth by biologist D'Arcy Thompson. Lastly, sub-Saharan African art is visually abstract, instead of naturalistic. Sub-Saharan African art represents spiritual notions, social norms, ideas, values, etc. An artist might exaggerate the head of a sculpture in relation to the body not because he does not know anatomy but because he wants to illustrate that the head is the seat of knowledge and wisdom. The visual abstraction of African art was very influential in the works o
The oldest abstract art in the world is a shell necklace, dated to 82,000 years, in the Cave of Pigeons in Taforalt, eastern Morocco. The second-oldest abstract form of art, and the oldest rock art, is found in the Blombos Cave at the Cape in South Africa, dated 77,000 years. Sub-Saharan Africa has some of the oldest and most varied style of rock art in the world.
Although sub-Saharan African art is very diverse, there are some common themes. One is the use of the human figure. Second, there is a preference for sculpture. Sub-Saharan African art is meant to be experienced in three dimensions, not two. A house is meant to be experienced from all angles. Third, art is meant to be performed. Sub-Saharan Africans have a specific name for masks. The name incorporates the sculpture, the dance, and the spirit that incorporates the mask. The name denotes all three elements. Fourth, art that serves a practical function. The artist and craftsman are not separate. A sculpture shaped like a hand can be used as a stool. Fifth, the use of fractals or non-linear scaling. The shape of the whole is the shape of the parts at different scales. Before the discovery of fractal geometry], Leopold Sedar Senghor, Senegal's first president, referred to this as "dynamic symmetry". William Buller Fagg, William Fagg, a British art historian, has compared it to the logarithmic mapping of natural growth by biologist D'Arcy Thompson. Lastly, sub-Saharan African art is visually abstract, instead of naturalistic. Sub-Saharan African art represents spiritual notions, social norms, ideas, values, etc. An artist might exaggerate the head of a sculpture in relation to the body not because he does not know anatomy but because he wants to illustrate that the head is the seat of knowledge and wisdom. The visual abstraction of African art was very influential in the works omodernist
artist like Pablo Picasso, Henri Matisse, and Jacques Lipchitz.
Architecture
Music
 Traditional sub-Saharan African music is as diverse as the region's various populations. The common perception of sub-Saharan African music is that it is rhythmic music centered around the drums. This is partially true. A large part of sub-Saharan music, mainly among speakers of Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan languages, is rhythmic and centered around the drum. Sub-Saharan music is polyrhythmic, usually consisting of multiple rhythms in one composition. Dance involves moving multiple body parts. These aspects of sub-Saharan music has been transferred to the new world by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans and can be seen in its influence on music forms as samba, jazz, rhythm and blues, rock and roll, salsa music, salsa, reggae and rap music.Bowden, Rob(2007). Africa South of the Sahara. Coughlan Publishing: p. 40, .
But sub-Saharan music involves a lot of music with strings, horns, and very little poly-rhythms. Music from the eastern sahel and along the nile, among the Nilo-Saharan, made extensive use of strings and horns in ancient times. Among the Afro-Asiatics of Horn of Africa, Northeast Africa, we see extensive use of Music of Ethiopia, string instruments and the pentatonic scale. Dancing involve swaying body movements and footwork. Among the San people, San is extensive use of string instruments with emphasis on footwork.
Modern sub-Saharan African music has been influence by music from the New World (Jazz, Salsa, Rhythm and Blues etc.) vice versa being influenced by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans. Popular styles are Mbalax in Senegal and Gambia, Highlife in
Traditional sub-Saharan African music is as diverse as the region's various populations. The common perception of sub-Saharan African music is that it is rhythmic music centered around the drums. This is partially true. A large part of sub-Saharan music, mainly among speakers of Niger–Congo and Nilo-Saharan languages, is rhythmic and centered around the drum. Sub-Saharan music is polyrhythmic, usually consisting of multiple rhythms in one composition. Dance involves moving multiple body parts. These aspects of sub-Saharan music has been transferred to the new world by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans and can be seen in its influence on music forms as samba, jazz, rhythm and blues, rock and roll, salsa music, salsa, reggae and rap music.Bowden, Rob(2007). Africa South of the Sahara. Coughlan Publishing: p. 40, .
But sub-Saharan music involves a lot of music with strings, horns, and very little poly-rhythms. Music from the eastern sahel and along the nile, among the Nilo-Saharan, made extensive use of strings and horns in ancient times. Among the Afro-Asiatics of Horn of Africa, Northeast Africa, we see extensive use of Music of Ethiopia, string instruments and the pentatonic scale. Dancing involve swaying body movements and footwork. Among the San people, San is extensive use of string instruments with emphasis on footwork.
Modern sub-Saharan African music has been influence by music from the New World (Jazz, Salsa, Rhythm and Blues etc.) vice versa being influenced by enslaved sub-Saharan Africans. Popular styles are Mbalax in Senegal and Gambia, Highlife in Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
, Zoblazo in Ivory Coast, Makossa in Cameroon, Soukous in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Kizomba in Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
, and Mbaqanga in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
. New World styles like Salsa, R&B/Rap, Reggae, and Zouk also have widespread popularity.
Cuisine
 African cuisine, Sub-Saharan African cuisine is very diverse. A lot of regional overlapping occurs, but there are dominant elements region by region.
West African cuisine can be described as starchy, flavorfully spicey. Dishes include fufu, kenkey, couscous, garri, foutou, and banku. Ingredients are of native starchy tubers, Yam (vegetable), yams, Eddoe, cocoyams, and cassava. Grains include millet, sorghum, and rice, usually in the Sahel, are incorporated. Oils include palm oil and shea butter (Sahel). One finds recipes that mix fish and meat. Beverages are palm wine(sweet or sour) and millet beer. Roasting, baking, boiling, frying, mashing, and spicing are all cooking techniques.
African cuisine, Sub-Saharan African cuisine is very diverse. A lot of regional overlapping occurs, but there are dominant elements region by region.
West African cuisine can be described as starchy, flavorfully spicey. Dishes include fufu, kenkey, couscous, garri, foutou, and banku. Ingredients are of native starchy tubers, Yam (vegetable), yams, Eddoe, cocoyams, and cassava. Grains include millet, sorghum, and rice, usually in the Sahel, are incorporated. Oils include palm oil and shea butter (Sahel). One finds recipes that mix fish and meat. Beverages are palm wine(sweet or sour) and millet beer. Roasting, baking, boiling, frying, mashing, and spicing are all cooking techniques.
 Southeast African cuisine especially those of the Swahili people, Swahilis reflects its Islamic, geographical Indian Ocean cultural links. Dishes include ugali, sukuma wiki, and halva. Spices such as curry, saffron, cloves, cinnamon, pomegranate juice, cardamon, ghee, and sage are used, especially among Muslims. Meat includes cattle, sheep, and goats, but is rarely eaten since its viewed as currency and wealth.
In the Horn of Africa, pork and non-fish seafood are avoided by Christians and Muslims. Dairy products and all meats are avoided during lent by Ethiopians. Maize (corn) is a major staple. Cornmeal is used to make ugali, a popular dish with different names. Teff is used to make injera or canjeero (Somali) bread. Other important foods include enset, noog, lentils, rice, banana, leafy greens, chiles, peppers, coconut milk, and tomatoes. Beverages are coffee (domesticated in Ethiopia), chai tea, fermented beer from banana or millet. Cooking techniques include roasting and marinating.
Southeast African cuisine especially those of the Swahili people, Swahilis reflects its Islamic, geographical Indian Ocean cultural links. Dishes include ugali, sukuma wiki, and halva. Spices such as curry, saffron, cloves, cinnamon, pomegranate juice, cardamon, ghee, and sage are used, especially among Muslims. Meat includes cattle, sheep, and goats, but is rarely eaten since its viewed as currency and wealth.
In the Horn of Africa, pork and non-fish seafood are avoided by Christians and Muslims. Dairy products and all meats are avoided during lent by Ethiopians. Maize (corn) is a major staple. Cornmeal is used to make ugali, a popular dish with different names. Teff is used to make injera or canjeero (Somali) bread. Other important foods include enset, noog, lentils, rice, banana, leafy greens, chiles, peppers, coconut milk, and tomatoes. Beverages are coffee (domesticated in Ethiopia), chai tea, fermented beer from banana or millet. Cooking techniques include roasting and marinating.
 Central African cuisine connects with all major regions of sub-Saharan Africa: Its cuisine reflects that. Ugali and fufu are eaten in the region. Central African cuisine is very starchy and spicy hot. Dominant crops include plantains, cassava, peanuts, chillis, and okra. Meats include beef, chicken, and sometimes exotic meats called bush meat (antelope, warthog, crocodile). Widespread spicy hot fish cuisine is one of the differentiating aspects. Mushroom is sometimes used as a meat substitute.
Traditional Southern African cuisine surrounds meat. Traditional society typically focused on raising, sheep, goats, and especially cattle. Dishes include braai (barbecue meat), sadza, bogobe, pap (food), pap (fermented cornmeal), milk products (buttermilk, yoghurt). Crops utilised are sorghum, maize (corn), pumpkin beans, leafy greens, and cabbage. Beverages include ting (fermented sorghum or maize), milk, chibuku (milky beer). Influences from the Indian and Malay communities can be seen in its use of curries, sambals, pickled fish, fish stews, chutney, and samosa. European influences can be seen in cuisines like biltong (dried beef strips), potjies (stews of maize, onions, tomatoes), French wines, and crueler or koeksister (sugar syrup cookie).
Central African cuisine connects with all major regions of sub-Saharan Africa: Its cuisine reflects that. Ugali and fufu are eaten in the region. Central African cuisine is very starchy and spicy hot. Dominant crops include plantains, cassava, peanuts, chillis, and okra. Meats include beef, chicken, and sometimes exotic meats called bush meat (antelope, warthog, crocodile). Widespread spicy hot fish cuisine is one of the differentiating aspects. Mushroom is sometimes used as a meat substitute.
Traditional Southern African cuisine surrounds meat. Traditional society typically focused on raising, sheep, goats, and especially cattle. Dishes include braai (barbecue meat), sadza, bogobe, pap (food), pap (fermented cornmeal), milk products (buttermilk, yoghurt). Crops utilised are sorghum, maize (corn), pumpkin beans, leafy greens, and cabbage. Beverages include ting (fermented sorghum or maize), milk, chibuku (milky beer). Influences from the Indian and Malay communities can be seen in its use of curries, sambals, pickled fish, fish stews, chutney, and samosa. European influences can be seen in cuisines like biltong (dried beef strips), potjies (stews of maize, onions, tomatoes), French wines, and crueler or koeksister (sugar syrup cookie).
Clothing
 Like most of the world, sub-Saharan Africans have adopted Western-style clothing. In some country like Zambia, used Western clothing has flooded markets, causing great angst in the retail community. Sub-Saharan Africa boasts its own traditiona
Like most of the world, sub-Saharan Africans have adopted Western-style clothing. In some country like Zambia, used Western clothing has flooded markets, causing great angst in the retail community. Sub-Saharan Africa boasts its own traditionaclothing style
Cotton seems to be the dominant material. In East Africa, one finds extensive use of cotton clothing. Shemma, shama, and kuta are types of Ethiopian clothing. Kanga (African garment), Kanga are Swahili culture, Swahili cloth that comes in rectangular shapes, made of pure cotton, and put together to make clothing. Kitenges are similar to kangas and kikoy, but are of a thicker cloth, and have an edging only on a long side.
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
, Uganda, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, and South Sudan are some of the African countries where kitenge is worn. In Malawi, Namibia and Zambia, kitenge is known as Chitenge. One of the unique materials, which is not a fiber and is used to make clothing is barkcloth, an innovation of the Baganda people of Uganda. It came from the Mutuba tree (Ficus natalensis). On Madagascar a type of draped cloth called Lamba (garment), lamba is worn.
 In West Africa, again cotton is the material of choice. In the Sahel and other parts of West Africa the boubou (clothing), boubou and kaftan style of clothing are featured. Kente cloth is created by the Akan people of Ghana and Ivory Coast, from silk of the various moth species in West Africa. Kente comes from the Akan language, Akan twi word ''kenten'' which means basket. It is sometimes used to make dashiki and kufi. Adire is a type of Yoruba cloth that is starch resistant. Raffia cloth and barkcloth are also utilised in the region.
In Central Africa, the Kuba people developed raffia cloth from the raffia plant fibers. It was widely used in the region. Barkcloth was also extensively used.
In Southern Africa one finds numerous uses of animal hide and skins for clothing. The Ndau in central Mozambique and the Shona mix hide with barkcloth and cotton cloth. Cotton cloth is referred to as machira. Xhosa, Tswana, Sotho, and Swazi also made extensive use of hides. Hides come from cattle, sheep, goat, and elephant. Leopard skins were coveted and were a symbol of kingship in Zulu society. Skins were tanned to form leather, dyed, and embedded with beads.
In West Africa, again cotton is the material of choice. In the Sahel and other parts of West Africa the boubou (clothing), boubou and kaftan style of clothing are featured. Kente cloth is created by the Akan people of Ghana and Ivory Coast, from silk of the various moth species in West Africa. Kente comes from the Akan language, Akan twi word ''kenten'' which means basket. It is sometimes used to make dashiki and kufi. Adire is a type of Yoruba cloth that is starch resistant. Raffia cloth and barkcloth are also utilised in the region.
In Central Africa, the Kuba people developed raffia cloth from the raffia plant fibers. It was widely used in the region. Barkcloth was also extensively used.
In Southern Africa one finds numerous uses of animal hide and skins for clothing. The Ndau in central Mozambique and the Shona mix hide with barkcloth and cotton cloth. Cotton cloth is referred to as machira. Xhosa, Tswana, Sotho, and Swazi also made extensive use of hides. Hides come from cattle, sheep, goat, and elephant. Leopard skins were coveted and were a symbol of kingship in Zulu society. Skins were tanned to form leather, dyed, and embedded with beads.
Theater
Film industry
Games
Sports
 Rugby union, Rugby is also popular in sub-Saharan Africa. The Confederation of African Rugby governs rugby games in the region. South Africa is a major force in the game and won the Rugby World Cup in 1995 Rugby World Cup, 1995, 2007 Rugby World Cup, 2007 and 2019 Rugby World Cup, 2019. Africa is also allotted one guaranteed qualifying place in the Rugby World Cup.
Boxing is also a popular sport. Battling Siki the first world champion to come out of sub-Saharan Africa. Countries such as Nigeria, Ghana and South Africa have produced numerous professional world champions such as Dick Tiger, Hogan Bassey, Gerrie Coetzee, Samuel Peter, Azumah Nelson and Jake Matlala.
Cricket has a following. The African Cricket Association is an international body which oversees cricket in African countries. South Africa and Zimbabwe have their own governing bodies. In 2003 the Cricket World Cup was held in South Africa, first time it was held in sub-Saharan Africa.
Over the years,
Rugby union, Rugby is also popular in sub-Saharan Africa. The Confederation of African Rugby governs rugby games in the region. South Africa is a major force in the game and won the Rugby World Cup in 1995 Rugby World Cup, 1995, 2007 Rugby World Cup, 2007 and 2019 Rugby World Cup, 2019. Africa is also allotted one guaranteed qualifying place in the Rugby World Cup.
Boxing is also a popular sport. Battling Siki the first world champion to come out of sub-Saharan Africa. Countries such as Nigeria, Ghana and South Africa have produced numerous professional world champions such as Dick Tiger, Hogan Bassey, Gerrie Coetzee, Samuel Peter, Azumah Nelson and Jake Matlala.
Cricket has a following. The African Cricket Association is an international body which oversees cricket in African countries. South Africa and Zimbabwe have their own governing bodies. In 2003 the Cricket World Cup was held in South Africa, first time it was held in sub-Saharan Africa.
Over the years, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
have produced many notable long-distance athletes. Each country has federations that identify and cultivate top talent. Athletes from Ethiopia and Kenya hold, save for two exceptions, all the men's outdoor records for Olympic distance events from 800m to the marathon. Famous runners include Haile Gebrselassie, Kenenisa Bekele, Paul Tergat, and John Cheruiyot Korir.
Tourism
The development of tourism in this region has been identified as having the ability to create jobs and improve the economy. South Africa, Namibia, Mauritius, Botswana, Ghana, Cape Verde, Tanzania and Kenya have been identified as having well developed tourism industries. Cape Town and the surrounding area is very popular with tourists.List of countries and regional organisation
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, Western Sahara (claimed by Morocco) and Sudan; they form the UN subregion of Northern Africa, which also makes up the largest bloc of the Arab World. Nevertheless, some international organisations include Sudan as part of sub-Saharan Africa. Although a long-standing member of the Arab League, Sudan has around 30% non-Arab populations in the west (Darfur, Masalit people, Masalit, Zaghawa people, Zaghawa), far north (Nubian people, Nubian) and south (Kordofan, Nuba). Mauritania and Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages
* ''cap.'' Juba ''cur.'' South Sudanese pound (£) ''lang.'' English
; ECCAS (Economic Community of Central African States)
* (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Luanda ''cur.'' Angolan kwanza (Kz) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* (also in EAC) ''cap.'' Gitega (former Bujumbura) ''cur.'' Burundian franc (FBu) ''lang.'' French
* (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Kinshasa ''cur.'' Congolese franc (FC) ''lang.'' French
* (also in EAC) ''cap.'' Kigali ''cur.'' Rwandan franc (RF) ''lang.'' Kinyarwanda, French, English
* ''cap.'' São Tomé ''cur.'' São Tomé and Príncipe dobra (Db) ''lang.'' Portuguese
;CEMAC (Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa)
* ''cap.'' Yaoundé ''cur.'' Central African CFA franc (FCFA) ''lang.'' English, French
* ''cap.'' Bangui ''cur.'' Central African CFA franc (FCFA) ''lang.'' Sango language, Sango, French
* ''cap.'' N'Djamena ''cur.'' Central African CFA franc (FCFA) ''lang.'' French, Arabic
* ''cap.'' Brazzaville ''cur.'' Central African CFA franc (FCFA) ''lang.'' French
* ''cap.'' Malabo ''cur.'' Central African CFA franc (FCFA) ''lang.'' Spanish, French
* ''cap.'' Libreville ''cur.'' Central African CFA franc (FCFA) ''lang.'' French
 * ''cap.'' Khartoum ''cur.'' Sudanese pound (£S.) ''lang.'' Arabic (Sudanese Arabic) and English language, English
* ''cap.'' Juba ''cur.'' South Sudanese pound (£) ''lang.'' English language, English and Arabic (Juba Arabic)
* ''cap.'' Mogadishu ''cur.'' Somali shilling (So.Sh /-) ''lang.'' Somali language, Somali, Arabic (official)
* ''cap.'' Nairobi ''cur.'' Kenyan shilling (KSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* ''cap.'' Kampala ''cur.'' Ugandan shilling (USh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Kigali ''cur.'' Rwandan franc (RF) ''lang.'' Kinyarwanda, French, English
* (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Dodoma ''cur.'' Tanzanian shilling (TSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Gitega (former Bujumbura) ''cur.'' Burundian franc (FBu) ''lang.'' Kirundi, French
* ''cap.'' Asmara ''cur.'' Eritrean nakfa (Nfk) '
* ''cap.'' Khartoum ''cur.'' Sudanese pound (£S.) ''lang.'' Arabic (Sudanese Arabic) and English language, English
* ''cap.'' Juba ''cur.'' South Sudanese pound (£) ''lang.'' English language, English and Arabic (Juba Arabic)
* ''cap.'' Mogadishu ''cur.'' Somali shilling (So.Sh /-) ''lang.'' Somali language, Somali, Arabic (official)
* ''cap.'' Nairobi ''cur.'' Kenyan shilling (KSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* ''cap.'' Kampala ''cur.'' Ugandan shilling (USh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Kigali ''cur.'' Rwandan franc (RF) ''lang.'' Kinyarwanda, French, English
* (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Dodoma ''cur.'' Tanzanian shilling (TSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Gitega (former Bujumbura) ''cur.'' Burundian franc (FBu) ''lang.'' Kirundi, French
* ''cap.'' Asmara ''cur.'' Eritrean nakfa (Nfk) '
 ;SADC (Southern African Development Community)
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Luanda ''cur.'' Angolan kwanza (Kz) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Gaborone ''cur.'' Botswana pula (P) ''lang.'' Tswana language, Tswana, English
* ''cap.'' Moroni, Comoros, Moroni ''cur.'' Comorian franc (FC) ''lang.'' Comorian language, Comorian, Arabic, French
* ''cap.'' Mbabane ''cur.'' Swazi lilangeni (L)(E) ''lang.'' SiSwati, English
* ''cap.'' Maseru ''cur.'' Lesotho loti (L)(M) ''lang.'' Sesotho, English
* ''cap.'' Antananarivo ''cur.'' Malagasy ariary (Ar.) ''lang.'' Malagasy language, Malagasy, French
* ''cap.'' Lilongwe ''cur.'' Malawian kwacha (MK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Port Louis ''cur.'' Mauritian rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Maputo ''cur.'' Mozambican metical (MTn) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Windhoek ''cur.'' Namibian dollar (N$) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Victoria, Seychelles, Victoria ''cur.'' Seychellois rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' Seychellois Creole, English, French
* ''cap.'' Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria ''cur.'' South African rand (R) ''lang.'' South Africa, 11 official languages
* ''cap.'' Lusaka ''cur.'' Zambian kwacha (ZK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Harare ''cur.'' Zimbabwean dollar ($) ''lang.'' English
;SADC (Southern African Development Community)
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Luanda ''cur.'' Angolan kwanza (Kz) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Gaborone ''cur.'' Botswana pula (P) ''lang.'' Tswana language, Tswana, English
* ''cap.'' Moroni, Comoros, Moroni ''cur.'' Comorian franc (FC) ''lang.'' Comorian language, Comorian, Arabic, French
* ''cap.'' Mbabane ''cur.'' Swazi lilangeni (L)(E) ''lang.'' SiSwati, English
* ''cap.'' Maseru ''cur.'' Lesotho loti (L)(M) ''lang.'' Sesotho, English
* ''cap.'' Antananarivo ''cur.'' Malagasy ariary (Ar.) ''lang.'' Malagasy language, Malagasy, French
* ''cap.'' Lilongwe ''cur.'' Malawian kwacha (MK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Port Louis ''cur.'' Mauritian rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Maputo ''cur.'' Mozambican metical (MTn) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Windhoek ''cur.'' Namibian dollar (N$) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Victoria, Seychelles, Victoria ''cur.'' Seychellois rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' Seychellois Creole, English, French
* ''cap.'' Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria ''cur.'' South African rand (R) ''lang.'' South Africa, 11 official languages
* ''cap.'' Lusaka ''cur.'' Zambian kwacha (ZK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Harare ''cur.'' Zimbabwean dollar ($) ''lang.'' English
 ;ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States)
* ''cap.'' Yamoussoukro, Abidjan ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Banjul ''cur.'' Gambian dalasi (D)
* ''cap.'' Accra ''cur.'' Ghanaian cedi (GH₵)
* ''cap.'' Conakry ''cur.'' Guinean franc (FG)
* ''cap.'' Monrovia ''cur.'' Liberian dollar (L$)
* ''cap.'' Nouakchott ''cur.'' Mauritanian ouguiya (UM)(sometimes, like Sudan, considered part of
;ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States)
* ''cap.'' Yamoussoukro, Abidjan ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Banjul ''cur.'' Gambian dalasi (D)
* ''cap.'' Accra ''cur.'' Ghanaian cedi (GH₵)
* ''cap.'' Conakry ''cur.'' Guinean franc (FG)
* ''cap.'' Monrovia ''cur.'' Liberian dollar (L$)
* ''cap.'' Nouakchott ''cur.'' Mauritanian ouguiya (UM)(sometimes, like Sudan, considered part of
From Chaos to Cohesion: A Regional Approach to Security, Stability, and Development in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Carlisle, Pa.: Strategic Studies Institute and U.S. Army War College Press, 2013. * Wm. Roger Louis and Jean Stengers: ''E.D. Morel's History of the Congo Reform Movement'', Clarendon Press Oxford, 1968.
African People website
(archived)
The Story of Africa
– BBC World Service {{Authority control Sub-Saharan Africa, Geography of Africa Historical regions Regions of Africa
East Africa
 * ''cap.'' Khartoum ''cur.'' Sudanese pound (£S.) ''lang.'' Arabic (Sudanese Arabic) and English language, English
* ''cap.'' Juba ''cur.'' South Sudanese pound (£) ''lang.'' English language, English and Arabic (Juba Arabic)
* ''cap.'' Mogadishu ''cur.'' Somali shilling (So.Sh /-) ''lang.'' Somali language, Somali, Arabic (official)
* ''cap.'' Nairobi ''cur.'' Kenyan shilling (KSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* ''cap.'' Kampala ''cur.'' Ugandan shilling (USh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Kigali ''cur.'' Rwandan franc (RF) ''lang.'' Kinyarwanda, French, English
* (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Dodoma ''cur.'' Tanzanian shilling (TSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Gitega (former Bujumbura) ''cur.'' Burundian franc (FBu) ''lang.'' Kirundi, French
* ''cap.'' Asmara ''cur.'' Eritrean nakfa (Nfk) '
* ''cap.'' Khartoum ''cur.'' Sudanese pound (£S.) ''lang.'' Arabic (Sudanese Arabic) and English language, English
* ''cap.'' Juba ''cur.'' South Sudanese pound (£) ''lang.'' English language, English and Arabic (Juba Arabic)
* ''cap.'' Mogadishu ''cur.'' Somali shilling (So.Sh /-) ''lang.'' Somali language, Somali, Arabic (official)
* ''cap.'' Nairobi ''cur.'' Kenyan shilling (KSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* ''cap.'' Kampala ''cur.'' Ugandan shilling (USh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Kigali ''cur.'' Rwandan franc (RF) ''lang.'' Kinyarwanda, French, English
* (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Dodoma ''cur.'' Tanzanian shilling (TSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Gitega (former Bujumbura) ''cur.'' Burundian franc (FBu) ''lang.'' Kirundi, French
* ''cap.'' Asmara ''cur.'' Eritrean nakfa (Nfk) 'Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
''cur.'' Djiboutian franc (Fdj) ''lang.'' Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, French language, French (official)
Northeast Africa
* Horn of Africa ** ''cap.''Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
''cur.'' Djiboutian franc (Fdj) ''lang.'' Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, French language, French (official)
** ''cap.'' Asmara ''cur.'' Eritrean nakfa (Nfk) 'Southeast Africa
;EAC * (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Gitega (former Bujumbura) ''cur.'' Burundian franc (FBu) ''lang.'' Kirundi, French * ''cap.'' Nairobi ''cur.'' Kenyan shilling (KSh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English * (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Kigali ''cur.'' Rwandan franc (RF) ''lang.'' Kinyarwanda, French, English * (also in SADC) ''cap.'' Dodoma ''cur.'' Tanzanian shilling (TSh. /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, English * ''cap.'' Kampala ''cur.'' Ugandan shilling (USh /=) ''lang.'' Swahili culture, Swahili, EnglishSouthern Africa
 ;SADC (Southern African Development Community)
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Luanda ''cur.'' Angolan kwanza (Kz) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Gaborone ''cur.'' Botswana pula (P) ''lang.'' Tswana language, Tswana, English
* ''cap.'' Moroni, Comoros, Moroni ''cur.'' Comorian franc (FC) ''lang.'' Comorian language, Comorian, Arabic, French
* ''cap.'' Mbabane ''cur.'' Swazi lilangeni (L)(E) ''lang.'' SiSwati, English
* ''cap.'' Maseru ''cur.'' Lesotho loti (L)(M) ''lang.'' Sesotho, English
* ''cap.'' Antananarivo ''cur.'' Malagasy ariary (Ar.) ''lang.'' Malagasy language, Malagasy, French
* ''cap.'' Lilongwe ''cur.'' Malawian kwacha (MK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Port Louis ''cur.'' Mauritian rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Maputo ''cur.'' Mozambican metical (MTn) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Windhoek ''cur.'' Namibian dollar (N$) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Victoria, Seychelles, Victoria ''cur.'' Seychellois rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' Seychellois Creole, English, French
* ''cap.'' Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria ''cur.'' South African rand (R) ''lang.'' South Africa, 11 official languages
* ''cap.'' Lusaka ''cur.'' Zambian kwacha (ZK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Harare ''cur.'' Zimbabwean dollar ($) ''lang.'' English
;SADC (Southern African Development Community)
* (also in ECCAS) ''cap.'' Luanda ''cur.'' Angolan kwanza (Kz) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Gaborone ''cur.'' Botswana pula (P) ''lang.'' Tswana language, Tswana, English
* ''cap.'' Moroni, Comoros, Moroni ''cur.'' Comorian franc (FC) ''lang.'' Comorian language, Comorian, Arabic, French
* ''cap.'' Mbabane ''cur.'' Swazi lilangeni (L)(E) ''lang.'' SiSwati, English
* ''cap.'' Maseru ''cur.'' Lesotho loti (L)(M) ''lang.'' Sesotho, English
* ''cap.'' Antananarivo ''cur.'' Malagasy ariary (Ar.) ''lang.'' Malagasy language, Malagasy, French
* ''cap.'' Lilongwe ''cur.'' Malawian kwacha (MK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Port Louis ''cur.'' Mauritian rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Maputo ''cur.'' Mozambican metical (MTn) ''lang.'' Portuguese
* ''cap.'' Windhoek ''cur.'' Namibian dollar (N$) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Victoria, Seychelles, Victoria ''cur.'' Seychellois rupee (Re/Rs /-) ''lang.'' Seychellois Creole, English, French
* ''cap.'' Bloemfontein, Cape Town, Pretoria ''cur.'' South African rand (R) ''lang.'' South Africa, 11 official languages
* ''cap.'' Lusaka ''cur.'' Zambian kwacha (ZK) ''lang.'' English
* ''cap.'' Harare ''cur.'' Zimbabwean dollar ($) ''lang.'' English
Sudan
Depending on classification Sudan is often not considered part of sub-Saharan Africa, as it is considered part of North Africa. * ''cap.'' Khartoum ''cur.'' Sudanese pound (SDG) ''lang.'' Arabic and EnglishWest Africa
 ;ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States)
* ''cap.'' Yamoussoukro, Abidjan ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Banjul ''cur.'' Gambian dalasi (D)
* ''cap.'' Accra ''cur.'' Ghanaian cedi (GH₵)
* ''cap.'' Conakry ''cur.'' Guinean franc (FG)
* ''cap.'' Monrovia ''cur.'' Liberian dollar (L$)
* ''cap.'' Nouakchott ''cur.'' Mauritanian ouguiya (UM)(sometimes, like Sudan, considered part of
;ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States)
* ''cap.'' Yamoussoukro, Abidjan ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Banjul ''cur.'' Gambian dalasi (D)
* ''cap.'' Accra ''cur.'' Ghanaian cedi (GH₵)
* ''cap.'' Conakry ''cur.'' Guinean franc (FG)
* ''cap.'' Monrovia ''cur.'' Liberian dollar (L$)
* ''cap.'' Nouakchott ''cur.'' Mauritanian ouguiya (UM)(sometimes, like Sudan, considered part of North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
)
* ''cap.'' Abuja ''cur.'' Nigerian naira (₦)
* ''cap.'' Freetown ''cur.'' Sierra Leonean leone (Le)
;UEMOA (West African Economic and Monetary Union)
* ''cap.'' Porto-Novo ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Ouagadougou ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Yamoussoukro, Abidjan ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Bissau ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Bamako ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Niamey ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Dakar ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
* ''cap.'' Lomé ''cur.'' West African CFA franc (CFA)
See also
* African diaspora * Black people * Geography of Africa * History of AfricaSources
References
Citation
* ''Taking Action to Reduce Poverty in Sub-Saharan Africa'', World Bank Publications (1997), .Further reading
* Chido, Diane EFrom Chaos to Cohesion: A Regional Approach to Security, Stability, and Development in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Carlisle, Pa.: Strategic Studies Institute and U.S. Army War College Press, 2013. * Wm. Roger Louis and Jean Stengers: ''E.D. Morel's History of the Congo Reform Movement'', Clarendon Press Oxford, 1968.
External links
*African People website
(archived)
The Story of Africa
– BBC World Service {{Authority control Sub-Saharan Africa, Geography of Africa Historical regions Regions of Africa