Regional Italian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Regional Italian ( it, italiano regionale) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units.
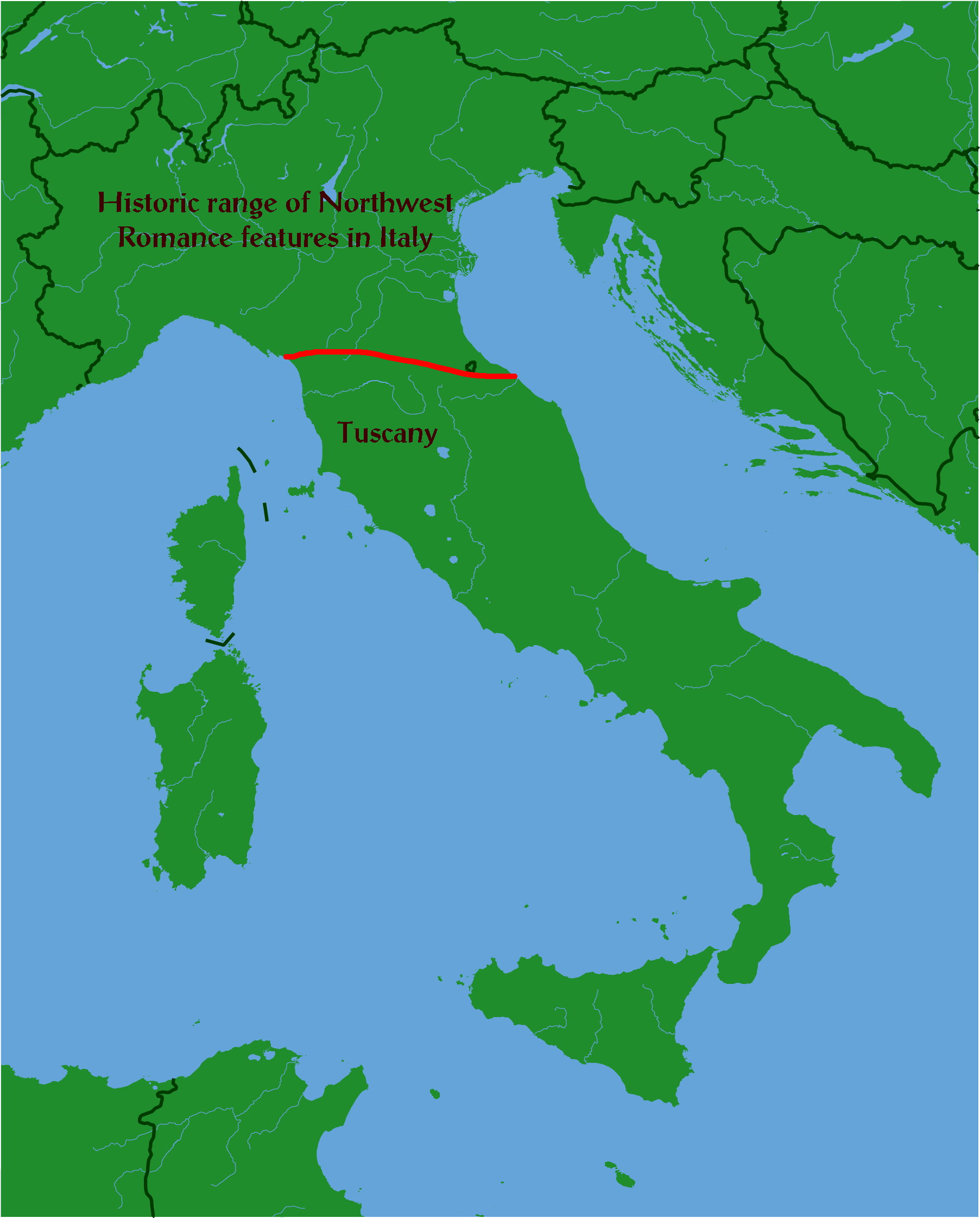 Establishing precise boundaries is very difficult in linguistics, and this operation at the limit can be accomplished for individual phenomena (such as the realization of a sound), but not for all of them: it is necessary to proceed in part by abstractions. In general, an isogloss is an imaginary line that marks the boundary of a linguistic phenomenon. The line traditionally referred to as La Spezia-Rimini (though it is currently moving to the Massa-Senigallia line) is an important isogloss for Southern Europe, which delimits a continuum of languages and dialects characterized by similar phenomena that differ from others for these same phenomena.
This imaginary line is used here to define not only a boundary between dialect groups, but also between Northern regional Italian on the one hand and Central and Southern regional Italian on the other. Other well-defined areas are the Tuscan, the
Establishing precise boundaries is very difficult in linguistics, and this operation at the limit can be accomplished for individual phenomena (such as the realization of a sound), but not for all of them: it is necessary to proceed in part by abstractions. In general, an isogloss is an imaginary line that marks the boundary of a linguistic phenomenon. The line traditionally referred to as La Spezia-Rimini (though it is currently moving to the Massa-Senigallia line) is an important isogloss for Southern Europe, which delimits a continuum of languages and dialects characterized by similar phenomena that differ from others for these same phenomena.
This imaginary line is used here to define not only a boundary between dialect groups, but also between Northern regional Italian on the one hand and Central and Southern regional Italian on the other. Other well-defined areas are the Tuscan, the
variety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of the Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 85 m ...
.
Such vernacular varieties and standard Italian exist along a sociolect continuum, and are not to be confused with the local indigenous languages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance gro ...
Notwithstanding their linguistic status, most of the actual languages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance gro ...
(with particular reference to the non-recognised ones) are called "dialects" () by the general population. that predate the national tongue or any regional variety thereof. Among these languages, the various Tuscan, Corsican and Central Italian lects are, to some extent, the closest ones to standard Italian in terms of linguistic features, since the latter is based on a somewhat polished form of Florentine.
The various forms of Regional Italian have phonological, morphological, syntactic
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), ...
, prosodic
In linguistics, prosody () is concerned with elements of speech that are not individual phonetic segments (vowels and consonants) but are properties of syllables and larger units of speech, including linguistic functions such as intonation, st ...
and lexical
Lexical may refer to:
Linguistics
* Lexical corpus or lexis, a complete set of all words in a language
* Lexical item, a basic unit of lexicographical classification
* Lexicon, the vocabulary of a person, language, or branch of knowledge
* Lex ...
features which originate from the underlying substrate of the original language.
Regional Italian and the languages of Italy
The difference between Regional Italian and the actuallanguages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance gro ...
, often imprecisely referred to as dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety (linguisti ...
s, is exemplified by the following: in Venetian, the language spoken in Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about five million, ranking fourth in Italy. The region's capital is Venice while the biggest city is Verona.
Veneto was part of the Roman Empire unt ...
, "we are arriving" would be translated into , which is quite distinct from the Standard Italian . In the regional Italian of Veneto, the same expression would be ''stémo rivando'' or ''siamo dietro ad arrivare''. The same relationship holds throughout the rest of Italy: the local version of standard Italian is usually influenced by the underlying local language, which can be very different from Italian with regard to phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
, morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
, syntax, and vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the la ...
. Anyone who knows Standard Italian well can usually understand Regional Italian quite well, while not managing to grasp the regional languages.
Origin
Many contemporary Italian regions already had different substrata before the conquest of Italy and the islands by the ancient Romans:Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
had a Ligurian, a Venetic
Venetic is an extinct Indo-European language, usually classified into the Italic subgroup, that was spoken by the Veneti people in ancient times in northeast Italy (Veneto and Friuli) and part of modern Slovenia, between the Po Delta and ...
, and a Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
substratum in the areas once known as ''Gallia Cisalpina'' "Gallia on this side of the Alps"; Central Italy
Central Italy ( it, Italia centrale or just ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first-level NUTS region, and a European Parliament constituency.
Regions
Central I ...
had an Umbrian
Umbrian is an extinct Italic language formerly spoken by the Umbri in the ancient Italian region of Umbria. Within the Italic languages it is closely related to the Oscan group and is therefore associated with it in the group of Osco-Umbrian ...
and Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
substratum; Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the peop ...
and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
had an Oscan
Oscan is an extinct Indo-European language of southern Italy. The language is in the Osco-Umbrian or Sabellic branch of the Italic languages. Oscan is therefore a close relative of Umbrian.
Oscan was spoken by a number of tribes, including ...
and Italic-Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
substratum respectively; and finally, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
had an indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
( Nuragic) and Punic
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of t ...
substratum. These languages in their respective territories contributed in creolising Latin, the official language of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
.
Even though the Sicilian School
The Sicilian School was a small community of Sicilian and mainland Italian poets gathered around Frederick II, most of them belonging to his imperial court. Headed by Giacomo da Lentini, they produced more than 300 poems of courtly love betwe ...
, using the Sicilian language
Sicilian ( scn, sicilianu, link=no, ; it, siciliano) is a Romance language that is spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands. A variant, ''Calabro-Sicilian'', is spoken in southern Calabria, where it is called Southern Calabro ...
, had been prominent earlier, by the 14th century the Tuscan dialect
Tuscan ( it, dialetto toscano ; it, vernacolo, label=locally) is a set of Italo-Dalmatian varieties of Romance mainly spoken in Tuscany, Italy.
Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, specifically on its Florentine dialect, and it became the ...
of Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
had gained prestige once Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: '' ...
, Francesco Petrarca (Petrarch) and Giovanni Boccaccio all wrote major works in it: the Divina Commedia, the Canzoniere
''Il Canzoniere'' (; en, Song Book), also known as the ''Rime Sparse'' ( en, Scattered Rhymes), but originally titled ' ( en, Fragments of common things, that is ''Fragments composed in vernacular''), is a collection of poems by the Italian hum ...
and the Decameron
''The Decameron'' (; it, label=Italian, Decameron or ''Decamerone'' ), subtitled ''Prince Galehaut'' (Old it, Prencipe Galeotto, links=no ) and sometimes nicknamed ''l'Umana commedia'' ("the Human comedy", as it was Boccaccio that dubbed Dan ...
. Italian, defined as such, began to spread and be used as a literary and prestigious means of expression across the whole peninsula, Sicily and Corsica in the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
; on the other hand, it would be introduced to Sardinia by a specific order only in the second half of the 18th century (1760), when the island's ownership passed over to the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
. It was up to Pietro Bembo, a Venetian, to identify Florentine as ''the'' language for the peninsula in the ''Prose nelle quali si ragiona della volgar lingua'' (1525), in which he set up Petrarch as the perfect model. Italian, however, was a literary language and so was a written rather than spoken language, except in Tuscany and Corsica.
The popular diffusion of a unified Italian language was the main goal of Alessandro Manzoni
Alessandro Francesco Tommaso Antonio Manzoni (, , ; 7 March 1785 – 22 May 1873) was an Italian poet, novelist and philosopher. He is famous for the novel '' The Betrothed'' (orig. it, I promessi sposi) (1827), generally ranked among the maste ...
, who advocated for a single national language mainly derived from "cultured" Florentine language. Having lived in Paris for many years, Manzoni had noticed that French (defined as the capital's dialect) was a very lively language, spoken by ordinary people in the city's streets. On the other hand, the only Italian city where even the commoners spoke something similar to literary Italian was Florence, so he thought that Italians should choose Florentine as the basis for the national language.
The Italian Peninsula's history of fragmentation and colonization by foreign powers (especially France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
) between the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
and its unification in 1861 played a considerable role in further jeopardizing the linguistic situation. When the unification process took place, the newly founded country used Italian mainly as a literary language. Many Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
and non-Romance regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
s were spoken throughout the Italian Peninsula and the islands, each with their own local dialects. Following Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
Massimo Taparelli, marquis d'Azeglio, one of Cavour's ministers, is said to have stated that while Italy had been created, Italians were still to be created (that is, a common national identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or to one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language". National identity ...
).
Italian as a spoken language was born in two "linguistic labs" consisting of the metropolitan areas in Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, which functioned as magnets for internal migration. Immigrants were only left with the national language as a lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
to communicate with both the locals and other immigrants. After unification, Italian started to be taught at primary schools and its use by ordinary people increased considerably, along with mass literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, huma ...
. The regional varieties of Italian, as a product of standard Italian mixing with the regional languages, were also born.
The various regional languages
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
would be retained by the population as their normal means of expression until the 1950s, when breakthroughs in literacy and the advent of TV broadcasting made Italian become more and more widespread, usually in its regional varieties.
Characteristics of regional Italian
 Establishing precise boundaries is very difficult in linguistics, and this operation at the limit can be accomplished for individual phenomena (such as the realization of a sound), but not for all of them: it is necessary to proceed in part by abstractions. In general, an isogloss is an imaginary line that marks the boundary of a linguistic phenomenon. The line traditionally referred to as La Spezia-Rimini (though it is currently moving to the Massa-Senigallia line) is an important isogloss for Southern Europe, which delimits a continuum of languages and dialects characterized by similar phenomena that differ from others for these same phenomena.
This imaginary line is used here to define not only a boundary between dialect groups, but also between Northern regional Italian on the one hand and Central and Southern regional Italian on the other. Other well-defined areas are the Tuscan, the
Establishing precise boundaries is very difficult in linguistics, and this operation at the limit can be accomplished for individual phenomena (such as the realization of a sound), but not for all of them: it is necessary to proceed in part by abstractions. In general, an isogloss is an imaginary line that marks the boundary of a linguistic phenomenon. The line traditionally referred to as La Spezia-Rimini (though it is currently moving to the Massa-Senigallia line) is an important isogloss for Southern Europe, which delimits a continuum of languages and dialects characterized by similar phenomena that differ from others for these same phenomena.
This imaginary line is used here to define not only a boundary between dialect groups, but also between Northern regional Italian on the one hand and Central and Southern regional Italian on the other. Other well-defined areas are the Tuscan, the Extreme Southern Italian
The Extreme Southern Italian:According to the classification of Giovan Battista Pellegrini, se dialects are a set of dialects spoken in Salento, Calabria, Sicily and southern Cilento with common phonetic and syntactic characteristics such as to ...
(comprising the peninsular part of Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, Salento
Salento (Salentino: ''Salentu'', Salentino Griko: ''Σαλέντο'') is a cultural, historical and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apulia in Southern Italy. It is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula, ...
and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
), and finally the Sardinian ones.
Based on borders like La Spezia-Rimini, here are the most well-identified groups of regional Italian.
Northern Italy
Northern regional Italian is characterized by a different distribution of the open and closed ''e'' and ''o'' () compared to the Florentine model, particularly evident inMilan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, where the open ''e'' is pronounced at the end of the word (''perché'' ) or in the word body in closed syllable (i.e. followed by consonant: ''stesso'' ) and the closed ''e'' in word body in open syllable (i.e. not followed by consonant: ''bene'' ). Except for the extreme Ligurian Levante, in Liguria
Liguria (; lij, Ligûria ; french: Ligurie) is a Regions of Italy, region of north-western Italy; its Capital city, capital is Genoa. Its territory is crossed by the Alps and the Apennine Mountains, Apennines Mountain chain, mountain range and is ...
, and especially in the capital, there is the opposite phenomenon: there is a tendency to close all the ''e'' even where the Italian standard does not envisage it. In Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian ce ...
and Bologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nat ...
for example the names ''Mattèo'', ''Irène'', ''Emanuèle'' and the name of the city itself are pronounced with the closed ''e''; moreover, there is no difference in the pronunciation of the word ''pesca'' either to mean "peach" (standard ) and "fishing" (standard ).
There is also a strong tendency to close all the e's before a nasal consonant (usually in the same syllable) so that /ɛ/ becomes /e/. Sempre (always) is pronounced as in Northern Italy while the standard pronunciation is .
A characteristic of the North in opposition to the South is the almost always voiced () consonant in intervocalic position, whereas in the south it is always voiceless: vs. . Also in opposition to the south, the north is characterized by the reduction of phonosyntactic doubling at the beginning of the word (after vowels) and the almost total abandonment of the preterite tense in verb forms as it is not present in the majority of Gallo-italic languages (they are replaced by the present perfect).
Widespread use of determiners before feminine names (''la Giulia'') is also noted in almost all the north while the determiner coupled with male names (''il Carlo'') is typical of the Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
.
In the northern vocabulary words like ''anguria'' (also common in Sardinia and Sicily), which means "watermelon
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 varieti ...
", instead of ''cocomero'', ''bologna'' for '' mortadella'' (but not everywhere), ''piuttosto che'' ("rather than") in the sense of "or" and not "instead", etc. are in use. The last, in particular, is a custom that has begun to spread also in other areas of Italy, stirring up linguistic concern, as it is used with a semantic sense in contrast to that of standard Italian.
Tuscany
In Tuscany and especially inFlorence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
, the Tuscan gorgia
The Tuscan gorgia ( it, gorgia toscana , ; "Tuscan throat") is a phonetic phenomenon governed by a complex of allophonic rules characteristic of the Tuscan dialects, in Tuscany, Italy, especially the central ones, with Florence traditionally viewe ...
is very well known. That is, the lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them more sonority hierarchy, sonorous. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronic analysis, s ...
of the occlusive consonants in the post-vocalic position, including at the beginning of the word if the previous word ends up by vowel: ''la casa'' "the house" , even to its total disappearance. Also phonological in nature are forms without the diphthong ''uo'' of Standard Italian (''ova'', ''scola'', ''bona'', ''foco'' instead of ''uova'', ''scuola'', ''buona'', ''fuoco''), while in the syntax a tripartite system of demonstrative adjectives is in use: ''questo'' ("this") to indicate something close to the speaker (first person), ''codesto'' (lost in other varieties) for something close to the contact person (second person), or ''quello'' "that" for something far from both (third person). A Tuscan stereotype is use of forms resembling the impersonal for the first person plural: ''(noi) si va'' instead of ''noi andiamo'' ("we are going"), past tense ''(noi) si è andati'', and use of ''te'' rather than ''tu'' as second person singular subject pronoun: ''Te che fai stasera?'' rather than ''Tu che fai stasera?'' ("What are you doing tonight?"). Also typical of several areas including Tuscany is the use of the article before a female given name (''la Elena'', ''la Giulia''); such use passed from Tuscany to other regions when used before the surname of well-known people, particularly of the past (''il Manzoni''). In the vocabulary there is the use of ''spenge'' instead of ''spegne'' ("extinguishes") or words like ''balocco'' instead of ''giocattolo'' ("toy"), ''busse'' instead of ''percosse'' or ''botte'' ("beatings"), ''rena'' instead of ''sabbia'' ("sand"), ''cencio'' instead of ''panno'' ("cloth").
The Tuscan historical dialects (including Corsican) belong to the same linguistic system as Italian, with few substantial morphological, syntactic or lexical differences compared to the standard language. As a result, unlike further from Tuscany in Italy, there are no major obstacles to mutual intelligibility of the local Romance languages and Regional Italian.
Central Italy, Southern Italy and Sicily
Central and Southern regional Italian is characterized by the usage of the affricate consonants in place offricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in t ...
s after nasal consonant
In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast majorit ...
s (''insolito'' instead of ), and by the doubling of the ''g''Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
for example), while in Calabria, Salento and Sicily closed vowels are completely missing and speakers just pronounce open vowels (), while in the other regions the discrepancies with the pronunciation Standards are minor (albeit relevant) and non-homogeneous; on the Adriatic side is more evident, as in certain areas of central-east Abruzzo
Abruzzo (, , ; nap, label=Neapolitan language, Abruzzese Neapolitan, Abbrùzze , ''Abbrìzze'' or ''Abbrèzze'' ; nap, label=Sabino dialect, Aquilano, Abbrùzzu; #History, historically Abruzzi) is a Regions of Italy, region of Southern Italy wi ...
(Chieti-Sulmona), largely in central-northern Apulia
it, Pugliese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographic ...
(Foggia-Bari-Taranto), and in eastern Basilicata (Matera) where it is present The so-called "syllabic isocronism": free syllable vowels are all pronounced closed and those in close syllables all open (see the well-known example ''un póco di pòllo'' instead of ''un pòco di póllo'' "a bit of chicken"); Even in the Teramo
Teramo (; nap, label= Abruzzese, Tèreme ) is a city and ''comune'' in the Italian region of Abruzzo, the capital of the province of Teramo.
The city, from Rome, is situated between the highest mountains of the Apennines ( Gran Sasso d'Itali ...
area (northern Abruzzo), and up to Pescara, the vowels are pronounced with a single open sound (for example ''dove volete andare stasera?'' , Thus showing an inexplicable coincidence with the phonetic outcomes of Sicily and Calabria, although there is no direct link with them. As already mentioned here, the intervocalic s is always voiced, and the use of the preterite
The preterite or preterit (; abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense or verb form serving to denote events that took place or were completed in the past; in some languages, such as Spanish, French, and English, it is equivalent to the simple pas ...
is also frequent instead of the use of the present perfect
The present perfect is a grammatical combination of the present tense and perfect aspect that is used to express a past event that has present consequences. The term is used particularly in the context of English grammar to refer to forms like " ...
. In continental southern Italy, from Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
down to Calabria, possessive pronouns often are placed after the noun: for example ''il libro mio'' instead of ''il mio libro'' ("my book").
Another characteristic of regional Italian varieties in central and southern Italy is deaffrication
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them more sonorous. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language at a ...
of /tʃ/ between vowels, both word-internally and across word boundaries. In almost all peninsular Italy from Tuscany to Sicily ''luce'' is pronounced rather than , ''la cena'' is pronounced instead of as it is pronounced in northern Italy and in standard Italian.
Sardinia
Based on the significant linguistic distance between the Sardinian language (and any other traditionally spoken by the islanders) and Italian, the Sardinian-influenced Italian emerging from thecontact
Contact may refer to:
Interaction Physical interaction
* Contact (geology), a common geological feature
* Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye
* Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects
* ...
between such languages is to be considered an ethnolect
An ethnolect is generally defined as a language variety that mark speakers as members of ethnic groups who originally used another language or distinctive variety. According to another definition, an ethnolect is any speech variety (language, diale ...
and sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language ( non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, an age group, or other social group.
Sociolects involve both passive acqui ...
of its own, as features divergent from Italian are local in origin, not attributable to more widespread Northern or Southern Italian varieties. While Sardinian phonetics and the introduction of Sardinian words in a full Italian conversation are prevalent, especially if they are Italianised in the process (e.g. "blind" and ''scimpru'' "dumb" becoming ''ciurpo'' and ''scimpro''), the regional Sardinian variety of Italian embracing the most diverging syntactic and morphological changes is situated at the low end of the diastratic spectrum, and its usage, though relatively common among the less educated, is not positively valued by either bilingual Sardinian speakers, who regard it as neither Sardinian nor Italian and nickname it ''italianu porcheddìnu'' ("piggy Italian", standing for "broken Italian"), or Italian monolinguals from Sardinia and other parts of the country.
Sardinianised Italian is marked by the prevalence, even in common speech, of the verb's inversion, following rules of Sardinian (and Latin) but not Italian, which uses a subject-verb-object structure. The (often auxiliary) verb usually ends up at the end of the sentence, especially in exclamatory and interrogative sentences (e.g. ''Uscendo stai?'', literally "Going out are you?", from the Sardinian ''Essinde ses?'', instead of ''Stai uscendo?''; ''Studiando stavo!'' "Been studying have I!", from ''Istudiende fia!'', instead of ''Stavo studiando!''; ''Legna vi serve?'' "In need of some wood are you?" from ''Linna bos serbit?'', instead of ''Avete bisogno di un po' di legna?''). It is also common for interrogative sentences to use a pleonastic ''tutto'' "all", from the Sardinian ''totu'', as in ''Cosa tutto hai visto?'' "What all have you seen?" from ''Ite totu as bidu?'' compared with the standard Italian ''Cosa hai visto?''. The present continuous makes use of the verb ''essere'' "to be" as in English rather than ''stare'' (e.g. ''Sempre andando e venendo è!'' "Always walking up and down she/he is!" from ''Semper/Sempri andande e beninde est!'' compared with the standard Italian ''Sta sempre andando e venendo!''): that is because the present continuous built with verb ''stare'' does not, in such regional variety, express the idea of an action ongoing at a certain point, but rather something that will take place in the very near future, almost on the point of happening (e.g. ''Sto andando a scuola'' with the meaning of "I'm about to go to school" rather than "Right now as we speak, I'm going to school"). It is also common to use antiphrastic formulas which are alien to Italian, by means of the particle ''già'' (Sard. ''jai'' / ''giai'') which is similar to the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
use of ''ja... schon'' especially for ironic purposes, in order to convey sardonic remarks (e.g. ''Già sei tutto studiato, tu!'' "You're so well educated!" from ''Jai ses totu istudiatu, tue!'' which roughly stands for "You are so ignorant and full of yourself!", or ''Già è poco bello!'' "He/It is not so beautiful!" from ''Jai est pacu bellu!'' meaning actually "He/It is so beautiful!"). One also needs to take into consideration the presence of a number of other Sardinian-specific idiomatic phrases being literally translated into Italian (like ''Cosa sembra?'' "What does it look like?" from ''Ite paret?'' meaning "How do you do?" compared to the standard Italian ''Come stai?'', ''Mi dice sempre cosa!'' "She/He's always scolding me!" from the Sardinian ''Semper cosa mi narat!'' compared to the standard Italian ''Mi rimprovera sempre!'', or again ''Non fa!'' "No chance!" from ''Non fachet!'' / ''Non fait!'' compared to standard Italian ''Non si può!''), that would make little sense to an Italian speaker from another region.
As mentioned earlier, a significant number of Sardinian and other local loanwords (be they Italianised or not) are also present in regional varieties of Italian (e.g. ''porcetto'' from the Sardinian ''porcheddu'' / ''porceddu'', ''scacciacqua'' from the Sardinian ''parabba'' / ''paracua'' "raincoat", ''continente'' "Mainland" and ''continentale'' "Mainlander" with reference to the rest of the country and its people as well,Antonietta Dettori, 2007, ''Tra identità e alterità. “Continente” e “continentale” in Sardegna'', in Dialetto, memoria & fantasia, Atti del Convegno (Sappada / Plodn, 28 giugno - 2 luglio 2006), a cura di G. Marcato, Padova, Unipress, pp. 393-403. etc.).
Some words may even reflect ignorance of the original language on the speaker's part when referring to a singular noun in Italian with Sardinian plurals, due to a lack of understanding of how singular and plurals nouns are formed in Sardinian: common mistakes are "una seadas", "un tenores", etc.
Regarding phonology, the regional Italian spoken in Sardinia follows the same five-vowel system of the Sardinian language without length differentiation, rather than the standard Italian seven-vowel system. Metaphony
In historical linguistics, metaphony is a class of sound change in which one vowel in a word is influenced by another in a process of assimilation. The sound change is normally "long-distance" in that the vowel triggering the change may be s ...
has also been observed: tonic ''e'' and ''o'' () have a closed sound whenever they are followed by a closed vowel (''i'', ''u''), and they have it open if they are followed by an open one (''a'', ''e'', ''o''). Hypercorrection is also common when applying the Italian rule of syntactic gemination; intervocalic ''t'', ''p'', ''v'', ''c'' are usually elongated. Intervocalic voicing is the same as in Northern Italy, that is .
See also
*Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 85 m ...
* Languages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, belong to the broader Romance gro ...
* Standard language
A standard language (also standard variety, standard dialect, and standard) is a language variety that has undergone substantial codification of grammar and usage, although occasionally the term refers to the entirety of a language that includes ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Avolio, Francesco: ''Lingue e dialetti d'Italia'', Rome: Carocci, 2009. * Berruto, Gaetano: ''Sociolinguistica dell'italiano contemporaneo'', Rome: Carocci, 2012. * Bruni, Francesco: ''L'italiano nelle regioni'', Turin: UTET, 1992. * Canepari. Luciano. 1983. ''Italiano standard a pronunce regionali.'' Padova: CLEUP. * Cardinaletti, Anna and Nicola Munaro, eds.: ''Italiano, italiani regionali e dialetti'', Milan: Franco Angeli, 2009. * Comrie, Bernard, Matthews, Stephen and Polinsky, Maria: ''The Atlas of Languages: The Origin and Development of Languages Throughout the World. Rev. ed.'', New York 2003. * Cortelazzo, Manlio and Carla Marcato, ''Dizionario etimologico dei dialetti italiani'', Turin: UTET libreria, 2005, . * Devoto, Giacomo and Gabriella Giacomelli: ''I dialetti delle regioni d'Italia'', Florence: Sansoni Editore, 1971 (3rd edition, Tascabili Bompiani, 2002). * Grassi, Corrado, Alberto A. Sobrero and Tullio Telmon: ''Fondamenti di dialettologia italiana'', Bari: Laterza, 2012. * Grimes, Barbara F. (ed.): ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World''. Vol. 1, 2000. * Hall, Robert A. Jr.: ''External History of the Romance Languages'', New York: Elsevier, 1974. * Haller, Hermann W.: ''The Hidden Italy: A Bilingual Edition of Italian Dialect Poetry'', Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1986. * Loporcaro, Michele: ''Profilo linguistico dei dialetti italiani'', Bari: Laterza, 2009. * Maiden, Martin and Parry, Mair, eds.: ''The Dialects of Italy'', London: Routledge, 1997. * Maiden, Martin: ''A Linguistic History of Italian'', London: Longman, 1995. * Marcato, Carla: ''Dialetto, dialetti e italiano'', Bologna: il Mulino, 2002. * Rognoni, Andrea: ''Grammatica dei dialetti della Lombardia'',Oscar Mondadori
Arnoldo Mondadori Editore () is the biggest publishing company in Italy.
History
The company was founded in 1907 in Ostiglia by 18-year-old Arnoldo Mondadori who began his publishing career with the publication of the magazine ''Luce!''. In 1 ...
, 2005.
{{Authority control
Italian language