RQ-4 Global Hawk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Northrop Grumman RQ-4 Global Hawk is a high-altitude, remotely-piloted
 The United States Navy took delivery of two of the Block 10 aircraft to evaluate their maritime surveillance capabilities, designated N-1 (BuNo 166509) and N-2 (BuNo 166510). The initial navalised example was tested at Edwards Air Force Base briefly, before moving to
The United States Navy took delivery of two of the Block 10 aircraft to evaluate their maritime surveillance capabilities, designated N-1 (BuNo 166509) and N-2 (BuNo 166510). The initial navalised example was tested at Edwards Air Force Base briefly, before moving to
U.S. Navy To Receive First Global Hawk Next Week
" ''
 In February 2011, the USAF reduced its planned purchase of RQ-4 Block 40 aircraft from 22 to 11 in order to cut costs. In June 2011, the U.S. Defense Department's Director, Operational Test and Evaluation (DOT&E) found the RQ-4B "not operationally effective" due to reliability issues. In June 2011, the Global Hawk was certified by the Secretary of Defense as critical to national security following a breach of the Nunn-McCurdy Amendment; the Secretary stated: "The Global Hawk is essential to national security; there are no alternatives to Global Hawk which provide acceptable capability at less cost; Global Hawk costs $220M less per year than the
In February 2011, the USAF reduced its planned purchase of RQ-4 Block 40 aircraft from 22 to 11 in order to cut costs. In June 2011, the U.S. Defense Department's Director, Operational Test and Evaluation (DOT&E) found the RQ-4B "not operationally effective" due to reliability issues. In June 2011, the Global Hawk was certified by the Secretary of Defense as critical to national security following a breach of the Nunn-McCurdy Amendment; the Secretary stated: "The Global Hawk is essential to national security; there are no alternatives to Global Hawk which provide acceptable capability at less cost; Global Hawk costs $220M less per year than the
Breaking Defense, retrieved 27 July 2022.
 The
The
Deutsche Welle, 15 May 2013. Reportedly, the additional cost to develop the EuroHawk to the standards needed for certification may not have guaranteed final approval for certification. German defense minister Thomas de Maizière stated EuroHawk was "very important" for Germany in 2012, then referred to the project as being "a horror without end" in his 2013 statement to the
Airrecognition.com, 5 October 2014 The
''FlightGlobal'', 6 July 2015"USAF and Northrop sign Global Hawk payload adaptor deal"
''FlightGlobal'', 23 July 2015 Northrop Grumman also expects to receive a contract to integrate the

Bga-Aeroweb.com The RQ-4B Block 30 is capable of multi-intelligence (multi-INT) collecting with SAR and EO/IR sensors along with the Airborne Signals Intelligence Payload (ASIP), a wide-spectrum SIGINT sensor. The RQ-4B Block 40 is equipped with the multi-platform radar technology insertion program (MP-RTIP)
Dvidshub.net, 24 September 2015

." Australian Ministry of Defence press release. 24 April 2001 On 22 March 2008, a Global Hawk set the endurance record for full-scale, operational uncrewed aircraft UAVs by flying for 33.1 hours at altitudes up to 60,000 feet over Edwards AFB. From its first flight in 1998 to 9 September 2013, the combined Global Hawk fleet flew 100,000 hours. 88 percent of flights were conducted by USAF RQ-4s, while the remaining hours were flown by NASA Global Hawks, the EuroHawk, the Navy BAMS demonstrator, and the MQ-4C Triton. Approximately 75 percent of flights were in combat zones; RQ-4s flew in operations over Afghanistan, Iraq, and Libya; and supported disaster response efforts in Haiti, Japan, and California."Northrop Grumman Unmanned Aircraft Systems Achieve 100,000 Flight Hours".
Defensemedianetwork.com, 13 September 2013 From 10 to 16 September 2014, the RQ-4 fleet flew a total of 781 hours, the most hours flown by the type during a single week. 87 percent of flights were made by USAF RQ-4s, with the rest flown by the Navy BAMS-D and NASA hurricane research aircraft. The longest Global Hawk combat sortie lasted 32.5 hours.
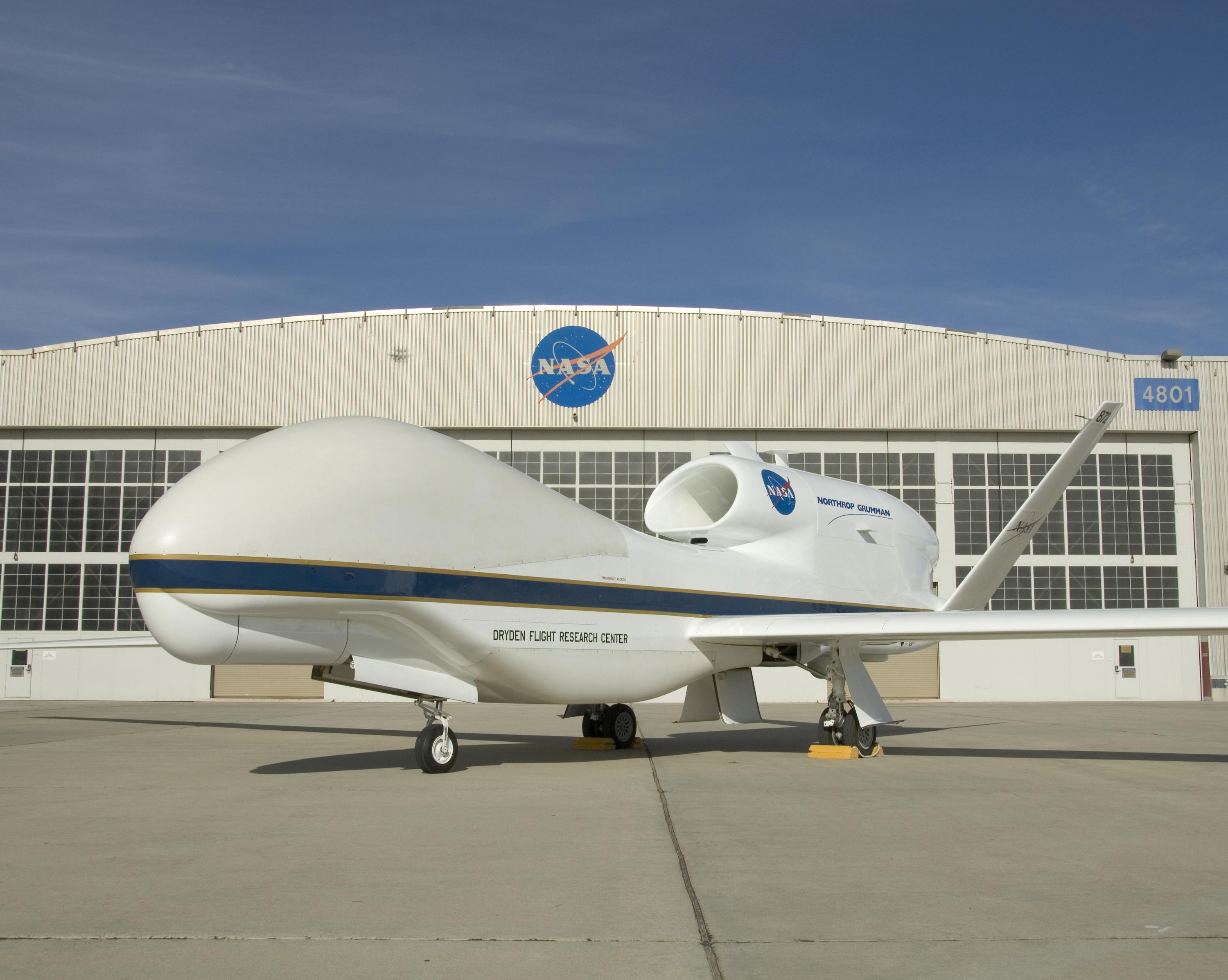 In December 2007, two Global Hawks were transferred from the USAF to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB. Initial research activities beginning in the second quarter of 2009 supported NASA's high-altitude, long-duration Earth science missions. The two Global Hawks were the first and sixth aircraft built under the original DARPA Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration program, and were made available to NASA when the Air Force had no further need for them. Northrop Grumman is an operational partner with NASA and will use the aircraft to demonstrate new technologies and to develop new markets for the aircraft, including possible civilian uses.
It was reported in the March 2010 issue of ''Scientific American'' that NASA's Global Hawks were to begin scientific missions that month, and had been undergoing tests in late 2009. Initial science applications included measurements of the ozone layer and cross-Pacific transport of air pollutants and aerosols. The author of the Scientific American article speculates that it could be used for Antarctic exploration while being based in Chile. In August–September 2010, one of the two Global Hawks was loaned for NASA's GRIP (Genesis and Rapid Intensification Program) mission.
Its long-term on station capabilities and long range made it a suitable aircraft for monitoring the development of Atlantic basin Tropical cyclone, hurricanes. It was modified to equip weather sensors including Ku-band radar, lightning sensors and dropsondes. It successfully flew into Hurricane Earl (2010), Hurricane Earl off the United States East Coast on 2 September 2010."Hurricane Earl News Release"
In December 2007, two Global Hawks were transferred from the USAF to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB. Initial research activities beginning in the second quarter of 2009 supported NASA's high-altitude, long-duration Earth science missions. The two Global Hawks were the first and sixth aircraft built under the original DARPA Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration program, and were made available to NASA when the Air Force had no further need for them. Northrop Grumman is an operational partner with NASA and will use the aircraft to demonstrate new technologies and to develop new markets for the aircraft, including possible civilian uses.
It was reported in the March 2010 issue of ''Scientific American'' that NASA's Global Hawks were to begin scientific missions that month, and had been undergoing tests in late 2009. Initial science applications included measurements of the ozone layer and cross-Pacific transport of air pollutants and aerosols. The author of the Scientific American article speculates that it could be used for Antarctic exploration while being based in Chile. In August–September 2010, one of the two Global Hawks was loaned for NASA's GRIP (Genesis and Rapid Intensification Program) mission.
Its long-term on station capabilities and long range made it a suitable aircraft for monitoring the development of Atlantic basin Tropical cyclone, hurricanes. It was modified to equip weather sensors including Ku-band radar, lightning sensors and dropsondes. It successfully flew into Hurricane Earl (2010), Hurricane Earl off the United States East Coast on 2 September 2010."Hurricane Earl News Release"
NASA GRIP News
''Flight International'', 14 January 2009. NATO signed a contract for five Block 40 Global Hawks in May 2012. 12 NATO members are participating in the purchase. On 10 January 2014, Estonia revealed it wanted to participate in NATO Global Hawk usage. In July 2017, the USAF assigned the Mission Designation Series (MDS) of RQ-4D to the NATO AGS air vehicle. The first RQ-4D aircraft arrived at Sigonella Air Base on 21 November 2019. At that time, all five aircraft were undergoing developmental test flights. Initial operational capability was expected in the first half of 2020. In October 2018, Italy certified five of the drones for use in Sigonella,
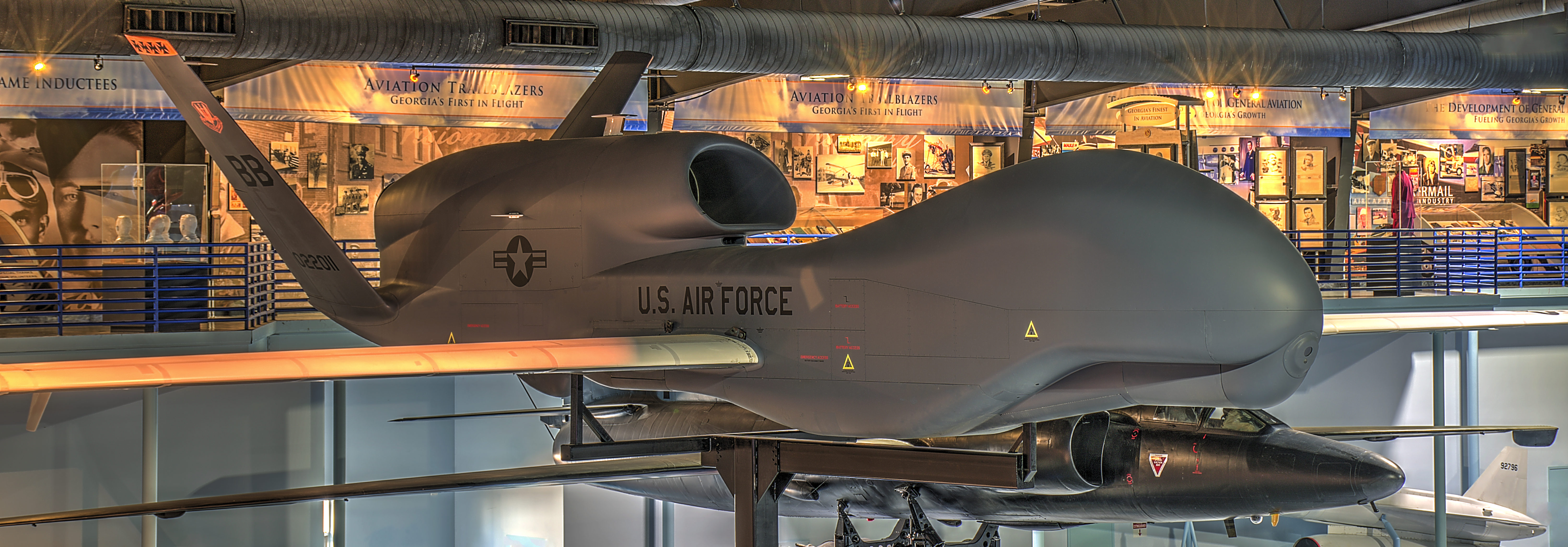 ;RQ-4A: Initial production version for the USAF, 16 built.
;RQ-4B: Improved version with increased payload, wingspan increased to and length increased to . Due to the increased size and payload the range is reduced to .
;RQ-4D Phoenix
: NATO Alliance Ground Surveillance (AGS).
;RQ-4E Euro Hawk
: Version for the Bundeswehr based on RQ-4B and equipped with an EADS reconnaissance payload for SIGINT. Germany canceled its order in May 2013; it received one of five Euro Hawks originally ordered.
;
;RQ-4A: Initial production version for the USAF, 16 built.
;RQ-4B: Improved version with increased payload, wingspan increased to and length increased to . Due to the increased size and payload the range is reduced to .
;RQ-4D Phoenix
: NATO Alliance Ground Surveillance (AGS).
;RQ-4E Euro Hawk
: Version for the Bundeswehr based on RQ-4B and equipped with an EADS reconnaissance payload for SIGINT. Germany canceled its order in May 2013; it received one of five Euro Hawks originally ordered.
;
 ;
* Republic of Korea Air Force – Ordered 4 in 2014. First aircraft delivered on 23 December 2019.
;
* Japan Air Self-Defense Force – Ordered 3 in November 2018, to be delivered by 1 September 2022. The purchase was made under a contract worth $USD1.2 billion.
;
* Alliance Ground Surveillance – Ordered 5 aircraft, first delivered 21 November 2019.
;
*
;
* Republic of Korea Air Force – Ordered 4 in 2014. First aircraft delivered on 23 December 2019.
;
* Japan Air Self-Defense Force – Ordered 3 in November 2018, to be delivered by 1 September 2022. The purchase was made under a contract worth $USD1.2 billion.
;
* Alliance Ground Surveillance – Ordered 5 aircraft, first delivered 21 November 2019.
;
*
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
' by Greg Goebel, which is public domain.''
RQ-4 Global Hawk U.S. Air Force fact sheet
Federation of American Scientists
"Global Hawk RQ-4A-B High Altitude Long Endurance UAV"
Defense Update
Raytheon product page on the Global Hawk Integrated Sensor Suite
Luftwaffe Euro Hawk pageBundeswehr Euro Hawk page
{{Q-UAVs Northrop Grumman aircraft, RQ-004 Global Hawk 1990s United States military reconnaissance aircraft Unmanned military aircraft of the United States Single-engined jet aircraft Low-wing aircraft V-tail aircraft Signals intelligence Synthetic aperture radar Aircraft first flown in 1998
surveillance aircraft
A surveillance aircraft is an aircraft used for surveillance. They are operated by military forces and other government agencies in roles such as intelligence gathering, battlefield surveillance, airspace surveillance, reconnaissance, observa ...
of the 1990s–2020s. It was initially designed by Ryan Aeronautical (now part of Northrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense technology company. With 90,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $30 billion, it is one of the world's largest weapons manufacturers and military techn ...
), and known as Tier II+ during development. The RQ-4 provides a broad overview and systematic surveillance using high-resolution synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide fine ...
(SAR) and electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) sensors with long loiter
Loitering is the act of remaining in a particular public place for a prolonged amount of time without any apparent purpose.
While the laws regarding loitering have been challenged and changed over time, loitering is still illegal in various j ...
times over target areas. It can survey as much as of terrain per day, an area the size of South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
or Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
.
The Global Hawk is operated by the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
(USAF). It is used as a high-altitude long endurance
Atmospheric satellite (United States usage, abbreviated atmosat) or pseudo-satellite (British usage) is a marketing term for an aircraft that operates in the atmosphere at high altitudes for extended periods of time, in order to provide servic ...
(HALE) platform covering the spectrum of intelligence collection
This is a list of intelligence gathering disciplines.
HUMINT
Human intelligence (HUMINT) are gathered from a person in the location in question. Sources can include the following:
* Advisors or foreign internal defense (FID) personnel wor ...
capability to support forces in worldwide military operations. According to the USAF, the superior surveillance capabilities of the aircraft allow more precise weapons targeting and better protection of friendly forces.
Cost overruns led to the original plan to acquire 63 aircraft being cut to 45, and to a 2013 proposal to mothball the 21 Block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
30 signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
variants. The initial flyaway cost of each of the first 10 aircraft was US$10 million in 1994. By 2001, this had risen to US$60.9 million, and then to $131.4 million (flyaway cost) in 2013. The U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ...
has developed the Global Hawk into the MQ-4C Triton
The Northrop Grumman MQ-4C Triton is an American high-altitude long endurance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) under development for the United States Navy as a surveillance aircraft. Together with its associated ground control station, it is an ...
maritime surveillance platform. As of 2022, the U.S. Air Force plans to retire its Global Hawks in 2027.
Development
Origins
In the 1990s, the Air Force was developing uncrewed aerial intelligence platforms. One was the stealthyLockheed Martin RQ-3 DarkStar
The RQ-3 DarkStar (known as Tier III- or "Tier three minus" during development) is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Its first flight was on March 29, 1996. The Department of Defense terminated DarkStar in January 1999, after determining the UAV ...
; another was the Global Hawk. Due to budget cuts, only one of the programs could survive. It was decided to proceed with the Global Hawk for its range and payload rather than go with the stealth Dark Star.
The Global Hawk took its first flight on 28 February 1998. The first seven aircraft were built under the Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration An Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration enables the evaluation of mature advanced technology for usage by the United States military. These demonstrations allow technology evaluation earlier and cheaper than is possible through the formal acqui ...
(ACTD) program, sponsored by DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Originally known as the Adv ...
, in order to evaluate the design and demonstrate its capabilities. Demand for the RQ-4's abilities was high in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
; thus, the prototype aircraft were actively operated by the USAF in the War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
*Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see als ...
. In an unusual move, the aircraft entered initial low-rate production while still in engineering and manufacturing development. Nine production Block 10 aircraft, sometimes referred to as RQ-4A, were produced; of these, two were sold to the US Navy and an additional two were deployed to Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
to support operations there. The final Block 10 aircraft was delivered on 26 June 2006.
To increase the aircraft's capabilities, the airframe was redesigned, with the nose section and wings being stretched. The modified aircraft, designated RQ-4B Block 20, can carry up to 3,000 lb (1,360 kg) of internal payload. These changes were introduced with the first Block 20 aircraft, the 17th Global Hawk produced, which was rolled out in a ceremony on 25 August 2006."Northrop unveils next generation Global Hawk", ''Aerotech News and Review
''Aerotech News and Review Inc.'', established in February 1986, is a bi-weekly aerospace trade journal and publishing company with corporate headquarters in Lancaster, California in the heart of America's “Aerospace Valley”.
Aerotech News is ...
'', 1 September 2006. First flight of the Block 20 from the USAF Plant 42 in Palmdale, California
Palmdale is a city in northern Los Angeles County in the U.S. state of California. The city lies in the Antelope Valley region of Southern California. The San Gabriel Mountains separate Palmdale from the Los Angeles Basin to the south.
On Aug ...
to Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is E ...
took place on 1 March 2007. Developmental testing of Block 20 took place in 2008.
United States Navy version
 The United States Navy took delivery of two of the Block 10 aircraft to evaluate their maritime surveillance capabilities, designated N-1 (BuNo 166509) and N-2 (BuNo 166510). The initial navalised example was tested at Edwards Air Force Base briefly, before moving to
The United States Navy took delivery of two of the Block 10 aircraft to evaluate their maritime surveillance capabilities, designated N-1 (BuNo 166509) and N-2 (BuNo 166510). The initial navalised example was tested at Edwards Air Force Base briefly, before moving to Naval Air Station Patuxent River
Naval Air Station Patuxent River , also known as NAS Pax River, is a United States naval air station located in St. Mary’s County, Maryland, on the Chesapeake Bay near the mouth of the Patuxent River.
It is home to Headquarters, Naval Air Sys ...
in March 2006 for the Global Hawk Maritime Demonstration (GHMD) program, operated by Navy squadron VX-20
VX-20, Air Test and Evaluation Squadron Twenty, (''AIRTEVRON TWO ZERO'') is a United States Navy air test and evaluation squadron based at Naval Air Station Patuxent River, Maryland.
Operations
VX-20 operates a variety of Naval aircraft for testin ...
.Selinger, M.U.S. Navy To Receive First Global Hawk Next Week
" ''
Aviation Week & Space Technology
''Aviation Week & Space Technology'', often abbreviated ''Aviation Week'' or ''AW&ST'', is the flagship magazine of the Aviation Week Network. The weekly magazine is available in print and online, reporting on the aerospace, defense and aviati ...
''. 1 October 2004.
In July 2006, the GHMD aircraft flew in the Rim of the Pacific ( RIMPAC exercise) for the first time. Although it was in the vicinity of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, the aircraft was operated from NBVC Point Mugu, requiring flights of approximately each way to the area. Four flights were performed, resulting in over 24 hours of persistent maritime surveillance coordinated with the aircraft carrier and amphibious warfare ship . For the GHMD program, the Global Hawk was tasked with maintaining maritime situational awareness, contact tracking, and imagery support of exercise operations. Images were transmitted to NAS Patuxent River for processing and then forwarded to the fleet off Hawaii.
Northrop Grumman entered a RQ-4B variant in the US Navy's Broad Area Maritime Surveillance
The Northrop Grumman MQ-4C Triton is an American high-altitude long endurance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) under development for the United States Navy as a surveillance aircraft. Together with its associated ground control station, it is an ...
(BAMS) UAV competition. On 22 April 2008, it was announced that Northrop Grumman's ''RQ-4N'' had won and that the Navy had awarded a US$1.16 billion contract. In September 2010, the RQ-4N was officially designated the ''MQ-4C''.
The Navy MQ-4C differs from the Air Force RQ-4 mainly in its wing. While the Global Hawk remains at high altitude to conduct surveillance, the Triton climbs to to see a wide area and can drop to to get further identification of a target. The Triton's wings are specially designed to take the stresses of rapidly decreasing altitude. Though similar in appearance to the Global Hawk's wings, the Triton's internal wing structure is much stronger and has additional features including anti-icing capabilities and impact and lightning strike protection.
On 17 June 2022, the Navy brought its last deployed RQ-4A BAMS-D back from the Middle East, ending what started as a six-month experiment but turned into a 13-year deployment. The Navy had acquired five Block 10 RQ-4As and since 2009 at least one had been kept on rotation in the Persian Gulf region. The aircraft accrued over 42,500 flight hours in 2,069 missions; one was lost in an accident and another was shot down by Iran. The BAMS-D was replaced in Navy service with the MQ-4C.
Cost increases and procurement
Developmentcost overrun
A cost overrun, also known as a cost increase or budget overrun, involves unexpected incurred costs. When these costs are in excess of budgeted amounts due to a value engineering underestimation of the actual cost during budgeting, they are known ...
s placed the Global Hawk at risk of cancellation. In mid-2006, per-unit costs were 25% over baseline estimates, caused by both the need to correct design deficiencies as well as to increase its capabilities. This caused concern over a possible congressional termination of the program if its national security benefits could not be justified. However, in June 2006, the program was restructured. Completion of an operational assessment report by the USAF was delayed from 2005 to 2007 due to manufacturing and development delays. The operational assessment report was released in March 2007 and production of the 54 air vehicles planned was extended by two years to 2015.
 In February 2011, the USAF reduced its planned purchase of RQ-4 Block 40 aircraft from 22 to 11 in order to cut costs. In June 2011, the U.S. Defense Department's Director, Operational Test and Evaluation (DOT&E) found the RQ-4B "not operationally effective" due to reliability issues. In June 2011, the Global Hawk was certified by the Secretary of Defense as critical to national security following a breach of the Nunn-McCurdy Amendment; the Secretary stated: "The Global Hawk is essential to national security; there are no alternatives to Global Hawk which provide acceptable capability at less cost; Global Hawk costs $220M less per year than the
In February 2011, the USAF reduced its planned purchase of RQ-4 Block 40 aircraft from 22 to 11 in order to cut costs. In June 2011, the U.S. Defense Department's Director, Operational Test and Evaluation (DOT&E) found the RQ-4B "not operationally effective" due to reliability issues. In June 2011, the Global Hawk was certified by the Secretary of Defense as critical to national security following a breach of the Nunn-McCurdy Amendment; the Secretary stated: "The Global Hawk is essential to national security; there are no alternatives to Global Hawk which provide acceptable capability at less cost; Global Hawk costs $220M less per year than the Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed "''Dragon Lady''", is an American single-jet engine, high altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) and previously flown by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). It provides day ...
to operate on a comparable mission; the U-2 cannot simultaneously carry the same sensors as the Global Hawk; and if funding must be reduced, Global Hawk has a higher priority over other programs."
On 26 January 2012, the Pentagon announced plans to end Global Hawk Block 30 procurement as the type was found to be more expensive to operate and with less capable sensors than the existing U-2. Plans to increase procurement of the Block 40 variant were also announced. The Air Force's fiscal year 2013 budget request said it had resolved to divest itself of the Block 30 variant; however, the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2013
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) for Fiscal Year 2013 (short title) is a United States federal law which specifies the budget and expenditures of the United States Department of Defense for fiscal year 2013. The full title is An Act to ...
mandated operations of the Block 30 fleet through the end of 2014. The USAF plans to procure 45 RQ-4B Global Hawks as of 2013. Before retiring in 2014, ACC commander, General Mike Hostage said of the U-2's replacement by the drone that "The combatant commanders are going to suffer for eight years and the best they’re going to get is 90 percent".
During 2010–2013, costs of flying the RQ-4 fell by more than 50%. In 2010, the cost per flight hour was $40,600, with contractor logistic support making up $25,000 per flight hour of this figure. By mid-2013, cost per flight hour dropped to $18,900, contractor logistic support having dropped to $11,000 per flight hour. This was in part due to higher usage, spreading logistics and support costs over a higher number of flight hours.
In July 2022, the US Air Force announced that it plans to retire the Global Hawk in 2027.Air Force’s RQ-4 Global Hawk drones headed for the boneyard in FY27Breaking Defense, retrieved 27 July 2022.
EuroHawk
 The
The German Air Force
The German Air Force (german: Luftwaffe, lit=air weapon or air arm, ) is the aerial warfare branch of the , the armed forces of Germany. The German Air Force (as part of the ''Bundeswehr'') was founded in 1956 during the era of the Cold War a ...
(''Luftwaffe'') ordered a variant of the RQ-4B, to be equipped with a customized sensor suite, designated "EuroHawk". The aircraft was based on the RQ-4B Block 20/30/40 and was to be equipped with an EADS
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft throughout the world. The company has three divisions: '' ...
-built signals intelligence
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ( ...
(SIGINT) package; it was intended to fulfill Germany's requirement to replace their aging Dassault-Breguet Atlantique electronic surveillance aircraft of the ''Marineflieger
The ''Marinefliegerkommando'' (Naval Aviation Command) is the naval air arm of the German Navy.
History
During the First World War, naval aviators were part of the . After the war Germany was no longer allowed to maintain a military aviation ca ...
'' (German Naval Air Arm). The EADS sensor package is composed of six wing-mounted pods; reportedly these sensor pods could potentially be used on other platforms, including crewed aircraft.
The EuroHawk was officially rolled out on 8 October 2009 and its first flight took place on 29 June 2010. It underwent several months of flight testing at Edwards Air Force Base. On 21 July 2011, the first EuroHawk arrived in Manching
Manching is a municipality in the district of Pfaffenhofen, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated on the river Paar, 7 km southeast of Ingolstadt. In the late Iron Age, there was a Celtic settlement, the Oppidum of Manching, on the location of ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
; after which it was scheduled to receive its SIGINT sensor package and undergo further testing and pilot training until the first quarter of 2012. The Luftwaffe planned to station the type with ''Taktisches Luftwaffengeschwader 51'' ("Reconnaissance wing 51"). In 2011 the German Ministry of Defence
The Federal Ministry of Defence (german: Bundesministerium der Verteidigung, ), abbreviated BMVg, is a top-level Federal agency (Germany), federal agency, headed by the Federal Minister of Defence as a member of the Cabinet of Germany. The mini ...
was aware of difficulties with the certification for use within the European airspace. During flight trials, problems with the EuroHawk's flight control system were found; the German certification process was also complicated by Northrop Grumman refusing to share technical data on the aircraft with which to perform evaluations.
On 13 May 2013, German media reported that the EuroHawk would not be certifiable under ICAO
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international a ...
rules without an anti-collision system; thus preventing any operations within European airspace or the airspace of any ICAO member. The additional cost of certification was reported to be more than €
The euro sign () is the currency sign used for the euro, the official currency of the eurozone and unilaterally adopted by Kosovo and Montenegro. The design was presented to the public by the European Commission on 12 December 1996. It consists ...
600 million (US$780 million). On 15 May 2013, the German government announced the immediate termination of the program, attributing the cancellation to the certification issue."De Maiziere defends Bundeswehr reforms and Euro Hawk halt"Deutsche Welle, 15 May 2013. Reportedly, the additional cost to develop the EuroHawk to the standards needed for certification may not have guaranteed final approval for certification. German defense minister Thomas de Maizière stated EuroHawk was "very important" for Germany in 2012, then referred to the project as being "a horror without end" in his 2013 statement to the
Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Commons ...
. The total cost of the project before it was canceled was €562 million. Northrop Grumman and EADS have described reports of flight control problems and high costs for certification as "inaccurate"; they have stated their intention to provide an affordable plan to complete the first EuroHawk's flight testing and produce the remaining four aircraft.
On 8 August 2013, the EuroHawk set an endurance record by flying continuously in European airspace for 25.3 hours, reaching an altitude of . It was the longest flight by an unrefueled UAS weighing more than in European skies. On 5 October 2014, German Minister of Defence Ursula von der Leyen
Ursula Gertrud von der Leyen (; Albrecht, born 8 October 1958) is a German politician who has been serving as the president of the European Commission since 2019. She served in the Cabinet of Germany, German federal government between 2005 an ...
was reportedly considering reactivating the EuroHawk program to test its reconnaissance abilities over a long period at altitudes of up to . Attempting to test the recon system on Airbus
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European Multinational corporation, multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace manufacturer, aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft througho ...
aircraft and an Israeli drone as alternate platforms had proven unsuccessful."Germany's Euro Hawk drone may take flight again"Airrecognition.com, 5 October 2014 The
Bundeswehr
The ''Bundeswehr'' (, meaning literally: ''Federal Defence'') is the armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany. The ''Bundeswehr'' is divided into a military part (armed forces or ''Streitkräfte'') and a civil part, the military part con ...
would use it to detect, decrypt, and potentially interfere with enemy communications signals. If tests prove successful, a carrier would be purchased, likely "similar" to the U.S. Global Hawk. Germany is considering installing the EuroHawk's SIGINT payloads onto the U.S. Navy MQ-4C Triton Global Hawk derivative, as the electronic and communications intelligence sensors would be more difficult to place on other substitute aircraft. It already has icing and lightning-strike protection, and was built with certification over civilian airspace in mind, meeting the STANAG 4671 requirements that had ended the EuroHawk program.
As of March 2021, Germany plans to put the single RQ-4E aircraft on display in the Bundeswehr Military History Museum
The Bundeswehr Military History Museum (german: Militärhistorisches Museum der Bundeswehr (MHMBw)) is the military museum of the German Armed Forces, the ''Bundeswehr'', and one of the major military history museums in Germany. It is located in ...
by 2022.
Universal Payload Adapter and new payloads
In January 2014, President Obama signed a budget that included a $10 million study on adapting the U-2's superior sensors for the RQ-4. In April 2015, Northrop Grumman reportedly installed the U-2's Optical Bar Camera (OBC) andSenior Year Electro-Optical Reconnaissance System
USA-231, or ORS-1 (Operationally Responsive Space-1) is an American reconnaissance satellite which was launched in 2011 from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia by a Minotaur I launch vehicle. It is the first operational satellite of the ...
(SYERS-2B/C) sensors onto the RQ-4 using a Universal Payload Adapter (UPA). Successful testing indicated that all RQ-4s could be similarly retrofitted.
On 14 July 2015, Northrop Grumman and the USAF signed an agreement to demonstrate an RQ-4B fitted with the U-2's OBC and SYERS-2C sensors. Two Global Hawks are to be fitted with the UPA, involving the installation of 17 payload adapter fixtures and a new payload bay cover, as well as software and mission system changes for each sensor. The UPA can support of sensors and will create a canoe-shaped sensor bay on the fuselage's underside.Northrop, USAF nearing deal for "Global Hawk universal payload adaptor"''FlightGlobal'', 6 July 2015"USAF and Northrop sign Global Hawk payload adaptor deal"
''FlightGlobal'', 23 July 2015 Northrop Grumman also expects to receive a contract to integrate the
UTC Aerospace Systems
UTC Aerospace Systems (UTAS) was one of the world’s largest suppliers of aerospace and defense products, headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, United States. The company was formed in August 2012 when parent United Technologies Corporation ...
MS-177 multispectral sensor used on the Northrop Grumman E-8C JSTARS onto the RQ-4. The MS-177 will replace the SYERS-2 and includes modernized optronics and a gimbaled rotation device to increase field of view by 20 percent. The RQ-4B flew with the SYERS-2 on 18 February 2016.
Raytheon developed the AN/ALR-89 self-protection suite consisting of the AN/AVR-3 laser warning receiver
A laser warning receiver is a type of warning system used as a passive military defence. It detects, analyzes, and locates directions of laser emissionsPDF version4.53 MB) from laser guidance systems and laser rangefinders. Then it alerts the crew ...
, AN/APR-49 radar warning receiver
Radar warning receiver (RWR) systems detect the radio emissions of radar systems. Their primary purpose is to issue a warning when a radar signal that might be a threat is detected, like a fighter aircraft's fire control radar. The warning can th ...
, and jamming system, along with the ALE-50 towed decoy for the Global Hawk.''Aerotech News and Review'', Vol 21, issue 27, 4 August 2006.
Range Hawk
Although the Global Hawk is being retired from combat use, the Department of Defense's Test Resource Management Center (TRMC) is acquiring them to support the SkyRange program to test hypersonic missiles by 2024. Tests are currently monitored by ships, but it can take a ship 21 days to be positioned and outfitted for use, limiting flights to about a dozen airborne demonstrations a year. By using unmanned aircraft to track hypersonic systems, faster availability and deployment could support a test rate of up to one per week. To perform this new mission, the Global Hawk is retrofitted into the Range Hawk, which involves configuring it to look up rather than down by repositioning onboard avionics and installing new sensors and instrumentation suites to track an overhead hypersonic vehicle. The program will use four Block 20 and 20 Block 30 airframes retired from USAF service.Design

Overview
The Global Hawk UAV system comprises the RQ-4 air vehicle, which is outfitted with various equipment such as sensor packages and communication systems; and a ground element consisting of a Launch and Recovery Element (LRE), and a Mission Control Element (MCE) with ground communications equipment. Each RQ-4 air vehicle is powered by an Allison Rolls-Royce AE3007Hturbofan
The turbofan or fanjet is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used in aircraft engine, aircraft propulsion. The word "turbofan" is a portmanteau of "turbine" and "fan": the ''turbo'' portion refers to a gas turbine engine which ac ...
engine with thrust, and carries a payload of . The fuselage uses aluminum, semi-monocoque construction with a V-tail
The V-tail or ''Vee-tail'' (sometimes called a butterfly tail or Rudlicki's V-tailGudmundsson S. (2013). "General Aviation Aircraft Design: Applied Methods and Procedures" (Reprint). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 489. , 9780123973290) of an aircraft ...
; the wings are made of composite materials.
There have been several iterations of the Global Hawk with different features and capabilities. The first version to be used operationally was the RQ-4A Block 10, which performed imagery intelligence
Imagery intelligence (IMINT), pronounced as either as ''Im-Int'' or ''I-Mint'', is an intelligence gathering discipline wherein imagery is analyzed (or "exploited") to identify information of intelligence value. Imagery used for defense intelli ...
(IMINT) with a payload of a synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide fine ...
(SAR) with electro-optical
Electro–optics is a branch of electrical engineering, electronic engineering, materials science, and material physics involving components, electronic devices such as lasers, laser diodes, LEDs, waveguides, etc. which operate by the propaga ...
(EO) and infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
(IR) sensors. Seven A-model Block 10s were delivered and all were retired by 2011. The RQ-4B Block 20 was the first of the B-model Global Hawks, which has a greater payload and employs upgraded SAR and EO/IR sensors. Four Block 20s were converted into communications relays with the Battlefield Airborne Communications Node (BACN) payload.RQ-4 Global Hawk & MQ-4C TritonBga-Aeroweb.com The RQ-4B Block 30 is capable of multi-intelligence (multi-INT) collecting with SAR and EO/IR sensors along with the Airborne Signals Intelligence Payload (ASIP), a wide-spectrum SIGINT sensor. The RQ-4B Block 40 is equipped with the multi-platform radar technology insertion program (MP-RTIP)
active electronically scanned array
An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled array antenna in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the an ...
(AESA) radar, which provides SAR and moving target indication
Moving target indication (MTI) is a mode of operation of a radar to discriminate a target against the clutter. It describes a variety of techniques used for finding moving objects, like an aircraft, and filter out unmoving ones, like hills or trees ...
(MTI) data for wide-area surveillance of stationary and moving targets.
Since the RQ-4 is capable of conducting sorties lasting up to 30 hours long, scheduled maintenance has to be performed sooner than on other aircraft with less endurance. However, since it flies at higher altitudes than normal aircraft, it experiences less wear during flight."Global Hawk maintainers deliver ISR capability to warfighters".Dvidshub.net, 24 September 2015
System and ground facilities
Raytheon
Raytheon Technologies Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense conglomerate headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It is one of the largest aerospace and defense manufacturers in the world by revenue and market capitaliza ...
's Integrated Sensor Suite (ISS) consists of the following sensors:
* a synthetic aperture radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide fine ...
(SAR)
* electro-optical (EO)
* thermographic camera
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared ...
(IR)
Either the EO or the IR sensors can operate simultaneously with the SAR. Each sensor provides wide area search imagery and a high-resolution spot mode. The SAR has a ground moving target indicator (GMTI) mode, which can provide a text message providing the moving target's position and velocity. Both SAR and EO/IR imagery are transmitted from the aircraft to the MCE as individual frames, and reassembled during ground processing. An onboard inertial navigation system, supplemented by Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
updates, comprises the navigational suite.
The Global Hawk is capable of operating autonomously and "untethered". A military satellite
A military satellite is an artificial satellite used for a military purpose. The most common missions are intelligence gathering, navigation and military communications.
The first military satellites were photographic reconnaissance missions. So ...
system (X Band Satellite Communication X band or SHF Satellite Communication is widely used by military forces for beyond line of sight communications. X band is used because it provides a compromise between the characteristics of different frequency bands which is particularly suited ...
) is used for sending data from the aircraft to the MCE. The common data link can also be used for direct down link of imagery when the UAV is within line-of-sight of compatible ground stations. For dense flight areas the autonomous navigation is switched off and the RQ-4 is remote controlled via the satellite link by pilots on the ground who are supplied with the same instrument data and who carry the same responsibilities as pilots in crewed planes.
The ground segment
A ground segment consists of all the ground-based elements of a space system used by operators and support personnel, as opposed to the space segment and user segment. The ground segment enables management of a spacecraft, and distribution of p ...
consists of a Mission Control Element (MCE) and Launch and Recovery Element (LRE), provided by Raytheon. The MCE is used for mission planning, command and control
Command and control (abbr. C2) is a "set of organizational and technical attributes and processes ... hatemploys human, physical, and information resources to solve problems and accomplish missions" to achieve the goals of an organization or en ...
, and image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
and dissemination; an LRE for controlling launch and recovery; and associated ground support equipment. The LRE provides precision Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately to .
DGPSs c ...
corrections for navigational accuracy during takeoff and landings, while precision coded GPS supplemented with an inertial navigation system
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (dire ...
is used during mission execution. By having separable elements in the ground segment, the MCE and the LRE can operate in geographically separate locations, and the MCE can be deployed with the supported command's primary exploitation site. Both ground segments are contained in military shelters with external antennas for line-of-sight and satellite communication
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. C ...
s with the air vehicles.
Sensor packages

Radar
The Global Hawk carries the Hughes Integrated Surveillance & Reconnaissance (HISAR) sensor system. HISAR is a lower-cost derivative of the ASARS-2 package that Hughes developed for the U-2. It is also fitted to the US Army's de Havilland Canada RC-7B Airborne Reconnaissance Low Multifunction (ARLM) crewed aircraft, and is being sold on the international market. HISAR integrates aSAR
SAR or Sar may refer to:
Places
* Sar (river), Galicia, Spain
* Sar, Bahrain, a residential district
* Sar, Iran (disambiguation), several places in Iran
* Sar, Tibet, Tibet Autonomous Region of China
* Šar Mountains, in southeastern Europe
...
- MTI system, along with an optical and a thermography
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a Thermographic camera, thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are ...
imager.
All three sensors are controlled and their outputs filtered by a common processor and transmitted in real time at up to 50 Mbit/s to a ground station. The SAR-MTI system operates in the X band in various operational modes; such as the wide-area MTI mode with a radius of , combined SAR-MTI strip mode provides resolution over wide sections, and a SAR spot mode providing resolution over .
In July 2006, the USAF began testing the Global Hawk Block 30 upgrades in the Benefield Anechoic Facility
Benefield Anechoic Facility (BAF) is an anechoic chamber located at the southwest side of the Edwards Air Force Base main base. It is currently the world's largest anechoic chamber. The BAF supports installed systems testing for avionics test pro ...
at Edwards AFB. Upgrades include the Advanced Signals Intelligence Payload, an extremely sensitive SIGINT processor. and a specialist AESA radar system, the Multi-Platform Radar Technology Insertion Program
The Multi-Platform Radar Technology Insertion Program (MP-RTIP), a U.S. Air Force project led by contractor Northrop Grumman to develop the next generation of airborne air-to-air and air-to-ground radar systems. While initially planned for multipl ...
, or MP-RTIP. In 2010, Northrop disclosed the sensor capabilities of the new Block 40 aircraft, including the MP-RTIP radar, emphasising surveillance over reconnaissance.
On 14 April 2014, a Block 40 Global Hawk completed the first Maritime Modes program risk-reduction flight to enhance the Air Force's maritime surveillance capabilities. Maritime Modes is made up of a Maritime Moving Target Indicator and a Maritime Inverse synthetic aperture radar
Inverse synthetic-aperture radar (ISAR) is a radar technique using radar imaging to generate a two-dimensional high resolution image of a target. It is analogous to conventional SAR, except that ISAR technology uses the movement of the target rath ...
(MISAR) that function together to provide ISR information on vessels traveling on the water's surface. During the 11.5-hour flight off of the California coast, the MISAR collected data on over 100 items of interest. Maritime Modes is planned to be integrated with the RQ-4B's existing MP-RTIP radar to detect and produce synthetic aperture radar imagery
Imaging radar is an application of radar which is used to create two-dimensional images, typically of landscapes. Imaging radar provides its light to illuminate an area on the ground and take a picture at radio wavelengths. It uses an antenna and ...
of ground vehicles.
In November 2015, Northrop Grumman selected the Garmin International GSX 70 weather radar to be installed on Air Force Global Hawks. The GSX 70 is designed to provide operators with real-time weather information, offering horizontal scan angles of up to 120 degrees for better visibility into the strength and intensity of convective activity and a vertical scanning mode to analyze storm tops, gradients, and cell buildup activity. It also has a Turbulence Detection feature to identify turbulence in air containing precipitation and other airborne particulates and Ground Clutter Suppression that removes ground returns from the display so operators can focus on weather. Installation is expected to begin in early 2016. Installation of weather radars on the Global Hawk fleet completed in late 2019.
Visible light/infrared
The visible and infrared imagers share the same gimballed sensor package, and use common optics, providing a telescopic close-up capability. It can be optionally fitted with an auxiliary SIGINT package.Operational history
U.S. Air Force
Following theSeptember 11th attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial ...
, the normal acquisition process was bypassed almost immediately and early developmental Global Hawk models were employed in overseas contingency operations beginning in November 2001. Global Hawk ACTD prototypes were used in the War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
*Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see als ...
and in the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
. Since April 2010, they fly the Northern Route, from Beale Air Force Base
Beale Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force base located approximately east of Marysville, California. It is located outside Linda, about east of the towns of Marysville and Yuba City, and about north of Sacramento.
The host ...
over Canada to South-East Asia and back, reducing flight time and improving maintenance. While their data-collection capabilities have been praised, the program lost three prototype aircraft to accidents, more than one quarter of the aircraft used in the wars.
The crashes were reported to be due to "technical failures or poor maintenance", with a failure rate per hour flown over 100 times higher than the F-16
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine Multirole combat aircraft, multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it ...
fighter. Northrop Grumman stated that it was unfair to compare the failure rates of a mature design to that of a prototype aircraft. In June 2012, a media report described the Global Hawk, the General Atomics MQ-1 Predator
The General Atomics MQ-1 Predator (often referred to as the predator drone) is an American remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) built by General Atomics that was used primarily by the United States Air Force (USAF) and Central Intelligence Agency ( ...
and the MQ-9 Reapers "... the most accident-prone aircraft in the Air Force fleet." On 11 February 2010, the Global Hawks deployed in the Central Command AOR accrued 30,000 combat hours and 1,500 plus sorties.
Initial operational capability was declared for the RQ-4 Block 30 in August 2011. The USAF did not plan to keep the RQ-4B Block 30 in service past 2014 due to the U-2 and other platforms being less expensive in the role. Congress sought to keep it in service until December 2016. The USAF had 18 RQ-4 Block 30s by the time of the passage of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2013, which directed a further three RQ-4s to be procured as part of Lot 11. The USAF felt that additional aircraft were "excess to need" and likely become backup or attrition reserve models.
Despite the potential retirement of the Block 30 fleet due to low reliability, low mission readiness, and high costs, the USAF released a pre-solicitation notice in September 2013 for Lot 12 aircraft. In planning the USAF's FY 2015 budget, the Pentagon reversed its previous decision, shifting $3 billion from the U-2 to the RQ-4 Block 30, which had become more competitive with the U-2 due to increased flying hours. Factors such as cost per flight hour (CPFH), information gathering rates, mission readiness, adverse weather operational capability, distance to targets, and onboard power still favored the U-2.
After the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes ...
, RQ-4s flew 300 hours over the affected areas in Japan. There were also plans to survey the No. 4 reactor at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
The is a disabled nuclear power plant located on a site in the towns of Ōkuma and Futaba in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The plant suffered major damage from the magnitude 9.0 earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan on March 11, 2011. The ...
.
By November 2012, Northrop Grumman had delivered 37 Global Hawks to the USAF. In March 2014, 42 Global Hawks are in use around the world, with 32 in use by the USAF.
The USAF stated that U-2 pilot and altitude advantages allow better functionality in the stormy weather and airspace restrictions of the East Asia region and its altitude and sensor advantages allow it to see further into hostile territory. In October 2013, the U.S. secured basing rights to deploy RQ-4s from Japan, the first time that basing rights for the type had been secured in Northeast Asia. RQ-4s are stationed at Andersen Air Force Base in Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, but bad weather often curtailed flights. Basing in Japan as opposed to Guam enhances spying capabilities against North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Y ...
by eliminating range as a factor.
Two RQ-4s moved from Anderson AFB to Misawa Air Base
is an air base of the Japan Air Self-Defense Force (JASDF), the United States Air Force, and the United States Navy located in Misawa, Aomori, in the northern part of the island of Honshū of Japan. It is located northeast of Misawa railwa ...
in mid-2014 in the type's first deployment to Japan. They were speculated to have focused on maritime patrol missions. The two RQ-4s successfully performed their missions from Misawa AB during a six-month deployment, with none cancelled due to poor weather. It was the first time that they had operated out of a civil-military airport, sharing airspace and runways with commercial aircraft safely without additional restrictions, usually taking off and landing during quieter periods of air traffic. Officials only stated that they had operated at "various places around the Pacific."
On 19 September 2013, the RQ-4 Block 40 Global Hawk conducted its first wartime flight from Grand Forks Air Force Base
Grand Forks Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in northeastern North Dakota, located north of Emerado and west of Grand Forks.
The host unit is the 319th Reconnaissance Wing (319 RW) assigned to the Air Combat Co ...
.
In November 2013, an USAF RQ-4 deployed to the Philippines after Typhoon Haiyan
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. On making landfall, Haiyan devastated portions of Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines. It is one of the ...
to assist in relief efforts. It flew from Andersen Air Force Base in Guam to relay imagery of afflicted areas to response personnel and ground commanders.
In planning for the FY 2015 budget, the U-2 was to be retired in favor of the RQ-4, made possible by reductions of RQ-4 operating costs and would be the first time an uncrewed aircraft would completely replace a crewed aircraft. The U-2 will continue to fly through 2018 without replacement.
In May 2014, a U.S. Global Hawk conducted a surveillance mission over Nigeria as part of the search for the kidnapped Nigerian schoolgirls. The Global Hawk joined MC-12 crewed aircraft in the search.
The Global Hawk was used in Operation Inherent Resolve
Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR) is the U.S. military's operational name for the International military intervention against IS, including both a campaign in Iraq and a campaign in Syria, with a closely-related campaign in Libya. Throu ...
(OIR) against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
An Islamic state is a State (polity), state that has a form of government based on sharia, Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical Polity, polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a t ...
(ISIL). The aircraft provided real-time imagery and signals intelligence to identify friendly and enemy forces, do long-term target development, and track enemy equipment movement, enabling combatant commanders to act on better information and make key decisions. The BACN version allowed ground troops to contact aircraft when they were in need of assistance, such as close air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and moveme ...
.
On 11 November 2015, an EQ-4 became the first Global Hawk aircraft to reach 500 sortie
A sortie (from the French word meaning ''exit'' or from Latin root ''surgere'' meaning to "rise up") is a deployment or dispatch of one military unit, be it an aircraft, ship, or troops, from a strongpoint. The term originated in siege warfare. ...
s. All three EQ-4s in operation supported OIR. Upon landing, maintainers could complete ground maintenance and make the aircraft mission ready again within five hours. Missions could last up to 30 hours, with each aircraft getting a "day off" in between combat flights. On 1 April 2017, the EQ-4 program completed 1,000 continuous sorties, without incurring a single maintenance cancellation, while supporting OIR.
On 4 April 2016, it was reported that a USAF Global Hawk had completed its third flight over Germany under an initiative (the European Reassurance Initiative) to reassure NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
members concerned over Russian involvement in the conflict in Ukraine
The following is a list of major conflicts fought by Ukraine, by Ukrainian people or by regular armies during periods when independent states existed on the modern territory of Ukraine, from the Kyivan Rus' times to the present day. It also ...
. Germany opened its airspace for up to five Global Hawk flights a month until the middle of October 2016. The Naval Air Station Sigonella
Naval Air Station (NAS) Sigonella is an Italian Air Force base ('' it, Aeroporto "Cosimo Di Palma" di Sigonella''), and a U.S. Navy installation at Italian Air Force Base Sigonella in Sicily, Italy. The whole NAS is a tenant of the Italian Air ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
-based Global Hawk flies over Italian and French airspace and an air corridor through Germany with its sensors switched off on its way to its area of operations over the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
.
In 2017, the USAF decided to begin the process of training enlisted airmen to fly the RQ-4 due to a shortage of pilots and an increased demand for the Global Hawk's capabilities. The RQ-4 is currently the only aircraft enlisted pilots are flying.
On 16 August 2018, a Global Hawk, assigned to 12th Reconnaissance Squadron, took off from Beale AFB, California, and landed at Eielson Air Force Base
Eielson Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base located approximately 26 miles (42 km) southeast of Fairbanks, Alaska and just southeast of Moose Creek, Alaska. It was established in 1943 as Mile 26 Satellite Field and redes ...
, Alaska for Red Flag – Alaska. This was the first time an RQ-4 had landed in Alaska during a simulated combat training exercise.
On 21 April 2021, a Global Hawk was reported to have made a reconnaissance flight in an airspace off the coast of southern Crimea which Russia had temporarily closed up to from Sevastopol to Feodosiya, issuing a relevant NOTAM. The Global Hawk reportedly departed from Naval Air Station Sigonella on Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
.
On 22 February 2022, a Global Hawk was reported to have made a reconnaissance flight over Southeastern Ukraine coinciding with a NOTAM order by Ukrainian government and increased Russian military activity. The Global Hawk departed from Naval Air Station Sigonella on Sicily.
Records
On 24 April 2001, a Global Hawk flew non-stop from Edwards Air Force Base, Edwards AFB to RAAF Base Edinburgh in Australia, making history by being the first pilotless aircraft to cross the Pacific Ocean. The flight took 22 hours, and set a world record for absolute distance flown by a UAV, .Aviation history as Global Hawk completes US–Australia flight." Australian Ministry of Defence press release. 24 April 2001 On 22 March 2008, a Global Hawk set the endurance record for full-scale, operational uncrewed aircraft UAVs by flying for 33.1 hours at altitudes up to 60,000 feet over Edwards AFB. From its first flight in 1998 to 9 September 2013, the combined Global Hawk fleet flew 100,000 hours. 88 percent of flights were conducted by USAF RQ-4s, while the remaining hours were flown by NASA Global Hawks, the EuroHawk, the Navy BAMS demonstrator, and the MQ-4C Triton. Approximately 75 percent of flights were in combat zones; RQ-4s flew in operations over Afghanistan, Iraq, and Libya; and supported disaster response efforts in Haiti, Japan, and California."Northrop Grumman Unmanned Aircraft Systems Achieve 100,000 Flight Hours".
Defensemedianetwork.com, 13 September 2013 From 10 to 16 September 2014, the RQ-4 fleet flew a total of 781 hours, the most hours flown by the type during a single week. 87 percent of flights were made by USAF RQ-4s, with the rest flown by the Navy BAMS-D and NASA hurricane research aircraft. The longest Global Hawk combat sortie lasted 32.5 hours.
Downing by Iran
On 19 June 2019, a U.S. Navy BAMS-D RQ-4A from NAS Patuxent River flying over the Persian Gulf near the Strait of Hormuz was shot down by a Sevom Khordad, 3rd Khordad surface-to-air missile fired from near Garuk, Hormozgan, Garuk, Iran. Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif, Javad Zarif said that the drone had been in Iranian airspace, while the United States maintained that the drone was in airspace, international airspace 18 nautical miles (34 Kilometre, km) away from Iran.NASA
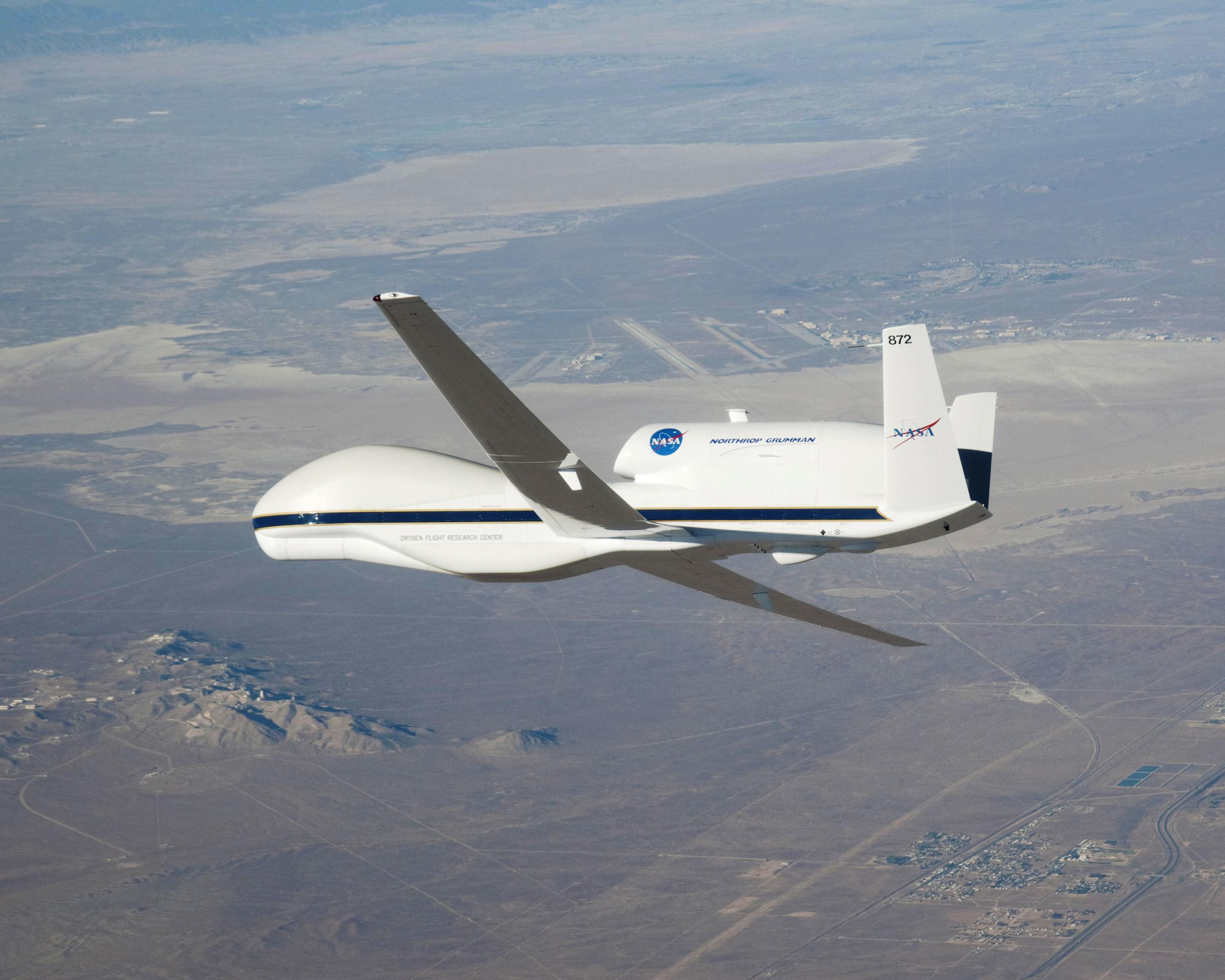
 In December 2007, two Global Hawks were transferred from the USAF to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB. Initial research activities beginning in the second quarter of 2009 supported NASA's high-altitude, long-duration Earth science missions. The two Global Hawks were the first and sixth aircraft built under the original DARPA Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration program, and were made available to NASA when the Air Force had no further need for them. Northrop Grumman is an operational partner with NASA and will use the aircraft to demonstrate new technologies and to develop new markets for the aircraft, including possible civilian uses.
It was reported in the March 2010 issue of ''Scientific American'' that NASA's Global Hawks were to begin scientific missions that month, and had been undergoing tests in late 2009. Initial science applications included measurements of the ozone layer and cross-Pacific transport of air pollutants and aerosols. The author of the Scientific American article speculates that it could be used for Antarctic exploration while being based in Chile. In August–September 2010, one of the two Global Hawks was loaned for NASA's GRIP (Genesis and Rapid Intensification Program) mission.
Its long-term on station capabilities and long range made it a suitable aircraft for monitoring the development of Atlantic basin Tropical cyclone, hurricanes. It was modified to equip weather sensors including Ku-band radar, lightning sensors and dropsondes. It successfully flew into Hurricane Earl (2010), Hurricane Earl off the United States East Coast on 2 September 2010."Hurricane Earl News Release"
In December 2007, two Global Hawks were transferred from the USAF to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB. Initial research activities beginning in the second quarter of 2009 supported NASA's high-altitude, long-duration Earth science missions. The two Global Hawks were the first and sixth aircraft built under the original DARPA Advanced Concept Technology Demonstration program, and were made available to NASA when the Air Force had no further need for them. Northrop Grumman is an operational partner with NASA and will use the aircraft to demonstrate new technologies and to develop new markets for the aircraft, including possible civilian uses.
It was reported in the March 2010 issue of ''Scientific American'' that NASA's Global Hawks were to begin scientific missions that month, and had been undergoing tests in late 2009. Initial science applications included measurements of the ozone layer and cross-Pacific transport of air pollutants and aerosols. The author of the Scientific American article speculates that it could be used for Antarctic exploration while being based in Chile. In August–September 2010, one of the two Global Hawks was loaned for NASA's GRIP (Genesis and Rapid Intensification Program) mission.
Its long-term on station capabilities and long range made it a suitable aircraft for monitoring the development of Atlantic basin Tropical cyclone, hurricanes. It was modified to equip weather sensors including Ku-band radar, lightning sensors and dropsondes. It successfully flew into Hurricane Earl (2010), Hurricane Earl off the United States East Coast on 2 September 2010."Hurricane Earl News Release"NASA GRIP News
NATO
In 2009, NATO announced that it expected to have a fleet of up to eight Global Hawks by 2012 to be equipped with MP-RTIP radar systems. NATO had budgeted US$1.4 billion (€1 billion) for the project, and a letter of intent was signed.Trimble, Stephen''Flight International'', 14 January 2009. NATO signed a contract for five Block 40 Global Hawks in May 2012. 12 NATO members are participating in the purchase. On 10 January 2014, Estonia revealed it wanted to participate in NATO Global Hawk usage. In July 2017, the USAF assigned the Mission Designation Series (MDS) of RQ-4D to the NATO AGS air vehicle. The first RQ-4D aircraft arrived at Sigonella Air Base on 21 November 2019. At that time, all five aircraft were undergoing developmental test flights. Initial operational capability was expected in the first half of 2020. In October 2018, Italy certified five of the drones for use in Sigonella,
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
in 2020. However, by 23 December 2019, there were regulatory issues for the Global Hawks concerning shared space between Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Italy. German government officials criticized the new drones for their lack of technology to avoid collisions with other aircraft.
South Korea
In 2011,South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
's Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) expressed interest in acquiring at least four RQ-4Bs to increase intelligence capabilities following the exchange of the Wartime Operational Control from the U.S. to the Republic of Korea. Officials debated on the topic of the Global Hawks and domestic UAV programs. In September 2011, the US and South Korea discussed aircraft deployments near its land border to view North Korea and the North Korea–China border.
In January 2012, DAPA announced that it would not proceed with a purchase due to a price rise from US$442M to US$899M, and that other platforms such as the AeroVironment Global Observer or the Boeing Phantom Eye were being investigated. However, in December 2012, South Korea notified Congress of a possible Foreign Military Sales, Foreign Military Sale of 4 RQ-4 Block 30 (I) Global Hawks with the Enhanced Integrated Sensor Suite (EISS) at an estimated cost of $1.2 billion. On 5 July 2013, the Korean National Assembly advised the government to re-evaluate the RQ-4 purchase, again citing high costs.
On 17 December 2014, Northrop Grumman was awarded a $657 million contract by South Korea for four RQ-4B Block 30 Global Hawks. The first RQ-4 arrived on 23 December 2019 at a base near Sacheon. The second arrived on 19 April 2020, and the third by June. The fourth and final Global Hawk was delivered in September 2020.
Japan
On 24 August 2013, Japan announced that the Japan Air Self-Defense Force planned to operate one Global Hawk jointly with the U.S. by 2015. On 21 November 2014, the Ministry of Defense (Japan), Japanese Ministry of Defense officially decided to procure the Global Hawk instead of the General Atomics General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper, Guardian ER; Japan has also been interested in the purchase of three aircraft. The first Japanese Global Hawk landed atMisawa Air Base
is an air base of the Japan Air Self-Defense Force (JASDF), the United States Air Force, and the United States Navy located in Misawa, Aomori, in the northern part of the island of Honshū of Japan. It is located northeast of Misawa railwa ...
on 12 March 2022.
Potential operators
Australia considered the purchase of a number of Global Hawks for maritime and land surveillance. The Global Hawk was to be assessed against the MQ-9 Reaper#SeaGuardian, General Atomics MQ-9 Mariner in trials in 2007. The Global Hawk aircraft would have operated in conjunction with crewed Boeing P-8 Poseidon aircraft, as a replacement of aging Lockheed AP-3C Orion aircraft. In the end, the Australian government decided not to proceed and canceled the order. In 2012, a procurement effort for seven UAVs by 2019 was initiated. In May 2013 the Australian government confirmed its interest in acquiring the MQ-4C Triton maritime surveillance variant. Canada has also been a potential customer, looking at the Global Hawk for maritime and land surveillance as either a replacement for its fleet of Lockheed CP-140 Aurora patrol aircraft or to supplement crewed patrols of remote Arctic and maritime environments, before withdrawing from the joint effort in August 2011. Spain has a similar requirement, and has existing contacts with Northrop Grumman. The New Zealand Defence Force is studying the Global Hawk, which has the range to conduct surveillance in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica, and in the Pacific Islands. The acquisition process has not moved beyond an expression of interest. The Indian Navy has expressed interest in acquiring six to eight MQ-4C Maritime Surveillance Unmanned Aircraft Systems. In September 2018, Transport Canada was looking into buying a former German Air Force EuroHawk for surveillance missions in the Arctic. The EuroHawk cannot currently fly and has no equipment inside such as GPS and navigation tools.Variants
 ;RQ-4A: Initial production version for the USAF, 16 built.
;RQ-4B: Improved version with increased payload, wingspan increased to and length increased to . Due to the increased size and payload the range is reduced to .
;RQ-4D Phoenix
: NATO Alliance Ground Surveillance (AGS).
;RQ-4E Euro Hawk
: Version for the Bundeswehr based on RQ-4B and equipped with an EADS reconnaissance payload for SIGINT. Germany canceled its order in May 2013; it received one of five Euro Hawks originally ordered.
;
;RQ-4A: Initial production version for the USAF, 16 built.
;RQ-4B: Improved version with increased payload, wingspan increased to and length increased to . Due to the increased size and payload the range is reduced to .
;RQ-4D Phoenix
: NATO Alliance Ground Surveillance (AGS).
;RQ-4E Euro Hawk
: Version for the Bundeswehr based on RQ-4B and equipped with an EADS reconnaissance payload for SIGINT. Germany canceled its order in May 2013; it received one of five Euro Hawks originally ordered.
; MQ-4C Triton
The Northrop Grumman MQ-4C Triton is an American high-altitude long endurance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) under development for the United States Navy as a surveillance aircraft. Together with its associated ground control station, it is an ...
: For USN Broad Area Maritime Surveillance (BAMS) role; previously known as the ''RQ-4N''; 4 ordered, 68 total planned.
;EQ-4B
: Equipped with the Battlefield Airborne Communications Node (BACN) system.
;KQ-X
: Proposed autonomous tanker variant.
;Model 396
: Scaled Composites and Northrop Grumman also offered an armed, 50% smaller version of the RQ-4A, known as the Scaled Composites Model 396, as part of the USAF Hunter-Killer program. The aircraft was rejected in favor of the MQ-9 Reaper.
Operators
 ;
* Republic of Korea Air Force – Ordered 4 in 2014. First aircraft delivered on 23 December 2019.
;
* Japan Air Self-Defense Force – Ordered 3 in November 2018, to be delivered by 1 September 2022. The purchase was made under a contract worth $USD1.2 billion.
;
* Alliance Ground Surveillance – Ordered 5 aircraft, first delivered 21 November 2019.
;
*
;
* Republic of Korea Air Force – Ordered 4 in 2014. First aircraft delivered on 23 December 2019.
;
* Japan Air Self-Defense Force – Ordered 3 in November 2018, to be delivered by 1 September 2022. The purchase was made under a contract worth $USD1.2 billion.
;
* Alliance Ground Surveillance – Ordered 5 aircraft, first delivered 21 November 2019.
;
* United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal ...
**Air Combat Command
***Grand Forks Air Force Base, 319th Reconnaissance Wing – Grand Forks Air Force Base
Grand Forks Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in northeastern North Dakota, located north of Emerado and west of Grand Forks.
The host unit is the 319th Reconnaissance Wing (319 RW) assigned to the Air Combat Co ...
, North Dakota
****319th Operations Group
*****397th Bombardment Squadron, 7th Reconnaissance Squadron – Naval Air Station Sigonella, Italy
***** 12th Reconnaissance Squadron – Beale Air Force Base, California
*****319th OG Detachment 1 – Andersen Air Force Base, Guam
***** 348th Bombardment Squadron, 348th Reconnaissance Squadron – Grand Forks Air Force Base, North Dakota
*** 53d Wing
**** 53d Test and Evaluation Group
***** 31st Test and Evaluation Squadron – Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is E ...
, California
** Air Force Reserve Command
*** 940th Wing – Beale Air Force Base
Beale Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force base located approximately east of Marysville, California. It is located outside Linda, about east of the towns of Marysville and Yuba City, and about north of Sacramento.
The host ...
, California
**** 940th Operations Group
***** 13th Reconnaissance Squadron – Beale Air Force Base
Beale Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force base located approximately east of Marysville, California. It is located outside Linda, about east of the towns of Marysville and Yuba City, and about north of Sacramento.
The host ...
, California
** 380th Expeditionary Operations Group – Al Dhafra AB, United Arab Emirates since early 2002
*** RQ-4B (Block 30), RQ-4B (Block 40), EQ-4B (BACN), RQ-4A (BAMS-D)
* NASA
** Dryden Flight Research Center
Accidents
* 29 March 1999: USAF RQ-4A 95-2002 crashed at China Lake Naval Weapons Center. * 30 Dec 2001: USAF RQ-4A 98-2005 crashed while returning to al-Dhafra Air Base, UAE. * 10 Jul 2002: USAF RQ-4A 98-2004 crashed near Shamsi AB, Pakistan due to engine failure. * 21 August 2011: USAF EQ-4B crashed southeast of Jalalabad, Afghanistan. * 11 June 2012: USN RQ-4A assigned to the Navy's BAMS program crashed nearNaval Air Station Patuxent River
Naval Air Station Patuxent River , also known as NAS Pax River, is a United States naval air station located in St. Mary’s County, Maryland, on the Chesapeake Bay near the mouth of the Patuxent River.
It is home to Headquarters, Naval Air Sys ...
, Maryland, US.
* 21 June 2017: USAF RQ-4B crashed near Lone Pine, California, US.
* 26 June 2018: USAF RQ-4B crashed into the sea off Naval Station Rota, Spain.
* August 2021: USAF RQ-4B crashed near Grand Forks Air Force Base, North Dakota, US.
Specifications (RQ-4B Block 30/40)
See also
References
* ''This article contains material that originally came from the web articleUnmanned Aerial Vehicles
' by Greg Goebel, which is public domain.''
External links
RQ-4 Global Hawk U.S. Air Force fact sheet
Federation of American Scientists
"Global Hawk RQ-4A-B High Altitude Long Endurance UAV"
Defense Update
Raytheon product page on the Global Hawk Integrated Sensor Suite
Luftwaffe Euro Hawk page
{{Q-UAVs Northrop Grumman aircraft, RQ-004 Global Hawk 1990s United States military reconnaissance aircraft Unmanned military aircraft of the United States Single-engined jet aircraft Low-wing aircraft V-tail aircraft Signals intelligence Synthetic aperture radar Aircraft first flown in 1998