Runway 32 Grise Fiord on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface ( grass, dirt,
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface ( grass, dirt,
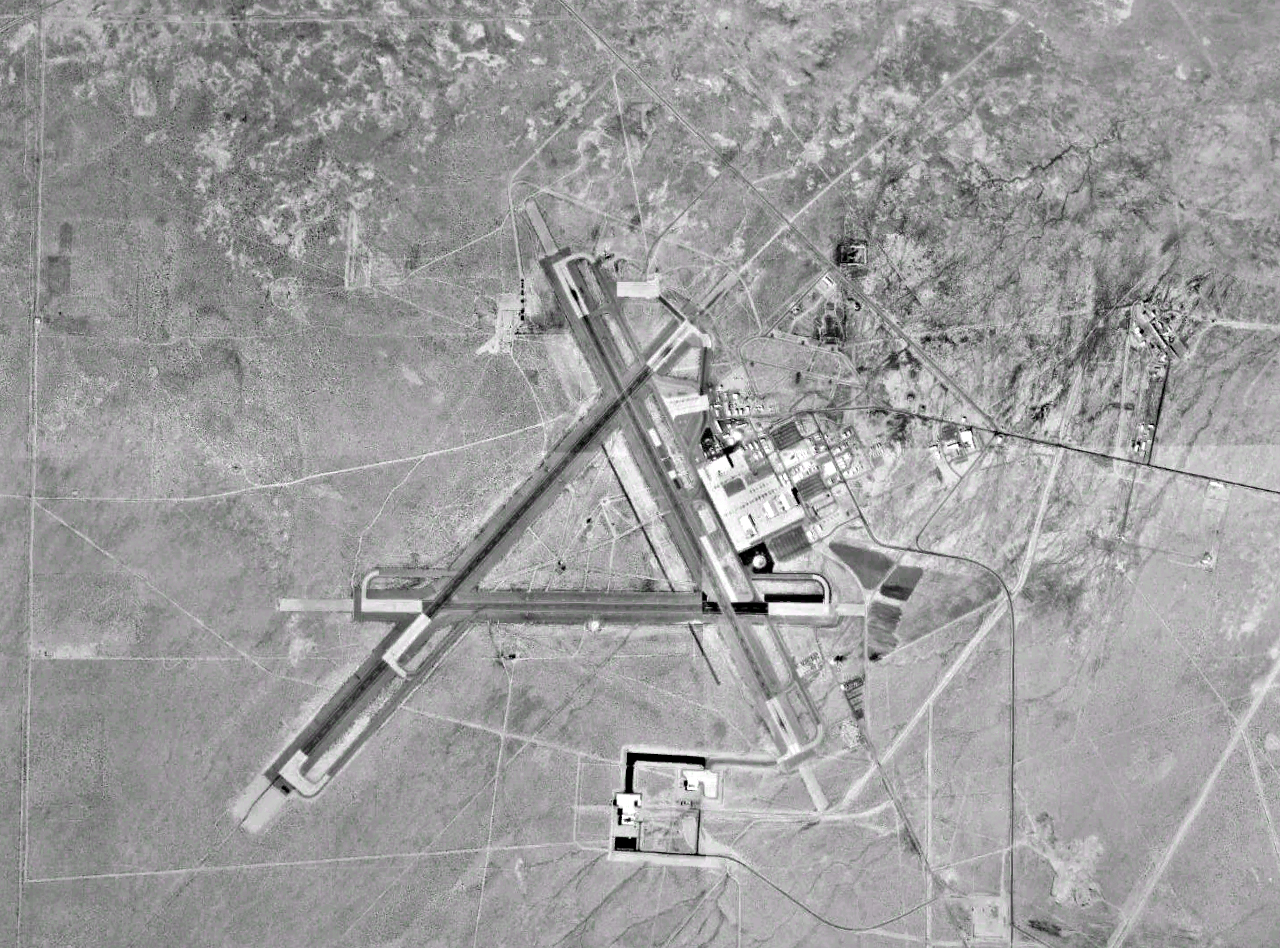 Originally in the 1920s and 1930s, airports and air bases (particularly in the United Kingdom) were built in a triangle-like pattern of three runways at 60° angles to each other. The reason was that back then aviation was only starting, and as a result although it was known that winds affect runway distance required, etc. not much was known about wind behaviour. As a result, three runways in a triangle-like pattern were built, and the runway with the heaviest traffic on it would eventually expand into an airport's main runway, while the other two runways would be either abandoned or converted into taxiways. For example
Originally in the 1920s and 1930s, airports and air bases (particularly in the United Kingdom) were built in a triangle-like pattern of three runways at 60° angles to each other. The reason was that back then aviation was only starting, and as a result although it was known that winds affect runway distance required, etc. not much was known about wind behaviour. As a result, three runways in a triangle-like pattern were built, and the runway with the heaviest traffic on it would eventually expand into an airport's main runway, while the other two runways would be either abandoned or converted into taxiways. For example

 Runways are named by a number between 01 and 36, which is generally the
Runways are named by a number between 01 and 36, which is generally the  A leading zero, for example in "runway zero-six" or "runway zero-one-left", is included for all ICAO and some U.S. military airports (such as
A leading zero, for example in "runway zero-six" or "runway zero-one-left", is included for all ICAO and some U.S. military airports (such as
 If there is more than one runway pointing in the same direction (parallel runways), each runway is identified by appending left (L), center (C) and right (R) to the end of the runway number to identify its position (when facing its direction)—for example, runways one-five-left (15L), one-five-center (15C), and one-five-right (15R). Runway zero-three-left (03L) becomes runway two-one-right (21R) when used in the opposite direction (derived from adding 18 to the original number for the 180° difference when approaching from the opposite direction). In some countries, regulations mandate that where parallel runways are too close to each other, only one may be used at a time under certain conditions (usually adverse weather).
At large airports with four or more parallel runways (for example, at Chicago O'Hare, Los Angeles, Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County, Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta, Denver, Dallas–Fort Worth and Orlando), some runway identifiers are shifted by 1 to avoid the ambiguity that would result with more than three parallel runways. For example, in Los Angeles, this system results in runways 6L, 6R, 7L, and 7R, even though all four runways are actually parallel at approximately 69°. At Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, there are five parallel runways, named 17L, 17C, 17R, 18L, and 18R, all oriented at a heading of 175.4°. Occasionally, an airport with only three parallel runways may use different runway identifiers, such as when a third parallel runway was opened at
If there is more than one runway pointing in the same direction (parallel runways), each runway is identified by appending left (L), center (C) and right (R) to the end of the runway number to identify its position (when facing its direction)—for example, runways one-five-left (15L), one-five-center (15C), and one-five-right (15R). Runway zero-three-left (03L) becomes runway two-one-right (21R) when used in the opposite direction (derived from adding 18 to the original number for the 180° difference when approaching from the opposite direction). In some countries, regulations mandate that where parallel runways are too close to each other, only one may be used at a time under certain conditions (usually adverse weather).
At large airports with four or more parallel runways (for example, at Chicago O'Hare, Los Angeles, Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County, Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta, Denver, Dallas–Fort Worth and Orlando), some runway identifiers are shifted by 1 to avoid the ambiguity that would result with more than three parallel runways. For example, in Los Angeles, this system results in runways 6L, 6R, 7L, and 7R, even though all four runways are actually parallel at approximately 69°. At Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, there are five parallel runways, named 17L, 17C, 17R, 18L, and 18R, all oriented at a heading of 175.4°. Occasionally, an airport with only three parallel runways may use different runway identifiers, such as when a third parallel runway was opened at
/ref> Runways that are numbered relative to true north rather than magnetic north will use the suffix T; this is advantageous for certain airfields in the far north such as Thule Air Base.
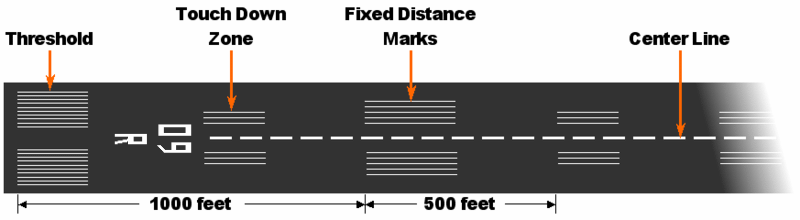
 * The runway thresholds are markings across the runway that denote the beginning and end of the designated space for landing and takeoff under non-emergency conditions.
* The
* The runway thresholds are markings across the runway that denote the beginning and end of the designated space for landing and takeoff under non-emergency conditions.
* The  *
*  * Clearway is an area beyond the paved runway, aligned with the runway centerline and under the control of the airport authorities. This area is not less than 500 ft and there are no protruding obstacles except for threshold lights provided that they aren't higher than 26 inches. There is a limit on the upslope of the clearway of 1.25%. The length of the clearway may be included in the length of the
* Clearway is an area beyond the paved runway, aligned with the runway centerline and under the control of the airport authorities. This area is not less than 500 ft and there are no protruding obstacles except for threshold lights provided that they aren't higher than 26 inches. There is a limit on the upslope of the clearway of 1.25%. The length of the clearway may be included in the length of the
 There are three types of runways:
* Visual runways are used at small airstrips and are usually just a strip of grass, gravel, ice, asphalt, or concrete. Although there are usually no markings on a visual runway, they may have threshold markings, designators, and centerlines. Additionally, they do not provide an instrument-based landing procedure; pilots must be able to see the runway to use it. Also, radio communication may not be available and pilots must be self-reliant.
* Non-precision instrument runways are often used at small- to medium-size airports. These runways, depending on the surface, may be marked with threshold markings, designators, centerlines, and sometimes a mark (known as an aiming point, sometimes installed at ). While centerlines provide horizontal position guidance, aiming point markers provide vertical position guidance to planes on visual approach.
* Precision instrument runways, which are found at medium- and large-size airports, consist of a blast pad/stopway (optional, for airports handling jets), threshold, designator, centerline, aiming point, and , /, , , and touchdown zone marks. Precision runways provide both horizontal and vertical guidance for instrument approaches.
Waterways may be unmarked or marked with
There are three types of runways:
* Visual runways are used at small airstrips and are usually just a strip of grass, gravel, ice, asphalt, or concrete. Although there are usually no markings on a visual runway, they may have threshold markings, designators, and centerlines. Additionally, they do not provide an instrument-based landing procedure; pilots must be able to see the runway to use it. Also, radio communication may not be available and pilots must be self-reliant.
* Non-precision instrument runways are often used at small- to medium-size airports. These runways, depending on the surface, may be marked with threshold markings, designators, centerlines, and sometimes a mark (known as an aiming point, sometimes installed at ). While centerlines provide horizontal position guidance, aiming point markers provide vertical position guidance to planes on visual approach.
* Precision instrument runways, which are found at medium- and large-size airports, consist of a blast pad/stopway (optional, for airports handling jets), threshold, designator, centerline, aiming point, and , /, , , and touchdown zone marks. Precision runways provide both horizontal and vertical guidance for instrument approaches.
Waterways may be unmarked or marked with
 A line of lights on an airfield or elsewhere to guide aircraft in taking off or coming in to land or an illuminated runway is sometimes also known as a flare path.
A line of lights on an airfield or elsewhere to guide aircraft in taking off or coming in to land or an illuminated runway is sometimes also known as a flare path.
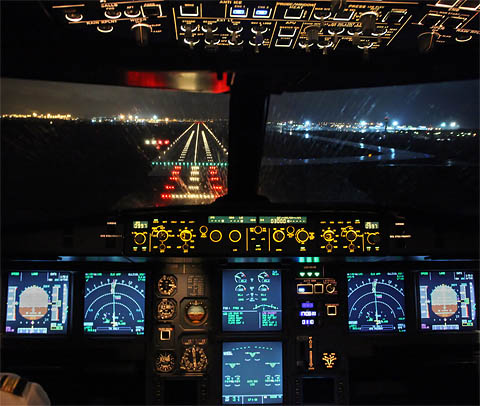

 Runway lighting are used at airports for use at night and low visibility. Seen from the air, runway lights form an outline of the runway. A runway may have some or all of the following:
* Runway end identifier lights (REIL) – unidirectional (facing approach direction) or omnidirectional pair of synchronized flashing lights installed at the runway threshold, one on each side.
* Runway end lights – a pair of four lights on each side of the runway on precision instrument runways, these lights extend along the full width of the runway. These lights show green when viewed by approaching aircraft and red when seen from the runway.
* Runway edge lights – white elevated lights that run the length of the runway on either side. On precision instrument runways, the edge-lighting becomes amber in the last of the runway, or last third of the runway, whichever is less. Taxiways are differentiated by being bordered by blue lights, or by having green center lights, depending on the width of the taxiway, and the complexity of the taxi pattern.
* Runway centerline lighting system (RCLS) – lights embedded into the surface of the runway at intervals along the runway centerline on some precision instrument runways. White except the last : alternate white and red for next and red for last .
* Touchdown zone lights (TDZL) – rows of white light bars (with three in each row) at intervals on either side of the centerline for .
* Taxiway centerline lead-off lights – installed along lead-off markings, alternate green and yellow lights embedded into the runway pavement. It starts with green light at about the runway centerline to the position of first centerline light beyond the Hold-Short markings on the taxiway.
* Taxiway centerline lead-on lights – installed the same way as taxiway centerline lead-off Lights, but directing airplane traffic in the opposite direction.
* Land and hold short lights – a row of white pulsating lights installed across the runway to indicate hold short position on some runways that are facilitating land and hold short operations (LAHSO).
*
Runway lighting are used at airports for use at night and low visibility. Seen from the air, runway lights form an outline of the runway. A runway may have some or all of the following:
* Runway end identifier lights (REIL) – unidirectional (facing approach direction) or omnidirectional pair of synchronized flashing lights installed at the runway threshold, one on each side.
* Runway end lights – a pair of four lights on each side of the runway on precision instrument runways, these lights extend along the full width of the runway. These lights show green when viewed by approaching aircraft and red when seen from the runway.
* Runway edge lights – white elevated lights that run the length of the runway on either side. On precision instrument runways, the edge-lighting becomes amber in the last of the runway, or last third of the runway, whichever is less. Taxiways are differentiated by being bordered by blue lights, or by having green center lights, depending on the width of the taxiway, and the complexity of the taxi pattern.
* Runway centerline lighting system (RCLS) – lights embedded into the surface of the runway at intervals along the runway centerline on some precision instrument runways. White except the last : alternate white and red for next and red for last .
* Touchdown zone lights (TDZL) – rows of white light bars (with three in each row) at intervals on either side of the centerline for .
* Taxiway centerline lead-off lights – installed along lead-off markings, alternate green and yellow lights embedded into the runway pavement. It starts with green light at about the runway centerline to the position of first centerline light beyond the Hold-Short markings on the taxiway.
* Taxiway centerline lead-on lights – installed the same way as taxiway centerline lead-off Lights, but directing airplane traffic in the opposite direction.
* Land and hold short lights – a row of white pulsating lights installed across the runway to indicate hold short position on some runways that are facilitating land and hold short operations (LAHSO).
*
 The choice of material used to construct the runway depends on the use and the local ground conditions. For a major airport, where the ground conditions permit, the most satisfactory type of pavement for long-term minimum maintenance is concrete. Although certain airports have used reinforcement in concrete pavements, this is generally found to be unnecessary, with the exception of expansion joints across the runway where a
The choice of material used to construct the runway depends on the use and the local ground conditions. For a major airport, where the ground conditions permit, the most satisfactory type of pavement for long-term minimum maintenance is concrete. Although certain airports have used reinforcement in concrete pavements, this is generally found to be unnecessary, with the exception of expansion joints across the runway where a
 Runway pavement surface is prepared and maintained to maximize friction for wheel braking. To minimize hydroplaning following heavy rain, the pavement surface is usually grooved so that the surface water film flows into the grooves and the peaks between grooves will still be in contact with the aircraft tires. To maintain the macrotexturing built into the runway by the grooves, maintenance crews engage in airfield rubber removal or
Runway pavement surface is prepared and maintained to maximize friction for wheel braking. To minimize hydroplaning following heavy rain, the pavement surface is usually grooved so that the surface water film flows into the grooves and the peaks between grooves will still be in contact with the aircraft tires. To maintain the macrotexturing built into the runway by the grooves, maintenance crews engage in airfield rubber removal or
 In aviation charts, the surface type is usually abbreviated to a three-letter code.
The most common hard surface types are asphalt and concrete. The most common soft surface types are grass and gravel.
In aviation charts, the surface type is usually abbreviated to a three-letter code.
The most common hard surface types are asphalt and concrete. The most common soft surface types are grass and gravel.
File:Lbiarunwayflyover.jpg, In the 1980s, Leeds Bradford International Airport extended its runway to take wide-body aircraft by building an
Bogie
/ref> * Runway visual range * Tabletop runway * Visual approach slope indicator
World Airport and Runway Map
(ICAO official site)
United States Aeronautical Information Manual
– Federal Aviation Administration (published yearly)
United States Airport/Facility Directory (d-AFD)
– Federal Aviation Administration (published every 56 days)
United States Terminal Procedures Publication/Airport Diagrams (d-TPP)
– Federal Aviation Administration (published every 28 days)
Visual Aids Handbook
–


 According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface ( grass, dirt,
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface ( grass, dirt, gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classifi ...
, ice, sand or salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using tarmac Tarmac may refer to:
Engineered surfaces
* Tarmacadam, a mainly historical tar-based material for macadamising road surfaces, patented in 1902
* Asphalt concrete, a macadamising material using asphalt instead of tar which has largely superseded ta ...
. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used.
History
In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local companyMichelin
Michelin (; ; full name: ) is a French multinational tyre manufacturing company based in Clermont-Ferrand in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes ''région'' of France. It is the second largest tyre manufacturer in the world behind Bridgestone and la ...
to manufacture Bréguet Aviation military aircraft.
In January 1919, aviation pioneer Orville Wright underlined the need for "distinctly marked and carefully prepared landing places, utthe preparing of the surface of reasonably flat ground san expensive undertaking ndthere would also be a continuous expense for the upkeep."
Headings
Forfixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinc ...
, it is advantageous to perform takeoffs and landings into the wind to reduce takeoff or landing roll and reduce the ground speed needed to attain flying speed. Larger airports usually have several runways in different directions, so that one can be selected that is most nearly aligned with the wind. Airports with one runway are often constructed to be aligned with the prevailing wind. Compiling a wind rose
A wind rose is a graphic tool used by meteorologists to give a succinct view of how wind speed and direction are typically distributed at a particular location. Historically, wind roses were predecessors of the compass rose (found on charts), as ...
is in fact one of the preliminary steps taken in constructing airport runways. Note that wind direction is given as the direction the wind is coming ''from'': a plane taking off from runway 09 faces east, into an "east wind" blowing from 090°.
 Originally in the 1920s and 1930s, airports and air bases (particularly in the United Kingdom) were built in a triangle-like pattern of three runways at 60° angles to each other. The reason was that back then aviation was only starting, and as a result although it was known that winds affect runway distance required, etc. not much was known about wind behaviour. As a result, three runways in a triangle-like pattern were built, and the runway with the heaviest traffic on it would eventually expand into an airport's main runway, while the other two runways would be either abandoned or converted into taxiways. For example
Originally in the 1920s and 1930s, airports and air bases (particularly in the United Kingdom) were built in a triangle-like pattern of three runways at 60° angles to each other. The reason was that back then aviation was only starting, and as a result although it was known that winds affect runway distance required, etc. not much was known about wind behaviour. As a result, three runways in a triangle-like pattern were built, and the runway with the heaviest traffic on it would eventually expand into an airport's main runway, while the other two runways would be either abandoned or converted into taxiways. For example Bristol Airport
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city centre. Built on ...
has only one runway—09/27 (9/27)—and two taxiways that form a 'V' which may have been runways on the original 1930s RAF Lulsgate Bottom
Bristol Airport , at Lulsgate Plateau, Lulsgate Bottom, on the northern slopes of the Mendip Hills, in North Somerset, is the commercial airport serving the city of Bristol, England, and the surrounding area. It is southwest of Bristol city ...
airbase.
Naming
magnetic
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particle ...
azimuth of the runway's heading
Heading can refer to:
* Heading (metalworking), a process which incorporates the extruding and upsetting processes
* Headline, text at the top of a newspaper article
* Heading (navigation), the direction a person or vehicle is facing, usually si ...
in deca degrees. This heading differs from true north by the local magnetic declination. A runway numbered 09 points east (90°), runway 18 is south (180°), runway 27 points west (270°) and runway 36 points to the north (360° rather than 0°). When taking off from or landing on runway 09, a plane is heading around 90° (east). A runway can normally be used in both directions, and is named for each direction separately: e.g., "runway 15" in one direction is "runway 33" when used in the other. The two numbers differ by 18 (= 180°). For clarity in radio communications, each digit in the runway name is pronounced individually: runway one-five, runway three-three, etc. (instead of "fifteen" or "thirty-three").
Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is E ...
). However, most U.S. civil aviation airports drop the leading zero as required by FAA regulation. This also includes some military airfields such as Cairns Army Airfield. This American anomaly may lead to inconsistencies in conversations between American pilots and controllers in other countries. It is very common in a country such as Canada for a controller to clear an incoming American aircraft to, for example, runway 04, and the pilot read back the clearance as runway 4. In flight simulation programs those of American origin might apply U.S. usage to airports around the world. For example, runway 05 at Halifax will appear on the program as the single digit 5 rather than 05.
Military airbases may include smaller paved runways known as "assault strips" for practice and training next to larger primary runways. These strips eschew the standard numerical naming convention and instead employ the runway's full three digit heading; examples include Dobbins Air Reserve Base's Runway 110/290 and Duke Field
Duke Field , also known as Eglin AFB Auxiliary Field #3, is a military airport located three miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Crestview, in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States.
History
Duke Field was one of the f ...
's Runway 180/360.
Runways with non-hard surfaces, such as small turf airfields and waterways for seaplanes, may use the standard numerical scheme or may use traditional compass point naming, examples include Ketchikan Harbor Seaplane Base
Ketchikan Harbor Seaplane Base is a privately owned, public use seaplane base located at the harbor of Ketchikan, a city in the Ketchikan Gateway Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located near the Ketchikan International Airport, which a ...
's Waterway E/W. Airports with unpredictable or chaotic water currents, such as Santa Catalina Island's Pebbly Beach Seaplane Base, may designate their landing area as Waterway ALL/WAY to denote the lack of designated landing direction.
Letter suffix
 If there is more than one runway pointing in the same direction (parallel runways), each runway is identified by appending left (L), center (C) and right (R) to the end of the runway number to identify its position (when facing its direction)—for example, runways one-five-left (15L), one-five-center (15C), and one-five-right (15R). Runway zero-three-left (03L) becomes runway two-one-right (21R) when used in the opposite direction (derived from adding 18 to the original number for the 180° difference when approaching from the opposite direction). In some countries, regulations mandate that where parallel runways are too close to each other, only one may be used at a time under certain conditions (usually adverse weather).
At large airports with four or more parallel runways (for example, at Chicago O'Hare, Los Angeles, Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County, Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta, Denver, Dallas–Fort Worth and Orlando), some runway identifiers are shifted by 1 to avoid the ambiguity that would result with more than three parallel runways. For example, in Los Angeles, this system results in runways 6L, 6R, 7L, and 7R, even though all four runways are actually parallel at approximately 69°. At Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, there are five parallel runways, named 17L, 17C, 17R, 18L, and 18R, all oriented at a heading of 175.4°. Occasionally, an airport with only three parallel runways may use different runway identifiers, such as when a third parallel runway was opened at
If there is more than one runway pointing in the same direction (parallel runways), each runway is identified by appending left (L), center (C) and right (R) to the end of the runway number to identify its position (when facing its direction)—for example, runways one-five-left (15L), one-five-center (15C), and one-five-right (15R). Runway zero-three-left (03L) becomes runway two-one-right (21R) when used in the opposite direction (derived from adding 18 to the original number for the 180° difference when approaching from the opposite direction). In some countries, regulations mandate that where parallel runways are too close to each other, only one may be used at a time under certain conditions (usually adverse weather).
At large airports with four or more parallel runways (for example, at Chicago O'Hare, Los Angeles, Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County, Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta, Denver, Dallas–Fort Worth and Orlando), some runway identifiers are shifted by 1 to avoid the ambiguity that would result with more than three parallel runways. For example, in Los Angeles, this system results in runways 6L, 6R, 7L, and 7R, even though all four runways are actually parallel at approximately 69°. At Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, there are five parallel runways, named 17L, 17C, 17R, 18L, and 18R, all oriented at a heading of 175.4°. Occasionally, an airport with only three parallel runways may use different runway identifiers, such as when a third parallel runway was opened at Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport
Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport is a civil–military public airport east of downtown Phoenix, in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States. It is Arizona's largest and busiest airport, and among the largest commercial airports in th ...
in 2000 to the south of existing 8R/26L—rather than confusingly becoming the "new" 8R/26L it was instead designated 7R/25L, with the former 8R/26L becoming 7L/25R and 8L/26R becoming 8/26.
Suffixes may also be used to denote special use runways. Airports that have seaplane waterways may chose to denote the waterway on charts with the suffix W; such as Daniel K. Inouye International Airport in Honolulu and Lake Hood Seaplane Base
Lake Hood Seaplane Base is a state-owned seaplane base located three nautical miles (6 km) southwest of the central business district of Anchorage in the U.S. state of Alaska. The Lake Hood Strip is a gravel runway located adjacent to th ...
in Anchorage
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Ma ...
. Small airports that host various forms of air traffic may employ additional suffixes to denote special runway types based on the type of aircraft expected to use them, including STOL
A short takeoff and landing (STOL) aircraft is a conventional fixed-wing aircraft that has short runway requirements for takeoff and landing. Many STOL-designed aircraft also feature various arrangements for use on airstrips with harsh conditio ...
aircraft (S), glider
Glider may refer to:
Aircraft and transport Aircraft
* Glider (aircraft), heavier-than-air aircraft primarily intended for unpowered flight
** Glider (sailplane), a rigid-winged glider aircraft with an undercarriage, used in the sport of glidin ...
s (G), rotorcraft (H), and ultralights (U).FAA AC 150/5200-35/ref> Runways that are numbered relative to true north rather than magnetic north will use the suffix T; this is advantageous for certain airfields in the far north such as Thule Air Base.
Renumbering
Runway designations may change over time because Earth's magnetic lines slowly drift on the surface and the magnetic direction changes. Depending on the airport location and how much drift occurs, it may be necessary to change the runway designation. As runways are designated with headings rounded to the nearest 10°, this affects some runways sooner than others. For example, if the magnetic heading of a runway is 233°, it is designated Runway 23. If the magnetic heading changes downwards by 5 degrees to 228°, the runway remains Runway 23. If on the other hand the original magnetic heading was 226° (Runway 23), and the heading decreased by only 2 degrees to 224°, the runway becomes Runway 22. Because magnetic drift itself is slow, runway designation changes are uncommon, and not welcomed, as they require an accompanying change in aeronautical charts and descriptive documents. When a runway designation does change, especially at major airports, it is often done at night, because taxiway signs need to be changed and the numbers at each end of the runway need to be repainted to the new runway designators. In July 2009 for example, London Stansted Airport in the United Kingdom changed its runway designations from 05/23 to 04/22 during the night.Declared distances
Runway dimensions vary from as small as long and wide in smaller general aviation airports, to long and wide at largeinternational airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
s built to accommodate the largest jets, to the huge lake bed runway 17/35 at Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is E ...
in California – developed as a landing site for the Space Shuttle.
Takeoff and landing distances available are given using one of the following terms:
;
* Takeoff Run Available (TORA) – The length of runway declared available and suitable for the ground run of an airplane taking off.
* Takeoff Distance Available (TODA) – The length of the takeoff run available plus the length of the clearway, if clearway is provided. (The clearway length allowed must lie within the aerodrome or airport boundary. According to the Federal Aviation Regulations and Joint Aviation Requirements
The Joint Aviation Requirements (JAR) were a set of common comprehensive and detailed aviation requirement issued by the Joint Aviation Authorities, intended to minimise Type Certification problems on joint ventures, and also to facilitate the expo ...
(JAR) TODA is the lesser of TORA plus clearway or 1.5 times TORA).
* Accelerate-Stop Distance Available (ASDA)– The length of the takeoff run available plus the length of the stopway, if stopway is provided.
* Landing Distance Available (LDA) – The length of runway that is declared available and suitable for the ground run of an airplane landing.
* Emergency Distance Available (EMDA) – LDA (or TORA) plus a stopway.
Sections
There are standards for runway markings.runway safety area
A runway safety area (RSA) or runway end safety area (RESA) is defined as "the surface surrounding the runway prepared or suitable for reducing the risk of damage to airplanes in the event of an undershoot, overshoot, or excursion from the runway. ...
is the cleared, smoothed and graded area around the paved runway. It is kept free from any obstacles that might impede flight or ground roll of aircraft.
* The runway is the surface from threshold to threshold (including displaced thresholds), which typically features threshold markings, numbers, and centerlines, but excludes blast pads and stopways at both ends.
* Blast pads are often constructed just before the start of a runway where jet blast produced by large planes during the takeoff roll could otherwise erode the ground and eventually damage the runway.
* Stopways, also known as overrun areas, are also constructed at the end of runways as emergency space to stop planes that overrun the runway on landing or a rejected takeoff.
** Blast pads and stopways look similar, and are both marked with yellow chevrons; stopways may optionally be surrounded by red runway lights. The differences are that stopways can support the full weight of an aircraft and are designated for use in an aborted takeoff, while blast pads are often not as strong as the main paved surface of the runway and are not to be used for taxiing, landing, or aborted takeoffs. FAA Advisory Circular 150/5300-13A (PDF) An engineered materials arrestor system
An engineered materials arrestor system, engineered materials arresting system (EMAS), or arrester bed is a bed of engineered materials built at the end of a runway to reduce the severity of the consequences of a runway excursion. Engineered ma ...
(EMAS) may also be present, which may overlap with the end of the blast pad or stopway and is painted similarly (although an EMAS does not count as part of a stopway).
 *
* Displaced threshold A displaced threshold or DTHR is a runway threshold located at a point other than the physical beginning or end of the runway.
The portion of the runway behind a displaced threshold may be used for takeoff in either direction and landings from the ...
s may be used for taxiing, takeoff, and landing rollout, but not for touchdown. A displaced threshold often exists because of obstacles just before the runway, runway strength, or noise restrictions making the beginning section of runway unsuitable for landings. It is marked with white paint arrows that lead up to the beginning of the landing portion of the runway. As with blast pads, landings on displaced thresholds are not permitted aside from emergency use or exigent circumstance.
 * Clearway is an area beyond the paved runway, aligned with the runway centerline and under the control of the airport authorities. This area is not less than 500 ft and there are no protruding obstacles except for threshold lights provided that they aren't higher than 26 inches. There is a limit on the upslope of the clearway of 1.25%. The length of the clearway may be included in the length of the
* Clearway is an area beyond the paved runway, aligned with the runway centerline and under the control of the airport authorities. This area is not less than 500 ft and there are no protruding obstacles except for threshold lights provided that they aren't higher than 26 inches. There is a limit on the upslope of the clearway of 1.25%. The length of the clearway may be included in the length of the takeoff distance available
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concrete, o ...
. For example, if a paved
Pavement may refer to:
* Pavement (architecture), an outdoor floor or superficial surface covering
* Road surface, the durable surfacing of roads and walkways
** Asphalt concrete, a common form of road surface
* Sidewalk or pavement, a walkway alo ...
runway is long and there are of clearway beyond the end of the runway, the takeoff distance available is long. When the runway is to be used for takeoff of a large airplane, the maximum permissible takeoff weight of the airplane can be based on the takeoff distance available, including clearway. Clearway allows large airplanes to take off at a heavier weight than would be allowed if only the length of the paved runway is taken into account.
Markings
There are runway markings and signs on most large runways. Larger runways have a distance remaining sign (black box with white numbers). This sign uses a single number to indicate the remaining distance of the runway in thousands of feet. For example, a 7 will indicate remaining. The runway threshold is marked by a line of green lights.
 There are three types of runways:
* Visual runways are used at small airstrips and are usually just a strip of grass, gravel, ice, asphalt, or concrete. Although there are usually no markings on a visual runway, they may have threshold markings, designators, and centerlines. Additionally, they do not provide an instrument-based landing procedure; pilots must be able to see the runway to use it. Also, radio communication may not be available and pilots must be self-reliant.
* Non-precision instrument runways are often used at small- to medium-size airports. These runways, depending on the surface, may be marked with threshold markings, designators, centerlines, and sometimes a mark (known as an aiming point, sometimes installed at ). While centerlines provide horizontal position guidance, aiming point markers provide vertical position guidance to planes on visual approach.
* Precision instrument runways, which are found at medium- and large-size airports, consist of a blast pad/stopway (optional, for airports handling jets), threshold, designator, centerline, aiming point, and , /, , , and touchdown zone marks. Precision runways provide both horizontal and vertical guidance for instrument approaches.
Waterways may be unmarked or marked with
There are three types of runways:
* Visual runways are used at small airstrips and are usually just a strip of grass, gravel, ice, asphalt, or concrete. Although there are usually no markings on a visual runway, they may have threshold markings, designators, and centerlines. Additionally, they do not provide an instrument-based landing procedure; pilots must be able to see the runway to use it. Also, radio communication may not be available and pilots must be self-reliant.
* Non-precision instrument runways are often used at small- to medium-size airports. These runways, depending on the surface, may be marked with threshold markings, designators, centerlines, and sometimes a mark (known as an aiming point, sometimes installed at ). While centerlines provide horizontal position guidance, aiming point markers provide vertical position guidance to planes on visual approach.
* Precision instrument runways, which are found at medium- and large-size airports, consist of a blast pad/stopway (optional, for airports handling jets), threshold, designator, centerline, aiming point, and , /, , , and touchdown zone marks. Precision runways provide both horizontal and vertical guidance for instrument approaches.
Waterways may be unmarked or marked with buoy
A buoy () is a floating device that can have many purposes. It can be anchored (stationary) or allowed to drift with ocean currents.
Types
Navigational buoys
* Race course marker buoys are used for buoy racing, the most prevalent form of yac ...
s that follow maritime notation instead.
National variants
* In Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom, as well as some other countries or territories ( Hong Kong and Macau) all 3-stripe and 2-stripe touchdown zones for precision runways are replaced with one-stripe touchdown zones. * In some South American countries likeColombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, Ecuador and Peru, one 3-stripe is added and a 2-stripe is replaced with the aiming point.
* Some European countries replace the aiming point with a 3-stripe touchdown zone.
* Runways in Norway have yellow markings instead of the usual white ones. This also occurs in some airports in Japan, Sweden, and Finland. The yellow markings are used to ensure better contrast against snow.
* Runways may have different types of equipment on each end. To reduce costs, many airports do not install precision guidance equipment on both ends. Runways with one precision end and any other type of end can install the full set of touchdown zones, even if some are past the midpoint. Runways with precision markings on both ends omit touchdown zones within of the midpoint, to avoid ambiguity over the end with which the zone is associated.
Lighting
 A line of lights on an airfield or elsewhere to guide aircraft in taking off or coming in to land or an illuminated runway is sometimes also known as a flare path.
A line of lights on an airfield or elsewhere to guide aircraft in taking off or coming in to land or an illuminated runway is sometimes also known as a flare path.
Technical specifications

Approach lighting system
An approach lighting system (ALS) is a lighting system installed on the approach end of an airport runway and consisting of a series of lightbars, strobe lights, or a combination of the two that extends outward from the runway end. ALS usually ...
(ALS) – a lighting system installed on the approach end of an airport runway and consists of a series of lightbars, strobe lights, or a combination of the two that extends outward from the runway end.
According to Transport Canada's regulations, the runway-edge lighting must be visible for at least . Additionally, a new system of advisory lighting, runway status lights
Runway Status Lights (RWSL) are a visual alerting system installed in some airport taxiways and runways for the purpose of collision-avoidance. When illuminated, red high-intensity LEDs indicate the presence of another vehicle either departing, o ...
, is currently being tested in the United States.
The edge lights must be arranged such that:
* the minimum distance between lines is , and maximum is
* the maximum distance between lights within each line is
* the minimum length of parallel lines is
* the minimum number of lights in the line is 8.
Control of lighting system
Typically the lights are controlled by acontrol tower
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airsp ...
, a flight service station
A flight service station (FSS) is an air traffic facility that provides information and services to aircraft pilots before, during, and after flights, but unlike air traffic control (ATC), is not responsible for giving instructions or clearances or ...
or another designated authority. Some airports/airfields (particularly uncontrolled ones) are equipped with pilot-controlled lighting, so that pilots can temporarily turn on the lights when the relevant authority is not available. This avoids the need for automatic systems or staff to turn the lights on at night or in other low visibility situations. This also avoids the cost of having the lighting system on for extended periods. Smaller airports may not have lighted runways or runway markings. Particularly at private airfields for light planes, there may be nothing more than a windsock beside a landing strip.
Safety
Types of runway safety incidents include: * Runway excursion – an incident involving only a single aircraft, where it makes an inappropriate exit from the runway (e.g. Thai Airways Flight 679). ** Runway overrun (also known as an overshoot) – a type of excursion where the aircraft is unable to stop before the end of the runway (e.g. Air France Flight 358, TAM Airlines Flight 3054,Air India Express Flight 812
Air India Express Flight 812 was a scheduled international flight from Dubai to Mangalore. On 22 May 2010, the Boeing 737-800 passenger jet operating the flight, crashed on landing at Mangalore. The captain had continued an unstabilised appro ...
).
* Runway incursion
A runway incursion is an Aviation accidents and incidents, aviation incident involving improper positioning of vehicles or people on any runway, airport runway or its Critical_area_(aeronautics), protected area. When an incursion involves an ''a ...
– an incident involving incorrect presence of a vehicle, person or another aircraft on the runway (e.g. Aeroflot Flight 3352
Aeroflot Flight 3352 was a Tupolev Tu-154 airline flight on a domestic route from Krasnodar to Novosibirsk, with an intermediate landing in Omsk. While landing at Omsk Airport on Thursday, 11 October 1984, the aircraft crashed into maintenanc ...
, Scandinavian Airlines Flight 686).
* Runway confusion – an aircraft makes use of the wrong runway for landing or takeoff (e.g. Singapore Airlines Flight 006
Singapore Airlines Flight 006 (SQ006/SIA006) was a scheduled Singapore Airlines passenger flight from Singapore Changi Airport to Los Angeles International Airport via Chiang Kai-shek International Airport (now Taiwan Taoyuan International Airp ...
, Western Airlines Flight 2605
Western Airlines Flight 2605, nicknamed the "Night Owl", was an international scheduled passenger flight from Los Angeles, California, to Mexico City, Mexico. On October 31, 1979, at 5:42 a.m. CST ( UTC−06:00), the McDonnell Douglas DC-10 o ...
).
* Runway undershoot – an aircraft that lands short of the runway (e.g. British Airways Flight 38, Asiana Airlines Flight 214).
Surface
 The choice of material used to construct the runway depends on the use and the local ground conditions. For a major airport, where the ground conditions permit, the most satisfactory type of pavement for long-term minimum maintenance is concrete. Although certain airports have used reinforcement in concrete pavements, this is generally found to be unnecessary, with the exception of expansion joints across the runway where a
The choice of material used to construct the runway depends on the use and the local ground conditions. For a major airport, where the ground conditions permit, the most satisfactory type of pavement for long-term minimum maintenance is concrete. Although certain airports have used reinforcement in concrete pavements, this is generally found to be unnecessary, with the exception of expansion joints across the runway where a dowel
A dowel is a cylindrical rod, usually made of wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is called a ''dowel rod''. Dowel rods are often cut into short lengths called dowel pins. Dowels are commonly used as structural ...
assembly, which permits relative movement of the concrete slabs, is placed in the concrete. Where it can be anticipated that major settlements of the runway will occur over the years because of unstable ground conditions, it is preferable to install asphaltic concrete surface, as it is easier to patch on a periodic basis. Fields with very low traffic of light planes may use a sod surface. Some runways make use of salt flats.
For pavement designs, borings are taken to determine the subgrade condition, and based on the relative bearing capacity
In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce she ...
of the subgrade, the specifications are established. For heavy-duty commercial aircraft, the pavement thickness, no matter what the top surface, varies from , including subgrade.
Airport pavements have been designed by two methods. The first, ''Westergaard'', is based on the assumption that the pavement is an elastic plate supported on a heavy fluid base with a uniform reaction coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves var ...
known as the K value. Experience has shown that the ''K'' values on which the formula was developed are not applicable for newer aircraft with very large footprint pressures.
The second method is called the '' California bearing ratio'' and was developed in the late 1940s. It is an extrapolation of the original test results, which are not applicable to modern aircraft pavements or to modern aircraft landing gear. Some designs were made by a mixture of these two design theories. A more recent method is an analytical system based on the introduction of vehicle response as an important design parameter. Essentially it takes into account all factors, including the traffic conditions, service life, materials used in the construction, and, especially important, the dynamic response of the vehicles using the landing area.
Because airport pavement construction is so expensive, manufacturers aim to minimize aircraft stresses on the pavement. Manufacturers of the larger planes design landing gear so that the weight of the plane is supported on larger and more numerous tires. Attention is also paid to the characteristics of the landing gear itself, so that adverse effects on the pavement are minimized. Sometimes it is possible to reinforce a pavement for higher loading by applying an overlay of asphaltic concrete or portland cement concrete that is bonded to the original slab. Post-tensioning concrete has been developed for the runway surface. This permits the use of thinner pavements and should result in longer concrete pavement life. Because of the susceptibility of thinner pavements to frost heave, this process is generally applicable only where there is no appreciable frost action
Frost weathering is a collective term for several mechanical weathering processes induced by stresses created by the freezing of water into ice. The term serves as an umbrella term for a variety of processes such as frost shattering, frost wedg ...
.
Pavement surface
 Runway pavement surface is prepared and maintained to maximize friction for wheel braking. To minimize hydroplaning following heavy rain, the pavement surface is usually grooved so that the surface water film flows into the grooves and the peaks between grooves will still be in contact with the aircraft tires. To maintain the macrotexturing built into the runway by the grooves, maintenance crews engage in airfield rubber removal or
Runway pavement surface is prepared and maintained to maximize friction for wheel braking. To minimize hydroplaning following heavy rain, the pavement surface is usually grooved so that the surface water film flows into the grooves and the peaks between grooves will still be in contact with the aircraft tires. To maintain the macrotexturing built into the runway by the grooves, maintenance crews engage in airfield rubber removal or hydrocleaning
Pressure washing or power washing is the use of high-pressure water spray to remove loose paint, mold, grime, dust, mud, and dirt from surfaces and objects such as buildings, vehicles and concrete surfaces. The volume of a mechanical pressure w ...
in order to meet required FAA friction levels.
Pavement subsurface drainage and underdrains
Subsurface underdrains help provide extended life and excellent and reliable pavement performance. At the Hartsfield Atlanta, GA airport the underdrains usually consist of trenches wide and deep from the top of the pavement. A perforated plastic tube ( in diameter) is placed at the bottom of the ditch. The ditches are filled with gravel size crushed stone. Excessive moisture under a concrete pavement can cause pumping, cracking, and joint failure.Surface type codes
 In aviation charts, the surface type is usually abbreviated to a three-letter code.
The most common hard surface types are asphalt and concrete. The most common soft surface types are grass and gravel.
In aviation charts, the surface type is usually abbreviated to a three-letter code.
The most common hard surface types are asphalt and concrete. The most common soft surface types are grass and gravel.
Length
A runway of at least in length is usually adequate for aircraft weights below approximately . Larger aircraft including widebodies will usually require at least at sea level. International widebody flights, which carry substantial amounts of fuel and are therefore heavier, may also have landing requirements of or more and takeoff requirements of . TheBoeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, t ...
is considered to have the longest takeoff distance of the more common aircraft types and has set the standard for runway lengths of larger international airports.
At sea level, can be considered an adequate length to land virtually any aircraft. For example, at O'Hare International Airport
Chicago O'Hare International Airport , sometimes referred to as, Chicago O'Hare, or simply O'Hare, is the main international airport serving Chicago, Illinois, located on the city's Northwest Side, approximately northwest of the Chicago Loop, ...
, when landing simultaneously on 4L/22R and 10/28 or parallel 9R/27L, it is routine for arrivals from East Asia, which would normally be vectored for 4L/22R () or 9R/27L () to request 28R (). It is always accommodated, although occasionally with a delay. Another example is that the Luleå Airport in Sweden was extended to to allow any fully loaded freight aircraft to take off.
An aircraft taking off at a higher altitude must do so at reduced weight due to decreased density of air at higher altitudes, which reduces engine power and wing lift. An aircraft must also take off at a reduced weight in hotter or more humid conditions (see density altitude). Most commercial aircraft carry manufacturer's tables showing the adjustments required for a given temperature.
In India, recommendations of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) are now followed more often. For landing, only altitude correction is done for runway length whereas for take-off, all types of correction are taken into consideration.
The world's longest paved runway, at Qamdo Bamda Airport in Tibet (China), has a total length of .
overpass
An overpass (called an overbridge or flyover in the United Kingdom and some other Commonwealth countries) is a bridge, road, railway or similar structure that crosses over another road or railway. An ''overpass'' and ''underpass'' together form ...
over the A658 road.
File:Sumburgh Airport Barrier.webm, Road crossing of (Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
) A970 with Sumburgh Airport
Sumburgh Airport is the main airport serving Shetland in Scotland. It is located on the southern tip of the mainland, in the parish of Dunrossness, south of Lerwick. The airport is owned by Highlands and Islands Airports Limited (HIAL) and s ...
's runway. The movable barrier closes when aircraft land or take off.
File:Gibraltar runway 09 & 27.jpg, Gibraltar International Airport's runway 09/27, crossed by the one road between Gibraltar and Spain.
File:Atlantis drag chute is open.jpg, A parachute may be used to slow down craft, in this case the Space Shuttle Atlantis.
See also
*Engineered materials arrestor system
An engineered materials arrestor system, engineered materials arresting system (EMAS), or arrester bed is a bed of engineered materials built at the end of a runway to reduce the severity of the consequences of a runway excursion. Engineered ma ...
* Helipad
A helipad is a landing area or platform for helicopters and powered lift aircraft.
While helicopters and powered lift aircraft are able to operate on a variety of relatively flat surfaces, a fabricated helipad provides a clearly marked hard s ...
* Highway strip
* ICAO recommendations on use of the International System of Units
* Instrument landing system (ILS)
* List of airports
* Pavement classification number (PCN)
* Precision approach path indicator
* Roll way, sometimes referred as a runway/ref> * Runway visual range * Tabletop runway * Visual approach slope indicator
References
External links
World Airport and Runway Map
(ICAO official site)
United States Aeronautical Information Manual
– Federal Aviation Administration (published yearly)
United States Airport/Facility Directory (d-AFD)
– Federal Aviation Administration (published every 56 days)
United States Terminal Procedures Publication/Airport Diagrams (d-TPP)
– Federal Aviation Administration (published every 28 days)
Visual Aids Handbook
–
Civil Aviation Authority
A civil aviation authority (CAA) is a national or supranational statutory authority that oversees the regulation of civil aviation, including the maintenance of an aircraft register.
Role
Due to the inherent dangers in the use of flight vehicles, ...
{{Authority control
Airport engineering
Airport infrastructure