|
Windsock
A windsock (also known as wind cone or wind sleeve) is a conical textile tube that resembles a giant sock. It can be used as a basic indicator of wind speed and direction, or as decoration. Windsocks are typically used at airports to show the direction and strength of the wind to pilots, and at chemical plants where there is risk of gaseous leakage. They are also sometimes located alongside highways at windy locations. At many airports, windsocks are externally or internally lit at night. Wind direction is opposite the direction in which the windsock is pointing. Wind speed is indicated by the windsock's angle relative to the mounting polein low winds it droops; in high winds, it flies horizontally. Design Alternating stripes of high-visibility orange and white were initially used to help estimate wind speed, with each stripe extended adding 3 knots (5.6km/h; 3.5mph) to the estimated speed. Some circular frame mountings cause windsocks to be held open at one end and the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Vane
A wind vane, weather vane, or weathercock is an instrument used for showing the direction of the wind. It is typically used as an architectural ornament to the highest point of a building. The word ''vane'' comes from the Old English word , meaning "flag". Although partly functional, wind vanes are generally decorative, often featuring the traditional cockerel design with letters indicating the points of the compass. Other common motifs include ships, arrows, and horses. Not all wind vanes have pointers. In a sufficiently strong wind, the head of the arrow or cockerel (or equivalent) will indicate the direction from which the wind is blowing. Wind vanes are also found on small wind turbines to keep the wind turbine pointing into the wind. History The oldest known textual references to weather vanes date from 1800-1600 BCE Babylon, where a fable called ''The Fable of the Willow'' describes people looking at a weather vane "for the direction of the wind." In China, the ''Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemoscope
An anemoscope is a device designed to show the direction of the wind, or to indicate a change of wind direction. The name is usually applied to an apparatus consisting of a wind vane above, connecting to a building below by some kind of coupling, and with a dial or index with pointers to show the direction and changes of the wind. Anemoscopes existed in antiquity and have evolved into modern mechanical and electronic instruments. The word is first recorded in English in the period 1700–10. It derives from the Greek word for wind + -scope. Should not be confused with the anemometer, a device to measure the speed of the wind, alongside which it is often deployed. History In antiquity the direction of the wind was indicated by the direction of smoke or the lifting of a flag. The anemoscope then formed a base by which the formal direction of the wind could be gauged. The wind indicator (anemoscope) of Timosthenes (fl. 270 BCE) consisted of a disc with radius which indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
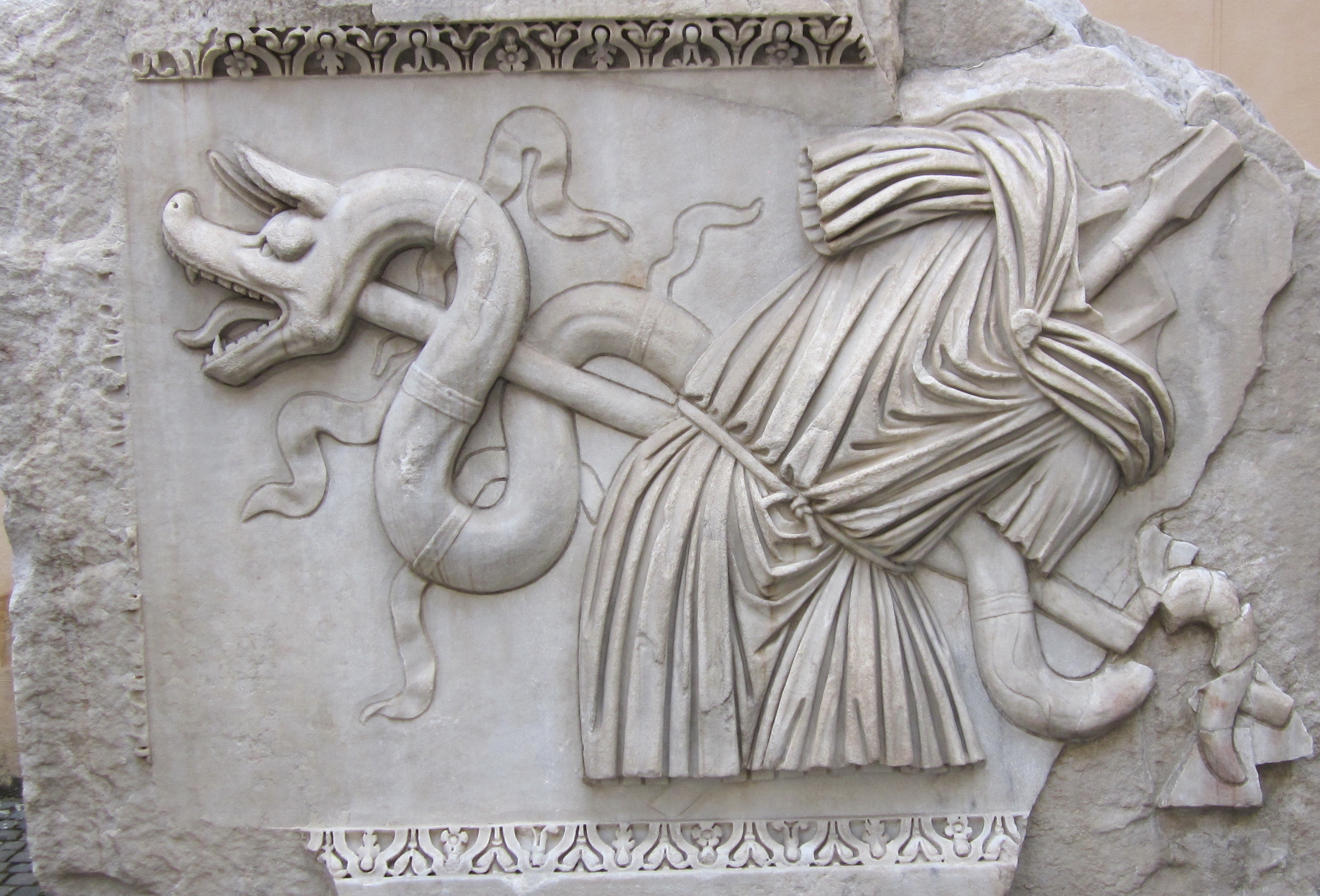
Draco (military Standard)
The ("dragon" or "serpent", plural ) was a military standard of the Roman cavalry. Carried by the , the was the standard of the cohort, as the eagle () was that of the legion. The may have been introduced to the Roman army after the Dacian Wars by Dacian (see Dacian ''draco'') and Sarmatian units in the second century. According to Vegetius, in the fourth century a was carried by each legionary cohort. Literary descriptions The Greek military writer Arrian describes the in his passage on cavalry training exercises, calling it "Scythian": The Scythian banners are ''dracontes'' held aloft on standard-length poles. They are made of colored cloths stitched together, and from the head along the entire body to the tail, they look like snakes. When the horses bearing these devices are not in motion, you see only variegated streamers hanging down. During the charge is when they most resemble creatures: they are inflated by the wind, and even make a sort of hissing soun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemoscope
An anemoscope is a device designed to show the direction of the wind, or to indicate a change of wind direction. The name is usually applied to an apparatus consisting of a wind vane above, connecting to a building below by some kind of coupling, and with a dial or index with pointers to show the direction and changes of the wind. Anemoscopes existed in antiquity and have evolved into modern mechanical and electronic instruments. The word is first recorded in English in the period 1700–10. It derives from the Greek word for wind + -scope. Should not be confused with the anemometer, a device to measure the speed of the wind, alongside which it is often deployed. History In antiquity the direction of the wind was indicated by the direction of smoke or the lifting of a flag. The anemoscope then formed a base by which the formal direction of the wind could be gauged. The wind indicator (anemoscope) of Timosthenes (fl. 270 BCE) consisted of a disc with radius which indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
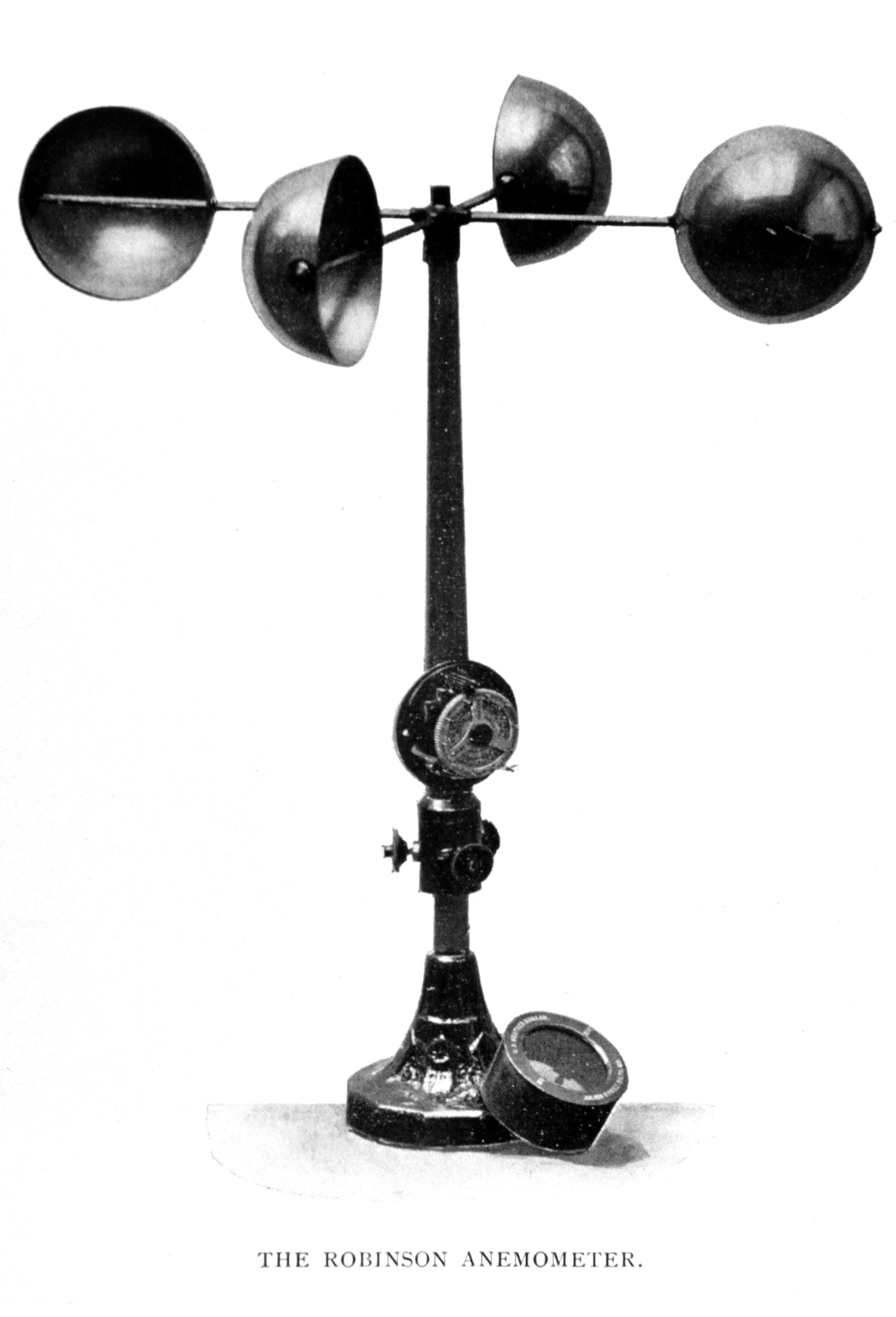
Anemometer
In meteorology, an anemometer () is a device that measures wind speed and direction. It is a common instrument used in weather stations. The earliest known description of an anemometer was by Italian architect and author Leon Battista Alberti (1404–1472) in 1450. History The anemometer has changed little since its development in the 15th century. Alberti is said to have invented it around 1450. In the ensuing centuries numerous others, including Robert Hooke (1635–1703), developed their own versions, with some mistakenly credited as its inventor. In 1846, Thomas Romney Robinson (1792–1882) improved the design by using four hemispherical cups and mechanical wheels. In 1926, Canadian meteorologist John Patterson (1872–1956) developed a three-cup anemometer, which was improved by Brevoort and Joiner in 1935. In 1991, Derek Weston added the ability to measure wind direction. In 1994, Andreas Pflitsch developed the sonic anemometer. Velocity anemometers Cup anemometers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freiburg Im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau or simply Freiburg is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fourth-largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Its built-up area has a population of about 355,000 (2021), while the greater Freiburg metropolitan area ("Einzugsgebiet") has about 660,000 (2018). Freiburg is located at the southwestern foothills of the Black Forest, on the Dreisam River, a tributary of the Elz (Rhine), Elz. It is Germany's southwestern- and southernmost city with a population exceeding 100,000. It lies in the Breisgau, one of Germany's warmest regions, in the south of the Upper Rhine Plain. Its city limits reach from the Schauinsland summit () in the Black Forest to east of the French border, while Switzerland is to the south. The city is situated in the major Baden (wine region), wine-growing region of Baden and, together with Offenburg, serves as a tourist entry-point to the scenic Black Forest. According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international scheduled air transport, air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. The ICAO headquarters are located in the Quartier international de Montréal of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation. ICAO defines the protocols for Aviation accidents and incidents, air accident investigation that are followed by :Organizations investigating aviation accidents and incidents, transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Convention on International Civil Aviation. The Air Navigation Commission (ANC) is the techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
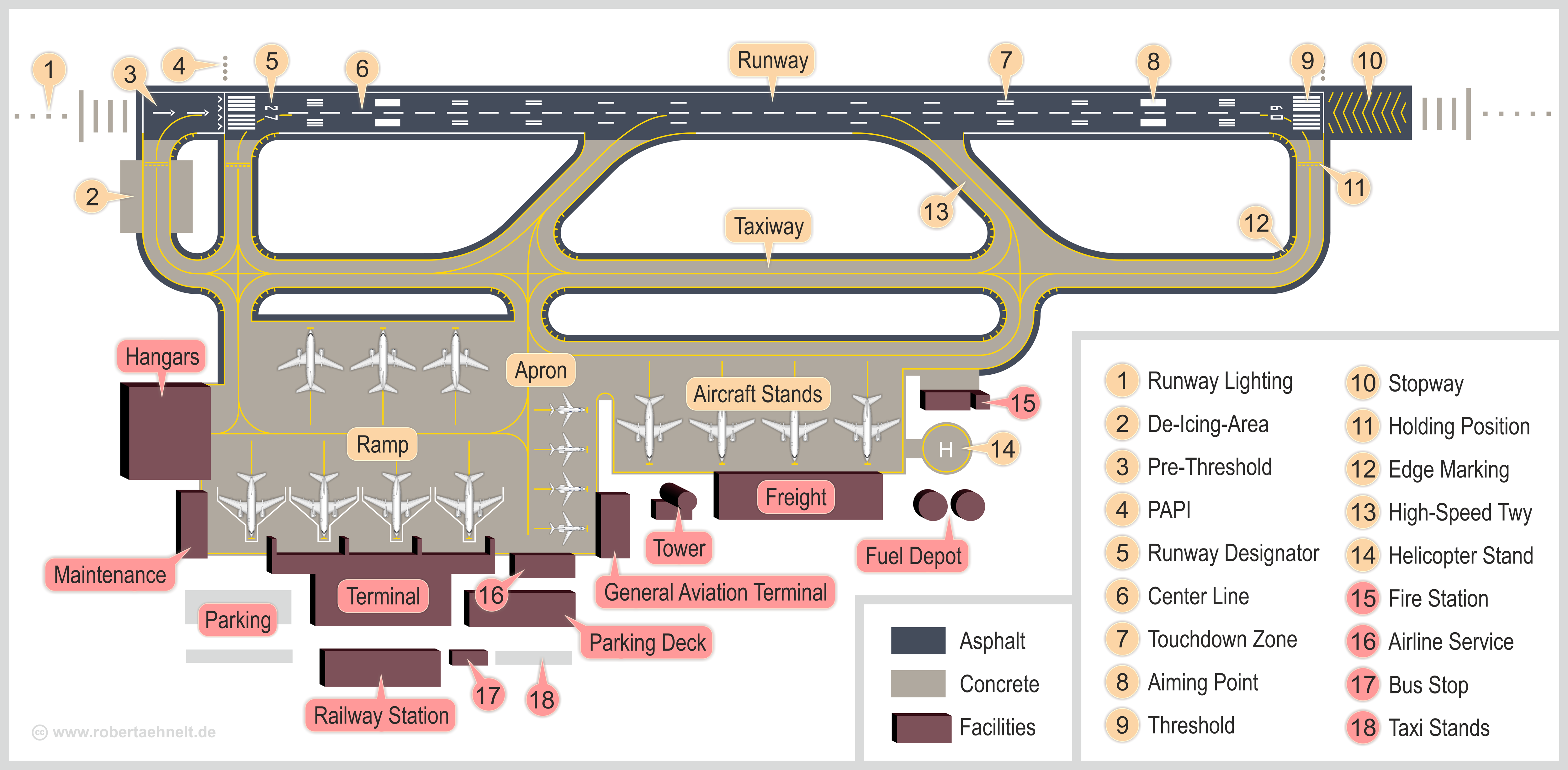
Airport Infrastructure
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial Aviation, air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a airplane, plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as Air traffic control, control towers, hangars and airport terminal, terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and Airport lounge, lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Airport operations are extremely complex, with a complicated system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Pattern Indicator
In aviation, a traffic pattern indicator is an L-shaped device which show the airfield traffic pattern to the in-flight aircraft over an aerodrome. The short arm of the "L" represents the base leg, and the long arm the final approach In aeronautics, the final approach (also called the final leg and final approach leg) is the last leg in an aircraft's approach to landing, when the aircraft is lined up with the runway and descending for landing.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of A .... If no segmented circle is installed, traffic pattern indicators may be installed on or near runway ends. References Air traffic control {{aviation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koinobori
, meaning in Japanese, are carp-shaped windsocks traditionally flown in Japan to celebrate , a traditional calendrical event which is now designated as , a national holiday in Japan. are made by drawing carp patterns on paper, cloth, or other nonwoven fabric. They are then allowed to flutter in the wind. They are also known as . Children's Day takes place on May 5, the last day of Golden Week (Japan), Golden Week, the largest break for workers and also a week in which many businesses, state schools, and some private schools close for up to 9–10 days for the designated national holidays. Landscapes across Japan are decorated with from April to early May, in honor of children for a good future and in the hope that they will grow up healthy and strong. The is included in Unicode as . Description A typical set consists of, from the top of the pole down, a pair of with a ball-shaped spinning Weather vane, vane, a mounting , and finally the . For the windsock above the , tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polytope, convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean geometry, Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid (geometry), pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such net (polyhedron), nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfield Wind Direction Indicators
An aerodrome, airfield, or airstrip is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes include small general aviation airfields, large commercial airports, and military air bases. The term ''airport'' may imply a certain stature (having satisfied certain certification criteria or regulatory requirements) that not all aerodromes may have achieved. That means that all airports are aerodromes, but not all aerodromes are airports. Usage of the term "aerodrome" (or "airfield") remains more common in Commonwealth English, and is conversely almost unknown in American English, where the term "airport" is applied almost exclusively. A water aerodrome is an area of open water used regularly by seaplanes, floatplanes or amphibious aircraft for landing and taking off. In formal terminology, as defined by the International Civil Aviation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |